1. Introduction
The ChatGPT plays a crucial role in the current university education environment [
1]. This technology not only provides a vast amount of information resources for modern university students through information and communication technology, effectively promoting personalized learning experiences, but also breaks geographical and temporal constraints, greatly enriching learning forms and approaches [
2]. Higher education institutions, research institutions, corporate teams, and other entities are important areas for the use and application of ChatGPT [
3,
4]. However, it should be noted that ChatGPT is typically considered a natural language generation and understanding technology rather than an intelligent learning tool. Therefore, while considering its application value, effective mitigation of the potential ethical risks and challenges posed by ChatGPT should also be addressed.
Despite the many benefits of using ChatGPT in higher education, there are still several barriers to its widespread adoption and effective use [
5]. One of these barriers is insufficient acceptance and usage of new technologies among university students. The key to addressing this issue is to explore the acceptance of ChatGPT among contemporary university students, assess the potential risks and influencing factors of using ChatGPT, and develop effective strategies to promote its scientific application [
6,
7]. Rasul et al. argued that the improvement of university students’ learning skills, comprehensive skills, and knowledge domains is considered the main benefit of ChatGPT at the organizational level [
8,
9]. In contrast, Menon et al. emphasized that the key determinants of ChatGPT success are user satisfaction and willingness to use [
10,
11]. Willingness to use, as a quantifiable indicator that measures the tendency of individuals to perform certain behaviors, determines the likelihood of users performing certain actions [
12]. By measuring behavioral intentions, we can predict and reflect actual usage situations more accurately [
13].
The Technology Acceptance Model (TAM), as a mature theoretical framework, has been widely used in such studies, and it has been confirmed that users’ attitudes towards use and perceived usefulness can be highly predictive of their behavioral intentions [
14,
15]. This is consistent with the TAM, which states that behavioral intention is determined by attitude towards use and perceived usefulness (BIU=ATU+PU). Therefore, this study, based on Innovation Diffusion Theory (IDT), primarily explores the influence of key concepts contained in IDT on the TAM structure and aims to provide a valuable addition to existing research. The importance of the current study lies in the fact that it can not only test and develop relevant theoretical models but also optimize strategies for the use of ChatGPT in higher education environments. The contribution of this study also extends to higher education policymakers, who can gain a deeper understanding of students’ acceptance of the ChatGPT, thereby assessing its usability and usefulness as a learning tool.
2. Theoretical Model and Hypothesis
Innovation adoption research primarily focuses on the adoption of information technology and information systems (IT and IS). Related studies have developed several complementary models to study adoption. Davis’s Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) and Rogers’ innovation diffusion theory (IDT) are the most influential theoretical perspectives in the innovation adoption research literature and have been widely used by scholars to study the adoption of various innovative technologies [
16,
17,
18]. A review of the IT research literature shows that innovation characteristics are primarily discussed in IT research literature [
19]. TAM and IDT share a similar premise in which adopters evaluate innovative technologies based on the perceived characteristics of the innovation [
16,
17]. Furthermore, value-oriented aspects include perceived usefulness and relative advantage, including perceived ease of use, complexity, and compatibility, which are important factors influencing the adoption of technological innovations [
16,
17,
20]. Therefore, the adoption of IT and IS is assessed by IDT and TAM, which are described as similar and complementary in certain constructs. Researchers report that the constructs used in TAM are essentially a subset of perceived innovation characteristics, suggesting that a more robust model can be created by combining these two theories [
21,
22,
23].
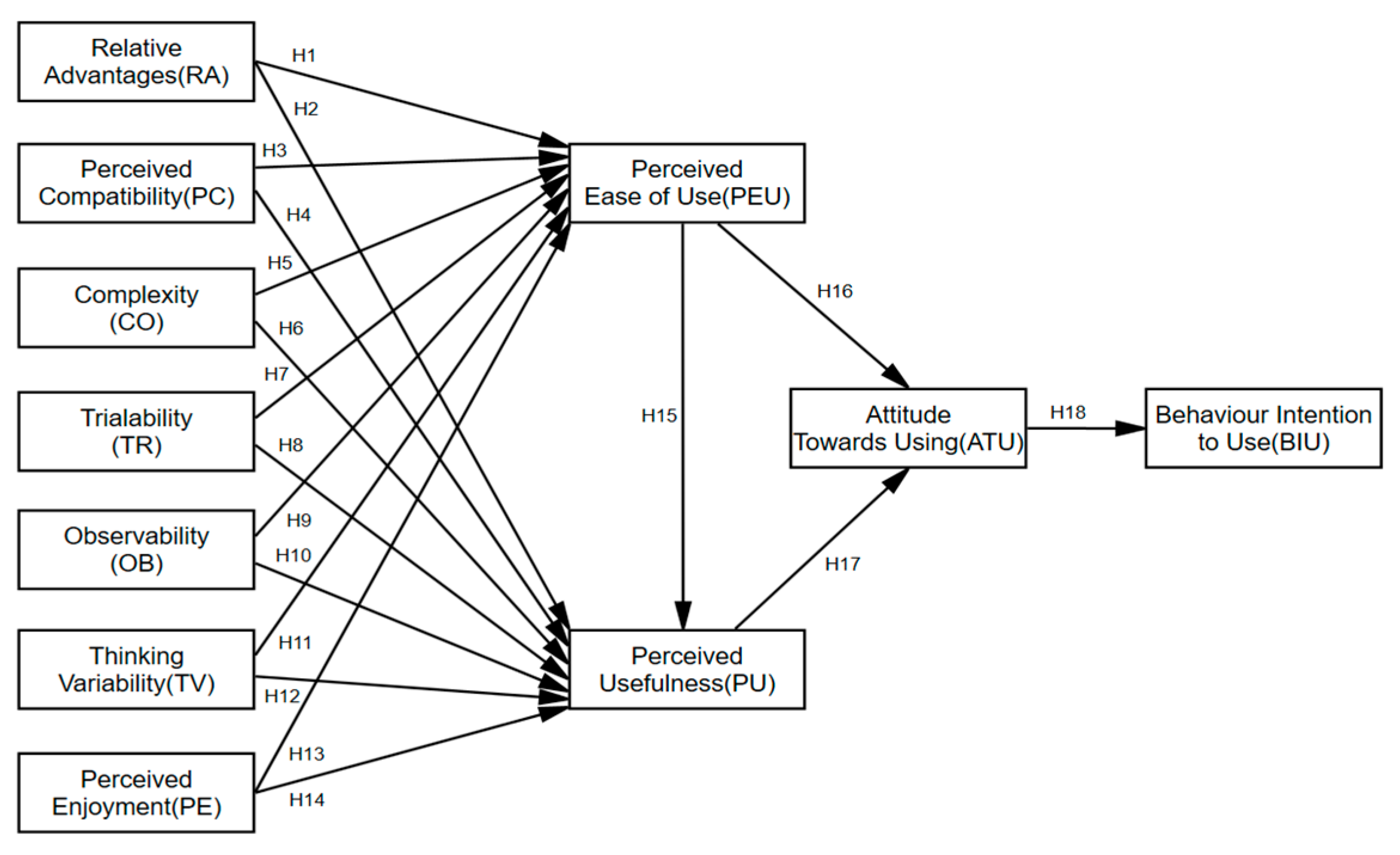
Against this background, this study extends the TAM by incorporating key constructs from IDT to analyze university students’ behavioral intentions, acceptance levels, and influencing factors related to the use of the new ChatGPT TAM model, which now includes five constructs: perceived ease of use (PEU), perceived usefulness (PU), perceived enjoyment (PE), attitude towards use (ATU), and behavioral intention to use (BIU). Innovation Diffusion Theory (IDT) includes six constructs: Relative Advantage (RA), Perceived Compatibility (PC), complexity (CO), trialability (TR), observability (OB), and Thought Variability (TV). See
Figure 1.
2.1. Innovation Diffusion Theory (IDT)
In the innovation research literature, Rogers developed a method for studying the diffusion of innovations using established theories from sociology, psychology and communication studies. Innovation can be defined in various ways [
24]. Innovation diffusion theory (IDT) emphasizes the relative advantage, compatibility with existing practices, simplicity, trialability, and observability of innovations [
25,
26], which facilitate the wider and faster diffusion of innovative technologies [
27]. IDT is not only important for guiding managers and organizations in their decisions and actions during the innovation implementation process but is also increasingly important in the field of education. Existing studies have shown that as a learning tool, compatibility and ease of use of ChatGPT are important factors influencing university students’ behavioral intention to use ChatGPT [
28,
29].
