Submitted:
25 June 2024
Posted:
26 June 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
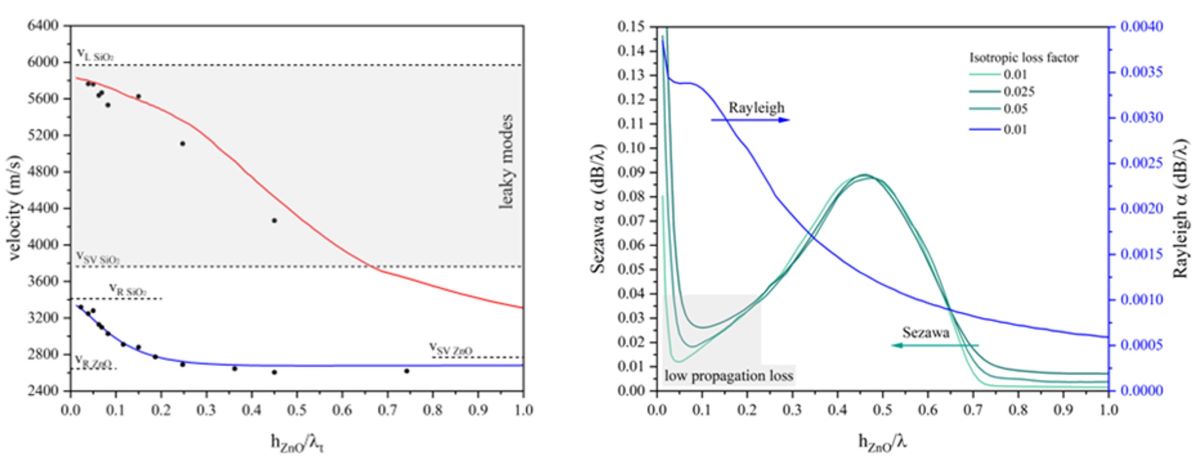
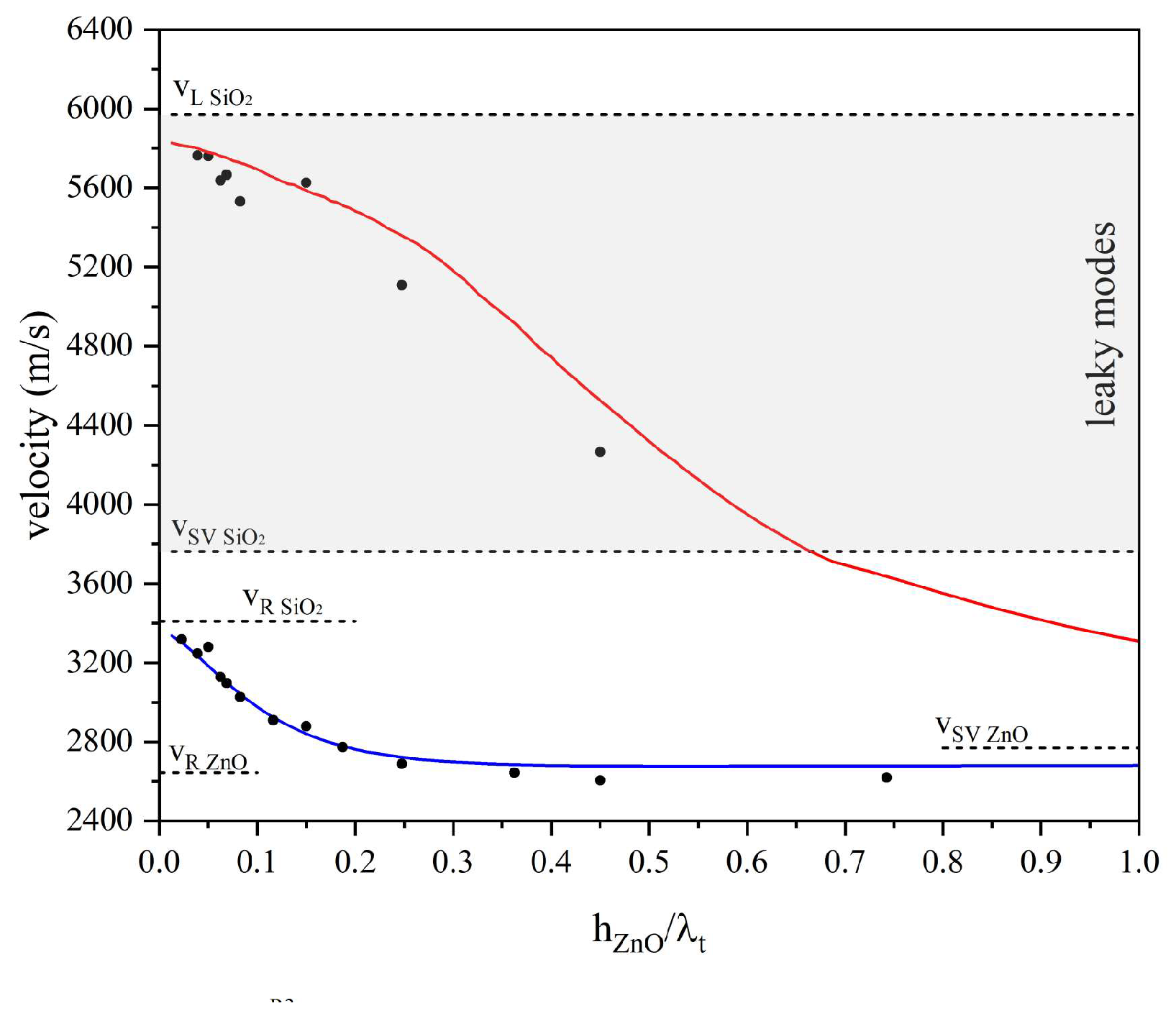
2.1. SAW Propagation in Layered Media
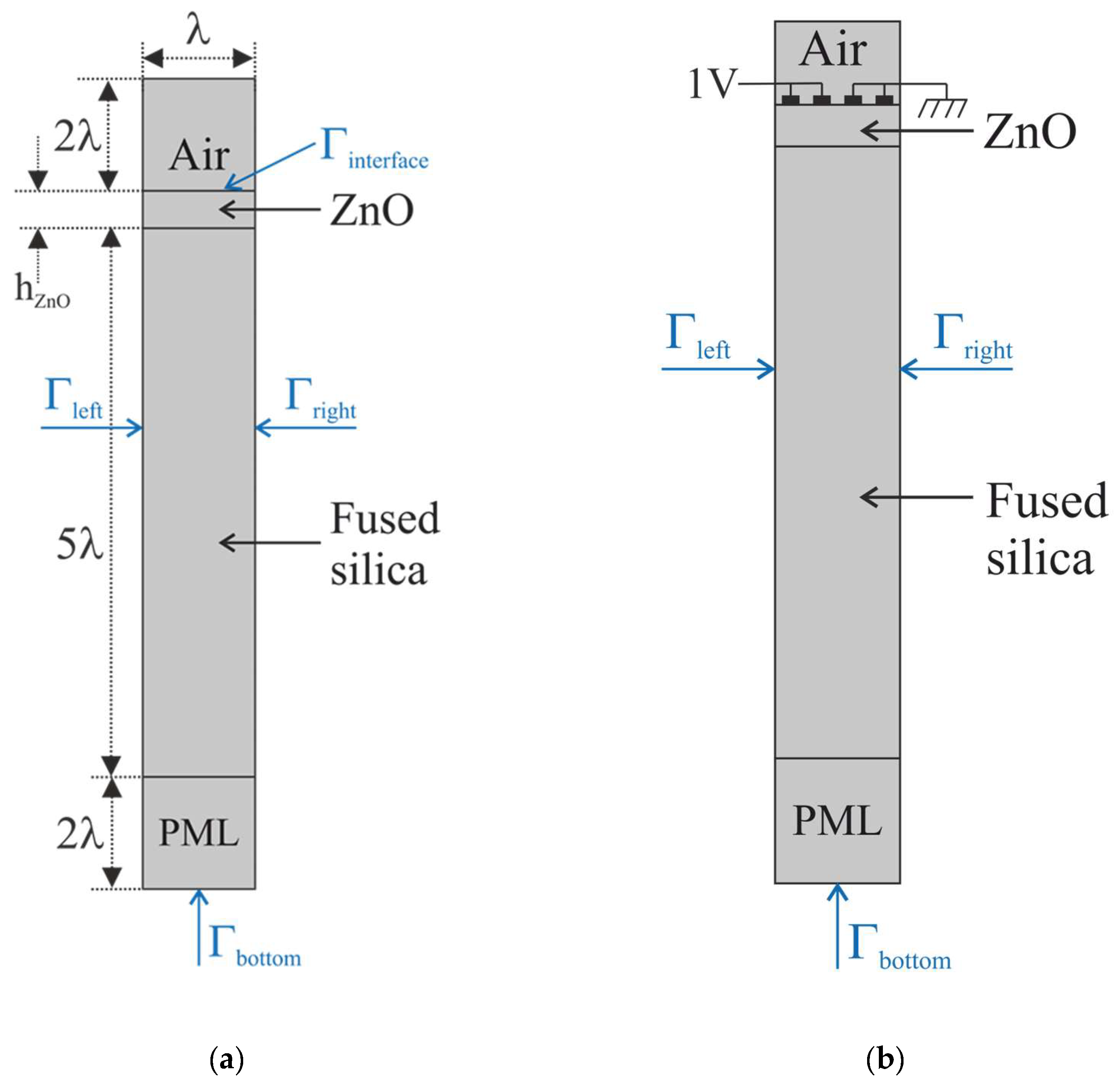
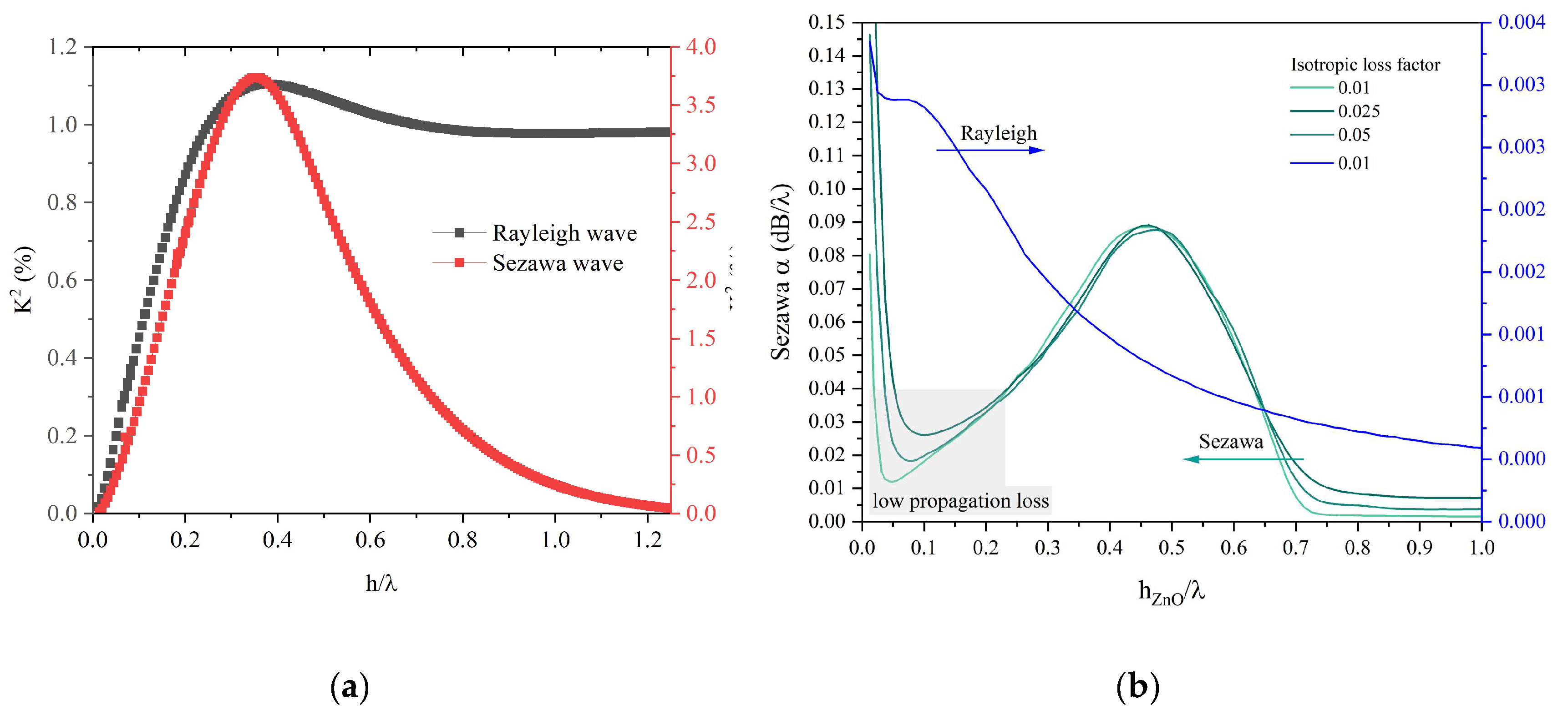
