Submitted:
27 June 2024
Posted:
29 June 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Methods
Design
Survey Instrument
Statistical Analysis
Ethical Considerations
Results
Sample Demographics and Baseline Characteristics
Questionnaire Items
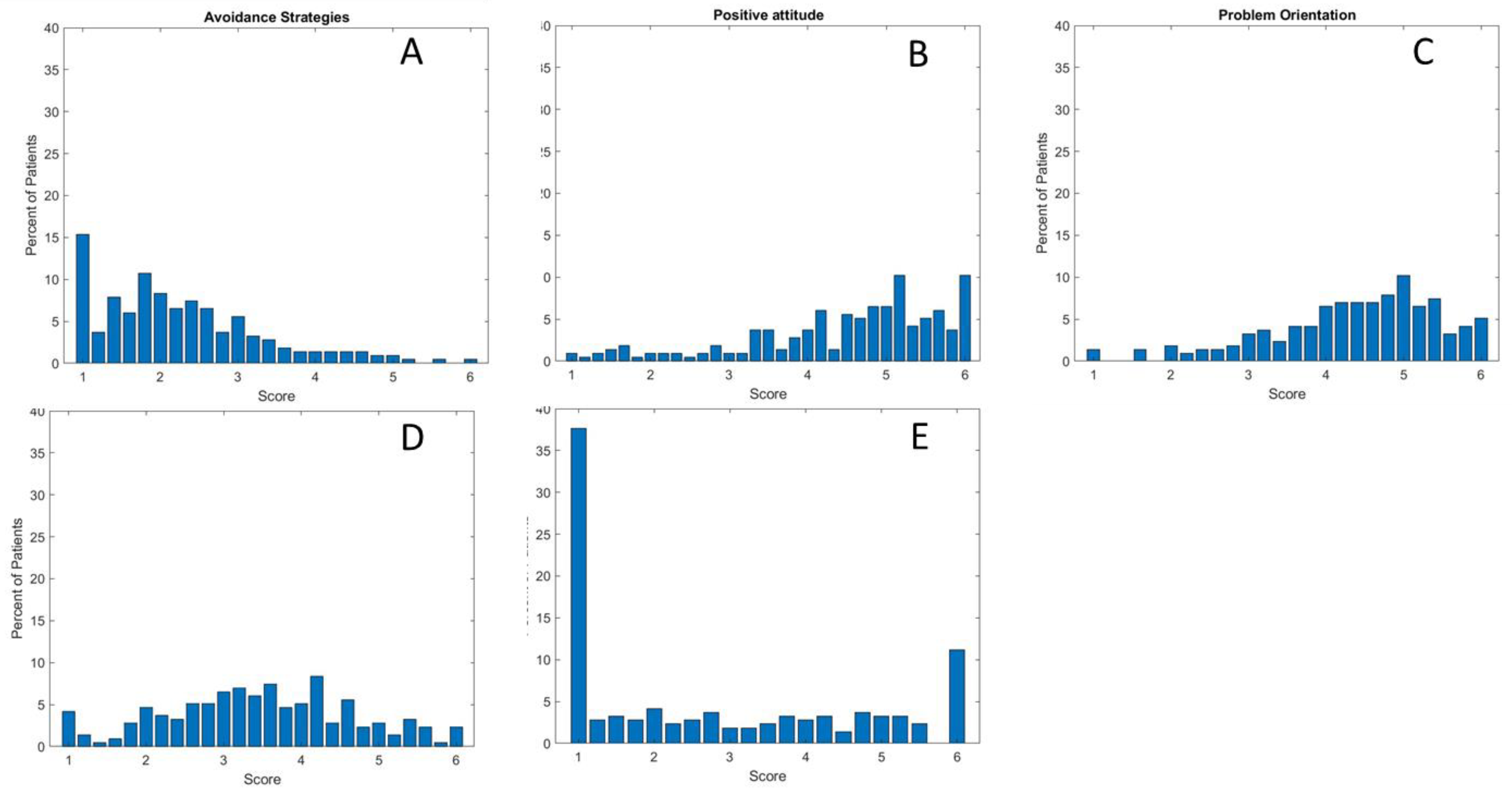
COPE Score Analysis
Discussion
Limits
Conclusions
Consent for publication:
Availability of data and materials:
Ethics approval:
Conflicts of interest:
Code availability:
Funding
References
- Conti-Fine, B.M.; Milani, M.; Kaminski, H.J. Myasthenia Gravis: Past, Present, and Future. J. Clin. Invest. 2006, 116, 2843–2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dresser, L.; Wlodarski, R.; Rezania, K.; Soliven, B. Myasthenia Gravis: Epidemiology, Pathophysiology and Clinical Manifestations. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayanaswami, P.; Sanders, D.B.; Wolfe, G.; Benatar, M.; Cea, G.; Evoli, A.; Gilhus, N.E.; Illa, I.; Kuntz, N.L.; Massey, J.; et al. International Consensus Guidance for Management of Myasthenia Gravis: 2020 Update. Neurology 2021, 96, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilhus, N.E.; Tzartos, S.; Evoli, A.; Palace, J.; Burns, T.M.; Verschuuren, J.J.G.M. Myasthenia Gravis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2019, 5, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdan, A.; Barnett, C.; Ali, A.; AlQwaifly, M.; Abraham, A.; Mannan, S.; Ng, E.; Bril, V. Chronic Stress, Depression and Personality Type in Patients with Myasthenia Gravis. Eur. J. Neurol. 2020, 27, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Law, N.; Davio, K.; Blunck, M.; Lobban, D.; Seddik, K. The Lived Experience of Myasthenia Gravis: A Patient-Led Analysis. Neurol. Ther. 2021, 10, 1103–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carriero, M.C.; Conte, L.; Calignano, M.; Lupo, R.; Calabrò, A.; Santoro, P.; Artioli, G.; Caldararo, C.; Ercolani, M.; Carvello, M.; et al. The Psychological Impact of the Coronavirus Emergency on Physicians and Nurses: An Italian Observational Study. Acta Biomed. 2021, 92, e2021030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitale, E.; Conte, L.; Dell’Aglio, A.; Calabrò, A.; Ilari, F.; Bardone, L.; Benedetto, A.; Caldararo, C.; Zacchino, S.; Lezzi, A.; et al. Healthcare Workers Perceptions in the Difficult Moment of the End of Life and Coping Strategies Adopted during the COVID-19 Pandemic: An Italian Pilot Study. Acta Biomed. 2021, 92, e2021330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupo, R.; Vitale, E.; Panzanaro, L.; Lezzi, A.; Lezzi, P.; Botti, S.; Rubbi, I.; Carvello, M.; Calabrò, A.; Puglia, A.; et al. Effects of Long COVID on Psycho-Physical Conditions in the Italian Population: A Statistical and Large Language Model Combined Description. Eur. J. Investig. Heal. Psychol. Educ. 2024, 14, 1153–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadali, J.; Ghavampour, N.; Beiranvand, F.; Maleki Takhtegahi, M.; Heidari, M.E.; Salarvand, S.; Arabzadeh, T.; Narimani Charan, O. Prevalence of Depression and Anxiety among Myasthenia Gravis (MG) Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Brain Behav. 2023, 13, e2840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stojanov, A.; Milošević, V.; Đorđević, G.; Stojanov, J. Quality of Life of Myasthenia Gravis Patients in Regard to Epidemiological and Clinical Characteristics of the Disease. Neurologist 2019, 24, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilhus, N.E.; Verschuuren, J.J.G.M.; Hovland, S.I.B.; Simmonds, H.; Groot, F.; Palace, J. Myasthenia Gravis: Do Not Forget the Patient Perspective. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2021, 31, 1287–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, R.H.; Mullins, L.L.; Gilchrist, J.M. The Impact of Myasthenia Gravis on Mood, Cognitive Function, and Quality of Life. In Myasthenia Gravis and Related Disorders; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, 2009; pp. 279–292. [Google Scholar]
- Tascilar, N.F.; Saracli, O.; Kurcer, M.A.; Ankarali, H.; Emre, U. Is There Any Relationship between Quality of Life and Polysomnographically Detected Sleep Parameters/Disorders in Stable Myasthenia Gravis? Acta Neurol. Belg. 2018, 118, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihalache, O.A.; Vilciu, C.; Petrescu, D.-M.; Petrescu, C.; Manea, M.C.; Ciobanu, A.M.; Ciobanu, C.A.; Popa-Velea, O.; Riga, S. Depression: A Contributing Factor to the Clinical Course in Myasthenia Gravis Patients. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marbin, D.; Piper, S.K.; Lehnerer, S.; Harms, U.; Meisel, A. Mental Health in Myasthenia Gravis Patients and Its Impact on Caregiver Burden. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 19275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrugia, M.E.; Goodfellow, J.A. A Practical Approach to Managing Patients With Myasthenia Gravis—Opinions and a Review of the Literature. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciceri, M.R.; Anolli, L.M. La Voce Delle Emozioni. Verso Una Semiosi Della Comunicazione Vocale Non-Verbale Delle Emozioni.; Angeli, F., Ed.; IV Edition.; Milano 2000. 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Nunnally, J. Psychometric Theory; Co, M.-H.B., Ed.; 2nd ed. Ne.; 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Caricati, L.; Foà, C.; Fruggeri, L.; Tonarelli, A. COPE-NVI-25: Validazione Italiana Della Versione Ridotta Della Coping Orientation to the Problems Experienced (COPE-NVI). Psicol. DELLA Salut. 2015, 123–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suñer, R.; Mascort, Z. [Evaluation of Nursing Care in Patients with Myasthenia Gravis]. Rev. Neurol. 1997, 25, 255–256. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hohls, J.K.; König, H.-H.; Quirke, E.; Hajek, A. Anxiety, Depression and Quality of Life—A Systematic Review of Evidence from Longitudinal Observational Studies. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 12022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Qian, X.; Chen, Z.; He, T. Health Literacy and Its Effect on Chronic Disease Prevention: Evidence from China’s Data. BMC Public Health 2020, 20, 690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
BASELINE CHARACTERISTICS |
N |
% |
|---|---|---|
| Socio-demographics | ||
|
Gender Female Male |
178 37 |
83 17 |
|
Age Range Mean SD |
19-82 46.17 14.59 |
|
| Nationality |
152 63 |
71 29 |
| Italians Non-Italians | ||
| Married status |
137 66 10 2 |
64 31 5 1 |
| Married Single/Celibate Separated/Divorced Widower | ||
|
Level of education No title |
4 |
2 |
| Lower secondary school certificate Higher Diploma Degree Postgraduate training |
14 73 76 48 |
7 34 35 22 |
| Employment status |
31 62 33 33 32 17 7 |
14 29 15 15 15 8 3 |
