1. Introduction
The continuous global population growth, as reported by the United Nations [
1], has led to a growing need for citizen participation in the supervision of public institutions [
2]. This growing demand for active involvement in the control and monitoring of public resources and policies has been intensified in the era of Industry 4.0 and rapid technological development [
3]. Consequently, there has been also an increase in the needs to search for innovative solutions and digital systems that enable more effective, transparent, and agile state supervision, in order to meet the demands of an increasingly connected and informed society [
4].
The supervision of public resources execution has generated a significant transformation in the face of “Fiscal Openness” [
5], moving towards the use of smart tools and technologies. Nowadays, such process heavily depends on manual methods and bureaucratic processes in several countries, limiting efficiency and accuracy in fiscal control. Nonetheless, with the presence of modern data analysis tools (e.g. artificial intelligence and automation) a more detailed supervision could be achieved. Such tools allow for: i) quasi real-time monitoring, ii) early detection of irregularities, and iii) comprehensive data analysis, which leads to optimizing the management of public resources and ensuring greater transparency and accountability in the use of government funds as reported in [
6,
7,
8]. This shift towards the implementation of smart technologies has significantly strengthened supervision capacity, facilitating more effective fiscal control adapted to the demands of an increasingly technology-oriented and citizen-centered society, namely Society 5.0.
The transition from Industry 4.0 to Society 5.0 has resulted in a significant change in the management of public spending. Society 5.0 focuses on the complete integration of technology to address social challenges and improve quality of life, in an approach known as human-centricity [
9,
10,
11], whereas Industry 4.0 was primarily focused on automation and the integration of technologies in industrial processes [
12]. In line with, this, Society 5.0 (a futuristic concept that advocates integrating technology into every aspect of daily life to enhance quality of life) will benefit society by facilitating quicker anomaly detection, better decision-making, and an increased ability to anticipate and prevent issues with the use of public funds [
11,
13].
The progression towards intelligent platforms in public expenditure control has proven to be key for governmental financial supervision. Solutions powered by innovative technologies can provide a more precise monitoring of state resources, thereby strengthening flexibility, transparency, efficiency, and public trust in the management of public funds [
14,
15,
16]. In this regard, one can find recent works that state that expenditure audits, which use better information, benefit fiscal transparency [
7]. Such quality information can be used by audit institutions through social media to communicate with stakeholders more efficiently by reaching wider audiences [
4]. Nguyen and Luong [
17] conducted a study highlighting the potential of enhanced expenditure control in reducing public debt, particularly in transition economies. This highlights the importance of public policies to strengthen independent fiscal institutions in the benefit of society [
18].
The use of modern technologies has been reported to be useful within several sectors to supervise the execution of resources at different levels. For instance, Barateiro et al. [
19] reported the use of blockchain in the oil & gas industry to perform fiscal measurement, which refers to the appropriate measurement for taxation and royalties calculation according to regulations published by official entities. On a wider and hierarchically superior level, [
20] proposed a dynamic control system to regulate taxation and market operations for fiat money-based economies. More recently, Li and Li [
21] provided key points around the government’s efforts to promote scientific and technological innovation while enhancing local fiscal decentralization through digital inclusion for an improved quality of economic development. Nonetheless, some authors have also addressed some ethical and legal implications [
22,
23] of the use of modern technologies supported by artificial intelligence. Finally, the use of modern technologies requires a cultural change that will encounter resistance in aging parts of societies.
Research on platforms, systems, planning, and challenges in fiscal control is highly relevant for understanding the development and progress in the formulation of digital transformation platforms for developing countries [
17]. However, the results from the search and literature review process reveal that, in the regional context of this research, there has not been to date a consolidated presence of such a platform for smart fiscal control in Colombia that allows the processing of large information volumes through cloud-distributed computing. In this scenario, this paper addresses the proposal for the design of a strategic platform for the Directorate of Information, Analysis, and Immediate Reaction (DIARI) of the General Comptroller of the Republic of Colombia, as a complementary approach related to smart city strategies, to address the challenges of its digital transformation and technological modernization process. The organization of the paper is as follows. In
Section 2 we provide the analysis of a systematic literature review that was performed; then,
Section 3 contains the definition of the steps required to design the strategic platform; then,
Section 4 shows the results with the architecture and the implementation plan;
Section 5 contains the discussion, and finally, conclusions are presented in
