Submitted:
28 June 2024
Posted:
01 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
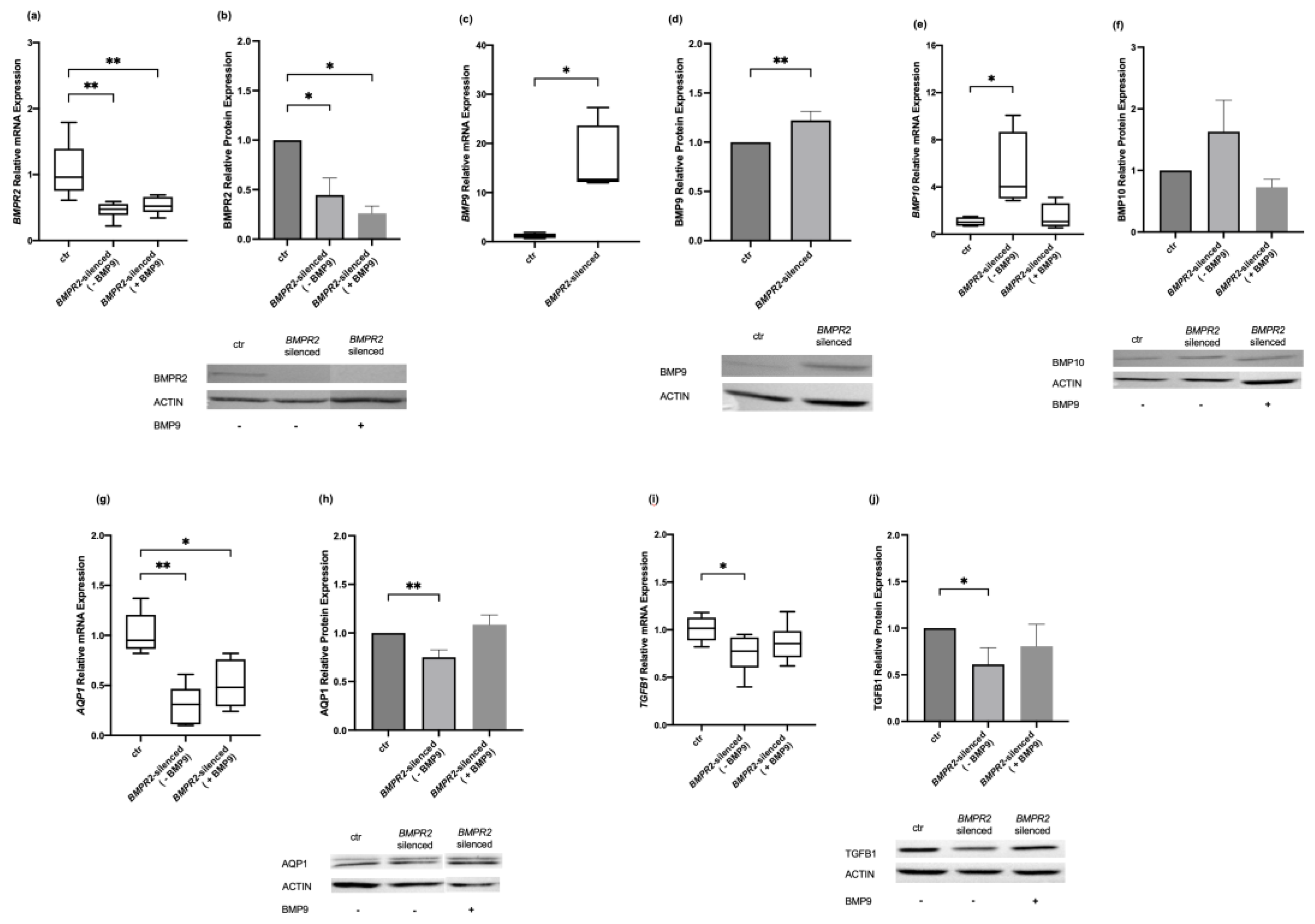
2.1. Effects of Modulating BMPR2 and BMP9 on BMP-Signaling Molecules in Human Pulmonary Microvascular Endothelial Cells
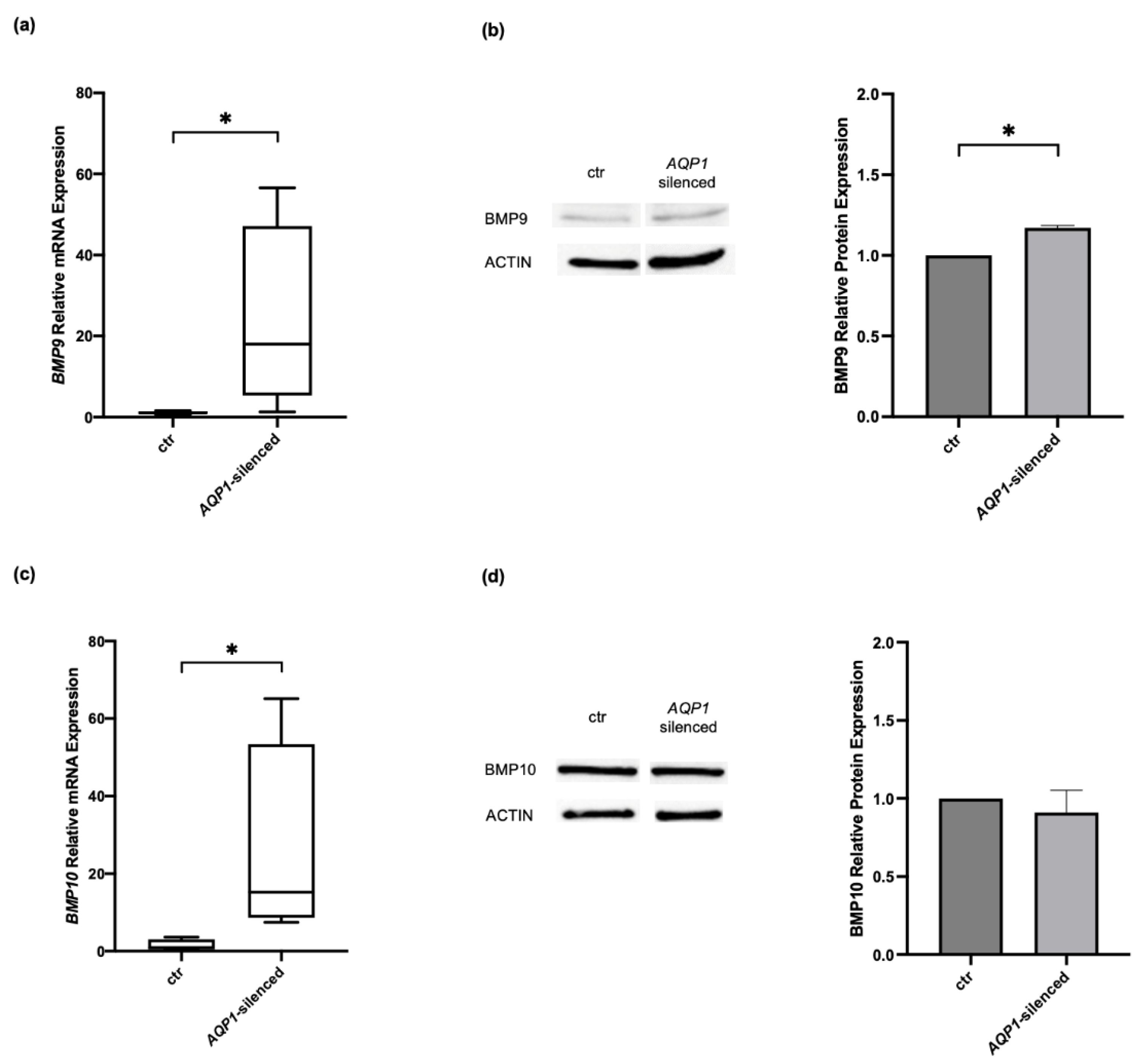
2.2. Effects of Modulating AQP1 on BMP-Signaling Molecules in Human Pulmonary Microvascular Endothelial Cells
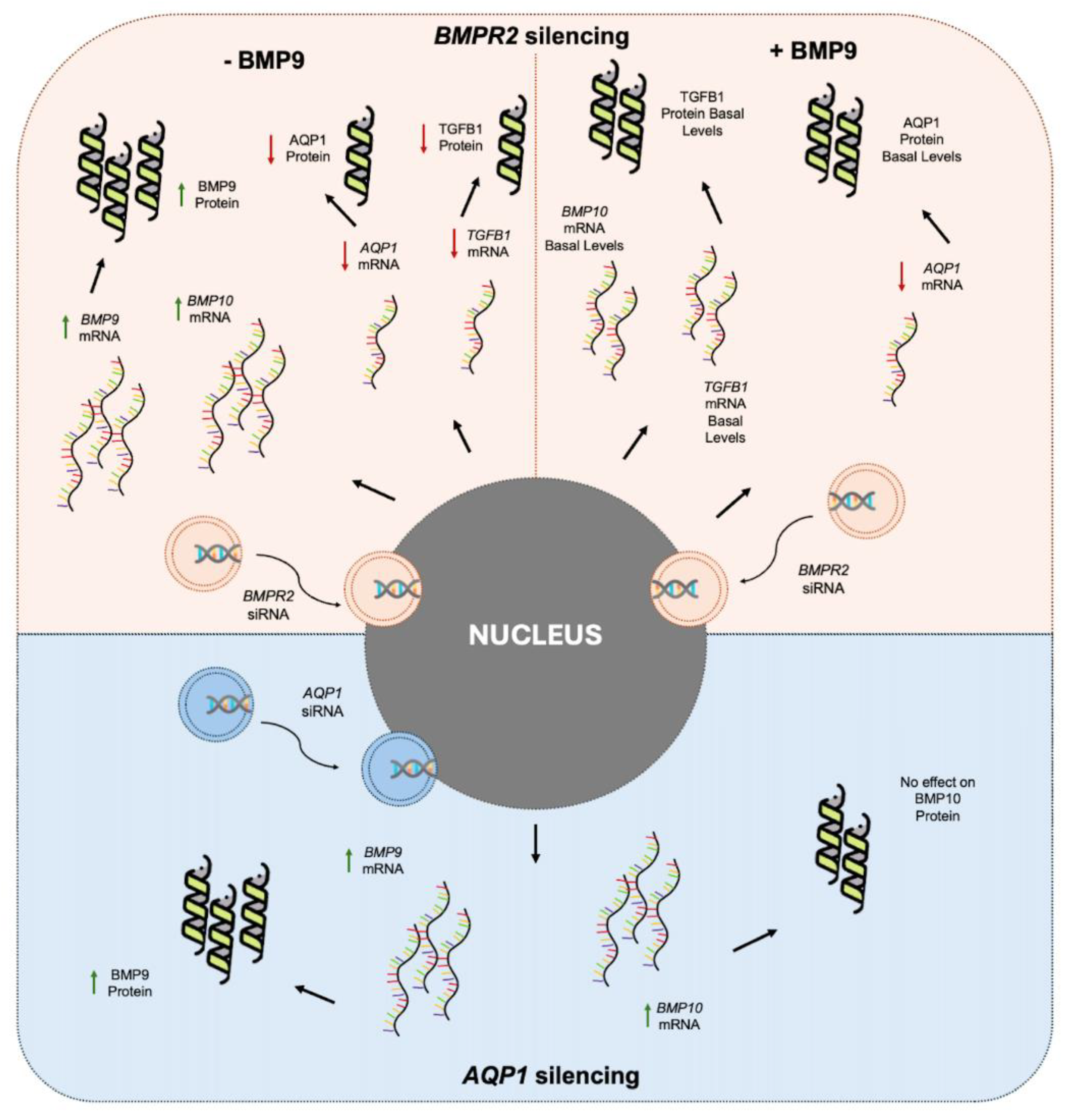
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. Transfection in Human Pulmonary Microvascular Endothelial Cells
4.3. BMP9 treatment of Human Pulmonary Microvascular Endothelial Cells
4.4. RNA Extraction
4.5. Reverse Transcription and Quantitative Real-Time PCR
4.6. Protein Determination
4.7. SDS-Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (PAGE) and Immunoblotting of Human Pulmonary Microvascular Endothelial Cells’ Homogenates
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Simonneau, G.; Montani, D.; Celermajer, D.S.; Denton, C.P.; Gatzoulis, M.A.; Krowka, M.; Williams, P.G.; Souza, R. Haemodynamic definitions and updated clinical classification of pulmonary hypertension. Eur Respir J 2019, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunmore, B.J.; Jones, R.J.; Toshner, M.R.; Upton, P.D.; Morrell, N.W. Approaches to treat pulmonary arterial hypertension by targeting BMPR2: from cell membrane to nucleus. Cardiovasc Res 2021, 117, 2309–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.J.; Lau, E.M. Pulmonary Hypertension Definition, Classification, and Epidemiology in Asia. JACC Asia 2022, 2, 538–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humbert, M.; Guignabert, C.; Bonnet, S.; Dorfmuller, P.; Klinger, J.R.; Nicolls, M.R.; Olschewski, A.J.; Pullamsetti, S.S.; Schermuly, R.T.; Stenmark, K.R.; et al. Pathology and pathobiology of pulmonary hypertension: state of the art and research perspectives. Eur Respir J 2019, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graf, S.; Haimel, M.; Bleda, M.; Hadinnapola, C.; Southgate, L.; Li, W.; Hodgson, J.; Liu, B.; Salmon, R.M.; Southwood, M.; et al. Identification of rare sequence variation underlying