2.2. FEM Analysis
3. Experimental
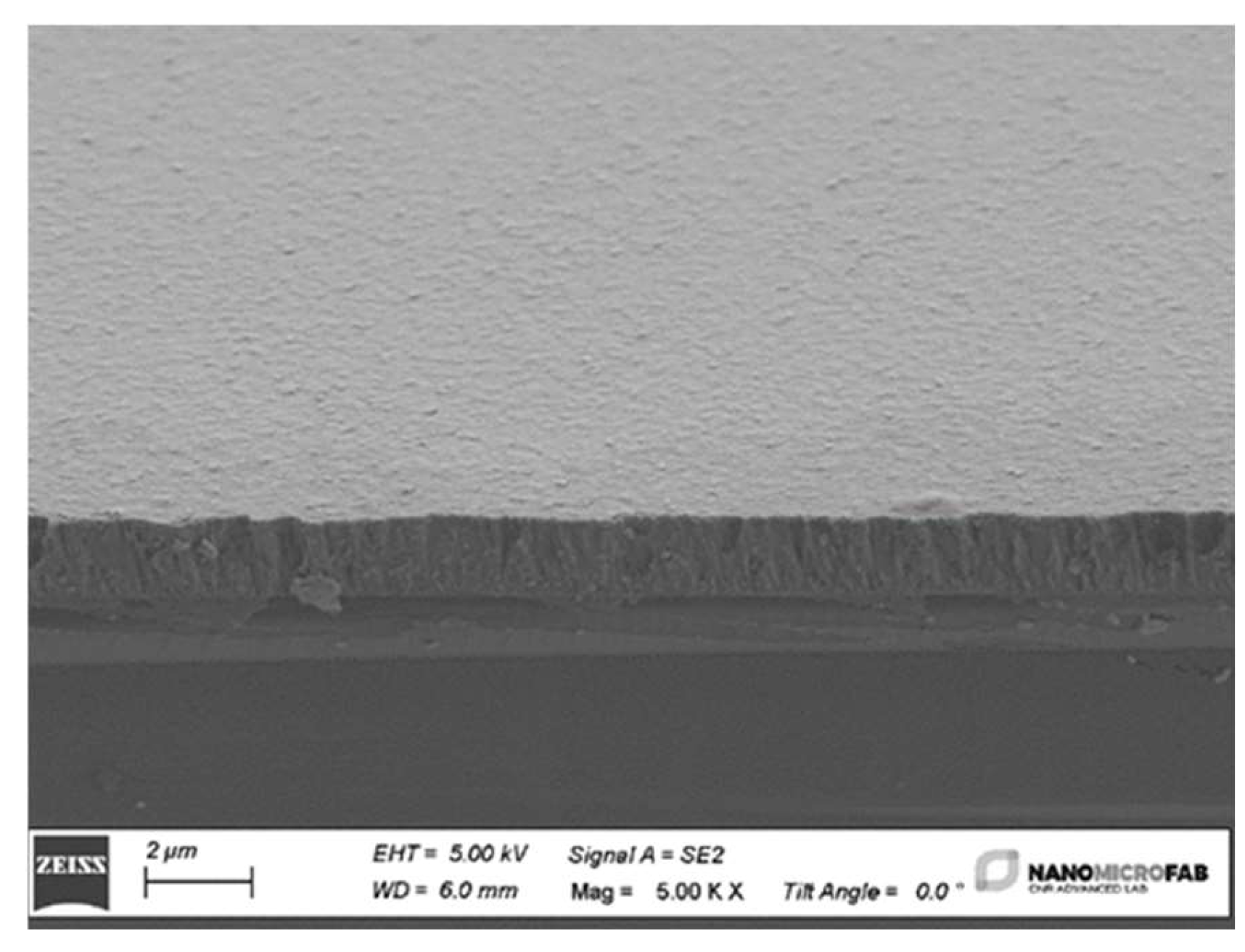
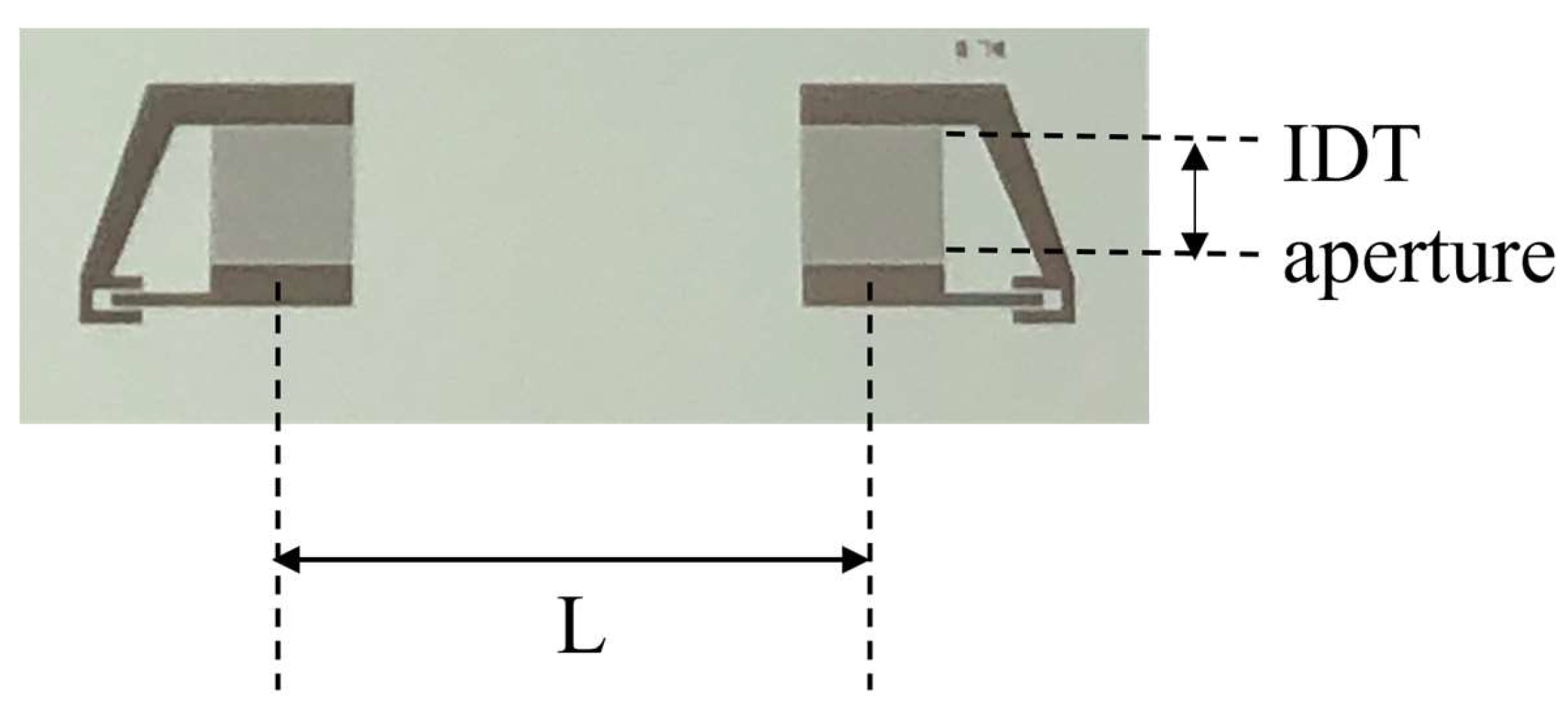
3.1. SAW Devices Fabrication
3.2. SAW Devices Test
5. Discussions
- Among the listed structures, the ZnO/SiO2 stands out for its technological ease and the low cost of the materials. Indeed, the reactive RF magnetron sputtering technique is a well-established, high-deposition rate, relatively low-temperature (T = 200°C) process which is compatible with standard microelectronic technology. Since the sputtered ZnO films are highly c-axis oriented, uniform and extremely adhesive to the substrate, they can be a valid alternative to thin epitaxial piezoelectric layers deposited using techniques that require expensive and dedicated equipment.
- Fused silica, unlike expensive and highly anisotropic substrates, is a low cost, optically transparent substrate: its high resistance to chemicals, low coefficient of thermal expansion and excellent optical qualities, make it attractive for applications in optics operating in the deep UV and visible wavelength range [16,25,26].