Relative advantage (RA) is defined as the degree to which people perceive a new innovative technology to be better than traditional technology [
30]. Therefore, this term is used in the current study to refer to the extent to which university students believe that using the ChatGPT can increase learning efficiency and optimize learning outcomes. In studies based on the Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) and Innovation Diffusion Theory (IDT), the complex relationships between relative advantage, perceived ease of use, and perceived usefulness have received considerable attention from researchers. Relevant literature reports that users’ perceived relative advantages positively influence their behavioral intention to use ChatGPT. In particular, a higher perceived relative advantage is often closely related to a higher positive evaluation of the usefulness of ChatGPT by students [
31,
32,
33]. Therefore, we propose the following hypotheses:
H1.
Relative advantage has a significant effect on the perceived ease of use of the ChatGPT.
H2.
Relative advantage has a significant effect on the perceived usefulness of ChatGPT.
Perceived compatibility (PC) refers to the degree to which an innovative invention can effectively convey existing values, past experiences, and the needs of potential users in a social environment [
34]. Moore defined perceived compatibility as the degree to which an observable innovative technology system conforms to current norms, conditions, and experiences [
35]. Therefore, this study used this term to refer to the role of the ChatGPT in helping university students improve their learning. Previous studies have often used perceived compatibility as an indicator to assess students’ behavioral intentions [
36,
37]. Therefore, based on existing research, we propose the following hypotheses:
H3.
Perceived compatibility has a significant effect on the perceived ease of use of the ChatGPT.
H4.
Perceived compatibility has a significant effect on the perceived usefulness of ChatGPT.
Complexity (CO) refers to the perceived difficulty of understanding and using innovative technology [
38]. Based on this definition, this study uses this term to refer to the level of difficulty experienced by university students when using the ChatGPT. Existing research shows that when users perceive ChatGPT as overly complex, they are less likely to continue using the technology [
39,
40]. In addition, Hardgrave and Lee et al. found a negative correlation between complexity and perceived ease of use [
41,
42]. In short, if users find ChatGPT difficult to understand and use, their intention to use it decreases. This complexity is defined from the user’s perspective and indicates the level of difficulty that users perceive when learning and using the ChatGPT. Based on this, we propose the following hypotheses:
H5.
Complexity has a significant effect on the perceived ease of use of ChatGPT.
H6.
Complexity has a significant effect on the perceived usefulness of ChatGPT.
Trialability (TR) as a key concept that reflects the need for users to experience technological innovation before adoption [
43]. Innovative technologies with high trialability often come with less uncertainty, so users tend to improve their experience through actual use.In this study, we define trialability as the extent to which university students perceive the acceptability of using ChatGPT as influencing their learning behavior.Existing research has confirmed that users’ attitudes and behavioral intentions are significantly influenced by trialability [
44,
45]. Based on this, we propose the following hypotheses:
H7.
Trialability has a significant effect on the perceived ease of use of ChatGPT.
H8.
Trialability has a significant effect on the perceived usefulness of ChatGPT.
Observability (OB) refers to the degree to which the results of an innovation are visible to others [
46] and is seen as a factor that stimulates the discussion of new ideas among peers [
47]. Therefore, in this study, observability was defined as the extent to which university students perceived the impact of ChatGPT on their learning behavior. Existing studies show that observability has a positive and significant effect on attitudes towards and intentions to use the ChatGPT [
48,
49]. In addition, research has found that a higher observability of individual expressions significantly increases users’ perceived usefulness and ease of use [
50]. Based on the existing research, we propose the following hypotheses:
H9.
Observability has a significant effect on the perceived ease of use of ChatGPT.
H10.
Observability has a significant effect on the perceived usefulness of ChatGPT.
Thinking variability (TV) refers to the ability of users to adapt their thinking patterns to different situations and needs, thereby generating innovative outcomes [
51,
52]. Thinking variability is closely related to users’ acceptance and use of information systems because information systems are innovative technologies that require users to have a certain level of thinking variability and adaptability [
36,
53]. The TAM is a widely used theoretical framework for studying users’ acceptance and use of information systems, the Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) is a widely used theoretical framework. It proposes that users’ perceived usefulness and perceived ease of use are two important cognitive factors that influence their attitudes, behavioral intentions, and actual use [
54]. These two factors may reflect users’ thinking variability towards information systems; that is, whether users can adjust their thinking patterns according to the features and functions of the information system to achieve their goals. In addition to perceived usefulness and perceived ease of use, some studies have introduced other cognitive factors, such as perceived risk and third-person effect perception, to further analyze users’ thinking variability towards information systems [
55]. Based on the existing research, we propose the following hypotheses:
H11.
Thinking variability has a significant effect on the perceived ease of use of the ChatGPT.
H12.
Thinking variability has a significant effect on the perceived usefulness of ChatGPT.
2.2. Technology Acceptance Model (TAM)
Perceived enjoyment (PE) refers to the subjective sense of pleasure and satisfaction that users experience when using a particular technology or service [
56], which is an important psychological factor influencing user behavior. The perceived enjoyment defined in this study refers to the pleasure and satisfaction that university students derive from using ChatGPT for learning activities [
16]. Existing research suggests that perceived enjoyment has a significant impact on users’ attitudes and behavioral intentions, and may also act as a mediator or moderator with other variables [
57,
58]. Research on perceived enjoyment is valuable in improving user satisfaction, loyalty, and engagement. Therefore, we propose the following hypotheses:
H13.
Perceived enjoyment had a significant effect on the perceived ease of use of the ChatGPT.
H14.
Perceived enjoyment has a significant effect on the perceived usefulness of ChatGPT.
Perceived ease of use (PEU) refers to the user’s perception of the ease or difficulty of using innovative technology [
17], and it is related to both Innovation Diffusion Theory (IDT) and the Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology (UTAUT) [
36]. These theories posit that users’ use of innovative technology is influenced by their perception of its complexity and effort expectancy; the easier users perceive the technology to be, the more likely they are to use it. In this study, we defined perceived ease of use as university students’ perceptions of the ease or difficulty of using the ChatGPT. Existing research has confirmed that perceived ease of use has a positive and significant impact on perceived usefulness, usage attitude, and behavioral intention [
48,
59]. Thus, the following hypothesis was proposed:
H15.
Perceived ease of use has a significant effect on the perceived usefulness of the ChatGPT.
H16.
Perceived ease of use had a significant effect on the attitudes towards using the ChatGPT.
Perceived usefulness (PU), an assessment of a user’s perception of a new technology’s ability to improve efficiency, is a key driver of user behavior and significantly influences user satisfaction and loyalty towards the new technology [
60]. In this study, perceived usefulness was defined as university students’ perceptions of their ability to use ChatGPT to improve their learning effectiveness. Previous research has shown a close relationship between behavioral intention and perceived usefulness, indicating that perceived usefulness has a positive and significant effect on user usage behavior [
21,
61]. Recent studies also indicate that perceived usefulness not only positively influences university students’ behavioral intention to use ChatGPT, but also significantly influences their attitude towards using ChatGPT [
62,
63]. Therefore, we propose the following hypotheses:
H17.
Perceived usefulness has a significant effect on the attitude towards using ChatGPT.
Attitude towards use (ATU) refers to users’ attitudes towards using a particular innovative technology, including cognitive, affective, and behavioral aspects [
16]. Therefore, in this study, usage attitude is defined as university students’ basic cognitive perceptions, emotional needs, and behavioral intentions when using ChatGPT.University students’ usage attitude towards ChatGPT is not only an important factor in determining their behavioral intentions, but also a crucial indicator for evaluating the effectiveness and satisfaction of ChatGPT.Usage attitude can be measured by dimensions such as perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, perceived risk, perceived enjoyment, and perceived social influence [
64]. Existing research has confirmed a significant relationship between attitude and intention to use: the more positive the students’ attitudes towards ChatGPT, the more likely they are to use it for learning, and the higher the frequency and duration of use [
65]. Furthermore, attitudes towards use can be enhanced by increasing users’ awareness and understanding of ChatGPT, improving its reliability and accuracy, increasing its innovativeness and attractiveness, establishing trust and reputation for ChatGPT, and fostering users’ sense of belonging and emotional connection to ChatGPT [
66]. Therefore, we propose the following hypothesis:
H18.
Attitude towards use has a significant impact on the behavioral intention to use the ChatGPT.
3. Research Methodology
This study focused on a group of users with experience using the ChatGPT. To construct the research framework, we referred to studies conducted by researchers from Harvard University, MIT, and Stanford University on the classification of MOOC platform users, as well as American scholar Hill’s classification criteria of Coursera’s learner groups through cluster analysis [
67,
68,
69]. Therefore, ChatGPT users in this study refer to ChatGPT users other than ‘dropouts’ and ‘registrants only.’