heritable pulmonary arterial hypertension. Nat Commun 2018, 9, 1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, H.; Takeda, N.; Morita, H.; Hatano, M.; Amiya, E.; Maki, H.; Minatsuki, S.; Taki, M.; Shiraishi, Y.; Fujiwara, T.; et al. Three novel BMPR2 mutations associated with advanced pulmonary arterial hypertension. Hum Genome Var 2017, 4, 17010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, C.; Liu, C.; Wang, W.; Zhang, N.; Hadadi, C.; Huang, J.; Zhong, N.; Lu, W. Functional mutations in 5'UTR of the BMPR2 gene identified in Chinese families with pulmonary arterial hypertension. Pulm Circ 2016, 6, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, J.D.; Girerd, B.; Montani, D.; Wang, X.J.; Galie, N.; Austin, E.D.; Elliott, G.; Asano, K.; Grunig, E.; Yan, Y.; et al. BMPR2 mutations and survival in pulmonary arterial hypertension: an individual participant data meta-analysis. Lancet Respir Med 2016, 4, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, C.; Stewart, S.; Upton, P.D.; Machado, R.; Thomson, J.R.; Trembath, R.C.; Morrell, N.W. Primary pulmonary hypertension is associated with reduced pulmonary vascular expression of type II bone morphogenetic protein receptor. Circulation 2002, 105, 1672–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David, L.; Mallet, C.; Mazerbourg, S.; Feige, J.J.; Bailly, S. Identification of BMP9 and BMP10 as functional activators of the orphan activin receptor-like kinase 1 (ALK1) in endothelial cells. Blood 2007, 109, 1953–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eyries, M.; Montani, D.; Nadaud, S.; Girerd, B.; Levy, M.; Bourdin, A.; Tresorier, R.; Chaouat, A.; Cottin, V.; Sanfiorenzo, C.; et al. Widening the landscape of heritable pulmonary hypertension mutations in paediatric and adult cases. Eur Respir J 2019, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Fan, R.; Ji, R.; Zou, W.; Penny, D.J.; Varghese, N.P.; Fan, Y. Novel homozygous BMP9 nonsense mutation causes pulmonary arterial hypertension: a case report. BMC Pulm Med 2016, 16, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.J.; Lian, T.Y.; Jiang, X.; Liu, S.F.; Li, S.Q.; Jiang, R.; Wu, W.H.; Ye, J.; Cheng, C.Y.; Du, Y.; et