1. Introduction
The use of 2D Electrical Resistivity Imaging proves to be a highly efficient method for the examination and analysis of the hydrogeological properties inherent in subsurface materials[
1]. When employing this methodology, the focus encompasses not solely the groundwater but also the geological formations and materials that possess the capacity to retain and convey the groundwater[
2] . The 2D Electrical Resistivity Imaging method has been applied in geophysical exploration for many years[
3]. Since its inception, this method has witnessed significant progress in data acquisition and interpretation techniques[
4] . Alongside advancements in computer technology, there has been a notable increase in the range of applications for this method[
5] . Consequently, it has become more precise and efficient to map small-scale and complex hydrogeological features[
6,
7] . Electrical resistivity methods have the potential to provide valuable insights into subsurface conditions in areas of hydrogeological importance. Numerous studies have been reported regarding the examination of conductive and resistive intrusive bodies through the utilization of resistivity soundings and profiling surveys [
8]. Resistivity is a measure of a material's resistance to electrical conduction [
9,
10]. It is a material property that depends on its water content, lithology, porosity, temperature, etc., but not on its size and shape. It decreases with increasing clay content. It decreases quickly with the water content[
11]. The distribution of subsurface resistivity can be interpreted from a hydrological point of view.
In addition, computer-based resistivity surveys have been conducted on fractured and fissured bedrocks. Geophysical techniques have proven to be highly effective in the mapping of subsurface areas for the purpose of identifying groundwater presence[
12,
13] . In regions characterized by lack of drilling data, the utilization of electrical methods presents a feasible strategy for the examination of groundwater resources. These methods can be employed to facilitate the identification of the appropriate location for groundwater exploration. The two most commonly utilized geophysical techniques for mapping the electrical characteristics of the underlying properties of the subsurface are resistivity and electromagnetic methods[
14,
15] . The Wenner, Schlumberger, pole-pole, dipole dipole, and pole dipole arrays are widely employed in various applications[
16] . The latter array has been effectively utilized in numerous studies for the differentiation of complex hydrogeological structures[
17,
18] . In the present study, the forward and inverse pole-dipole array was used because it has substantially higher measurement efficiency to obtain high resolution 2D resistivity data, is less affected by the remote electrode, has greater vertical sensitivity, and a large depth of investigation. In mountainous regions, geoelectric surveys can be impacted by lateral surface irregularities and steep gradients, regardless of the array used [
19,
20]. Changes in topography create distortions in the measured potential field, which can result in terrain anomalies[
21,
22] . The objectives of this work were to assess the distribution of the subsurface resistivity, the distribution of the fractures and fault zones in the study area, and the location and depth of the zone probable for groundwater exploration. In this research work, the 2D Electrical Resistivity Imaging method was used to characterize the subsurface layers for groundwater exploration in Nanshan Township, Huarong County, Hunan Province, China. It's crucial to remember that resistivity analysis in this paper is our primary focus, as the IP parameters of the area are not considered because of the interference that caused noises to the profiles in close proximity to a production plant.
The present study was conducted upon the request of the Hunan Survey and Design Institute, with the collaboration and support of the geological survey research group from Central South University. The aim of this project was to create a comprehensive map of the groundwater resources in the study area.
2. Study Area and Location
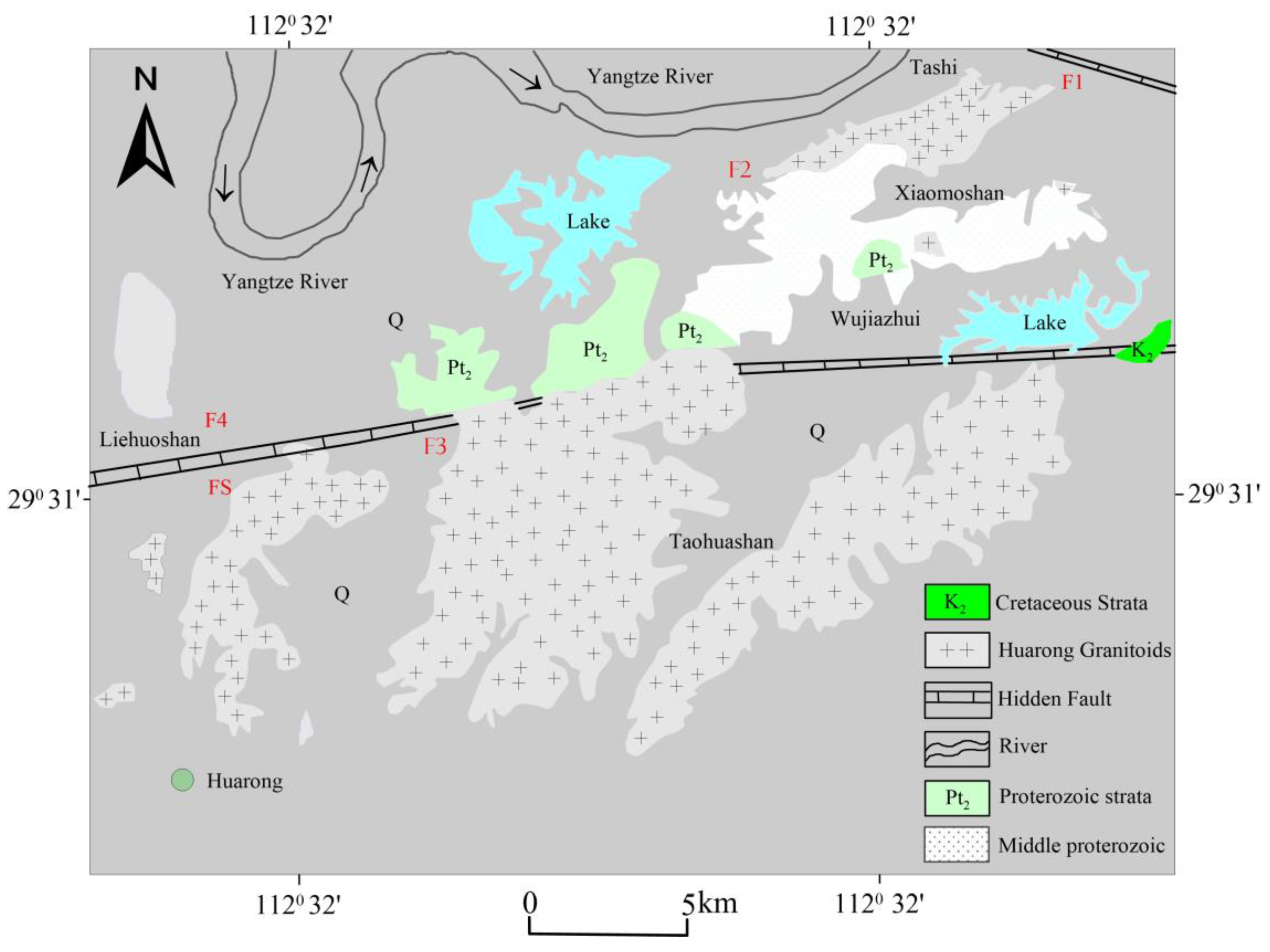
Located within the complex geological landscape of Nanshan Township, Huarong County presents itself as an intriguing trek into the northern boundary of Hunan Province, China. Situated in the western region of Yueyang City, this area is geographically next to Junshan District in the east and Nan County of Yiyang City in the west. To the south, it intersects with the state-owned Beizhouzi Farm County, while to the north, it shares a boundary with Shishou City in Hubei Province. It is located along the Yangtze River, covers an area of 1590.95 square kilometres, and has a population of 548,400 as of 2022. Huarong County encompasses 12 towns and 2 townships, showcasing a combination of cultural abundance and administrative importance. The historical transformation of the territory in 1986, when it became part of the city-governed county system of Yueyang City
Figure 1, has significantly influenced its governance and growth trajectory.
3. Geological Setting
This The area is situated within the central region of the second settlement zone in the Neo-Cathaysian system. The Huarong uplift traverses the eastern portion of this region in a northwestern direction. The geological phenomenon observed can be classified as a fault-block uplift[
23]. The formation of the Dongting Lake depression in the southern region and the Hanshui depression in the northern region can be attributed to the gradual development of large Meso-Cenozoic depression basins, which commenced during the Yanshanian period. The distribution of bedrock outcrops in the region is characterized by scattering. Notably, the area exhibits the presence of the Mesoproterozoic Lengjiaxi Group, Taohua Mountain, and Xiaomushan rock mass. Additionally, a limited occurrence of the Upper Cretaceous Uniform Tertiary system distribution can be observed see,
Figure 2.
The Huarong granitoids include the Xiaomoshan and Taohuashan plutons and are part of a NE-trending magmatic belt along the southern margin of the Jianghan Basin in the northeastern Hunan province[
24] . The Huarong granitoids intrude the Mesoproterozoic Lengjiaxi Formation that is dominated by low-grade phyllite, schist, and variolite formations, which collectively form a complex fold structure known as the Huarong uplift [
26]. This fold has an axial direction ranging from 280° to 290° and exhibits a relatively gentle wing angle of 10° to 20°. The rock bodies of Xiaomushan and Taohuashan are believed to have originated during the Yanshan stages, specifically in the early and late periods of this geological epoch[
25] . The predominant lithological composition of the rock bodies is monzogranite, accompanied by multiple stages of dike intrusion and a variety of dike types. The predominant structural orientation in the region was primarily northwest, with the exception of the Huarong uplift and Hanshui depression. Situated between the aforementioned depression and uplift, the Jianli hidden base fault (F) exhibited a fracture pattern extending approximately 25 kilometers in a direction of 290°[
26] .
