Submitted:
24 June 2024
Posted:
24 June 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
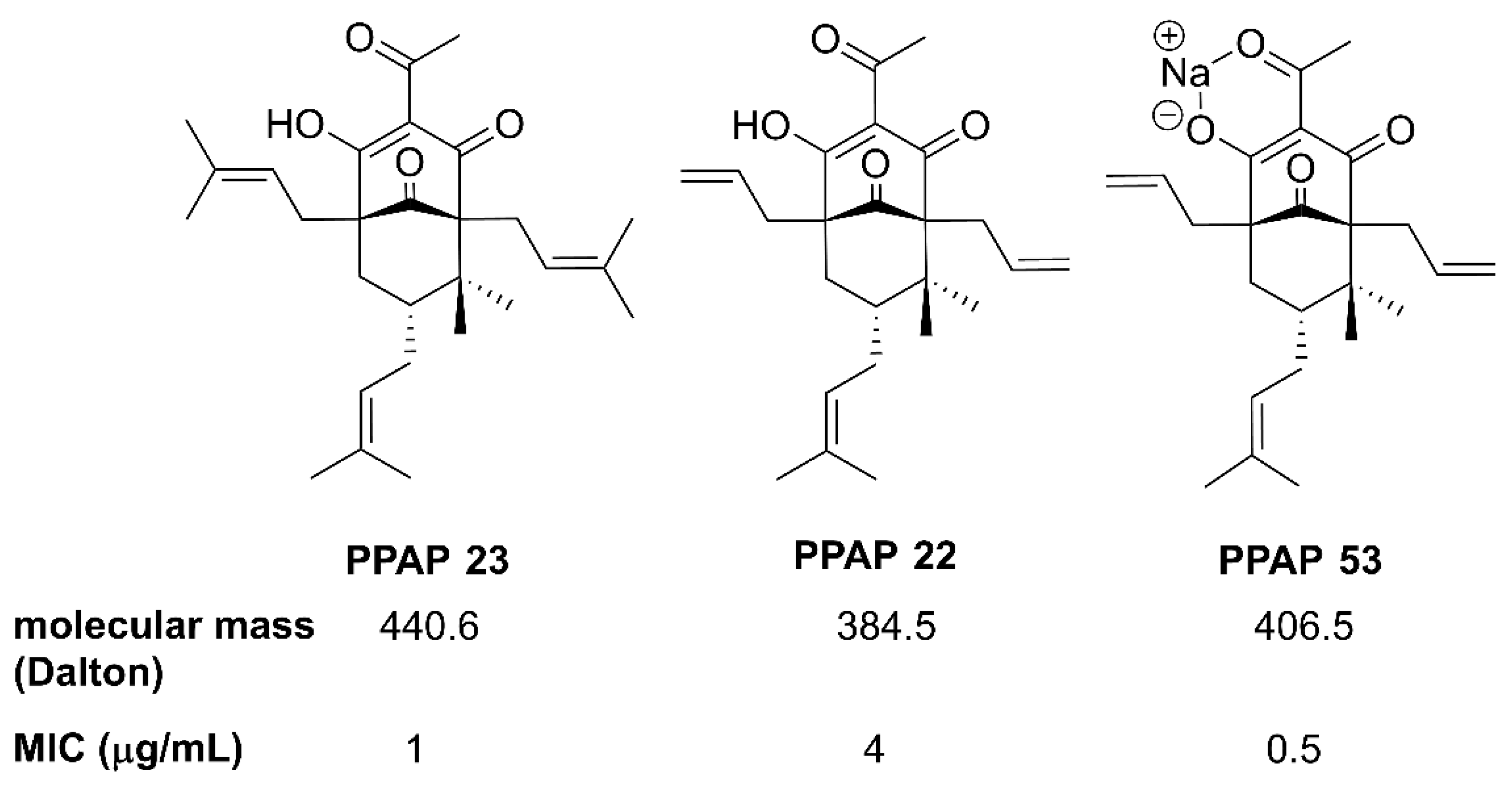
2.1. The PPAP Compounds 23 and 53
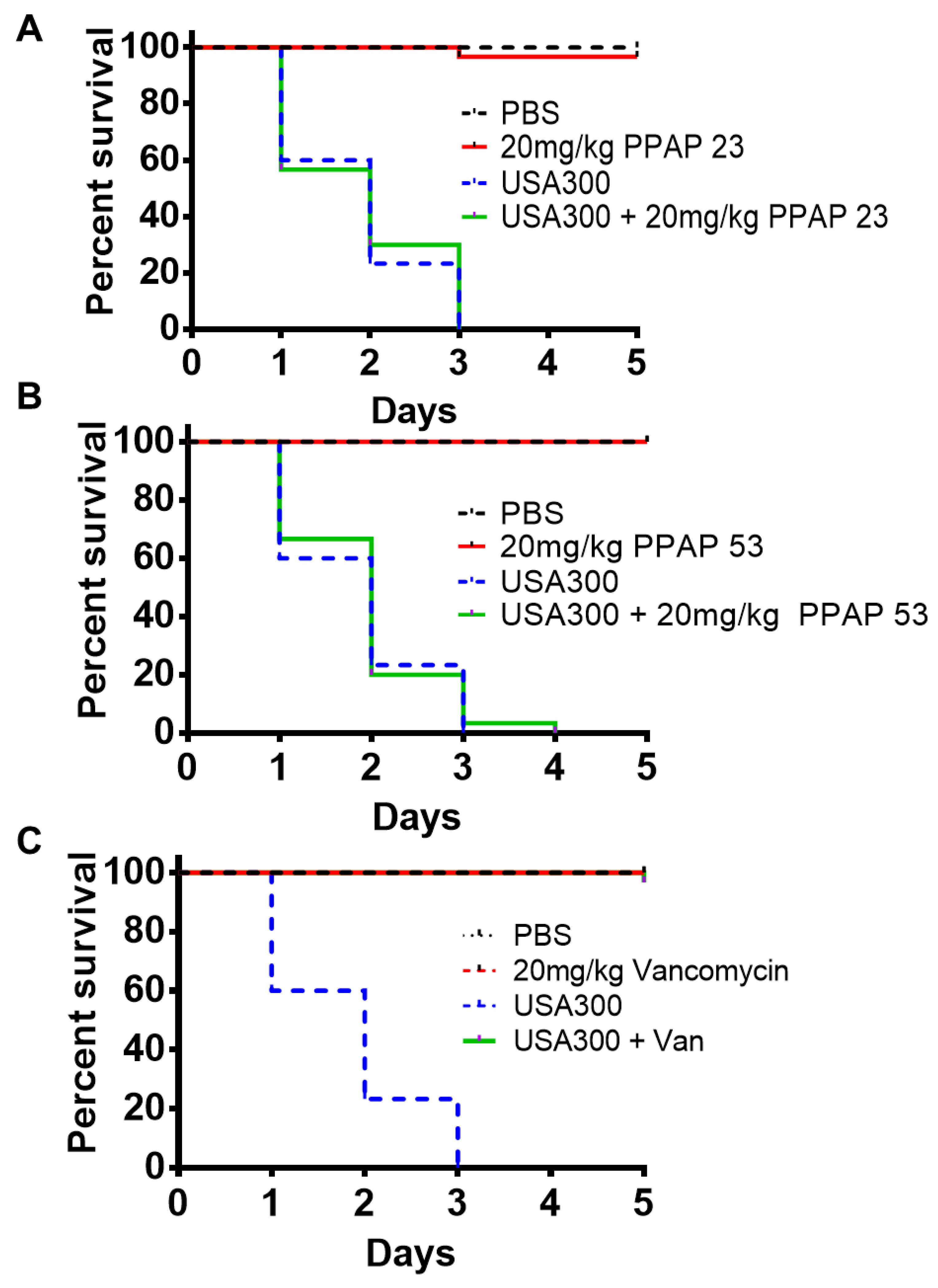
2.2. PPAP 23 and PPAP 53 Had No Toxic Effect on Larvae But Could Not Rescue Larvae In An Infection Model
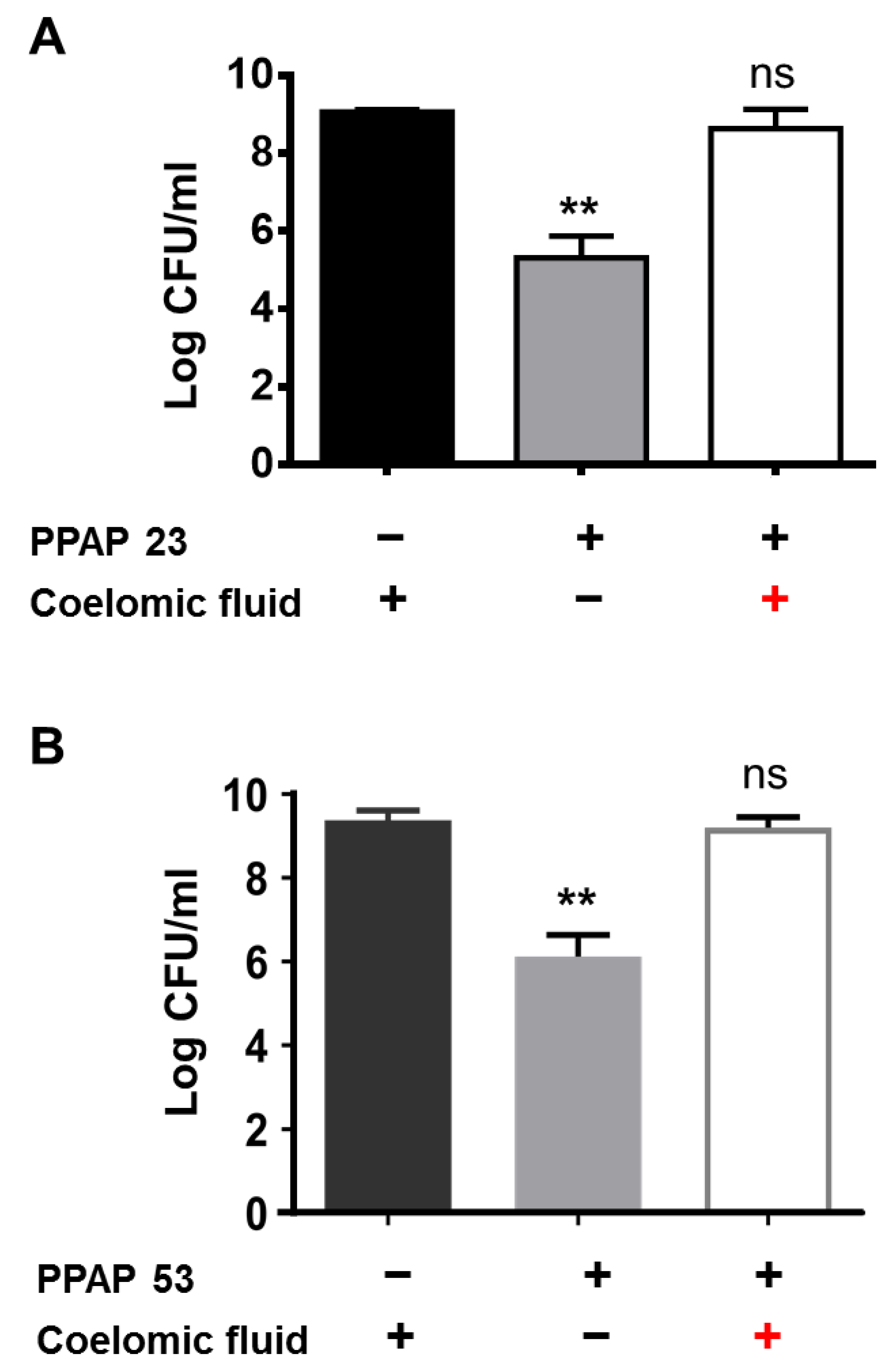
2.3. The coelomic Fluid of the Larvae Antagonized the Activity of PPAP 23 and PPAP 53. We Suspected that Coelomic Fluid Neutralized the Effect of PPAPs. So, to Mimic the In Vivo Larval Experiment, 10 µg of PPAP 23 and PPAP 53 Were Added to 100 μl of Sterile Larval Coelomic Fluid and then Incubated with 106 CFU/ml S. Aureus USA300 Overnight. PPAP 23 or PPAP 53 and USA300 Incubated with PBS Served as Positive Controls. As Expected, No Antibacterial Activity of PPAP 23 and PPAP 53 Towards S. Aureus Was Observed in the Presence of the Coelomic Fluid (Figure 3A and B). This Suggests That Components in the Larval Coelomic Fluid Have an Antagonizing Effect on the PPAPs. This Raised The Question Whether Mammalian Serum and Albumin, One of the Main Proteins of Blood Plasma, Could Also Neutralize the Antibacterial Activity of PPAPs