3.1. Data Collection
The data were collected, cleaned, sorted, and analyzed to ensure their accuracy, reliability, and validity. First, in terms of sample selection, we randomly selected 700 undergraduate, master’s, and doctoral students from the China University of Geosciences (Beijing), University of Science and Technology Beijing, and Beijing Language and Culture University, with an age range of 18–35 years and a male-to-female ratio of 3:2. After rigorous manual screening, we identified and removed 23 outlier questionnaires to ensure data quality, resulting in 677 valid questionnaires with an effective rate of 96.71%. Outlier screening was based on the method of Sánchez et al. because outliers can affect the accuracy of statistical analysis [
70]. Second, regarding the questionnaire survey, this study used a five-point Likert scale for item scoring, covering several dimensions of the Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) and Diffusion of Innovations Theory (IDT). Finally, in terms of data analysis, we used SPSS 27.0 and Amos 27.0 statistical software packages for data processing, with structural equation modelling (SEM-Amos) as the main analytical tool. SEM was divided into two stages. First, we assessed the structural, convergent, and discriminant validity of the measurement model to ensure its stability and reliability. Second, we conduct an in-depth evaluation and analysis of the structural model. Both steps strictly followed the technical guidelines and recommendations of scholars such as Hair et al. in the relevant field [
71].
3.2. Sample Characteristics
A total of 700 questionnaires were distributed and collected offline. After manual screening, 677 valid questionnaires were obtained with an effective response rate of 96.71%. The age distribution of the patients was 392 males (57.90%) and 285 females (42.10%). Among the respondents, 44 (6.50%) were 18 years old, 309 (45.64%) were 19–24 years old, 243 (35.89%) were 25–29 years old, and 81 (11.96%) were 30–35. In terms of educational level, there were 90 first-year students (24.00%), 127 second-year students (33.87%), 102 third-year students (27.20%), 56 fourth-year students (14.93%), 201 Master’s students (29.69%), and 101 doctoral students (14.92%). In terms of discipline type, 273 individuals (40.32%) were in science and engineering, 225 (33.23%) were in business and management, and 179 (26.44%) were in literature and history. These sample characteristics indicate rich diversity, which ensures the representativeness of the survey data and the feasibility of an in-depth analysis of the survey results. The detailed data are shown in
Table 1.
3.3. Measuring Instruments
This research adapted certain items in the questionnaire to ensure rationality of the design and validity of the content. The survey was conducted in three parts. The first part collected the respondents’ demographic variables, including sex, age, level of education, type of course, and academic year. The second part concerns students’ perceptions of ease of use, perceived usefulness, perceived enjoyment, attitudes towards use, and behavioral intentions towards ChatGPT, based on the Technology Acceptance Model (TAM). This section contains 24 items: perceived enjoyment (PE, 4 items), perceived ease of use (PEU, 5 items), perceived usefulness (PU, 5 items), attitudes towards using ChatGPT (ATU, 5 items), and behavioral intentions to use ChatGPT (BIU, 5 items). These items were adapted from the measures of Davis et al. [
16,
55,
72]. The third part is based on the Innovation Diffusion Theory (IDT) and consists of 24 items: Relative Advantage (RA, four items), Perceived Compatibility (PC, four items), complexity (CO, four items), trialability (TR, four items), observability (OB, four items), and Thought Variability (TV, four items). The content was adapted from previous studies [
17,
35]. Finally, this study included 48 measurement items, each rated on a 5-point scale ranging from 1 (strongly disagree) to 5 (strongly agree).
4. Results and Analysis
