Submitted:
26 June 2024
Posted:
26 June 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
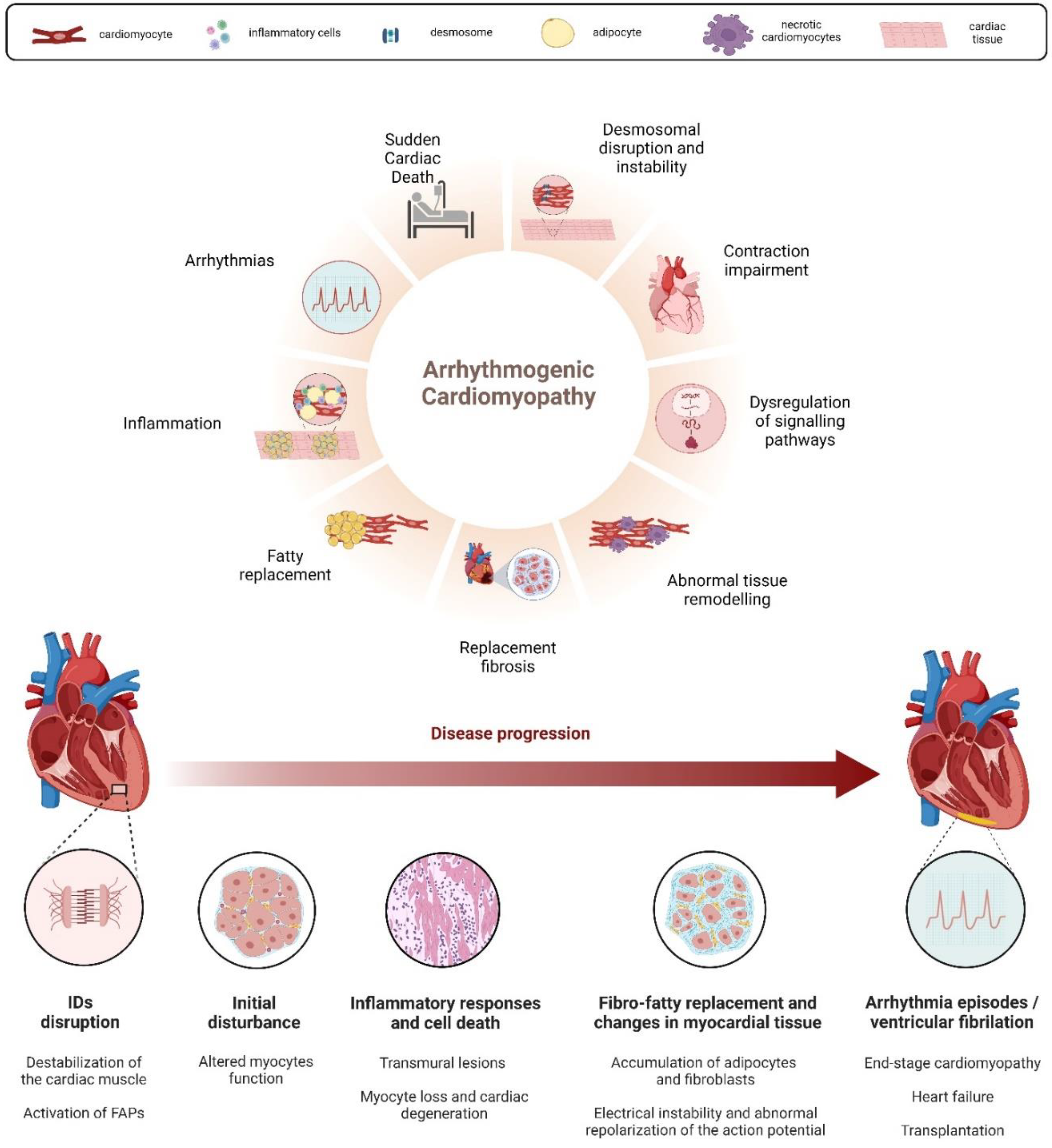
Introduction
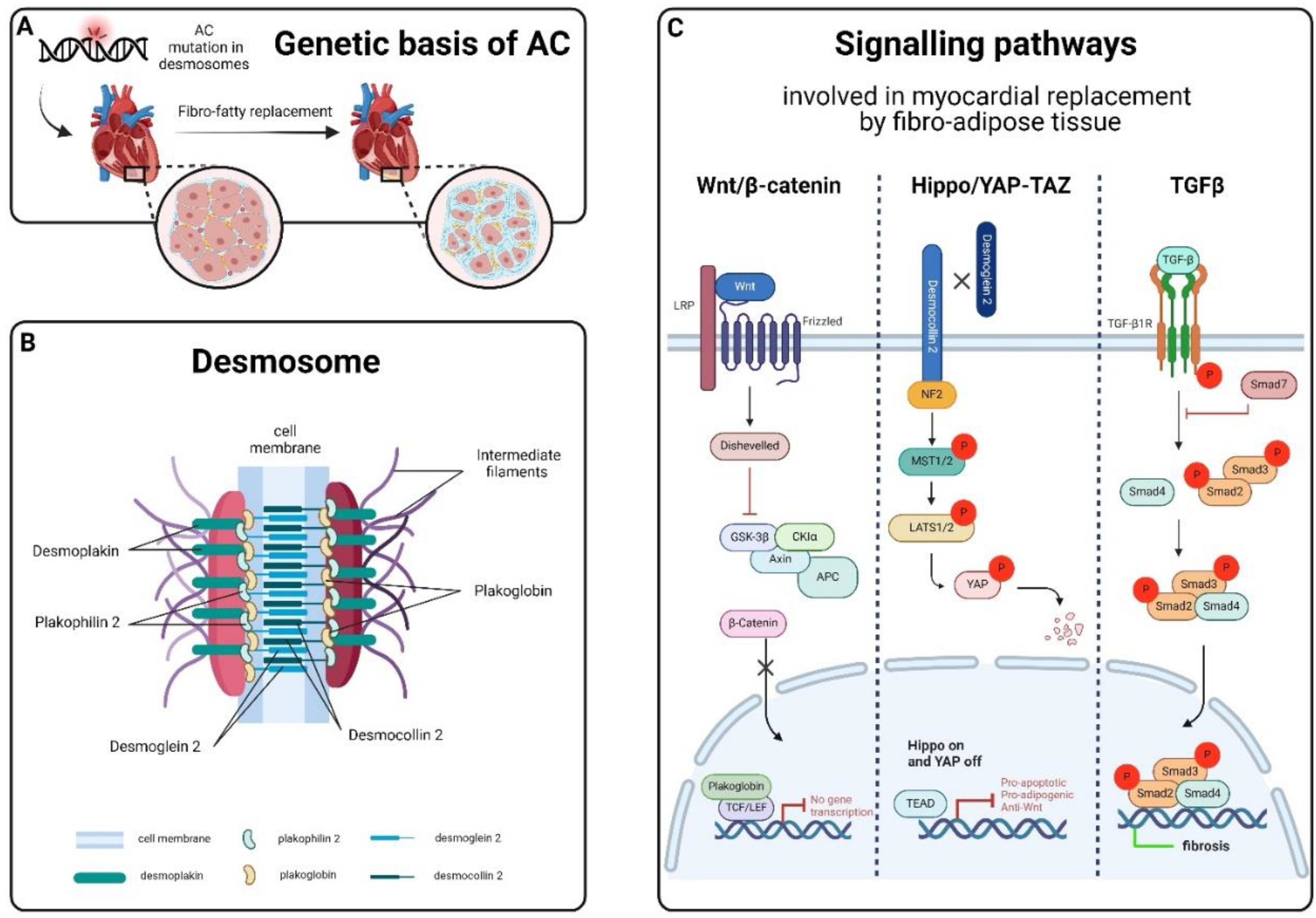
Genetics of AC
Signalling Pathways Related to AC
Search Strategies and Selection Criteria
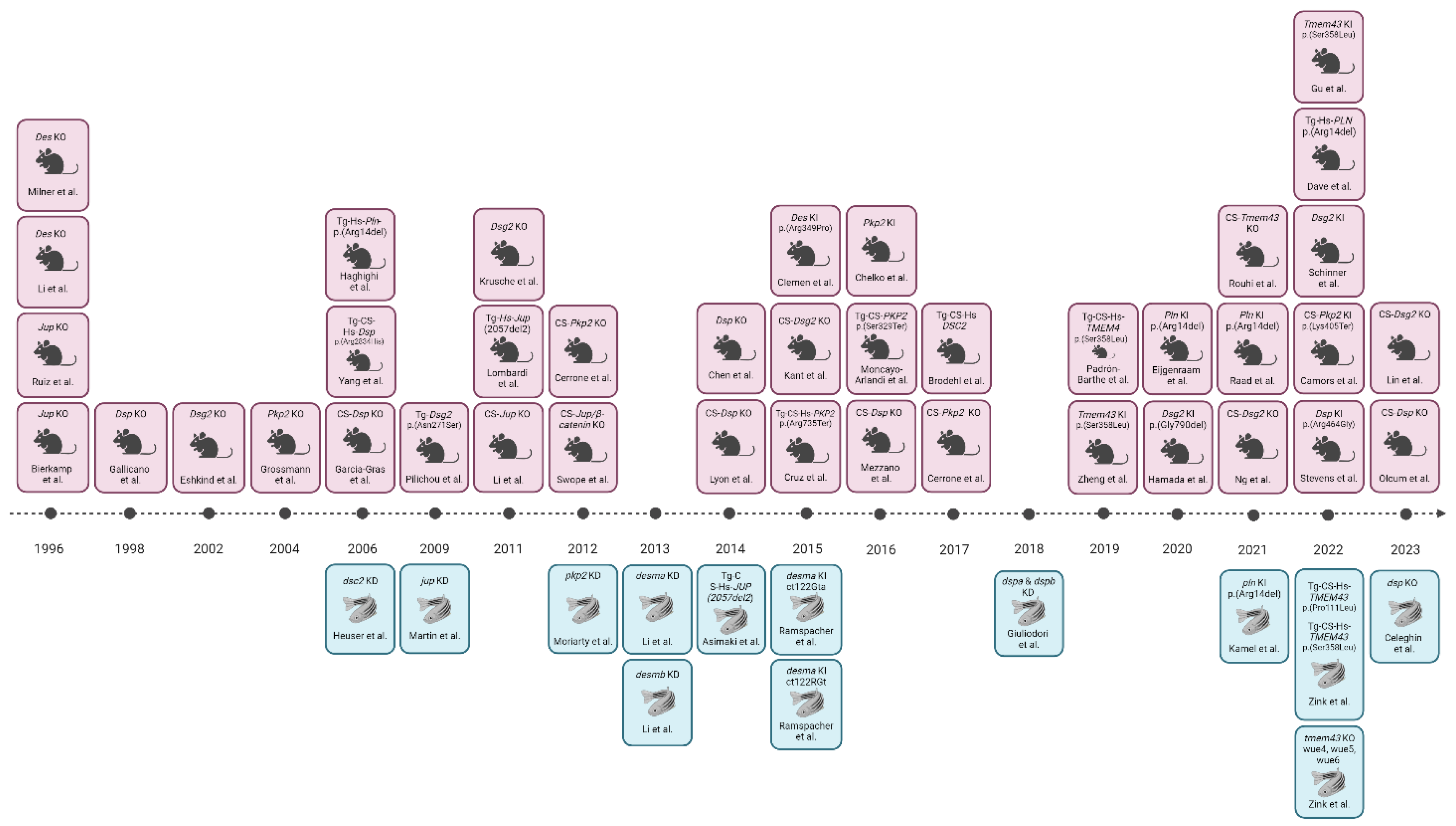
Animal Models for AC
Gene Definitively Associated to AC
Plakoglobin
Desmoplakin
Plakophilin-2
Desmoglein-2
Desmocollin-2
Transmembrane Protein-43
Genes Strongly or Moderately Associated to AC
Phospholamban
Desmin
Non-Desmosomal Genes with Disputed, Limited or no- Curated Evidence of Disease Association
Conclusions and Limitations
Acknowledgments
References
- Thiene, G.; Nava, A.; Corrado, D.; Rossi, L.; Pennelli, N. Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy and Sudden Death in Young People. N Engl J Med 1988, 318, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basso, C.; Thiene, G.; Corrado, D.; Angelini, A.; Nava, A.; Valente, M. Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy. Dysplasia, Dystrophy, or Myocarditis? Circulation 1996, 94, 983–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basso, C.; Corrado, D.; Marcus, F.I.; Nava, A.; Thiene, G. Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy. Lancet 2009, 373, 1289–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basso, C.; Bauce, B.; Corrado, D.; Thiene, G. Pathophysiology of Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathy. Nat Rev Cardiol 2011, 9, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zorzi, A.; Cipriani, A.; Bariani, R.; Pilichou, K.; Corrado, D.; Bauce, B. Role of Exercise as a Modulating Factor in Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathy. Curr Cardiol Rep 2021, 23, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nava, A.; Bauce, B.; Basso, C.; Muriago, M.; Rampazzo, A.; Villanova, C.; Daliento, L.; Buja, G.; Corrado, D.; Danieli, G.A.; et al. Clinical Profile and Long-Term Follow-up of 37 Families with Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy. J Am Coll Cardiol 2000, 36, 2226–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corrado, D.; Thiene, G. Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy/Dysplasia: Clinical Impact of Molecular Genetic Studies. Circulation 2006, 113, 1634–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiene, G.; Corrado, D.; Basso, C. Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy/Dysplasia. Orphanet J Rare Dis 2007, 2, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, C.A.; Bhonsale, A.; Tichnell, C.; Murray, B.; Russell, S.D.; Tandri, H.; Tedford, R.J.; Judge, D.P.; Calkins, H. Exercise Increases Age-Related Penetrance and Arrhythmic Risk in Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Dysplasia/Cardiomyopathy-Associated Desmosomal Mutation Carriers. J Am Coll Cardiol 2013, 62, 1290–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigato, I.; Bauce, B.; Rampazzo, A.; Zorzi, A.; Pilichou, K.; Mazzotti, E.; Migliore, F.; Marra, M.P.; Lorenzon, A.; De Bortoli, M.; et al. Compound and Digenic Heterozygosity Predicts Lifetime Arrhythmic Outcome and Sudden Cardiac Death in Desmosomal Gene-Related Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy. Circ Cardiovasc Genet 2013, 6, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, N.; Tompkins, C.; Polonsky, B.; McNitt, S.; Calkins, H.; Mark Estes, N.A.; Krahn, A.D.; Link, M.S.; Marcus, F.I.; Towbin, J.A.; et al. Clinical Presentation and Outcomes by Sex in Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy: Findings from the North American ARVC Registry. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 2016, 27, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akdis, D.; Saguner, A.M.; Shah, K.; Wei, C.; Medeiros-Domingo, A.; von Eckardstein, A.; Lüscher, T.F.; Brunckhorst, C.; Chen, H.S.V.; Duru, F. Sex Hormones Affect Outcome in Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy/Dysplasia: From a Stem Cell Derived Cardiomyocyte-Based Model to Clinical Biomarkers of Disease Outcome. Eur Heart J 2017, 38, 1498–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcus, F.I.; Fontaine, G.H.; Guiraudon, G.; Frank, R.; Laurenceau, J.L.; Malergue, C.; Grosgogeat, Y. Right Ventricular Dysplasia: A Report of 24 Adult Cases. Circulation 1982, 65, 384–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- North, A.J.; Bardsley, W.G.; Hyam, J.; Bornslaeger, E.A.; Cordingley, H.C.; Trinnaman, B.; Hatzfeld, M.; Green, K.J.; Magee, A.I.; Garrod, D.R. Molecular Map of the Desmosomal Plaque. J Cell Sci 1999, 112 ( Pt 23) Pt 23, 4325–4336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, M.M.; Calkins, H.; Judge, D.P. Mechanisms of Disease: Molecular Genetics of Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Dysplasia/Cardiomyopathy. Nat Clin Pract Cardiovasc Med 2008, 5, 258–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estigoy, C.B.; Pontén, F.; Odeberg, J.; Herbert, B.; Guilhaus, M.; Charleston, M.; Ho, J.W.K.; Cameron, D.; Dos Remedios, C.G. Intercalated Discs: Multiple Proteins Perform Multiple Functions in Non-Failing and Failing Human Hearts. Biophys Rev 2009, 1, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, G.; Qiu, Y.; Zhang, H.M.; Yang, D. Intercalated Discs: Cellular Adhesion and Signaling in Heart Health and Diseases. Heart Fail Rev 2019, 24, 115–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merritt, A.J.; Berika, M.Y.; Zhai, W.; Kirk, S.E.; Ji, B.; Hardman, M.J.; Garrod, D.R. Suprabasal Desmoglein 3 Expression in the Epidermis of Transgenic Mice Results in Hyperproliferation and Abnormal Differentiation. Mol Cell Biol 2002, 22, 5846–5858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilichou, K.; Bezzina, C.R.; Thiene, G.; Basso, C. Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathy: Transgenic Animal Models Provide Novel Insights Into Disease Pathobiology. Circ Cardiovasc Genet 2011, 4, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilichou, K.; Thiene, G.; Bauce, B.; Rigato, I.; Lazzarini, E.; Migliore, F.; Perazzolo Marra, M.; Rizzo, S.; Zorzi, A.; Daliento, L.; et al. Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathy. Orphanet J Rare Dis 2016, 11, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nava, A.; Canciani, B.; Buja, G.; Martini, B.; Daliento, L.; Scognamiglio, R.; Thiene, G. Electrovectorcardiographic Study of Negative T Waves on Precordial Leads in Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Dysplasia: Relationship with Right Ventricular Volumes. J Electrocardiol 1988, 21, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corrado, D.; Basso, C.; Thiene, G.; McKenna, W.J.; Davies, M.J.; Fontaliran, F.; Nava, A.; Silvestri, F.; Blomstrom-Lundqvist, C.; Wlodarska, E.K.; et al. Spectrum of Clinicopathologic Manifestations of Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy/Dysplasia: A Multicenter Study. J Am Coll Cardiol 1997, 30, 1512–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lubos, N.; van der Gaag, S.; Gerçek, M.; Kant, S.; Leube, R.E.; Krusche, C.A. Inflammation Shapes Pathogenesis of Murine Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathy. Basic Res Cardiol 2020, 115, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.-N.; Ibrahim, A.; Marbán, E.; Cingolani, E. Pathogenesis of Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathy: Role of Inflammation. Basic Res Cardiol 2021, 116, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallat, Z.; Tedgui, A.; Fontaliran, F.; Frank, R.; Durigon, M.; Fontaine, G. Evidence of Apoptosis in Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Dysplasia. N Engl J Med 1996, 335, 1190–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valente, M.; Calabrese, F.; Thiene, G.; Angelini, A.; Basso, C.; Nava, A.; Rossi, L. In Vivo Evidence of Apoptosis in Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy. Am J Pathol 1998, 152, 479–484. [Google Scholar]
- Pilichou, K.; Remme, C.A.; Basso, C.; Campian, M.E.; Rizzo, S.; Barnett, P.; Scicluna, B.P.; Bauce, B.; van den Hoff, M.J.B.; de Bakker, J.M.T.; et al. Myocyte Necrosis Underlies Progressive Myocardial Dystrophy in Mouse Dsg2-Related Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy. J Exp Med 2009, 206, 1787–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narula, J.; Haider, N.; Virmani, R.; DiSalvo, T.G.; Kolodgie, F.D.; Hajjar, R.J.; Schmidt, U.; Semigran, M.J.; Dec, G.W.; Khaw, B.A. Apoptosis in Myocytes in End-Stage Heart Failure. N Engl J Med 1996, 335, 1182–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayment, N.B.; Haven, A.J.; Madden, B.; Murday, A.; Trickey, R.; Shipley, M.; Davies, M.J.; Katz, D.R. Myocyte Loss in Chronic Heart Failure. J Pathol 1999, 188, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groeneweg, J.A.; Bhonsale, A.; James, C.A.; te Riele, A.S.; Dooijes, D.; Tichnell, C.; Murray, B.; Wiesfeld, A.C.P.; Sawant, A.C.; Kassamali, B.; et al. Clinical Presentation, Long-Term Follow-Up, and Outcomes of 1001 Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Dysplasia/Cardiomyopathy Patients and Family Members. Circ Cardiovasc Genet 2015, 8, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bueno Marinas, M.; Celeghin, R.; Cason, M.; Bariani, R.; Frigo, A.C.; Jager, J.; Syrris, P.; Elliott, P.M.; Bauce, B.; Thiene, G.; et al. A microRNA Expression Profile as Non-Invasive Biomarker in a