Furthermore, it should be noted that there exists a fracture known as the Yongbungyeong fracture (F2), which spans approximately 4 kilometers in length. This fracture is characterized by a relatively narrow structural change belt and is composed of breccia with tensile properties. It is worth mentioning that the fracture is believed to have originated from the secondary elongation of the Huarong rise, with a speculated orientation of 290° (strike) and an inclination of 60° (dip) towards the northeast. The presence of a northwest-trending structure gives rise to a secondary northwest-trending fault characterized by tension-torsion, as exemplified by the Fire Mountain fault (F3). The Jiufulgang fault (F4) holds significant importance in the context of the NE-E-W structure. The formation of this fault seems to have occurred during a later stage of its tectonic development, and it is distinguished by the presence of multiple phases of activity as observed in the field. The Jiangnan Fault (FS) is an underlying fault belt that is not readily apparent, spanning approximately 2,000 kilometers in length and exhibiting variable widths typically ranging from 30 to 50 kilometers[
27]. The precise geographical coordinates of this location lie to the south of Xingzi and to the north of Wuning in Jiangxi Province. Furthermore, it is situated to the south of Tongshan, Chongyang, and Puqi in Hubei Province, as well as to the south of Linxiang, to the north of Huarong, and to the south of Lixian County in Hunan Province. Subsequently, a connection can be established between the aforementioned phenomenon and the Yongshun Yisong and Cili deep faults. The formation of this entity occurred during the Mesoproterozoic era, and its activity persisted until the Meso-Cenozoic era. During the initial phase, the geological conditions were primarily marked by subterranean faults that exerted control over the process of sedimentation. Subsequently, in the early Miocene epoch, the region experienced the emergence of numerous thrusting nappes, which propagated in a northward direction from the southern part of the area.
4. Hydrogeological and Stratigraphic Characteristics
The study area has hydrogeological and stratigraphic conditions that are characterised by the exposure of formations from the Lower Cambrian Lengjiaxi Group and the Middle-Upper Quaternary Baishajing Formation, listed in order of age. The Baishajing Formation (Q2b) is mostly found in the eastern and western mountain depressions. It is made up of three layers: a yellowish-red silty clay layer with rock fragments; a dark red sandy silty clay layer with quartz and rock fragments; and a dark red reticulated or granular silty clay layer with black iron-manganese thin films.
The Lower Cambrian Lengjiaxi Group (Ptln) encompasses five sections
Table 1: Ptln
a, exposed in the southern part, comprises argillaceous slate interbedded with sandy slate; Ptln
b, found in Shamucong Wangmaling and Límāoshān areas, with sandy slate and argillaceous slate are interbedded with quartz sandstone; Ptln
c, visible in Jiowān, Wángjiāwān, Ōu Zhāngjiāwān areas, characterized by Argillaceous slate interspersed with sandy slate; Ptln
d, exposed in Māozi Mountain, Dōngguā Mountain, and the southern slope of Yǔshān, comprising argillaceous slate and sandy slate are interbedded with quartz sandstone containing phyrite; and Ptln
e, found in Fei'e Tiebi and the northern slope of Yǔshān, consisting of sandy slate is interspersed with argillaceous slate
Figure 3. Overall, these formations exhibit gentle dips, with inclination angles typically less than 15° to 35°, providing crucial insights into the geological makeup of the study area.
5. Methodology and Field Survey
In this study, the 2D Electrical Resistivity Imaging method is used. The essence of the electrical resistivity imaging instrument is that different frequency signals of special waveforms are sent and received simultaneously to investigate the electrical properties of the subsurface by measuring the resistivity distribution of the materials. The electrical resistivity of the materials depends on a combination of ohmic and dielectric effects related to the lithology of the subsurface [
28]. The apparent resistivity,
ρα, is calculated based on equation 1.
Where
V=voltage
I=current
k=geometric factor
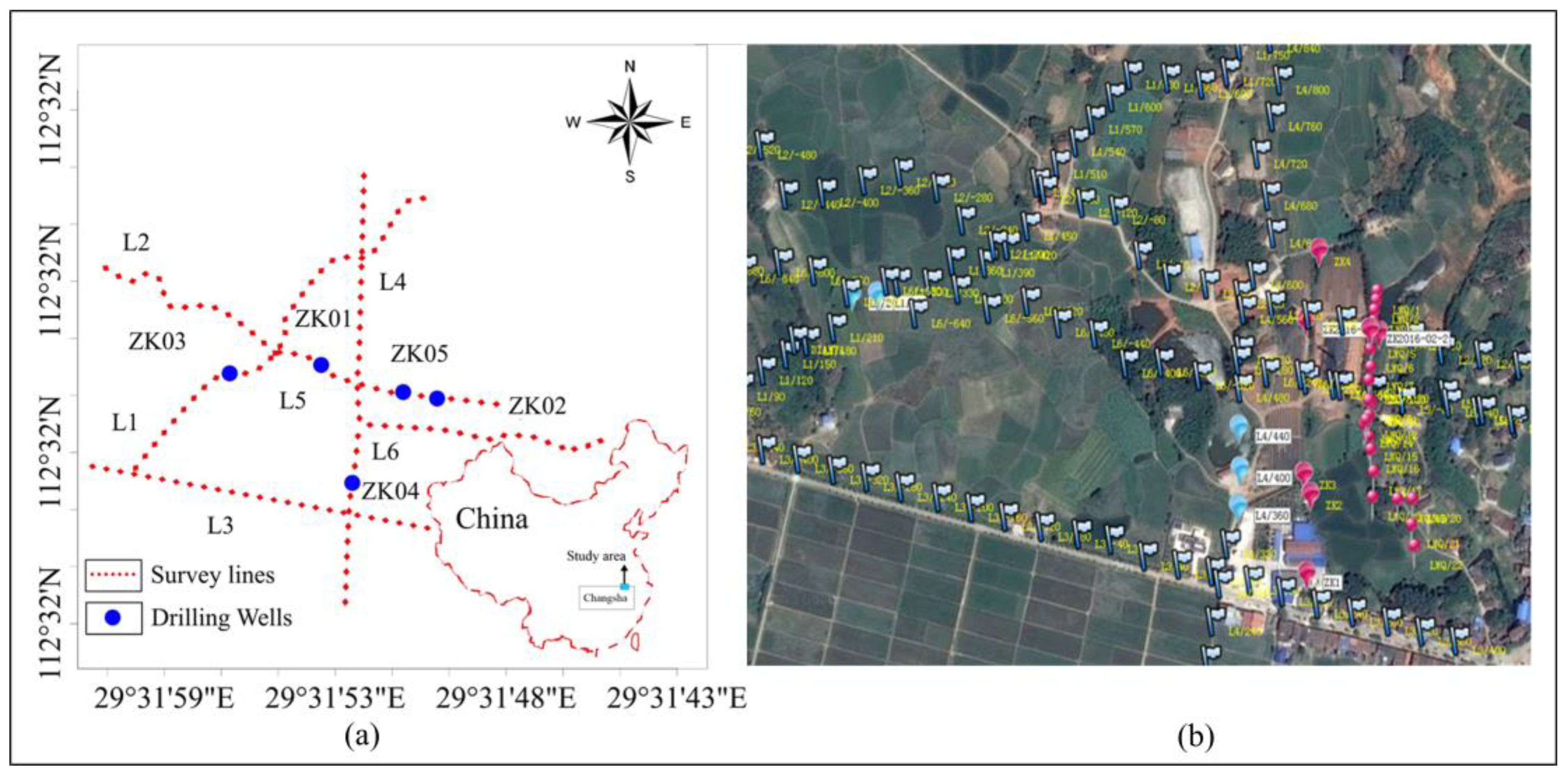
The depth of penetration depends on the current injected, subsurface materials, and is also dependent on the k value for the distance between the current electrodes. In this survey, the Electrical Resistivity Imaging measuring instrument employed is the SQ-3C portable, and its work frequency is in the range of 4-10 Hz. The distance between the Electrical Resistivity sounding points is 20, 30, and 40 meters, and an infinity electrode distance from the nearest measuring point is of greater than 800m. A total of 6 survey lines were laid out; the survey lines were numbered L1 to L6. All physical points are measured using RTK dynamic real-time kinematics; the survey lines layout is shown in
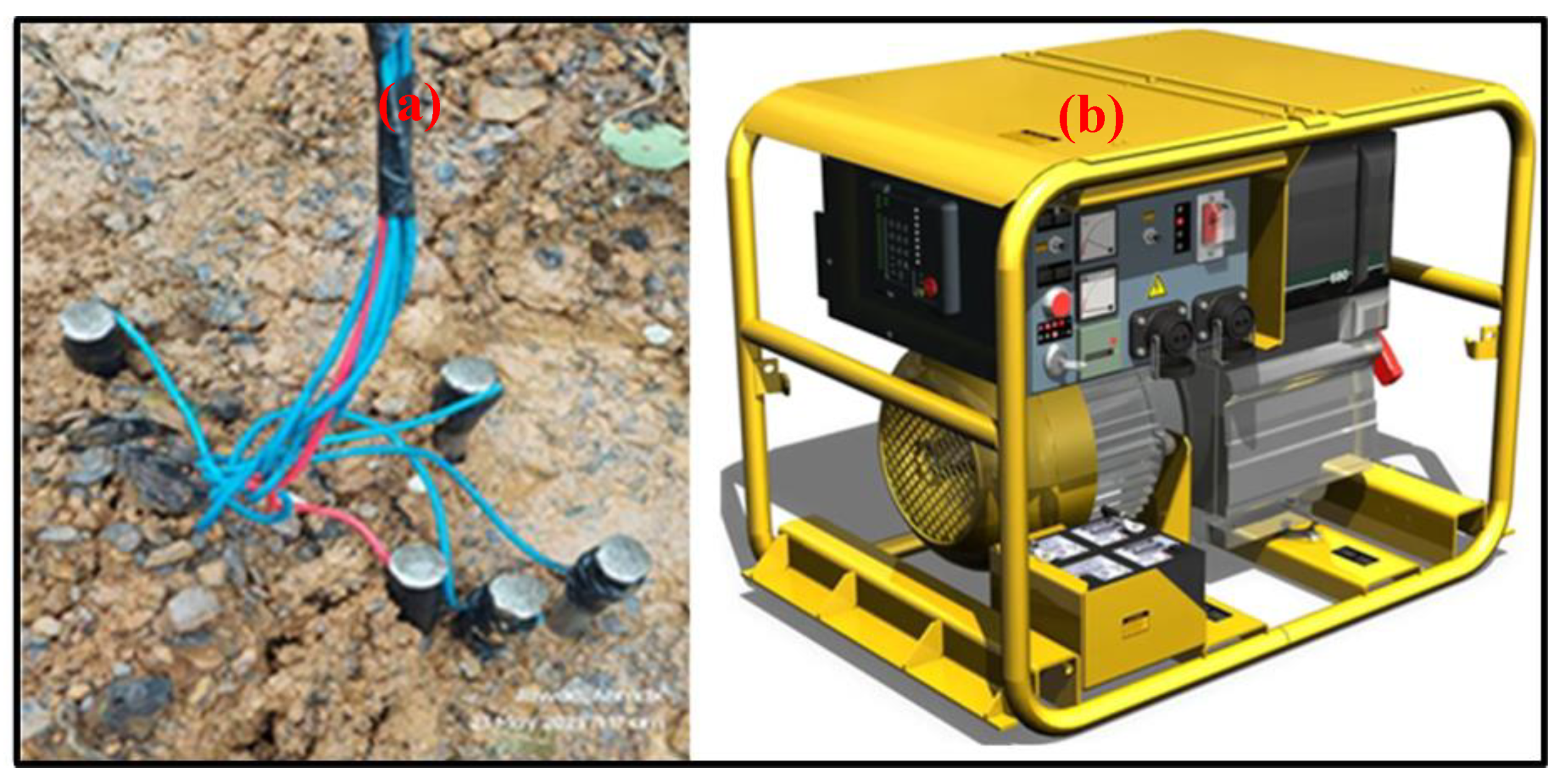
Figure 4. The electrodes used for measurement consist of a single copper electrode. The powered electrodes consist of four or five parallel groups of aluminum foils
Figure 5 (a). A 1-kilowatt (kW) small power generator, along with a rectifier source, was employed to provide power to the equipment
Figure 5 (b).