| Civil servant Private employee Freelancer Unemployed Retired Student Invalid | ||
| N | % | |
|---|---|---|
| Before your diagnosis, had you ever heard of MG? |
179 36 |
83 17 |
| No Yes | ||
| If you answered YES to the previous question, in which field did you hear about it? |
0 0 15 19 181 2 0 9 7 197 1 2 9 12 191 0 0 7 11 197 |
0 0 7 9 84 1 0 4 3 92 0 1 4 6 89 0 0 3 5 92 |
|
MASS MEDIA Always Often Occasionally Rarely Never FAMILY Always Often Occasionally Rarely Never SCHOOL Always Often Occasionally Rarely Never FRIENDS Always Often Occasionally Rarely Never SANITARY | ||
| Always Often Occasionally Rarely Never |
4 0 20 28 163 |
2 0 9 13 76 |
|
For the management of the condition, have you ever received health education from the nurse practitioner at the outpatient clinic you go to? No Yes |
155 60 |
72 28 |
|
Have you ever received home health education from the nursing professional? No Yes |
198 17 |
92 8 |
|
In the outpatient clinic, does the nurse advise you on what strategies to implement on a daily basis and whether there are alternative solutions to alleviate your symptoms? No Yes |
173 42 |
80 20 |
|
In your opinion, is MG still an unknown or under-recognised pathology compared to other diseases? No Yes In part |
4 175 36 |
2 81 17 |
|
Do you believe that new forms of telecommunication can help to better manage MG- related problems? No Yes |
11 204 |
5 95 |
| N | % | |
|---|---|---|
|
Do you live alone? No Yes Yes, but I have children/neighbours who help me |
186 24 5 |
87 11 2 |
|
Are you autonomous? Yes but only at home, while I need help going out Yes, I am completely autonomous No, I totally need help No I need help in part |
19 142 24 30 |
9 66 11 14 |
|
To move around, do you need an aid? No, I don’t need anything Yes, I use the stick Yes, I use the wheelchair Yes, I use the walker |
174 23 10 8 |
81 11 5 4 |
|
What signs and symptoms did you experience in the early phase of the disease (more than one answer possible) Unsteady gait Blurred or double vision Eyelid ptosis Limb weakness Difficulty breathing Nothing |
67 145 138 142 81 6 |
31 67 64 66 38 3 |
|
Do you attend a centre and/or outpatient clinic that deals with the disease? No Yes In part |
27 156 32 |
13 73 15 |
| If you attend the centre and/or clinic, are you satisfied with the care you receive? |
29 114 71 1 |
13 53 33 0 |
| No Yes In part missing | ||
| Do you think that your life will now burden your family’s? |
40 89 |
19 41 |
| No Yes |
| ChatGPT-found categories: | ChatGPT Summary of Results | |
|---|---|---|
| If you find the treatments you are receiving unsatisfactory, can you indicate the reasons why? |
Improvement of Therapies and Treatments:
|
Questionnaire participants expressed a range of suggestions and opinions regarding the management of MG. The majority emphasized the importance of personalized therapies, including alternative treatments and experimental interventions. Furthermore, they highlighted the need for open and collaborative communication with medical professionals, emphasizing active listening and psychological support. A common theme was the lack of information about the disease, with a call for greater awareness campaigns and education for both medical professionals and the general public. Participants stressed the significance of swift and accurate diagnosis, along with improved access to specialized tests and