Large Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathy Cohort. IJMS 2020, 21, 1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Protonotarios, N.; Tsatsopoulou, A.; Patsourakos, P.; Alexopoulos, D.; Gezerlis, P.; Simitsis, S.; Scampardonis, G. Cardiac Abnormalities in Familial Palmoplantar Keratosis. Br Heart J 1986, 56, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvajal-Huerta, L. Epidermolytic Palmoplantar Keratoderma with Woolly Hair and Dilated Cardiomyopathy. J Am Acad Dermatol 1998, 39, 418–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKoy, G.; Protonotarios, N.; Crosby, A.; Tsatsopoulou, A.; Anastasakis, A.; Coonar, A.; Norman, M.; Baboonian, C.; Jeffery, S.; McKenna, W.J. Identification of a Deletion in Plakoglobin in Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy with Palmoplantar Keratoderma and Woolly Hair (Naxos Disease). Lancet 2000, 355, 2119–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norgett, E.E.; Hatsell, S.J.; Carvajal-Huerta, L.; Cabezas, J.C.; Common, J.; Purkis, P.E.; Whittock, N.; Leigh, I.M.; Stevens, H.P.; Kelsell, D.P. Recessive Mutation in Desmoplakin Disrupts Desmoplakin-Intermediate Filament Interactions and Causes Dilated Cardiomyopathy, Woolly Hair and Keratoderma. Hum Mol Genet 2000, 9, 2761–2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, C.A.; Jongbloed, J.D.H.; Hershberger, R.E.; Morales, A.; Judge, D.P.; Syrris, P.; Pilichou, K.; Domingo, A.M.; Murray, B.; Cadrin-Tourigny, J.; et al. International Evidence Based Reappraisal of Genes Associated With Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy Using the Clinical Genome Resource Framework. Circ Genom Precis Med 2021, 14, e003273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Gras, E.; Lombardi, R.; Giocondo, M.J.; Willerson, J.T.; Schneider, M.D.; Khoury, D.S.; Marian, A.J. Suppression of Canonical Wnt/Beta-Catenin Signaling by Nuclear Plakoglobin Recapitulates Phenotype of Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy. J Clin Invest 2006, 116, 2012–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asimaki, A.; Kapoor, S.; Plovie, E.; Karin Arndt, A.; Adams, E.; Liu, Z.; James, C.A.; Judge, D.P.; Calkins, H.; Churko, J.; et al. Identification of a New Modulator of the Intercalated Disc in a Zebrafish Model of Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathy. Sci Transl Med 2014, 6, 240ra74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giuliodori, A.; Beffagna, G.; Marchetto, G.; Fornetto, C.; Vanzi, F.; Toppo, S.; Facchinello, N.; Santimaria, M.; Vettori, A.; Rizzo, S.; et al. Loss of Cardiac Wnt/β-Catenin Signalling in Desmoplakin-Deficient AC8 Zebrafish Models Is Rescuable by Genetic and Pharmacological Intervention. Cardiovasc Res 2018, 114, 1082–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brade, T.; Männer, J.; Kühl, M. The Role of Wnt Signalling in Cardiac Development and Tissue Remodelling in the Mature Heart. Cardiovasc Res 2006, 72, 198–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fressart, V.; Duthoit, G.; Donal, E.; Probst, V.; Deharo, J.-C.; Chevalier, P.; Klug, D.; Dubourg, O.; Delacretaz, E.; Cosnay, P.; et al. Desmosomal Gene Analysis in Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Dysplasia/Cardiomyopathy: Spectrum of Mutations and Clinical Impact in Practice. Europace 2010, 12, 861–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobaczewski, M.; Chen, W.; Frangogiannis, N.G. Transforming Growth Factor (TGF)-β Signaling in Cardiac Remodeling. J Mol Cell Cardiol 2011, 51, 600–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heallen, T.; Zhang, M.; Wang, J.; Bonilla-Claudio, M.; Klysik, E.; Johnson, R.L.; Martin, J.F. Hippo Pathway Inhibits Wnt Signaling to Restrain Cardiomyocyte Proliferation and Heart Size. Science 2011, 332, 458–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Li, L.; Zhao, B.; Guan, K.-L. The Hippo Pathway in Heart Development, Regeneration, and Diseases. Circ Res 2015, 116, 1431–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenzon, A.; Calore, M.; Poloni, G.; De Windt, L.J.; Braghetta, P.; Rampazzo, A. Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway in Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathy. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 60640–60655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mia, M.M.; Singh, M.K. The Hippo Signaling Pathway in Cardiac Development and Diseases. Front Cell Dev Biol 2019, 7, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calore, M.; Lorenzon, A.; De Bortoli, M.; Poloni, G.; Rampazzo, A. Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathy: A Disease of Intercalated Discs. Cell Tissue Res 2015, 360, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.N.; Gurha, P.; Lombardi, R.; Ruggiero, A.; Willerson, J.T.; Marian, A.J. The Hippo Pathway Is Activated and Is a Causal Mechanism for Adipogenesis in Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathy. Circ Res 2014, 114, 454–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, K.M.; Trembley, M.A.; Chandler, S.F.; Sanders, S.P.; Saffitz, J.E.; Abrams, D.J.; Pu, W.T. Molecular Mechanisms of Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathy. Nat Rev Cardiol 2019, 16, 519–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heldin, C.-H.; Moustakas, A. Signaling Receptors for TGF-β Family Members. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2016, 8, a022053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzavlaki, K.; Moustakas, A. TGF-β Signaling. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maione, A.S.; Stadiotti, I.; Pilato, C.A.; Perrucci, G.L.; Saverio, V.; Catto, V.; Vettor, G.; Casella, M.; Guarino, A.; Polvani, G.; et al. Excess TGF-Β1 Drives Cardiac Mesenchymal Stromal Cells to a Pro-Fibrotic Commitment in Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathy. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22, 2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frangogiannis, N.G. Transforming Growth Factor-β in Myocardial Disease. Nat Rev Cardiol 2022, 19, 435–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcus, F.I.; Nava, A.; Thiene, G. Arrhythmogenic RV Cardiomyopathy - Dysplasia: Recent Advances; Springer-Verlag: Milan, 2007; ISBN 978-88-470-0489-4. [Google Scholar]
- Holdt, S.L.; Peckens, N.K.; Rosenthal, S.; Cober, R. Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy in Bulldogs: Evaluation of Clinical and Histopathologic Features, Progression, and Outcome in 71 Dogs (2004-2016). J Vet Cardiol 2022, 40, 170–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palermo, V.; Stafford Johnson, M.J.; Sala, E.; Brambilla, P.G.; Martin, M.W.S. Cardiomyopathy in Boxer Dogs: A Retrospective Study of the Clinical Presentation, Diagnostic Findings and Survival. Journal of Veterinary Cardiology 2011, 13, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belerenian, G.; Donati, P.A.; Rodríguez, C.D.; Castillo, V.; Guevara, J.M.; Olivares, R.W.I. Left-Dominant Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathy in a Fila Brasileiro Dog. Open Vet J 2022, 12, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertola, L.; Cappelleri, A.; Tomba, R.M.; Dotti, E.; Caniatti, M.; Dall’Ara, P.; Recordati, C. Vaccine-Associated Anaphylactic Shock in a Springer Spaniel Dog with Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy. J Comp Pathol 2022, 194, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möhr, A.J.; Kirberger, R.M. Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy in a Dog. J S Afr Vet Assoc 2000, 71, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eason, B.D.; Leach, S.B.; Kuroki, K. Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy in a Weimaraner. Can Vet J 2015, 56, 1035–1039. [Google Scholar]
- Nakao, S.; Hirakawa, A.; Yamamoto, S.; Kobayashi, M.; Machida, N. Pathological Features of Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy in Middle-Aged Dogs. J Vet Med Sci 2011, 73, 1031–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández del Palacio, M.J.; Bernal, L.J.; Bayón, A.; Bernabé, A.; Montes de Oca, R.; Seva, J. Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Dysplasia/Cardiomyopathy in a Siberian Husky. J Small Anim Pract 2001, 42, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, P.R.; Maron, B.J.; Basso, C.; Liu, S.-K.; Thiene, G. Spontaneously Occurring Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy in the Domestic Cat: A New Animal Model Similar to the Human Disease. Circulation 2000, 102, 1863–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvey, A.M.; Battersby, I.A.; Faena, M.; Fews, D.; Darke, P.G.G.; Ferasin, L. Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy in Two Cats. J Small Anim Pract 2005, 46, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciaramella, P.; Basso, C.; Di Loria, A.; Piantedosi, D. Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy Associated with Severe Left Ventricular Involvement in a Cat. J Vet Cardiol 2009, 11, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahm, R.; Geisler, R. Learning from Small Fry: The Zebrafish as a Genetic Model Organism for Aquaculture Fish Species. Mar Biotechnol (NY) 2006, 8, 329–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howe, K.; Clark, M.D.; Torroja, C.F.; Torrance, J.; Berthelot, C.; Muffato, M.; Collins, J.E.; Humphray, S.; McLaren, K.; Matthews, L.; et al. The Zebrafish Reference Genome Sequence and Its Relationship to the Human Genome. Nature 2013, 496, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genge, C.E.; Lin, E.; Lee, L.; Sheng, X.; Rayani, K.; Gunawan, M.; Stevens, C.M.; Li, A.Y.; Talab, S.S.; Claydon, T.W.; et al. The Zebrafish Heart as a Model of Mammalian Cardiac Function. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol 2016, 171, 99–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vornanen, M.; Hassinen, M. Zebrafish Heart as a Model for Human Cardiac Electrophysiology. Channels (Austin) 2016, 10, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giardoglou, P.; Beis, D. On Zebrafish Disease Models and Matters of the Heart. Biomedicines 2019, 7, E15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowley, G.; Kugler, E.; Wilkinson, R.; Lawrie, A.; van Eeden, F.; Chico, T.J.A.; Evans, P.C.; Noël, E.S.; Serbanovic-Canic, J. Zebrafish as a Tractable Model of Human Cardiovascular Disease. Br J Pharmacol 2022, 179, 900–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poss, K.D.; Wilson, L.G.; Keating, M.T. Heart Regeneration in Zebrafish. Science 2002, 298, 2188–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrod, D.; Chidgey, M. Desmosome Structure, Composition and Function. Biochim Biophys Acta 2008, 1778, 572–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitaev, N.A.; Leube, R.E.; Troyanovsky, R.B.; Eshkind, L.G.; Franke, W.W.; Troyanovsky, S.M. The Binding of Plakoglobin to Desmosomal Cadherins: Patterns of Binding Sites and Topogenic Potential. J Cell Biol 1996, 133, 359–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asimaki, A.; Syrris, P.; Wichter, T.; Matthias, P.; Saffitz, J.E.; McKenna, W.J. A Novel Dominant Mutation in Plakoglobin Causes Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy. Am J Hum Genet 2007, 81, 964–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, M.G.P.J.; van der Zwaag, P.A.; van der Werf, C.; van der Smagt, J.J.; Noorman, M.; Bhuiyan, Z.A.; Wiesfeld, A.C.P.; Volders, P.G.A.; van Langen, I.M.; Atsma, D.E.; et al. Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Dysplasia/Cardiomyopathy: Pathogenic Desmosome Mutations in Index-Patients Predict Outcome of Family Screening: Dutch Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Dysplasia/Cardiomyopathy Genotype-Phenotype Follow-up Study. Circulation 2011, 123, 2690–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celeghin, R.; Pilichou, K. The Complex Molecular Genetics of Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathy. Int J Cardiol 2019, 284, 59–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bierkamp, C.; Mclaughlin, K.J.; Schwarz, H.; Huber, O.; Kemler, R. Embryonic Heart and Skin Defects in Mice Lacking Plakoglobin. Dev Biol 1996, 180, 780–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, P.; Brinkmann, V.; Ledermann, B.; Behrend, M.; Grund, C.; Thalhammer, C.; Vogel, F.; Birchmeier, C.; Günthert, U.; Franke, W.W.; et al. Targeted Mutation of Plakoglobin in Mice Reveals Essential Functions of Desmosomes in the Embryonic Heart. The Journal of cell biology 1996, 135, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchhof, P.; Fabritz, L.; Zwiener, M.; Witt, H.; Schäfers, M.; Zellerhoff, S.; Paul, M.; Athai, T.; Hiller, K.-H.; Baba, H.A.; et al. Age- and Training-Dependent Development of Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy in Heterozygous Plakoglobin-Deficient Mice. Circulation 2006, 114, 1799–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabritz, L.; Hoogendijk, M.G.; Scicluna, B.P.; van Amersfoorth, S.C.M.; Fortmueller, L.; Wolf, S.; Laakmann, S.; Kreienkamp, N.; Piccini, I.; Breithardt, G.; et al. Load-Reducing Therapy Prevents Development of Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy in Plakoglobin-Deficient Mice. J Am Coll Cardiol 2011, 57, 740–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Swope, D.; Raess, N.; Cheng, L.; Muller, E.J.; Radice, G.L. Cardiac Tissue-Restricted Deletion of Plakoglobin Results in Progressive Cardiomyopathy and Activation of {beta}-Catenin Signaling. Mol Cell Biol 2011, 31, 1134–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swope, D.; Cheng, L.; Gao, E.; Li, J.; Radice, G.L. Loss of Cadherin-Binding Proteins β-Catenin and Plakoglobin in the Heart Leads to Gap Junction Remodeling and Arrhythmogenesis. Mol Cell Biol 2012, 32, 1056–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lombardi, R.; da Graca Cabreira-Hansen, M.; Bell, A.; Fromm, R.R.; Willerson, J.T.; Marian, A.J. Nuclear Plakoglobin Is Essential for Differentiation of Cardiac Progenitor Cells to Adipocytes in Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy. Circ Res 2011, 109, 1342–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Stroud, M.J.; Zhang, J.; Fang, X.; Ouyang, K.; Kimura, K.; Mu, Y.; Dalton, N.D.; Gu, Y.; Bradford, W.H.; et al. Normalization of Naxos Plakoglobin Levels Restores Cardiac Function in Mice. J Clin Invest 2015, 125, 1708–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoykhet, M.; Dervishi, O.; Menauer, P.; Hiermaier, M.; Moztarzadeh, S.; Osterloh, C.; Ludwig, R.J.; Williams, T.; Gerull, B.; Kääb, S.; et al. EGFR Inhibition Leads to Enhanced Desmosome Assembly and Cardiomyocyte Cohesion via ROCK Activation. JCI Insight 2023, 8, e163763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, E.D.; Moriarty, M.A.; Byrnes, L.; Grealy, M. Plakoglobin Has Both Structural and Signalling Roles in Zebrafish Development. Dev Biol 2009, 327, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Z.-Y.; Cheng, L.-T.; Wang, Z.-F.; Wu, Y.-Q. Desmoplakin and Clinical Manifestations of Desmoplakin Cardiomyopathy. Chin Med J (Engl) 2021, 134, 1771–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delva, E.; Tucker, D.K.; Kowalczyk, A.P. The Desmosome. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2009, 1, a002543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, S.R.; Gard, J.J.; Carvajal-Huerta, L.; Ruiz-Cabezas, J.C.; Thiene, G.; Saffitz, J.E. Structural and Molecular Pathology of the Heart in Carvajal Syndrome. Cardiovasc Pathol 2004, 13, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, D.K.; McKenna, K.E.; Purkis, P.E.; Green, K.J.; Eady, R.A.; Leigh, I.M.; Hughes, A.E. Haploinsufficiency of Desmoplakin Causes a Striate Subtype of Palmoplantar Keratoderma. Hum Mol Genet 1999, 8, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rampazzo, A.; Nava, A.; Malacrida, S.; Beffagna, G.; Bauce, B.; Rossi, V.; Zimbello, R.; Simionati, B.; Basso, C.; Thiene, G.; et al. Mutation in Human Desmoplakin Domain Binding to Plakoglobin Causes a Dominant Form of Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy. Am J Hum Genet 2002, 71, 1200–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallicano, G.I.; Kouklis, P.; Bauer, C.; Yin, M.; Vasioukhin, V.; Degenstein, L.; Fuchs, E. Desmoplakin Is Required Early in Development for Assembly of Desmosomes and Cytoskeletal Linkage. J Cell Biol 1998, 143, 2009–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheedipudi, S.M.; Hu, J.; Fan, S.; Yuan, P.; Karmouch, J.; Czernuszewicz, G.; Robertson, M.J.; Coarfa, C.; Hong, K.; Yao, Y.; et al. Exercise Restores Dysregulated Gene Expression in a Mouse Model of Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathy. Cardiovasc Res 2020, 116, 1199–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olcum, M.; Fan, S.; Rouhi, L.; Cheedipudi, S.; Cathcart, B.; Jeong, H.-H.; Zhao, Z.; Gurha, P.; Marian, A.J. Genetic Inactivation of β-Catenin Is Salubrious, Whereas Its Activation Is Deleterious in Desmoplakin Cardiomyopathy. Cardiovasc Res 2023, 119, 2712–2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mezzano, V.; Liang, Y.; Wright, A.T.; Lyon, R.C.; Pfeiffer, E.; Song, M.Y.; Gu, Y.; Dalton, N.D.; Scheinman, M.; Peterson, K.L.; et al. Desmosomal Junctions Are Necessary for Adult Sinus Node Function. Cardiovasc Res 2016, 111, 274–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Protonotarios, N.; Tsatsopoulou, A. Naxos Disease and Carvajal Syndrome: Cardiocutaneous Disorders That Highlight the Pathogenesis and Broaden the Spectrum of Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy. Cardiovasc Pathol 2004, 13, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbert Pratt, C.; Potter, C.S.; Fairfield, H.; Reinholdt, L.G.; Bergstrom, D.E.; Harris, B.S.; Greenstein, I.; Dadras, S.S.; Liang, B.T.; Schofield, P.N.; et al. Dsp Rul: A Spontaneous Mouse Mutation in Desmoplakin as a Model of Carvajal-Huerta Syndrome. Exp Mol Pathol 2015, 98, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malireddi, R.K.S.; Kesavardhana, S.; Kanneganti, T.-D. ZBP1 and TAK1: Master Regulators of NLRP3 Inflammasome/Pyroptosis, Apoptosis, and Necroptosis (PAN-Optosis). Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2019, 9, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, C.; Cao, P.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Gong, Z. PANoptosis: A Cell Death Characterized by Pyroptosis, Apoptosis, and Necroptosis. J Inflamm Res 2023, 16, 1523–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olcum, M.; Rouhi, L.; Fan, S.; Gonzales, M.M.; Jeong, H.