Submitted:
27 June 2024
Posted:
27 June 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Background of the Problem
1.2. Problem Formulation
2. Models and Methods
2.1. Problem Analysis
2.1.1. Analysis of Task One
2.1.2. Analysis of Task Two
2.1.3. Analysis of Task Three
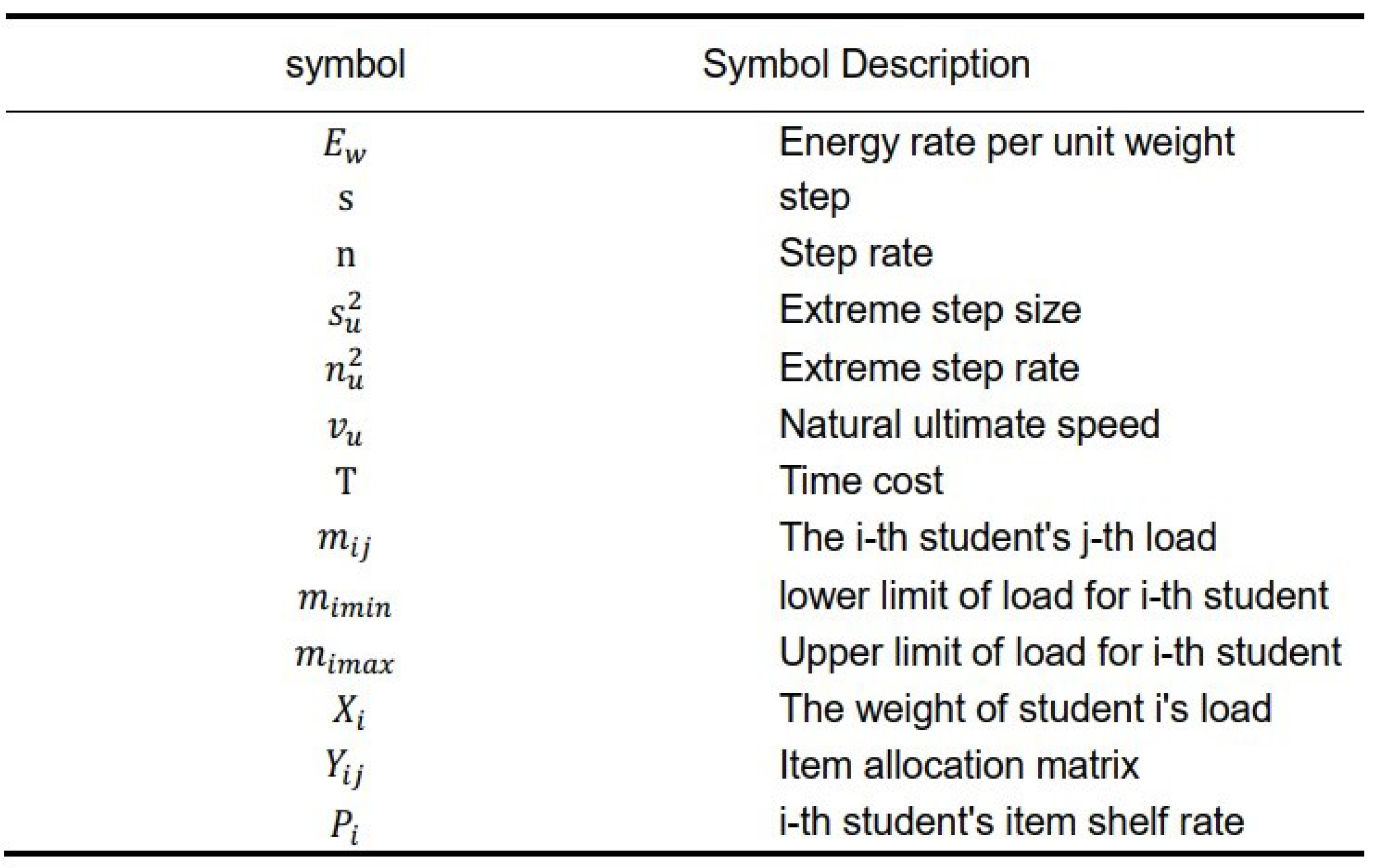
2.2. Model Assumptions and Symbols Description
2.3. Establishment and Solution of the Model for Task One
2.3.1. Analysis and Solution of Task One
2.3.2. Model Preparation-Energy Consumption Model for Natural Walking
2.4. Establishment of Energy Consumption Model for Load Travel of Task One
2.5. Solving the Model for Task One
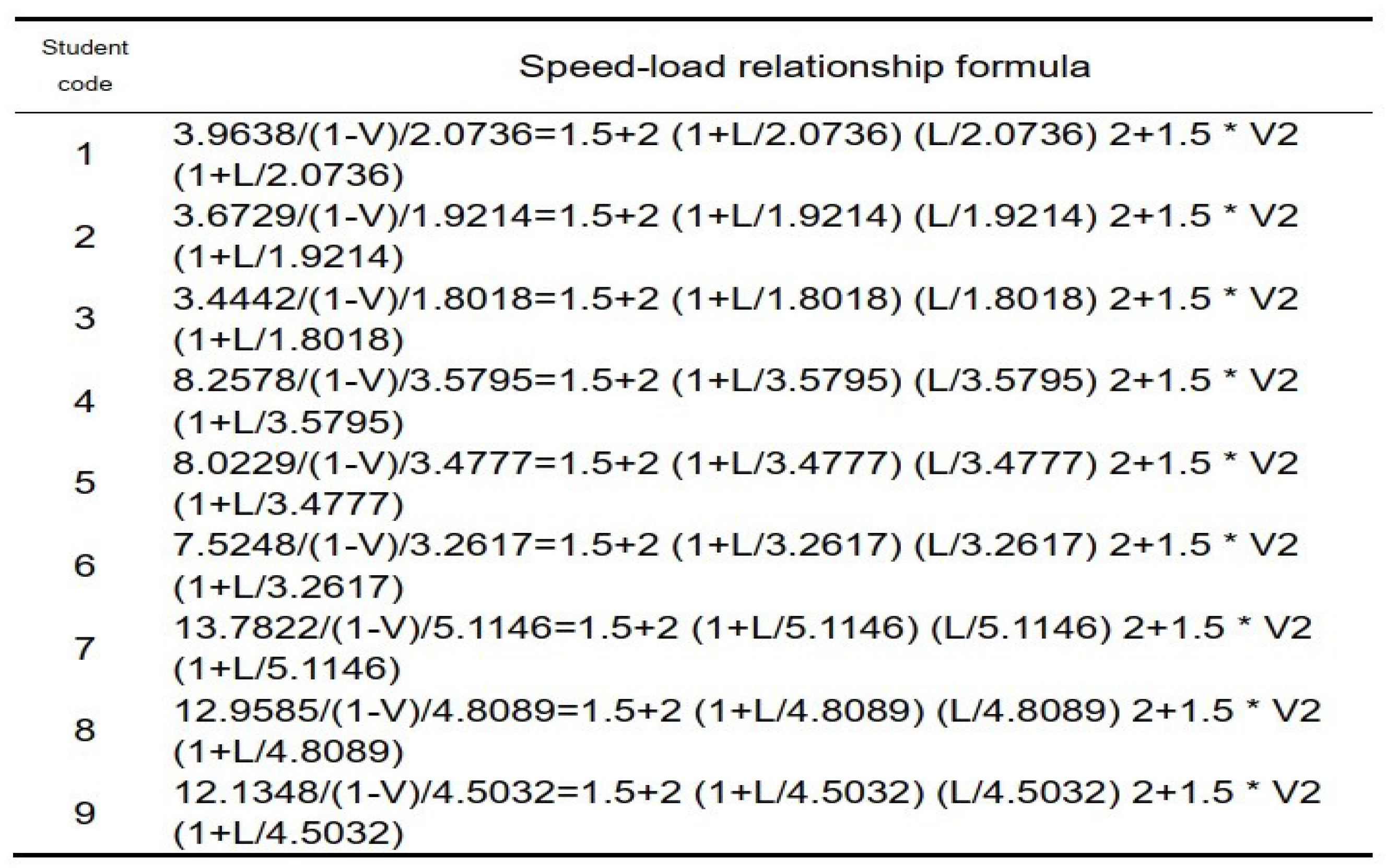
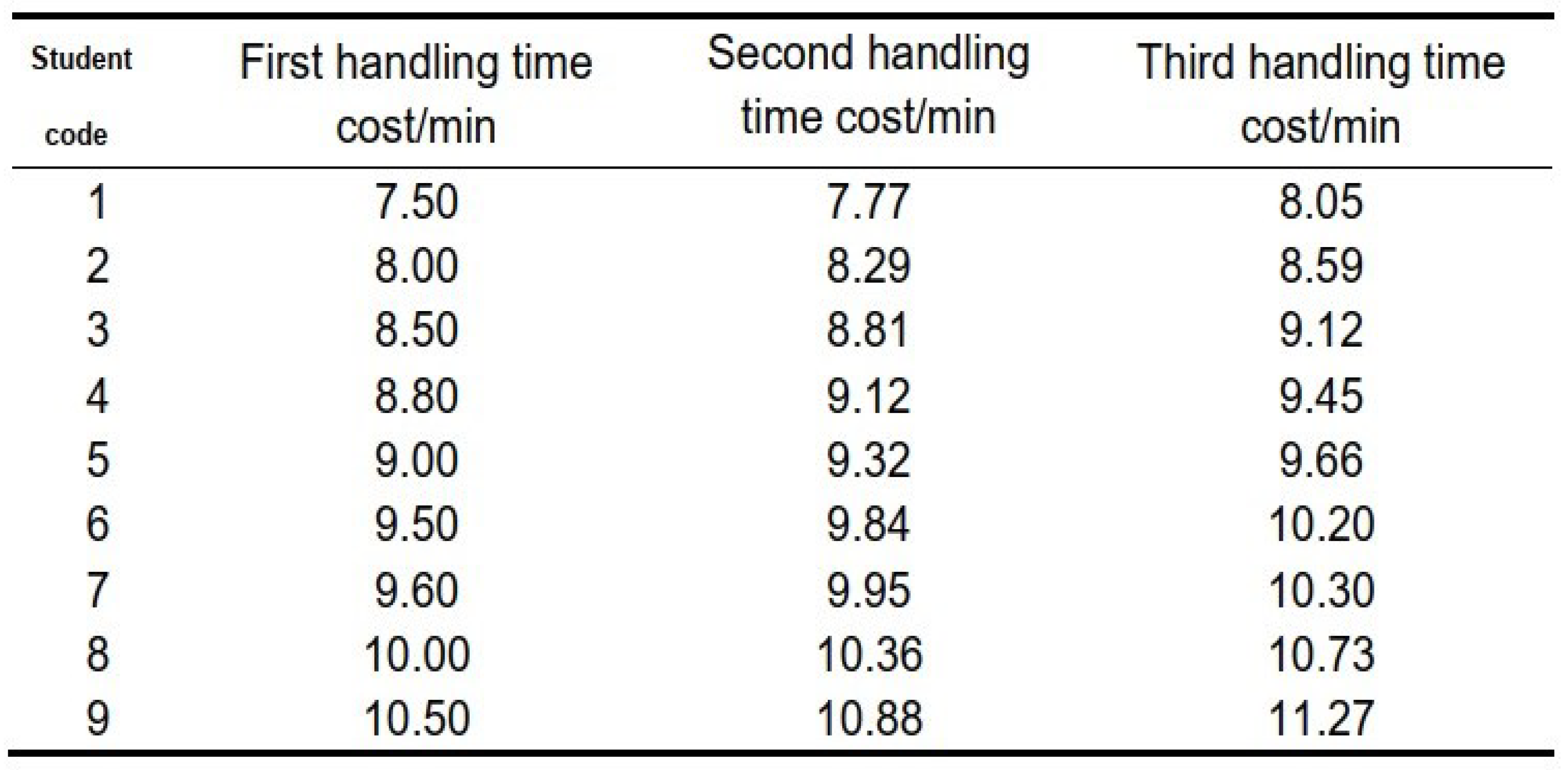
2.6. Conclusion of Model for Task One
2.7. Analysis for Task Two
2.8. Model Establishment for Task Two-Data Preprocessing
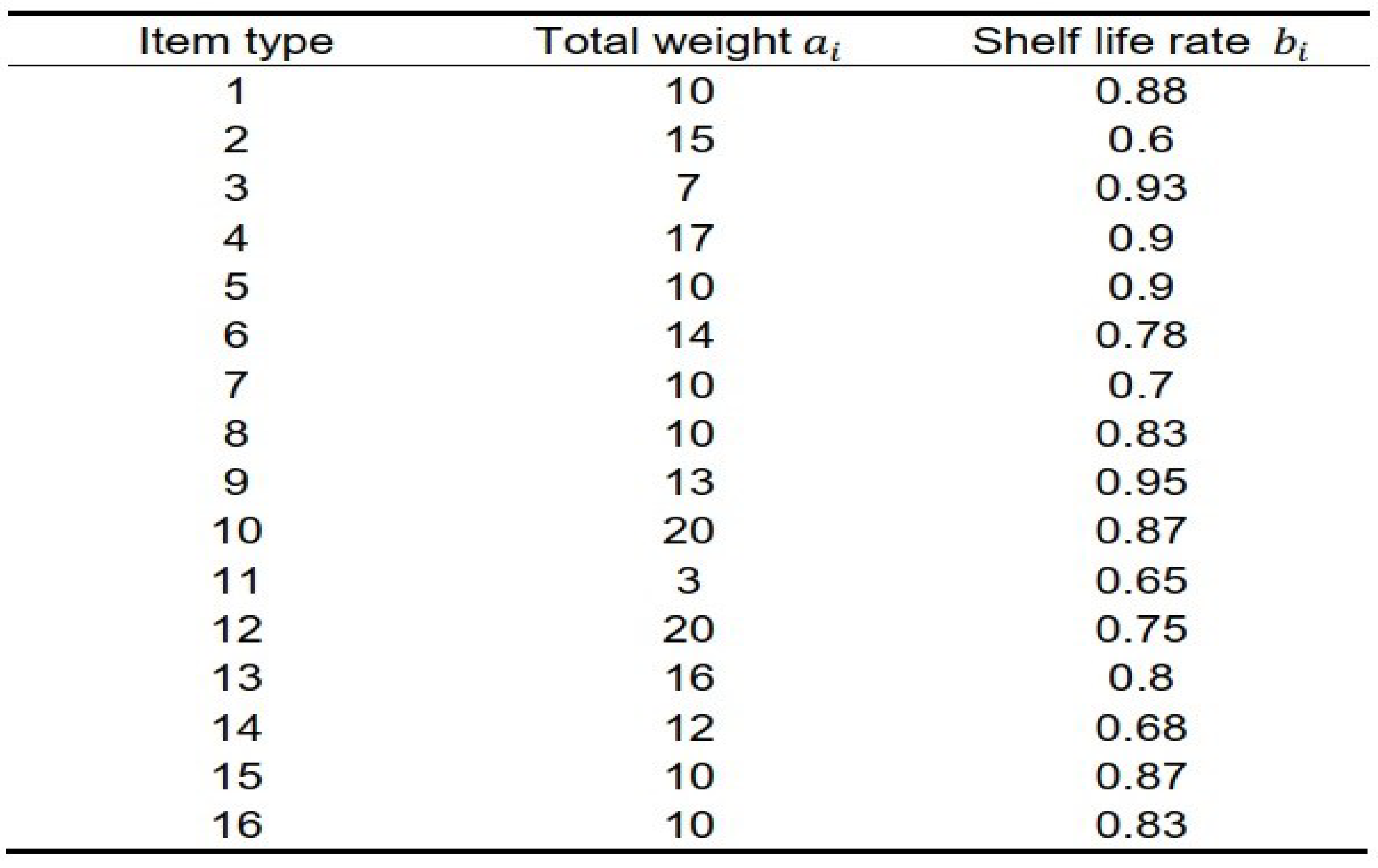
2.9. Model for Task Two
2.10. Solving the Model for Task Two
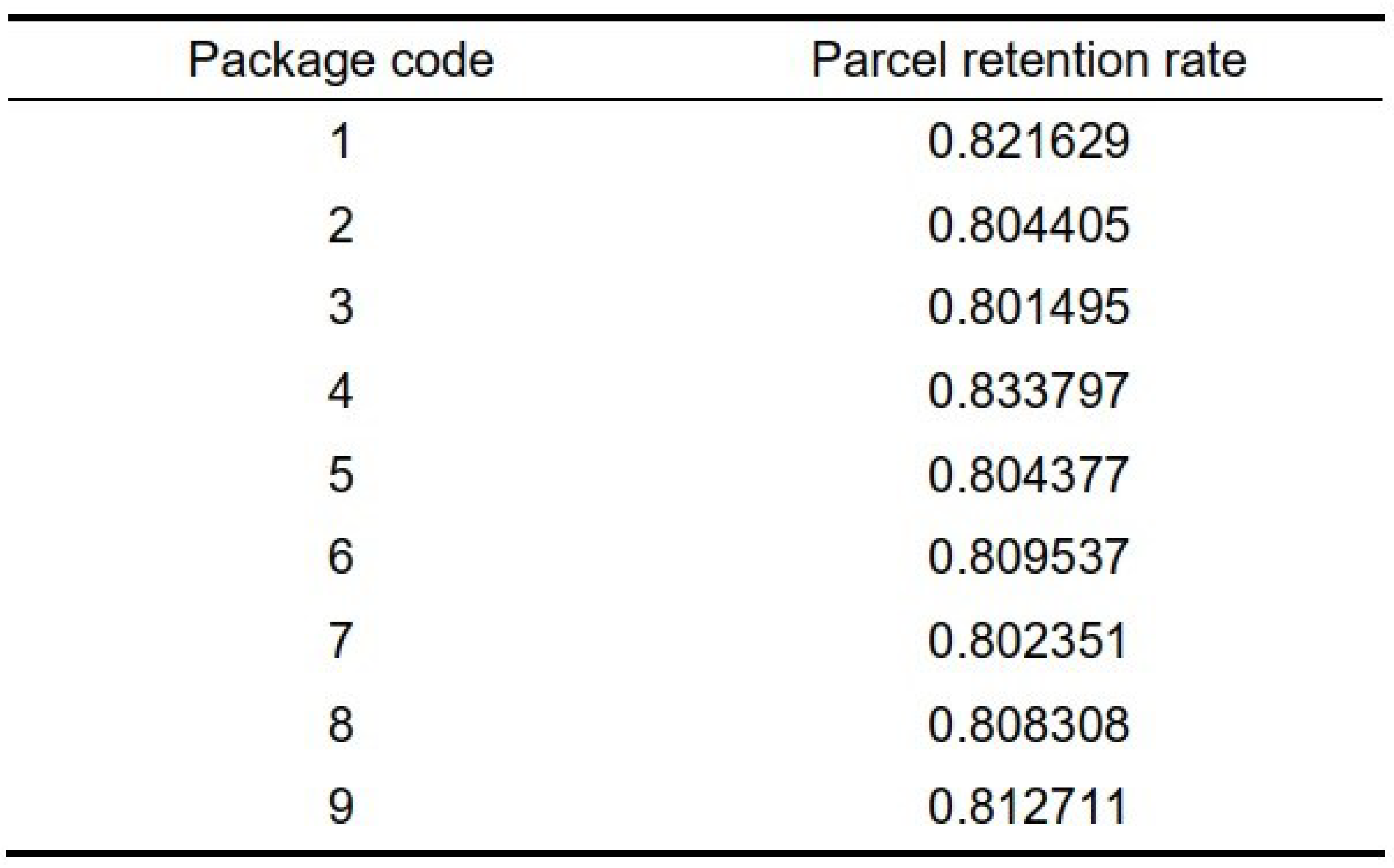