From an empirical research perspective, university students’ attitudes towards and intentions to use ChatGPT in higher education are significantly influenced by factors related to the Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) and Innovation Diffusion Theory (IDT). Regarding the reliability of the research data, Cronbach’s alpha reliability coefficient was used, and the result was 0.963, indicating a high internal consistency. To assess discriminant validity (DV), this study followed these standards: first, the indices between variables were less than 0.80 to avoid multicollinearity [
73]. Second, the average variance extracted (AVE) for each construct should be greater than or equal to 0.50 to ensure sufficient explanation of the construct model. Third, the square root of the AVE for each construct should be greater than its correlation coefficient (IC) with all other constructs to validate the discriminant ability of the measurement tool [
74]. In addition, in the structural equation model analysis, the factor loading (FL), which measures the strength of the relationship between the observed variables and their latent variables, should be ≥0.70 to ensure that the model has good explanatory power. Similarly, Cronbach’s alpha (CA), as an indicator of internal consistency, should also meet the standard of ≥0.70 [
74]. Finally, Composite Reliability (CR), as an indicator of overall reliability, should also be ≥0.70 to ensure the robustness of the research findings.
4.1. Model Analysis
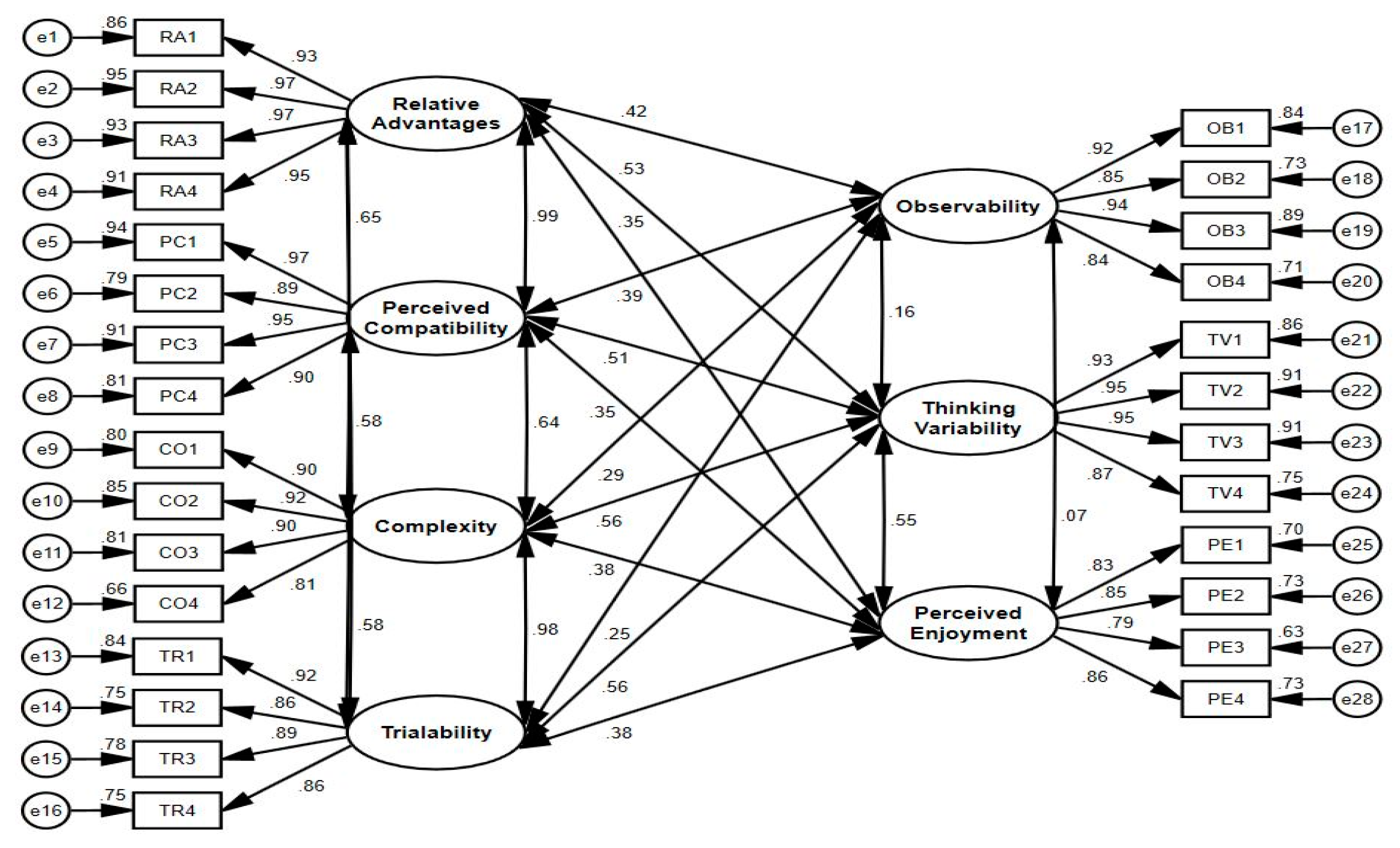
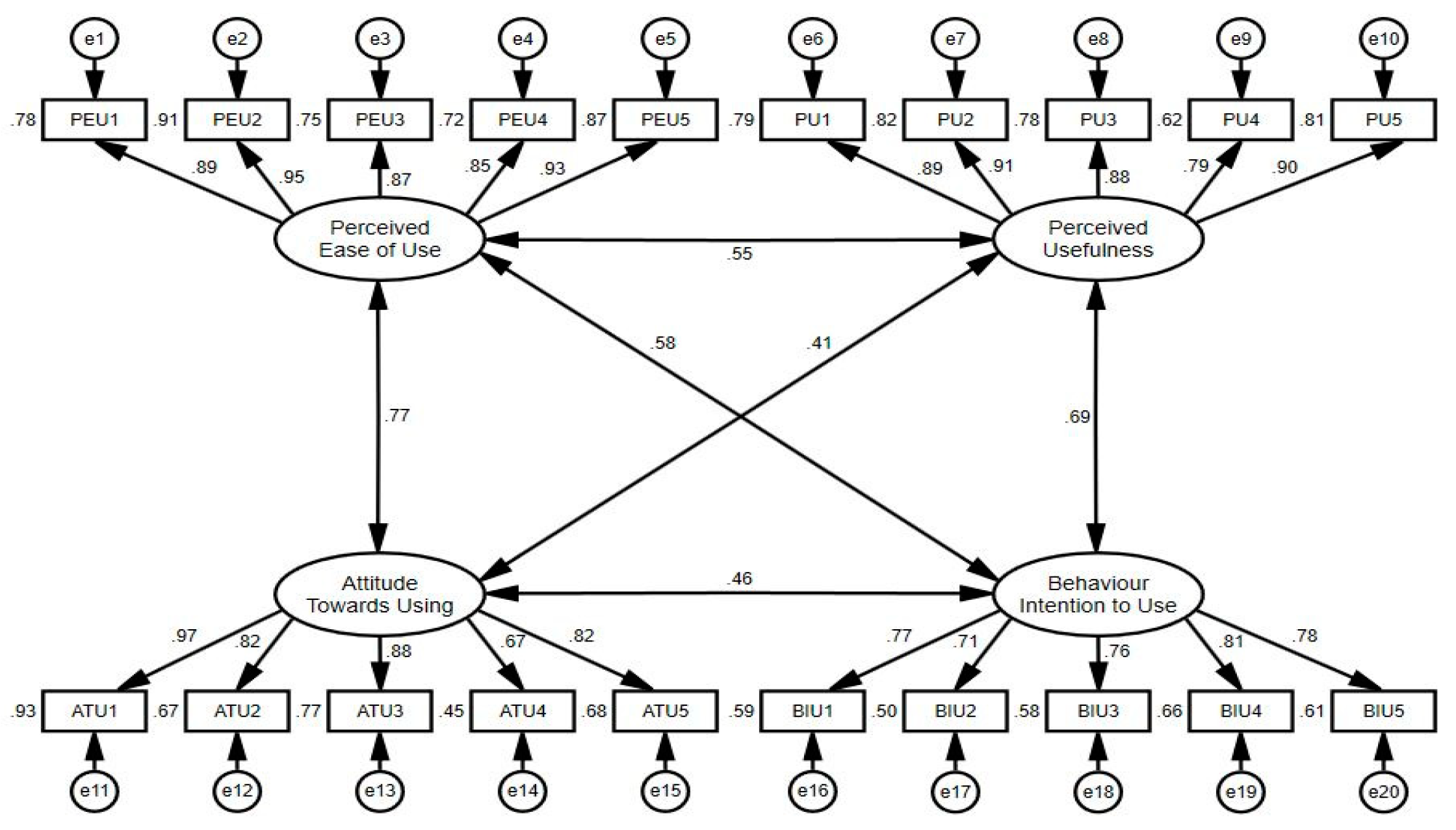
This study employed AMOS 27.0 software as the analysis tool, primarily relying on Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) and Confirmatory Factor Analysis (CFA) for in-depth data analysis. To assess the quality of the measurement model, this study followed the methodology of Hair et al., conducting a comprehensive evaluation through multiple dimensions, including unidimensionality, discriminant validity, fit indices, and convergent validity [
71]. Additionally, this study drew upon the research by Sabry, Byrne, and Kline, incorporating a series of fit indices. These indicators (
Table 2) collectively form an effective toolkit for assessing model fit [
75,
76,
77]. The specific fit indices of the survey data are detailed in
Table 2 and a visual representation of the measurement model is presented in
Figure 2. We conducted a normality test to ensure the robustness and reliability of the data. This testing process primarily relied on statistical measures such as the Variance Inflation Factor (VIF<10), tolerance (>0.1), and Pearson product-moment correlation coefficient (<0.90). According to widely accepted standards, VIF values should be less than three, as higher values typically indicate multicollinearity issues. As shown in
Table 3, the VIF values for all variables were below three, demonstrating the normality of the data used in this study and the absence of multicollinearity issues.
4.2. Reliability and Validity Verification
This study conducted an in-depth assessment of the reliability and validity of the data; detailed results are presented in
Table 4. We employed two indicators, Composite Reliability (CR) and Cronbach’s alpha (CA), to measure the reliability of the data. The results showed that the CR and CA values for all measurement items reached high levels of ≥ 0.80 or above, fully demonstrating the stability and reliability of the measurement tools. Additionally, we calculated the Average Variance Extracted (AVE) to assess the convergent validity of the measurement tools for latent constructs. The results showed that The AVE values exceeded the benchmark level of 0.50, further confirming the effectiveness and accuracy of the measurement tools. Specifically, the range of CR values was from 0.848 to 0.964, which significantly exceeded the acceptance criterion of 0.80, indicating the excellent internal consistency of our measurement tools. The CA values exhibited a similar trend, ranging from 0.821 to 0.961, exceeding the critical value of 0.80, further supporting the reliability test standards of the measurement tools. Furthermore, the AVE values ranged from 0.536 to 0.871, all significantly greater than the benchmark level of 0.50. This not only demonstrates the good convergent validity of the measurement tools, but also reflects their strong ability to capture latent constructs, aligning with conventional assessment guidelines [
71].