Section 6.
2. Literature Review
In the context of this research, an analysis of repositories, reports, and multidisciplinary scientific publications from recognized sources such as Science Direct and Scopus was conducted. The aim was to identify and examine similar projects implemented in the region. This exploration focused on studies, platforms, and initiatives related to the intelligent supervision of public investment in the world, and then in Latin American countries with a specific focus on the Colombian context. To better understand the context and seek references, a review of scientific literature was conducted, focusing on three key concepts: “digital transformation in the public sector”, “emerging strategy”, “strategic platform”, “fiscal control”, “public expenditure”, “smart supervision”, and the crucial concept of “society 5.0” [
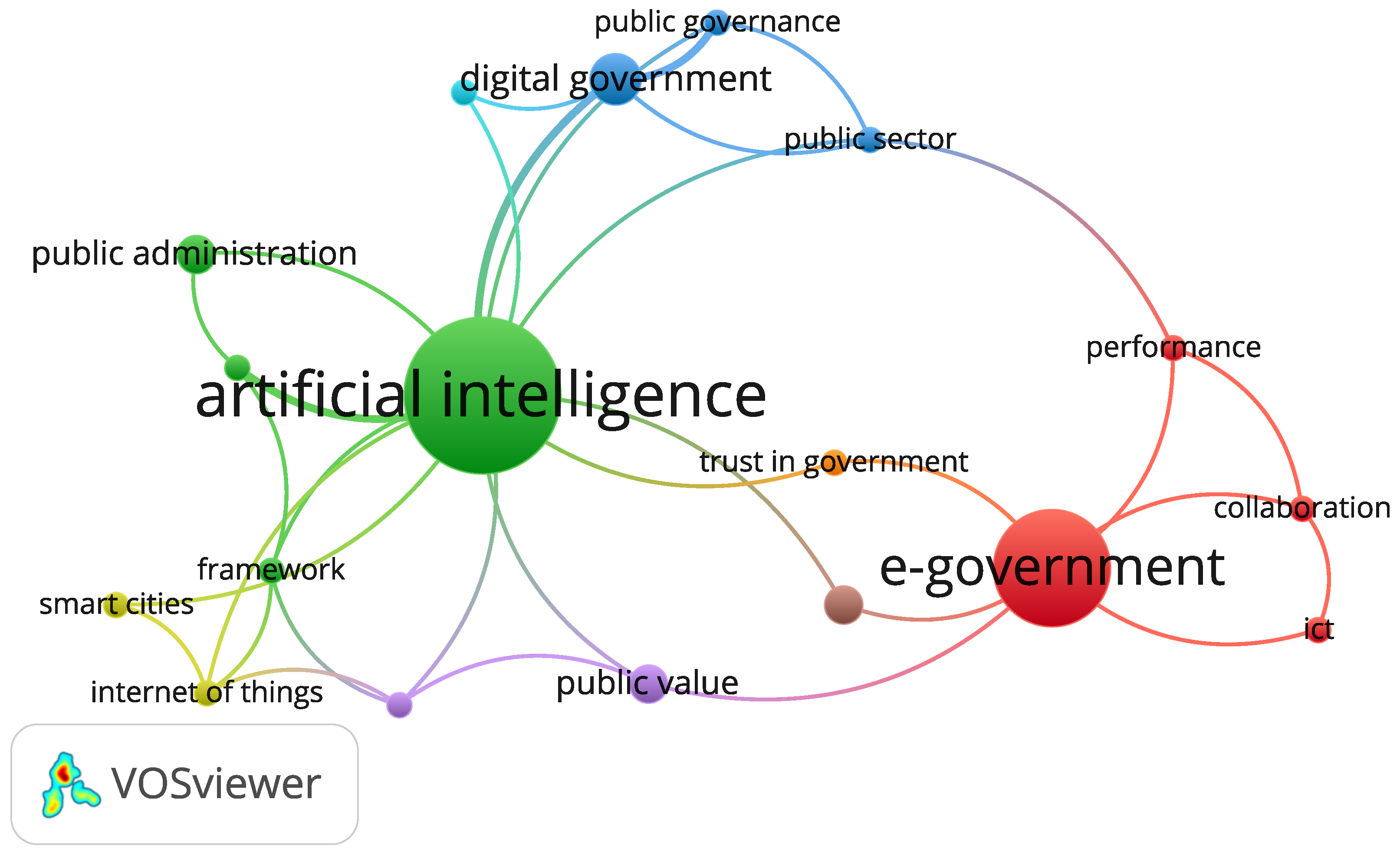
24], among others. In this search, 276 references were integrated into a database to perform a co-occurrence analysis of keywords,
Figure 1.
As can be seen in
Figure 1, the main nodes of the co-occurrence description are artificial intelligence, e-government, digital government, public administration, and public value. On a minor scale, one can identify smart cities, the Internet of Things, collaboration, performance, public governance, the public sector, and trust in government. This verifies that the integration of these concepts offers a comprehensive and updated view of the historical, technological, and prospective landscape related to the supervision of public spending, the implementation of new technologies in the public sector, and strategic advancements driving civilizations and governments toward the new revolution of Industry 5.0 [
3]. This literature review enables the identification of good practices, lessons learned, and potential opportunities for adaptation or improvement for the implementation of the proposed strategic platform for Colombia within the framework of Society 5.0.
In the regional and national contexts, some research and projects focused on governance security models, have been identified at the Office of the Comptroller General of the Republic of Colombia, commonly known as the “Contraloría General de la República (CGR)”, which is an independent entity of the Colombian state responsible for supervising and controlling the management of public resources in Colombia. The CGR is an independent body, whose mission is related to ensuring transparency, efficiency, and accountability in the use of public funds in Colombia through the fiscal control, which in addition to being subsequent and selective, may be exercised preventively and concomitantly [
25]. An example is the study by García-Valencia [
26] “Information Security Governance Model for the General Comptroller’s Office of the Republic of Colombia”. It addresses how this Colombian entity began the digital transformation in response to the emerging needs of users to perform procedures online, and a growing interest in establishing and improving digital security, both for users and in data and information management [
27]. Additionally, Pinilla-Cárdenas [
28] presented a work related to the challenges that the entity faces in combating corruption “Fiscal Control Challenges to combat corruption in Colombia”, highlighting the key financial aspects of the entity and the mechanisms for corruption prevention in such institutions and countries.
In parallel, some works focused on strategy and development plans for the implementation of emerging technologies and public management of the CGR have been found. Márquez-Alzate et al. [
29] presented the “Strategic Plan 2020-2021” by the General Comptroller of Quindío, focusing on fiscal surveillance and continuous auditing. Abadia-Benitez [
30] proposed the “Departmental Comptroller’s Strategic Plan of Valle del Cauca 2020 – 2021 Version II”, for the Department of Valle del Cauca, to implement improvements in areas such as the use of technologies in the region. Erazo-Montenegro [
31] worked on the “Institutional Strategic Plan 2020-2023: Transforming Fiscal Control”, for the CGR, to strengthen institutional capacity. More recently, Castro [
32] developed the “Institutional Strategic Plan Fiscal Control Our Social Commitment” for the Department of Casanare, as a strategic plan for the period 2022-2025.
As a significant point in the literature review, and about the previously mentioned research, it was concluded that in Colombia there is a scant presence of research in the area of creation and design of digital platforms for innovation and digital transformation. This significantly indicates that the design of the strategic platform represents an innovative opportunity and improvement for the field of fiscal control, and can contribute significant technological advances in Colombia, positioning the country as a prominent reference at a global level in society 5.0. The absence of similar initiatives suggests a gap in the implementation of specific solutions the field of smart cities and smart government, particularly at the national level. Therefore, the current research represents an opportunity to bridge this gap by introducing an innovative strategic platform proposal for smart fiscal control. The design of such a platform is based on the following definitions.
A
strategic platform is an assembly of technologies, tools, resources, and processes [
33], that is based on the emerging strategy’s foundations [
34]. It acts as a centralized framework that facilitates data management, decision-making, and the implementation of actions aligned with an organization’s strategic objectives. Designing such a platform provides a solid foundation for process optimization, continuous innovation, and adaptability to environmental changes, essential for any entity [
35].
