1. Introduction
Dental implants have been widely used for restoring partially edentulous and edentulous areas since Branemark discovered osseointegration in dental implants. Dental implants are currently recognized as the ideal treatment method for reconstructing missing teeth [
1].
The success rate of implants has gradually increased with technological advances; however, there are still instances of implant failure. Factors influencing implant failure include the following: host-related factors, such as age, sex, systemic diseases, smoking, and oral hygiene status; site-related factors, such as location within the jaw, bone quality, quantity, and presence of infection; surgery-related factors, such as initial stability, implant placement location and orientation, and surgeon skill; implant-related factors, including macro and microstructure, surface characteristics, length, and diameter; restoration-related factors, such as prosthesis type and maintenance method (screw or cement type) and occlusal scheme [
2,
3].
Among these, excessive stress and improper stress distribution transmitted to the bone around the implant pose a significant concern of bone resorption, making research in this area a highly relevant field of interest. Bone resorption around dental implants can be classified as early bone resorption occurring shortly after implant placement and progressive bone resorption continuing over time [
4].
The causes of early bone resorption after implant surgery include damage to surrounding tissues and supporting bone during surgery or inappropriate forces applied to the implant during healing [
4]. Additionally, progressive bone resorption leading to implant osseointegration failure is often attributed to excessive external forces post-implantation, with long-term peri-implantitis contributing as an additional factor [
5,
6,
7,
8,
9]. Beyond these factors, several studies suggest that biomechanical issues could also contribute to implant bone resorption [
10]. Biomechanical factors encompass implant surface shape and form, bone quality, and patient-specific elements such as bone volume. Therefore, various factors, including load position, direction, external load transmitted to the supporting bone, implant-bone interface conditions, implant diameter and length, implant thread design, and surface structure, contribute to the long-term success of implant-supported restorations [
11,
12,
13,
14].
The choice of abutment material used for implant procedures can influence stress distribution in implant systems and supporting bone [
15]. The success of implants in edentulous areas is determined by implant form, surgical approach, healing time, and the initial load applied to the bone during the early stages of restoration [
16]. Therefore, the appropriate distribution of biomechanical stresses in the supporting bone is crucial for the long-term success of implant restorations.
Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) has been introduced as an alternative to titanium abutments. PEEK, first commercially used in 1998 as a thermoplastic polymer with outstanding properties, offers excellent machinability and esthetics [
17]. It has been reported as a material in orthopedic surgery to replace titanium. PEEK is a thermoplastic material, lighter than metal materials and more efficiently machinable than robust metal materials. Pure PEEK has weak mechanical properties; hence, it is often reinforced with glass or carbon fiber to enhance its mechanical and physical characteristics [
17]. Previous studies evaluated stress distribution during load transmission in reinforced PEEK and compared it to titanium abutments with 30% carbon fiber added [
18]. Schwitalla et al. used finite element analysis for abutments with 60% added carbon fiber [
19]. However, adding carbon fiber influenced the color of PEEK significantly, with increasing carbon fiber content resulting in a darker shade [
19].
Engineering analysis is necessary to understand stress distribution in implant systems due to the risk of damage to the implant-bone interface based on the degree of osseointegration. Finite element analysis has been used in medicine and dentistry for decades [
20]. This method allows for the simulation of interactions between implants and surrounding tissues. Previous research has explored stress distribution based on load direction and constraints in implant restorations, the impact of abutment material on stress distribution, and the influence of implant structure on stress distribution [
21,
22,
23]. However, there is insufficient research on evaluating stress distribution in supporting bone around implants when using pure PEEK as an abutment material, and its extensive impact on the structural elements of implant systems lacks thorough investigation. Furthermore, reinforced PEEK with added carbon fiber lacks esthetics. Therefore, this study used three-dimensional finite element analysis to compare and evaluate stress distribution in the supporting bone around implant systems with titanium and PEEK abutments.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Finite Element Model
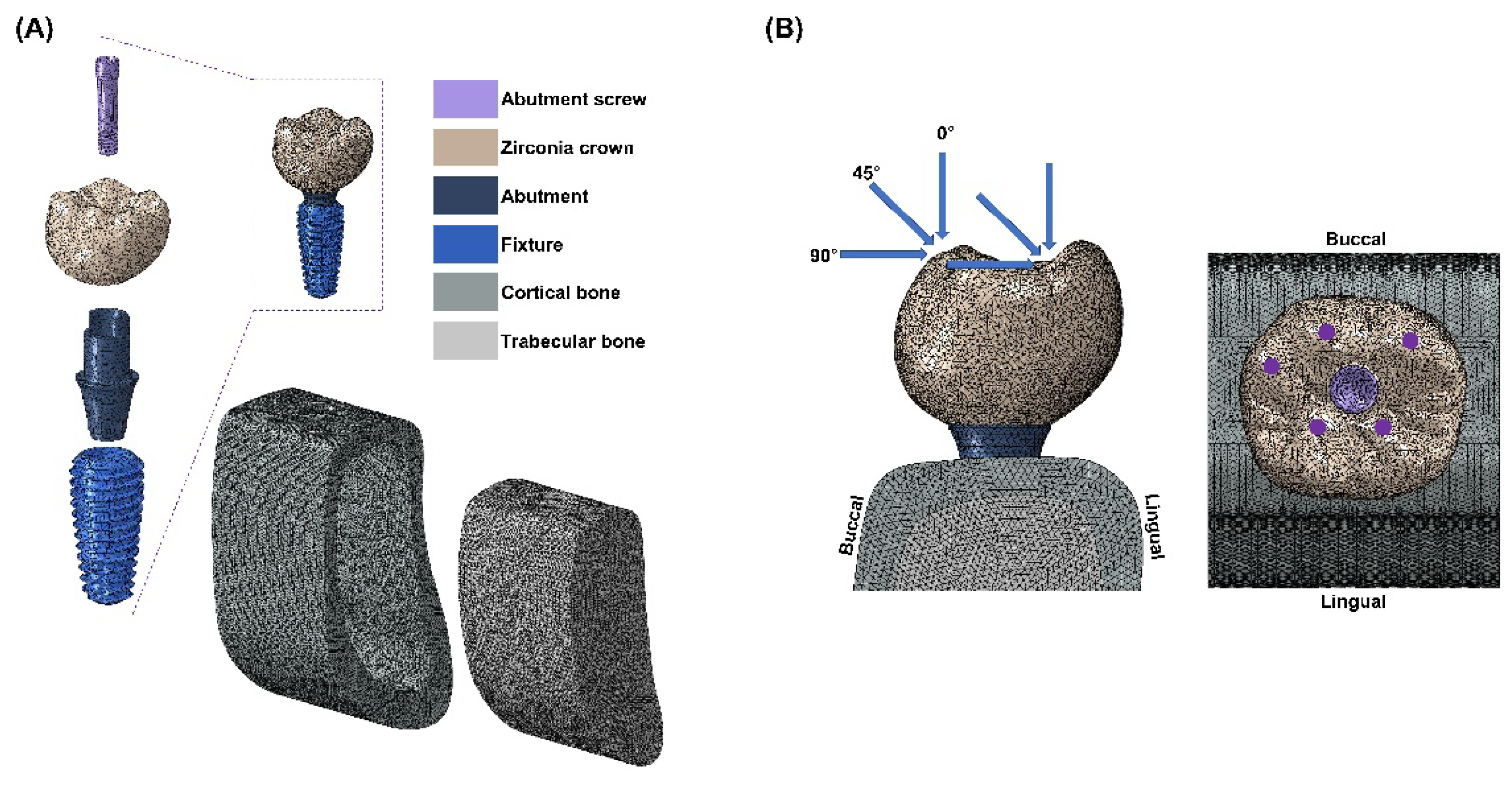
This study used CATIA software (Dassault Systèmes, Vélizy-Villacoublay, France) to design components of a single-unit implant system mimicking the mandibular first molar (e.g., fixture, abutment, abutment screw, superstructure, cortical bone, and cancellous bone). For the convenience of finite element analysis, teeth adjacent to the mandibular first molar were excluded.
The implant system design was based on the commercially available MEGAGEN implant system and a previously conducted study. An implant fixture (Anyone
