1. Introduction
Wildfires are an integral part of terrestrial ecosystems with both beneficial and adverse impacts. Despite the complicated relationship between climate, weather, and fire, climate change has been implicated with the increasing number of forest fires [
1]. Many countries have recently been experiencing megafires, i.e., wildfires that burn more than 40,500 ha of land as per US interagency fire center or have an unusually large impact on people and the environment. Unparalleled in the last 200 years, Australian “Black Summer” 2019-2020 bushfires burned more than 8 million hectares, and up to 67-83% of globally significant rainforests, eucalyptus forests, and woodlands putting in question their regeneration and recovery of species and landscape [
2]. The Amazon wildfires in 2019 burned an area approximately the size of New Jersey and were repeated, with 2,500 major fires erupting from May to November 2020, and again in 2021, mostly set deliberately in order to claim cultivating land [
3]. Wildfires are classified as first-, second-, and third- generation based on fuel continuity, intensity, and speed. Fourth-generation fires take place at the wildland-urban interface (WUI), and the fifth generation describes the simultaneity of fire events, which exceed national resources. Finally, sixth-generation fires create their own atmosphere with pyrocumulus clouds and cannot be contained with airplanes or other fire suppression measures [
4]. The increase of megafires resulting from global climate change has led some authors to describe pessimistically the coming era as the
Pyrocene epoch [
5].
The warmer and drier climate has supplied abundant fuel and optimal conditions for wildfires, increasing fire activity across the globe by an order of magnitude since the 1980s [
6,
7]. Wildfire spread and reduced vegetation cover are expected to continue due to the changing climate [
8]. In combination with climate change, human activities are responsible for the initiation of wildfires because of development/urbanization pressures [
9] and the fire risk posed by communities within or near forest areas, as well as the replacement of rural by urban populations at WUI zones [
10], and the interaction of abiotic, biotic, and human factors [
11]. Human activities that cause wildfires span the entire range, from accidental or negligent actions to deliberate arsons to clear up land for cultivation, as in Brazil, or for tourist and second home developments, as in many Mediterranean countries [
12,
13,
14].
The current article gives a summary of the occurrence and causes of wildfires in the U.S. and Europe, which together with Australia’s bushfires and the fires in the Amazon aim to illustrate the extent and urgency of a current global problem that in many cases exceeds national response capabilities. A comprehensive exposition is provided of the effects of wildfires on the geoenvironment, analyzing the dominant processes on physicochemical properties of the soil such as soil organic matter, carbon content, soil hydrophobicity, nutrient availability, and leachability; and the water resources, geomorphology, and vegetation patterns of affected regions.
2. Occurrence and Causes of Wildfires and Mega Fires
A large portion of wildfires are initiated by humans, mainly due to a lack of care, and the rest are initiated by natural events such as dry lightning. However, the probability and extent of the resulting wildfires have drastically increased due to the higher level of availability of fuel for wildfires. In other words, the improper care taken to extinguish the fires during camping and recreational activities by human beings is one of the primary reasons. On the other hand, warmer, drier, and longer summers have supplied abundant fuel for wildfire (e.g., dry brush), which in turn have increased wildfire activity across much of western North America by an order of magnitude since the 1980s [
6,
15]. This is also the case in Australia and most recently Europe.
In the past decades, large wildfires have increased in the U.S. at an alarming rate, especially in the Western part of the U.S.A. Between 1984-2011 in the Western U.S., the number of large fires (>400 ha) increased at a rate of seven fires per year with an increase in associated fire area of 355 km2 per year [
16]. The smoke from the 2020 Western U.S. wildfires extended across the U.S.A. reaching the United Kingdom and Northern Europe [
17].
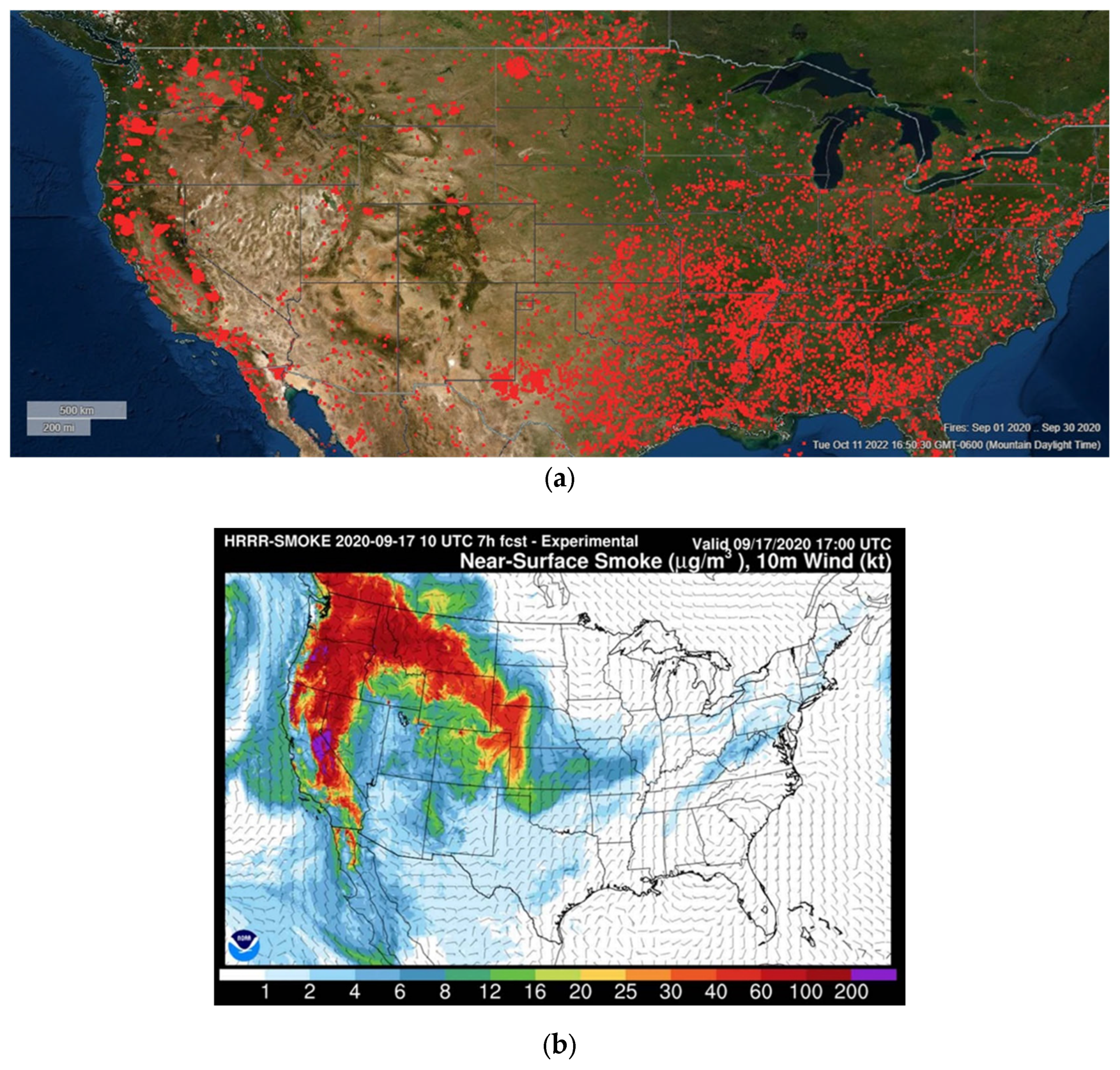
Figure 1 shows the extent of these wildfires and the poor air quality in the Western U.S. as a result of them. Near-surface smoke in this figure refers to air that hovers within 8 m of the ground surface and causes asthma attacks and burning eyes.
In the Western U.S., wildfires have expanded spatially and temporally, with fires early in the spring, and late in the fall and winter, due to earlier warming and drying seasons (
Figure 2). The U.S. National Interagency Coordination Center (NICC) reported that 68,988 wildfires occurred in the United States in 2022, which was noticeably higher than the 10-year average, compared to 58,985 wildfires reported in 2021, consuming about 7.5 million acres. There are more fires occurring in forested areas due to the lack of access and distance from critical areas such as populated and industrial regions. Of those 89% were caused by human activities, which were responsible for about 44% of the burned areas [
20]. Anthropogenic climate change has doubled the Western U.S. Forest fire area since 1984 [
21].
Detrimental short- and long-term health impacts of wildfires include increased mortality and aggravated respiratory, cardiovascular, mental, and perinatal health issues [
23], adding to the vulnerability to pandemics. Wildfires have imposed an economic toll of
$76B and
$450B on the Western U.S. annually, from short- and long-term exposure to wildfire smoke, respectively [
24]. Wildfires’ impact extends beyond a burned region and over many years, imposing a chronic, complex driver on ecosystems.
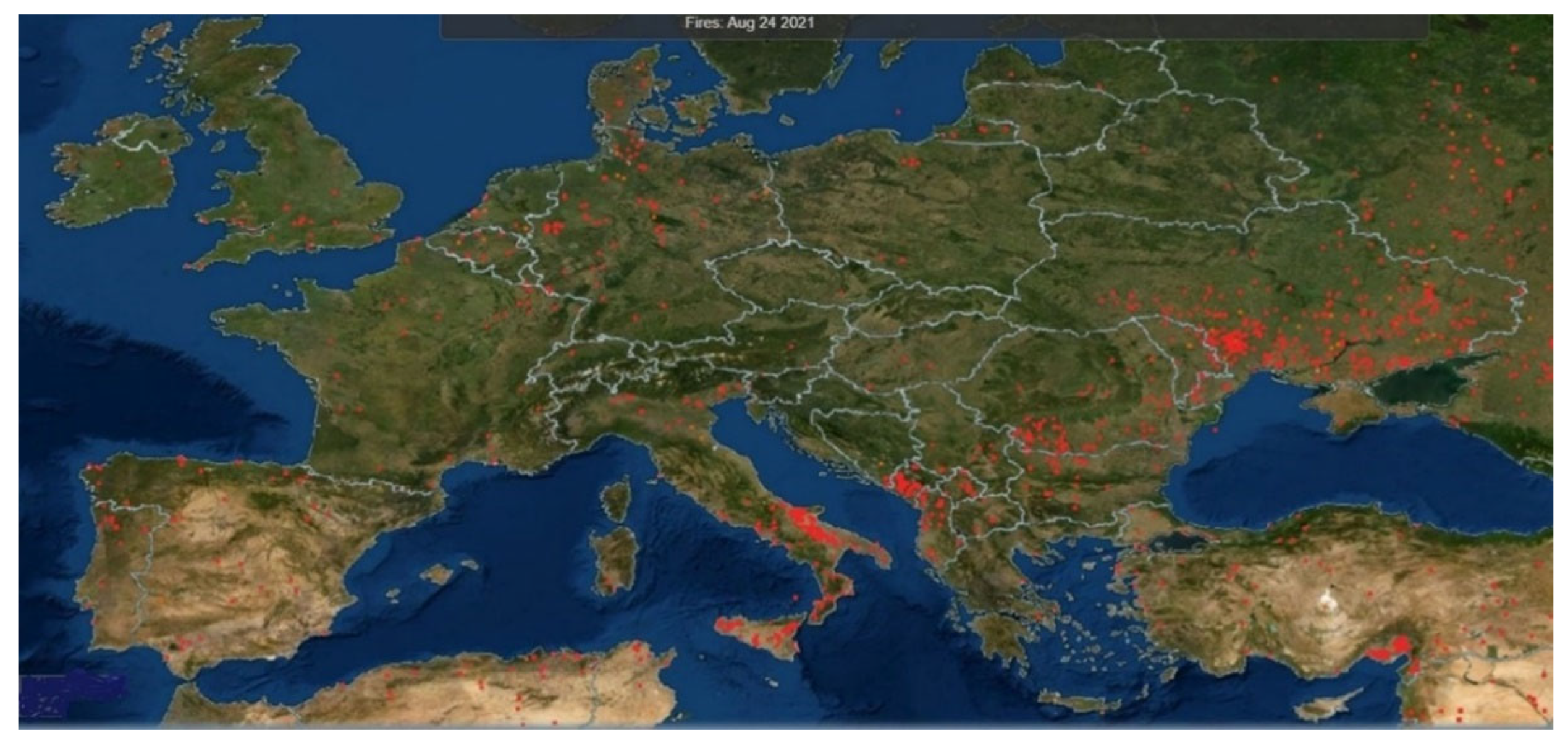
The situation in Europe is similar to the U.S.A., with the likelihood of occurrence and severity of wildfires increasing, especially in the Northern and Eastern European countries and the Mediterranean region (
Figure 3), with 2018 exhibiting 40% more fires than the previous year [
25]. About half a million hectares are burned in Europe, annually, 75% of which are in Mediterranean countries. In the north of Europe, countries such as the United Kingdom, Ireland, Finland, Latvia, Germany, Poland, Sweden, and Norway have seen unusual fire waves since 2018 (seen in
Figure 3). Expenditures for fire prevention and suppression in Europe approached US
$3B per year, and economic damages during the period of 2000-2017 exceeded US
$60.5B [
26,
27].