al. Germline BMP9 mutation causes idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension. Eur Respir J 2019, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, L.; Ormiston, M.L.; Yang, X.; Southwood, M.; Graf, S.; Machado, R.D.; Mueller, M.; Kinzel, B.; Yung, L.M.; Wilkinson, J.M.; et al. Selective enhancement of endothelial BMPR-II with BMP9 reverses pulmonary arterial hypertension. Nat Med 2015, 21, 777–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szulcek, R.; Sanchez-Duffhues, G.; Rol, N.; Pan, X.; Tsonaka, R.; Dickhoff, C.; Yung, L.M.; Manz, X.D.; Kurakula, K.; Kielbasa, S.M.; et al. Exacerbated inflammatory signaling underlies aberrant response to BMP9 in pulmonary arterial hypertension lung endothelial cells. Angiogenesis 2020, 23, 699–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theilmann, A.L.; Hawke, L.G.; Hilton, L.R.; Whitford, M.K.M.; Cole, D.V.; Mackeil, J.L.; Dunham-Snary, K.J.; Mewburn, J.; James, P.D.; Maurice, D.H.; et al. Endothelial BMPR2 Loss Drives a Proliferative Response to BMP (Bone Morphogenetic Protein) 9 via Prolonged Canonical Signaling. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2020, 40, 2605–2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, L.; Desroches-Castan, A.; Mallet, C.; Guyon, L.; Cumont, A.; Phan, C.; Robert, F.; Thuillet, R.; Bordenave, J.; Sekine, A.; et al. Selective BMP-9 Inhibition Partially Protects Against Experimental Pulmonary Hypertension. Circ Res 2019, 124, 846–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rol, N.; Kurakula, K.B.; Happe, C.; Bogaard, H.J.; Goumans, M.J. TGF-beta and BMPR2 Signaling in PAH: Two Black Sheep in One Family. Int J Mol Sci 2018, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poniatowski, L.A.; Wojdasiewicz, P.; Gasik, R.; Szukiewicz, D. Transforming growth factor Beta family: insight into the role of growth factors in regulation of fracture healing biology and potential clinical applications. Mediators Inflamm 2015, 2015, 137823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakao, S.; Tatsumi, K.; Voelkel, N.F. Endothelial cells and pulmonary