4.3. Structural Model Analysis
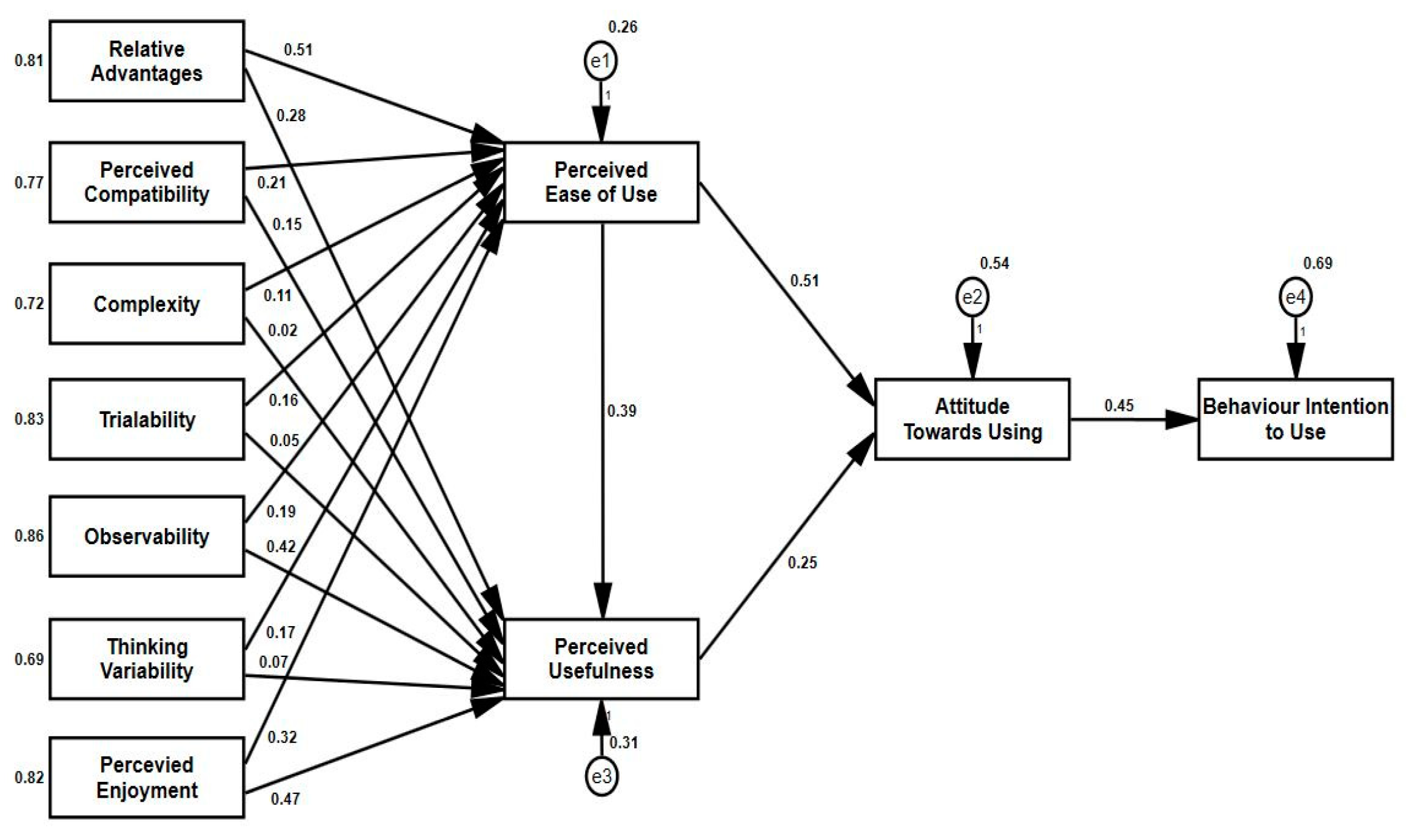
This study employed the path modeling analysis technique to comprehensively analyze university students’ attitudes towards and behavioral intentions to use ChatGPT, as well as their influencing factors, through the theoretical frameworks of the Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) and Innovation Diffusion Theory (IDT). Through this research method, we aimed to gain a more accurate understanding of university students’ levels of acceptance, motivation for use, and potential risks and obstacles regarding ChatGPT technology, thereby providing strong theoretical support and practical guidance for the application and promotion of educational technology. After collecting and analyzing relevant data on university students’ use of ChatGPT, this study systematically tested all hypotheses and validated the models presented in
Figure 2,
Figure 3 and
Figure 4 using Confirmatory Factor Analysis (CFA) within the structural equation Modeling (SEM) framework.
Figure 4 provides a detailed description of all hypotheses related to the structure of the 11 key variables in this study. Through statistical testing, 15 hypotheses were supported by the data, whereas only three were rejected.
Table 5 presents the main calculation results of the ChatGPT usage intention model, from which it can be seen that the main statistical indicators of the model performed well. The values of unstandardized coefficients and standard errors of the structural model further demonstrate the validity of the model and reliability of the hypothesis testing. The results of this study significantly support the core hypothesis of the Technology Acceptance Model (TAM), which states that perceived usefulness and perceived ease of use significantly influence university students’ attitudes towards and behavioral intentions to use ChatGPT. This conclusion is consistent with previous academic research [
78,
79], further confirming the effectiveness of the TAM framework in predicting and explaining technology adoption behavior. Therefore, it can be inferred that ChatGPT, as an emerging technological tool, has a significant potential to enhance the learning and working efficiency of university students.
5. Discussion and Implications
5.1. Innovation Diffusion Theory (IDT) Hypothesis
This study utilized AMOS 27.0 software to conduct Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) analysis to evaluate the relevant hypotheses. First, we discuss 12 key hypotheses in Innovation Diffusion Theory (IDT). By analyzing the data in
Figure 4 and
Table 5, we observed a significant positive relationship between relative advantage and perceived ease of use (β=0.513, t=11.860, p<0.001), indicating that Hypothesis 1 (H1) is supported. This finding further reveals that when adopting new technologies, such as ChatGPT, university students consider their advantages over traditional methods and whether the technology is easy to learn and use. Next, we validated the relationship between relative advantage and perceived usefulness. The data analysis showed a significant positive correlation between the two (β=0.278, t=7.514, p<0.001), indicating that Hypothesis 2 (H2) is supported. This suggests that when deciding whether to use ChatGPT, university students consider its advantages over other tools and whether it can provide substantial help in their studies. The data analysis showed a significant positive relationship between these two variables (β=0.278, t=7.514, p<0.001), supporting Hypothesis 2 (H2). This suggests that when deciding whether to use ChatGPT, university students consider its advantages over other tools and whether it can provide substantial benefits to their learning. These findings are consistent with those of previous studies [
32,
80,
81], further validating the applicability of the IDT framework in the field of new technology adoption.
There was a significant positive relationship between perceived compatibility and ease of use (β=0.211, t=8.115, p<0.001). This supports Hypothesis 3 (H3), implying that perceived compatibility positively influences users’ perceived ease of use. In other words, in the current model, when evaluating their willingness to use ChatGPT, university students focus on the compatibility of the new technology with their existing learning tools, behaviors, or content and whether this compatibility enhances the ease of use in learning. Next, we analyzed the direct effects of perceived compatibility and perceived usefulness. The statistical results show a significant positive relationship between the two (β=0.153, t=3.122, p<0.01), indicating that Hypothesis 4 (H4) is supported. This suggests that among university students, the compatibility of the technology not only affects the ease of use, but also directly influences their perception of its usefulness in learning. In the current research model, university students consider the compatibility of ChatGPT, and whether this compatibility can enhance their learning efficiency. This is consistent with previous research findings [
6,
29,
82].
There is a significant relationship between complexity and perceived ease of use (β=-0.112, t=-4.870, p<0.001), which supports Hypothesis 5 (H5), revealing the important relationship between technology complexity and perceived ease of use. Specifically, in the current research model, when ChatGPT technology is perceived as more complex, university students’ perception of its ease of use decreases accordingly, which is consistent with the views of Al-Rahmi et al. [
38]. This finding provides important insights into the cognitive processes in user-technology interactions and highlights the importance of understanding user behavior and focusing on ease of use from a user’s perspective. However, different results were observed when exploring the relationship between complexity and perceived usefulness, different results were observed. There was a negative correlation between complexity and perceived usefulness (β=-0.022, t=-0.564, p>0.05), but this relationship was not significant. Therefore, Hypothesis 6 (H6) is rejected, indicating that the complexity of the new technology does not have a positive or substantial impact on perceived usefulness. Although this finding does not support our hypothesis, it provides new insights into the acceptance and use of new technology.
There was a significant positive relationship between trialability and perceived ease of use (β=0.159, t=6.625, p<0.001). This result supports Hypothesis 7 (H7), indicating that trialability has a positive and significant impact on perceived ease of use. Specifically, according to the current research model, the experience of using ChatGPT among university students indicates that the higher the trialability of the system, the stronger is their perception of its ease of use. This finding is valuable for enhancing user satisfaction and experiences, particularly when designing and developing educational technology tools for university students. However, when examining the relationship between trialability and perceived usefulness, we obtained different results. Statistical data showed a negative relationship between these two variables (β=-0.052, t=-0.852, p>0.05), but this relationship was not significant. Therefore, Hypothesis 8 (H8) is rejected, indicating that, in the current model, university students cannot significantly enhance their perception of the usefulness of learning through the trialability of ChatGPT. This is consistent with the findings of Alyoussef et al., who found that the trialability of ChatGPT did not have a positive and significant impact on perceived usefulness among university students [
83].
There was a significant positive relationship between observability and perceived ease of use (β=0.191, t=7.346, p<0.001). Thus, Hypothesis 9 (H9) is supported. Specifically, according to the analysis of the current model, we found that university students place a high value on the observability of the system when using ChatGPT and consider it an important factor in assessing ease of use. In other words, the higher the observability of ChatGPT, the more likely university students are to positively perceive its ease of use. We further analyzed the relationship between observability and perceived usefulness, and found a similarly positive and significant relationship between the two (β=0.442, t=11.722, p<0.001). This result supports hypothesis 10 (H10). Specifically, in the current model, university students can assess the potential benefits of ChatGPT in learning by observing certain characteristics or the effects of the system. In other words, the usefulness of the ChatGPT can be perceived through observation, which effectively enhances university students’ recognition of its usefulness in learning. These test results are consistent with those of previous studies [
81,
84].