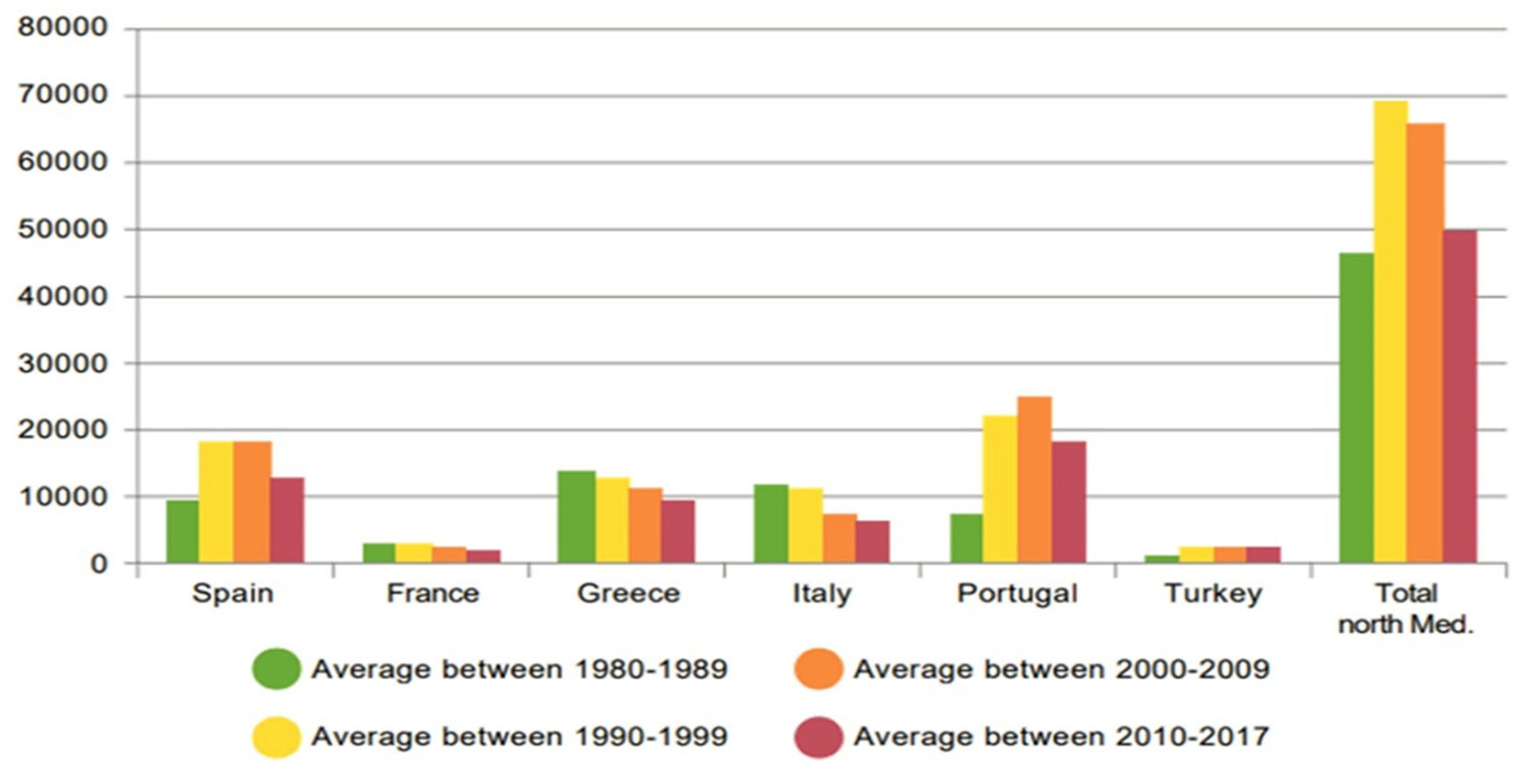
Portugal, Spain, Greece, Italy, and France are listed as the top five countries in Europe with regard to the occurrence and extent of wildfires (
Figure 4). The fire statistics between 2009 to 2018, indicate that 2.84% of Portugal’s forests have been burned, on average each year, with the equivalent numbers for Greece, Italy, Spain, and France being 0.77%, 0.66%, 0.35%, and 0.17%, respectively [
29,
30]. Incidentally, it can be observed that all European countries discussed above are on the southern part of the continent, which are prone to high temperatures and longer dry periods, which are conducive for wildfires to occur. Turco et al. [
31] conducted Monte Carlo simulations to estimate the effect of climate change on rural fires in the Mediterranean region and found that depending on the global warming scenarios the burned area would increase from 40% to 100%.
The Mediterranean region is vulnerable because the conditions for the so-called mega-fire triangle, or 30-30-30 rule, hold during most of the summers. The rule refers to surface temperatures over 30°C combined with relative humidity less than 30% and wind speeds over 30km/hr. [
32]. At the same time, the Mediterranean region has become the top tourist destination in the world with a 32% share of the international travel industry (World Tourism Organization [
33]. As a result of this, arsons, aiming to expand urban, summer housing, and resort developments inside forest areas—especially in coastal locations—have become responsible for 26% of the fires (in Spain almost 55% of rural fires are considered intentional) [
34]. This situation is accentuated by poor urban planning that allows the embedding of communities within or in the vicinity of forested areas, classified as wildland-urban interface (WUI), with little public understanding, participation in forest protection, and infrastructure measures [
26,
30]. Due to the spread of wildfires, railroad and transportation operations have been impacted, and operation teams must implement new procedures to reroute train flows affected by fires. For example, BNSF railways in California rerouted some trains to the Central Rockies, and even on some longer routes further east, to reach their destinations [
35]. In addition to the direct hazard of fire on rail transportation, the embankment can be impacted by the deteriorating impacts of wildfires. However, further research is needed. In the absence of research results, most transportation authorities, for the time being, have resorted to prescribed low-severity fires to mitigate this impact [
36]. In addition, the monoculture, such as of eucalyptus, which accounts for almost 25% of Portugal’s trees, and of Aleppo pine forests in Greece (
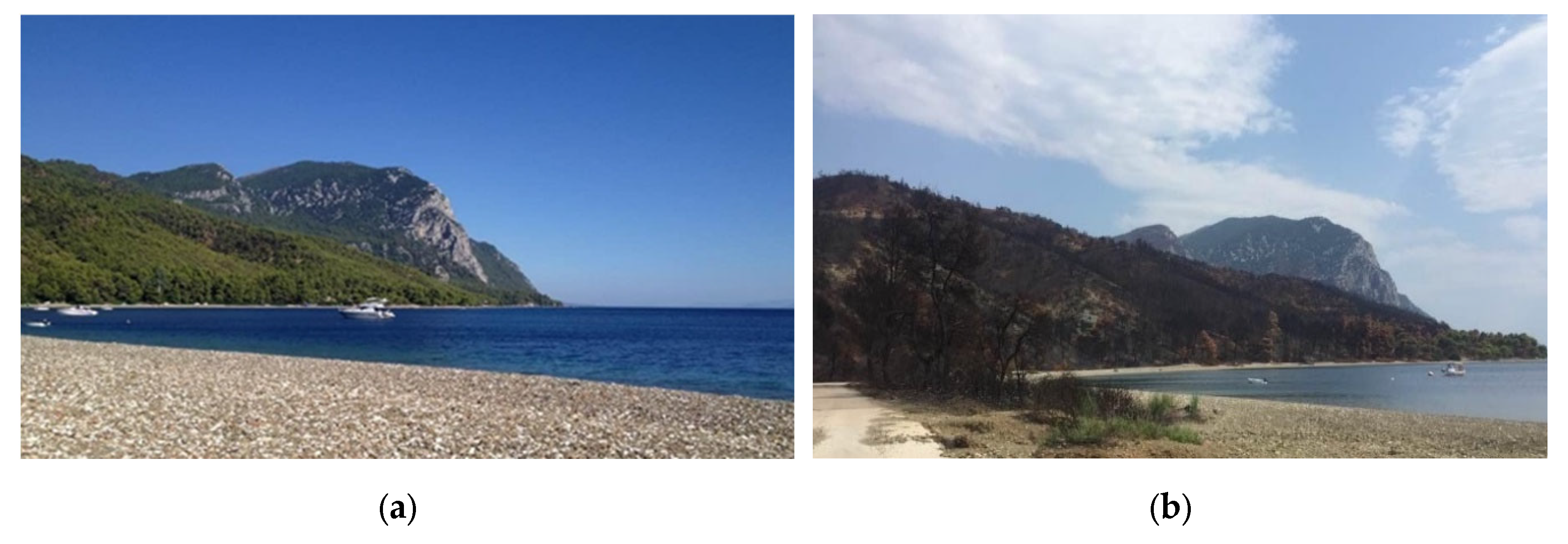
Figure 5) and France, with their rapid burning rate and flying sparks that can travel great distances make ground fire-suppression efforts extremely difficult to be successful.
