1. Introduction
The incidence of pancreatic cancer is rising, with > 90% mortality largely owing to lack of an effective treatment [
1]. Surgical resection may be curative but is only applicable to < 20% of patients at diagnosis [
2]. This leaves the over 80% of patients with only a palliative treatment (mainly chemotherapy) option, with a median survival <1 year, regardless of the use of various therapy regimens [
3,
4]. Gemcitabine-based therapies, either alone or in combination with agents including nab-paclitaxel [
5], are favored approaches for the treatment of patients with locally advanced or metastatic pancreatic cancer. Although the combination of folinic acid, 5-fluorouracil, irinotecan, and oxaliplatin (FOLFIRINOX) increases survival compared to treatment with gemcitabine alone, it often cannot be tolerated due to the high toxicity and poor performance status of patients [
6]. There is an urgent need to develop more effective approaches that can improve the treatment of pancreatic cancer to increase patients’ survival.
Inorganic arsenic, specifically arsenic trioxide (ATO), has been recognised as a toxic compound[
7] and a medically effective agent. Although this arsenic compound has been used as a drug to treat various diseases in traditional medicine, its FDA approval in the year 2000 and subsequent successful application for the treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL) triggered research into its role in solid tumor therapy. ATO has been shown to inhibit the growth of solid tumors including breast, hepatic, oesophageal, gastric, pancreatic, ovarian and prostate carcinomas [
8], generally by induction of apoptosis. However, the lower specificity of ATO towards the cellular targets in these cancers and the subsequent requirement to administer higher doses has meant that clinical trials using ATO as a single reagent in patients with breast, hepatic and pancreatic cancers have not been successful [
9,
10].
To develop novel strategies for the treatment of pancreatic cancer, the effects of ATO, alone and in combination with other reagents, on pancreatic cancer have been explored. ATO inhibited pancreatic cancer cell growth by inducing apoptosis [
11], via downregulation of the S-phase kinase-associated protein 2 (Skp2) [
12]. ATO also sensitized the response of pancreatic cancer cells to gemcitabine by inhibition of Skp2. ATO promoted the inhibitory effects of either gemcitabine [
13], or the hypoxia-inducible factor 1 inhibitor PX-478 [
14], on pancreatic cancer. However, the high toxicity of ATO limited its clinical application as an anticancer agent and contributed to the failure of a clinical trial using ATO in the treatment of patients with pancreatic adenocarcinoma refractory to gemcitabine [
10]. The difference between the promising results in pre-clinical mouse models and the failure in clinical trials on patients with pancreatic cancer may have been caused by several factors including the different doses used in mice (5-8 mg/Kg) [
13,
14,
15] and in humans (300-350 μg/Kg) [
10].
The leukemia-homing peptide CAYHRLRRC (LHP) has been shown to target the macropinocytotic pathway in leukemia and lymphoma cells [
16]. The presence of cysteine residues at both the
N- and
C-termini of the peptide have enabled the synthesis of a cyclic arsenic derivative that could enter cells via macropinocytotic-type pathways [
7]. Recognizing that 95% of pancreatic cancer cases exhibit mutant KRAS protein and that KRAS-transformed cells have been shown to have enhanced macropinocytosis [
17], it was anticipated that the peptide-linked arsenic compound might also target pancreatic cancers. To test the hypothesis that the peptide-linked arsenic compound could reduce indiscriminate toxicity and hence increase anticancer efficacy compared to ATO, the peptide-linked phenylarsine compound (herein referred to as PhAs-LHP) was prepared and its effects on pancreatic cancer growth were assessed
in vitro and
in vivo.