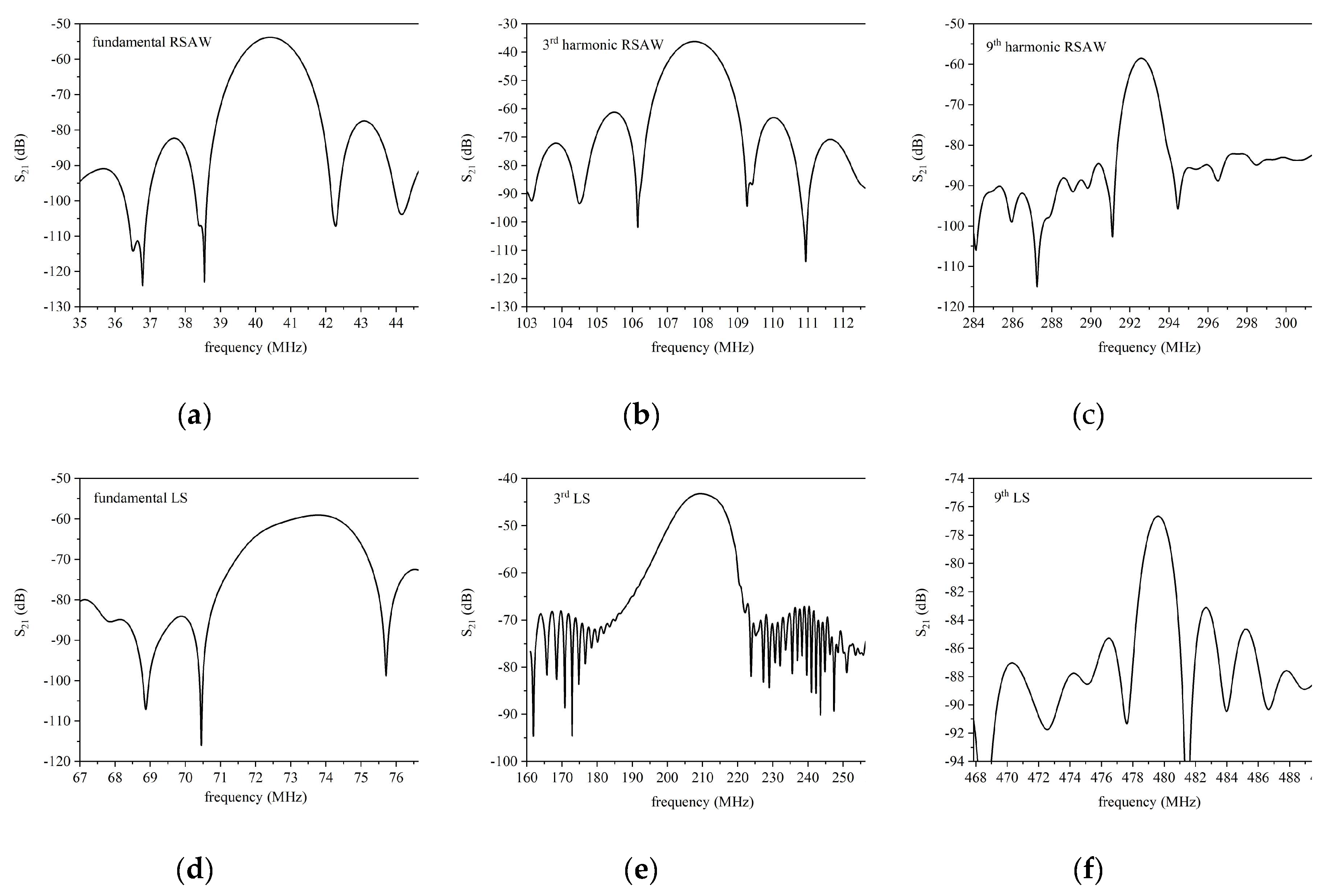
- The value of the losses that can be read from the S21 curves of Figure 6 basically comprises 6 dB from IDTs bidirectionality loss (attributed to the SAW propagation toward both sides of each IDT), miscellaneous losses (due to electrical finger resistance and IDTs electrical mismatch with the peripheral circuits), and acoustic propagation loss. The largest contribution to the overall loss, the electrical mismatch of the IDTs with the characteristic impedance of the VNA, comes from using a non-optimized SAW delay line geometry implemented on the tested devices. This geometry is general purpose and not specifically designed for ZnO/SiO2-based devices. By optimizing the IDT parameters (the directivity and the number of finger pairs) on the K2 dispersion curve and possibly adopting a tuning circuit to match the VNA load impedance to the input and output ports, the frequency response of the based devices on LS it can be improved.