3. Wildfire Effect on Soils Properties
In a burned area, the physical, chemical, biological, and hydrological properties of the soil change, especially the shallow soil, which is difficult to recover to their initial levels several years or even decades after a fire. Depending on fire intensity, severity, and frequency, fire events may significantly alter soil's physical properties, such as soil gradation, soil structure and texture, plasticity, bulk density, porosity, soil water-repellence, infiltration rates, and water storage capacity. The impacts of wildfire on the geoenvironment are broad and diverse. Some of these impacts are not known or foreseen, and even for a large fraction of impacts that have been observed or well documented, quantitative evaluation of the impact may not be available.
3.1. Fire Impact on Organic Matter and Clay
Organic Matter (OM) serves as a powerful aggregating agent, holding sand, silt, and clay particles into aggregates. Hence, a loss of OM results in a loss of soil structure and a reduction of macropore void space. Even in low-severity fires, soil OM undergoes a series of physical and chemical transformations depending on burning conditions.
Charring/oxidation of soil OM typically commences at temperatures of ~85°C [
37] with free moisture vaporized as soon as temperatures approach 100°C. Lignin and hemicellulose begin to degrade between 130 and 190°C, those reactions being endothermic. The decomposition of lignin and hemicellulose becomes rapid at 200°C, while cellulose undergoes chemical dehydration at 280°C. About 35% of the total mass loss occurs before soil OM reaches 280°C, with exothermic reactions predominating, while OM ignites once soil temperatures exceed 280°C. When the surface temperature of soil OM reaches 500 to 600°C, glowing combustion occurs if oxygen is not excluded from the char surface [
38].
For severe fires, the decrease in soil OM and resulting ash generally produce increased soil bulk density, reduced porosity, and a decrease in water storage capacity. In addition to resulting physical-chemical properties, changes in soil OM of the surface horizons may affect the microbiological properties of the underlying mineral soil. Following severe fires, changes in soil properties are greatest at the 0–5cm depth, since the temperature rarely exceeds 100°C below this depth [
39].
Most volatilized OM is lost upward as smoke. However, for intense burns, a small number of hydrophobic substances in the litter layer are forced downward along steep temperature gradients in the upper 5cm of soil, condensing to form a water-repellent layer. These hydrophobic organic compounds coat soil aggregates or minerals creating a discrete water-repellent soil layer parallel to the ground surface. Water-repellent soil layers are reportedly formed at temperatures of 176–288°C and destroyed at >288°C [
40].
Clays have a texture class susceptible to modification by elevated temperature through the irreversible removal of structural hydroxyl ions and destruction of the crystalline structure commencing at temperatures of ~400°C [
41,
42]. Fusion of clay mineral particles can occur at temperatures between 600°C and 700°C, and complete destruction of clay may occur at 700–900°C [
43]. The fusion of clay particles could cause aggregation of clay particles to form stable sand-sized particles, thus increasing sand content at the expense of clay content [
44].
After clayey mineral soils are burned between 100°C and 300°C, the liquid limit (LL) monotonically decreases, with minimal impact by a temperature rise above 400°C. On the other hand, the plastic limit (PL) decreases rapidly up to 300°C, reaching a nonplastic (NP) state at 400°C [
45], indicating that such soils can only retain small amounts of water despite their low abundance of clay minerals.
Noraini [
46] reported that wildfires reduced the Atterberg limits of clayey soil (major minerals being montmorillonite) from initial LL = 55% and PL = 35% (plasticity index of
IP = 20%) to final values of 30% and 14% (
IP = 16%), respectively, such that the investigated soil transitions from the high-plasticity silt type to that of low-plasticity clay. Awn et al. [
47] performed four burning cycles on natural fine-grained soils, with burning temperatures of 150 and 300°C, producing progressive reductions in the Atterberg limits from LL = 56% and PL = 51% for the natural soil to LL= 42% and PL = 39% for the fourth burning cycle, respectively. However, some aspects of laboratory tests (e.g., 10-h burn cycle duration) make the results not directly relevant to real wildfire scenarios [
48]. Furthermore, the burning methodology can influence the outcome, e.g., heating soils in a muffle furnace does not address the movement of hydrophobic substances into a soil profile and does not allow for the direct effect of flames on the soil.
3.2. Effect on Carbon Content, Soil Nutrient Availability, and Leachability
Soil is the largest reservoir of Carbon I, storing 2157–2293 Pg of C in the top 1m of soil, where 1462–1548 Pg of Carbon (C) is soil organic carbon (SOC) and the remaining is soil inorganic carbon (SIC) [
49,
50]. Soil and surface litter contains two or three times as much C as the atmosphere, playing an important role in the global carbon balance [
51]. Forests account for the largest quantities of global soil carbon pools [
52].
SOC is mainly formed from the decay processes of plant litter [
53], the metabolism of organisms, and the substances of microbes and fungi [
50]. SOC is closely related to soil fertility and carbon cycling, the structure, and properties of soil [
54], the adsorption of contaminants [
55], water retention and pH buffering [
56], and soil biodiversity [
57]. In contrast, SIC is present mainly in the form of soil carbonates from the weathering process of silicate carbon, as well as CO
2 in the gas phase, and CO
32- and HCO
3- in the liquid phase. SIC is the main form of soil carbon in arid and semi-arid areas [
58]. Despite that SIC is a large C pool, it is generally considered not to affect the concentration of atmospheric CO
2. It is worth mentioning that available studies showed that SIC may also sequester CO
2 and has a promising application prospect [
59].
Fires on forests and peatlands constitute one of the most important natural disturbance modes in forest ecosystems with the global annual burned area varying from 301 to 377Mha from 1997 to 2011 [
60] and causing emissions to the order of 0.4 Pg C or 1.3 Pg CO
2 per year, which have a great impact on the carbon balance and global climate [
61].
The effect of fires on SOC depends on the fire severity, frequency, season, soil types, forest type, and terrain. Some studies have found that burning increases SOC content [
62]. On the other hand, other have shown that fires either reduce the SOC content in soil [
63,
64] or that do not significantly change the SOC content in soil but only redistributes SOC. Johnson and Curtis [
65] found no significant effect on carbon content after a fire but observed a significant long-term fire-induced increase after 10 years due to the decline in mineralization rate.
Many studies have shown that the effect of fire on SOC content is varied. Zhao et al. [
66] found that the SOC content in spring-burned plots is higher than in autumn-burned plots, due to the consumption of burned litter and soil OM matter by snowmelt and wind erosion. Frequent fires have a dual effect on SOC content. They reduce lower biomass and litter, thus, leading to a reduction in organic inputs to soils and to a decline in the SOC content [
67]. In contrast, frequent fires can increase the SOC in some cases by promoting the establishment of more-productive plant species, burning more dead roots, and leaching more ash downwards into soils [
68]. The loss of the SOC content by wildfires is generally higher than in prescribed fires [
69]. High-severity wildfires are associated with large SOC losses, while moderate- and low-severity wildfires can promote the renovation of dominant vegetation, physically protect SOC, and increase the quantity of carbon mineralization [
63].
It has been observed that wildfires could cause an increase in soil pH due to liming activity caused by the precipitation of Calcium Oxide (CaO) in the form of combustion ash [
70]. The influence of fires on phosphorous availability is more complex. It was observed that the phosphorous availability could be reduced due to: (i) adsorption on the exposed/created hydroxides based on Fe and Al and/or (ii) precipitation. On the contrary, the phosphorous availability could increase due to the: (i) degradation and partial oxidation of OM and/or (ii) desorption of phosphorous from hydroxides of Fe and Al owing to an increase in the pH caused by the liming activity [
71].
The influence of wildfires on nutrient availability and leachability is significant given that this influences soil fertility. Chungu et al. [
70] found that the total nitrogen (TN) was doubled after a fire, promoting the growth of
Eucalyptus Grandis, which was attributed to the increase in ammonium (NH
4+) and nitrates (NO
32) in the soil. These findings contradicted the study by Murphy et al. [
71] that reported a decrease in the TN and an increase in the mineral nitrogen due to the heat-induced degeneration of organic nitrogen. It should be noted that the former used an oxidation method for the measurement of TN that ignores the inorganic form of nitrogen.
3.3. Wildfire-Induced Hydrophobicity
Wildfire-burned soils can show varying levels of hydrophobicity depending on the severity of the fire, the amount of OM left, and the ultimate temperature the soil was under for a given duration of time [
63]. Water repellence in soils is generated by five dominant mechanisms: fungal and microbial activity, growth of particular vegetation species, organic matter, heating of the soils by wildfires, and soil characteristics. The fluctuation in levels of water repellence, following a wildfire, can lead to significant changes in the hydrologic response of soils [
72], enhancing runoff and erosion [
73], or increasing unsteady or reduced infiltration [
74,
75]. Due to soil heterogeneity, the cause of changing levels of water repellence is often unclear and can be considered as an accumulation of the influence of several factors. Lower temperatures at depth result in vapor cooling and condensing on the fabric of the soil, coating particles in the cooled organic substance [
76]. Similarly, aliphatic hydrocarbons are released from OM when subject to extreme heat, generating hydrophobic compounds [
77]. Temperatures between 175°C and 280°C are necessary to cause an increase in hydrophobicity, whereas beyond this range leads to the nonuniform spread of water repellence close to the surface [
76,
78]. While elevated levels of water repellence are seen initially, they break down over time due to instability. As
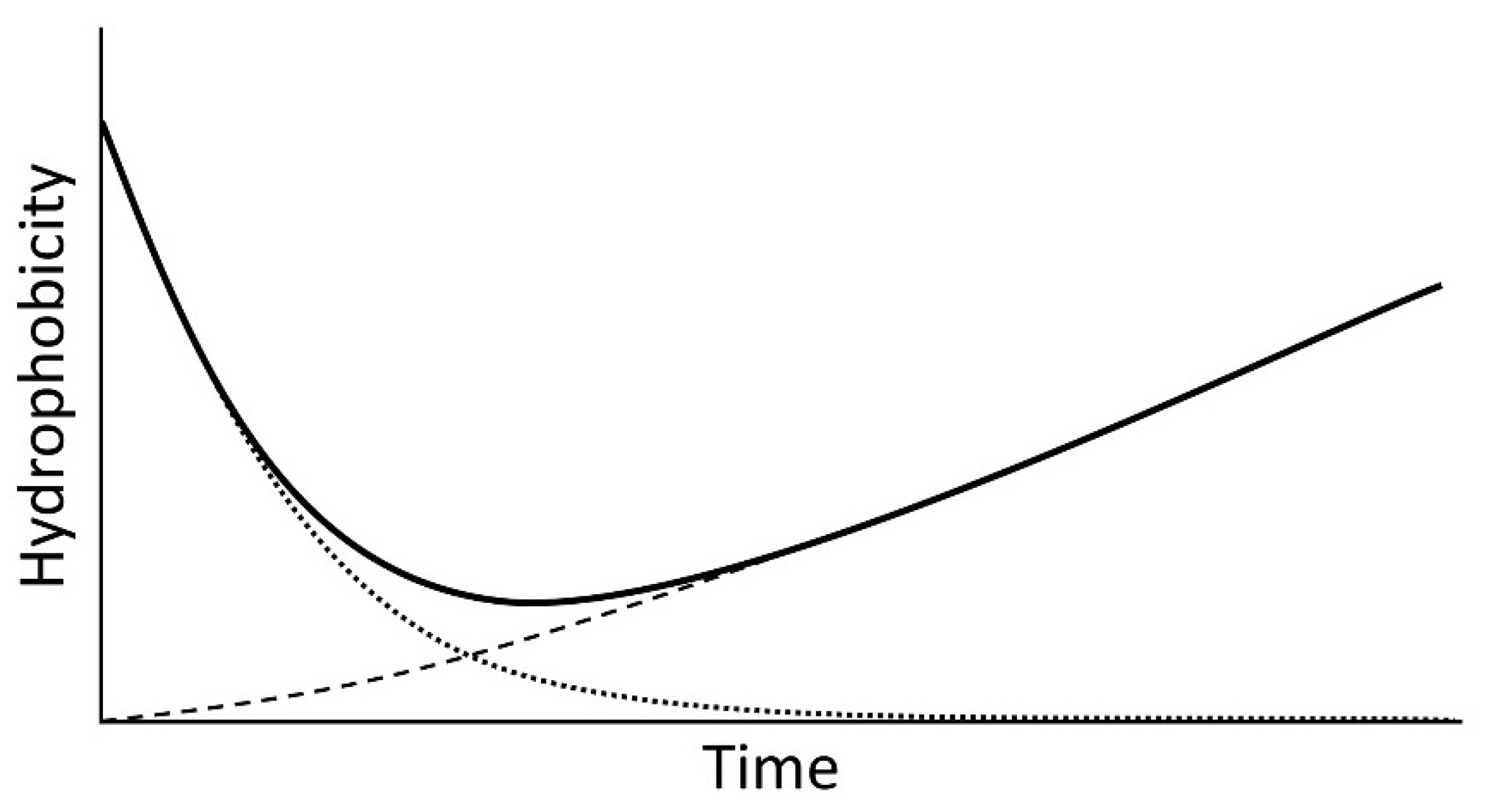
Figure 6 suggests, given a longer timescale, hydrophobicity levels begin to rise, and this is thought to be due to organic matter recovery.