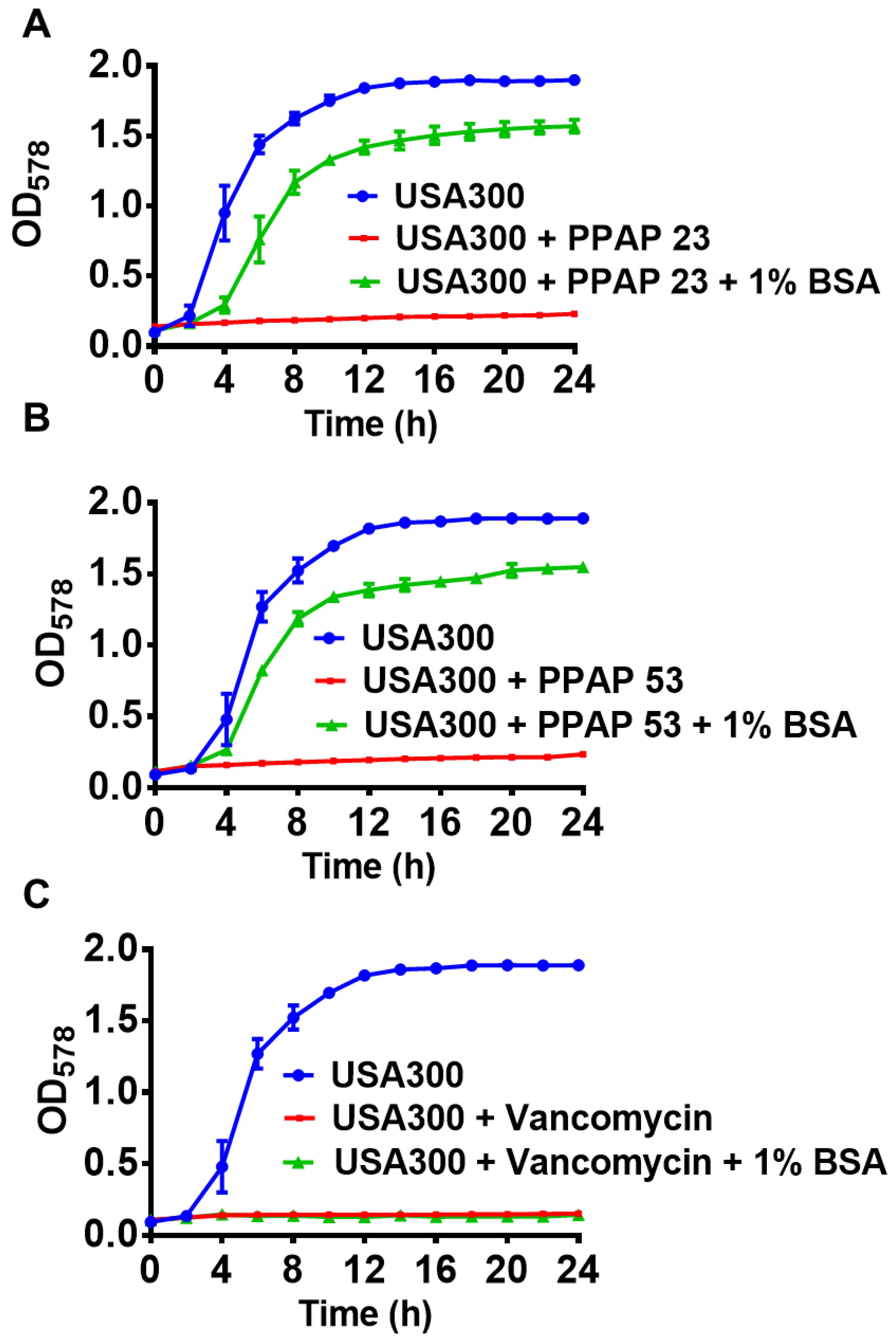
2.4. Bovine serum and Albumin Abrogated The Bactericidal Activity of PPAP 53
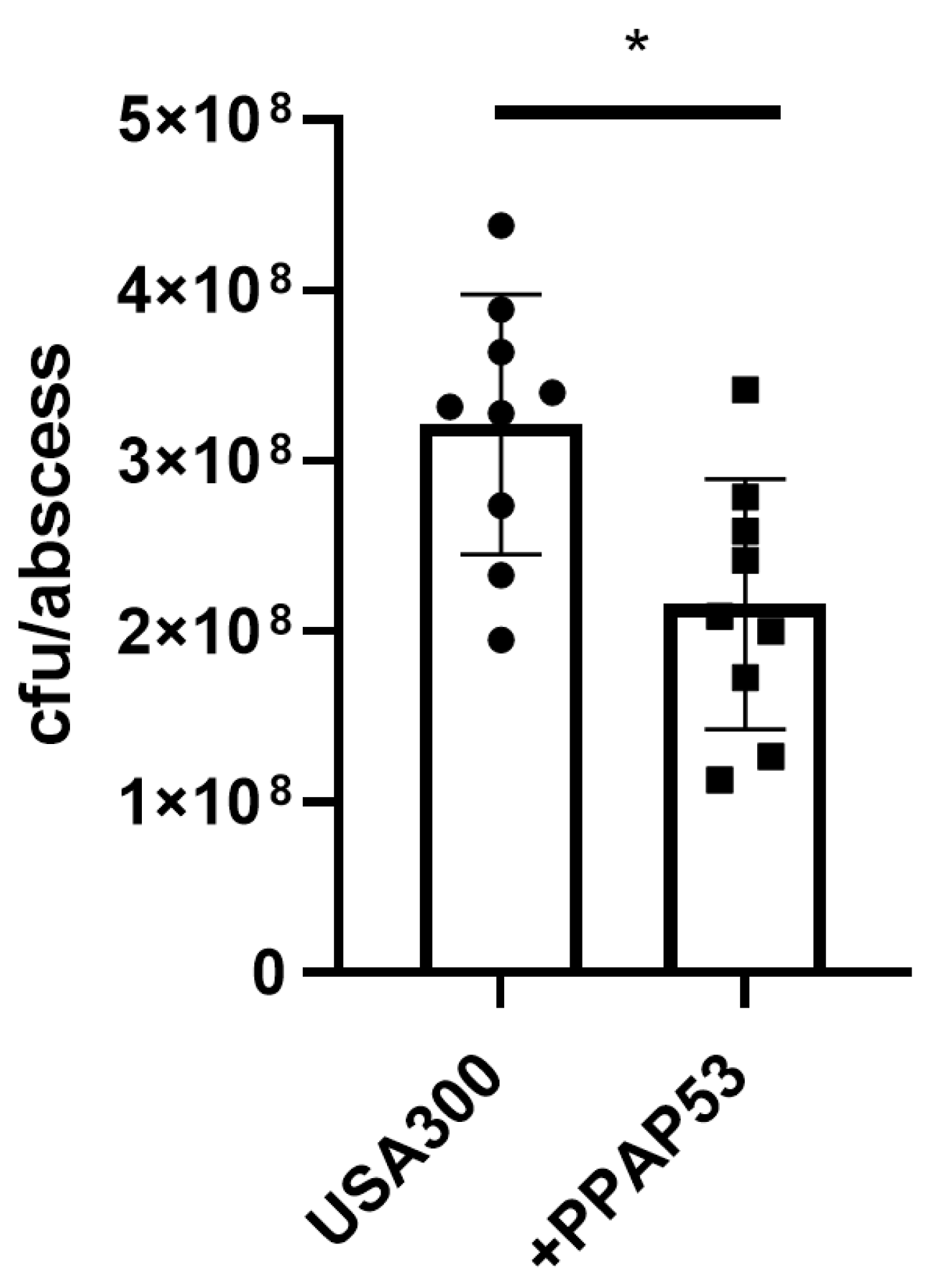
2.5. PPAP 53 Reduced Growth of S. Aureus USA300 in Subcutaneous Abscesses
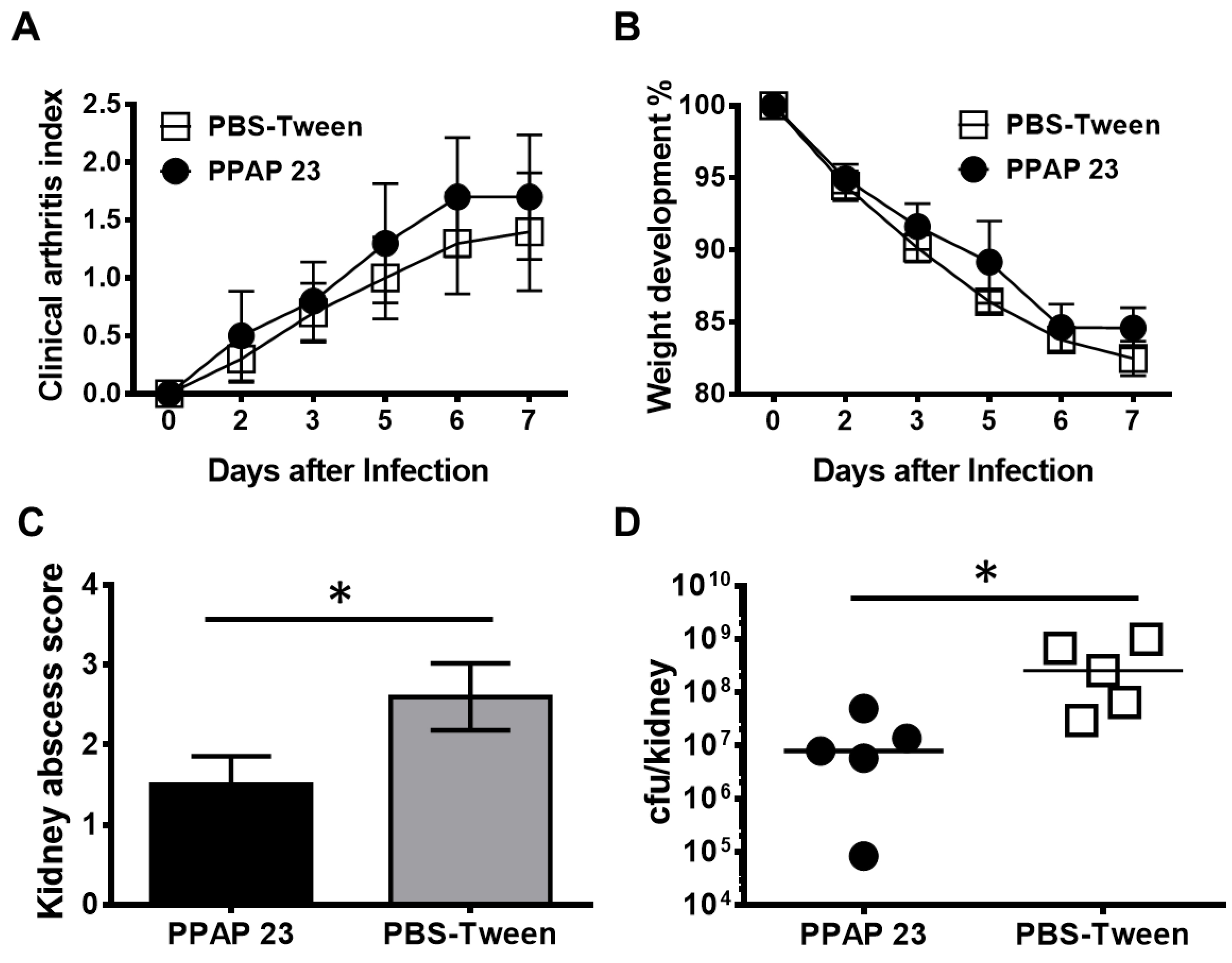
2.6. PPAP 23 Showed A Beneficial But Not Fully Protective Effect on S. Aureus Septic Arthritis Mouse Model
2.7. PPAP 23 and PPAP 53 Showed Activity Against Gut, Gram+ Anaerobic Pathogens
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strains, Growth Conditions and Antibiotics
4.2. Synthesis of PPAP 53
4.3. Bacterial Growth Kinetics
4.4. Antibiotic Susceptibility Testing
4.5. Galleria Mellonella Infection Model
4.6. Ex Vivo Killing Assay of Galleria Mellonella Larvae
4.7. Mouse Model for Hematogenous S. Aureus Arthritis
4.8. Mouse Model of Subcutaneous Abscess Formation
4.9. IC25 Values of PPAP 23 Against Some of The Anaerobic Bacterial Strains