®; Megagen, Daegu, Korea) with a diameter of 5 mm and a length of 11.8 mm, widely used in the mandibular molar region, was used. The abutment (ZrGen Abutment; MegaGen, Daegu, Korea) had a cuff of 1.5 mm, a diameter of 4.5 mm, and a post height of 4.5 mm. The abutment screw was designed with a diameter of 1.8 mm and a length of 5.1 mm. The overall shape was designed based on a cross-sectional image of the mandible, creating a model of the mandibular bone block. The overall design of the mandible was shaped with a height of 29.5 mm, a width of 14 mm, and a thickness ranging from 1.4 to 3.7 mm, surrounded by cortical bone and separated from the cancellous bone (
Figure 1-A). With this model configuration, two implant system models were created, each incorporating two different abutment materials: PEEK and titanium.
2.2. Boundary and Loading Conditions
All materials used in the study were assumed to be homogeneous, isotropic, and linearly elastic. The Poisson’s ratio and elastic modulus of the materials were incorporated into the 3D model (
Table 1.) [
24,
25]. The finite element (FE) model underwent discretization for division into small elements. A mesh size (mean size 250 µm) was set to minimize geometric errors. Each node was assumed to be interconnected at individual points. The analysis model of the single-unit implant system, consisting of approximately 200,000 tetra 10-node elements, was analyzed using a general-purpose analysis program (Abaqus; Dassault Systemes, Waltham, MA, USA) by applying loads and boundary conditions. External loads were applied in vertical and oblique directions to describe occlusal loading. Three load directions were used to simulate occlusal loading: vertical (0 º) direction, angular (45 º) direction, and horizontal (90 º) direction. Loads were applied at 5 different loading points on occlusal surfaces: 60 nodes located at 3 points on the outer inclines of the buccal cusps, and 60 nodes located at 2 points on the inner inclines of the lingual cusps (
Figure 1-B). These loading points resembled contact points during mastication. The magnitude of the load was 280 N, which simulated normal masticatory force. [
26] Maximum equivalent stresses were evaluated at the abutment, abutment screw, and fixture. Maximum and minimum principal stresses were evaluated for cortical and cancellous bone.
3. Results
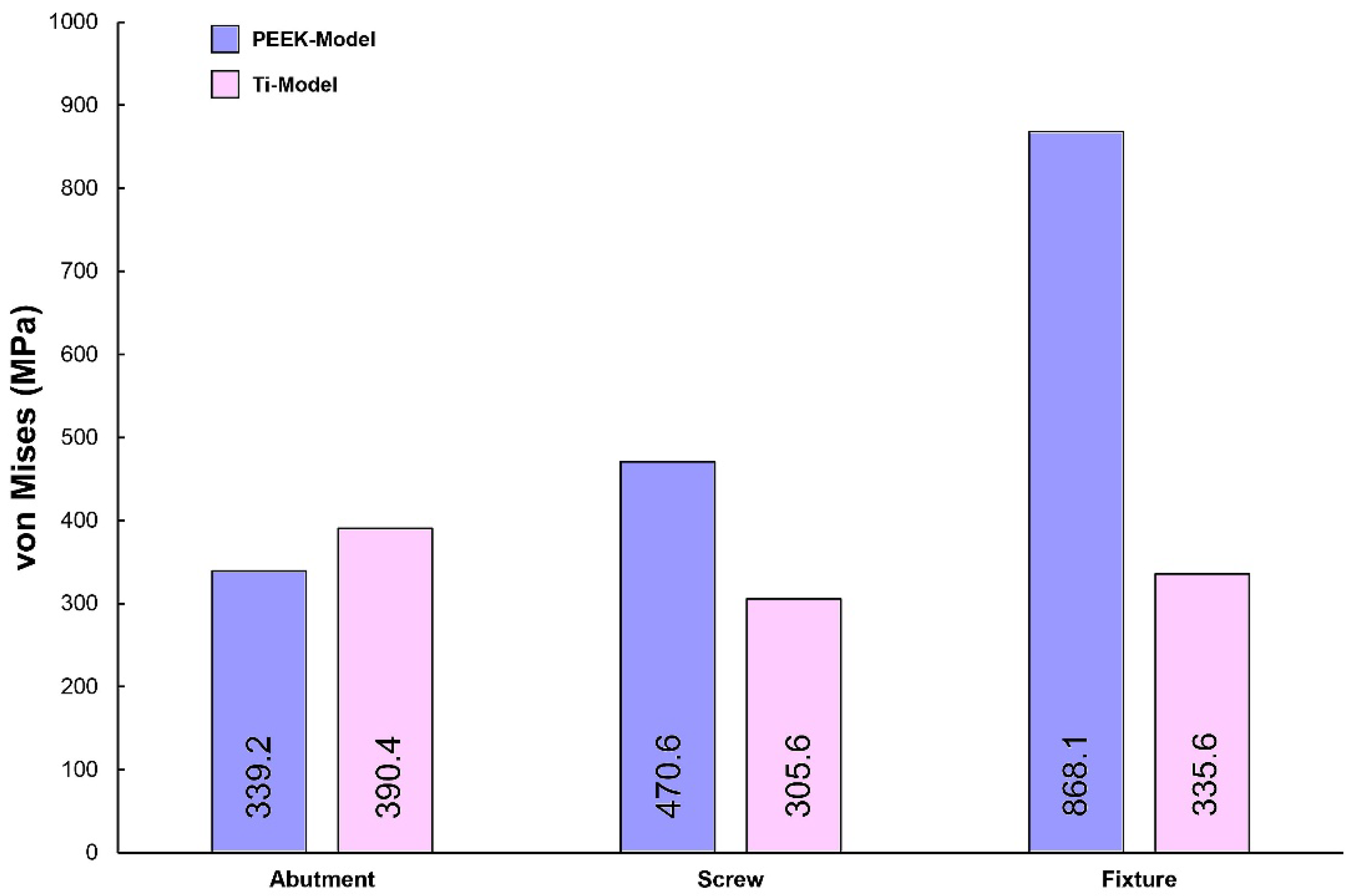
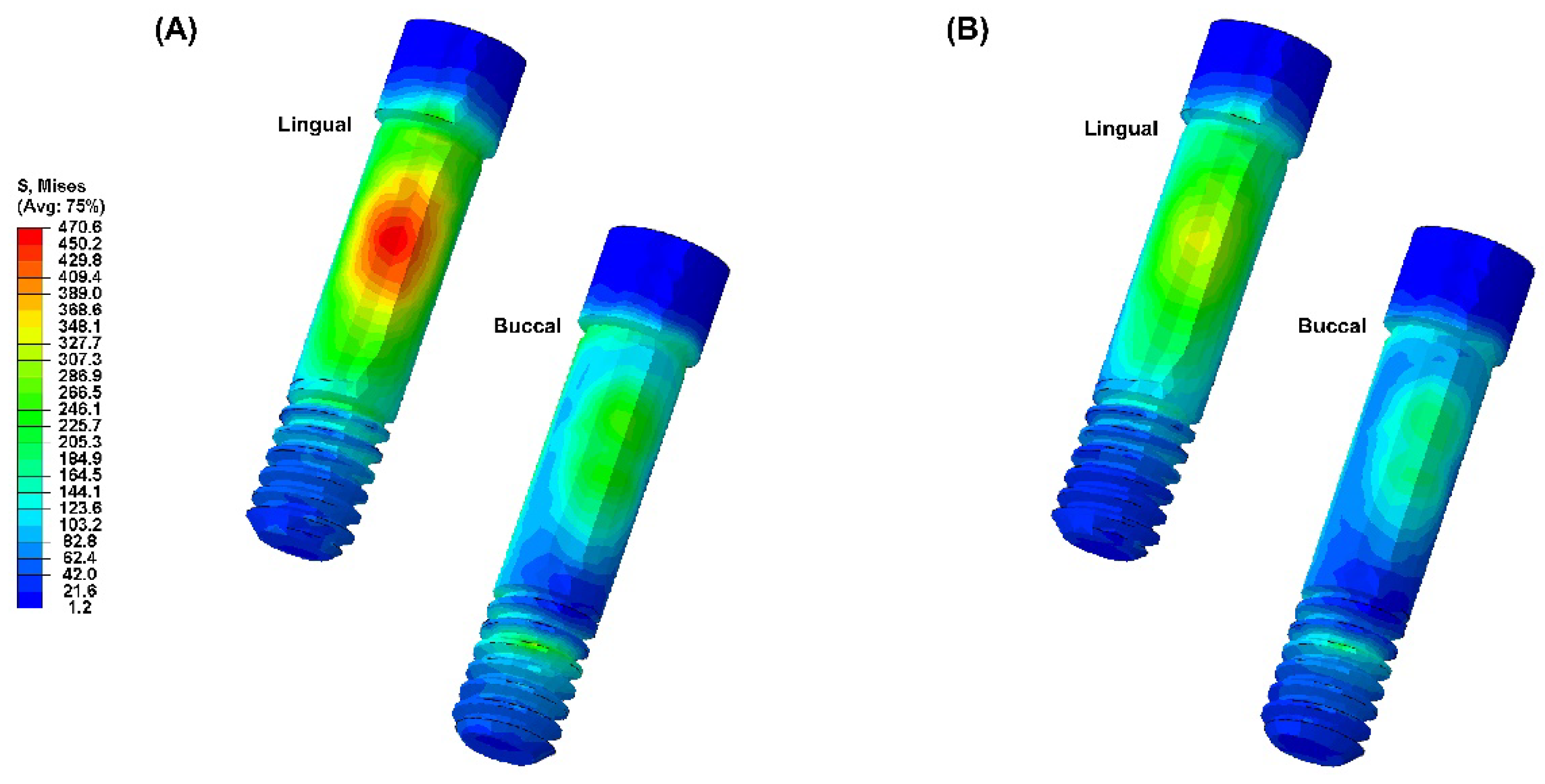
Figure 2 illustrates the maximum von Mises stress (VMS) values for the abutment, abutment screw, and fixture under external loading. Under external loading application, the fixture of the PEEK-Model exhibited a higher VMS value compared to that of the Ti-Model. The lowest VMS value was observed in the abutment screw of the Ti-Model. Furthermore, the Ti-Model showed slightly higher VMS values for the abutment than the PEEK-Model.