2. Results
2.1. ATO Suppressed Pancreatic Cancer Cell Growth, and this Inhibitory Effect Was Enhanced by Gemcitabine and PF-3758309
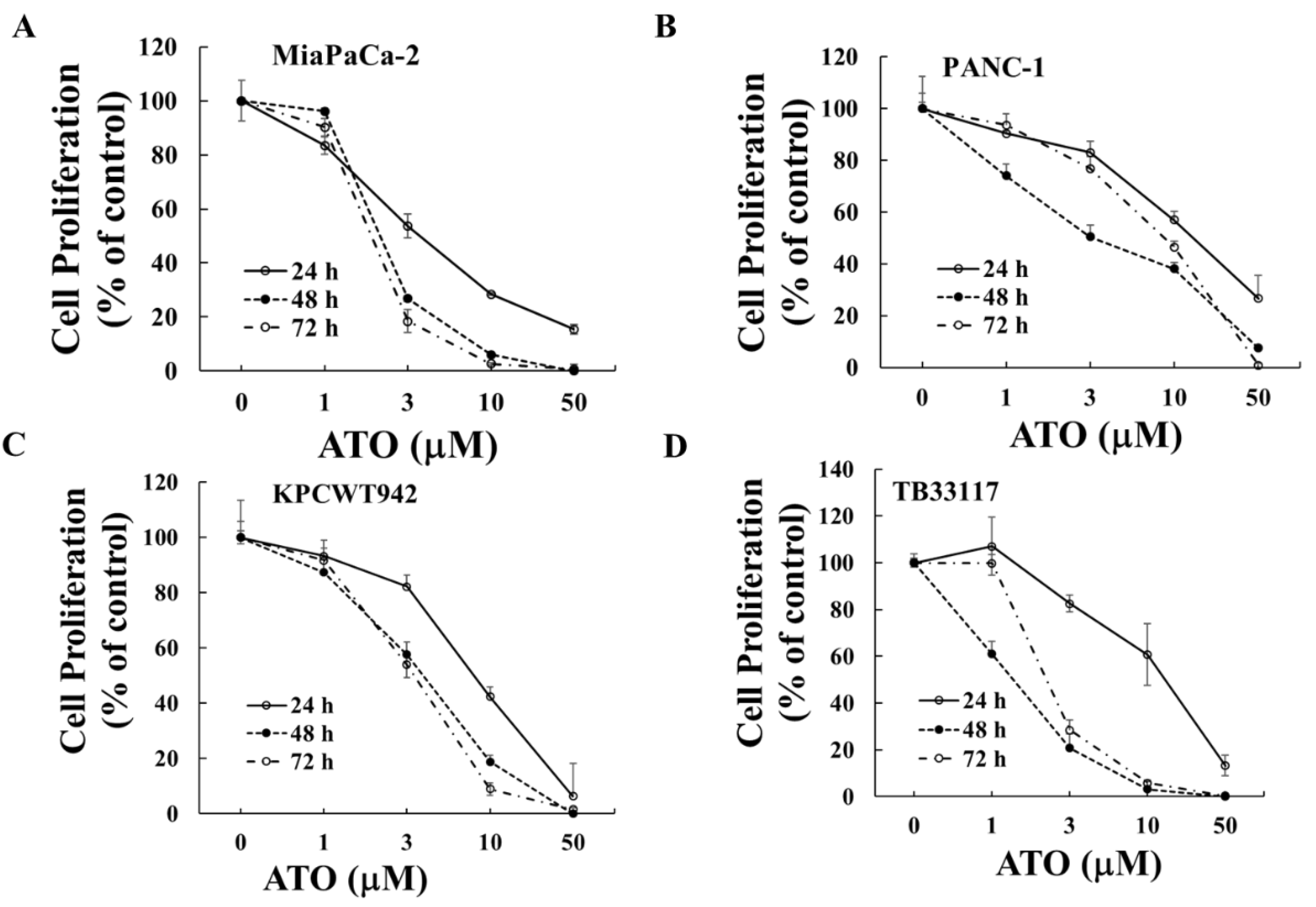
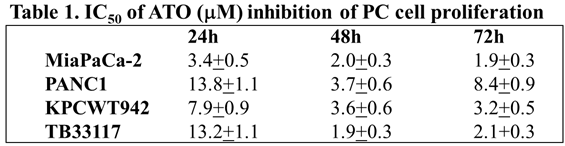
Human (PANC-1 and MiaPaCa-2) and murine (KPCWT942 and TB33117) pancreatic cancer (PC) cells were treated with ATO (1-50 M) for 24, 48 and 72 h. Cell proliferation was measured by MTT assay and the readouts from the untreated control cells were taken as 100%. ATO decreased the proliferation of all four PC cell lines in a dose-dependent manner (
Figure 1). The maximal inhibitory effects of ATO were reached after 48 h incubation (Table 1) when the minimal IC50 values were reached in most cell lines.
