Submitted:
22 June 2024
Posted:
24 June 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
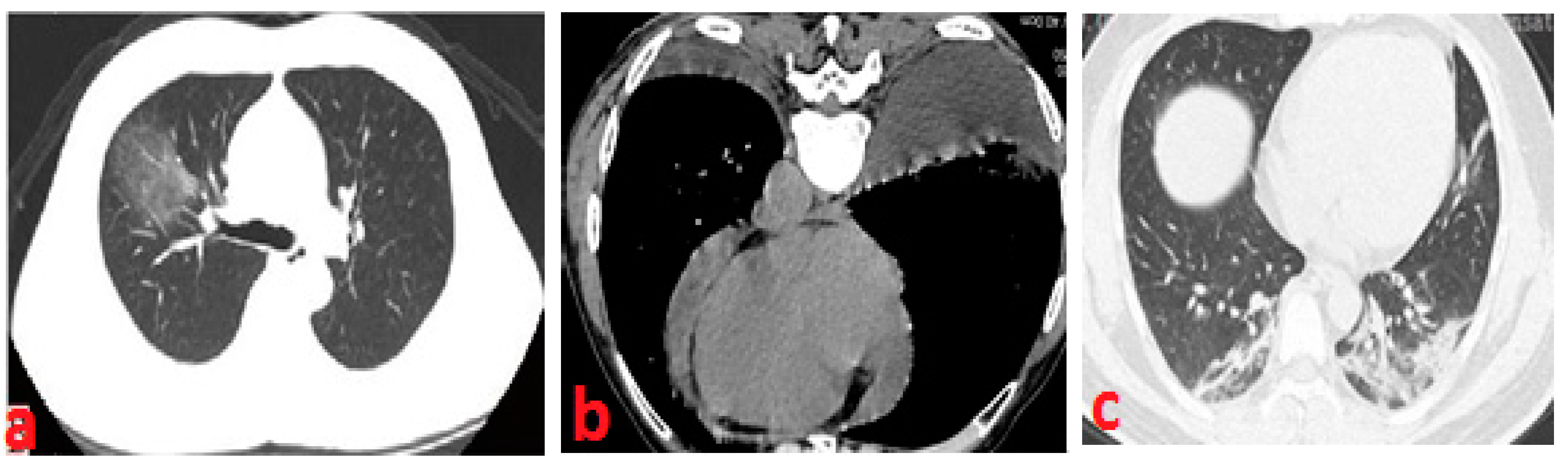
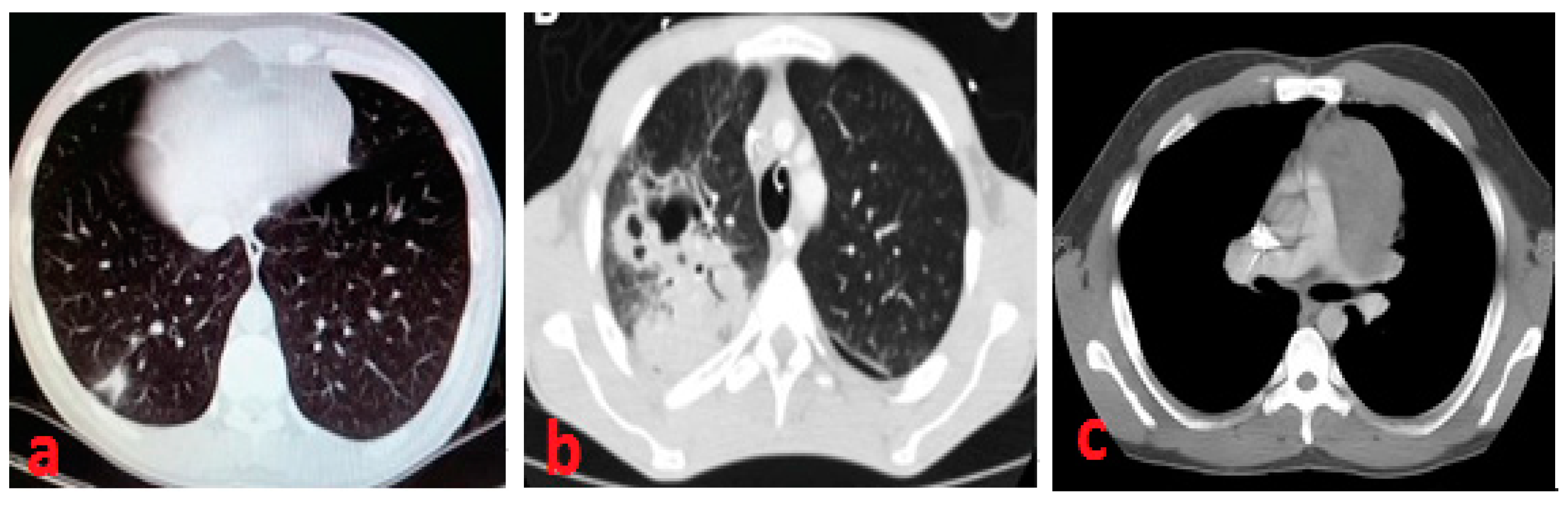
2.1. Medical Methodology
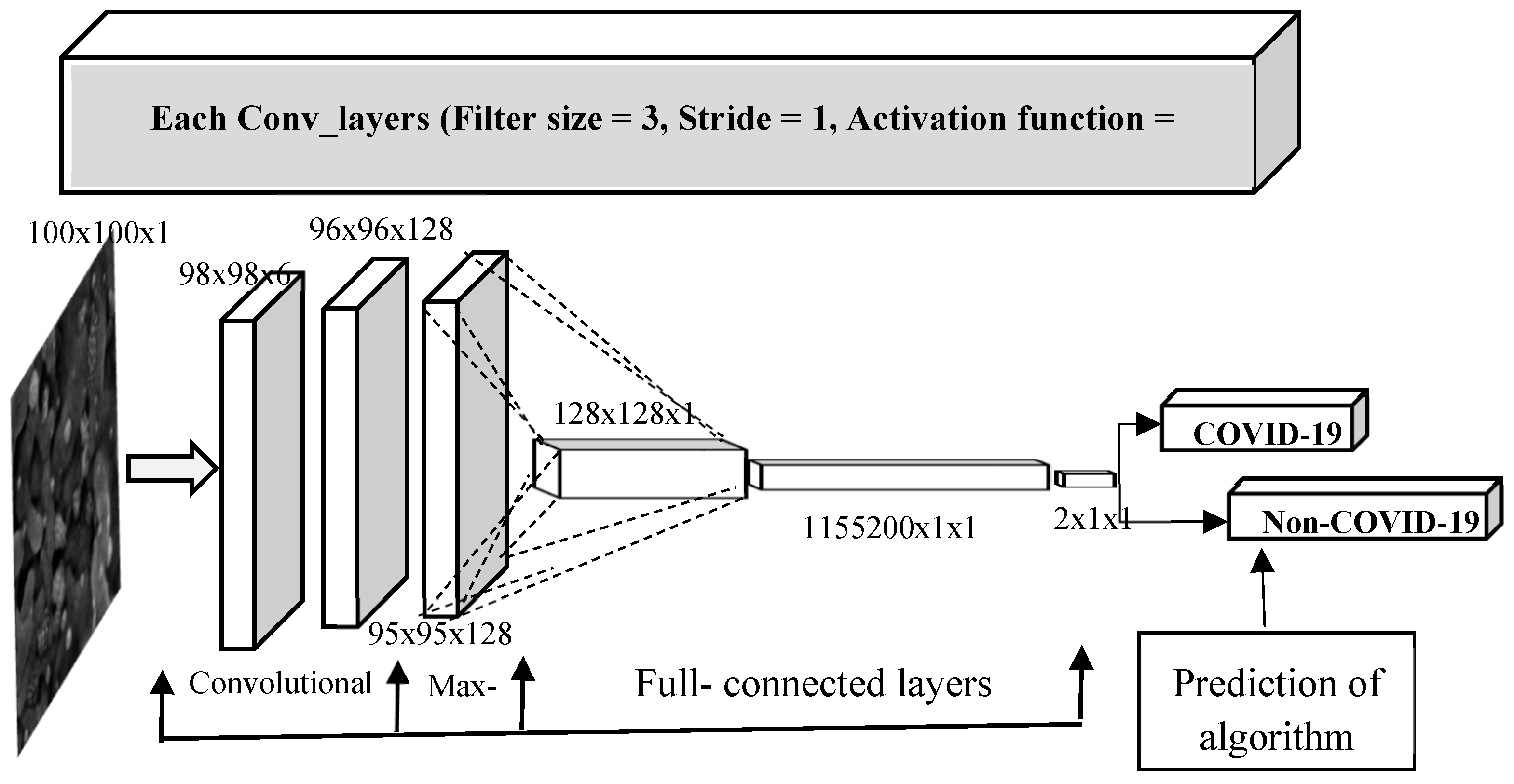
2.2. Proposed Convolutional Neural Network Architecture
2.3. Transfer Learning and Tuning of Previously Trained Models
2.4. Learning Mode
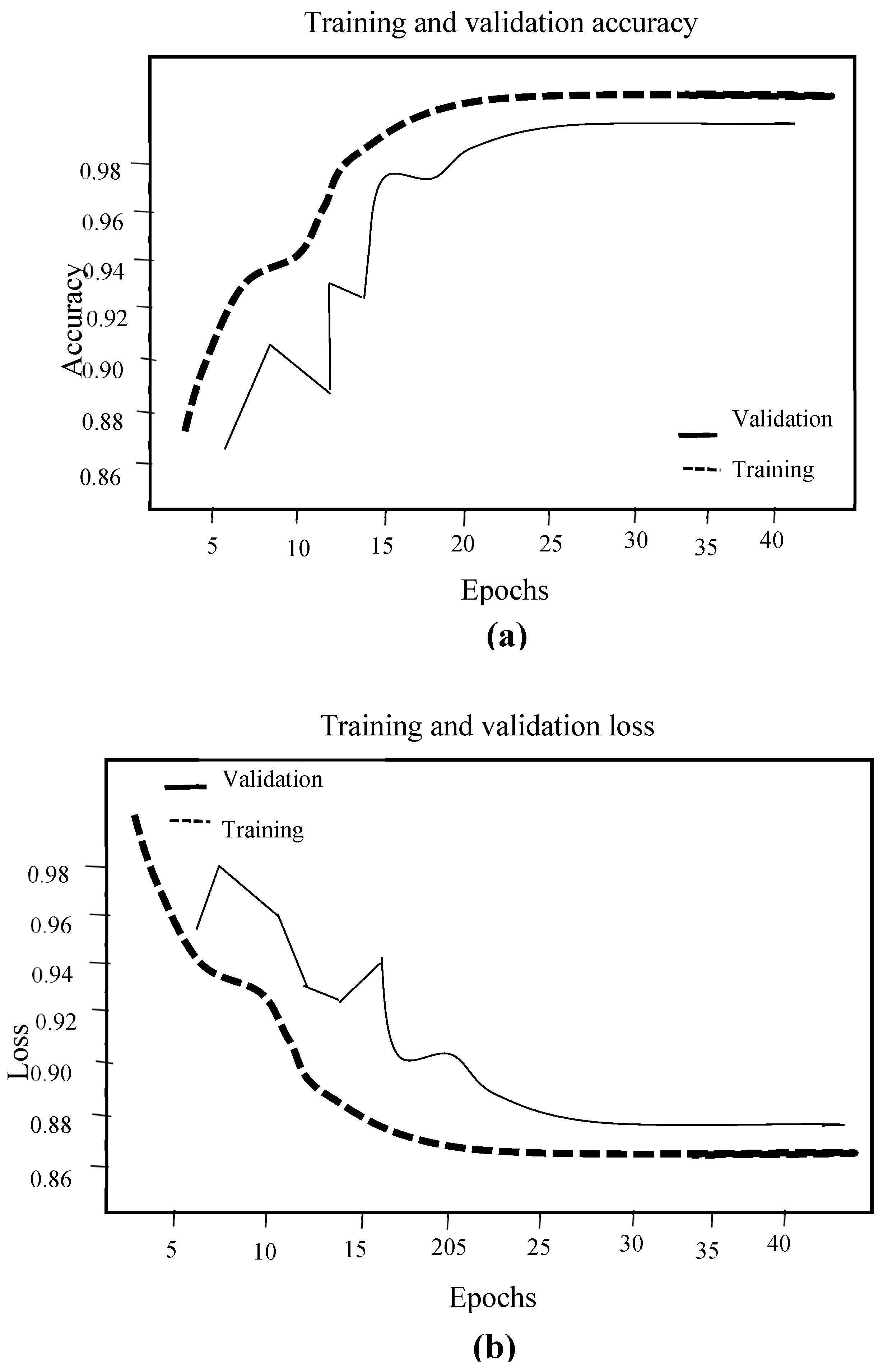
3. Experimental Results. Analysis and Discussion
3.1. Implementation