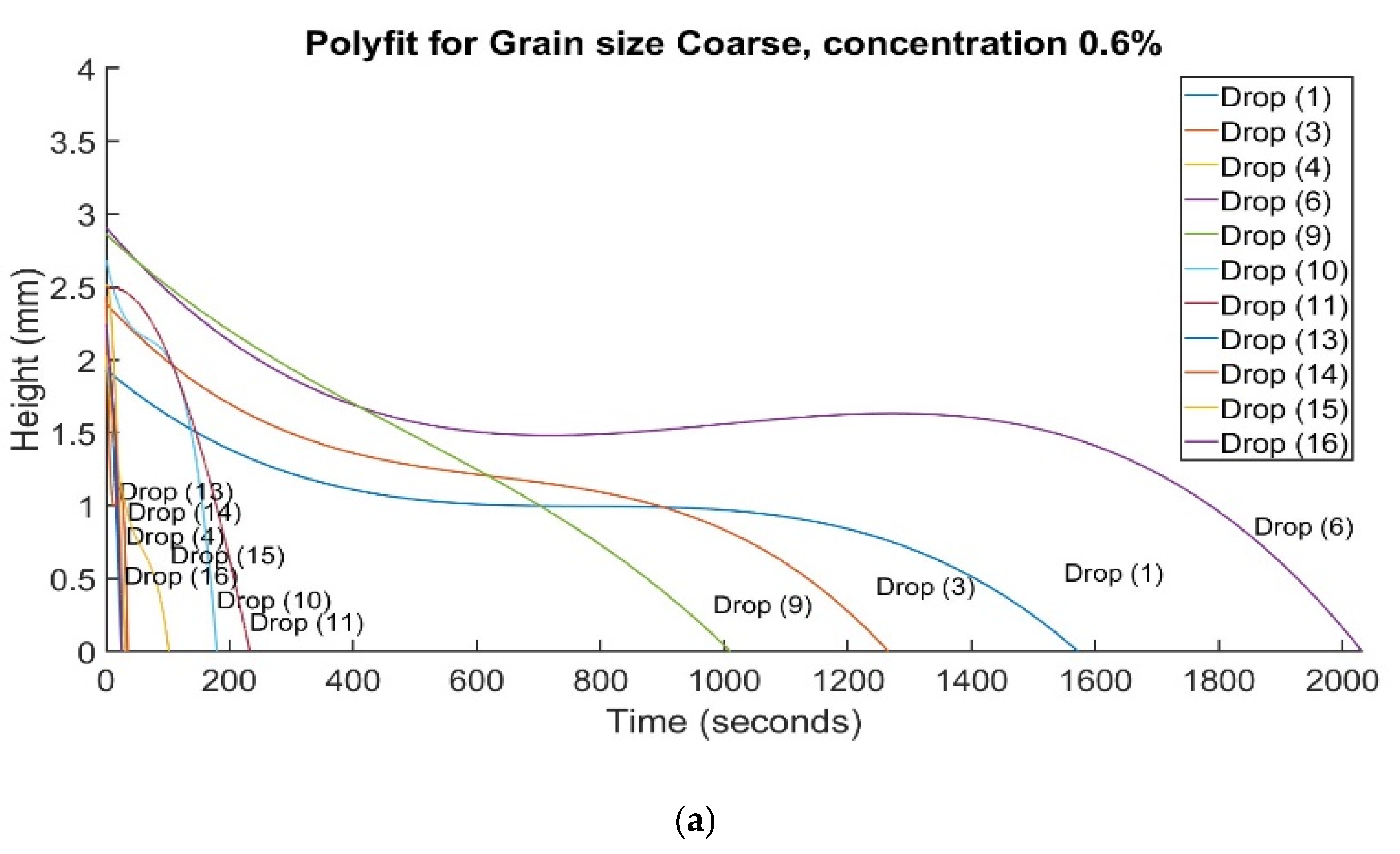
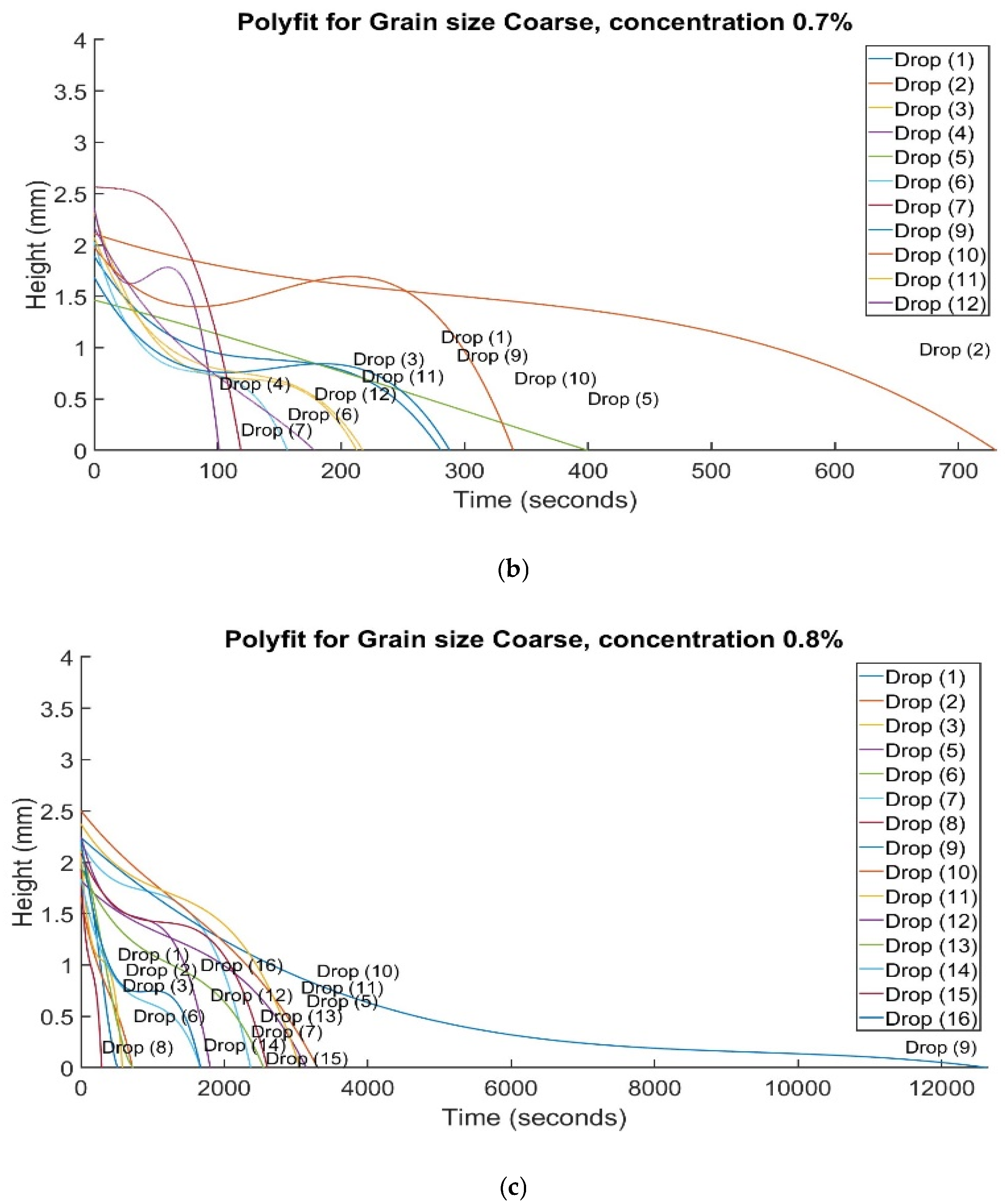
The Water Droplet Penetration Test (WDPT) is among the most widely utilized methods to identify and measure soil hydrophobicity. The method is, however, subjective when used for beyond identification and for classification. The method does not consider differing site conditions, environmental factors, grain sizes, and soil types. Other test methods are needed to classify soil water repellence. The method needs to be calibrated for grain size or other environmental conditions. Veneris et al. [
79] investigated the impact of various levels of hydrophobicity on soil samples of various grain sizes during WDPT. They used a hydrophobicity inducing surrogate at various rates of dilution in deionized water to highlight the impact of lifted hydrophobic particles on delaying water droplet infiltration across soil grain size and hydrophobicity level. Particle lift, especially in coarser soils, delay water droplet penetration. Hydrophobicity-induced particle lift causes instability, leading to randomly occurring distinct regimes (
Figure 7), requiring their consideration in hydrophobicity measurement using the WDPT.