therapies. The social and economic dimensions emerged as relevant factors, with requests for increased financial support and legal recognition for patients. Participants also indicated the need for patient support networks and groups, in addition to underscoring the importance of a multidisciplinary approach to treatment. Overall, the responses underscore the importance of a holistic approach to managing MG, encompassing personalized therapies, effective communication, accurate information, and adequate social and economic support. |
| Write freely what you would recommend or believe is essential to change in the management of the disease |
Therapies and Treatments:
|
In the collected responses, a series of key points and suggestions for improving the management of MG emerge: Patients are calling for a more targeted and personalized approach to therapy, taking into account the variation in symptoms and their severity among patients. There is hope for a more effective therapy and the provision of innovative and personalized therapeutic options. Improving access to exams and treatments is a crucial aspect, reducing wait times for diagnoses and treatments. This could be facilitated through the implementation of specialized centers and the creation of medical support networks. A greater understanding of the disease among doctors from various specialties is requested, as well as better training for primary care physicians to promptly recognize symptoms and initiate the diagnostic process. The desire for better communication and interaction between doctors and patients is evident, with increased patient involvement in the decision-making process and greater attention to their needs. Psychological support, both in the form of therapy and counseling, is considered important for addressing the emotional aspects of the disease. Patients want to be treated with humanity and sensitivity by healthcare providers. Information and awareness are deemed crucial for both patients and society at large. MG is often poorly understood, so increased awareness could help combat ignorance and promote better understanding. Work-related concerns are evident, with requests for workplace support and potential adjustments to working conditions. Access to experimental treatments and alternative therapies is an interest, emphasizing the need for diverse therapeutic options. Lastly, patients desire to be treated with respect, understanding, and attention by medical staff, and they hope that the disease will be recognized as disabling to facilitate legal and social support. These suggestions and patient desires reflect the importance of a comprehensive and personalized approach to managing MG, aiming to improve patients’ quality of life and ensure adequate support in all aspects of their battle against the disease. |
|
COPE-NVI-25 QUESTIONNAIRE ITEMS |
N |
% |
|---|---|---|
|
1. I try to get advice from someone on what to do 1 2 3 4 5 6 |
32 25 49 39 34 36 |
15 12 23 18 16 17 |
|
2. I learn to live with the problem 1 2 3 4 5 6 |
10 10 24 25 51 95 |
5 5 11 12 24 44 |
|
3. I concentrate on dealing with this problem and, if necessary, put other things aside 1 2 3 4 5 6 |
14 17 45 49 45 45 |
7 8 21 23 21 21 |
|
4. I do not put much effort into solving the problem 1 2 3 4 5 6 |
101 37 33 21 13 10 |
47 17 15 10 6 5 |
|
5. I try to prevent other things from interfering with my coping efforts 1 2 3 4 5 6 |