2.11. Conclusion for Model of Task Two
3. Evaluation of the Models
3.1. Evaluation of the Model
3.1.1. Advantages of the Models
3.1.2. Disadvantages of the Models
3.2. Improvement of the Models
4. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
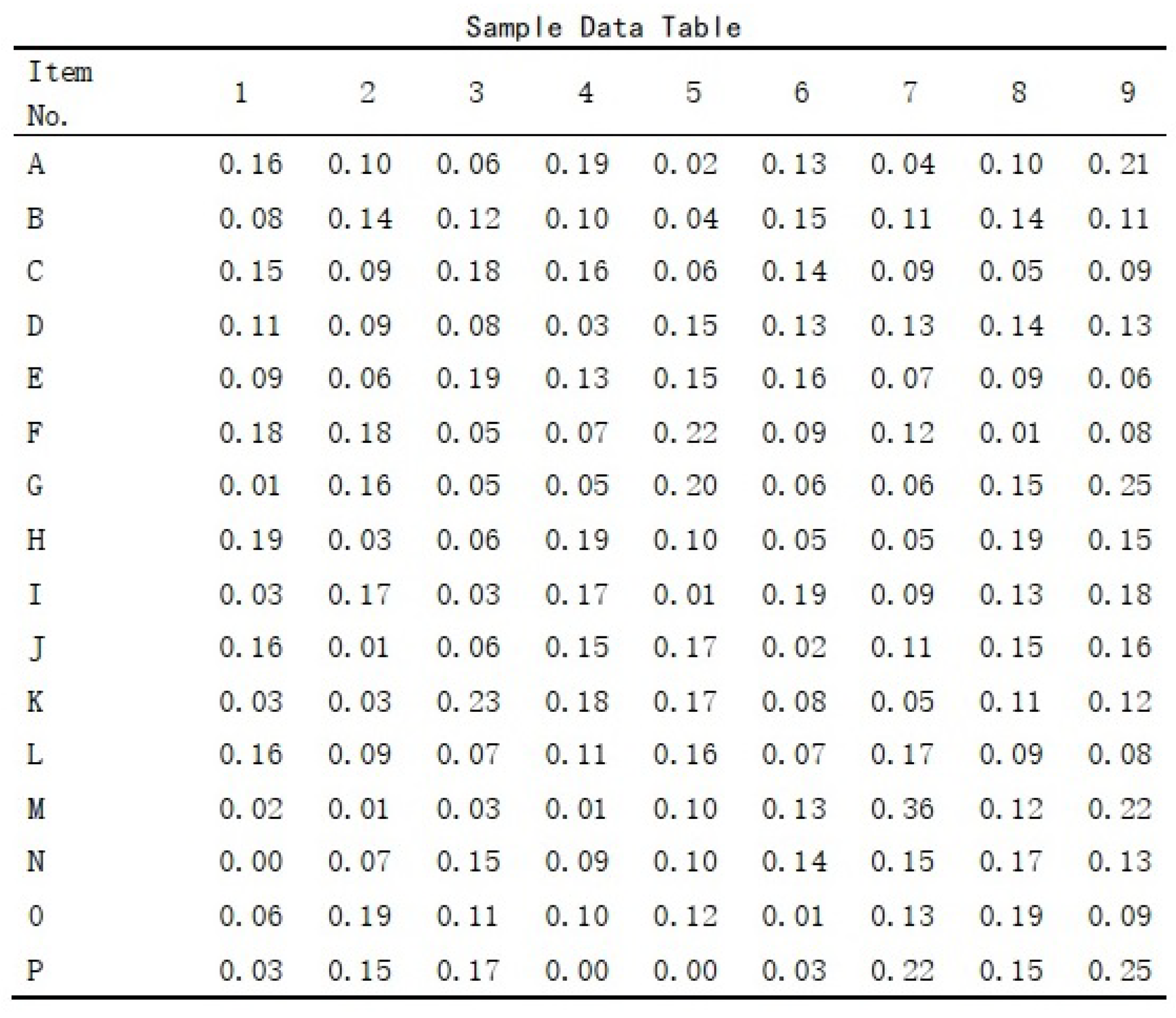
Appendix A. Student-Item Sample Data (For Test in This Work)
Appendix B. Matlab Code
References
- Bertsch, C.; Unger, H.; Winkelmann, W.; et al. Evaluation of early walking patterns from plantar pressure distribution measurements. Gait Posture 2004, 19(3), 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eleftherios, K. Plantar pressure distribution during barefoot standing, walking and landing in preschool boys. Gait Posture 2001, 14, 92–97. [Google Scholar]
- Willems, T.; Witvrouw, E.; Itvrouw, E.; Delbaere, K.; et al. Relationship between gait biomechanics and inversion sprains: a prospective study of risk factors. Gait Posture 2005, 21, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, P.C.; Stebbins, J.; Theologis, T.; et