Fiscal control comprises a set of actions, regulations, mechanisms, and procedures whose main objective is to oversee, verify, and ensure the proper use of public resources [
36]. It aims to ensure transparency, efficiency, legality, and accountability in the management of state funds and assets. This control comprises the audit of income, expenditures, investments, contracting, and any other financial activity related to the public sector.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Context for the Strategic Platform
The transition towards the digital environment by various governments and societies worldwide is currently driving a transformation among several organizations, including governmental entities. This evolution becomes a crucial strategic element since those organizations are moving towards digital transformation in their processes and strategic objectives, within a society that is transforming cities into smart cities [
37]. However, the effective adoption of digital technologies poses significant challenges, especially in the context of governmental and fiscal control entities in developing countries [
38], such as Colombia. In this context, we are providing the foundation of concepts required for the design of the platform.
3.1.1. Emerging Strategy
Contrary to the traditional vision of strategy as an analytical and rational process of long-term planning, the concept of Emerging Strategy [
39] has surfaced, which focuses on adaptation and continuous experimentation. According to the Emerging Perspective, the strategy unfolds organically in response to a changing and uncertain environment. The successful adoption of the strategy requires monitoring, communication, decision-making authority, and learning. The Emerging Strategy has been useful in dynamic environments, which are characterized by constant changes, such as the technological sector. It has enabled adaptations within organizations according to trends in different markets. It has been demonstrated that is essential to have clear objectives and appropriate organizational capabilities to execute changes effectively [
39].
3.1.2. Strategic Functional Modules
The implementation of the Emerging Strategy can be done by creating specialized functional modules [
40]. These modules can operate as semi-independent units, and each of them is aimed at a specific strategic goal such as learning methodology, process optimization, or the development of key capabilities within the organization. Being coupled in a relatively general manner, the modules enable experimentation and agile adaptation amongst themselves. The implementation of modules embodies the concept of having “real options” [
41] in strategy, where entities or organizations can invest in multiple flexible capabilities tailored to their contexts, which can be enhanced or abandoned as the needs of their users evolve. This modular structure of strategic implementation fosters innovation by allowing for the combination of capabilities in various ways.
3.1.3. Digital Transformation in the Public Sector
The digital transformation (DT) of the public sector requires the adoption of digital technologies (mostly from Industry 4.0) to improve services and interactions with citizens [
42]. DT has encountered several challenges in the transition to Society 5.0, including systems integration (interoperability), public budget constraints, lack of technical skills, and potential cultural resistance to changes, among others. Additionally, digital transformation must be comprehensive, including both technological adoption and organizational transformations. To achieve this, it is essential to adopt agile development models, foster a culture open to innovation, enhance collaboration among organizations, and encourage the active participation of external stakeholders, whether they are from the national territory or international. In the public sector, leadership is critical to achieving this transformation, thus establishing a clear and achievable vision and managing the inherent tensions in the digital transformation adoption process [
43].
3.1.4. Strategic ICT Management
The strategic management of Information and Communication Technologies (ICT) can help achieving organizational goals proposed in the DT process of any organization. In this sense, it is crucial to align the business strategy and Information Technology (IT), with the joint participation of top management and technology leaders in the country’s context [
34]. Analyzing the competitive environment and technological trends is crucial for identifying how ICT can provide a differential value in strategic management. Besides having an analytical planning, it is essential to adopt an agile approach that incorporates learning and experimentation into the management process [
34]. Such planning and the dynamic capabilities resulting from the process allow for a swift adaptation of ICT and digital strategy in the public sector of the region.
3.1.5. Fiscal Control and New Technologies
Analyzing the competitive environment and technological trends is crucial for identifying how ICT can provide a differential value in strategic management. This is linked to the need of having an analytical planning, which is essential to adopt an agile approach that incorporates learning and experimentation into the management process [