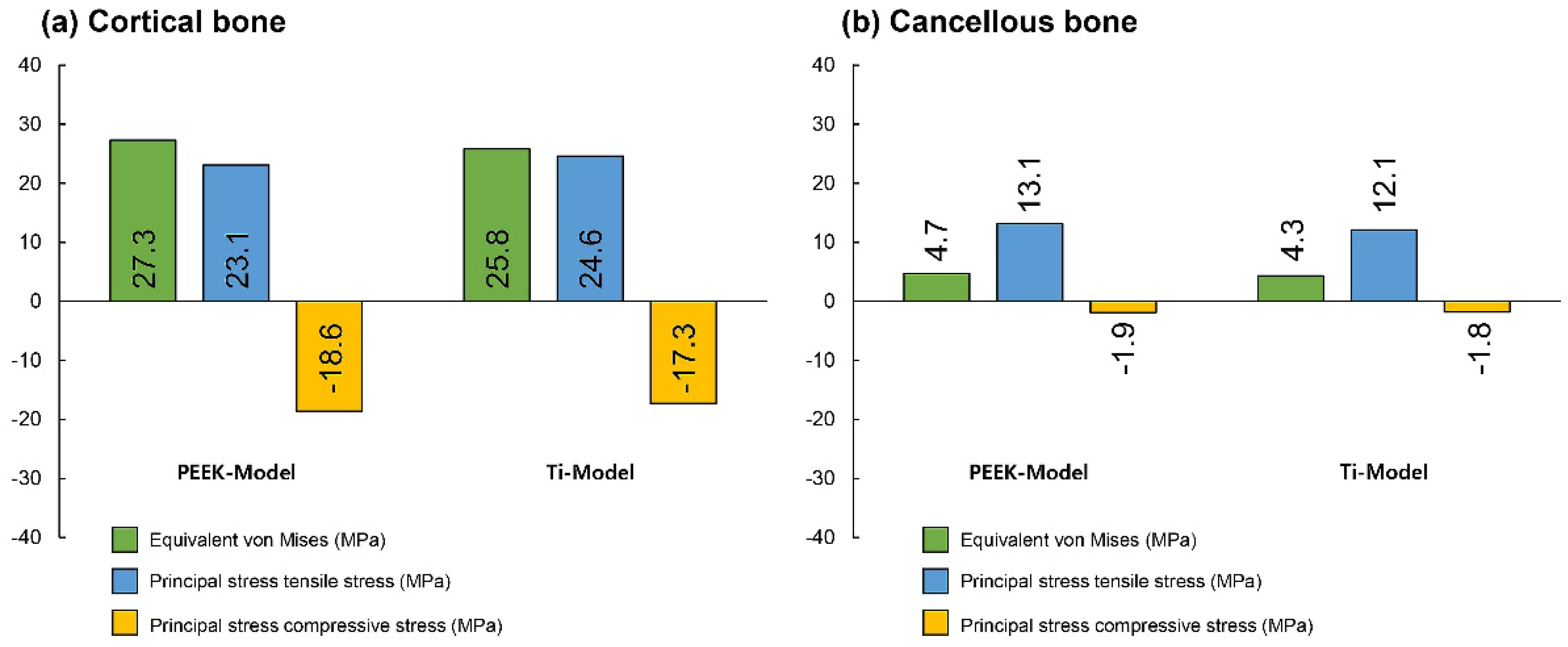
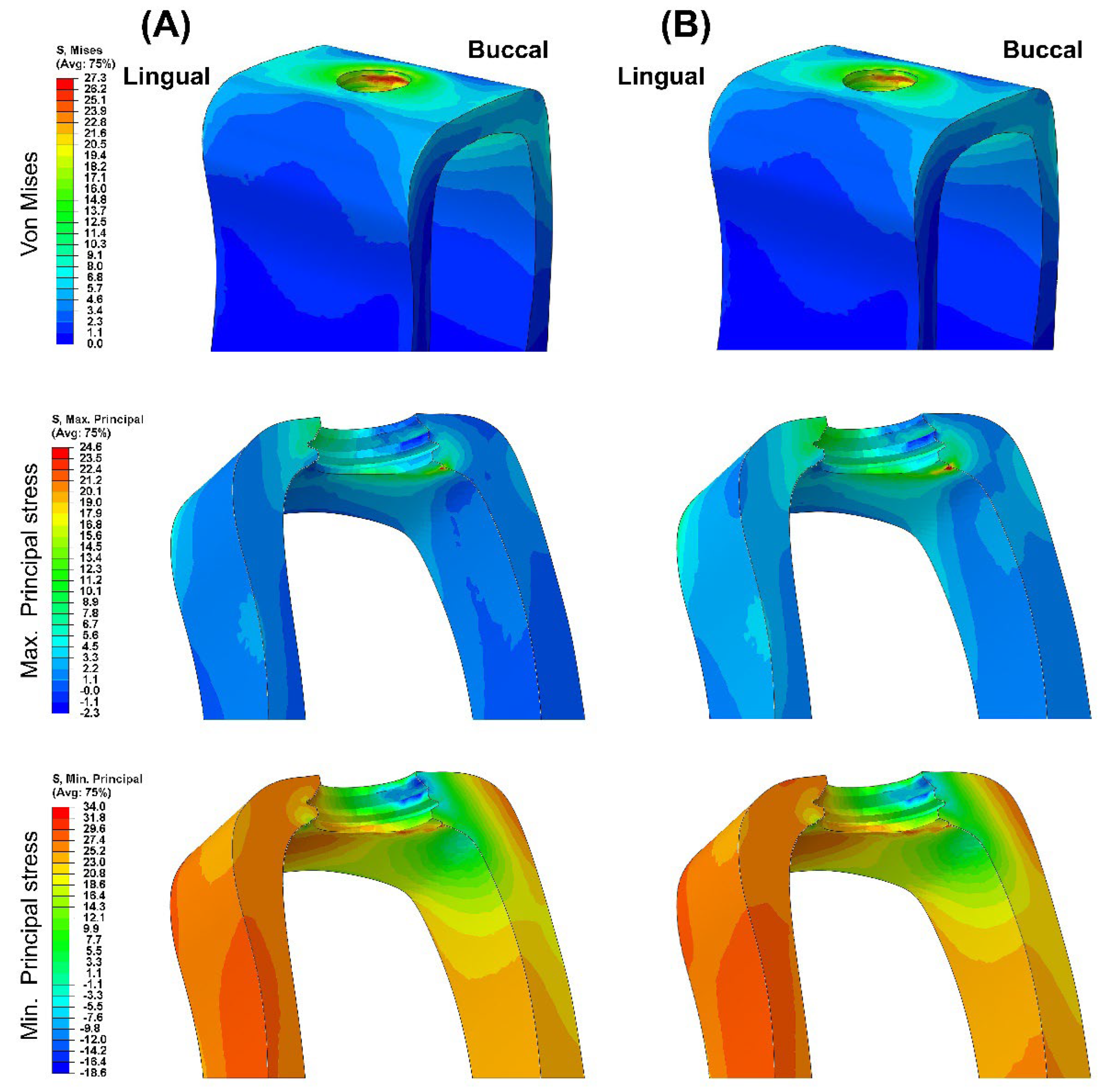
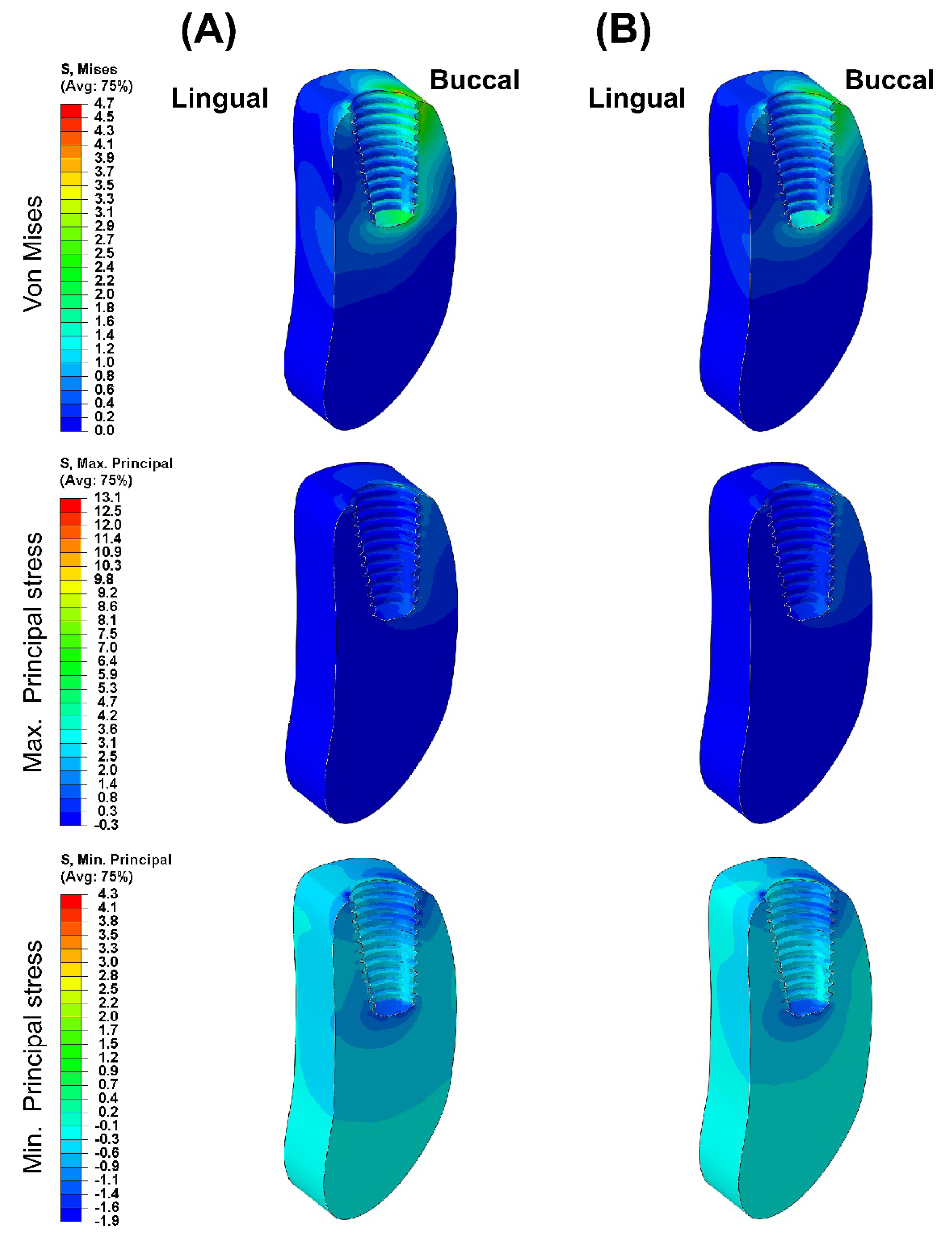
Figure 3 presents the VMS transmitted to the cortical and cancellous bone with the maximum/minimum principal stresses. Overall, in all FE models, the maximum and minimum stress levels were higher in the cortical bone than in the cancellous bone. Additionally, similar stress concentration points were observed in the Ti-Model and PEEK-Model.