Increased biotic activity due to vegetation and microfauna populations can lead to increased levels of water repellency [
80]. Certain species of plants, such as evergreens and differing eucalyptus species can induce stronger hydrophobicity in soils [
77]. Contrary to this, as ash settles on the surface, a wettable layer can be deposited and reduce the effects of heating on the soil leading to a reduced water repellency and less risk of surface runoff and erosion [
73,
81].
The temperature of the ash layer can have a significant effect on the hydrologic response with the ash that settles on the surface either increasing or decreasing runoff depending on the temperature of the burn [
82]. Lower-temperature ash usually contains significant amounts of organic carbon inducing hydrophobicity and increasing runoff, while higher temperatures destroy said carbons, leaving the layer more hydrophilic and causing water ponding/storage in the ash layer (and decreasing surface runoff) with a gradual release to the underlying layer. In case of high-temperature fires, there will then be hydrophobic-burned soil covered with layers of hydrophilic ash that can retain water after a wetting event. The heat generated during wildfires dries water present in (i) larger pores, (ii) inter-aggregate pores, and (iii) intra-aggregate pores [
83]. This heat can be sufficient to drive off residual water leading to the creation of hyper-dry conditions (soil-water content < 0.02 cm
3/cm
3) similar to oven-dried soils and causing the decomposition of OM [
83]. Thus, the ponded water cannot readily infiltrate through the hyper-dry burned soil until the water uptake mechanism transitions from adsorption to capillary condensation [
84,
85].
The transition water content is soil specific and corresponds to 65% to 85% relative humidity [
85]. During the transition, burned hillslopes are more prone to runoff-dominated erosion and associated debris flows. A fire event can cause hydrophobicity within the top few inches of the ground surface, and the resulting layer has the potential to increase runoff by more than ten times the average rate when combined with the removal of exterior stabilizers such as root systems.
In this context, Gabet and Sternberg [
86] and Ebel and Moody [
87] studied saturated soils’ water content, sorptivity, and the wetting-front potential of the 2017 Thomas Fire in California that produced catastrophic debris flow. Their results indicated that the presence of wildfire ash reduced the field saturated hydraulic conductivity. In addition, soil-water repellency behavior was also observed due to a decrease in sorptivity and wetting front potential at the burned sites [
88]. Hydrophobic soils burned by high-temperature fires present a Type-II isotherm shape, which shows incremental adsorption of water molecules onto particle surfaces, unlike other hydrophobic materials that exhibit a nonuniform behavior in adsorbed water content at high relative humidity. Even though the shape of the isotherms is not influenced, the amount of adsorbed water content was found to be different in hydrophobic soils [
72,
89]. As the Type-II isotherm shape is maintained in hydrophobic soils, isotherm models that are based on incremental adsorption remain valid.
The deposited hydrophilic ash layer will eventually clear, highlighting its importance in short-term water repellency levels post-fire [
90]. This process could be the cause of reduced levels of hydrophobicity found when trying to replicate wildfire-induced changes [
91]. As the ash cover deteriorates, the topsoil will be left with no vegetation, which has been seen to be the primary cause of increased runoff and erosion rates [
92]. Similarly, as the short-term water repellency increases on the surface, the coatings upon the minerals will impede the formation of a soil crust, causing an increased risk of splash erosion [
93].
Rill erosion is also observed, due to the water-repellent layer causing a build-up of pore pressure and consequent reduction in shear strength in the overlying saturated soil [
94,
95]. Fingered flow can also result from this, as the distinct paths caused by rill erosion offer less resistance to infiltration. With increasing levels of hydrophobicity as well as distinct paths of eroded soil, the chances of preferential flow and fingering are much higher, which often arises from changes in wettability [
96,
97]. Currently, there is little modelling work related to the processes of wildfire-induced changing water repellency, with most research focusing on either varied wettability or wildfire effects as unconnected processes [
98].
Erosion because of increased repellency has been explored through the Morgan-Morgan-Finney (MMF) model [
99], which has seen varying advancements in the past decade [
100,
101]. Zema et al. [
102] modified the MMF model to include the effects of water repellency, to quantify the impact of wildfire on seasonal runoff and soil loss prediction. Similarly, the Limburg Soil Erosion Model (LISEM) [
103] was evaluated in its applicability for representing rainfall-runoff response based on varied stages of vegetation recovery [
104]. A multiple regression model that tested several key factors for their impact on erosion found that erosion processes were mainly due to rainfall intensity and ground cover [
105].
The instability of infiltration following wildfires has also been studied. Nyman et al. [
75] modelled an ash-covered soil post-wildfire, to address the poor depiction of water retention and preferential flow in existing models. This layered model was able to depict the accelerated transport of water, synonymous with the preferential flow. Malkinson and Wittenberg [
77] included erosion and OM in a model to analyze wildfires' long-term effects on soil water repellency. Timescales in the analysis of wettability effects [
106], OM, and fungal/bacterial processes should also be considered when modelling the development and impact of soil hydrophobicity by wildfires.
Even though hydrophobicity has become a key area of research in post-fire-events, almost all research analyses specimens in the field at the location of burn or in the laboratory after a specimen has been collected from the field. When testing techniques for post-fire remediation, the test environments or samples need to be consistent in order to fully understand the effects of any remedial technique, and there is not currently any standard for consistently developing a hydrophobic soil specimen simulated within the lab.
3.4. Effect on Soil Desiccation Cracking and Plant-Soil Interaction
The heat during a wildfire can lead to rapid reduction of water content in the shallow soil and even induce desiccation cracking. Under an elevated temperature, the vapor-pressure gradient of the soil-air interface increases, and the evaporation of water from the soil intensifies [
107,
108,
109]. Continuous evaporation of soil water caused by a wildfire leads to significant drying-induced shrinkage of surface soil and numerous desiccation cracks. Fires with larger intensity led to simpler soil cracking morphology with a larger surface-crack ratio and crack depth. This is because as the evaporation rate of soil-water increases with temperature, a large gradient tension-stress field develops within a brief period of time leading to the creation of desiccation cracks more rapidly and more severely [
110,
111].
The generation of desiccation cracks destroys the integrity of soil, greatly weakens its bearing capacity, increases its compressibility, and reduces its shear strength, exacerbating slope instability and landslides, aggravating soil erosion, and damaging the ecological environment [
112].
Wildfires can negatively affect the reinforcement provided to the soil by plant roots [
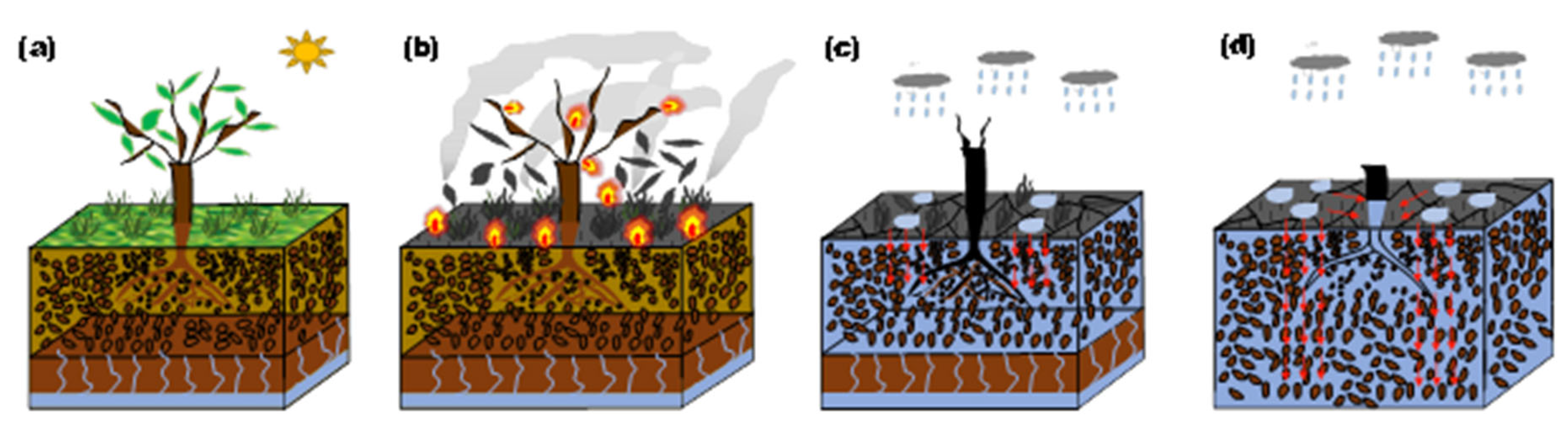
113]. The failure of the root-soil system evolves [
76,
95], as shown in
Figure 8. Kamchoom et al. [
114] observed exponential reduction with the time of tensile strength and Young’s modulus of
Cynodan dactylon during a one-year root decay after burning. This was explained by the decline in root chemical components that provide root biomechanical strength, such as lignin and cellulose [
115]. Experimental campaigns carried out by Ni et al. [
116] and Ng et al. [
117] have demonstrated that the process of root decay could substantially reduce the water retention capacity but increase both the saturated and unsaturated hydraulic conductivity of soils. Eventually, the soil not only loses its mechanical reinforcement but also becomes more fragile than that without vegetation cover, creating conditions for soil instability. A numerical study by Ni et al. [
118] indicated that the root-induced changes could lead to landslides and debris flow under heavy rainfall events, as well as soil erosion. Initially, after a fire, post-fire debris flows are dominated by a surge in surface runoff [
119], while several years after a fire, the slope instability is mainly due to the decrease of soil strength, which triggers shallow landslides [
120].
3.5. Hydrogeological Effects of Wildfires
In steep landscapes, post-fire mass-wasting events generate substantial, sometimes dramatic, inputs of sediment to stream networks [
81,
119,
122]. Such events, which transport most of their material from storage in small channels, provide the dominant source of sediment to streams. Mass-wasting events take the form of debris flow caused both by bulking of overland flow leading to gully erosion or the formation of debris flow initiated by shallow landslides [
119,
123]. Hydrologically, bulking debris flow is driven primarily by intense rainfall on water-repellent soils, typically by summer convective storms [
81]. On the other hand, shallow landslides are more commonly initiated by long, heavy rainfalls [
124], or rainfalls combined with rapid snowmelts exacerbated by the loss of canopy [
125].
The yield of sediment from severely burned basins can be extreme, with values ranging up to 280,000 T/km
2 per event, and values of several tens of thousands of T/km
2 being common [
123,
125]. Long-term small-basin yields tend to be limited by soil formation rates and are of the order of 100T/km
2/yr. [
126]. Yields in the years after fires are very large compared to long-term average rates, owing to the need for fuels to regrow. Under undisturbed conditions between periodic pulses from fire, small-basin sediment yields are of the order of 10 T/km
2/yr. [
127].
Punctuated sediment supplies have different effects on the disposition of sediments within a channel compared to chronic sediment inputs. Large-debris-flow deposits in rivers tend to “smear” down the channel over time such that inputs of individual events that are quite severe and rare in smaller basins generate a somewhat steadier supply of gravel-sized sediment in downstream reaches [
128]. Only a fraction of topographic hollows generally fails or gully after a given fire event, taking many centuries to refill from hillslope processes. Locally extreme sediment yields by debris flow in catchments of less than one km
2 tend to damp rapidly with scale [
129].