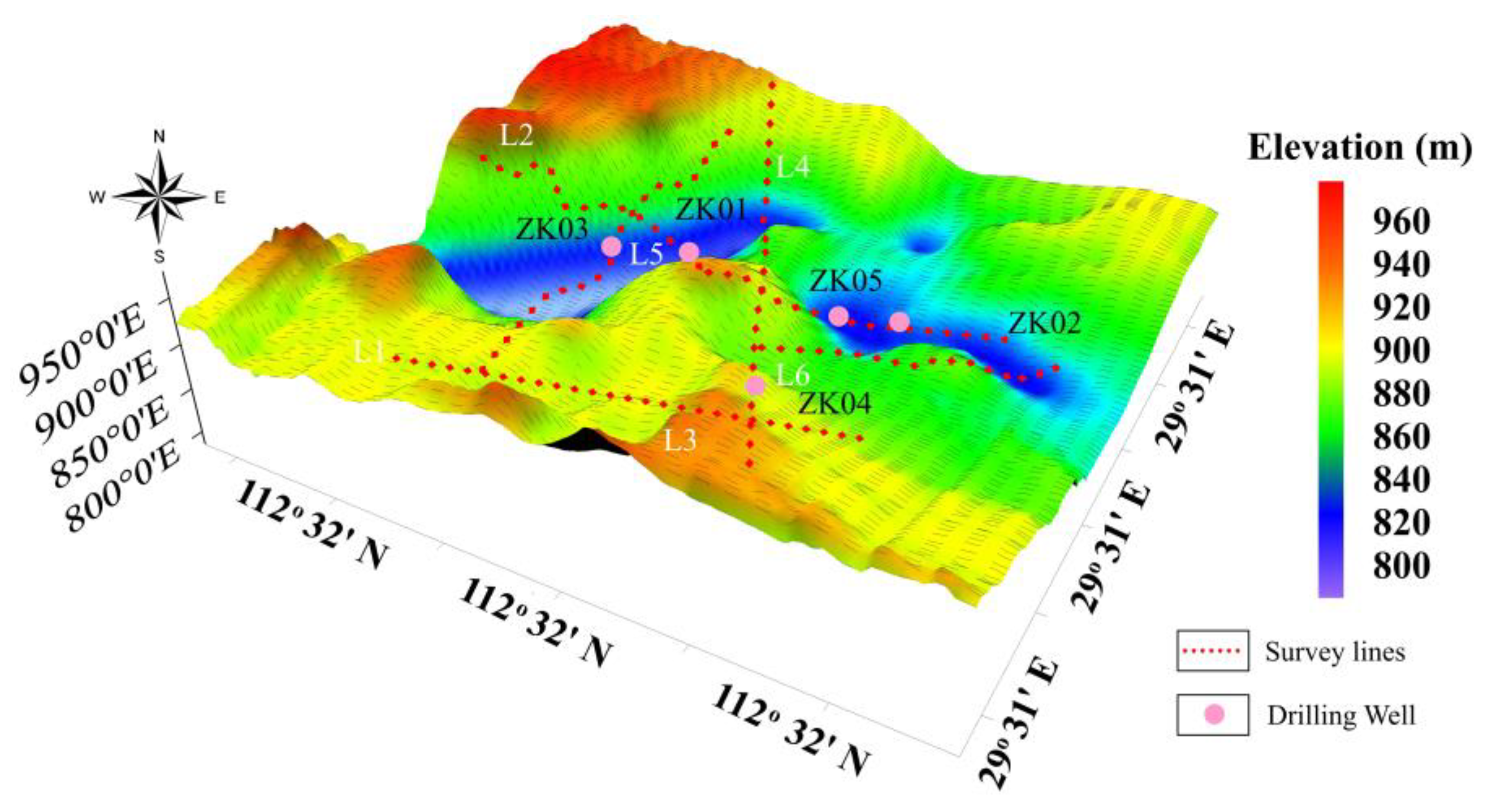
Figure 6 displays the topographic variations in the study area.
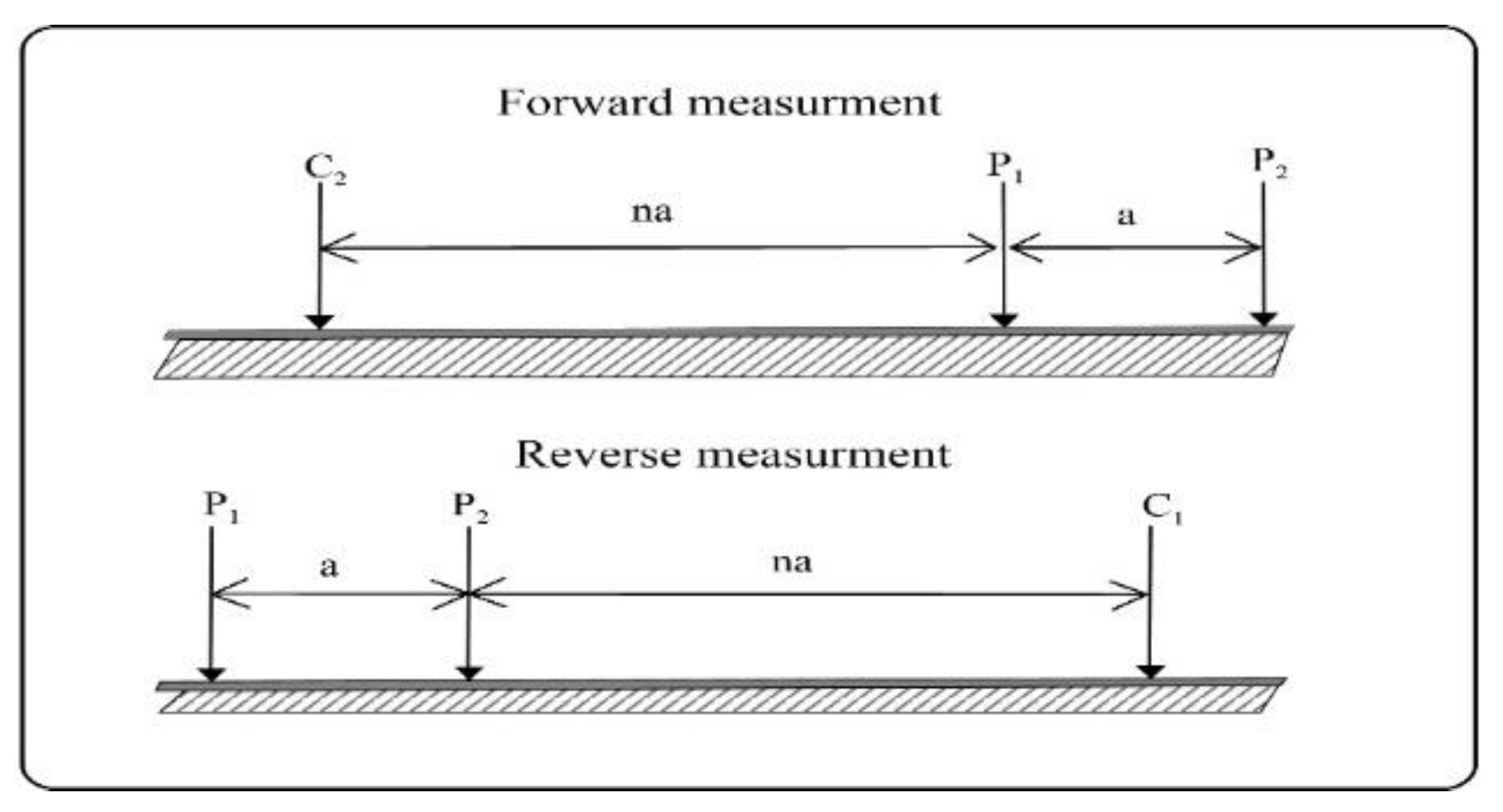
The selection of array configuration, electrode separation, and frequency allocation plays a crucial role in accurate data acquisition. The forward and inverse pole-dipole array was employed in our survey
Figure 7, a widely utilized method for conducting measurements in both profile and area exploration. 2D Electrical Resistivity imaging enhances data resolution at different depths, allowing a comprehensive subsurface analysis. We employed IPINV 3.2 geophysical software for data inversion developed by Central South University[
29]. Before inversion, we quality-checked the data to remove noise. Inversion incorporates multiple information sources to refine potential models and match actual environmental conditions. Multiple inversion techniques are applied iteratively to minimize model-data discrepancies.