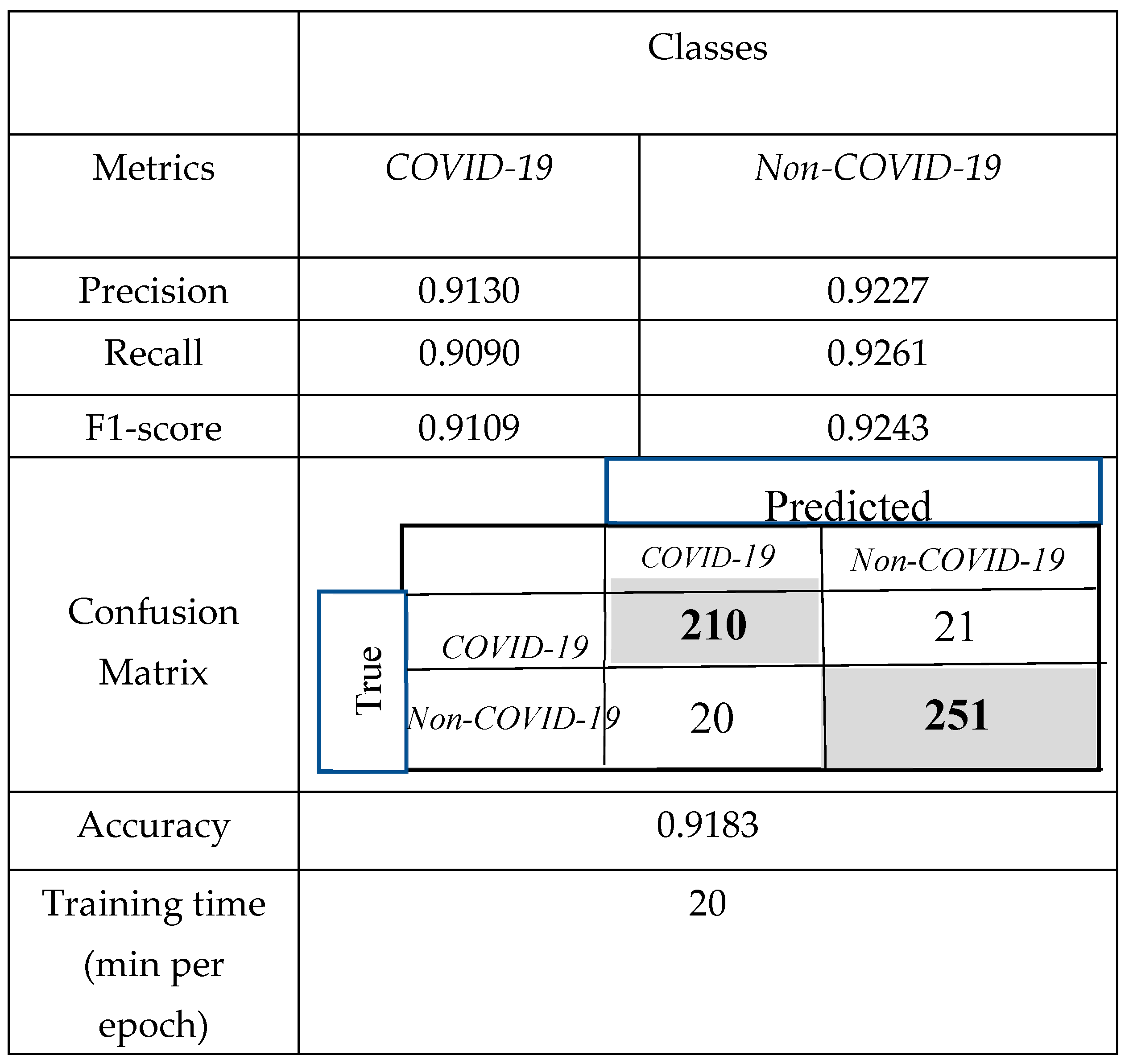
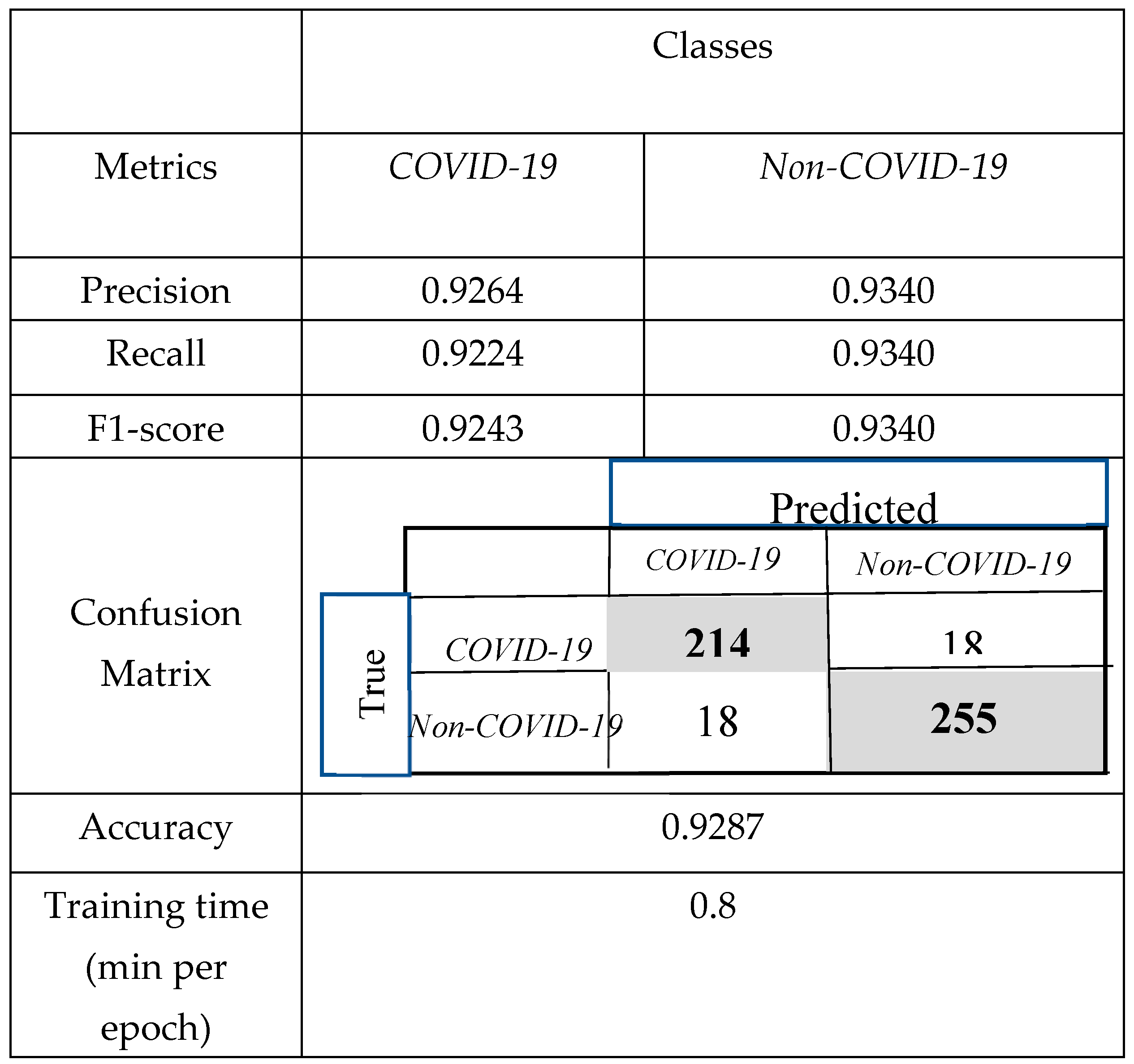
3.2. Comparison of the Obtained Results with CNNs and Support Vector Machine
4. Conclusions
References
- Brian Mondeja, Odalys Valdes, Sonia Resik, Ananayla Vizcaino, Emilio Acosta, Adelmo Montalván, Amira Paez, Mayra Mune, Roberto Rodríguez, Juan Valdés, Guelsys Gonzalez, Daisy Sanchez, Viviana Falcón, Yorexis González, Vivian Kourí, The IPK Virology Research Group, Angelina Díaz and María Guzmán: SARS-CoV-2: preliminary study of infectedhuman nasopharyngeal tissue by high resolution microscopy, Virology Journal, 18:149, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z., Zhao, H., Ren, J., Maclellan, C., Xia, Y., Sun, M. and Ren, K.: SC2Net: A Novel Segmentation-based Classification Network for Detection of COVID-19 in Chest X-ray Images, IEEE journal of biomedical and health informatics, [online], 2022. [CrossRef]
- Pedro Silvaa, Eduardo Luza, Guilherme Silvab, Gladston Moreiraa, Rodrigo Silvaa, Diego Lucioc and David Menottic: COVID-19 detection in CT images with deep learning: A voting-based scheme and cross-datasets analysis, Informatics in Medicine Unlocked, Vol. 20, 100427, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Md. K. Islama, Sultana U. Habibaa, Tahsin A. Khana and Farzana Tasnimb: COV-RadNet: A Deep Convolutional Neural Network for Automatic Detection of COVID-19 from Chest X-Rays and CT Scans, Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine Update, Vol. 2, 100064, 2022. [CrossRef]
- H. M. Shyni and E. Chitra: A comparative study of X-ray and CT images in COVID-19 detection using image processing and deep learning techniques, Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine Update, Vol. 2, 1000054, 2022. [CrossRef]
- C. Long, H. Xu, Q. Shen, X. Zhang, B. Fan, C. Wang, H. Li, Diagnosis of the Coronavirus disease (COVID-19): rRT-PCR or CT?, European journal of radiology, Vol. 126, 108961, 2020.