On the other hand, wildfires are an important and integral part of many ecosystems playing a key role in ecosystem dynamics, regulation of pest population, and species preservation. In areas where frequent fires occur, local plant species have adapted to fire events. Species that successfully survive fires are referred to as fire-resistant species (pyrophyte). Certain species form a thick layer of nonflammable tissue (cork) on their surface, e.g.,
Quercus suber.
Pinus palustris, Sequoiadendron giganteum, and Sequoia sempervirens are also capable of resisting fires. Some species need a mild fire to release seeds from cones, e.g.,
Pinus halepensis, and Pinus contorta [
130].
4. Conclusions
This paper reviews and critically analyses the cause of various impacts of wildfires on the geoenvironment. A range of impacts on the geoenvironment is discussed and, in most cases, qualitatively analyzed. Historically, wildfires have been caused mostly by human activities as well as in part by natural causes such as dry lightning. However, warmer, and drier weather has resulted in an abundance of ample fuel and favorable wildfire conditions, which have been accentuated by anthropogenic activities. Wildfires have short- and long-term impacts on the environment in general and on the geoenvironment.
In general, soil properties viz., the physical, chemical, biological, and hydrologic characteristics are altered within the burned areas depending on the intensity, severity, and frequency of the wildfires. Natural recovery of this alteration takes years or decades. The heat from wildfires can provoke desiccation cracks in relatively fine-grained soils, destroying soil integrity by reducing bearing capacity, increasing compressibility, and decreasing shear strength. Soil deterioration can lead to exacerbation of slope instability and landslides, aggravate soil erosion, and harmed the ecological environment. Depending on fire severity and intensity, burned soils can also exhibit various degrees of hydrophobicity (leading to water repellency) or hydrophilicity. On one hand, high-severity wildfires result in significant SOC losses, whereas moderate- and low-severity wildfires can promote dominant vegetation renovation, physically protect SOC, and increase the amount of carbon mineralization. Post-wildfire, changes in water repellency can cause major changes in soil hydrologic response, lowering infiltration, increasing runoff, erosion, and soil instability. Wildfires can also degrade soils through plant root decay, loss of vegetation, and nutrient leachability. Furthermore, field studies have discovered elevated amounts of chemical and organic pollutants long after fire events. Beyond the impacts of individual fires, frequent fires have a dual effect on soil organic carbon content. Unlike the above-mentioned negative impacts and despite the direct loss of some nutrients by wildfires, wildfires can also have positive impacts on nutrient availability and leachability, improving soil fertility.
Wildfires can cause soil contamination by post-fire ash, polyaromatic hydrocarbons, and debris caused by wildfires. At the same time, human response methods can also be problematic and cause soil contamination, e.g., current fire-suppression agents can release toxic, persistent, and mobile contaminants (e.g., PFAS) into the geoenvironment.
As a natural response to wildfires, some local plant species have adapted to frequent fire events, either forming a thick covering of non-flammable tissue on their surface or becoming fire-resistant.
Some impacts are still not well understood, and some are only qualitatively analyzed. Further research is needed to quantify these impacts in order to better prioritize properties in need of attention and the minimum level of restoration for each property.
Moreover, the change in the spatial and temporal scales and the nature and extent of wildfires—due to the progressing climate change can lead to new unforeseen impacts or extensions and changes in the nature of known impacts. These calls for increased research to better understand the impacts of wildfires on the geoenvironment and a complete rethinking of national and international policies and measures in the prevention, mitigation, control, and suppression of fires, as well as forest and landscape restoration actions.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.F.; formal analysis, A.F., M.K. A., V.S. N. S. G., I.D. A., T.A., X.C., Q.C., P.C., S.C., V.F., S.G., L.I., P.I. D., F.C. H. L., E.K., S.B. M., B.C. O’K., E.K. P., D.P., E.R., M.S., T.S. S., D.N. S., P.S., C.S. T., G.T., M.D. V., M.V., J.W.; writing—original draft preparation, A.F., M.K. A., V.S. N. S. G., I.D. A., T.A., X.C., Q.C., P.C., S.C., V.F., S.G., L.I., P.I. D., F.C. H. L., E.K., S.B. M., B.C. O’K., E.K. P., D.P., E.R., M.S., T.S. S., D.N. S., P.S., C.S. T., G.T., M.D. V., M.V., J.W.; writing—review and editing, A.F., M.K. A., V.S. N.; visualization, A.F., M.K. A., E.K. P., and M. V.; supervision, A.F.; project administration, A.F..; funding acquisition, A.F., and M.S.; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Science Foundation, NSF, through the Engineering Research Centers, ERC, Program, Award No. 1840654. The authors appreciate the support by NSF and its EEC program.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Keeley, J.E.; Syphard, A.D. Climate change and future fire regimes: examples from California. Geosciences 2016, 6, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godfree, R.C.; Knerr, N.; Encinas-Viso, F.; Albrecht, D.; Bush, D.; Christine Cargill, D.; Clements, M.; Gueidan, C.; Guja, L.K.; Harwood, T.; Joseph, L. Implications of the 2019–2020 Megafires for the Biogeography and Conservation of Australian Vegetation. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, B. Fires in the Amazon out of control. Again. Available online: https://www.vox.com/down-to-earth/2021/8/27/22639885/amazon-rainforest-fires-climate-change-2021 (accessed on 25 April 2024).
- Ramajo, R.J. Qué es un incendio de sexta generación y por qué los expertos creen que el de Sierra Bermeja lo es. [Online] elDiario.es, 2021. Available online: https://www.eldiario.es/andalucia/incendio-sexta-generacion-expertos-creen-sierra-bermeja_1_8297333.html (accessed on 26 January 2024).
- Pyne, S.J. The Pyrocene: How We Created an Age of Fire, and What Happens Next; Univ of California Press, 2021.
- Marlon, J.R.; Bartlein, P.J.; Gavin, D.G.; Long, C.J.; Anderson, R.S.; Briles, C.E.; Brown, K.J.; Colombaroli, D.; Hallett, D.J.; Power, M.J.; Scharf, E.A. Long-term perspective on wildfires in the western USA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, E535–E543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jolly, W.M.; Cochrane, M.A.; Freeborn, P.H.; Holden, Z.A.; Brown, T.J.; Williamson, G.J.; Bowman, D.M. Climate-induced variations in global wildfire danger from 1979 to 2013. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krawchuk, M.A.; Moritz, M.A.; Parisien, M.A.; Van Dorn, J.; Hayhoe, K. Global pyrogeography: the current and future distribution of wildfire. PLoS One 2009, 4, e5102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radeloff, V.C.; Helmers, D.P.; Kramer, H.A.; Mockrin, M.H.; Alexandre, P.M.; Bar-Massada, A.; Butsic, V.; Hawbaker, T.J.; Martinuzzi, S.; Syphard, A.D.; Stewart, S.I. Rapid growth of the US wildland-urban interface raises wildfire risk. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 3314–3319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- chAs-AMil, M.L.; PresTeMon, J.P.; MccleAn, C.J.; TouzA, J. Human-Ignited Wildfire Patterns and Responses to Policy Shifts. Appl. Geogr. 2015, 56, 164–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardille, J.A.; Ventura, S.J.; Turner, M.G. Environmental and Social Factors Influencing Wildfires in the Upper Midwest, United States. Ecol. Appl. 2001, 11, 111–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, R. Amazon Deforestation Rises to 11 Year High in Brazil. Mongabay Environmental News, 2019. https://news.mongabay.com/2019/11/amazon-deforestation-rises-to-11-year-high-in-brazil/.
- Halofsky, J.E.; Peterson, D.L.; Harvey, B.J. Changing wildfire, changing forests: The effects of climate change on fire regimes and vegetation in the Pacific Northwest, USA. Fire Ecol. 2020, 16, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, H. The causes of wildfires are clear. How they burn through communities is not. Nature 2023, 620, 923–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerling, A.L. Increasing Western US Forest Wildfire Activity: Sensitivity to Changes in the Timing of Spring. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B 2016, 371, 20150178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dennison, P.E.; Brewer, S.C.; Arnold, J.D.; Moritz, M.A. Large Wildfire Trends in the Western United States, 1984–2011. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 2928–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copernicus Atmosphere Monitoring Service (CAMS). CAMS Monitors Smoke Release from Devastating US Wildfires. Available online: https://atmosphere.copernicus.eu/cams-monitors-smoke-release-devastating-us-wildfires (accessed on 25 April 2024).
- NASA FIRMS (Fires Information for Resource Management System). Available online: https://firms.modaps.eosdis.nasa.gov/map/#t:adv;d:2020-09-01..2020-09-30;@-100.8,39.5,5z (accessed on 11 October 2023).
- Gabbert, B. Smoke and Air Quality Maps for September 17, 2020. Wildfire Today, 2020. Available online: https://wildfiretoday.com/2020/09/17/smoke-and-air-quality-maps-for-september-17-2020/ (accessed on 3 January 2024).
- National Interagency Coordination Center. Wildland Fire: Summary and Statistics. Annual Report 2021. Available online: https://www.predictiveservices.nifc.gov/intelligence/2021_statssumm/annual_report_2021.pdf (accessed on 20 March 2024).
- Abatzoglou, J.T.; Williams, A.P. Climate change has added to western US forest fire. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2016, 113, 11770–11775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U.S. Drought Monitor. Map Released April 21, 2022. Available online: https://droughtmonitor.unl.edu/ (accessed on 25 April 2024).
- Reid, C.E.; Brauer, M.; Johnston, F.H.; Jerrett, M.; Balmes, J.R.; Elliott, C.T. Critical review of health impacts of wildfire smoke exposure. Environ. Health Perspect. 2016, 124, 1334–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fann, N.; Alman, B.; Broome, R.A.; Morgan, G.G.; Johnston, F.H.; Pouliot, G.; Rappold, A.G. The Health Impacts and Economic Value of Wildland Fire Episodes in the US: 2008–2012. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 610, 802–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Anez, N.; Krasovskiy, A.; Müller, M.; Vacik, H.; Baetens, J.; Hukić, E.; Kapovic Solomun, M.; Atanassova, I.; Glushkova, M.; Bogunović, I.; Fajković, H. Current Wildland Fire Patterns and Challenges in Europe: A Synthesis of National Perspectives. Air, Soil Water Res. 2021, 14, 11786221211028185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldammer, J.G. Vegetation Fires and Global Change: Challenges for Concerted International Action. A White Paper Directed to the United Nations and International Organizations. Kessel, 2013.
- International Association of Wildland Fire (IAWF). Sixth-generation fires: Public-policy change toward prevention required to address large-scale events. Available online: https://www.iawfonline.org/article/sixth-generation-fires-public/ (accessed on 20 January 2024).
- NASA FIRMS (Fires Information for Resource Management System). Available online: https://firms.modaps.eosdis.nasa.gov/map/#t:adv;d:2021-08-24;@21.2,43.8,5z (accessed on 3 February 2023).