Figure 4,
Figure 5,
Figure 6,
Figure 7 and
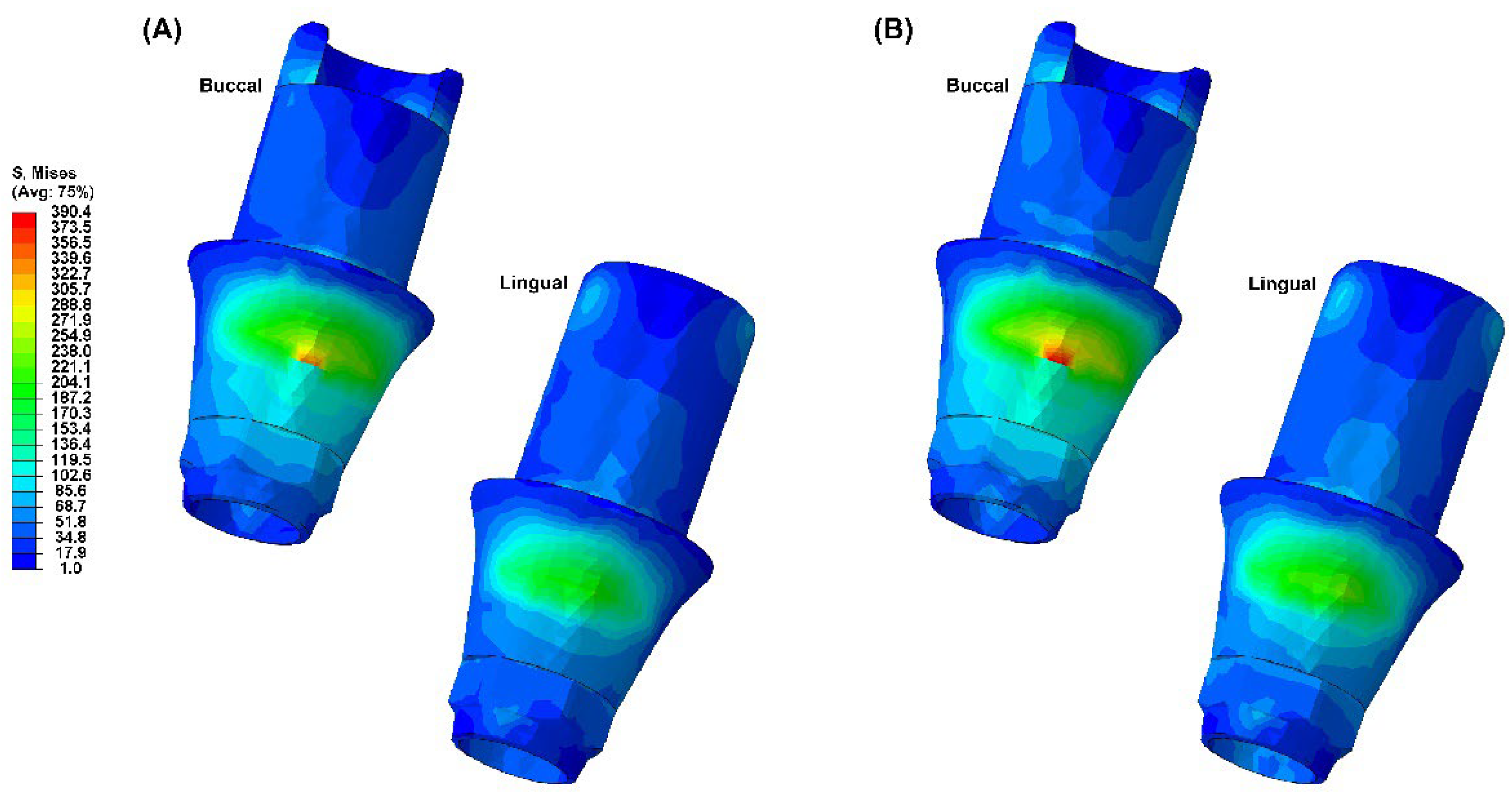
Figure 8 visually present the VMS distribution in the abutment, abutment screw, fixture, cortical bone, and cancellous bone for both models. Both models showed stress concentration in the inner aspect of the fixture and the abutment base (
Figure 4). The stress on the abutment screw was highest at the abutment screw body, especially in the PEEK-Model (
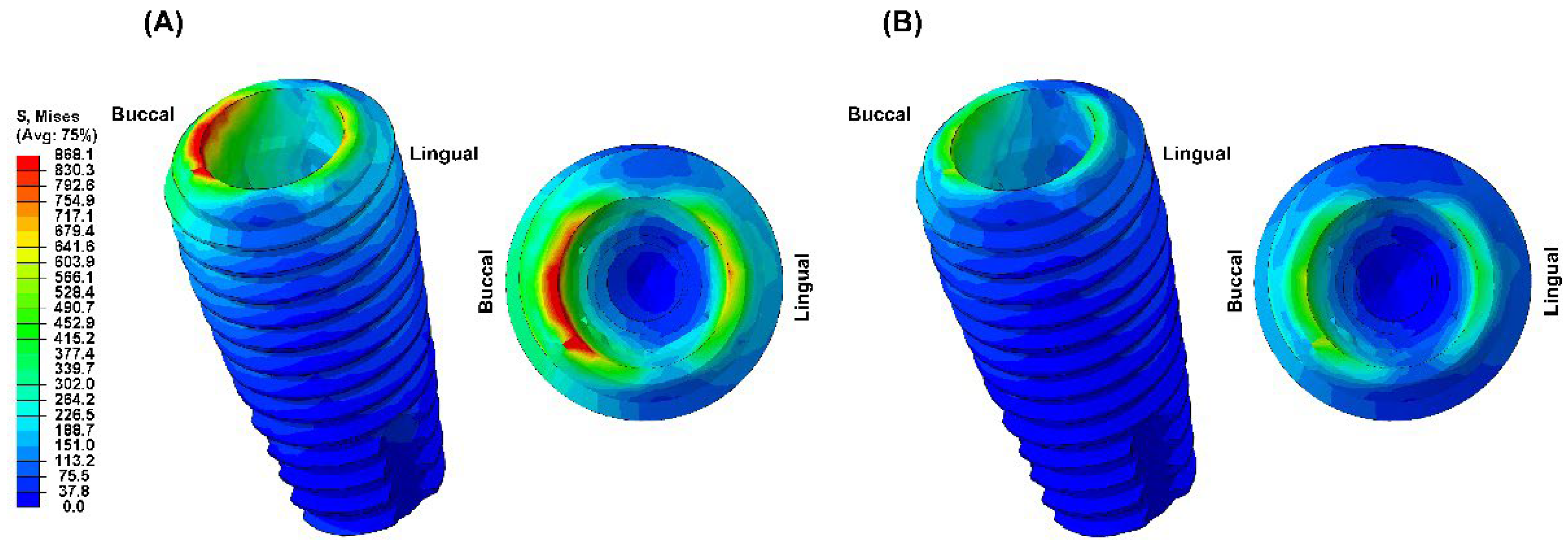
Figure 5). The fixture exhibited stress concentration in the adjacent cervical region, especially in the PEEK-Model (
Figure 6). For maximum and minimum principal stresses, stress concentration points were observed in the adjacent cortical bone (
Figure 7) and the apical region of the cancellous bone (
Figure 8).