17 22 42 50 42 42 |
8 10 20 23 20 20 |
|
6. I look for something positive in what happened 1 2 3 4 5 6 |
27 18 25 41 41 63 |
13 8 12 19 19 29 |
|
7. I refuse to believe that this happened 1 2 3 4 5 6 |
121 33 21 17 9 14 |
56 15 10 8 4 7 |
|
8. Seeking help in God 1 2 3 4 5 6 |
96 13 18 23 17 48 |
45 6 8 11 8 22 |
|
9. I do what needs to be done, one step at a time 1 2 3 4 5 6 |
8 7 16 33 54 97 |
4 3 7 15 25 45 |
|
10. I talk to someone to do something concrete to solve the problem 1 2 3 4 5 6 |
33 17 41 34 40 50 |
15 8 19 16 19 23 |
|
11. I pray more than usual 1 2 3 4 5 6 |
104 17 32 28 7 27 |
48 8 15 13 3 13 |
|
12. I try to learn something from experience 1 2 3 4 5 6 |
13 13 26 28 51 84 |
6 6 12 13 24 39 |
|
13. I make every effort to act on the situation 1 2 3 4 5 6 |
7 7 24 33 55 89 |
3 3 11 15 26 41 |
|
14. I try to find solace in my religion 1 2 3 4 5 6 |
102 20 20 23 13 37 |
47 9 9 11 6 7 |
|
15. I ask people how they have acted when faced with similar experiences 1 2 3 4 5 6 |
33 32 38 49 28 35 |
15 15 18 23 13 16 |
|
16. I try to use this experience to grow as a person 1 2 3 4 5 6 |
16 11 29 33 48 78 |
7 5 13 15 22 36 |
|
17. I act as if it never happened 1 2 3 4 5 6 |
101 35 31 23 12 13 |
47 16 14 11 6 6 |
|
18. Seeking moral support from friends and relatives 1 2 3 4 5 6 |
53 31 40 33 34 24 |
25 14 19 15 16 11 |
|
19. I put my hope in God 1 2 3 4 5 6 |
95 24 19 20 15 42 |
44 11 9 9 7 20 |
|
20. I think hard about what moves to make to deal with the problem 1 2 3 4 5 6 |
19 15 39 48 39 55 |
9 7 18 22 18 26 |
|
21. I recognise that I cannot do anything about it and abandon all attempts to act 1 2 3 4 5 6 |
115 41 27 13 4 15 |
53 19 13 6 2 7 |
|
22. I tend to fantasise to distract myself 1 2 3 4 5 6 |
80 35 35 30 23 12 |
37 16 16 14 11 6 |
|
23. I accept the reality of the facts 1 2 3 4 5 6 |
15 13 20 39 48 80 |
7 6 9 18 22 37 |
|
24. Trying to get used to the idea that this happened 1 2 3 4 5 6 |
12 13 21 47 51 71 |
6 6 10 22 24 33 |
|
25. Seeking someone’s understanding and solidarity 1 2 3 4 5 6 |
49 34 38 41 28 25 |
23 16 18 19 13 12 |
| Subscale COPE-NVI-25 |
No. of items | Score |
95% CI | Median | SD | % floor† | % ceiling‡ | Skewness | Cronbach’s α* Total items = 0.87 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Avoidance_Strategies | 5 | 2.25 | 2.25-2.26 | 1.6 | 0.0501 | 9.64 | 1.19 | 1.07 | 0.71 |
| Transcendent_Orientation | 4 | 2.75 | 2.75-2.77 | 2 | 0.12 | 11.54 | 4.48 | 0.59 | 0.96 |
| Positive Attitude | 6 | 4.50 | 4.50-4.51 | 0.093 | 1.57 | 1.20 | 6.09 | -0.84 | 0.88 |
| Social Support | 5 | 3.54 | 3.46-3.46 | 3.6 | 0.036 | 3.72 | 3.16 | -0.00403 | 0.76 |
| Problem Orientation | 5 | 4.36 | 4.36-4.37 | 4.4 | 0.104 | 1.21 | 6.10 | -0.68 | 0.81 |
|
µ±s.d |
COPE-NVI-25 subscales p-value |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| COPE-NVI-25/ Socio-demographic characteristics |
Avoidance Strategies |
Transcendent Orientation |
Positive attitude | Social Support | Problem Orientation |
|
|
Gender Female Male |
112.1 ± 61.8 88 ± 60.8 |
0.315 |
0.468 |
0.755 |
0.476 |
0.722 |
|
Age <20 20-30 31-40 41-50 51-60 61-70 71-80 >81 |
93.3 ± 40.2 100.8 ± 71.5 90.09 ± 64.9 110.31 ± 3.26 115.37 ± 53.2 119.3 ± 62.04 109.2 ± 50.7 130.5 ± 14.8 |
0.209 |
0.545 |
0.334 |
0.260 |
<0.05* |
|