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
References
- Barnes, J.; Anderson, L.A.; Phillipson, J.D. St John’s Wort (Hypericum Perforatum L.): A Review of Its Chemistry, Pharmacology and Clinical Properties. J Pharm Pharmacol 2001, 53, 583–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.S.; Bhattacharya, S.K.; Wonnemann, M.; Singer, A.; Müller, W.E. Hyperforin as a Possible Antidepressant Component of Hypericum Extracts. Life Sci 1998, 63, 499–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciochina, R.; Grossman, R.B. Polycyclic Polyprenylated Acylphloroglucinols. Chem Rev 2006, 106, 3963–3986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bystrov, N.S.; Dobrynin, V.N.; Kolosov, M.N.; Chernov, B.K.; Chervin, I.I. Structure of the Antibiotic Hyperforin. Dokl Akad Nauk SSSR 1976, 226, 88–90. [Google Scholar]
- Beerhues, L. Hyperforin. Phytochemistry 2006, 67, 2201–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavone, B.I.P.; Rosato, A.; Marilena, M.; Gibbons, S.; Bombardelli, E.; Verotta, L.; Franchini, C.; Corbo, F. Biological Evaluation of Hyperforin and Its Hydrogenated Analogue on Bacterial Growth and Biofilm Production. J Nat Prod 2013, 76, 1819–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biber, N.; Möws, K.; Plietker, B. The Total Synthesis of Hyperpapuanone, Hyperibone L, Epi-Clusianone and Oblongifolin A. Nat Chem 2011, 3, 938–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horeischi, F.; Biber, N.; Plietker, B. The Total Syntheses of Guttiferone A and 6-Epi-Guttiferone A. J Am Chem Soc 2014, 136, 4026–4030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socolsky, C.; Plietker, B. Total Synthesis and Absolute Configuration Assignment of MRSA Active Garcinol and Isogarcinol. Chemistry – A European Journal 2015, 21, 3053–3061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verotta, L.; Appendino, G.; Belloro, E.; Bianchi, F.; Sterner, O.; Lovati, M.; Bombardelli, E. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Hyperforin Analogues. Part I. Modification of the Enolized Cyclohexanedione Moiety. J Nat Prod 2002, 65, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peslalz, P.; Vorbach, A.; Bleisch, A.; Liberini, E.; Kraus, F.; Izzo, F.; Brötz-Oesterhelt, H.; Götz, F.; Plietker, B.; Peslalz, P.; et al. Chemical Predictive Modelling and Natural Product-Based Divergent Synthesis – Design of Type B PPAPs with Nanomolar Activities against MRSA. Chemistry – A European Journal, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Guttroff, C.; Baykal, A.; Wang, H.; Popella, P.; Kraus, F.; Biber, N.; Krauss, S.; Götz, F.; Plietker, B. Polycyclic Polyprenylated Acylphloroglucinols: An Emerging Class of Non-Peptide-Based MRSA- and VRE-Active Antibiotics. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 2017, 56, 15852–15856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Kraus, F.; Popella, P.; Baykal, A.; Guttroff, C.; François, P.; Sass, P.; Plietker, B.; Götz, F. The Polycyclic Polyprenylated Acylphloroglucinol Antibiotic PPAP 23 Targets the Membrane and Iron Metabolism in Staphylococcus Aureus. Front Microbiol 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanner, S.; Schade, J.; Keinhörster, D.; Weller, N.; George, S.E.; Kull, L.; Bauer, J.; Grau, T.; Winstel, V.; Stoy, H.; et al. Wall Teichoic Acids Mediate Increased Virulence in Staphylococcus Aureus. Nature Microbiology 2017 2:4 2017, 2, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailly, C.; Vergoten, G. Anticancer Properties and Mechanism of Action of Oblongifolin C, Guttiferone K and Related Polyprenylated Acylphloroglucinols. Nat Prod Bioprospect 2021, 11, 629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, J.A.; Pouwer, R.H.; Chen, D.Y.K. The Chemistry of the Polycyclic Polyprenylated Acylphloroglucinols. Angewandte Chemie International Edition 2012, 51, 4536–4561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.W.; Grossman, R.B.; Xu, G. Research Progress of Polycyclic Polyprenylated Acylphloroglucinols. Chem Rev 2018, 118, 3508–3558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossman, R.B. , Table of PPAPs Available online:. Available online: https://organicchemistrydata.org/grossman/ppap/allPPAPs.html (accessed on 11 June 2024).