4. Discussion
This study aimed to compare the stability of implant systems using PEEK abutments with those using titanium abutments through three-dimensional finite element analysis. This analysis allowed for a qualitative evaluation of biomechanical behaviors occurring in the oral cavity based on complex structures and various material variables, enabling an understanding of stress distribution tendencies [
27].
To enhance the reliability of finite element analysis in this study, the materials applied were homogeneous and isotropic, with material properties assumed to be consistent in all directions and only two independent variables (elastic modulus and Poisson’s ratio) defined for simulation. Three-dimensional finite element analysis incorporating ideal implant designs and surrounding bone can yield successful results. For ideal modeling, element sizes should be set between 150 and 300 µm. Element sizes larger than 300 µm may produce inaccurate results, while reducing element sizes to less than 150 µm may significantly increase analysis time, reducing efficiency [
28]. Therefore, this study used an average element size of 250 µm. The mechanical and physical properties of the FE model were based on validated data from previous studies. However, despite these efforts, the detailed aspects of the models and the numerical analysis of biomechanics could not encompass all biochemical ranges within the oral cavity [
22,
24,
26]. Nonetheless, the results obtained through finite element analysis could predict the stability and efficacy of implant systems, aiding in the improvement of new designs and products [
25,
29].
Minimizing and evenly distributing stress transmitted to the supporting bone from loaded implant structures is essential for the long-term success of implant systems [
30,
31]. The experimental conditions of this study were designed to simulate an ideally treated clinical prosthetic situation. Therefore, this study used external loads in three different load directions at 5 points: 60 nodes located at 3 cusps on the buccal cusps and 60 nodes located at 2 cusps on the lingual cusps. Thus, external loads were appropriately distributed.
The von Mises stress is primarily used to evaluate the yield condition of isotropic and ductile metals under complex loading conditions, while the principal stress refers to the maximum and minimum stress values at a specific point in brittle solid materials when subjected to force [
32]. Therefore, in this study, von Mises stress was measured for the abutment, abutment screw, and fixture, whereas maximum and minimum principal stresses were measured for supporting bone.
In this study, the PEEK abutment material demonstrated similar stress distribution and magnitudes in supporting bone compared to the conventional titanium abutment implant system. However, the stress generated in the fixture of the PEEK-Model was 868.1 MPa, which was 159% higher than that of the Ti-Model. This result corresponds to a stress level similar to the yield strength of titanium material, which is 880 MPa [
33]. Moreover, stress concentration on the abutment screw was also higher in the PEEK-Model than in the Ti-Model. This interpretation arises from the inherent properties of the PEEK abutment material, which has a lower modulus of elasticity than titanium, resulting in stress distribution differences between the two materials during load transmission [
23,
24,
29]. Sarot et al. reported that implant systems using PEEK and CRF-PEEK abutments showed similar stress distributions in cortical and cancellous bone to titanium implant systems, consistent with our findings [
18]. Finite element analysis studies applying PEEK abutments have shown that titanium implant systems exhibit higher maximum equivalent stresses in abutments than PEEK implant systems, which aligns with our results [
18,
19]. While the implant system with PEEK abutments demonstrated similar stress distribution and magnitude in supporting bone to the titanium implant system, the high stress generated in the fixture suggests potential loss of supporting bone at the implant boundary.
Therefore, the mechanical properties of PEEK abutments need improvements to match or slightly exceed those of titanium abutments. Also, there has been no studies reporting the successful long-term prognosis of implant prosthesis using PEEK abutment. Therefore, follow-up studies are needed to demonstrate that implant systems with PEEK abutments are a viable clinical alternative to titanium implant systems.
5. Conclusions
In this study, the stress distribution of surrounding supporting bone in implant systems with titanium and PEEK abutments was compared and evaluated using three-dimensional finite element analysis. The following conclusions were drawn:
1. Due to the low elastic modulus of the PEEK abutment, high VMS values were observed in the implant fixture.
2. Based on the results of this study, PEEK abutment requires improved mechanical and physical properties for clinical application, and its clinical use is limited.
3. Different abutment materials did not significantly affect the stress distribution and magnitude in the bone around the implant.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.-H.H. and H.C.; methodology, M.-H.H.; software, M.-H.H.; validation, H.C.; formal analysis, M.-H.H.; investigation, H.C.; resources, M.-H.H.; data curation, M.-H.H.; writing—original draft preparation, M.-H.H.; writing—review and editing, H.C.; visualization, M.-H.H.; supervision, H.C.; project administration, H.C.; funding acquisition, H.C.