arterial hypertension: apoptosis, proliferation, interaction and transdifferentiation. Respir Res 2009, 10, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, K.W.; Chang, S.K.; Chen, Y.W.; Tsai, W.J.; Wang, K.Y. A cluster of heritable pulmonary arterial hypertension cases in a family with all three siblings carrying the same novel AQP1 c.273C>G variant-a case report. Pulm Circ 2023, 13, e12211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreida, S.; Tornroth-Horsefield, S. Structural insights into aquaporin selectivity and regulation. Curr Opin Struct Biol 2015, 33, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verkman, A.S.; Anderson, M.O.; Papadopoulos, M.C. Aquaporins: important but elusive drug targets. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2014, 13, 259–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vassiliou, A.G.; Keskinidou, C.; Kotanidou, A.; Frantzeskaki, F.; Dimopoulou, I.; Langleben, D.; Orfanos, S.E. Decreased bone morphogenetic protein type II receptor and BMP-related signalling molecules' expression in aquaporin 1-silenced human pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells. Hellenic J Cardiol 2021, 62, 84–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vassiliou, A.G.; Keskinidou, C.; Kotanidou, A.; Frantzeskaki, F.; Dimopoulou, I.; Langleben, D.; Orfanos, S.E. Knockdown of bone morphogenetic protein type II receptor leads to decreased aquaporin 1 expression and function in human pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 2020, 98, 834–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouvard, C.; Tu, L.; Rossi, M.; Desroches-Castan, A.; Berrebeh, N.; Helfer, E.; Roelants, C.; Liu, H.; Ouarne, M.; Chaumontel, N.; et al. Different cardiovascular and pulmonary phenotypes for single- and double-knock-out mice deficient in BMP9 and BMP10. Cardiovasc Res 2022, 118, 1805–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tielemans, B.; Delcroix, M.; Belge, C.; Quarck, R. TGFbeta and BMPRII signalling pathways in the pathogenesis of pulmonary arterial hypertension. Drug Discov Today 2019, 24, 703–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorelova, A.; Berman, M.; Al