al. Spatio-temporal parameters and lower -limb kinematics of turning gait in typically developing children. Gait and Posture 2013, 38, 870–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerrigan, D.C.; Riley, P.O.; Nieto, T.J.; et al. Knee joint torques: a comparison between women and men during barefoot walking. Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 2000, 81, 1162–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Pascoe, D.D.; Weimar, W. Evaluation of book back-pack load during walking. Ergonomics 2001, 44, 858–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goh, J.H.; Thambyah, A.; Bose, K. Effects of varying backpackloads on peak forces in the lumbosacral spine during walking[J]. Clinical Biomechanics 1998, 13(1- supp -S1), s26–s31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, M.P.; Figueiredo, M.C.; Abreu, S.; et al. The influenceof gait cadence on the ground reaction forces and plantar pressuresduring load cariage of young adults. Applied Ergonomics 2015, 49, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stergiou, N.; Moraiti, C.; Giakas, G.; et al. The effect of the walking speed on the stability of the anterior cruciate ligament deficient knee. ClinBiomech 2004, 19, 957–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grieve, D.W.; Gear, R.J. The relationship between length of stride,step requency,time ofswing,and speed of walking for children and adults. Ergonomics 1966, 5, 379–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bobet,J.; and Norman, R.W. Effects of load placement on back muscle activity in loadcarriage. Eur.J Appl physiol 1984, 53, 71–75. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, J.C.; Hashemi, E.; Arami, A. Natural Walking With Musculoskeletal Models Using Deep Reinforcement Learning. IEEE ROBOTICS AND AUTOMATION LETTERS 2021, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Q.; Fu, S.; Tan, K.; Muralidharan, S.T.; Lagrelius, K.; Danelia, D.; et