Funding
This research was funded by the grant of Research Institute of Medical Science, Daegu Catholic University (2023), grant number RD-23-0024.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are included in the article.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank MEGAGEN Implants Co., Ltd. for providing and supporting samples for this work.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Le Guéhennec, L.; Soueidan, A.; Layrolle, P.; Amouriq, Y. Surface treatments of titanium dental implants for rapid osseointegration. Dent. Mater. 2006, 23, 844–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Askary, A.S.; Meffert, R.M.; Griffin, T. Why do dental implants fail? Part I. 1999, 8, 173–185. [Google Scholar]
- El Askary, A.S.; Meffert, R.M.; Griffin, T. Why Do Dental Implants Fail? Part II. Implant. Dent. 1999, 8, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Oh, T.-J.; Misch, C.E.; Wang, H.-L. Occlusal considerations in implant therapy: Clinical guidelines with biomechanical rationale. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2005, 16, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misch, C.E.; Suzuki, J.B.; Misch-Dietsh, F.M.; Bidez, M.W. A Positive Correlation Between Occlusal Trauma and Peri-implant Bone Loss: Literature Support. Implant. Dent. 2005, 14, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isidor, F. Influence of forces on peri-implant bone. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2006, 17, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quirynen M, De Soete M, Van Steenberghe D. Infectious risks for oral implants: A review of the literature. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2002, 13, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindhe J, Berglundh T, Ericsson I, Liljenberg B, Marinello C. Experimental breakdown of peri-implant and periodontal tissues. A study in the beagle dog. Clin Oral Implants Res. 1992, 3, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang NP, Brägger U, Walther D, Bearner B, Kornman KS. Ligature-induced peri-implant infection in cynomolgus monkeys. Clin Oral Implants Res. 1993, 4, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansson, S. Surface roughness parameters as predictors of anchorage strength in bone: A critical analysis. J. Biomech. 2000, 33, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duyck, J.; Naert, I.; Van Oosterwyck, H.; Van der Sloten, J.; De Cooman, M.; Lievens, S.; Puers, B. Biomechanics of oral implants: A review of the literature. Technol. Heal. Care 1997, 5, 253–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindquist, L.W.; Rockler, B.; Carlsson, G.E. Bone resorption around fixtures in edentulous patients treated with mandibular fixed tissue-integrated prostheses. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1988, 59, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodacre, C.J.; Bernal, G.; Rungcharassaeng, K.; Kan, J.Y. Clinical complications with implants and implant prostheses. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2003, 90, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isidor, F. Loss of osseointegration caused by occlusal load of oral implants. A clinical and radiographic study in monkeys. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 1996, 7, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, M.-H. Comparison of stress distribution in bone and implant-supported dental prosthesis with zirconia and titanium implants: A 3-dimensional finite element analysis. J. Korean Acedemy Dent. Technol. 2020, 42, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevimay, M.; Turhan, F.; Kiliçarslan, M.; Eskitascioglu, G. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of the effect of different bone quality on stress distribution in an implant-supported crown. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2005, 93, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtz, S.M.; Devine, J.N. PEEK biomaterials in trauma, orthopedic, and spinal implants. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 4845–4869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarot JR, Contar CMM, Cruz ACCD, de Souza Magini R. Evaluation of the stress distribution in CFR-PEEK dental implants by the three-dimensional finite element method. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2010;21:2079-2085.
- Schwitalla, A.; Abou-Emara, M.; Spintig, T.; Lackmann, J.; Müller, W. Finite element analysis of the biomechanical effects of PEEK dental implants on the peri-implant bone. J. Biomech. 2015, 48, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belser UC, Grütter L, Vailati F, Bornstein MM, Weber HP, Buser D. Outcome evaluation of early placed maxillary anterior single-tooth implants using objective esthetic criteria: A cross-sectional, retrospective study in 45 patients with a 2-to 4-year follow-up using pink and white esthetic scores. J Periodontol. 2009, 80, 140–151.
- Hansson, S.; Werke, M. The implant thread as a retention element in cortical bone: The effect of thread size and thread profile: A finite element study. J. Biomech. 2003, 36, 1247–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.Y.; Hong, M.-H. Influence of zirconia and titanium fixture materials on stress distribution in abutment screws: A three-dimensional finite element analysis. J. Korean Acedemy Dent. Technol. 2021, 43, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pjetursson, B.E.; Zarauz, C.; Strasding, M.; Sailer, I.; Zwahlen, M.; Zembic, A. A systematic review of the influence of the implant-abutment connection on the clinical outcomes of ceramic and metal implant abutments supporting fixed implant reconstructions. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2018, 29, 160–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohal, R.-J.; Papavasiliou, G.; Kamposiora, P.; Tripodakis, A.; Strub, J.R. Three-dimensional computerized stress analysis of commercially pure titanium and yttrium-partially stabilized zirconia implants. Int J Prosthodont. 2002, 15, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jörn, D.; Kohorst, P.; Besdo, S.; Rücker, M.; Stiesch, M.; Borchers, L. Influence of lubricant on screw preload and stresses in a finite element model for a dental implant. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2014, 112, 340–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, JR. Clinically relevant approach to failure testing of all-ceramic restorations. J Prosthet Dent. 1999, 81, 652–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Çaglar, A.; Bal, B.T.; Karakoca, S.; Aydın, C.; Yılmaz, H.; Sarısoy, S. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of titanium and yttrium-stabilized zirconium dioxide abutments and implants. . 2011, 26, 961–969. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Caglar, A.; Bal, B.T.; Aydin, C.; Yilmaz, H.; Ozkan, S. Evaluation of stresses occurring on three different zirconia dental implants: Three-dimensional finite element analysis. . 2010, 25, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alkan, I.; Sertgöz, A.; Ekici, B. Influence of occlusal forces on stress distribution in preloaded dental implant screws. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2004, 91, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verri, F.R.; Júnior, J.F.S.; Almeida, D.A.d.F.; Verri, A.C.G.; Batista, V.E.d.S.; Lemos, C.A.A.; Noritomi, P.Y.; Pellizzer, E.P. Three-Dimensional Finite Element Analysis of Anterior Single Implant-Supported Prostheses with Different Bone Anchorages. Sci. World J. 2015, 2015, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha SR, Kim SH, Lee JB, Han JS, Yeo IS, Yoo SH; et al. Biomechanical three-dimensional finite element analysis of monolithic zirconia crown with different cement type. J Adv Prosthodont. 2015;7:475-483.
- Choi, S.-M.; Choi, H.; Lee, D.-H.; Hong, M.-H. Comparative finite element analysis of mandibular posterior single zirconia and titanium implants: A 3-dimensional finite element analysis. J. Adv. Prosthodont. 2021, 13, 396–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licausi, M.P.; Muñoz, A.I.; Borrás, V.A.; Espallargas, N. Tribocorrosion Mechanisms of Ti6Al4V in Artificial Saliva by Zero-Resistance Ammetry (ZRA) Technique. J. Bio- Tribo-Corrosion 2015, 1, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).