Ghouleh, I. Endothelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Antioxid Redox Signal 2021, 34, 891–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodgson, J.; Swietlik, E.M.; Salmon, R.M.; Hadinnapola, C.; Nikolic, I.; Wharton, J.; Guo, J.; Liley, J.; Haimel, M.; Bleda, M.; et al. Characterization of GDF2 Mutations and Levels of BMP9 and BMP10 in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2020, 201, 575–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgson, J.; Ruiz-Llorente, L.; McDonald, J.; Quarrell, O.; Ugonna, K.; Bentham, J.; Mason, R.; Martin, J.; Moore, D.; Bergstrom, K.; et al. Homozygous GDF2 nonsense mutations result in a loss of circulating BMP9 and BMP10 and are associated with either PAH or an "HHT-like" syndrome in children. Mol Genet Genomic Med 2021, 9, e1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chomette, L.; Hupkens, E.; Romitti, M.; Dewachter, L.; Vachiery, J.L.; Bailly, S.; Costagliola, S.; Smits, G.; Tillet, E.; Bondue, A. Pediatric pulmonary arterial hypertension due to a novel homozygous GDF2 missense variant affecting BMP9 processing and activity. Am J Med Genet A 2023, 191, 2064–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Upton, P.; Richards, S.; Bates, A.; Niederhoffer, K.Y.; Morrell, N.W.; Christian, S. A rare homozygous missense GDF2 (BMP9) mutation causing PAH in siblings: Does BMP10 status contribute? Am J Med Genet A 2023, 191, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolic, I.; Yung, L.M.; Yang, P.; Malhotra, R.; Paskin-Flerlage, S.D.; Dinter, T.; Bocobo, G.A.; Tumelty, K.E.; Faugno, A.J.; Troncone, L.; et al. Bone Morphogenetic Protein 9 Is a Mechanistic Biomarker of Portopulmonary Hypertension. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2019, 199, 891–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Upton, P.D.; Davies, R.J.; Trembath, R.C.; Morrell, N.W. Bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) and activin type II receptors balance BMP9 signals mediated by activin receptor-like kinase-1 in human pulmonary artery endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 