Geographic area Argentina Australia Bulgaria Canada Egitto Germania Giordania Grecia India Inghilterra Italia Libia Macedonia Malta Paesi Bassi Portorico Scozia Sud Africa USA |
186.5 ± 0.7 179.5 ± 17.6 193 ± 0 204 ± 0 164 ± 0 171 ± 0 179 ± 0 194.3 ± 18.9 190.6 ± 22.5 185 ± 14.1 77.3 ± 45.7 177 ± 0 185.6 ± 29.5 111 ± 0 185.5 ± 3.5 200 ± 0 182 ± 23.06 174.5 ± 28.9 181.06 ± 20.01 |
0.895 |
<0.01* |
0.841 |
0.566 |
0.786 |
|
Level of education No title Lower secondary school Higher Diploma Degree Postgraduate training |
88.2 ± 39.8 84.6 ± 48.7 78.9 ± 49.9 111.5 ± 4.3 155.06 ± 51.4 |
0.09 |
0.608 |
0.772 |
0.200 |
0.775 |
|
Employment status Employee Freelancer Student Retired Unemployed |
125.6 ± 63.09 96.6 ± 59.3 96.5 ± 62.2 126.5 ± 63.3 93.7 ± 62.8 |
0.362 |
0.08 |
0.837 |
0.560 |
0.428 |
|
Marital status Married Single/Celibate Separated/Divorced Widower |
110.4 ± 59.8 99.07 ± 66.2 131 ± 61.7 122 ± 100.4 |
0.125 |
0.3006 |
0.229 |
0.292 |
0.219 |
|
Before your diagnosis, had you ever heard of MG? No Yes |
103.3 ± 60.7 131 ± 65.01 |
<0.05* |
0.828 |
0.364 |
0.626 |
0.217 |
|
If you answered YES to the previous question, in which field did you hear about it? MASS MEDIA Always Often Occasionally Rarely Never FAMILY Always Often Occasionally Rarely Never SCHOOL Always Often Occasionally Rarely Never FRIENDS Always Often Occasionally Rarely Never HEALTHCARE SECTOR Always Often Occasionally Rarely Never |
0 0 84.7 ± 49.8 114.7 ± 70.6 106.01 ± 61.2 133.5 ± 37.4 0 89 ± 39.8 81.8 ± 74.3 107.3 ± 62.1 71 ± 0 190 ± 11.3 134 ± 0 136.6 ± 65.05 102.1 ± 60.5 0 0 128.7 ± 15.9 103.1 ± 72.7 106.7 ± 62.01 111.5 ± 30.1 0 80.3 ± 40.5 126.9 ± 63.6 102.3 ± 61.8 |
0.253 0.409 0.552 0.400 0.07 |
0.01** 0.109 <0.05* 0.258 0.403 |
0.905 0.348 <0.05* 0.222 0.267 |
0.483 0.349 <0.05* 0.423 0.305 |
0.523 0.199 <0.01* <0.05* 0.287 |
|
Have you ever received home health education from the nursing professional? No Yes |
111.4 ± 61.6 99.08 ± 63.3 |
0.07 |
0.203 |
0.435 |
0.09 |
0.345 |
|
Have you ever received home health education from the nursing professional? No Yes |
104.7 ± 61.8 146.5 ± 53.8 |
0.06 |
<0.05* |
0.332 |
<0.001*** |
0.05* |
|
In the outpatient clinic, does the nurse advise you on what strategies to implement on a daily basis and whether there are alternative solutions to alleviate your symptoms? No Yes |
108.1 ± 61.2 107.5 ± 66.8 |
<0.05* |
0.334 |
0.289 |
0.114 |
0.874 |
|
Are you autonomous? No, I totally need help No, I need help in part Yes |
93.6 ± 62.2 164.7 ± 36.05 103.3 ± 60.8 |
0.759 |
<0.05* |
0.429 |
0.01** |
<0.05* |
| Dependent variable |
Independent variable | R2 | R2 adj | F-statistic | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Avoiding strategies |
Prior to diagnosis, had you ever heard of MG In the outpatient clinic, does the nurse advise you on strategies to alleviate your symptoms? |
0.04 | 0.03 | 4.82 | <0.01** |
|
Transcendent Orientation |
Geographical area Heard about in the media Heard at School Have you ever received home health education? Autonomy |
0.07 | 0.05 | 3.38 | <0.01** |
| Positive attitude | Heard at School |
0.0004 | -0.004 | 0.09 | 0.761 |
| Social Support | Heard at School Have you ever received home health education? Autonomy |
0.05 | 0.04 | 3.9 | <0.01** |
|
Problem Orientation |
Age Heard at School Sentito parlare da Amici Have you ever received home health education? Autonomy |
0.03 | 0.01 | 1.58 | 0.168 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