34]. Such planning and the dynamic capabilities resulting from the process allow for a swift adaptation of ICT and digital strategy in the public sector of the region. To address these challenges, a strategic approach is needed to balance the opportunities of emerging technologies with the mitigation of their potential risks. This involves implementing data governance processes, promoting stakeholder’s engagement, ensuring accountability, and maintaining proactive communication to build public trust in the DT of regulatory bodies [
28]. Hence, a comprehensive strategic approach that blends analytical planning with adaptability to achieve an effective DT of regulatory entities is required. Specialized functional modules facilitate this blend. Furthermore, responsible governance of emerging technologies, such as artificial intelligence, is crucial for realizing their potential benefits in fiscal control, carefully balancing opportunities and risks [
28]. The literature review on fiscal control and new technologies has revealed a research gap, indicating the necessity for further research on the ethical and inclusive use of these technologies in the public sector, especially in regions like Latin America.
3.2. Design Methodology
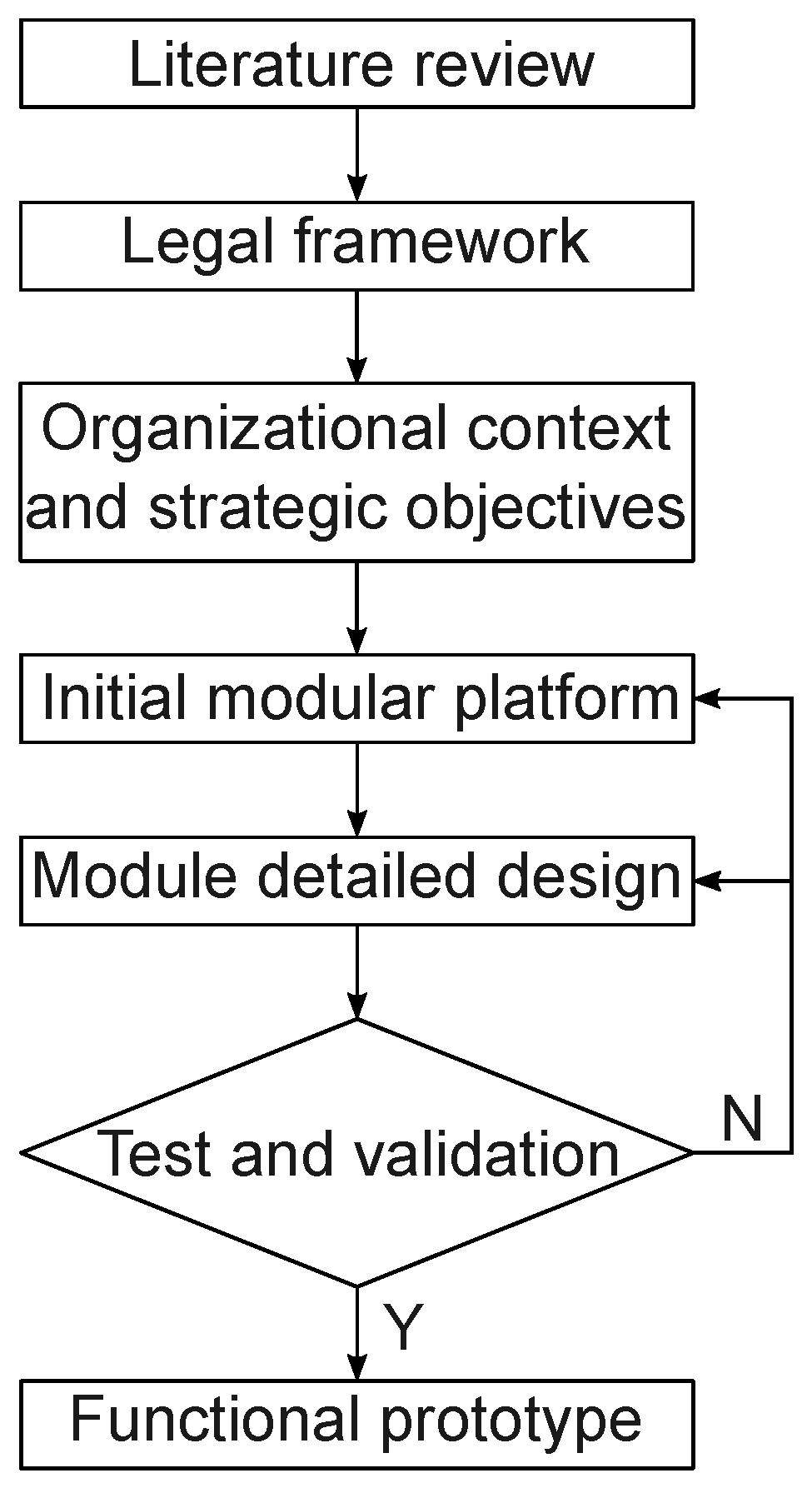
The design of the modular strategic platform for the DIARI, which is a specialized unit within the CGR responsible for gathering, analyzing, and responding to information related to its oversight and control functions, requires using rigorous techniques,
Figure 2. Within this work, qualitative and quantitative methods were employed under a mixed approach, enabling a detailed understanding of the organizational context of DIARI and CGR in Colombia, incorporating international references, as well as integrating relevant technical and statistical data within the platform’s context.
An extensive
literature review of various articles and technical documents was initially conducted using databases such as Ebsco and SCOPUS. Search terms used within the search equations were reported in
Section 2. The studies found through this review helped establish a theoretical and conceptual framework, essential for the appropriate advancement and development of the platform.
Subsequently, a review of the legal framework relevant to fiscal control in Colombia was conducted. This included the comparison to various international benchmarks to identify key elements to be included into the platform design. Additionally, a practical project took place in Bogotá during September 2023, through a series of workshops with the DIARI and technology sector companies. These workshops allowed the discussion of relevant legal topics regarding the DT of the CGR in the national context.
Several internal documents of the DIARI were reviewed to gain a comprehensive understanding of the organizational context and strategic objectives of a unit that operates at the national level within the CGR. To supplement this information, several stakeholders participated in workshops, featuring the presence of DIARI staff, technology experts, and academia.
With the gathered information, a draft of the initial modular platform was outlined. This initial platform focused on defining the objectives, functionalities, and required technologies for each module connected to the strategy. In this phase, alignment with the strategic requirements, as well as the mission-critical and support processes of the DIARI, were considered. It was ensured that this proposal was in harmony with the general strategy of the CGR, guaranteeing that the platform’s elements accurately reflected the institutional needs and objectives.
After completing the conceptual proposal, a rigorous technical design process for each module was carried out, and specific technologies suitable for each module were selected. This process was conducted in close collaboration with the DIARI’s technological infrastructure team, involving analysts and developers with extensive experience. In addition, decision matrices were used to evaluate technological options, and concept tests and validation processes were conducted to evaluate their feasibility.
With the technical design validated, construction of a functional prototype for the six strategic modules proceeded. This prototype underwent testing by a diverse group of future DIARI users to gather feedback on usability and identify potential improvements. Additionally, comprehensive technical tests were conducted to assess the prototype’s performance, stability, and scalability.
Finally, all documentation related to the conceptual and technical design of the modular strategic platform was consolidated into a technical report. This document underwent thorough review by a committee of experts, both internal to DIARI and external, who verified its technical accuracy and alignment with organizational needs.
4. Results
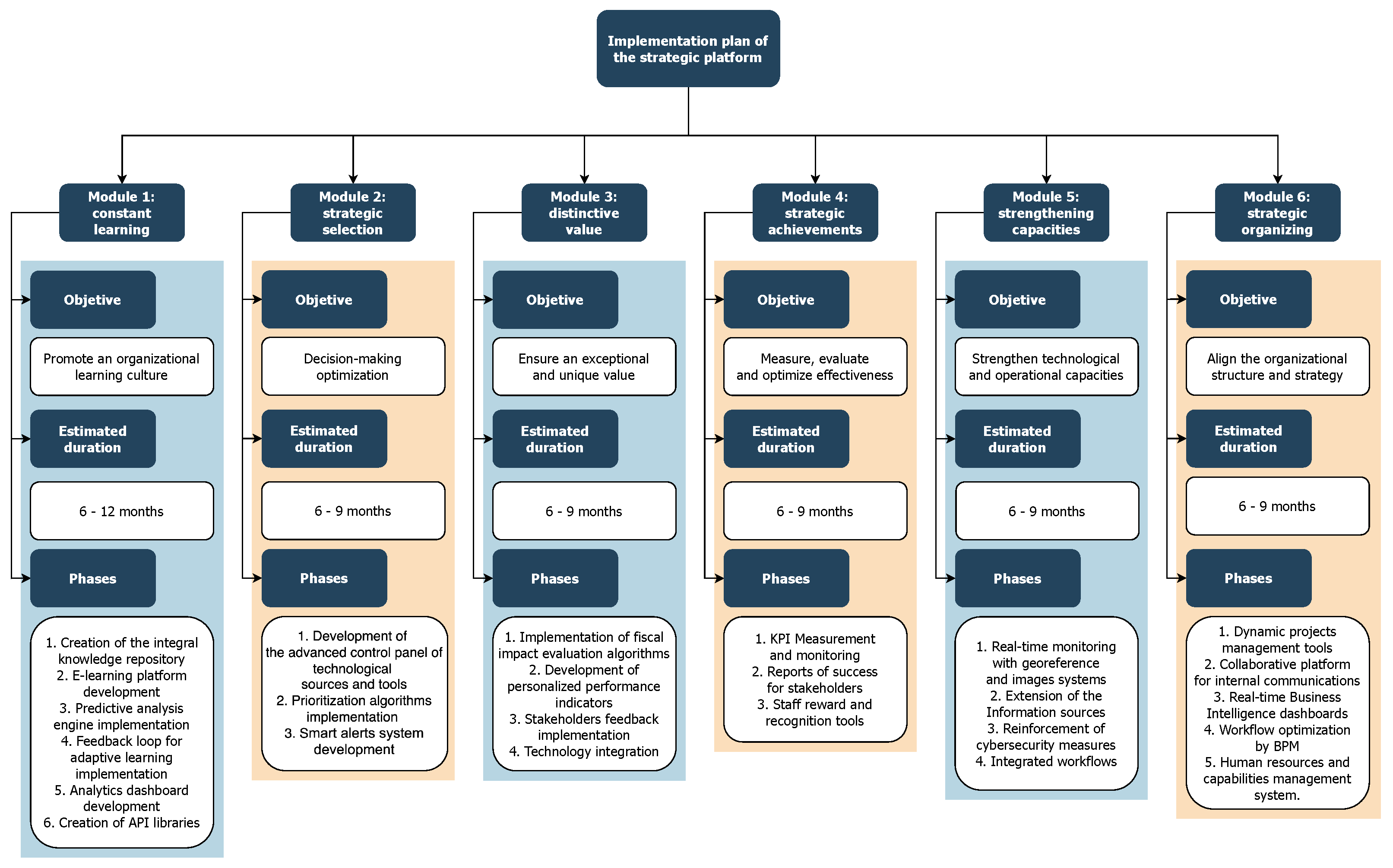
The prototype of the strategic platform developed for the Directorate of Information, Analysis, and Immediate Reaction (DIARI) of the Comptroller General of the Republic (CGR) of Colombia, incorporates an approach of six interconnected functional modules. Each one is designed to achieve specific strategic objectives through the integration of innovative information technologies.
Figure 3 shows the six designed functional modules, their objectives, their key functionalities, and the technologies that can be adapted to them.
4.1. Module 1: Continuous Learning