In addition, thinking variability and perceived ease of use showed a positive and significant relationship (β=0.174, t=3.867, p<0.001), supporting Hypothesis 11 (H11). Specifically, in the current research model, we found that university students’ adaptability to ChatGPT–that is, their thinking variability–significantly positively influenced their perceived ease of use of this technology. In other words, students who can flexibly adjust their thinking to use ChatGPT are more likely to find it easier. This finding aligns with the views of Strzelecki and Robert et al. [
51,
85], further validating the important role of thinking variability in enhancing technological acceptance. However, when exploring the relationship between thinking variability and perceived usefulness, we obtained a different result (β=-0.071, t=-1.203, p>0.05). This result indicates that in the current research model, thinking variability does not have a positive or significant impact on perceived usefulness; thus, Hypothesis 12 (H12) is rejected. Although H12 was not supported, this finding reminds us that when considering technology acceptance, it is still necessary to consider the differences in the thinking variability and adaptability of university students when using the ChatGPT. Additionally, students who are skeptical about ChatGPT generally face issues with the complexity of the technology system and a lack of thinking variability. To better understand these phenomena, future research could explore the potential relationship between thinking variability and perceived usefulness. Further empirical studies are required to investigate and explore the important relationships between these two factors.
5.2. Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) Assumptions
This study utilized AMOS 27.0 software to perform structural equation modeling (SEM) analysis to evaluate six key hypotheses within the framework of the Technology Acceptance Model (TAM). Specifically, we conducted an in-depth examination of the relationship between perceived enjoyment and perceived ease of use of ChatGPT.As shown in
Figure 4 and
Table 5, we observed a significant positive relationship between perceived enjoyment and perceived ease of use (β=0.318, t=5.782, p<0.001), indicating that Hypothesis 13 (H13) is supported. In the current research model, university students’ satisfaction with using ChatGPT significantly positively influenced their perceived ease of use of this tool. Specifically, the subjective satisfaction of university students using ChatGPT directly and effectively promoted their positive evaluation of its ease of use. This positive perception of ease of use helps enhance their learning outcomes.Additionally, we further examined the relationship between perceived enjoyment and perceived usefulness.The data results show a significant positive relationship between these two factors (β=0.468, t=11.415, p<0.001), thus validating Hypothesis 14 (H14). This indicates that, in the current research model, university students’ satisfaction with ChatGPT is closely related to their positive perception of its usefulness in learning. That is, students tend to recognize the utility of ChatGPT in learning because of the genuine enjoyment they perceive during its use, which is consistent with the findings of previous reports [
57,
58].
This study also demonstrated a significantly positive relationship between perceived ease of use and perceived usefulness (β=0.391, t=10.289, p<0.001), supporting Hypothesis 15 (H15). Specifically, in the current research model, university students had a high level of recognition of both the ease of use and usefulness of ChatGPT. In other words, the ease of use of the ChatGPT significantly promoted students’ positive perceptions of its usefulness. Additionally, this positive relationship is of great value for understanding the psychology and behavior of users in the technology acceptance process. Subsequently, we explored the relationship between perceived ease of use and usage attitude, and the results were significant (β=0.507, t=11.523, p<0.001), indicating that Hypothesis 16 (H16) was supported. In the current model, this finding not only highlights the core role of ChatGPT’s ease of use in enhancing students’ usage attitudes but also reinforces the academic value of ease of use as a key antecedent variable in predicting user behavioral intentions. Furthermore, we analyzed the relationship between perceived usefulness and usage attitude (β=0.251, t=9.296, p<0.001), and this result supports Hypothesis 17 (H17). This indicates that in the current research model, university students generally agree that the usefulness of ChatGPT has a significant positive impact on their learning attitude. In other words, perceived usefulness is a key factor in promoting a positive learning attitude towards ChatGPT among university students. Finally, we examined the relationship between usage attitude and students’ behavioral intention to use ChatGPT (β=0.447, t=12.771, p<0.001), which supported Hypothesis 18 (H18). Specifically, in the current model, students’ attitudes towards using ChatGPT significantly influenced their behavioral intention to use it. This result not only illustrates the core role of usage attitude in predicting user behavioral intention but also further validates the theoretical framework of the Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) regarding the relationship between usage attitude and behavioral intention.
Overall, the results of this study support the core theoretical assumptions of the Technology Acceptance Model (TAM), which are highly consistent with previous research. Specifically, the three key dimensions of perceived enjoyment, perceived ease of use, and perceived usefulness collectively influence university students’ behavioral intention to use ChatGPT. The integrated perception of these dimensions not only significantly predicted university students’ intention to use ChatGPT but also effectively promoted their utilization of this technological tool to enhance their learning behavioral performance and learning outcomes. These findings not only provide empirical evidence for understanding how university students accept and use technological tools to assist learning but also offer valuable references for future related research and educational practices.
6. Research Limitations and Future Work
Despite achieving certain results in exploring the influence of factors such as the Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) and Innovation Diffusion Theory (IDT) on the intention to use the ChatGPT, this study still has some limitations. First, regarding sample selection, this study mainly focused on student populations from the China University of Geosciences (Beijing), University of Science and Technology Beijing, and Beijing Language and Culture University. Therefore, the research results may not reflect the performance of students from private universities, normal universities, military academies, or school teachers. Second, from the perspective of research methodology, this study primarily employed quantitative research methods and collected data through questionnaire surveys. The limitation of this method lies in its potential inability to capture the deep and complex cognitive situations of the respondents. Future research could consider integrating qualitative research methods, such as individual interviews, group discussions, or expert interviews, to enrich and deepen the understanding of research questions and phenomena while validating and complementing the results of quantitative research. Furthermore, in terms of the research model, although this study extended based on the Technology Acceptance Model (TAM), it did not fully incorporate factors such as performance expectancy (PE), effort expectancy (EE), social influence (SI), and facilitating conditions (FC) from the Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology (UTAUT), as well as potential moderating variables such as gender, age, and experience. Future research should further improve model construction by fully considering these variables to enhance the explanatory power and predictive ability of the model. Finally, in terms of sample size, although the sample size of this study is sufficient for model testing and structural equation modeling analysis, future research should continue to expand the sample size to ensure the stability and generalizability of the research results.
7. Conclusions
This study leverages the Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) and Innovation Diffusion Theory (IDT) to elucidate factors influencing university students’ adoption of ChatGPT, testing 18 hypotheses with three rejections. The model effectively predicts student usage behavior, with perceived innovation characteristics significantly impacting perceived ease of use (PEU) and perceived usefulness (PU). Although complexity (CO), trialability (TR), and thinking variability (TV) negatively correlate with PU, these effects are not significant. Significant relationships exist among perceived enjoyment (PE), PEU, PU, attitude towards use (ATU), and behavioral intention to use (BIU), with PU and PEU influencing continued usage through ATU. Despite extensive research on technology acceptance, empirical studies in mainland China remain limited. This study fills the gap using quantitative methods to assess 11 key variables of the integrated TAM, providing strong academic and practical insights for integrating ChatGPT in Chinese higher education. Introducing thinking variability enriches the research and underscores its importance through empirical data. Future research should explore ChatGPT’s complexity and compatibility with other educational technologies, and its scalability within educational systems. Given current imperfections in ChatGPT, a balanced view is necessary to harness its educational potential while mitigating risks, ensuring alignment between machine capabilities and human values.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.L. and J.Y.; methodology, C.L.; software, J.Y.and H.Z.; validation,C.L., QL.T. and J.G.; formal analysis, C.L. and G.Y.; investigation, H.Z.; resources, L.T.; data curation,C.L. and J.Y; writing—original draft preparation, C.L. and J.Y.; writing—review and editing, C.L. and J.Y.;visualization, C.L. and H.Z.; supervision, C.L.; project administration, C.L. and J.Y.; funding acquisition,J.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The research work of this paper is supported by the key project of the National Social Science Fund for the Research of Ideological and Political Theory Courses in Colleges and Universities, National Social Science Fund, Grant No.22VSZ010.
Institutional Review Board Statement
All subjects gave their informed consent for inclusion beforethey participated in the study. The study protocol was approved by the Local Ethics Committee of the School of Marxism, China University of Geosciences (Beijing) (approval date: December 13, 2023) (protocol number 20231213).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used in this study are available from the first author on reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to all participants in this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study, in the collection, analysis, or interpretation of data, in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Adeshola, Ibrahim, and Adeola Praise Adepoju. “The opportunities and challenges of ChatGPT in education.” Interactive Learning Environments (2023): 1-14. [CrossRef]
- Ajlouni, Aseel O., Fatima Abd-Alkareem Wahba, and Abdallah Salem Almahaireh. “Students’ Attitudes Towards Using ChatGPT as a Learning Tool: The Case of the University of Jordan.” International Journal of Interactive Mobile Technologies 17.18 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Saif, Naveed, et al. “Chat-GPT; validating Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) in education sector via ubiquitous learning mechanism.” Computers in Human behavior 154 (2024): 108097. [CrossRef]
- Rudolph, Jürgen, Shannon Tan, and Samson Tan. “War of the chatbots: Bard, Bing Chat, ChatGPT, Ernie and beyond. The new AI gold rush and its impact on higher education.” Journal of Applied Learning and Teaching 6.1 (2023).