-H.; Zhao, Z.; Gurha, P.; Marian, A.J. PANoptosis Is a Prominent Feature of Desmoplakin Cardiomyopathy. J Cardiovasc Aging 2023, 3, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, J.; Finlay, M.; Ahmed, A.K.; Ciaccio, E.J.; Asimaki, A.; Saffitz, J.E.; Quarta, G.; Nobles, M.; Syrris, P.; Chaubey, S.; et al. Electrophysiological Abnormalities Precede Overt Structural Changes in Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy Due to Mutations in Desmoplakin-A Combined Murine and Human Study. Eur Heart J 2012, 33, 1942–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyon, R.C.; Mezzano, V.; Wright, A.T.; Pfeiffer, E.; Chuang, J.; Banares, K.; Castaneda, A.; Ouyang, K.; Cui, L.; Contu, R.; et al. Connexin Defects Underlie Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy in a Novel Mouse Model. Hum Mol Genet 2014, 23, 1134–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Bowles, N.E.; Scherer, S.E.; Taylor, M.D.; Kearney, D.L.; Ge, S.; Nadvoretskiy, V.V.; DeFreitas, G.; Carabello, B.; Brandon, L.I.; et al. Desmosomal Dysfunction Due to Mutations in Desmoplakin Causes Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Dysplasia/Cardiomyopathy. Circ Res 2006, 99, 646–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martherus, R.; Jain, R.; Takagi, K.; Mendsaikhan, U.; Turdi, S.; Osinska, H.; James, J.F.; Kramer, K.; Purevjav, E.; Towbin, J.A. Accelerated Cardiac Remodeling in Desmoplakin Transgenic Mice in Response to Endurance Exercise Is Associated with Perturbed Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 2016, 310, H174–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, T.L.; Manring, H.R.; Wallace, M.J.; Argall, A.; Dew, T.; Papaioannou, P.; Antwi-Boasiako, S.; Xu, X.; Campbell, S.G.; Akar, F.G.; et al. Humanized Dsp ACM Mouse Model Displays Stress-Induced Cardiac Electrical and Structural Phenotypes. Cells 2022, 11, 3049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celeghin, R.; Risato, G.; Beffagna, G.; Cason, M.; Bueno Marinas, M.; Della Barbera, M.; Facchinello, N.; Giuliodori, A.; Brañas Casas, R.; Caichiolo, M.; et al. A Novel DSP Zebrafish Model Reveals Training- and Drug-Induced Modulation of Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathy Phenotypes. Cell Death Discov 2023, 9, 441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hatzfeld, M. Plakophilins: Multifunctional Proteins or Just Regulators of Desmosomal Adhesion? Biochim Biophys Acta 2007, 1773, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Bonne, S.; Hatzfeld, M.; van Roy, F.; Green, K.J. Protein Binding and Functional Characterization of Plakophilin 2. Evidence for Its Diverse Roles in Desmosomes and Beta -Catenin Signaling. J Biol Chem 2002, 277, 10512–10522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mertens, C.; Kuhn, C.; Franke, W.W. Plakophilins 2a and 2b: Constitutive Proteins of Dual Location in the Karyoplasm and the Desmosomal Plaque. J Cell Biol 1996, 135, 1009–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandjbakhch, E.; Charron, P.; Fressart, V.; Lorin de la Grandmaison, G.; Simon, F.; Gary, F.; Vite, A.; Hainque, B.; Hidden-Lucet, F.; Komajda, M.; et al. Plakophilin 2A Is the Dominant Isoform in Human Heart Tissue: Consequences for the Genetic Screening of Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy. Heart 2011, 97, 844–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossmann, K.S.; Grund, C.; Huelsken, J.; Behrend, M.; Erdmann, B.; Franke, W.W.; Birchmeier, W. Requirement of Plakophilin 2 for Heart Morphogenesis and Cardiac Junction Formation. J Cell Biol 2004, 167, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerrone, M.; Noorman, M.; Lin, X.; Chkourko, H.; Liang, F.-X.; van der Nagel, R.; Hund, T.; Birchmeier, W.; Mohler, P.; van Veen, T.A.; et al. Sodium Current Deficit and Arrhythmogenesis in a Murine Model of Plakophilin-2 Haploinsufficiency. Cardiovasc Res 2012, 95, 460–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leo-Macías, A.; Liang, F.-X.; Delmar, M. Ultrastructure of the Intercellular Space in Adult Murine Ventricle Revealed by Quantitative Tomographic Electron Microscopy. Cardiovasc Res 2015, 107, 442–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camors, E.M.; Roth, A.H.; Alef, J.R.; Sullivan, R.D.; Johnson, J.N.; Purevjav, E.; Towbin, J.A. Progressive Reduction in Right Ventricular Contractile Function Attributable to Altered Actin Expression in an Aging Mouse Model of Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathy. Circulation 2022, 145, 1609–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerrone, M.; Montnach, J.; Lin, X.; Zhao, Y.-T.; Zhang, M.; Agullo-Pascual, E.; Leo-Macias, A.; Alvarado, F.J.; Dolgalev, I.; Karathanos, T.V.; et al. Plakophilin-2 Is Required for Transcription of Genes That Control Calcium Cycling and Cardiac Rhythm. Nat Commun 2017, 8, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Opbergen, C.J.M.; Bagwan, N.; Maurya, S.R.; Kim, J.-C.; Smith, A.N.; Blackwell, D.J.; Johnston, J.N.; Knollmann, B.C.; Cerrone, M.; Lundby, A.; et al. Exercise Causes Arrhythmogenic Remodeling of Intracellular Calcium Dynamics in Plakophilin-2-Deficient Hearts. Circulation 2022, 145, 1480–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz, F.M.; Sanz-Rosa, D.; Roche-Molina, M.; García-Prieto, J.; García-Ruiz, J.M.; Pizarro, G.; Jiménez-Borreguero, L.J.; Torres, M.; Bernad, A.; Ruíz-Cabello, J.; et al. Exercise Triggers ARVC Phenotype in Mice Expressing a Disease-Causing Mutated Version of Human Plakophilin-2. J Am Coll Cardiol 2015, 65, 1438–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moncayo-Arlandi, J.; Guasch, E.; Sanz-de la Garza, M.; Casado, M.; Garcia, N.A.; Mont, L.; Sitges, M.; Knöll, R.; Buyandelger, B.; Campuzano, O.; et al. Molecular Disturbance Underlies to Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathy Induced by Transgene Content, Age and Exercise in a Truncated PKP2 Mouse Model. Hum Mol Genet 2016, 25, 3676–3688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriarty, M.A.; Ryan, R.; Lalor, P.; Dockery, P.; Byrnes, L.; Grealy, M. Loss of Plakophilin 2 Disrupts Heart Development in Zebrafish. Int J Dev Biol 2012, 56, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, K.J.; Simpson, C.L. Desmosomes: New Perspectives on a Classic. J Invest Dermatol 2007, 127, 2499–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, S.; Koch, P.J.; Franke, W.W. Identification of the Ubiquitous Human Desmoglein, Dsg2, and the Expression Catalogue of the Desmoglein Subfamily of Desmosomal Cadherins. Exp Cell Res 1994, 211, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuber, U.A.; Schäfer, S.; Schmidt, A.; Koch, P.J.; Franke, W.W. The Widespread Human Desmocollin Dsc2 and Tissue-Specific Patterns of Synthesis of Various Desmocollin Subtypes. Eur J Cell Biol 1995, 66, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pilichou, K.; Nava, A.; Basso, C.; Beffagna, G.; Bauce, B.; Lorenzon, A.; Frigo, G.; Vettori, A.; Valente, M.; Towbin, J.; et al. Mutations in Desmoglein-2 Gene Are Associated with Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy. Circulation 2006, 113, 1171–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eshkind, L.; Tian, Q.; Schmidt, A.; Franke, W.W.; Windoffer, R.; Leube, R.E. Loss of Desmoglein 2 Suggests Essential Functions for Early Embryonic Development and Proliferation of Embryonal Stem Cells. Eur J Cell Biol 2002, 81, 592–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krusche, C.A.; Holthöfer, B.; Hofe, V.; van de Sandt, A.M.; Eshkind, L.; Bockamp, E.; Merx, M.W.; Kant, S.; Windoffer, R.; Leube, R.E. Desmoglein 2 Mutant Mice Develop Cardiac Fibrosis and Dilation. Basic Res Cardiol 2011, 106, 617–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kant, S.; Krull, P.; Eisner, S.; Leube, R.E.; Krusche, C.A. Histological and Ultrastructural Abnormalities in Murine Desmoglein 2-Mutant Hearts. Cell Tissue Res 2012, 348, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerçek, M.; Gerçek, M.; Kant, S.; Simsekyilmaz, S.; Kassner, A.; Milting, H.; Liehn, E.A.; Leube, R.E.; Krusche, C.A. Cardiomyocyte Hypertrophy in Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathy. Am J Pathol 2017, 187, 752–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buck, V.U.; Hodecker, M.; Eisner, S.; Leube, R.E.; Krusche, C.A.; Classen-Linke, I. Ultrastructural Changes in Endometrial Desmosomes of Desmoglein 2 Mutant Mice. Cell Tissue Res 2018, 374, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelko, S.P.; Asimaki, A.; Andersen, P.; Bedja, D.; Amat-Alarcon, N.; DeMazumder, D.; Jasti, R.; MacRae, C.A.; Leber, R.; Kleber, A.G.; et al. Central Role for GSK3β in the Pathogenesis of Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathy. JCI Insight 2016, 1, 85923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelko, S.P.; Asimaki, A.; Lowenthal, J.; Bueno-Beti, C.; Bedja, D.; Scalco, A.; Amat-Alarcon, N.; Andersen, P.; Judge, D.P.; Tung, L.; et al. Therapeutic Modulation of the Immune Response in Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathy. Circulation 2019, 140, 1491–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chelko, S.P.; Keceli, G.; Carpi, A.; Doti, N.; Agrimi, J.; Asimaki, A.; Beti, C.B.; Miyamoto, M.; Amat-Codina, N.; Bedja, D.; et al. Exercise Triggers CAPN1-Mediated AIF Truncation, Inducing Myocyte Cell Death in Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathy. Sci Transl Med 2021, 13, eabf0891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrimi, J.; Scalco, A.; Agafonova, J.; Williams Iii, L.; Pansari, N.; Keceli, G.; Jun, S.; Wang, N.; Mastorci, F.; Tichnell, C.; et al. Psychosocial Stress Hastens Disease Progression and Sudden Death in Mice with Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathy. J Clin Med 2020, 9, 3804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamstra, S.I.; Braun, J.L.; Chelko, S.P.; Fajardo, V.A. GSK3-Inhibition Improves Maximal SERCA Activity in a Murine Model of Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathy. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis 2022, 1868, 166536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kant, S.; Holthöfer, B.; Magin, T.M.; Krusche, C.A.; Leube, R.E. Desmoglein 2-Dependent Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathy Is Caused by a Loss of Adhesive Function. Circ Cardiovasc Genet 2015, 8, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, K.E.; Delaney, P.J.; Thenet, D.; Murtough, S.; Webb, C.M.; Zaman, N.; Tsisanova, E.; Mastroianni, G.; Walker, S.L.M.; Westaby, J.D.; et al. Early Inflammation Precedes Cardiac Fibrosis and Heart Failure in Desmoglein 2 Murine Model of Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathy. Cell Tissue Res 2021, 386, 79–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Liu, R.; Huang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Xian, J.; Huang, J.; Qiu, Z.; Lin, X.; Zhang, M.; Chen, H.; et al. Reactivation of PPARα Alleviates Myocardial Lipid Accumulation and Cardiac Dysfunction by Improving Fatty Acid β-Oxidation in Dsg2-Deficient Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathy. Acta Pharm Sin B 2023, 13, 192–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzo, S.; Lodder, E.M.; Verkerk, A.O.; Wolswinkel, R.; Beekman, L.; Pilichou, K.; Basso, C.; Remme, C.A.; Thiene, G.; Bezzina, C.R. Intercalated Disc Abnormalities, Reduced Na(+) Current Density, and Conduction Slowing in Desmoglein-2 Mutant Mice Prior to Cardiomyopathic Changes. Cardiovasc Res 2012, 95, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schinner, C.; Xu, L.; Franz, H.; Zimmermann, A.; Wanuske, M.-T.; Rathod, M.; Hanns, P.; Geier, F.; Pelczar, P.; Liang, Y.; et al. Defective Desmosomal Adhesion Causes Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathy by Involving an Integrin-αVβ6/TGF-β Signaling Cascade. Circulation 2022, 146, 1610–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syrris, P.; Ward, D.; Evans, A.; Asimaki, A.; Gandjbakhch, E.; Sen-Chowdhry, S.; McKenna, W.J. Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Dysplasia/Cardiomyopathy Associated with Mutations in the Desmosomal Gene Desmocollin-2. Am J Hum Genet 2006, 79, 978–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heuser, A.; Plovie, E.R.; Ellinor, P.T.; Grossmann, K.S.; Shin, J.T.; Wichter, T.; Basson, C.T.; Lerman, B.B.; Sasse-Klaassen, S.; Thierfelder, L.; et al. Mutant Desmocollin-2 Causes Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy. Am J Hum Genet 2006, 79, 1081–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamada, Y.; Yamamoto, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Sufu-Shimizu, Y.; Nanno, T.; Fukuda, M.; Ono, M.; Oda, T.; Okuda, S.; Ueyama, T.; et al. G790del Mutation in DSC2 Alone Is Insufficient to Develop the Pathogenesis of ARVC in a Mouse Model. Biochemistry and Biophysics Reports 2020, 21, 100711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brodehl, A.; Belke, D.D.; Garnett, L.; Martens, K.; Abdelfatah, N.; Rodriguez, M.; Diao, C.; Chen, Y.-X.; Gordon, P.M.K.; Nygren, A.; et al. Transgenic Mice Overexpressing Desmocollin-2 (DSC2) Develop Cardiomyopathy Associated with Myocardial Inflammation and Fibrotic Remodeling. PLoS One 2017, 12, e0174019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bengtsson, L.; Otto, H. LUMA Interacts with Emerin and Influences Its Distribution at the Inner Nuclear Membrane. Journal of Cell Science 2008, 121, 536–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franke, W.W.; Dörflinger, Y.; Kuhn, C.; Zimbelmann, R.; Winter-Simanowski, S.; Frey, N.; Heid, H. Protein LUMA Is a Cytoplasmic Plaque Constituent of Various Epithelial Adherens Junctions and Composite Junctions of Myocardial Intercalated Disks: A Unifying Finding for Cell Biology and Cardiology. Cell Tissue Res 2014, 357, 159–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zink, M.; Seewald, A.; Rohrbach, M.; Brodehl, A.; Liedtke, D.; Williams, T.; Childs, S.J.; Gerull, B. Altered Expression of TMEM43 Causes Abnormal Cardiac Structure and Function in Zebrafish. IJMS 2022, 23, 9530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merner, N.D.; Hodgkinson, K.A.; Haywood, A.F.M.; Connors, S.; French, V.M.; Drenckhahn, J.-D.; Kupprion, C.; Ramadanova, K.; Thierfelder, L.; McKenna, W.; et al. Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy Type 5 Is a Fully Penetrant, Lethal Arrhythmic Disorder Caused by a Missense Mutation in the TMEM43 Gene. Am J Hum Genet 2008, 82, 809–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haywood, A.F.M.; Merner, N.D.; Hodgkinson, K.A.; Houston, J.; Syrris, P.; Booth, V.; Connors, S.; Pantazis, A.; Quarta, G.; Elliott, P.; et al. Recurrent Missense Mutations in TMEM43 (ARVD5) Due to Founder Effects Cause Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathies in the UK and Canada. Eur Heart J 2013, 34, 1002–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milting, H.; Klauke, B.; Christensen, A.H.; Müsebeck, J.; Walhorn, V.; Grannemann, S.; Münnich, T.; Šarić, T.; Rasmussen, T.B.; Jensen, H.K.; et al. The TMEM43 Newfoundland Mutation p.S358L Causing ARVC-5 Was Imported from Europe and Increases the Stiffness of the Cell Nucleus. Eur Heart J 2015, 36, 872–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez, F.; Zorio, E.; Jimenez-Jaimez, J.; Salguero-Bodes, R.; Zwart, R.; Gonzalez-Lopez, E.; Molina, P.; Bermúdez-Jiménez, F.; Delgado, J.F.; Braza-Boïls, A.; et al. Clinical Characteristics and Determinants of the Phenotype in TMEM43 Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy Type 5. Heart Rhythm 2020, 17, 945–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouhi, L.; Cheedipudi, S.M.; Chen, S.N.; Fan, S.; Lombardi, R.; Chen, X.; Coarfa, C.; Robertson, M.J.; Gurha, P.; Marian, A.J. Haploinsufficiency of Tmem43 in Cardiac Myocytes Activates the DNA Damage Response Pathway Leading to a Late-Onset Senescence-Associated pro-Fibrotic Cardiomyopathy. Cardiovasc Res 2021, 117, 2377–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.; Jiang, C.; Li, Y.; Yang, D.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, B.; Li, X.; Zhang, P.; Hu, X.; Zhao, X.; et al. TMEM43-S358L Mutation Enhances NF-κB-TGFβ Signal Cascade in Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Dysplasia/Cardiomyopathy. Protein Cell 2019, 10, 104–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Q.; Xu, F.; Orgil, B.-O.; Khuchua, Z.; Munkhsaikhan, U.; Johnson, J.N.; Alberson, N.R.; Pierre, J.F.; Black, D.D.; Dong, D.; et al. Systems Genetics Analysis Defines Importance of TMEM43/LUMA for Cardiac- and Metabolic-Related Pathways. Physiol Genomics 2022, 54, 22–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orgil, B.-O.; Munkhsaikhan, U.; Pierre, J.F.; Li, N.; Xu, F.; Alberson, N.R.; Johnson, J.N.; Wetzel, G.T.; Boukens, B.J.D.; Lu, L.; et al. The TMEM43 S358L Mutation Affects Cardiac, Small Intestine, and Metabolic Homeostasis in a Knock-in Mouse Model. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 2023, 324, H866–H880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padrón-Barthe, L.; Villalba-Orero, M.; Gómez-Salinero, J.M.; Domínguez, F.; Román, M.; Larrasa-Alonso, J.; Ortiz-Sánchez, P.; Martínez, F.; López-Olañeta, M.; Bonzón-Kulichenko, E.; et al. Severe Cardiac Dysfunction and Death Caused by Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy Type 5 Are Improved by Inhibition of Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3β. Circulation 2019, 140, 1188–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez, F.; Lalaguna, L.; López-Olañeta, M.; Villalba-Orero, M.; Padrón-Barthe, L.; Román, M.; Bello-Arroyo, E.; Briceño, A.; Gonzalez-Lopez, E.; Segovia-Cubero, J.; et al. Early Preventive Treatment With Enalapril Improves Cardiac Function and Delays Mortality in Mice With Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy Type 5. Circ Heart Fail 2021, 14, e007616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLennan, D.H.; Kranias, E.G. Phospholamban: A Crucial Regulator of Cardiac Contractility. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2003, 4, 566–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eijgenraam, T.R.; Boukens, B.J.; Boogerd, C.J.; Schouten, E.M.; van de Kolk, C.W.A.; Stege, N.M.; Te Rijdt, W.P.; Hoorntje, E.T.; van der Zwaag, P.A.; van Rooij, E.; et al. The Phospholamban p.(Arg14del) Pathogenic Variant Leads to Cardiomyopathy with Heart Failure and Is Unreponsive to Standard Heart Failure Therapy. Sci Rep 2020, 10, 9819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haghighi, K.; Pritchard, T.; Bossuyt, J.; Waggoner, J.R.; Yuan, Q.; Fan, G.-C.; Osinska, H.; Anjak, A.; Rubinstein, J.; Robbins, J.; et al. The Human Phospholamban Arg14-Deletion Mutant Localizes to Plasma Membrane and Interacts with the Na/K-ATPase. J Mol Cell Cardiol 2012, 52, 773–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeWitt, M.M.; MacLeod, H.M.; Soliven, B.; McNally, E.M. Phospholamban R14 Deletion Results in Late-Onset, Mild, Hereditary Dilated Cardiomyopathy. Journal of the American College of Cardiology 2006, 48, 1396–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haghighi, K.; Kolokathis, F.; Gramolini, A.O.; Waggoner, J.R.; Pater, L.; Lynch, R.A.; Fan, G.