Aim: to promote a culture of organizational learning that allows DIARI to quickly adapt to changing conditions in fiscal and regulatory matters.
Features: the Comprehensive Knowledge Repository functions as a NoSQL database with advanced search capabilities provided by diverse search engines. This setup enables the structured and accessible storage of documentation, fiscal laws, case studies, and industry trends.
E-Learning Platform: the Learning Management System (LMS) is integrated with the Knowledge Repository to provide adaptive training to staff on fiscal fundamentals, use of data analysis tools, and programming.
Predictive Analysis Engine: machine learning algorithms implemented on diverse platforms are used to analyze patterns in fiscal data and predict potential irregularities and future trends.
Feedback Loop for Adaptive Learning: real-time feedback systems and chatbots are implemented to collect staff evaluations on the effectiveness of implemented strategies and enhance learning processes.
Analytical Dashboard: business intelligence tools are used to display organizational learning metrics, including staff performance and strategy effectiveness.
API Library: a set of APIs is available to easily integrate with external systems and public databases, facilitating collaborative learning.
4.2. Module 2: Strategic Selection
Aim: to optimize decision-making in surveillance and fiscal control through an informed and dynamic selection of data sources and technological tools.
Features: the source and tool selection control panel is designed as a high-capacity user interface, currently implemented and developed using different tools, web development frameworks, and data query and manipulation languages, to efficiently select information sources and technological tools.
Prioritization Algorithms: machine learning models are applied to historical metrics to identify areas prone to irregularities and prioritize actions.
Smart Alert System: the back-end is developed in the cross-platform runtime environment, with the front-end using the bidirectional communication channel to send real-time notifications about significant changes in the fiscal environment. Open-source message brokering software is used for event management.
4.3. Module 3: Distinctive Value
Aim: to ensure that the DIARI generates and delivers exceptional and unique value in its surveillance and fiscal control functions.
Features: for the fiscal impact assessment, machine learning algorithms and cost-benefit analysis are developed to estimate the impact of interventions and predict future benefits.
Performance Indicators: customized Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) in real-time metric control dashboards are used to measure value generation and adjust strategies effectively.
Stakeholder Feedback: stakeholders’ perception classification systems based on natural language processing (NLP) are implemented to assess perception among citizens and stakeholders.
Technology Integration: data consolidation in data lakes, the use of APIs, and security technologies are carried out to enable advanced analysis and protect information.
4.4. Module 4: Strategic Achievements
Objective: to measure, evaluate, and optimize the effectiveness of DIARI’s operations in its mission of surveillance and fiscal control.
Functionalities: for KPI measurement, relevant KPIs are configured, and online analytical processing (OLAP) is implemented to consolidate data and facilitate multidimensional analysis.
Report Generation: data visualization software like Tableau and Power BI are used for the interactive creation of reports and dashboards that assess progress towards strategic objectives.
Recognition Tools: an incentive and gamification system linked to performance KPIs is implemented to motivate and reward staff.
Enabling Technologies: Big Data analytics, cloud computing, and APIs such as RESTful and blockchain are used to ensure scalability, data integrity, and traceability.
4.5. Module 5: Capacity Building
Objective: to strengthen technological, analytical, and operational capabilities for effective real-time monitoring and information integrity.
Functionalities: for georeferenced monitoring, geographic information systems (GIS), IoT sensors, and image processing are integrated for real-time tracking of fiscal projects.
Expanding Information Sources: API connectors, web scraping techniques, and machine learning are used to classify and evaluate new external data sources.
Reinforcing Cybersecurity: multi-factor authentication, data encryption, and SIEM systems are implemented for threat detection and response.
Integrated Workflows: coordination between the Information, Analysis, and Immediate Reaction units for the acquisition, analysis, and efficient use of data.
4.6. Module 6: Strategic Organization
Objective: to align strategy and organizational structure for efficient and effective execution of surveillance and fiscal control responsibilities.
Functionalities: agile project management allows for flexibility and adaptability to environmental needs. Traditional project management offers more detailed planning and a solid methodology. Hybrid project management techniques are used for complex issues, merging elements from both agile and traditional methodologies to enhance their strengths in organizational development.
Internal Communication: an encrypted corporate collaborative platform is used for secure communication, including instant messaging and video conferencing.