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adler, E.L.; Farnell, G.W.; Galligan, J.M.; Joyce, G.C.; N-Nagy, F.L.; Sittig, E.K.; Spencer, W.J.; Suenaga, M. In Physical Acoustics: Principles and Methods, Mason, W.P., Thurston, R.N., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 1972; Volume IX.
- Caliendo, C.; Laidoudi, F. Experimental and Theoretical Study of Multifrequency Surface Acoustic Wave Devices in a Single Si/SiO2/ZnO Piezoelectric Structure. 2020, 20, 1380. [CrossRef]
- Pedrós, J.; Calle, F.; Grajal, J.; Jiménez Riobóo, R.J.; Takagaki, Y.; Ploog, K.H.; Bougrioua, Z. Anisotropy-induced polarization mixture of surface acoustic waves in $\mathrm{Ga}\mathrm{N}∕c$-sapphire heterostructures. Physical Review B 2005, 72, 075306. [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Madrid, J.G.; Iriarte, G.F.; Pedros, J.; Williams, O.A.; Brink, D.; Calle, F. Super-High-Frequency SAW Resonators on AlN/Diamond. Ieee Electron Device Letters 2012, 33, 495–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glushkov, E.; Glushkova, N.; Zhang, C. Surface and pseudo-surface acoustic waves piezoelectrically excited in diamond-based structures. Journal of Applied Physics 2012, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takagaki, Y.; Santos, P.V.; Wiebicke, E.; Brandt, O.; Schönherr, H.P.; Ploog, K.H. Guided propagation of surface acoustic waves in AlN and GaN films grown on $4H--\mathrm{SiC}(0001)$ substrates. Physical Review B 2002, 66, 155439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrós, J.; Calle, F.; Grajal, J.; Jiménez Riobóo, R.J.; Prieto, C.; Pau, J.L.; Pereiro, J.; Hermann, M.; Eickhoff, M.; Bougrioua, Z. Anisotropic propagation of surface acoustic waves on nitride layers. Superlattices and Microstructures 2004, 36, 815–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralib, A.A.M.; Nordin, A.N.; Alam, A.H.M.Z.; Hashim, U.; Othman, R. Piezoelectric thin films for double electrode CMOS MEMS surface acoustic wave (SAW) resonator. Microsystem Technologies 2015, 21, 1931–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, D. Surface Acoustic Wave Filters, 2nd Edition ed.; Academic Press: Amsterdam (NL), 2007.
- Datta, S. Surface Acoustic Wave Devices; Prentice-Hall: 1986.
- Morgan, D.P. Quasi-static analysis of floating-electrode unidirectional SAW transducers (FEUDT's). In Proceedings of the 1999 IEEE Ultrasonics Symposium. Proceedings. International Symposium (Cat. No.99CH37027), 17-20 Oct. 1999, 1999; pp. 107-111 vol.101.
- Morgan, D.P. Quasi-static analysis of floating electrode unidirectional SAW transducers. IEEE Transactions on Ultrasonics, Ferroelectrics, and Frequency Control 2001, 48, 1289–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Royer, D.; Dieulesaint, E. Free and Guided Propagation. In Elastic Waves in Solids; Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg New York, 2000; Volume I.
- Engan, H. Excitation of elastic surface waves by spatial harmonics of interdigital transducers. IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices 1969, 16, 1014–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokhale, V.J.; Downey, B.P.; Hardy, M.T.; Jin, E.N.; Roussos, J.A.; Meyer, D.J. Epitaxial Single-Crystal ScAlN on 4H-SiC for High-Velocity, Low-Loss SAW Devices. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 33rd International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems (MEMS), 18-22 Jan. 2020, 2020; pp. 1262-1265.
- Caliendo, C.; Benetti, M.; Cannatà, D.; Buzzin, A.; Grossi, F.; Verona, E.; de Cesare, G. UV Sensor Based on Surface Acoustic Waves in ZnO/Fused Silica. Sensors 2023, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benetti, M.; Cannata, D.; Di Pietrantonio, F.; Fedosov, V.I.; Verona, E.; Ieee. Theoretical and experimental investigation of PSAW and SAW properties of AlN films on isotropic diamond substrates. In 2005 Ieee Ultrasonics Symposium, Vols 1-4; Ultrasonics Symposium; 2005; pp. 1868-1871.