-C.; Tsiapras, D.; Parekh, R.R.; Dorn, G.W.; et al. A Mutation in the Human Phospholamban Gene, Deleting Arginine 14, Results in Lethal, Hereditary Cardiomyopathy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2006, 103, 1388–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posch, M.G.; Perrot, A.; Geier, C.; Boldt, L.-H.; Schmidt, G.; Lehmkuhl, H.B.; Hetzer, R.; Dietz, R.; Gutberlet, M.; Haverkamp, W.; et al. Genetic Deletion of Arginine 14 in Phospholamban Causes Dilated Cardiomyopathy with Attenuated Electrocardiographic R Amplitudes. Heart Rhythm 2009, 6, 480–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Zwaag, P.A.; van Rijsingen, I.A.W.; Asimaki, A.; Jongbloed, J.D.H.; van Veldhuisen, D.J.; Wiesfeld, A.C.P.; Cox, M.G.P.J.; van Lochem, L.T.; de Boer, R.A.; Hofstra, R.M.W.; et al. Phospholamban R14del Mutation in Patients Diagnosed with Dilated Cardiomyopathy or Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy: Evidence Supporting the Concept of Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathy. Eur J Heart Fail 2012, 14, 1199–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Ayala, J.M.; Boven, L.; Van Den Wijngaard, A.; Peñafiel-Verdú, P.; Van Tintelen, J.P.; Gimeno, J.R. Phospholamban p.Arg14del Mutation in a Spanish Family With Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathy: Evidence for a European Founder Mutation. Revista Española de Cardiología (English Edition) 2015, 68, 346–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Song, J.; Chen, X.; Chen, K.; Ren, J.; Zhang, N.; Rao, M.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Gu, M.; et al. A Novel Genotype-Based Clinicopathology Classification of Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathy Provides Novel Insights into Disease Progression. European Heart Journal 2019, 40, 1690–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, C.C.; Healey, J.S.; Hamilton, R.; Spears, D.; Gollob, M.H.; Mellor, G.; Steinberg, C.; Sanatani, S.; Laksman, Z.W.; Krahn, A.D. Phospholamban Cardiomyopathy: A Canadian Perspective on a Unique Population. Neth Heart J 2019, 27, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raad, N.; Bittihn, P.; Cacheux, M.; Jeong, D.; Ilkan, Z.; Ceholski, D.; Kohlbrenner, E.; Zhang, L.; Cai, C.-L.; Kranias, E.G.; et al. Arrhythmia Mechanism and Dynamics in a Humanized Mouse Model of Inherited Cardiomyopathy Caused by Phospholamban R14del Mutation. Circulation 2021, 144, 441–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogalska, M.E.; Vafiadaki, E.; Erpapazoglou, Z.; Haghighi, K.; Green, L.; Mantzoros, C.S.; Hajjar, R.J.; Tranter, M.; Karakikes, I.; Kranias, E.G.; et al. Isoform Changes of Action Potential Regulators in the Ventricles of Arrhythmogenic Phospholamban-R14del Humanized Mouse Hearts. Metabolism 2023, 138, 155344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maniezzi, C.; Eskandr, M.; Florindi, C.; Ferrandi, M.; Barassi, P.; Sacco, E.; Pasquale, V.; Maione, A.S.; Pompilio, G.; Teixeira, V.O.N.; et al. Early Consequences of the Phospholamban Mutation PLN-R14del+/- in a Transgenic Mouse Model. Acta Physiol (Oxf) 2024, e14082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dave, J.; Raad, N.; Mittal, N.; Zhang, L.; Fargnoli, A.; Oh, J.G.; Savoia, M.E.; Hansen, J.; Fava, M.; Yin, X.; et al. Gene Editing Reverses Arrhythmia Susceptibility in Humanized PLN-R14del Mice: Modelling a European Cardiomyopathy with Global Impact. Cardiovasc Res 2022, 118, 3140–3150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamel, S.M.; van Opbergen, C.J.M.; Koopman, C.D.; Verkerk, A.O.; Boukens, B.J.D.; de Jonge, B.; Onderwater, Y.L.; van Alebeek, E.; Chocron, S.; Polidoro Pontalti, C.; et al. Istaroxime Treatment Ameliorates Calcium Dysregulation in a Zebrafish Model of Phospholamban R14del Cardiomyopathy. Nat Commun 2021, 12, 7151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarantitis, I.; Papanastasopoulos, P.; Manousi, M.; Baikoussis, N.G.; Apostolakis, E. The Cytoskeleton of the Cardiac Muscle Cell. Hellenic J Cardiol 2012, 53, 367–379. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Brodehl, A.; Hedde, P.N.; Dieding, M.; Fatima, A.; Walhorn, V.; Gayda, S.; Šarić, T.; Klauke, B.; Gummert, J.; Anselmetti, D.; et al. Dual Color Photoactivation Localization Microscopy of Cardiomyopathy-Associated Desmin Mutants. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2012, 287, 16047–16057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brodehl, A.; Gaertner-Rommel, A.; Milting, H. Molecular Insights into Cardiomyopathies Associated with Desmin (DES) Mutations. Biophys Rev 2018, 10, 983–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otten, E.; Asimaki, A.; Maass, A.; Van Langen, I.M.; Van Der Wal, A.; De Jonge, N.; Van Den Berg, M.P.; Saffitz, J.E.; Wilde, A.A.M.; Jongbloed, J.D.H.; et al. Desmin Mutations as a Cause of Right Ventricular Heart Failure Affect the Intercalated Disks. Heart Rhythm 2010, 7, 1058–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Colucci-Guyon, E.; Pinçon-Raymond, M.; Mericskay, M.; Pournin, S.; Paulin, D.; Babinet, C. Cardiovascular Lesions and Skeletal Myopathy in Mice Lacking Desmin. Developmental Biology 1996, 175, 362–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemen, C.S.; Stöckigt, F.; Strucksberg, K.-H.; Chevessier, F.; Winter, L.; Schütz, J.; Bauer, R.; Thorweihe, J.-M.; Wenzel, D.; Schlötzer-Schrehardt, U.; et al. The Toxic Effect of R350P Mutant Desmin in Striated Muscle of Man and Mouse. Acta Neuropathol 2015, 129, 297–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winter, L.; Wittig, I.; Peeva, V.; Eggers, B.; Heidler, J.; Chevessier, F.; Kley, R.A.; Barkovits, K.; Strecker, V.; Berwanger, C.; et al. Mutant Desmin Substantially Perturbs Mitochondrial Morphology, Function and Maintenance in Skeletal Muscle Tissue. Acta Neuropathol 2016, 132, 453–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stöckigt, F.; Eichhorn, L.; Beiert, T.; Knappe, V.; Radecke, T.; Steinmetz, M.; Nickenig, G.; Peeva, V.; Kudin, A.P.; Kunz, W.S.; et al. Heart Failure after Pressure Overload in Autosomal-Dominant Desminopathies: Lessons from Heterozygous DES-p.R349P Knock-in Mice. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0228913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milner, D.J.; Weitzer, G.; Tran, D.; Bradley, A.; Capetanaki, Y. Disruption of Muscle Architecture and Myocardial Degeneration in Mice Lacking Desmin. The Journal of cell biology 1996, 134, 1255–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavroidis, M.; Davos, C.H.; Psarras, S.; Varela, A.; C Athanasiadis, N.; Katsimpoulas, M.; Kostavasili, I.; Maasch, C.; Vater, A.; van Tintelen, J.P.; et al. Complement System Modulation as a Target for Treatment of Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathy. Basic Res Cardiol 2015, 110, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavroidis, M.; Athanasiadis, N.C.; Rigas, P.; Kostavasili, I.; Kloukina, I.; Te Rijdt, W.P.; Kavantzas, N.; Chaniotis, D.; van Tintelen, J.P.; Skaliora, I.; et al. Desmin Is Essential for the Structure and Function of the Sinoatrial Node: Implications for Increased Arrhythmogenesis. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 2020, 319, H557–H570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Tsilafakis, K.; Chen, L.; Lekkos, K.; Kostavasili, I.; Varela, A.; Cokkinos, D.V.; Davos, C.H.; Sun, X.; Song, J.; et al. Crosstalk between Coagulation and Complement Activation Promotes Cardiac Dysfunction in Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy. Theranostics 2021, 11, 5939–5954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Andersson-Lendahl, M.; Sejersen, T.; Arner, A. Knockdown of Desmin in Zebrafish Larvae Affects Interfilament Spacing and Mechanical Properties of Skeletal Muscle. J Gen Physiol 2013, 141, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramspacher, C.; Steed, E.; Boselli, F.; Ferreira, R.; Faggianelli, N.; Roth, S.; Spiegelhalter, C.; Messaddeq, N.; Trinh, L.; Liebling, M.; et al. Developmental Alterations in Heart Biomechanics and Skeletal Muscle Function in Desmin Mutants Suggest an Early Pathological Root for Desminopathies. Cell Rep 2015, 11, 1564–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Hu, J.; Dai, X.; Cao, Q.; Xiong, Q.; Liu, X.; Liu, X.; Shen, Y.; Chen, Q.; Hua, W.; et al. SCN5A Mutation in Chinese Patients with Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Dysplasia. Herz 2014, 39, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadatos, G.A.; Wallerstein, P.M.R.; Head, C.E.G.; Ratcliff, R.; Brady, P.A.; Benndorf, K.; Saumarez, R.C.; Trezise, A.E.O.; Huang, C.L.-H.; Vandenberg, J.I.; et al. Slowed Conduction and Ventricular Tachycardia after Targeted Disruption of the Cardiac Sodium Channel Gene Scn5a. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2002, 99, 6210–6215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hesse, M.; Kondo, C.S.; Clark, R.B.; Su, L.; Allen, F.L.; Geary-Joo, C.T.M.; Kunnathu, S.; Severson, D.L.; Nygren, A.; Giles, W.R.; et al. Dilated Cardiomyopathy Is Associated with Reduced Expression of the Cardiac Sodium Channel Scn5a. Cardiovasc Res 2007, 75, 498–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, H.; Yang, T.; Stroud, D.M.; Lowe, J.S.; Harris, L.; Atack, T.C.; Wang, D.W.; Hipkens, S.B.; Leake, B.; Hall, L.; et al. Striking In Vivo Phenotype of a Disease-Associated Human SCN5A Mutation Producing Minimal Changes in Vitro. Circulation 2011, 124, 1001–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, L.L.; Yang, T.; Kroncke, B.; Hall, L.; Stroud, D.; Roden, D.M. SCN5A Variant R222Q Generated Abnormal Changes in Cardiac Sodium Current and Action Potentials in Murine Myocytes and Purkinje Cells. Heart Rhythm 2019, 16, 1676–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huttner, I.G.; Trivedi, G.; Jacoby, A.; Mann, S.A.; Vandenberg, J.I.; Fatkin, D. A Transgenic Zebrafish Model of a Human Cardiac Sodium Channel Mutation Exhibits Bradycardia, Conduction-System Abnormalities and Early Death. J Mol Cell Cardiol 2013, 61, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, S.S.; Stroud, D.M.; Watanabe, H.; Bennett, J.S.; Burns, C.G.; Wells, K.S.; Yang, T.; Zhong, T.P.; Roden, D.M. Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels Are Required for Heart Development in Zebrafish. Circ Res 2010, 106, 1342–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayosi, B.M.; Fish, M.; Shaboodien, G.; Mastantuono, E.; Kraus, S.; Wieland, T.; Kotta, M.-C.; Chin, A.; Laing, N.; Ntusi, N.B.A.; et al. Identification of Cadherin 2 (CDH2) Mutations in Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy. Circ Cardiovasc Genet 2017, 10, e001605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turkowski, K.L.; Tester, D.J.; Bos, J.M.; Haugaa, K.H.; Ackerman, M.J. Whole Exome Sequencing with Genomic Triangulation Implicates CDH2-Encoded N-Cadherin as a Novel Pathogenic Substrate for Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathy. Congenit Heart Dis 2017, 12, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostetskii, I.; Li, J.; Xiong, Y.; Zhou, R.; Ferrari, V.A.; Patel, V.V.; Molkentin, J.D.; Radice, G.L. Induced Deletion of the N-Cadherin Gene in the Heart Leads to Dissolution of the Intercalated Disc Structure. Circ Res 2005, 96, 346–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, M.; Graw, S.; Sinagra, G.; Barnes, C.; Slavov, D.; Brun, F.; Pinamonti, B.; Salcedo, E.E.; Sauer, W.; Pyxaras, S.; et al. Genetic Variation in Titin in Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy-Overlap Syndromes. Circulation 2011, 124, 876–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gramlich, M.; Michely, B.; Krohne, C.; Heuser, A.; Erdmann, B.; Klaassen, S.; Hudson, B.; Magarin, M.; Kirchner, F.; Todiras, M.; et al. Stress-Induced Dilated Cardiomyopathy in a Knock-in Mouse Model Mimicking Human Titin-Based Disease. J Mol Cell Cardiol 2009, 47, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Meiler, S.E.; Zhong, T.P.; Mohideen, M.; Crossley, D.A.; Burggren, W.W.; Fishman, M.C. Cardiomyopathy in Zebrafish Due to Mutation in an Alternatively Spliced Exon of Titin. Nat Genet 2002, 30, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, J.; Tran, D.; Baalbaki, M.; Tang, L.F.; Poon, A.; Pelonero, A.; Titus, E.W.; Yuan, C.; Shi, C.; Patchava, S.; et al. An Internal Promoter Underlies the Difference in Disease Severity between N- and C-Terminal Truncation Mutations of Titin in Zebrafish. Elife 2015, 4, e09406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, Y.-H.; Dvornikov, A.V.; Zhu, P.; Ma, X.; Kim, M.J.; Ding, Y.; Xu, X. Exon- and Contraction-Dependent Functions of Titin in Sarcomere Assembly. Development, 1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago, C.F.; Huttner, I.G.; Fatkin, D. Mechanisms of TTNtv-Related Dilated Cardiomyopathy: Insights from Zebrafish Models. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis 2021, 8, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quarta, G.; Syrris, P.; Ashworth, M.; Jenkins, S.; Zuborne Alapi, K.; Morgan, J.; Muir, A.; Pantazis, A.; McKenna, W.J.; Elliott, P.M. Mutations in the Lamin A/C Gene Mimic Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy. Eur Heart J 2012, 33, 1128–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolova, V.; Leimena, C.; McMahon, A.C.; Tan, J.C.; Chandar, S.; Jogia, D.; Kesteven, S.H.; Michalicek, J.; Otway, R.; Verheyen, F.; et al. Defects in Nuclear Structure and Function Promote Dilated Cardiomyopathy in Lamin A/C-Deficient Mice. J Clin Invest 2004, 113, 357–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, C.M.; Wang, L.; Alcalai, R.; Pizard, A.; Burgon, P.G.; Ahmad, F.; Sherwood, M.; Branco, D.M.; Wakimoto, H.; Fishman, G.I.; et al. Lamin A/C Haploinsufficiency Causes Dilated Cardiomyopathy and Apoptosis-Triggered Cardiac Conduction System Disease. J Mol Cell Cardiol 2008, 44, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Z.-J.; Lee, Y.-K.; Lau, Y.-M.; Ho, J.C.-Y.; Lai, W.-H.; Wong, N.L.-Y.; Huang, D.; Hai, J.-J.; Ng, K.-M.; Tse, H.-F.; et al. Expression of Lmna-R225X Nonsense Mutation Results in Dilated Cardiomyopathy and Conduction Disorders (DCM-CD) in Mice: Impact of Exercise Training. Int J Cardiol 2020, 298, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Sun, J.; Chen, Z.; Liu, L.; Sun, Y.; Lin, J.; Hu, X.; Zhao, M.; Ma, Y.; Lu, D.; et al. The LMNA p.R541C Mutation Causes Dilated Cardiomyopathy in Human and Mice. Int J Cardiol 2022, 363, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beffagna, G.; Occhi, G.; Nava, A.; Vitiello, L.; Ditadi, A.; Basso, C.; Bauce, B.; Carraro, G.; Thiene, G.; Towbin, J.A.; et al. Regulatory Mutations in Transforming Growth Factor-Beta3 Gene Cause Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy Type 1. Cardiovasc Res 2005, 65, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiso, N.; Stephan, D.A.; Nava, A.; Bagattin, A.; Devaney, J.M.; Stanchi, F.; Larderet, G.; Brahmbhatt, B.; Brown, K.; Bauce, B.; et al. Identification of Mutations in the Cardiac Ryanodine Receptor Gene in Families Affected with Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy Type 2 (ARVD2). Hum Mol Genet 2001, 10, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kannankeril, P.J.; Mitchell, B.M.; Goonasekera, S.A.; Chelu, M.G.; Zhang, W.; Sood, S.; Kearney, D.L.; Danila, C.I.; De Biasi, M.; Wehrens, X.H.T.; et al. Mice with the R176Q Cardiac Ryanodine Receptor Mutation Exhibit Catecholamine-Induced Ventricular Tachycardia and Cardiomyopathy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2006, 103, 12179–12184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, J.; Xie, W.; Betzenhauser, M.; Reiken, S.; Chen, B.-X.; Wronska, A.; Marks, A.R. Calcium Leak through Ryanodine Receptors Leads to Atrial Fibrillation in 3 Mouse Models of Catecholaminergic Polymorphic Ventricular Tachycardia. Circ Res 2012, 111, 708–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okudaira, N.; Kuwahara, M.; Hirata, Y.; Oku, Y.; Nishio, H. A Knock-in Mouse Model of N-Terminal R420W Mutation of Cardiac Ryanodine Receptor Exhibits Arrhythmogenesis with Abnormal Calcium Dynamics in Cardiomyocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2014, 452, 665–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bround, M.J.; Asghari, P.; Wambolt, R.B.; Bohunek, L.; Smits, C.; Philit, M.; Kieffer, T.J.; Lakatta, E.G.; Boheler, K.R.; Moore, E.D.W.; et al. Cardiac Ryanodine Receptors Control Heart Rate and Rhythmicity in Adult Mice. Cardiovasc Res 2012, 96, 372–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeshima, H. Embryonic Lethality and Abnormal Cardiac Myocytes in Mice Lacking Ryanodine Receptor Type 2. The EMBO Journal 1998, 17, 3309–3316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz-Genga, M.F.; Cuenca, S.; Dal Ferro, M.; Zorio, E.; Salgado-Aranda, R.; Climent, V.; Padrón-Barthe, L.; Duro-Aguado, I.; Jiménez-Jáimez, J.; Hidalgo-Olivares, V.M.; et al. Truncating FLNC Mutations Are Associated With High-Risk Dilated and Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathies. J Am Coll Cardiol 2016, 68, 2440–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalkilic, I.; Schienda, J.; Thompson, T.G.; Kunkel, L.M. Loss of FilaminC (FLNc) Results in Severe Defects in Myogenesis and Myotube Structure. Mol Cell Biol 2006, 26, 6522–6534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, M.; Tan, C.; Zhou, X.; Evans, S.M.; Fang, X.; Feng, W.; Chen, J. Loss of Filamin C Is Catastrophic for Heart Function. Circulation 2020, 141, 869–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powers, J.D.; Kirkland, N.J.; Liu, C.; Razu, S.S.; Fang, X.; Engler, A.J.; Chen, J.; McCulloch, A.D. Subcellular Remodeling in Filamin C Deficient Mouse Hearts Impairs Myocyte Tension Development during Progression of Dilated Cardiomyopathy. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23, 871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruparelia, A.A.; Zhao, M.; Currie, P.D.; Bryson-Richardson, R.J. Characterization and Investigation of Zebrafish Models of Filamin-Related Myofibrillar Myopathy. Human Molecular Genetics 2012, 21, 4073–4083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begay, R.L.; Graw, S.L.; Sinagra, G.; Asimaki, A.; Rowland, T.J.; Slavov, D.B.; Gowan, K.; Jones, K.L.; Brun, F.; Merlo, M.; et al. Filamin C Truncation Mutations Are Associated With Arrhythmogenic Dilated Cardiomyopathy and Changes in the Cell-Cell Adhesion Structures. JACC Clin Electrophysiol 2018, 4, 504–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodehl, A.; Rezazadeh, S.; Williams, T.; Munsie, N.M.; Liedtke, D.; Oh, T.; Ferrier, R.; Shen, Y.; Jones, S.J.M.; Stiegler, A.L.; et al. Mutations in ILK, Encoding Integrin-Linked Kinase, Are Associated with Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathy. Transl Res 2019, 208, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quang, K.L.; Maguy, A.; Qi, X.