- Tsai, C.J.Y.; Loh, J.M.S.; Proft, T. Galleria Mellonella Infection Models for the Study of Bacterial Diseases and for Antimicrobial Drug Testing. Virulence 2016, 7, 214–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obradović, D.; Radan, M.; Đikić, T.; Nikolić, M.P.; Oljačić, S.; Nikolić, K. The Evaluation of Drug-Plasma Protein Binding Interaction on Immobilized Human Serum Albumin Stationary Phase, Aided by Different Computational Approaches. J Pharm Biomed Anal 2022, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zsila, F.; Bikadi, Z.; Malik, D.; Hari, P.; Pechan, I.; Berces, A.; Hazai, E. Evaluation of Drug-Human Serum Albumin Binding Interactions with Support Vector Machine Aided Online Automated Docking. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 1806–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrow, R.J.; Lawson, N.; Hussaini, S.H.; Asquith, P. The Usefulness of Faecal Haemoglobin, Albumin and Alpha-1-Antitrypsin in the Detection of Gastrointestinal Bleeding. Ann Clin Biochem 1990, 27 ( Pt 3) Pt 3, 208–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, P.N.; Blirup-Jensen, S.; Svendsen, P.J.; Wandall, J.H. Characterization and Quantification of Plasma Proteins Excreted in Faeces from Healthy Humans. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 1995, 55, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Q.; Li, X.; Mo, W.; Yang, Z. Low Serum Bilirubin, Albumin, and Uric Acid Levels in Patients with Crohn’s Disease. Medicine 2019, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abt, M.C.; McKenney, P.T.; Pamer, E.G. Clostridium Difficile Colitis: Pathogenesis and Host Defence. Nature Reviews Microbiology 2016 14:10 2016, 14, 609–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eichner, M.; Augustin, C.; Fromm, A.; Piontek, A.; Walther, W.; Bücker, R.; Fromm, M.; Krause, G.; Schulzke, J.D.; Günzel, D.; et al. In Colon Epithelia, Clostridium Perfringens Enterotoxin Causes Focal Leaks by Targeting Claudins Which Are Apically Accessible Due to Tight Junction Derangement. J Infect Dis 2017, 217, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legaria, M.C.; García, S.D.; Tudanca, V.; Barberis, C.; Cipolla, L.; Cornet, L.; Famiglietti, A.M.R.; Stecher, D.; Vay, C.A. Clostridium Ramosum Rapidly Identified by MALDI-TOF MS. A Rare Gram-Variable Agent of Bacteraemia. Access Microbiol 2020, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezeji, J.C.; Sarikonda, D.K.; Hopperton, A.; Erkkila, H.L.; Cohen, D.E.; Martinez, S.P.; Cominelli, F.; Kuwahara, T.; Dichosa, A.E.K.; Good, C.E.; et al. Parabacteroides Distasonis: Intriguing Aerotolerant Gut Anaerobe with Emerging Antimicrobial Resistance and Pathogenic and Probiotic Roles in Human Health. Gut Microbes 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henke, M.T.; Kenny, D.J.; Cassilly, C.D.; Vlamakis, H.; Xavier, R.J.; Clardy, J. Ruminococcus Gnavus, a Member of the Human Gut Microbiome Associated with Crohn’s Disease, Produces an Inflammatory Polysaccharide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2019, 116, 12672–12677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traeger, A.; Voelker, S.; Shkodra-Pula, B.; Kretzer, C.; Schubert, S.; Gottschaldt, M.; Schubert, U.S.; Werz, O. Improved Bioactivity of the Natural Product 5-Lipoxygenase Inhibitor Hyperforin by Encapsulation into Polymeric Nanoparticles. Mol Pharm 2020, 17, 810–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Füller, J.; Kellner, T.; Gaid, M.; Beerhues, L.; Müller-Goymann, C.C. Stabilization of Hyperforin Dicyclohexylammonium Salt with Dissolved Albumin and Albumin Nanoparticles for Studying Hyperforin Effects on 2D Cultivation of Keratinocytes in Vitro. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 2018, 126, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gemmell, C.G.; Edwards, D.I.; Fraise, A.P.; Gould, F.K.; Ridgway, G.L.; Warren, R.E. Guidelines for the Prophylaxis and Treatment of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA) Infections in the UK. J Antimicrob Chemother 2006, 57, 589–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rennie, R.P.; Turnbull, L.; Brosnikoff, C.; Cloke, J. First Comprehensive Evaluation of the M.I.C. Evaluator Device Compared to Etest and CLSI Reference Dilution Methods for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing of Clinical Strains of Anaerobes and Other Fastidious Bacterial Species. J Clin Microbiol 2012, 50, 1153–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiegand, I.; Hilpert, K.; Hancock, R.E.W. Agar and Broth Dilution Methods to Determine the Minimal Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) of Antimicrobial Substances. Nature Protocols 2008 3:2 2008, 3, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popella, P.; Krauss, S.; Ebner, P.; Nega, M.; Deibert, J.; Götz, F. VraH Is the Third Component of the Staphylococcus Aureus VraDEH System Involved in Gallidermin and Daptomycin Resistance and Pathogenicity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2016, 60, 2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herigstad, B.; Hamilton, M.; Heersink, J. How to Optimize the Drop Plate Method for Enumerating Bacteria. J Microbiol Methods 2001, 44, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Welin, A.; Schwarze, J.C.; Svensson, M.N.D.; Na, M.; Jarneborn, A.; Magnusson, M.; Mohammad, M.; Kwiecinski, J.; Josefsson, E.; et al. CTLA4 Immunoglobulin but Not Anti-Tumor Necrosis Factor Therapy Promotes Staphylococcal Septic Arthritis in Mice. J Infect Dis 2015, 212, 1308–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, L.; Pruteanu, M.; Kuhn, M.; Zeller, G.; Telzerow, A.; Anderson, E.E.; Brochado, A.R.; Fernandez, K.C.; Dose, H.; Mori, H.; et al. Extensive Impact of Non-Antibiotic Drugs on Human Gut Bacteria. Nature 2018, 555, 623–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Medium | MIC (µg/ml) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| PPAP 23 | PPAP 53 | Vancomycin | |
| MHB | 1 | 0.5 | 1 |
| MHB + 25% FBS | 32 | 32 | 2 |
| MHB + 0.5% BSA | 4 | 8 | 1 |
| MHB +1% BSA | 8 | 8 | 1 |
| MHB + 2.5% BSA | 16 | 16 | 1 |
| MHB + 5% BSA | 32 | 32 | 2 |
| MHB + 1% IgG | 1 | 0.5 | 1 |
| MHB + 2.5% IgG | 1 | 0.5 | 1 |
| MHB + 1% Fg | 1 | 0.5 | 1 |
| MHB + 2.5% Fg | 1 | 0.5 | 1 |
| Strains | PPAP 23 IC25 (µM) | PPAP 53 IC53 (µM) |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| Pathogenic G (+) gut anaerobes |
Clostridium difficile | < 2 | > 80 |
| Clostridium perfringens | < 2 | 5 | |
| Ruminococcus gnavus | < 2 | 5 | |
| Clostridium ramosum | < 2 | 10 | |
| Commensal gut anaerobes (+/-) | Streptococcus salivarius | < 2 | 5 |
| Dorea formicigenerans | 4 | 10 | |
| Streptococcus parasanguinis | 4 | 10 | |
| Roseburia intestinalis | 4 | 10 | |
| Coprococcus comes | 4 | 10 | |
| Collinsella aerofaciens | 4 | 10 | |
| Eubacterium rectale | 4 | 5 | |
| Clostridium bolteae | 22 | 10 | |
| Parabacteroides merdae | 22 | 5 | |
| Clostridium saccharolyticum | 22 | 10 | |
| Fusobacterium nucleatum subsp. Nucleatum | > 45 | 40 | |
| Bacteroides vulgatus | 22 | 5 | |
| Bacteroides uniformis | > 45 | 10 | |
| Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron | > 45 | 20 | |
| Bacteroides fragilis NT | 22 | 10 | |
| Pathogenic G (–) gut anaerobes |
Yersinia pseudotuberculosis | > 22 | 2.5 |
| Yersinia enterocolitica WA-314 | > 45 | > 80 | |
| Vibrio cholerae | > 45 | 80 | |
| Shigella sonnei 53G | > 45 | > 80 | |
| Shigella flexneri | > 45 | > 80 | |
| Salmonella enterica typhimurium LT2 | > 45 | > 80 | |
| Salmonella enterica typhimurium | > 45 | > 80 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