- Aubert, T.; Naumenko, N.; Bartoli, F.; Pigeat, P.; Streque, J.; Ghanbaja, J.; Elmazria, O. Non-leaky longitudinal acoustic modes in ScxAl1-xN/sapphire structure for high-temperature sensor applications. Applied Physics Letters 2019, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naumenko, N.F.; Didenko, I.S. High-velocity surface acoustic waves in diamond and sapphire with zinc oxide film. Applied Physics Letters 1999, 75, 3029–3031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Every, A.G.; Maznev, A.A. Fano line shapes of leaky surface acoustic waves extending from supersonic surface wave points. Wave Motion 2018, 79, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushibiki, J.; Ishikawa, T.; Chubachi, N. Cut-off characteristics of leaky Sezawa and pseudo-Sezawa wave modes for thin-film characterization. Applied Physics Letters 1990, 57, 1967–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suenaga, R.; Suzuki, M.; Kakio, S.; Ohashi, Y.; Arakawa, M.; Kushibiki, J.-i. Propagation properties of leaky surface acoustic wave on water-loaded piezoelectric substrate. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics 2018, 57, 07LC10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valle, S.; Singh, M.; Cryan, M.J.; Kuball, M.; Balram, K.C. High frequency guided mode resonances in mass-loaded, thin film gallium nitride surface acoustic wave devices. Applied Physics Letters 2019, 115, 212104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Wang, W.; Qian, L.; Li, Q.; Lu, Z.; Shen, J.; Song, C.; Zeng, F.; Pan, F. High-Frequency Surface Acoustic Wave Devices Based on ZnO/SiC Layered Structure. IEEE Electron Device Letters 2019, 40, 103–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzzin, A.; Grossi, F.; Cannatà, D.; Benetti, M.; Cesare, G.d.; Caliendo, C. ZnO based Back- and Front-Illuminated Photoresistor for UV Sensing Applications. In Proceedings of the 2023 9th International Workshop on Advances in Sensors and Interfaces (IWASI), 8-9 June 2023, 2023; pp. 273-276.
- Caliendo, C.; Cannatà, D.; Benetti, M.; Buzzin, A. UV sensors based on the propagation of the fundamental and third harmonic Rayleigh waves in ZnO/fused silica. In Proceedings of the 2023 9th International Workshop on Advances in Sensors and Interfaces (IWASI), 8-9 June 2023, 2023; pp. 261-266.
- Uehara, K.; Aota, Y.; Shibata, T.; Kameda, S.; Nakase, H.; Isota, Y.; Tsubouchi, K. Surface Acoustic Wave Properties of Atomically Flat-Surface Aluminum Nitride Epitaxial Film on Sapphire. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics 2005, 44, 4512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, S.; Yamada, H.; Omori, T.; Hashimoto, K.y.; Torii, H.; Umezawa, H.; Shikata, S.i. One-port SAW resonators fabricated on single-crystal diamond. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE MTT-S International Microwave Symposium Digest (MTT), 2-7 June 2013, 2013; pp. 1-3.
- Caliendo, C.; Hamidullah, M. A Theoretical Study of Love Wave Sensors Based on ZnO–Glass Layered Structures for Application to Liquid Environments. 2016, 6, 59.

| Propagating medium | h/λ | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| GaN/sapphire(11-20) | 0.2125 | [7] |
| GaN/sapphire | 0.125 – 0.875 | [7] |
| AlN(0001)/diamond(111) | 0.1875 – 0.75 | [4] |
| AlN/Diamond | 0.15 | [5] |
| AlN/iso-Diamond | * | [5] |
| AlN/iso-Diamond/c-TiAl | * | [5] |
| AlN/diamond | 0.09 | [17] |
| AlN/4H–SiC(0001)[1-100] | 0.3-0.5 | [6] |
| GaN/4H–SiC(0001)[11-20] | ~0.7 | [6] |
| Sc0.09Al0.91N/c-sapphire | 0.425 | [18] |
| ZnO/(001)<110>diamond | * | [19] |
| Iso-Cd/iso-Cr | Appr. 0.08 | [20] |
| Au/fused quartz | 0.0328 | [21] |
| a-SiO2/128°YX-LiNbO3 | 0.41 and 0.62 | [22] |
| ScAlN/4H-SiC | 0.1, 0.12 and 0.17 | [15] |
| GaN/SiC | from 0.2 to 0.48 | [23] |
| ZnO/SiC | ~0.1 | [24] |
| ZnO/fused silica | 0.05 to x | Present paper |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