al. Synthesizing the optimal gait of a quadruped robot with soft actuators using deep reinforcement learning. Robotics and Computer Integrated Manufacturing: An International Journal of Manufacturing and Product and Process Development 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, U. A. Learning Control Policies for Imitating Human Gaits. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seay, J.F.; Gregory, V.A.; Frykman, P.N.; Smith, N.I.; Fellin, R.E. Spatiotemporal Comparisons Between Male and Female Soldiers While Walking With Heavy Loads:124 Board #5 May 30 9. Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise, 2018, 50. [Google Scholar]
- Simpkins, C.; Yang, F. Dynamic Gait Stability and Spatiotemporal Gait Parameters During Overground Walking in Professional Ballet Dancers[J]. Journal of dance medicine & science 2024, 28. [Google Scholar]
- Seay, J.F.; Bode, V.G.; Frykman, P.N.; et al. Pelvis and Trunk Motion Comparisons Between Male and Female Soldiers While Walking With Heavy Loads: 85 Board #1 May 29 9:30 AM - 11:30 AM[J]. Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise 2019, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, K.M.; Munro, B.J.; Steele, J.R. Effects of prolonged load carriage on ground reaction forces, lower limb kinematics and spatio-temporal parameters in female recreational hikers[J]. Ergonomics 2012, 55, 316–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houck, J.R.; Duncan, A.; Haven, K.E.D. Comparison of frontal plane trunk kinematics and hip and knee moments during anticipated and unanticipated walking and side step cutting tasks[J]. Gait & Posture 2006, 24, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- S. Yoganandaan,V. P. Effect of Walking with and without LoadIntermittent Walking on Cardio Respiratory EnduranceMuscular Strength and Muscular Endurance of Adolescent Boys[J]. International Journal of Innovative Research and Development 2014, 3.