- San-Miguel-Ayanz, J.; Durrant, T.; Boca, R.; Liberta, G.; Branco, A.; De Rigo, D.; Ferrari, D.; Maianti, P.; Artes Vivancos, T.; Schulte, E.; Loffler, P. Forest Fires in Europe, Middle East and North Africa 2016; EUR 28707 EN; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2017.
- WWF. The Mediterranean Burns. WWF’s Mediterranean Proposal for the Prevention of Rural Fires; WWF 2019 Report. Available online: http://awsassets.panda.org/downloads/wwf__the_mediterranean_burns_2019_eng_final.pdf (accessed on 20 June 2024).
- Turco, M.; Rosa-Cánovas, J.J.; Bedia, J.; Jerez, S.; Montávez, J.P.; Llasat, M.C.; Provenzale, A. Exacerbated fires in Mediterranean Europe due to anthropogenic warming projected with non-stationary climate-fire models. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seijo, F. European Fire Governance in the era of wildfires. [Online] Green European Journal, 2017. Available online: https://www.greeneuropeanjournal.eu/european-fire-governance-in-the-era-of-megafires/ (accessed on 30 January 2024).
- World Tourism Organization (UNWTO), Ed. UNWTO Tourism Highlights: 2018 Edition; UNWTO: 2018. [CrossRef]
- Vélez, R. Causes of Forest Fires in the Mediterranean Basin. In Risk Management and Sustainable Forestry; EFI Proceedings, 2002; Vol. 42, pp 35–42. Available online: https://efi.int/sites/default/files/files/publication-bank/2018/proc45_net.pdf#page=35 (accessed on 20 June 2024).
- Marsh, J. Northern California wildfires damage BNSF’s rail infrastructure. [Online] FreightWaves, 2022. Available online: https://www.freightwaves.com/news/northern-california-wildfires-damage-bnsfs-rail-infrastructure (accessed on 11 October 2023).
- International Forest Fire News (IFFN). The Use of Prescribed Fire on Embankments along Railway Tracks for Reducing Wildfire Ignition in Germany. Available online: https://gfmc.online/iffn/iffn_30/13-IFFN-30-Germany-Railways.pdf (accessed on 11 October 2024).
- O'Kelly, B.C.; Sivakumar, V. Water content determinations for peat and other organic soils using the oven-drying method. Dry. Technol. 2014, 32, 631–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandler, C.; Cheney, P.; Thomas, P.; Trabaud, L.; Williams, D. Fire in Forestry; John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 1983.
- Úbeda, X.; Outeiro, L.R. Physical and chemical effects of fire on soil. In Fire Effects on Soils and Restoration Strategies; CRC Press, 2009; pp 121-148.
- DeBano, L.F. Water Repellent Soils: A State-of-the-Art. Vol. 46. US Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Pacific Southwest Forest and Range Experiment Station, 1981.
- DeBano, L.F.; Neary, D.G. Part A—The Soil Resource: Its Importance, Characteristics, and General Responses to Fire. In Wildland Fire in Ecosystems: Effects of Fire on Soil and Water; Gen. Tech. Rep. RMRS-GTR-42; 2005; Vol. 4, pp 21-28.
-
Pollution Assessment for Sustainable Practices in Applied Sciences and Engineering; Butterworth-Heinemann, 2020.
- Jiménez-Pinilla, P.; Mataix-Solera, J.; Arcenegui, V.; Delgado, R.; Martín-García, J.M.; Lozano, E.; Martínez-Zavala, L.; Jordán, A. Advances in the knowledge of how heating can affect aggregate stability in Mediterranean soils: A XDR and SEM-EDX approach. Catena 2016, 147, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhariya, M.K.; Singh, L. Effect of fire severity on soil properties in a seasonally dry forest ecosystem of Central India. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 18, 3967–3978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Zreig, M.M.; Al-Akhras, N.M.; Attom, M.F. Influence of heat treatment on the behavior of clayey soils. Applied Clay Science 2001, 20, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noraini, A.A. Effect of Wildfire on Geotechnical Properties of Clayey Soil. Int. Res. J. Eng. Technol. 2018, 5, 2137–2139. [Google Scholar]
- Awn, S.H.A.; Hussain, W.A. S.; Abbas, H.O. Effect of Burning Cycles on the Physical Properties of Clay. J. Eng. Sustain. Dev. 2019, 23. [Google Scholar]
- González, Y.V.; Patiño-Restrepo, J.; Álvarez-Guerra, M.C.; Ortega-Ramírez, D.; Echeverri-Ramírez, Ó. Cambio en las Propiedades Geotécnicas de un Suelo Sometido a Ignición en Laboratorio. Rev. Ing. Univ. Medellín 2018, 17, 85–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batjes, N.H. Total Carbon and Nitrogen in the Soils of the World. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 1996, 47, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharlemann, J.P.; Tanner, E.V.; Hiederer, R.; Kapos, V. Global soil carbon: understanding and managing the largest terrestrial carbon pool. Carbon Manage. 2014, 5, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doetterl, S.; Berhe, A.A.; Nadeu, E.; Wang, Z.; Sommer, M.; Fiener, P. Erosion, Deposition, and Soil Carbon: A Review of Process-Level Controls, Experimental Tools, and Models to Address C Cycling in Dynamic Landscapes. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2016, 154, 102–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Birdsey, R.A.; Fang, J.; Houghton, R.; Kauppi, P.E.; Kurz, W.A.; Phillips, O.L.; Shvidenko, A.; Lewis, S.L.; Canadell, J.G.; Ciais, P. A large and persistent carbon sink in the world’s forests. Science 2011, 333, 988–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, E.A., Ed. Soil Microbiology, Ecology, and Biochemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, 2007.
- Knicker, H. How does fire affect the nature and stability of soil organic nitrogen and carbon? A review. Biogeochemistry 2007, 85, 91–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Impellitteri, C.A.; You, S.J.; Allen, H.E. The Importance of Organic Matter Distribution and Extract Soil: Solution Ratio on the Desorption of Heavy Metals from Soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2002, 287, (1–2). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Wang, Y.P.; Yu, M.; Cao, N.; Yan, J. Soil organic matter is important for acid buffering and reducing aluminum leaching from acidic forest soils. Chem. Geol. 2018, 501, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, M.; Prescott, C.E.; Abaker, W.E.; Augusto, L.; Cécillon, L.; Ferreira, G.W.; James, J.; Jandl, R.; Katzensteiner, K.; Laclau, J.P.; Laganière, J. Tamm Review: Influence of forest management activities on soil organic carbon stocks: A knowledge synthesis. For. Ecol. Manage. 2020, 466, 118127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Awasthi, M.K.; Zhu, Q.; Chen, X.; Wu, F.; Wu, F.; Tong, X. Modified Soil Physicochemical Properties Promoted Sequestration of Organic and Inorganic Carbon Synergistically During Revegetation in Desertified Land. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monger, H.C.; Kraimer, R.A.; Khresat, S.E.; Cole, D.R.; Wang, X.; Wang, J. Sequestration of inorganic carbon in soil and groundwater. Geology 2015, 43, 375–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giglio, L.; Randerson, J.T.; Van Der Werf, G.R. Analysis of Daily, Monthly, and Annual Burned Area Using the Fourth-Generation Global Fire Emissions Database (GFED4). J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2013, 118, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Werf, G.R.; Randerson, J.T.; Giglio, L.; Van Leeuwen, T.T.; Chen, Y.; Rogers, B.M.; Mu, M.; Van Marle, M.J.; Morton, D.C.; Collatz, G.J.; Yokelson, R.J. Global fire emissions estimates during 1997–2016. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2017, 9, 697–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, L.T.; Kasel, S.; Tibbits, J. Are a Typology of Fire Effects and Determinants Needed for the Global Change Research Community? Global Change Biol. 2014, 20, 4258–4261. [Google Scholar]
- Certini, G. Effects of Fire on Properties of Forest Soils: A Review. Oecologia 2005, 143, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nave, L.E.; Vance, E.D.; Swanston, C.W.; Curtis, P.S. Fire effects on temperate forest soil C and N storage. Ecol. Appl. 2011, 21, 1189–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, D.W.; Curtis, P.S. Effects of forest management on soil C and N storage: meta-analysis. For. Ecol. Manage. 2001, 140, (2–3). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Tong, D.Q.; Lin, Q.; Lu, X.; Wang, G. Effect of Fires on Soil Organic Carbon Pool and Mineralization in a Northeastern China Wetland. Geoderma 2012, 189, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrini, A.F.; Ahlström, A.; Hobbie, S.E.; Reich, P.B.; Nieradzik, L.P.; Staver, A.C.; Scharenbroch, B.C.; Jumpponen, A.; Anderegg, W.R.; Randerson, J.T.; Jackson, R.B. Fire frequency drives decadal changes in soil carbon and nitrogen and ecosystem productivity. Nature 2018, 553, 194–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czimczik, C.I.; Schmidt, M.W.I.; Schulze, E.-D. Effects of Increasing Fire Frequency on Black Carbon and Organic Matter in Podzols of Siberian Scots Pine Forests. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2005, 56, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
-
Natural and Prescribed Fire in Pacific Northwest Forests; Oregon State University Press: Corvallis, OR, 1990.