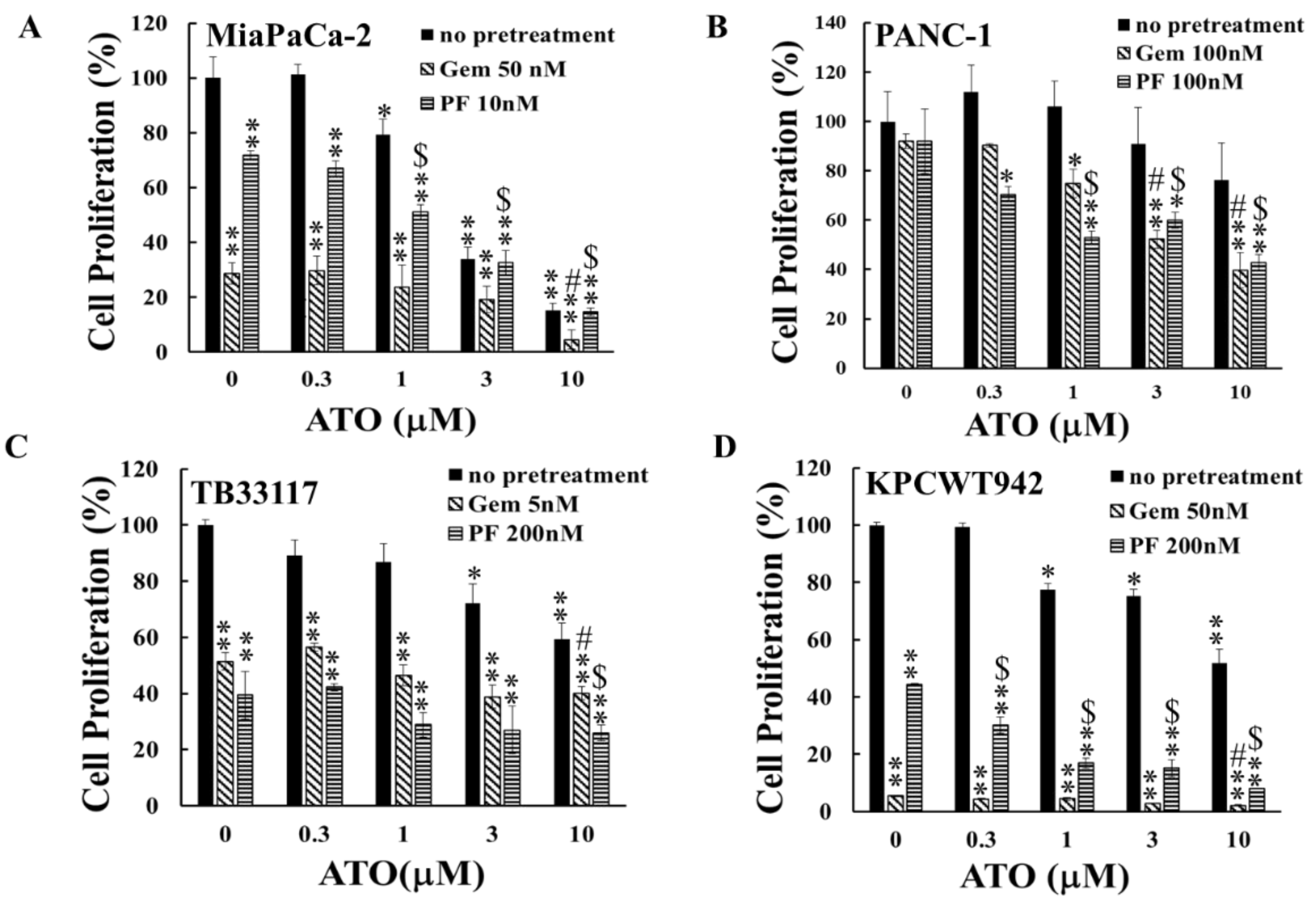
Gemcitabine is used as a standard treatment for PC and tremendous efforts have been made to develop gemcitabine combination therapies aimed at improving therapeutic outcomes and increasing patients’ survival. PF-3758309 is a chemical inhibitor that targets p-21-activated kinases (PAKs) and is specific to PAK4. PAKs, particularly PAK1 and PAK4, play critical roles in PC progression. Inhibition of PAK4 by PF-3758309 has enhanced the sensitivity to multiple chemotherapeutic reagents in patient-derived PC cell lines [
18]. To determine the effects of ATO in combination with gemcitabine or PF-3758309, both human and murine PC cells were pre-incubated with gemcitabine or PF-3758309 for 24 h, followed by 48 h incubation with ATO at the concentrations indicated in
Figure 2. The observation that pre-treatment of PC cells with either gemcitabine or PF-3758309 enhanced the inhibitory effects of ATO on PC cell growth to different degrees (
Figure 2) indicated that the combination of ATO with either gemcitabine or PF-3758309 suppressed PC growth more potently than treatment with either single reagent.