- Alshahrani, A. “The impact of ChatGPT on blended learning: Current trends and future research directions.” International Journal of Data and Network Science 7.4 (2023): 2029-2040. [CrossRef]
- Abdaljaleel, Maram, et al. “A multinational study on the factors influencing university students’ attitudes and usage of ChatGPT.” Scientific Reports 14.1 (2024): 1983. [CrossRef]
- Strzelecki, Artur. “To use or not to use ChatGPT in higher education? A study of students’ acceptance and use of technology.” Interactive Learning Environments (2023): 1-14. [CrossRef]
- Rasul, Tareq, et al. “The role of ChatGPT in higher education: Benefits, challenges, and future research directions.” Journal of Applied Learning and Teaching 6.1 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Oranga, Josephine. “Benefits of artificial intelligence (chatgpt) in education and learning: is chat gpt helpful?.” International Review of Practical Innovation, Technology and Green Energy (IRPITAGE) 3.3 (2023): 46-50.
- Menon, Devadas, and K. Shilpa. ““Chatting with ChatGPT”: Analyzing the factors influencing users’ intention to Use the Open AI’s ChatGPT using the UTAUT model.” Heliyon 9.11 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Xing, JiaMan, and Qianling Jiang. “Factors influencing user experience in AI chat systems–a satisfaction study based on factor analysis and linear regression.” Kybernetes (2024). [CrossRef]
- Haglund, Jakob Hasselqvist. “Students Acceptance and Use of ChatGPT in Academic Settings.” Uppsala Universitet (2023).
- Chu, Tsai-Hsin, and Yi-Ying Chen. “With good we become good: Understanding e-learning adoption by theory of planned behavior and group influences.” Computers & Education 92 (2016): 37-52. [CrossRef]
- Tosuntaş, Ş. Betul, Engin Karadağ, and Sevil Orhan. “The factors affecting acceptance and use of interactive whiteboard within the scope of FATIH project: A structural equation model based on the Unified Theory of acceptance and use of technology.” Computers & Education 81 (2015): 169-178. [CrossRef]
- Park, Sung Youl. “An analysis of the technology acceptance model in understanding university students’ behavioral intention to use e-learning.” Journal of Educational Technology & Society 12.3 (2009): 150-162.
- Davis, Fred D., Richard P. Bagozzi, and Paul R. Warshaw. “User acceptance of computer technology: A comparison of two theoretical models.” Management science 35.8 (1989): 982-1003.
- Rogers, Everett M., Arvind Singhal, and Margaret M. Quinlan. “Diffusion of innovations.” An integrated approach to communication theory and research. Routledge, 2014. 432-448.
- Hameed, Mumtaz Abdul, Steve Counsell, and Stephen Swift. “A conceptual model for the process of IT innovation adoption in organizations.” Journal of Engineering and Technology Management 29.3 (2012): 358-390. [CrossRef]
- Puklavec, Borut, Tiago Oliveira, and Aleš Popovič. “Unpacking business intelligence systems adoption determinants: An exploratory study of small and medium enterprises.” Economic and business review 16.2 (2014): 5. [CrossRef]
- Li, Xiaolin, et al. “Decision factors for the adoption and continued use of online direct sales channels among SMEs.” Journal of the Association for Information Systems 12.1 (2011): 4. [CrossRef]
- Wu, Jen-Her, and Shu-Ching Wang. “What drives mobile commerce?: An empirical evaluation of the revised technology acceptance model.” Information & management 42.5 (2005): 719-729. [CrossRef]
- Gefen, David. “What makes an ERP implementation relationship worthwhile: Linking trust mechanisms and ERP usefulness.” Journal of Management Information Systems 21.1 (2004): 263-288. [CrossRef]
- Moore, Gary C., and Izak Benbasat. “Development of an instrument to measure the perceptions of adopting an information technology innovation.” Information systems research 2.3 (1991): 192-222. [CrossRef]
- Wonglimpiyarat, Jarunee, and Napaporn Yuberk. “In support of innovation management and Roger’s Innovation Diffusion theory.” Government Information Quarterly 22.3 (2005): 411-422. [CrossRef]
- Dillon, Andrew, and Michael G. Morris. “User acceptance of new information technology: theories and models.” (1996).
- Rahardja, Untung, Taqwa Hariguna, and Qurotul Aini. “Understanding the Impact of Determinants in Game Learning Acceptance: An Empirical Study.” International Journal of Education and Practice 7.3 (2019): 136-145.
- Yuen Kum Fai, et al. Factors influencing autonomous vehicle adoption: an application of the technology acceptance model and innovation diffusion theory. Technology Analysis & Strategic Management. Vol.33, no. 5, pp. 505-519, Oct, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, Chandan Kumar, et al. “What drives students toward ChatGPT? An investigation of the factors influencing adoption and usage of ChatGPT.” Interactive Technology and Smart Education (2023). [CrossRef]
- Romero Rodríguez, José María, et al. “Use of ChatGPT at university as a tool for complex thinking: Students’ perceived usefulness.” (2023). [CrossRef]
- Foroughi, Behzad, et al. “Determinants of intention to use ChatGPT for educational purposes: Findings from PLS-SEM and fsQCA.” International Journal of Human–Computer Interaction (2023): 1-20. [CrossRef]
- Raman, Raghu, et al. “University students as early adopters of ChatGPT: Innovation Diffusion Study.” (2023). [CrossRef]
- Enriquez, Benicio Gonzalo Acosta, et al. “Analysis College Students’ attitude towards the use of ChatGPT in their academic activities: Effect of intent to use, verify information and responsible use.” (2023). [CrossRef]
- Valova, Irena, Tsvetelina Mladenova, and Gabriel Kanev. “Students’ Perception of ChatGPT Usage in Education.” International Journal of Advanced Computer Science & Applications 15.1 (2024).
- Al-Rahmi, W.M.; Alias, N.; Othman, M.S.; Ahmed, I.A.; Zeki, A.M.; Saged, A.A. Social Media Use, Collaborative Learning and Students’ academic Performance: A Systematic Literature Review of Theoretical Models. J. Theor. Appl. Inf. Technol. 2017, 95,5399–5414.
- Moore, G.C.; Benbasat, I. Development of an instrument to measure the perceptions of adopting an information technologyinnovation. Inf. Syst. Res. 1991, 2, 192–222. [CrossRef]
- V. Venkatesh, M. G. Morris, G. B. Davis, and F. D. Davis, “User acceptance of information technology: Toward a unified view,” MIS Quart., vol. 27, no. 3, pp. 425–478, 2003. [CrossRef]
- Faqih, Khaled MS. “The influence OF perceived usefulness, social influence, internet self-efficacy and compatibility ON USERS’INTENTIONS to adopt e-learning: investigating the moderating effects OF culture.” IJAEDU-International E-Journal of Advances in Education 5.15 (2020): 300-320.
- Al-Rahmi, Waleed Mugahed, et al. “Integrating technology acceptance model with innovation diffusion theory: An empirical investigation on students’ intention to use E-learning systems.” Ieee Access 7 (2019): 26797-26809. [CrossRef]
- Ma, Xiaoyue, and Yudi Huo. “Are users willing to embrace ChatGPT? Exploring the factors on the acceptance of chatbots from the perspective of AIDUA framework.” Technology in Society 75 (2023): 102362. [CrossRef]
- Andersson, Mattias, and Tom Marshall Olsson. “ChatGPT as a Supporting Tool for System Developers: Understanding User Adoption.” (2023).
- B. C. Hardgrave, F. D. Davis, and C. K. Riemenschneider,“Investigating determinants of software developers’intentions to follow methodologies,”J. Manage. Inf. Syst., vol. 20, no. 1, pp. 123–151, 2003. [CrossRef]
- Y. H. Lee,“Exploring key factors that affect consumers to adopt ereading services,” M.S. Thesis, Dept. Inf. Service Economy, Huafan Univ.,New Taipei City, Taiwan, 2007.