Management Dashboards: business intelligence tools are used for the integration of data and real-time metrics, facilitating decision-making.
Process Automation: Business Process Management (BPM) software and business rules are used to optimize and enhance the efficiency of internal workflows.
Talent Management: a system for tracking staff skills and competencies, allowing for better alignment with project requirements.
Collectively, these six functional modules are the core components of the strategic platform developed for DIARI. Through their implementation, DIARI will be able to leverage advanced technologies in data analytics, artificial intelligence, information security, and strategic collaboration. This will enable this CGR’s unit to become a benchmark for innovation in smart fiscal control and public resource management in Colombia and Latin America.
The effective integration of these functional modules will provide DIARI with a more robust and adaptable platform, significantly enhancing its ability to make informed strategic decisions. By working in coordination, these components will ensure agile and secure access to relevant data, facilitate the generation of predictive insights, and optimize internal processes. The successful implementation of this strategic platform will not only increase operational efficiency but also improve the oversight of public resources and strengthen transparency in fiscal control processes. This will establish DIARI as a key player in promoting exemplary governmental practices, raising its profile both nationally and regionally in the responsible management of public resources.
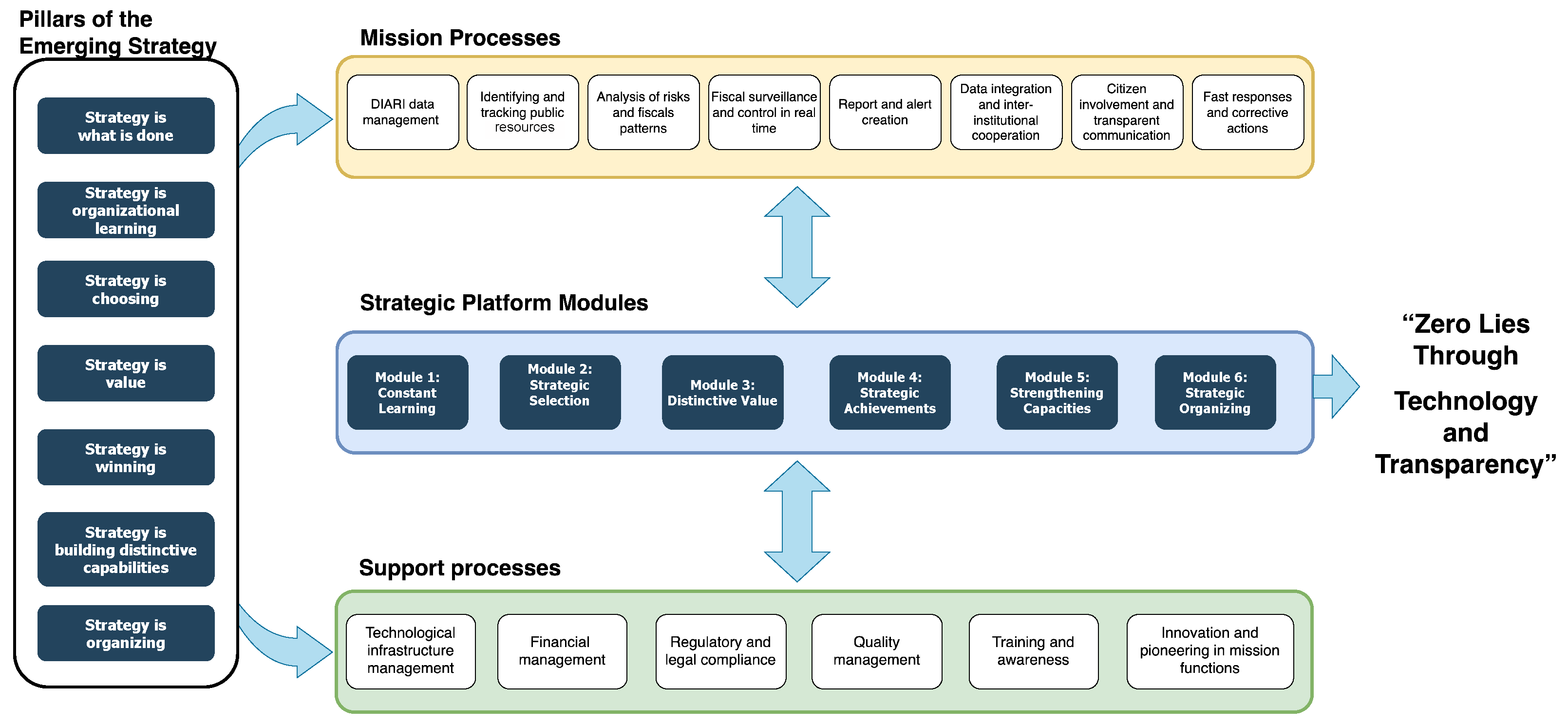
Finally, the modular strategic platform designed through a co-creation process with DIARI provides a viable roadmap for the entity to face the challenges of digital transformation in the coming years of development and grow of smart cities. Although there are significant challenges to overcome, particularly in terms of training and change management, the proposed approach enables an agile, adaptable, and financially sustainable implementation. This platform will serve as the foundation for DIARI to establish itself as a model entity in innovation for fiscal control in Latin America. To detail its strategic architecture,
Figure 4 shows a conceptual map that has been created. This map contains the relationships between the pillars of the Emerging Strategy, Mission-Critical Processes, Strategic Platform Modules, and Support Processes.
5. Discussion
The findings from this research process indicate that the proposal of a modular strategic platform is a promising solution for strengthening the DIARI to address the challenges of its digital transformation and technological modernization process at national level. Through a participatory approach, which included a series of workshops with the entity’s staff and the application of foresight methodologies with experts in technological innovation, it was possible to design a functional module architecture aligned with both the current needs and the future vision of the DIARI.
One of the main strengths of the developed strategic platform lies in its adaptability. Being structured in independent but interconnected modules, it allows for a gradual implementation, enabling the progressive incorporation of new capabilities without compromising existing functionalities. This significantly reduces the risks associated with large-scale digital transformation projects in public sector entities.
Another positive aspect of the developed platform, due to its modularity, is that it facilitates change management within the organization. Modules can be implemented sequentially, allowing teams to gradually adapt to new processes and technologies. Furthermore, the approach based on functional modules encourages greater interdisciplinary collaboration among areas such as technology, operations, and strategy.