6. Interpretation and Results
6.1. Line 1 and Line 2
The length of the L1 line measures 570 meters, with 19 measuring points spaced at intervals of 30 meters. L1 is running from SW-NE with azimuth angle of 57 degrees. Based on the findings obtained from the inversion of the electric sounding analysis of the L1 line, there is a hypothesis suggesting the presence of a fault in the northwest direction, which is believed to traverse in close proximity to the measuring point 255. The electric sounding results clearly indicate the presence of a shallow anomaly characterized by low resistivity. Additionally, it is evident that the resistivity gradually increases to a value exceeding 400 ohm-m at a depth of approximately 100 meters. Based on the available evidence, it can be deduced that there exists a proficient water-conducting fault in this particular region. Additionally, the presence of a contact surface between the mud and sand layers suggests the likelihood of a well-developed aquifer.
The length of the L2 line measures 640 meters, with 16 measuring points spaced at intervals of 40 meters. L2 is running NW-SE with azimuth as angle of 105 degrees. The F2 fault is hypothesized to extend from No. 160 to 240 along line L2. The resistivity sounding data reveals a V shaped low resistivity anomaly zone. This anomaly exhibits considerable thickness, exceeding 200 meters. The observed low resistivity anomaly in the vicinity of this measurement location is believed to be primarily attributed to the presence of argillaceous slate. The presence of a resistivity interface at this specific measuring point suggests the likelihood of it being the contact surface between argillaceous slate and quartz sandstone strata. Additionally, it is hypothesized that there may be water-bearing cracks within this contact surface.
6.2. Drilling Verification Results
Through the geophysical exploration work carried out in Nanshan Township, Huarong County, five verification boreholes have been constructed so far.
6.2.1. ZK05, ZK01 and ZK02 Verification Results Analysis
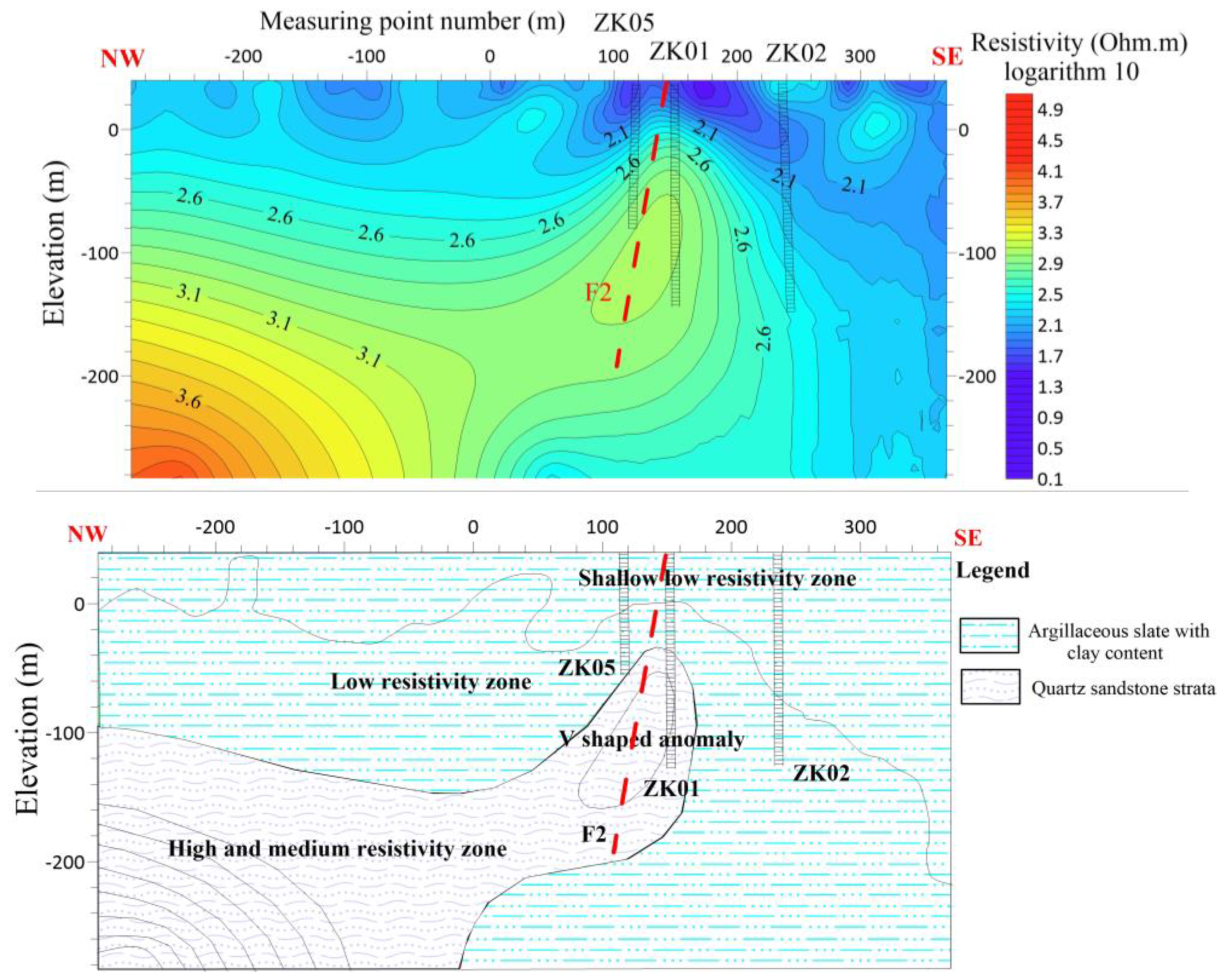
During the advanced phase, verification holes ZK05, ZK01, and ZK02 are strategically positioned in close proximity to measuring points No. 120, 160, and 220, respectively
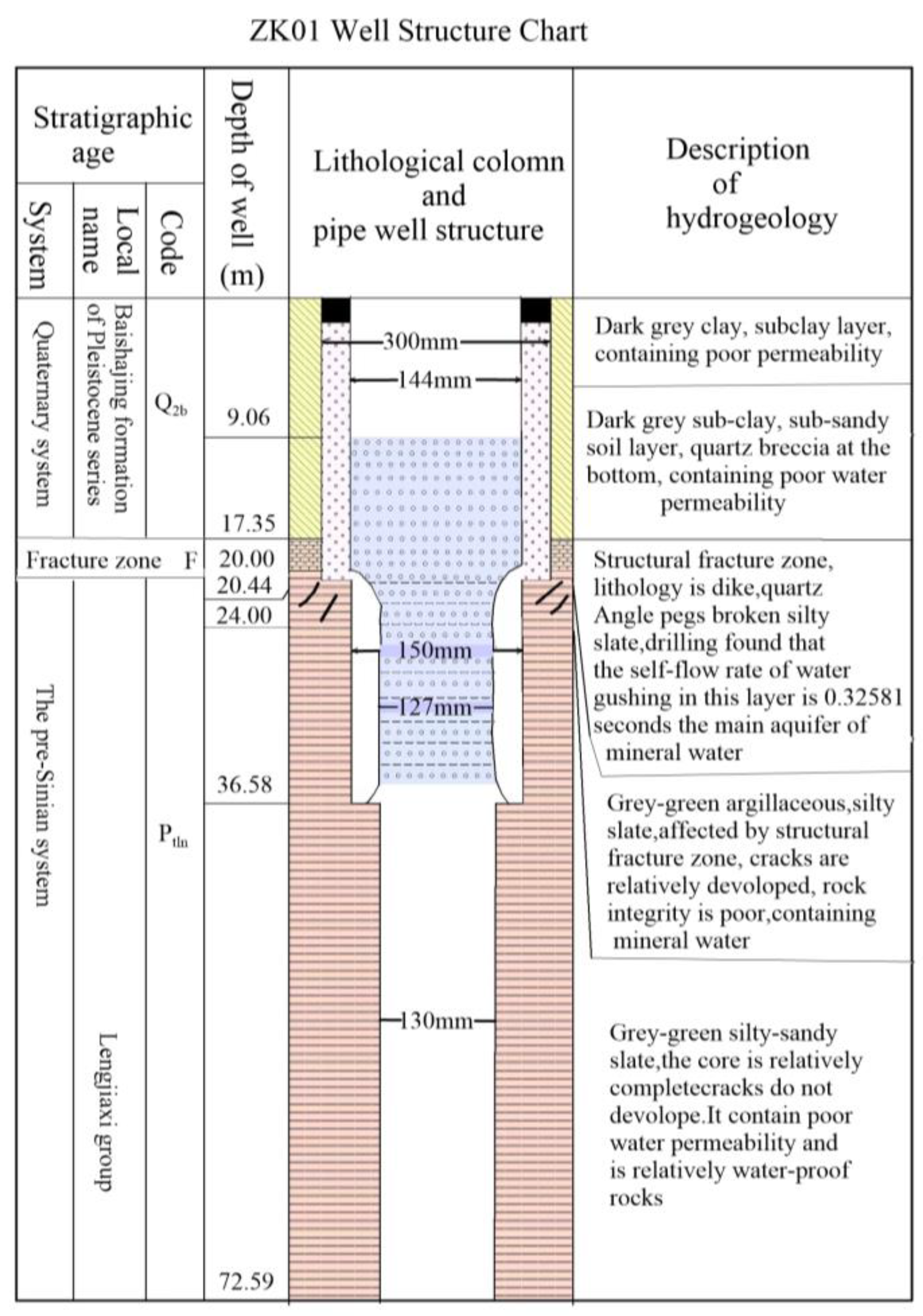
Figure 8. The verification results indicate that the slate containing a significant amount of clay minerals is predominantly found at a depth of 100 meters. Furthermore, it should be noted that as the slate descends to a depth of 100 meters, there is an observable increase in the proportion of sandy composition. A discernible compressive phenomenon is observed at the interface, resulting in the formation of fractures within the underlying sandy stratum. The subsequent pumping test reveals that the ZK01 well has a maximum water output of approximately 460 tons, the ZK02 well has a maximum water output of approximately 170 tons, and the ZK05 well has a maximum water output of approximately 100 tons. It is speculated that the change in water output is due to the F2 fault. The well structure of ZK01 is presented in (
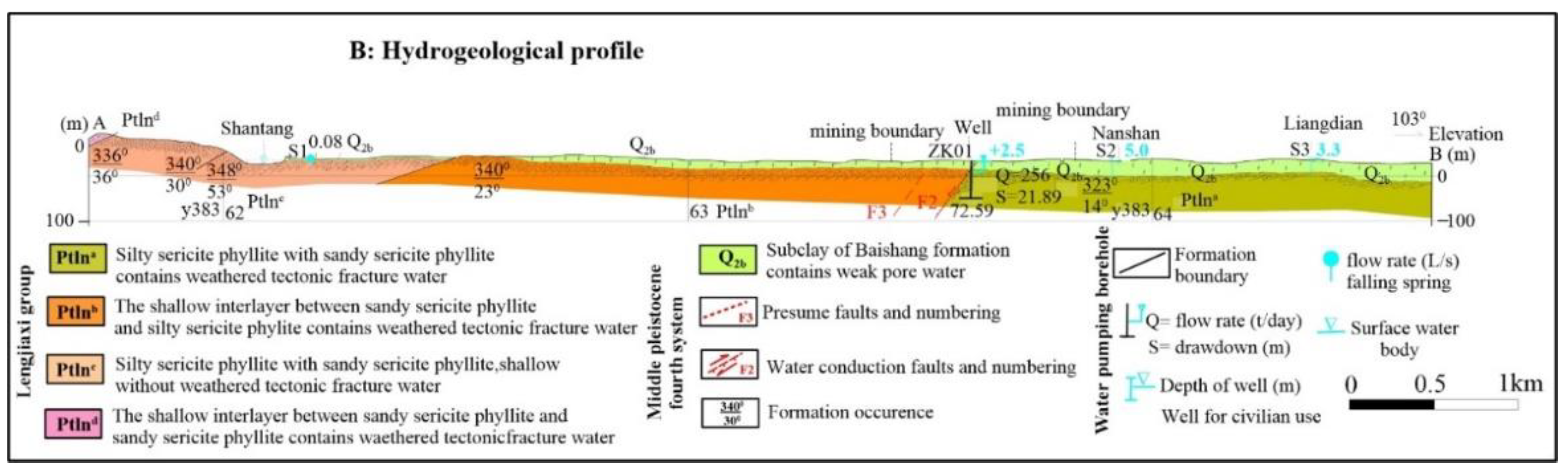