- Lee, J.S.; et al. Effects of Forest-Walking Exercise on Isokinetic Muscular Strength, Muscular Endurance, and Bone Mineral Density in the Elderly Women[J]. Journal of the Korean Institute of Forest Recreation 2016, 20, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wernbom, M.; et al. EFFECTS OF VASCULAR OCCLUSION ON MUSCULAR ENDURANCE IN DYNAMIC KNEE EXTENSION EXERCISE AT DIFFERENT SUBMAXIMAL LOADS. Journal of Strength & Conditioning Research 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Harrison, P.W.; James, L.P.; Jenkins, D.G.; et al. The Effects of Low-Load Squat Jump and Maximal Isometric Priming Exercise on Muscular Performance and Perceptual State[J]. Journal of strength and conditioning research 2024, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
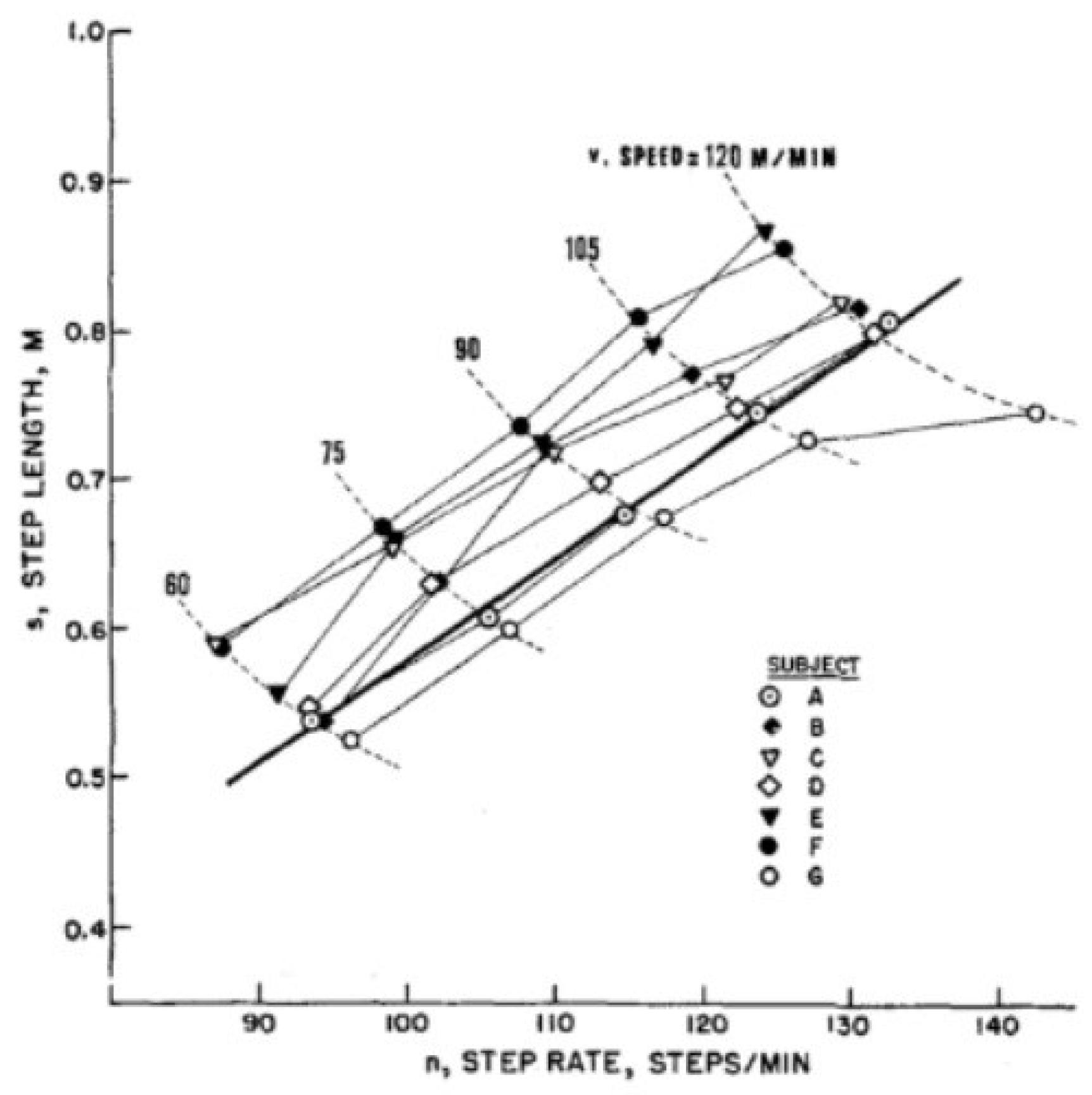
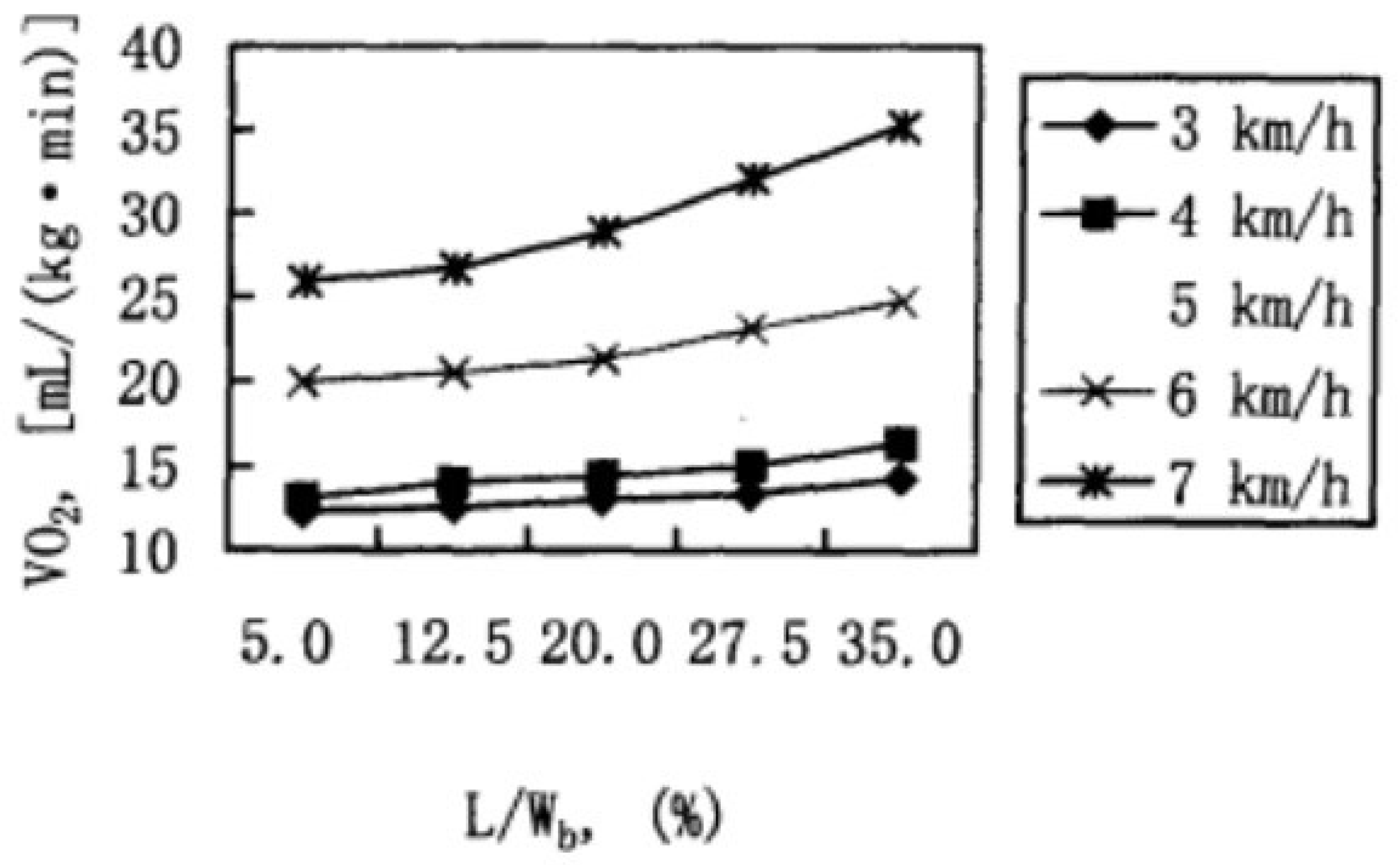
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