Regarding the technologies proposed for each module, the focus has been on scalable, open-source solutions based on standards. This strategy is advantageous as it minimizes licensing costs, reduces dependence on specific vendors, and facilitates the integration of key elements for effective implementation. Additionally, the adoption of flexible architectures, such as microservices and containers, will allow DIARI to quickly adjust its systems to new demands and technological trends.
Compared to previous studies on digital transformation in public expenditure control entities, this proposal for a strategic platform for DIARI presents several innovative elements and stands out as a pioneering initiative in the sector and in the Colombian context. The incorporation of cutting-edge technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and blockchain represents the innovative core of this proposal and is essential for its successful implementation. Innovation goes beyond the technological realm and presents an opportunity to foster greater citizen participation in fiscal oversight through mechanisms of transparency and collaboration embedded within the platform’s functionalities.
Nonetheless, the design of the strategic platform also has some limitations and drawbacks that must be addressed during implementation. A key aspect is the need to strengthen DIARI’s internal capabilities, both in terms of human resources and infrastructure. Overcoming these limitations is crucial and involves hiring highly qualified personnel, training existing staff within the organization, budgeting for, and investing in the improvement of networks, computers, and security systems to support the platform. Additionally, proper data governance and organizational change management will be ongoing and constant challenges throughout the operation time of the strategic platform.
The design of this strategic platform for the DIARI of the CGR holds significant importance both for Smart Cities and Society 5.0. In the context of Smart Cities definitions, efficient management of public expenditure is expected for sustainable development of citizen-centric services. Since the strategic platform uses modern technologies and data analytics, the CGR can enhance transparency, accountability, and decision-making processes related to public expenditure. In the broader context of Society 5.0, where technologies are in the service of society to enhance human capabilities, such a 6-module platform empowers citizens by providing access to information, enhancing trust in public institutions, and facilitating active participation in governance processes.
6. Conclusions
This work addressed the design of strategic modular platform for the smart supervision of public expenditure in Colombia. Considering that an entity can provide society with goods and services to meet the emerging technological and social needs of the environment, especially in a context where any individual can easily access high-quality services and information [
12] regardless of their geographic location, the integration of smart technologies in the supervision of public spending aligns with the vision of the CGR. This enables a more efficient and transparent management of state resources in Colombia.
The strategically designed platform can be considered a turning point in DIARI’s operations, positioning it at the forefront of regional use of advanced technologies for fiscal control and smart supervision. The six interconnected functional modules create a comprehensive and adaptable structure that efficiently integrates technological solutions contributing to the transition from Industry 4.0 to Industry and Society 5.0.
This technological approach not only aims to ensure the availability of goods and services but also to guarantee an equitable and timely distribution of these resources to meet diverse social needs, thus marking a genuine progress toward Society 5.0 in developing countries like Colombia. Thus, the convergence between the vision of an inclusive society and the implementation of smart tools in public spending control lays the foundation for advancing towards a more precise and effective resource management. This aligns with the vision of a robust and equitable society through the implementation plan and design of the strategic platform in the case of the DIARI of the CGR.
Once successfully implemented, this plan will transform DIARI’s ability to protect public resources and combat corruption. The functionalities of real-time monitoring, early detection of irregularities, predictive risk analysis, and process optimization represent quantitative and qualitative leaps in fiscal control. Beyond technical capabilities, this project will position DIARI as a leader in the transparent, ethical, and effective use of cutting-edge technologies for collective well-being. The strategic platform will solidify the institution’s commitment to responsible innovation and become an international model of fiscal control for Society 5.0 and Smart Cities.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.A.R.C., D.A.F., M.S.G., C.A.E., J.S.P., and R.E.V.; methodology, J.A.R.C., D.A.F., M.S.G.; validation, J.A.R.C., J.C.Z., R.M.V., O.M., A.M.H., J.S.P., and R.E.V.; formal analysis, J.A.R.C., D.A.F., M.S.G., C.A.E., J.S.P., and R.E.V.; investigation, J.A.R.C., J.C.Z., R.M.V., D.A.F., M.S.G., L.L., G.G., O.M., A.M.H., C.A.E., J.S.P., and R.E.V.; writing—original draft preparation, J.A.R.C., D.A.F., M.S.G., L.L. and G.G., writing—review and editing, J.A.R.C., J.S.P., and R.E.V.; supervision, J.A.R.C., J.C.Z., R.M.V., C.A.E., J.S.P., and R.E.V. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was developed with the funding of Contraloría General de la República (CGR) and Universidad Nacional de Colombia (UNAL) in the frame of Contract CGR-373-2023, with the support of Universidad Pontificia Bolivariana (UPB).
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| AI |
Artificial Intelligence |
| CGR |
Contraloría General de la República (Office of the Comptroller General of the Republic) |
| DIARI |
Directorate of Information, Analysis, and Immediate Reaction of the CGR |
| DT |
Digital Transformation |
| ICTs |
Information and Communication Technologies |
| IoT |
Internet of things (IoT) |
| IT |
Information Technology |
| KPI |
Key Performance Indicator |
References
- United Nations. State of World Population 2023 - 8 Billion Lives, Infinite Possibilities: The Case for Rights and Choices. techreport, United Nations Population Fund, New York, NY, 2023.
- Bastos, D.; Fernández-Caballero, A.; Pereira, A.; Rocha, N.P. Smart City Applications to Promote Citizen Participation in City Management and Governance: A Systematic Review. Informatics 2022, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Haleem, A.; Javaid, M. Changes and improvements in Industry 5.0: A strategic approach to overcome the challenges of Industry 4.0. Green Technologies and Sustainability 2023, 1, 100020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, L.; Royo, S.; Garcia-Rayado, J. Social media adoption by Audit Institutions. A comparative analysis of Europe and the United States. Government Information Quarterly 2020, 37, 101433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haus, M.; Wehner, J.; de Renzio, P. (When) Do Open Budgets Transform Lives? Progress and Next Steps in Fiscal Openness Research. Open Goverment Partnerchip, Document, 2022.