-Y.; Naud, P.; Xiong, F.; Tadevosyan, A.; Shi, Y.-F.; Chartier, D.; Tardif, J.-C.; Dobrev, D.; et al. Loss of Cardiomyocyte Integrin-Linked Kinase Produces an Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathy in Mice. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol 2015, 8, 921–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendig, G.; Grimmler, M.; Huttner, I.G.; Wessels, G.; Dahme, T.; Just, S.; Trano, N.; Katus, H.A.; Fishman, M.C.; Rottbauer, W. Integrin-Linked Kinase, a Novel Component of the Cardiac Mechanical Stretch Sensor, Controls Contractility in the Zebrafish Heart. Genes Dev 2006, 20, 2361–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pott, A.; Shahid, M.; Köhler, D.; Pylatiuk, C.; Weinmann, K.; Just, S.; Rottbauer, W. Therapeutic Chemical Screen Identifies Phosphatase Inhibitors to Reconstitute PKB Phosphorylation and Cardiac Contractility in ILK-Deficient Zebrafish. Biomolecules 2018, 8, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cason, M.; Celeghin, R.; Marinas, M.B.; Beffagna, G.; Della Barbera, M.; Rizzo, S.; Remme, C.A.; Bezzina, C.R.; Tiso, N.; Bauce, B.; et al. Novel Pathogenic Role for Galectin-3 in Early Disease Stages of Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathy. Heart Rhythm 2021, 18, 1394–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Fan, Y.; Gu, J.; Han, Z.; Wang, Y.; Gao, L.; Zeng, H.; Mao, C.; Wang, C. Effect of Lgals3a on Embryo Development of Zebrafish. Transgenic Res 2021, 30, 739–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, M.; Guo, G.; Li, M.; Chen, S.; Chen, K.; Chen, X.; Song, J.; Hu, S. The Homozygous Variant c.245G > A/p.G82D in PNPLA2 Is Associated with Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathy Phenotypic Manifestations. Clin Genet 2019, 96, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, L.-L.; Sun, X.; Yang, J.; Wang, X.-L.; Ackerman, M.J.; Wang, R.-X.; Xu, X.; Lee, H.-C.; Lu, T. Changes in Ion Channel Expression and Function Associated with Cardiac Arrhythmogenic Remodeling by Sorbs2. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis 2021, 1867, 166247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommariva, E.; Stadiotti, I.; Perrucci, G.L.; Tondo, C.; Pompilio, G. Cell Models of Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathy: Advances and Opportunities. Dis Model Mech 2017, 10, 823–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| GENE | MOUSE MODEL | ZEBRAFISH MODEL |
|---|---|---|
| LIMITED | ||
| Sodium voltage-gated channel alpha subunit 5 (SCN5A) [186] |
CS-Scn5A-KO mouse models showed severe biventricular cardiomyopathy and conduction defects in heterozygosity, whereas homozygotes can also present foetal lethality [187,188]. Scn5A-KI mouse models presenting human p.(Asp1275Asn) or p.Asp222Gln mutations showed a progressive cardiac dysfunction but not a clear AC morphological phenotype [189,190]. | A CS-Tg zebrafish expressing the human Asp1275Asn mutation displayed bradycardia, conduction-system abnormalities and premature death, highlighting zebrafish as a valuable model for understanding the gene’s role in the disease [191]. Similarly, KD of scn5a in zebrafish delayed early chamber development and disrupted the ventricle’s patterned growth, suggesting that cardiac sodium channels influence heart development through a non-electrophysiological mechanism [192]. |
| N-cadherin (CDH2) [193,194] |
Ventricular arrhythmia and aberrant conduction in mice with CS-Cdh2 deletion were observed, resulting in early death after two months. However, more studies are needed to understand CDH2 role in the pathogenesis of the disease [195]. | According to the ZFIN database, insertional, ENU- and CRISPR-induced mutants are available but not characterized as putative AC models. |
| Titin (TTN) [196] |
Only after hemodynamic stress, the Ttn KI mouse model, mimicking the human p.(Met14544*) mutation, developed left ventricular dilatation, impaired fractional shortening and diffuse myocardial fibrosis [197]. | Homozygous N-terminal and C-terminal titin truncations led to severe cardiac contractility defects and premature death in zebrafish. C-terminal truncations caused severe skeletal muscle myopathies, while heterozygous truncations resulted in spontaneous DCM with decreased baseline ventricular systolic function, mirroring human conditions [198,199,200,201]. |
| Lamin A/C (LMNA) [202] |
Homozygous Lmna-KO mice died in few weeks due to delayed postnatal development and the onset of DCM [203]. Heterozygous KO mutant mice, instead, survived showing conduction defects, arrhythmia events and cardiac contractility problems [204]. KI mouse models expressing human mutations p(Arg225Ter) and p.(Arg541Cis) confirmed the conductions alterations and in general the phenotype observed in KO ones [205,206]. | According to the ZFIN database, morphants, insertional, ENU- and CRISPR-induced mutants are available but not characterized as putative AC models. |
| Transforming growth factor β-3 (TGFB3) [207] |
Tgfβ3-KO mice failed to display cardiac defects or AC phenotypes, therefore this protein is nowadays more recognized for its indirect role in the disease, being found differently expressed in several other AC models [39,42,52,53,152]. | According to the ZFIN database, morphants, ENU- and CRISPR-induced mutants are available but not characterized as putative AC models. |
| DISPUTED | ||
| Cardiac Ryanodine receptor 2 (RYR2) [208] |
RYR2 primarily impacts cardiac electrical activity rather than tissue remodelling. The KI mouse model with the human disease-associated RYR2 mutation p.Arg176Gln exhibited calcium-dependent ventricular arrhythmias without histological changes [209], like other KI models [210,211] and a CS-KO one [212]. Whole body KO homozygosity provoked embryonic lethality [213]. | According to the ZFIN database, ENU- and CRISPR-induced mutants are available but so far not characterized. |
| NOT CURATED | ||
| Filamin C (FLNC) [214] |
CS-Flnc deficient mice exhibited cardiac fibrosis, dysfunction, elevated expression of cardiac stress markers and early mortality. These findings connected FLNC with the regulation of cardiomyocyte structure [215,216,217]. | Zebrafish flnc models (morphants and Tg) display cardiac alterations both functionally and structurally, with reduced survival. The observed effects included pericardial oedema, dysmorphic or dilated cardiac chambers with protein aggregation, abnormal heart tube looping, reduced blood circulation and overall weaker contractility. TEM analysis revealed irregular or seemingly absent Z-discs [218,219]. |
| Integrin-linked kinase (ILK) [220] |
In mouse cardiomyocytes, Ilk deletion produced a lethal AC phenotype with relevant ion channel and structural remodelling, connecting this protein to the disease [221]. | CS expression of human wild-type and mutated variants (H77Y and P70L) of ILK resulted in cardiac malfunction, decreased fractional shorting and premature mortality by the time the fish were two to three weeks old [220]. Likewise, a spontaneous homozygous ilk mutation (p.Leu308Pro) in zebrafish resulted in cardiac oedema, reduced heart function, and early mortality [222,223]. |
| Galectin-3 (LGALS-3/GAL-3) [224] |
Gal-3 emerged as one of the differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in the myocardium of Tg mice with the early AC phenotype. Dysregulation in the myocardium was found in Tg mice overexpressing the DSG2 p.Asn271Ser mutation. This finding was further validated in three AC patients who experienced SCD without structural remodelling [224]. | A pharmacological KD zebrafish lgals3a line exhibited developmental defects, decreased macrophages, apoptotic cardiomyocytes, and dysregulation of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway, suggesting a potential role of lgals3a in the aetiology of AC and other cardiac diseases [224,225]. |
| Patatin Like Phospholipase Domain Containing 2 (PNPLA2) [226] |
A KI mouse model carrying the human Pnpla2 mutation presented with arrhythmias and significant cardiac dysfunction. Moreover, those mice suffered SCD with extensive lipogenesis in cardiomyocytes and cardiac fibrosis in the myocardium [226]. | According to the ZFIN database, morphants and CRISPR-induced mutants are available but not characterized as putative AC models. |
| SH3 domain-containing 2b (SORBS2) [227] |
KO mice with a complete SORBS2 depletion exhibited a phenotype resembling that of AC patients, featuring right ventricular dilatation, dysfunction, spontaneous ventricular tachycardia, and sudden cardiac death. The absence of SORBS2 caused significant cardiac electrical remodelling, affecting action potentials, impulse conduction, and inducing life-threatening arrhythmias [227]. | According to the ZFIN database, morphants and mutants are available but not characterized as putative AC models. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