Figure 10) and the hydrogeological profile of lithological log and the surrounding research area is presented in
Figure 11.
Figure 8.
Line 1 (a) shows the resistivity distribution with depth (b) Shows hydrogeological profile of the survey line.
Figure 8.
Line 1 (a) shows the resistivity distribution with depth (b) Shows hydrogeological profile of the survey line.
Figure 9.
Line 2 (a) shows the resistivity distribution with depth (b) Shows hydrogeological profile of the survey line.
Figure 9.
Line 2 (a) shows the resistivity distribution with depth (b) Shows hydrogeological profile of the survey line.
Figure 10.
Lithological map and drilling verification borehole chart of the ZK01 Well.
Figure 10.
Lithological map and drilling verification borehole chart of the ZK01 Well.
Figure 11.
Hydrogeological profile of lithological log ZK01 and the surrounding research area.
Figure 11.
Hydrogeological profile of lithological log ZK01 and the surrounding research area.
6.2.2. ZK03 Verification Results Analysis
The selection of the location for ZK03 verification hole is primarily based on the information obtained from ZK01 and ZK02 verification holes, as well as the analysis conducted above. It is presumed that the F-NW1 fault passes through the chosen location of the verification hole in a northwestern direction. The electric sounding results indicate a clear presence of a shallow low-resistivity anomaly. Additionally, the resistivity at a depth of 100m exceeds 400 ohms, suggesting the existence of a well-conductive fault in the study area. It is further hypothesized that a contact zone between layers of mud and sand textures is present, indicating the likely presence of a productive aquifer. The subsequent verification findings indicate that at a depth of 100m, the predominant lithology is slate, characterized by a high proportion of clay minerals. Below this depth, there is an increase in the presence of sandy materials. Notably, there is a distinct occurrence of fracturing at the contact surface, with the development of cracks in the underlying sandy layer. In terms of water discharge, the water that is exposed through the hole primarily consists of confined water, and the flow of water tends to exit from the periphery of the surface borehole pipe. The results of the recent pumping test indicate a daily water yield of approximately 410 tons from the borehole, which is considered to be significantly high. Furthermore, the verification outcomes align well with the inferred results.
6.3. Line 3 and Line 4
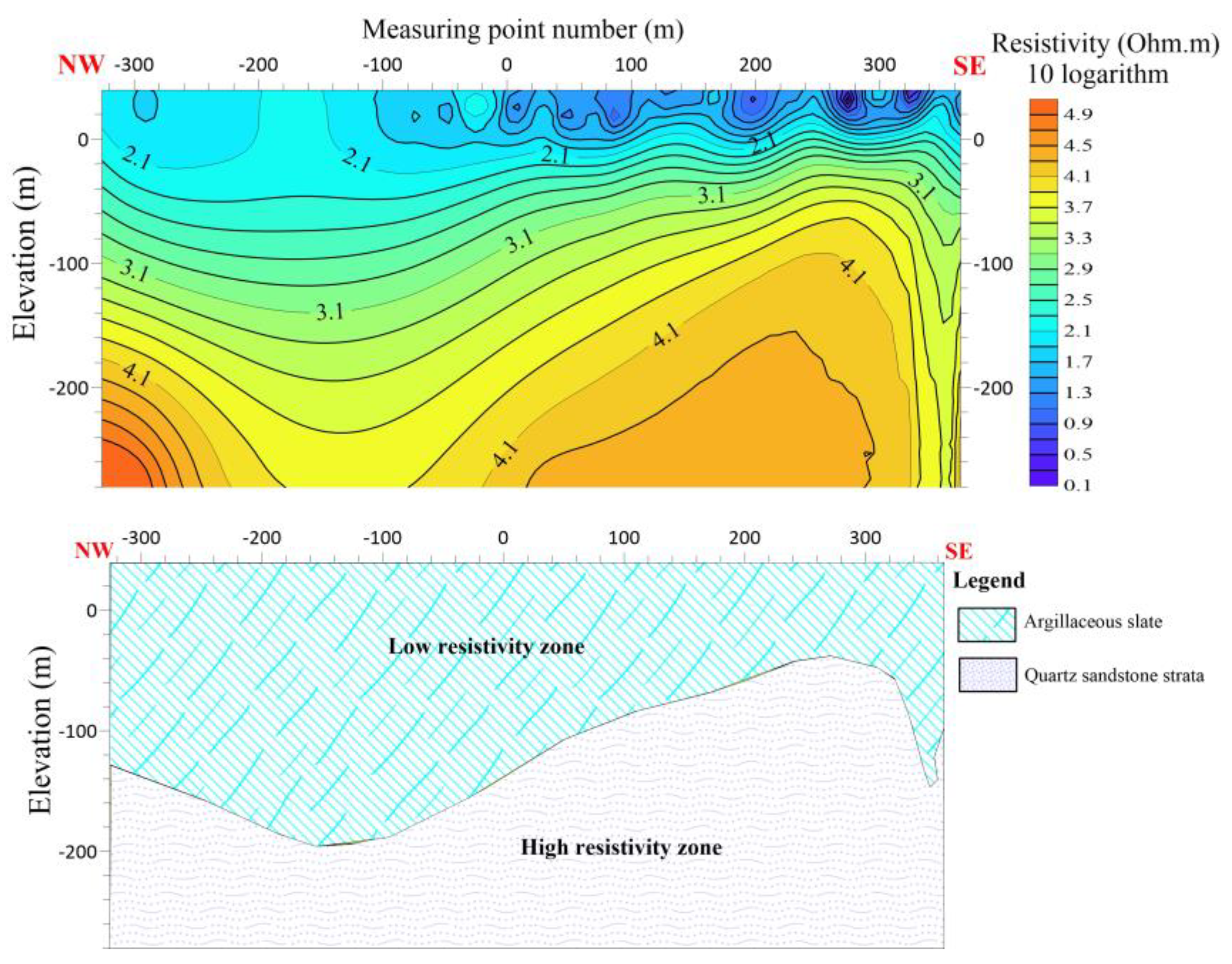
The length of the L3 line is 680 meters, with 17 measuring points spaced 40 meters apart. L3 is running NW-SE with azimuth angle of 105 degrees. The electric sounding inversion results of the L3 line indicate that the survey line predominantly exhibits the typical contact between two stratigraphic layers. The upper section primarily consists of argillaceous slate characterized by low resistivity and anomalous reaction, whereas the lower section is predominantly composed of quartz sandstone exhibiting high resistivity and anomalous reaction. An anomalous response in the resistivity between the measuring points (160-120) suggests the presence of cracks in this particular region.