- Mugellini, G.; Della Bella, S.; Colagrossi, M.; Isenring, G.L.; Killias, M. Public sector reforms and their impact on the level of corruption: A systematic review. Campbell Systematic Reviews 2021, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capasso, S.; Cicatiello, L.; De Simone, E.; Gaeta, G.L.; Mourão, P.R. Fiscal transparency and tax ethics: does better information lead to greater compliance? Journal of Policy Modeling 2021, 43, 1031–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spicker, P. The effect of treating public services as commodities. Public Money & Management 2024, 44, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Wang, B.; Li, X.; Zheng, P.; Mourtzis, D.; Wang, L. Industry 5.0 and Society 5.0—Comparison, complementation and co-evolution. Journal of Manufacturing Systems 2022, 64, 424–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghobakhloo, M.; Iranmanesh, M.; Mubarak, M.F.; Mubarik, M.; Rejeb, A.; Nilashi, M. Identifying industry 5.0 contributions to sustainable development: A strategy roadmap for delivering sustainability values. Sustainable Production and Consumption 2022, 33, 716–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziatdinov, R.; Atteraya, M.S.; Nabiyev, R. The Fifth Industrial Revolution as a Transformative Step towards Society 5.0. Societies 2024, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranda López, N.; Hoyos Raigosa, P. El líder de la sociedad 5.0, 2020.
- Çipi, A.; Fernandes, A.C.R.; Ferreira, F.A.; Ferreira, N.C.; Meidutė-Kavaliauskienė, I. Detecting and developing new business opportunities in society 5.0 contexts: A sociotechnical approach. Technology in Society 2023, 73, 102243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martí, C. Performance Budgeting and Medium-Term Expenditure Frameworks: A Comparison in OECD Central Governments. Journal of Comparative Policy Analysis: Research and Practice 2019, 21, 313–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piatti-Funfkirchen, M.; Hashim, A.; Farooq, K. Balancing Control and Flexibility in Public Expenditure Management: Using Banking Sector Innovations for Improved Expenditure Control and Effective Service Delivery. techreport 9029, World Bank, 2019.
- Albassam, B.A. A model for assessing the efficiency of government expenditure. Cogent Economics & Finance 2020, 8, 1823065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.A.N.; Luong, T.T.H. Fiscal Policy, Institutional Quality, and Public Debt: Evidence from Transition Countries. Sustainability 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onofrei, M.; Toader, T.; Vatamanu, A.F.; Oprea, F. Impact of Governments’ Fiscal Behaviors on Public Finance Sustainability: A Comparative Study. Sustainability 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barateiro, C.; Faria, A.; Farias Filho, J.; Maggessi, K.; Makarovsky, C. Fiscal Measurement and Oil and Gas Production Market: Increasing Reliability Using Blockchain Technology. Applied Sciences 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, K. Taxation of Fiat Money Using Dynamic Control. Systems 2022, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Li, D. How does Technological Innovation Affect the Fiscal Decentralisation of Local Governments? Evidence from China. Heliyon, 2024; e30132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atabekov, A. Artificial Intelligence in Contemporary Societies: Legal Status and Definition, Implementation in Public Sector across Various Countries. Social Sciences 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, P.M.A.R.; Pedro, R.L.D.; Mendes, I.d.O.; Serra, A.D.C.S. The Challenges of Artificial Intelligence in Public Administration in the Framework of Smart Cities: Reflections and Legal Issues. Social Sciences 2024, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanishi, H.; Kitano, H. Society 5.0 Co-Creating the future, 2018.
- Presidencia de la República de Colombia. Decreto Ley 403 de 2020. Available online: https://www.funcionpublica.gov.co/eva/gestornormativo/norma.php?i=110374 (accessed on april 2024)., 2020.
- García-Valencia, O.L. Modelo de gobierno de seguridad de la información para la Contraloría General de la República de Colombia, 2019.
- Departamento Nacional de Planeación. Documento Conpes 3975 Política Nacional para la Transformación Digital e Inteligencia Artificial. Available online: https://colaboracion.dnp.gov.co/CDT/Conpes/Econ%C3%B3micos/3975.pdf (accessed on april 2024)., 2019.
- Pinilla-Cárdenas, D.F. Desafíos del Control Fiscal para combatir la corrupción en Colombia, 2021.
- Márquez-Alzate, L.F.; Muñoz-Muñoz, C.; Restrepo-Gómez, A.J.; González-Quintero, C.P.; Fernández-Osorio, C.P. Plan Estratégico 2020-2021, Vigilancia Fiscal Hacia La Auditoría Continua, Contraloría General Del Quindío, 2020.
- Abadia-Benitez, L. Plan Estratégico Contraloría Departamental del Valle del Cauca 2020 – 2021 Version II, 2020.
- Erazo-Montenegro, A.C. Plan Estratégico Institucional 2020 – 2023, Auditoría General De La República, 2020.
- Castro, C. Plan Estrategico Institucional Control Fiscal Nuestro Compromiso Social 2022-2025, 2022.
- Ruvalcaba-Gomez, E.A.; Cifuentes-Faura, J. Analysis of the perception of digital government and artificial intelligence in the public sector in Jalisco, Mexico. International Review of Administrative Sciences 2023, 0, 208523231164587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eom, S.J.; Lee, J. Digital government transformation in turbulent times: Responses, challenges, and future direction. Government Information Quarterly 2022, 39, 101690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, D.; Huth, T.; Vietor, T. Development of an Industry 4.0 method and knowledge platform for strategic technology implementation. Procedia CIRP 2021, 100, 613–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svec, J. Optimal fiscal policy with robust control. Journal of Economic Dynamics and Control 2012, 36, 349–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Gracias, J.; Parnell, G.S.; Specking, E.; Pohl, E.A.; Buchanan, R. Smart Cities—A Structured Literature Review. Smart Cities 2023, 6, 1719–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, K.; Hajrizi, E. Building Pillars for Adapting Society 5.0 in Post-Conflict Countries. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2019, 52, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar-Yusti, A. La Estrategia Emergente y la Muerte del Plan Estratégico; La Estrategia Emergente, 2020. El ISBN es real pero JabRef no lo lee bien.
- Sun, M.; Zhang, J. Research on the application of block chain big data platform in the construction of new smart city for low carbon emission and green environment. Computer Communications 2020, 149, 332–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, M.; Zabala, S.; Bellorin, O.P. Technology management model for Venezuelan municipalities. Proceedings of the 6th Euro American Conference on Telematics and Information Systems; ACM - Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2012; EATIS ’12, pp. 57–64. [CrossRef]
- Giuseppe Iuliano, B.C.B.; Bisogno, M. Citizens’ e-participation in the digital world: empirical insights from Europe. Public Money & Management 2024, 0, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerman, G.; Calméjane, C.; Bonnet, B.; Ferraris, P.; McAfee, A. Digital Transformation: A roadmap for billion-dollar organizations. MIT Center for digital business and capgemini consulting 2011, 1, 1–68. [Google Scholar]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).