2009, 284, 15794–15804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verkman, A.S. More than just water channels: unexpected cellular roles of aquaporins. J Cell Sci 2005, 118, 3225–3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, K.; Unger, L.; Salman, M.M.; Kitchen, P.; Bill, R.M.; Yool, A.J. Signaling Mechanisms and Pharmacological Modulators Governing Diverse Aquaporin Functions in Human Health and Disease. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Long, L.; Yang, X.; Tong, Z.; Southwood, M.; King, R.; Caruso, P.; Upton, P.D.; Yang, P.; Bocobo, G.A.; et al. Circulating BMP9 Protects the Pulmonary Endothelium during Inflammation-induced Lung Injury in Mice. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2021, 203, 1419–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krump-Konvalinkova, V.; Bittinger, F.; Unger, R.E.; Peters, K.; Lehr, H.A.; Kirkpatrick, C.J. Generation of human pulmonary microvascular endothelial cell lines. Lab Invest 2001, 81, 1717–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lleu, P.L.; Rebel, G. Interference of Good's buffers and other biological buffers with protein determination. Anal Biochem 1991, 192, 215–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batteiger, B.; Newhall, W.J.t.; Jones, R.B. The use of Tween 20 as a blocking agent in the immunological detection of proteins transferred to nitrocellulose membranes. J Immunol Methods 1982, 55, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Gene | Sequence (5’-3’) | nt | |
|---|---|---|---|
| AQP1 | F | 5’-TATGCGTGCTGGCTACTACCGA-3’ | 22 |
| R | 5’-GGTTAATCCCACAGCCAGTGTAG-3’ | 23 | |
| BMP9 | F | 5’-CCTGCCCTTCTTTGTTGTCTTCTC-3’ | 24 |
| R | 5’-TGACTGCTCTCACCTGCCTCTGTG-3’ | 24 | |
| BMP10 | F | 5’-AAGCCTATGAATGCCGTGGTG-3’ | 21 |
| R | 5’-AGGCCTGGATAATTGCATGCTT-3’ | 20 | |
| BMPR2 | F | 5’-CCACCTCCTGACACAACACC-3’ | 20 |
| R | 5’-TGTGAAGACCTTGTTTACGGT-3’ | 21 | |
| GAPDH | F | 5’-ATGGGGAAGGTGAAGGTCG-3’ | 19 |
| R | 5’-GGGGTCATTGATGGCAACAATA-3’ | 22 | |
| TGFB1 | F | 5’-GCGTGCTAATGGTGGAAAC-3’ | 19 |
| R | 5’-CGGTGACATCAAAAGATAACCAC-3’ | 23 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