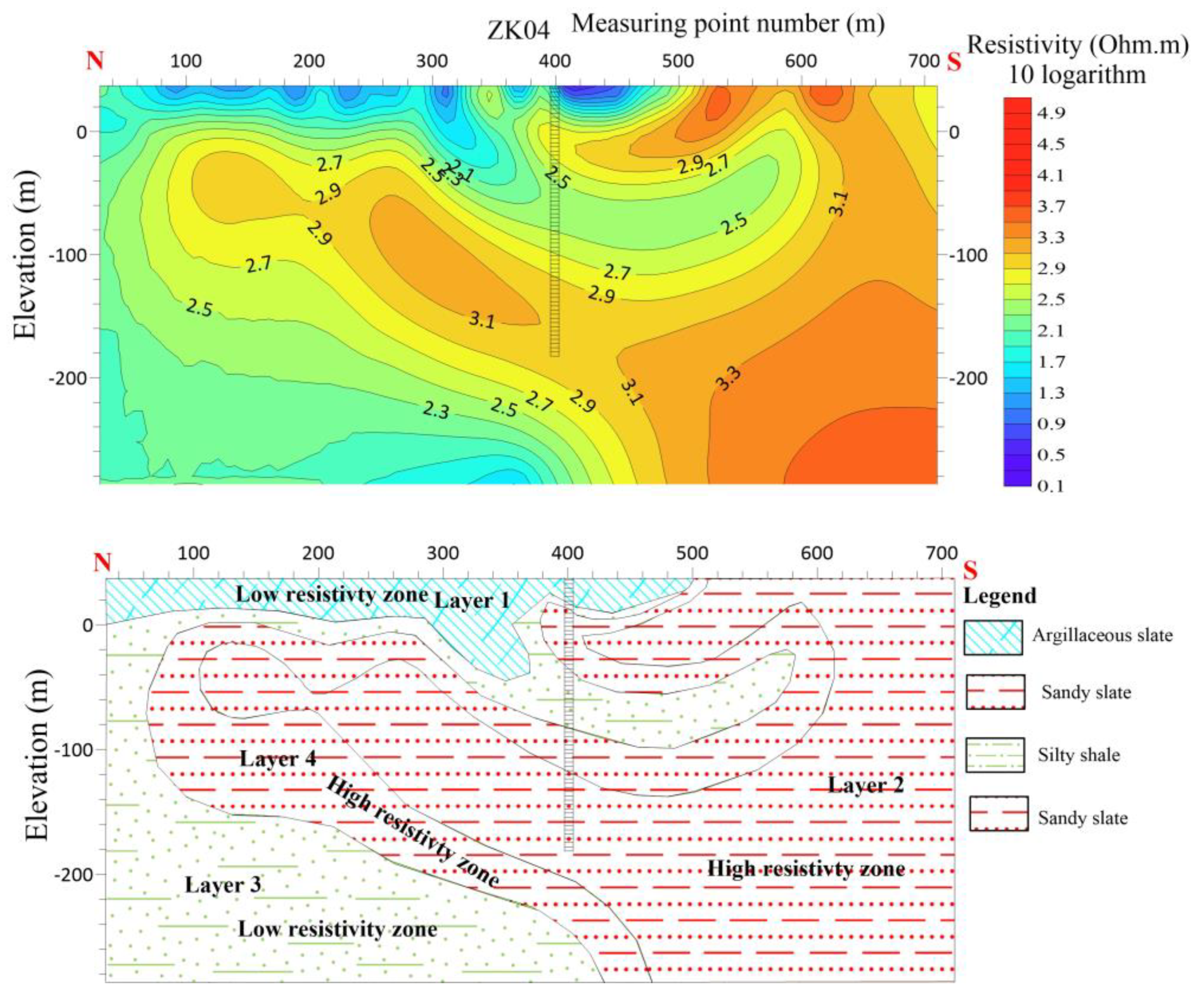
The length of L4 line is 640 meters, with 16 measuring points and the distance between them is 40 meters L4 is running N-S with azimuth angle of 10 degrees. The findings of the electrical sounding conducted on L4 indicate that the upper section of the profile primarily consists of argillaceous slate with a low resistivity. Conversely, the lower section is characterized by a higher resistivity, primarily attributed to the presence of quartz sand slate. There is speculation regarding the presence of fissures within the contact interface of the two strata.
Figure 12.
Line 3 (a) shows the resistivity distribution with depth (b) Shows hydrogeological profile of the survey line.
Figure 12.
Line 3 (a) shows the resistivity distribution with depth (b) Shows hydrogeological profile of the survey line.
Figure 13.
Line 4 (a) shows the resistivity distribution with depth (b) Shows hydrogeological profile of the survey line.
Figure 13.
Line 4 (a) shows the resistivity distribution with depth (b) Shows hydrogeological profile of the survey line.
6.3.1. ZK04 Verification Results Analysis
The ZK04 verification hole was drilled to investigate the potential for aquifers in the area based on electrical sounding data and the results from previous verification holes. The hole was found to have four resistivity layers, with the first layer being a low-resistivity layer of quaternary and argillaceous slate. The second layer was a high-resistivity sandy slate, while the third layer had reduced resistivity and was believed to have a high argillaceous composition. The fourth layer was another high-resistivity sandy slate. Although the lithological layers were identified as expected, the core of the hole had no obvious traces of water passage, and the pumping test yielded only 30 tons per day, which was unsatisfactory. Analysis of the verification results indicated that the relatively flat contact surface of the lithological layers hindered the formation of crushing, leading to the low water yield. To improve results in future verifications, it is recommended to choose areas with more favorable lithological interfaces that are easier to form broken contact surfaces.
After employing the Electrical resistivity imaging method in the Nanshan Huarong groundwater survey, it is determined that the survey area contains relatively evident indications of faults. In addition, there are two areas of structural damage, which are presumed to be the result of the intersection of distinct directional faults, causing rock fragmentation, an increase in water content, and a decrease in resistivity.
6.4. Line 5 and Line 6
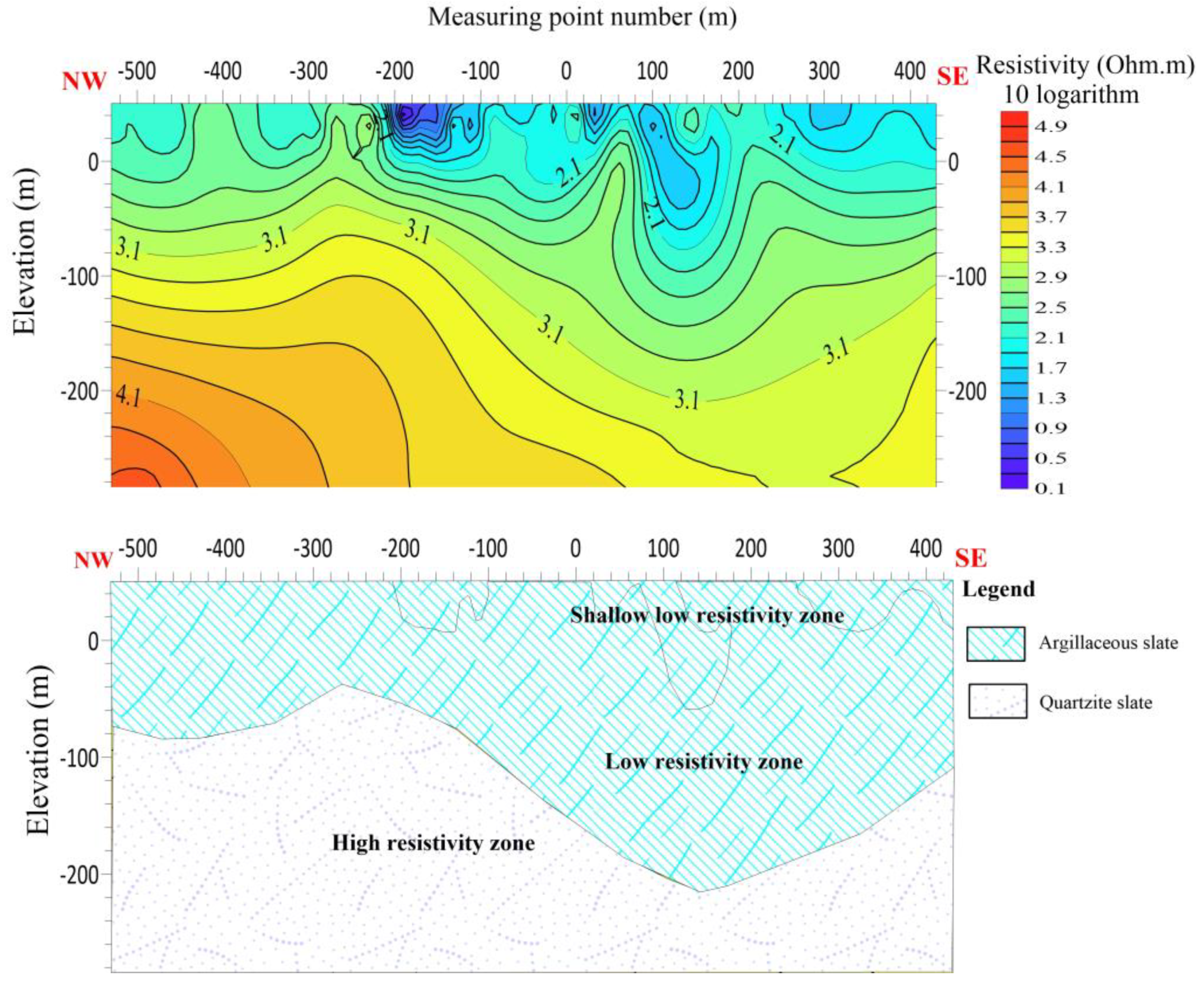
The length of the L5 line is 920 meters, with 24 measuring points and the distance between the points is 40 meters. L5 is running NW-SE with azimuth angle of 102 degrees. The electric sounding results of the L5 line indicate the presence of a noticeable decrease in resistivity between measuring points 80 and 200 at 100 m depth, suggesting the occurrence of a low resistivity anomaly. There is speculation regarding the presence of a fault or crack in this particular component. Additionally, it is postulated that there is both a contact surface with high resistance and a contact surface with low resistance within this component. Furthermore, it is hypothesized that there is a favorable contact surface for water in this component. The shallow portion of the line is hypothesized to consist primarily of argillaceous slate exhibiting a low resistivity abnormal response. In contrast, the deeper section is characterized by quartzite slate, which exhibits a high resistivity reaction. There is speculation regarding the presence of fissures within the contact interface of the two strata.