- Shuai Wang, Bo Kang, Jinlu Ma, Xianjun Zeng, Mingming Xiao, Jia Guo, Mengjiao Cai, Jingyi Yang, Yaodong Li, Xiangfei Meng and Bo Xu: A deep learning algorithm using CT images to screen for Corona virus disease (COVID-19), European Radiology, Vol. 31: 6096–6104, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Abeer Aljuaid and· Mohd Anwar: Survey of Supervised Learning for Medical Image Processing, SN Computer Science, Vol. 3:292, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Eyad Elyan, Pattaramon Vuttipittayamong, Pamela Johnston, Kyle Martin, Kyle McPherson, Carlos F. M. García, Chrisina Jayne and Md. M. K. Sarker: Computer vision and machine learning for medical image analysis: recent advances, challenges, and way forward, Artificial Intelligence Surgery, Vol. 2:2445, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Geert Litjens, Thijs Kooi, Babak E. Bejnordi, Arnaud A. A. Setio, Francesco Ciompi, Mohsen Ghafoorian, Jeroen A.W.M. van der Laak, Bram van Ginneken and Clara I. Sánchez: A Survey on Deep Learning in Medical Image Analysis, arXiv:1702.05747v1 [cs.CV], 2017.
- Kenji Suzuki: Survey on Deep Learning Applications to Medical Image Analysis: Medical Imaging Technology, Vol. 35: 4, 2017.
- Laura Brito and Roberto Rodríguez: Classification of some epidemics through microscopic images by using deep learning. Comparison, Imaging and Radiation Research, Vol. 6:1, 2023. [CrossRef]
- A. Jeddi, M. J. Shafiee and A. Wong, A: Simple Fine-tuning Is All You Need: Towards Robust Deep Learning Via Adversarial Fine-tuning, arXiv preprint (2020) arXiv: 2012.13628, 2020.
- R. Yamashita, M. Nishio, R. Do and K. Togashi: Convolutional neural networks: an overview and application in radiology, Insights Imaging, Vol. 9: 4, 2018. [CrossRef]
- Borja-Robalino R, Monleón-Getino A, Rodellar J. Standardization of performance metrics for classifiers (Spanish). Revista Ibérica de Sistemas e Tecnologias de Informação, E30: 184-196, 2020.
- Fernando Berzal: Redes neuronales & Deep Learning, 2018. https://deep-learning.ikor.org.
- Xavier Glorot, and Yoshua Bengio: Understanding the difficulty of training deep feedforward neural networks, Proceedings of the Thirteenth International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, PMLR 9:249-256, 2010.
- Andreas Weigend, David E. Rumelhart and Bernardo A. Huberman: Generalization by Weight-Elimination with Application to Forecasting, IPS’1990 Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Vol. 3; 875-882, 1990. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/221620459.
- Stephan Mandt, Matthew D. Hoffman and David M. Blei: Stochastic gradient descent as approximate Bayesian inference, Journal of Machine Learning Research, Vol. 18: 1-35, 2017. https://arxiv.org/abs/1704.04289.
- Diederik P. Kingma and Jimmy Ba: Adam: A Method for Stochastic Optimization, Third International Conference for Learning Representations, San Diego, 2015. https://arxiv.org/abs/1412.6980.
- Geoffrey E. Hinton, Nitish Srivastava, Alex Krizhevsky, Ilya Sutskever and Ruslan R. Salakhutdinov: Improving neural networks by preventing co-adaptation of feature detectors, 2012. https://arxiv.org/abs/1207.0580.
- T. Mahmud, M. A. Rahman and S. A. Fattah: CovXNet: A multi-dilation convolutional neural network for automatic COVID-19 and other pneumonia detection from chest X-ray images with transferable multi-receptive feature optimization, Computers in biology and medicine Vol.122:103869, 2020.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