- Hussein Saleh Zolait, Ali, Minna Mattila, and Ainin Sulaiman. “The effect of User’s Informational-Based Readiness on innovation acceptance.” International Journal of Bank Marketing 27.1 (2009): 76-100. [CrossRef]
- Jackson, Cynthia M., Simeon Chow, and Robert A. Leitch. “Toward an understanding of the behavioral intention to use an information system.” Decision sciences 28.2 (1997): 357-389. [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, Ritu, and Jayesh Prasad. “The role of innovation characteristics and perceived voluntariness in the acceptance of information technologies.” Decision sciences 28.3 (1997): 557-582. [CrossRef]
- Almaiah, Mohammed Amin, et al. “Measuring institutions’ adoption of artificial intelligence applications in online learning environments: Integrating the innovation diffusion theory with technology adoption rate.” Electronics 11.20 (2022): 3291. [CrossRef]
- Zolkepli, Izzal Asnira, and Yusniza Kamarulzaman. “Social media adoption: The role of media needs and innovation characteristics.” Computers in human behavior 43 (2015): 189-209. [CrossRef]
- Teerawongsathorn, Jidapa. Understanding the Influence Factors on the Acceptance and Use of ChatGPT in Bangkok: A Study Based on the Technology Acceptance Model. Diss. Mahidol University, 2023.
- Ghaniabadi, Mahdieh. Factors that impact users’ attitudes toward chatbots and their intentions to use chatbot in online services. Diss. Vilniaus universitetas., 2024.
- Yu, Chengcheng, Jinzhe Yan, and Na Cai. “ChatGPT in higher education: factors influencing ChatGPT user satisfaction and continued use intention.” Frontiers in Education. Vol. 9. Frontiers Media SA, 2024. [CrossRef]
- Gould, Robert. “Variability: One statistician’s view.” (2004).
- Siegler, Robert S. “Cognitive variability.” Developmental science 10.1 (2007): 104-109. [CrossRef]
- Grover, Purva, et al. “Perceived usefulness, ease of use and user acceptance of blockchain technology for digital transactions–insights from user-generated content on Twitter.” Enterprise Information Systems 13.6 (2019): 771-800. [CrossRef]
- Bhattacherjee, A. Understanding information systems continuance: an expectation-confirmation model. MIS quarterly, 2001, 351-370.
- Venkatesh, V., & Davis, F. D. A theoretical extension of the technology acceptance model: Four longitudinal field studies. Management science, 46(2),2000, 186-204. [CrossRef]
- Van der Heijden, Hans. “User acceptance of hedonic information systems.” MIS quarterly (2004): 695-704.
- Atombo, Charles, et al. “Perceived enjoyment, concentration, intention, and speed violation behavior: Using flow theory and theory of planned behavior.” Traffic injury prevention 18.7 (2017): 694-702. [CrossRef]
- Balog, Alexandru, and Costin Pribeanu. “The role of perceived enjoyment in the students’ acceptance of an augmented reality teaching platform: A structural equation modelling approach.” Studies in Informatics and Control 19.3 (2010): 319-330.
- Teerawongsathorn, Jidapa. Understanding the Influence Factors on the Acceptance and Use of ChatGPT in Bangkok: A Study Based on the Technology Acceptance Model. Diss. Mahidol University, 2023.
- Kumar, M. Sendhil, and Dr S. Gokula Krishnan. “Perceived Usefulness (PU), Perceived Ease of Use (PEOU), and behavioral Intension to Use (BIU): Mediating effect of Attitude toward Use (AU) with reference to Mobile wallet Acceptance and Adoption in Rural India.” (2020).
- Roca, Mónica De La, et al. “The impact of a chatbot working as an assistant in a course for supporting student learning and engagement.” Computer Applications in Engineering Education (2024): e22750. [CrossRef]
- S.-C. Chang and F.-C. Tung, “An empirical investigation of students’behavioral intentions to use the online learning course websites,”Brit.J. Educ. Technol., vol. 39, no. 1, pp. 71–83, 2008. [CrossRef]
- Maheshwari, Greeni. “Factors influencing students’ intention to adopt and use ChatGPT in higher education: A study in the Vietnamese context.” Education and Information Technologies (2023): 1-29. [CrossRef]
- Abdaljaleel, Maram, et al. “Factors Influencing Attitudes of University Students towards ChatGPT and its Usage: A Multi-National Study Validating the TAME-ChatGPT Survey Instrument.” (2023). [CrossRef]
- Dempere, Juan, et al. “The impact of ChatGPT on higher education.” Dempere J, Modugu K, Hesham A and Ramasamy LK (2023) The impact of ChatGPT on higher education. Front. Educ 8 (2023): 1206936. [CrossRef]
- Robledo, Dave Arthur R., et al. “Development and Validation of a Survey Instrument on Knowledge, Attitude, and Practices (KAP) Regarding the Educational Use of ChatGPT among Preservice Teachers in the Philippines.” International Journal of Information and Education Technology 13.10 (2023).
- Ho, Andrew, et al. “HarvardX and MITx: Two years of open online courses fall 2012-summer 2014.” Available at SSRN 2586847 (2015). http://dx.doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.2586847.
- Kizilcec, René F., Chris Piech, and Emily Schneider. “Deconstructing disengagement: analyzing learner subpopulations in massive open online courses.” Proceedings of the third international conference on learning analytics and knowledge. 2013. [CrossRef]
- Hill, Phil. “Emerging student patterns in MOOCs: A (revised) graphical view.” (2013).
- Sánchez, R. Arteaga, Virginia Cortijo, and Uzma Javed. “Students’ perceptions of Facebook for academic purposes.” Computers & Education 70 (2014): 138-149. [CrossRef]
- Hair Jr, Joseph F., Barry J. Babin, and Nina Krey. “Covariance-based structural equation modeling in the Journal of Advertising: Review and recommendations.” Journal of Advertising 46.1 (2017): 163-177. [CrossRef]
- Lee, Seyoung, and Gain Park. “Exploring the impact of ChatGPT literacy on user satisfaction: The mediating role of user motivations.” Cyberpsychology, behavior, and Social Networking 26.12 (2023): 913-918. [CrossRef]
- Ali, Faizan, et al. “An assessment of the use of partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM) in hospitality research.” International journal of contemporary hospitality management 30.1 (2018): 514-538. [CrossRef]
- Hair, Joe F., et al. “An assessment of the use of partial least squares structural equation modeling in marketing research.” Journal of the academy of marketing science 40 (2012): 414-433.
- Abd-El-Fattah, Sabry M. “Structural equation modeling with AMOS: basic concepts, applications and programming.” Journal of applied quantitative methods 5.2 (2010): 365-368.
- Byrne, Barbara M. Structural equation modeling with EQS: Basic concepts, applications, and programming. Routledge, 2013.
- Kline, Rex B. Principles and practice of structural equation modeling. Guilford publications, 2023.
- Jo, Hyeon. “Understanding AI tool engagement: A study of ChatGPT usage and word-of-mouth among university students and office workers.” Telematics and Informatics 85 (2023): 102067. [CrossRef]
- Yu, Chengcheng, Jinzhe Yan, and Na Cai. “ChatGPT in Higher Education: Factors Influencing ChatGPT User Satisfaction and Continued Use Intention.” Frontiers in Education. Vol. 9. Frontiers, 2024. [CrossRef]
- Ngo, Thi Thuy An, et al. “ChatGPT for Educational Purposes: Investigating the Impact of Knowledge Management Factors on Student Satisfaction and Continuous Usage.” IEEE Transactions on Learning Technologies (2024). [CrossRef]
- Teerawongsathorn, Jidapa. Understanding the Influence Factors on the Acceptance and Use of ChatGPT in Bangkok: A Study Based on the Technology Acceptance Model. Diss. Mahidol University, 2023.
- Faqih, Khaled MS. “The influence OF perceived usefulness, social influence, internet self-efficacy and compatibility ON USERS’INTENTIONS to adopt e-learning: investigating the moderating effects OF culture.” IJAEDU-International E-Journal of Advances in Education 5.15 (2020): 300-320.
- Alyoussef, Ibrahim Youssef. “The Impact of Massive Open Online Courses (MOOCs) on Knowledge Management Using Integrated Innovation Diffusion Theory and the Technology Acceptance Model.” Education Sciences 13.6 (2023): 531. [CrossRef]
- Kotni, VV Devi Prasad, et al. “Adoption of ChatGPT in Higher Education-Application of IDT Model, Testing and Validation.” 2023 3rd International Conference on Technological Advancements in Computational Sciences (ICTACS). IEEE, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Strzelecki, Artur. “To use or not to use ChatGPT in higher education? A study of students’ acceptance and use of technology.” Interactive Learning Environments (2023): 1-14. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).