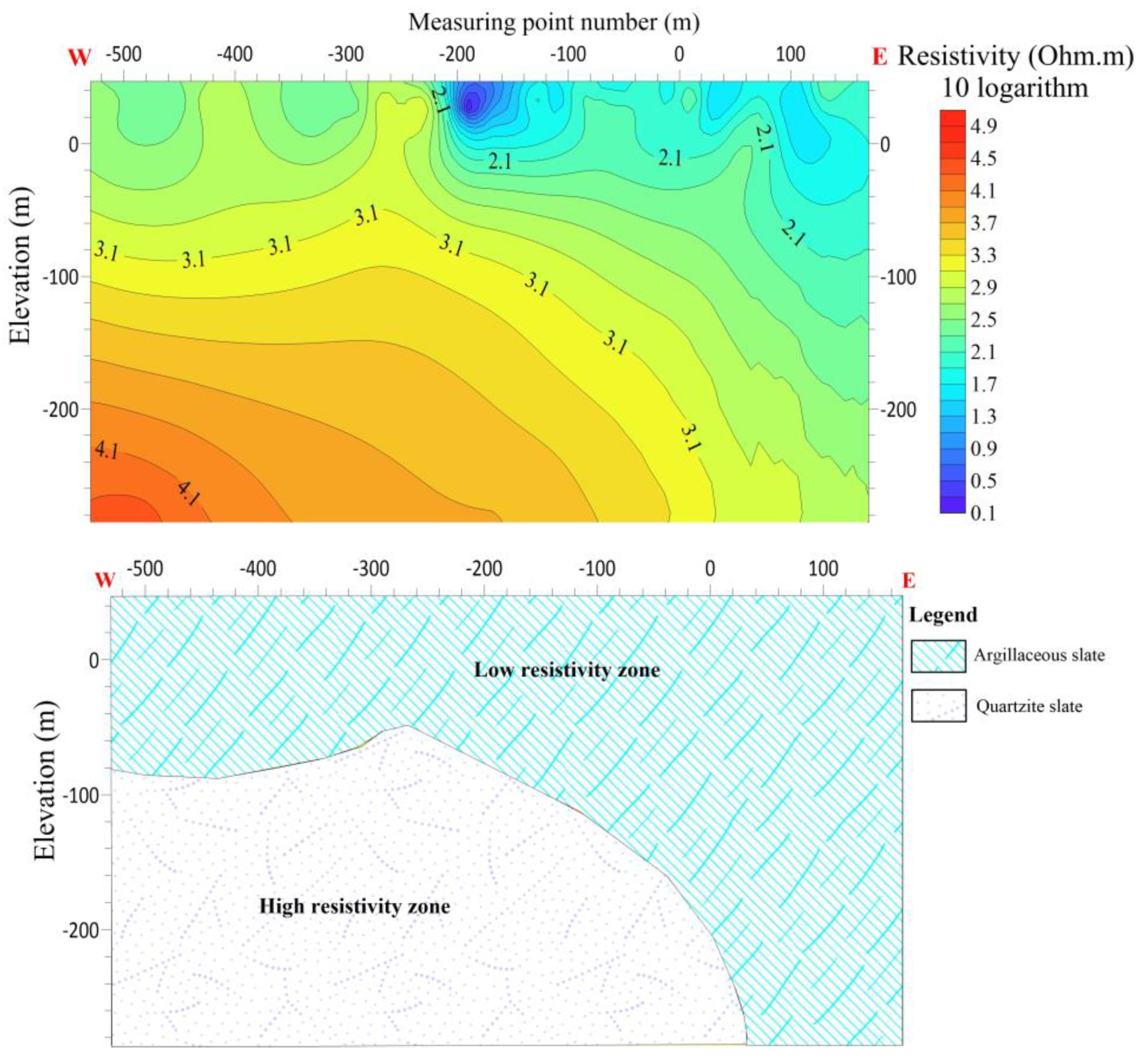
The L6 line is 560 meters long, with 28 measuring points and the distance between the points are 20 meters apart. L6 is running W-E with an azimuth angle of 110 degrees. The results of the electrical sounding conducted on line L6 reveal a decrease in resistivity between measuring points -100 and -200. This observation suggests the presence of a fault or crack in this section, characterized by a contact surface exhibiting both high and low resistance. Furthermore, it is hypothesized that this specific area may possess a favorable water contact surface. There is speculation regarding the composition of the shallow portion of the line, which is believed to consist predominantly of argillaceous slate exhibiting low resistivity abnormal reactions. Conversely, the deep portion of the line is characterized by a high resistivity body primarily composed of quartzite slate reactions. There is speculation regarding the presence of fractures within the contact interfaces of the two strata.
Figure 14.
Line 5 (a) shows the resistivity distribution with depth (b) Shows hydrogeological profile of the survey line.
Figure 14.
Line 5 (a) shows the resistivity distribution with depth (b) Shows hydrogeological profile of the survey line.
Figure 15.
Line 6 (a) shows the resistivity distribution with depth (b) Shows hydrogeological profile of the survey line.
Figure 15.
Line 6 (a) shows the resistivity distribution with depth (b) Shows hydrogeological profile of the survey line.
6.5. Total Analysis of the Borehole Wells
During geophysical exploration in Nanshan Township, situated in Huarong County, five verification boreholes have been constructed. Initial evaluations from pumping tests indicate that ZK01 shows a discernible water production rate of approximately 460 tons per day, whereas ZK02 and ZK03 showed volumes of nearly 170 tons per day and 410 tons per day, respectively. In contrast, ZK04 exhibits a much-reduced output of around 30 tons per day, as it is rendered unproductive due to water quality problems. Similarly, ZK05 will produced a maximum of 100 tons per day, while also having similar worries about the quality of water.
The ZK04 borehole was chosen based on electrical soundings and its proximity to the F2 fault zone. However, despite expectations, it yielded minimal water during pumping tests, suggesting poor water flow. Learning from this, the ZK05 location was selected about 40 meters west of ZK01, guided by electrical soundings indicating favorable conditions. Yet, despite encountering thicker fracture layers, ZK05 also lacked sufficient water, indicating limited aquifer development. While the F2 fault had minimal impact on ZK05, its effects were primarily seen east of ZK01. This highlights the challenges in predicting groundwater behavior accurately.
6.5.1. Evaluation of the Boreholes Mineral Water Quality
Colorless, tasteless, transparent, with a color range of 0 to 5, and turbidity between 0 to 0.5. The water quality is pure and the taste is genuine.Based on the current water quality analysis and historical data, the mineral water in this area has been exploited for over 30 years since 1986. The silicic acid content ranges from 37.96 to 56.27 mg/L, all meeting the standards for drinking mineral water in China. The pH ranges from 6.8 to 7.87 and the hardness is between 8.3 to 8.69 degrees German, indicating it is moderately hard water, mainly composed of calcium, magnesium, and sodium bicarbonates. The bicarbonate content ranges from 233.89 to 534.72 mg/L, calcium from 10.4 to 124.99 mg/L, sodium from 11.69 to 36.51 mg/L, magnesium from 2.81 to 43.56 mg/L, and total dissolved solids from 127 to 570 mg/L.
- 2.
Ion content and bacterial analysis
According to the water quality analysis, the zinc content ranges from 0.003 to 0.05 mg/L, selenium from 0 to 0.005 mg/L, iron from 0.012 to 0.018 mg/L, strontium from 0.1 to 0.211 mg/L, lithium from 0.036 to 0.05 mg/L, fluoride from 0.03 to 0.80 mg/L, cyanide from 0 to 0.002 mg/L, mercury from 0.0002 to less than 0.05 mg/L, hexavalent chromium from 0.0014 to less than 0.004 mg/L, lead from 0.0004 to less than 0.01 mg/L, cadmium from 0.0001 to less than 0.002 mg/L, phenol from 0 to less than 0.002 mg/L, anionic synthetic detergent less than 0.10 mg/L, all of which are within permissible limits.
The total bacterial count is less than 3 per ml, and coliform bacteria are less than 3 per L, indicating good sanitary conditions for the water.
- 3.
Radioactivity indicators
According to the water quality analysis, radon ranges from 12.7 to 30.61 Eman, uranium from 0.00 to 7.8 × 10^-8 g/L, radium from 2.36 × 10^-12 to 7.28 × 10^-12 Curie/L, total alpha radiation is 0.25 Bq/L, and total beta radiation is 1.096 Bq/L see
Table 2 for further details.