- Chungu, D.; Ng’andwe, P.; Mubanga, H.; Chileshe, F. Fire Alters the Availability of Soil Nutrients and Accelerates Growth of Eucalyptus grandis in Zambia. J. For. Res. 2020, 31, 1637–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, J.D.; Johnson, D.W.; Miller, W.W.; Walker, R.F.; Carroll, E.F.; Blank, R.R. Wildfire effects on soil nutrients and leaching in a Tahoe Basin watershed. J. Environ. Qual. 2006, 35, 479–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; McGuire, K.J.; Stewart, R.D. Effect of Soil Water-Repellent Layer Depth on Post-Wildfire Hydrological Processes. Hydrol. Processes 2020, 34, 270–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerdà, A. Changes in Overland Flow and Infiltration after a Rangeland Fire in a Mediterranean Scrubland. Hydrol. Processes 1998, 12, 1031–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granged, A.J.; Jordán, A.; Zavala, L.M.; Bárcenas, G. Fire-Induced Changes in Soil Water Repellency Increased Fingered Flow and Runoff Rates Following the 2004 Huelva Wildfire. Hydrol. Processes 2011, 25, 1614–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyman, P.; Sheridan, G.J.; Smith, H.G.; Lane, P.N. Modeling the effects of surface storage, macropore flow and water repellency on infiltration after wildfire. J. Hydrol. 2014, 513, 301–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeBano, L.F. The Role of Fire and Soil Heating on Water Repellency in Wildland Environments: A Review. J. Hydrol. 2000, 231, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malkinson, D.; Wittenberg, L. Post-fire-induced soil water repellency—Modeling short and long-term processes. Geomorphology 2011, 125, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mataix-Solera, J.; Doerr, S.H. Hydrophobicity and aggregate stability in calcareous topsoils from fire-affected pine forests in southeastern Spain. Geoderma 2004, 118, (1–2). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veneris, M.; Farid, A. Finer Measurement Scales for Induced Hydrophobicity Using the Water Droplet Penetration Test. Geotechnics J. 2024, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallett, P.D. A brief overview of the causes, impacts and amelioration of soil water repellency–a review. Soil Water Res. 2008, 3, 521–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakesby, R.A.; Doerr, S.H. Wildfire as a hydrological and geomorphological agent. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2006, 74, 269–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebel, B.A.; Moody, J.A.; Martin, D.A. Hydrologic Conditions Controlling Runoff Generation Immediately After Wildfire. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moody, J.A.; Ebel, B.A. Hyper-dry conditions provide new insights into the cause of extreme floods after wildfire. Catena 2012, 93, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieting, C.; Ebel, B.A.; Singha, K. Quantifying the Effects of Wildfire on Changes in Soil Properties by Surface Burning of Soils from the Boulder Creek Critical Zone Observatory. J. Hydrol.: Reg. Stud. 2017, 13, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akin, I.D.; Akinleye, T.O. Water Vapor Sorption Behavior of Wildfire-Burnt Soil. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2021, 147, 04021115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabet, E.J.; Sternberg, P. The Effects of Vegetative Ash on Infiltration Capacity, Sediment Transport, and the Generation of Progressively Bulked Debris Flows. Geomorphology 2008, 101, 666–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebel, B.A.; Moody, J.A. Parameter Estimation for Multiple Post-Wildfire Hydrologic Models. Hydrol. Processes 2020, 34, 4049–4066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbert, K.R.; Oriol, V. Temporal fluctuations in soil water repellency following wildfire in chaparral steeplands, southern California. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2005, 14, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Shang, C.; Eick, M.J.; Stewart, R.D. Water Repellency Decreases Vapor Sorption of Clay Minerals. Water Resour. Res. 2018, 54, 6114–6125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerdà, A.; Doerr, S.H. The Effect of Ash and Needle Cover on Surface Runoff and Erosion in the Immediate Post-Fire Period. Catena 2008, 74, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, A.J.D.; Coelho, C.O. A.; Boulet, A.K.; Leighton-Boyce, G.; Keizer, J.J.; Ritsema, C.J. Influence of Burning Intensity on Water Repellency and Hydrological Processes at Forest and Shrub Sites in Portugal. Soil Res. 2005, 43, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansen, M.P.; Hakonson, T.E.; Breshears, D.D. Post-fire runoff and erosion from rainfall simulation: contrasting forests with shrublands and grasslands. Hydrol. Processes 2001, 15, 2953–2965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terry, J.P.; Shakesby, R.A. Soil hydrophobicity effects on rainsplash: simulated rainfall and photographic evidence. Earth Surf. Processes Landforms 1993, 18, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robichaud, P.R.; Wagenbrenner, J.W.; Pierson, F.B.; Spaeth, K.E.; Ashmun, L.E.; Moffet, C.A. Infiltration and interrill erosion rates after a wildfire in western Montana, USA. Catena 2016, 142, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeBano, L.F. Water Repellency in Soils: A Historical Overview. J. Hydrol. 2000, 231, 4–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauters, T.W.; Steenhuis, T.S.; Parlange, J.Y.; DiCarlo, D.A. Preferential Flow in Water-Repellent Sands. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1998, 62, 1185–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritsema, C.J.; Dekker, L.W. Preferential flow in water repellent sandy soils: principles and modeling implications. J. Hydrol. 2000, 231, 308–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Dios Benavides-Solorio, J.; MacDonald, L.H. Measurement and Prediction of Post-Fire Erosion at the Hillslope Scale, Colorado Front Range. Int. J. Wildland Fire 2005, 14, 457–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, R.P.C.; Morgan, D.D. V.; Finney, H.J. A predictive model for the assessment of soil erosion risk. J. Agric. Eng. Res. 1984, 30, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, D.C.S.; Prats, S.A.; Nunes, J.P.; Shakesby, R.A.; Coelho, C.O. A.; Keizer, J.J. Modelling Runoff and Erosion, and Their Mitigation, in Burned Portuguese Forest Using the Revised Morgan–Morgan–Finney Model. For. Ecol. Manage. 2014, 314, 150–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, M.; Nunes, J.P.; Pelayo, O.G.; Keizer, J.J.; Ritsema, C.; Geissen, V. Developing generalized parameters for post-fire erosion risk assessment using the revised Morgan-Morgan-Finney model: A test for north-central Portuguese pine stands. Catena 2018, 165, 358–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zema, D.A.; Nunes, J.P.; Lucas-Borja, M.E. Improvement of Seasonal Runoff and Soil Loss Predictions by the MMF (Morgan-Morgan-Finney) Model after Wildfire and Soil Treatment in Mediterranean Forest Ecosystems. Catena 2020, 188, 104415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Roo, A.P.J.; Wesseling, C.G.; Ritsema, C.J. LISEM: A Single-Event Physically Based Hydrological and Soil Erosion Model for Drainage Basins. I: Theory, Input and Output. Hydrol. Processes 1996, 10, 1107–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Eck, C.M.; Nunes, J.P.; Vieira, D.C.; Keesstra, S.; Keizer, J.J. Physically Based Modelling of the Post-Fire Runoff Response of a Forest Catchment in Central Portugal: Using Field Versus Remote Sensing-Based Estimates of Vegetation Recovery. Land Degrad. Dev. 2016, 27, 1535–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, D.C.S.; Malvar, M.C.; Martins, M.A. S.; Serpa, D.; Keizer, J.J. Key Factors Controlling the Post-Fire Hydrological and Erosive Response at Micro-Plot Scale in a Recently Burned Mediterranean Forest. Geomorphology 2018, 319, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayor, A.G.; Bautista, S.; Llovet, J.; Bellot, J. Post-fire hydrological and erosional responses of a Mediterranean landscape: Seven years of catchment-scale dynamics. Catena 2007, 71, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.J.; Lu, Y.F.; Delage, P.; Riffard, M. Field Simulation of in situ Water Content and Temperature Changes Due to Ground-Atmospheric Interactions. Géotechnique 2005, 55, 557–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; Shi, B.; Gu, K. Experimental investigation on evaporation process of water during drying. J. Eng. Geol. 2011, 19, 875–881. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, C.S.; Cheng, Q.; Leng, T.; Shi, B.; Zeng, H.; Inyang, H.I. Effects of wetting-drying cycles and desiccation cracks on mechanical behavior of an unsaturated soil. Catena 2020, 194, 104721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peron, H.; Hueckel, T.; Laloui, L.; Hu, L. Fundamentals of desiccation cracking of fine-grained soils: experimental characterisation and mechanisms identification. Can. Geotech. J. 2009, 46, 1177–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Tang, C.S.; Chen, Z.G.; El-Maarry, M.R.; Zeng, H.; Shi, B. Tensile Behavior of Clayey Soils during Desiccation Cracking Process. Eng. Geol. 2020, 279, 105909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.S.; Zhu, C.; Cheng, Q.; Zeng, H.; Xu, J.J.; Tian, B.G.; Shi, B. Desiccation cracking of soils: A review of investigation approaches, underlying mechanisms, and influencing factors. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2021, 216, 103586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Mao, Z.; Langendoen, E.J. How Does Root Biodegradation after Plant Felling Change Root Reinforcement to Soil? Plant Soil 2020, 446, 211–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamchoom, V.; Boldrin, D.; Leung, A.K.; Sookkrajang, C.; Likitlersuang, S. Biomechanical properties of the growing and decaying roots of Cynodon dactylon. Plant Soil 2022, 471, 193–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genet, M.; Stokes, A.; Salin, F.; Mickovski, S.B.; Fourcaud, T.; Dumail, J.F.; Van Beek, R. The Influence of Cellulose Content on Tensile Strength in Tree Roots. Plant Soil 2005, 278, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.J.; Leung, A.K.; Ng, C.W. W. Modelling effects of root growth and decay on soil water retention and permeability. Can. Geotech. J. 2019, 56, 1049–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, C.W.W.; Ni, J.J.; Leung, A.K. Effects of plant growth and spacing on soil hydrological changes: a field study. Géotechnique 2020, 70, 867–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, J.J.; Leung, A.K.; Ng, C.W.W.; Shao, W. Modelling hydro-mechanical reinforcements of plants to slope stability. Comput. Geotech. 2018, 95, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, S.H.; Bigio, E.R.; Mine, E. A Process for Fire-Related Debris Flow Initiation, Cerro Grande Fire, New Mexico. Hydrol. Processes 2001, 15, 3011–3023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gartner, J.E.; Cannon, S.H.; Bigio, E.R.; Davis, N.K.; Parrett, C.; Pierce, K.L.; Rupert, M.G.; Thurston, B.L.; Trebish, M.J.; Garcia, S.P.; Rea, A.H. Compilation of Data Relating to the Erosive Response of 606 Recently Burned Basins in the Western US. US Geological Survey Open-File Report 2005, 1218.
- Lei, M.; Cui, Y.; Ni, J.; Zhang, G.; Li, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, D.; Yi, S.; Jin, W.; Zhou, L. Temporal evolution of the hydromechanical properties of soil-root systems in a forest fire in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 809, 151165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neary, D.G.; Ryan, K.C.; DeBano, L.F. Wildland Fire in Ecosystems: Effects of Fire on Soils and Water; Gen. Tech. Rep. RMRS-GTR-42-vol. 4; US Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station: Ogden, UT, 2005; p 250.
- Istanbulluoglu, E.; Tarboton, D.G.; Pack, R.T.; Luce, C.H. Modeling of the interactions between forest vegetation, disturbances, and sediment yields. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2004, 109 (F1). [CrossRef]
- Florsheim, J.L.; Keller, E.A.; Best, D.W. Fluvial Sediment Transport in Response to Moderate Storm Flows Following Chaparral Wildfire, Ventura County, Southern California. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1991, 103, 504–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, G.A.; Pierce, J.L.; Wood, S.H.; Jull, A.J. T. Fire, storms, and erosional events in the Idaho batholith. Hydrol. Processes 2001, 15, 3025–3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reneau, S.L.; Dietrich, W.E. Erosion rates in the southern Oregon Coast Range: Evidence for an equilibrium between hillslope erosion and sediment yield. Earth Surf. Processes Landforms 1991, 16, 307–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirchner, J.W.; Finkel, R.C.; Riebe, C.S.; Granger, D.E.; Clayton, J.L.; King, J.G.; Megahan, W.F. Mountain erosion over 10 yr, 10 ky, and 10 my time scales. Geology 2001, 29, 591–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, D.F.; Gabet, E.J. Effects of sediment pulses on channel morphology in a gravel-bed river. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 2007, 119, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, D.; Luce, C.; Benda, L. Time, Space, and Episodicity of Physical Disturbance in Streams. Forest Ecol. Manage. 2003, 178, 121–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pausas, J.G.; Keeley, J.E. Evolutionary ecology of resprouting and seeding in fire-prone ecosystems. New Phytol. 2014, 204, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).