Table 2, shows water quality analysis results of the five drilled wells.
7. Discussion
The utilization of the 2D Electrical Resistivity Imaging method in this study has proven highly effective in delineating subsurface features and gaining insights into groundwater occurrence within complex hydrogeological conditions. Employing forward and inverse pole-dipole configurations, with IPINV 3.2 inversion software, allowed for a comprehensive investigation of groundwater conditions across the study area. The method's success was evident as it revealed multiple faults and structural failure zones along six surveyed lines, offering valuable insights into the subsurface environment. This geophysical survey at the Nanshan Mineral Water Factory in Huarong County yielded crucial data regarding the geological composition and optimal water exploration techniques. Notably, the identification of fault zones, often associated with rock fragmentation and fissure development, emerged as a key outcome, with two structural damage areas identified at fault intersections, significantly enhancing potential water supply pathways. Furthermore, the identification of a steep resistivity contact surface between argillaceous slate and sandy slate, through electrical sounding, presented an opportunity for targeted water collection and borehole placement. This information can guide the selection of verification borehole locations and aid in assessing aquifer suitability based on resistivity values. Five verification boreholes (ZK01, ZK02, ZK03, ZK04, and ZK05) were constructed in Nanshan Township, Huarong County, following the initial survey, with preliminary pumping tests revealing variable water outputs. ZK01 displayed the highest output at approximately 460 tons per day, followed by ZK03 (410 tons/day), ZK02 (170 tons/day), and ZK05 (100 tons/day). These findings confirmed both the viability of the method and the variability in groundwater availability across the study area. During the advanced verification phase, boreholes ZK05, ZK01, and ZK02 were strategically positioned in proximity to specific measuring points (No. 120, 160, and 220)
Figure 9. Results indicated that argillaceous slate with a significant clay mineral content primarily occurred at a depth of 80 meters, transitioning to a greater sandy composition at shallower depths. This transition was associated with compressive phenomena and the development of fractures within the underlying sandy stratum. Subsequent pumping tests reaffirmed the variability in water output, with ZK01, ZK02, and ZK05 exhibiting maximum water outputs of approximately 460 tons, 170 tons, and 100 tons per day, respectively. Notably, changes in water output in ZK05 were attributed to the presence of the F2 fault, underscoring the significant influence of fault zones on groundwater dynamics. In summary, the 2D Electrical Resistivity imaging method, integrated with borehole data and advanced verification techniques, provided a comprehensive understanding of subsurface conditions and groundwater potential within the complex hydrogeological setting of the study area. These findings hold substantial implications for groundwater resource management and exploration, guiding critical decisions in this critical domain.
8. Conclusions
The geophysical survey carried out at the Nanshan Mineral Water Factory in Huarong County has yielded noteworthy results pertaining to the geological makeup of the area and optimal techniques for water exploration. The survey has successfully identified multiple faults as well as two instances of structural damage that have occurred due to the intersection of distinct directional faults. The presence of fault zones can result in the fragmentation of rocks, the development of fissures, and the formation of an improved channel for water supply. The identification of a steeper resistivity contact surface between argillaceous slate and sandy slate, as determined by electrical sounding, can offer favorable conditions for water collection and serve as a guide for selecting verification holes. The utilization of resistivity values pertaining to lithological contact surfaces can serve as a means to assess the location and extent of side contact surfaces. This assessment can prove beneficial in identifying areas characterized by resistivity values that are either excessively low or high, thereby rendering them unsuitable for the identification of aquifers.
Author Contributions
Osama Abdul Rahim, conceptualized and designed the study, collected and analyzed the data, and wrote the manuscript. Liu Chunming, contributed to the study design and data analysis. Hesham El-Kaliouby critically revised the manuscript for important intellectual and technical content. Liu Chunming & Chen Rujun, provided technical support and expertise in the data analysis, and contributed to the interpretation of the results. Jawad Ahmad, Shahid Ali Shah, Shah Fahad, Ijaz Ahmed and Farid Ullah contributed in data collection process.
Funding
This research was funded by Basic Science Center Project of National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number 72088101.
Data Availability Statement
Data will be available upon request to the authors.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the anonymous reviewers and academic editors for taking the time and effort to review the manuscript. We appreciate all valuable comments and suggestions, which improved the quality of the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Asry, Z.; Samsudin, A.R.; Yaacob, W.Z.; Yaakub, J. Groundwater exploration using 2-D geoelectrical resistivity imaging technique at Sungai. Udang, Melaka. Journal of Earth Science and Engineering 2012, 2, 624. [Google Scholar]
- Hamzah, U.; Yaacup, R.; Samsudin, A.R.; Ayub, M.S. Electrical imaging of the groundwater aquifer at Banting, Selangor, Malaysia. Environmental Geology 2006, 49, 1156–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.C. An evaluation of electrical resistivity imaging in hummocky terrain in southern Alberta. 2006.
- Barker, R. The offset system of electrical resistivity sounding and its use with a multicore cable. Geophysical prospecting 1981, 29, 128–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revil, A.; Karaoulis, M.; Johnson, T.; Kemna, A. Some low-frequency electrical methods for subsurface characterization and monitoring in hydrogeology. Hydrogeology Journal 2012, 20, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemna, A.; Binley, A.; Ramirez, A.; Daily, W. Complex resistivity tomography for environmental applications. Chemical Engineering Journal 2000, 77, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandberg, S.; Slater, L.; Versteeg, R. An integrated geophysical investigation of the hydrogeology of an anisotropic unconfined aquifer. Journal of Hydrology 2002, 267, 227–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batayneh, A.T. Resistivity imaging for near-surface resistive dyke using two-dimensional DC resistivity techniques. Journal of Applied Geophysics 2001, 48, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loke, M. Tutorial: 2D and 3D electrical imaging surveys, University of Alberta: Edmonton, AB, Canada. 2018.
- Dahlin, T.; Loke, M.H. Resolution of 2D Wenner resistivity imaging as assessed by numerical modelling. Journal of applied geophysics 1998, 38, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loke, M.H. Electrical imaging surveys for environmental and engineering studies. A practical guide to 1999, 2, 70. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Q.; Shang, Y.; Hasan, M.; Jin, W.; Yang, P. Evaluation of a weathered rock aquifer using ERT method in South Guangdong, China. Water 2018, 10, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loke, M.; Chambers, J.; Rucker, D.; Kuras, O.; Wilkinson, P. Recent developments in the direct-current geoelectrical imaging method. Journal of applied geophysics 2013, 95, 135–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.; Shang, Y.; Akhter, G.; Khan, M. Geophysical investigation of fresh-saline water interface: A case study from South Punjab, Pakistan. Groundwater 2017, 55, 841–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morse, M.S.; Lu, N.; Godt, J.W.; Revil, A.; Coe, J.A. Comparison of soil thickness in a zero-order basin in the Oregon Coast Range using a soil probe and electrical resistivity tomography. Journal of geotechnical and geoenvironmental engineering 2012, 138, 1470–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xianxin, S.; Kai, W. Induced Polarization Method applied for groundwater resource exploration. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Symposium on Water Resource and Environmental Protection; 2011; pp. 365–368. [Google Scholar]
- Schulz, R. Interpretation and depth of investigation of gradient measurements in direct current geoelectrics. Geophysical prospecting 1985, 33, 1240–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shettigara, V.; Adams, W. Detection of Lateral Variations in Geological Structures Using Electrical Resistivity Gradient PROFILING1. Geophysical prospecting 1989, 37, 293–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szalai, S.; Novák, A.; Szarka, L. Which geoelectric array sees the deepest in a noisy environment? Depth of detectability values of multielectrode systems for various two-dimensional models. Physics and Chemistry of the Earth, Parts A/B/C 2011, 36, 1398–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahlin, T.; Zhou, B. A numerical comparison of 2D resistivity imaging with 10 electrode arrays. Geophysical prospecting 2004, 52, 379–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pous, J.; Queralt, P.; Chavez, R. Lateral and topographic effects in geoelectric soundings. Journal of applied geophysics 1996, 35, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.; Shang, Y.; Jin, W. Delineation of weathered/fracture zones for aquifer potential using an integrated geophysical approach: A case study from South China. Journal of Applied Geophysics 2018, 157, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daoyuan, B.; Zhou, L.C.a.W.X.; Yunyi, K.M.T.P. Tectonic activities| genesis and dynamic mechanisms of Quaternary Huarong uplift. Chinese Journal of Geology 2010, 45, 411–427. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, C.; Mei, L.; Min, K.; Jonckheere, R.; Ratschbacher, L.; Yang, Z.; Peng, L.; Liu, Z. Multi-chronometric dating of the Huarong granitoids from the Middle Yangtze Craton: implications for the tectonic evolution of eastern China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences 2012, 52, 73–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J. New understanding about the geologic and structural features of Huarong region. Hunan Geology 1991, 3, 189–196. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.-X.; Ma, C.-Q.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, J.-Y.; Marks, M.A. Genesis of leucogranite by prolonged fractional crystallization: a case study of the Mufushan complex, South China. Lithos 2014, 206, 147–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapponnier, P.; Molnar, P. Active faulting and tectonics in China. Journal of Geophysical Research 1977, 82, 2905–2930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahab, S.; Saibi, H.; Mizunaga, H. Groundwater aquifer detection using the electrical resistivity method at Ito Campus, Kyushu University (Fukuoka, Japan). Geoscience Letters 2021, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubang, J.; Liu, H.; Chen, R. Combined application of hydrogeological and geoelectrical study in groundwater exploration in Karst-Granite areas, Jiangxi Province. Water 2023, 15, 865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).