2.2. Peptide-Linked Arsenic Compounds Inhibited Pancreatic Cancer Cell Growth More Potently Than ATO via Regulating Cell Cycle and Cell Death
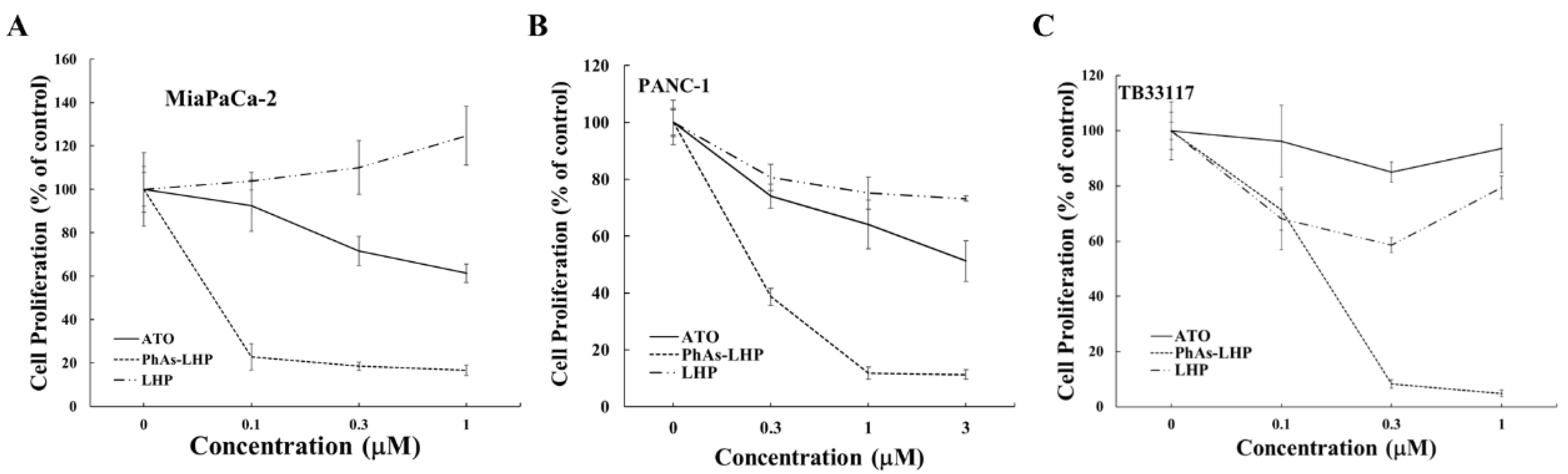
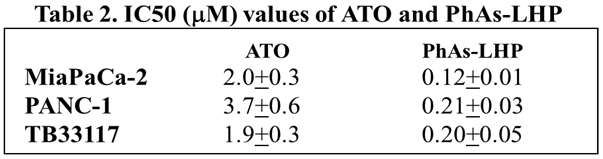
To facilitate its entry into cells, arsenic was coupled to the leukemia homing peptide CAYHRLRRC (LHP) by reacting the peptide with phenylarsine oxide (PAO) to generate PhAs-LHP. The effect of PhAs-LHP on PC cell growth was then compared with LHP and ATO. Human (PANC-1 and MiaPaCa-2) and murine (TB33117) PC cells were treated with ATO, PhAs-LHP, or free peptide LHP for 48 h and cell proliferation was measured by MTT assay. PhAs-LHP inhibited the proliferation of human (MiaPaCa-2 and PANC-1) and murine (TB33117) PC cells (
Figure 3) and LHP did not affect the proliferation of these PC cells (
Figure 3). More importantly, PhAs-LHP suppressed the proliferation of both human and murine PC cells more potently compared to ATO, as the IC
50 values obtained for PhAs-LHP were 10 times less than the IC
50 values for ATO as shown in Table 2. These results suggested that coupling to the small peptide LHP facilitated the entry of arsenic into cells and hence promoted its inhibition of cell proliferation. While the highest IC50 of ATO on PC cells was less than 4 μM, both ATO and PhAs-LHP had only reduced the proliferation of a normal pancreatic epithelial cell line (HPDE) by 10% at 5 μM and there was no difference in inhibition between ATO and PhAs-LHP up to 5 μM as shown in supplementary
Figure 1 (
Figure S1).
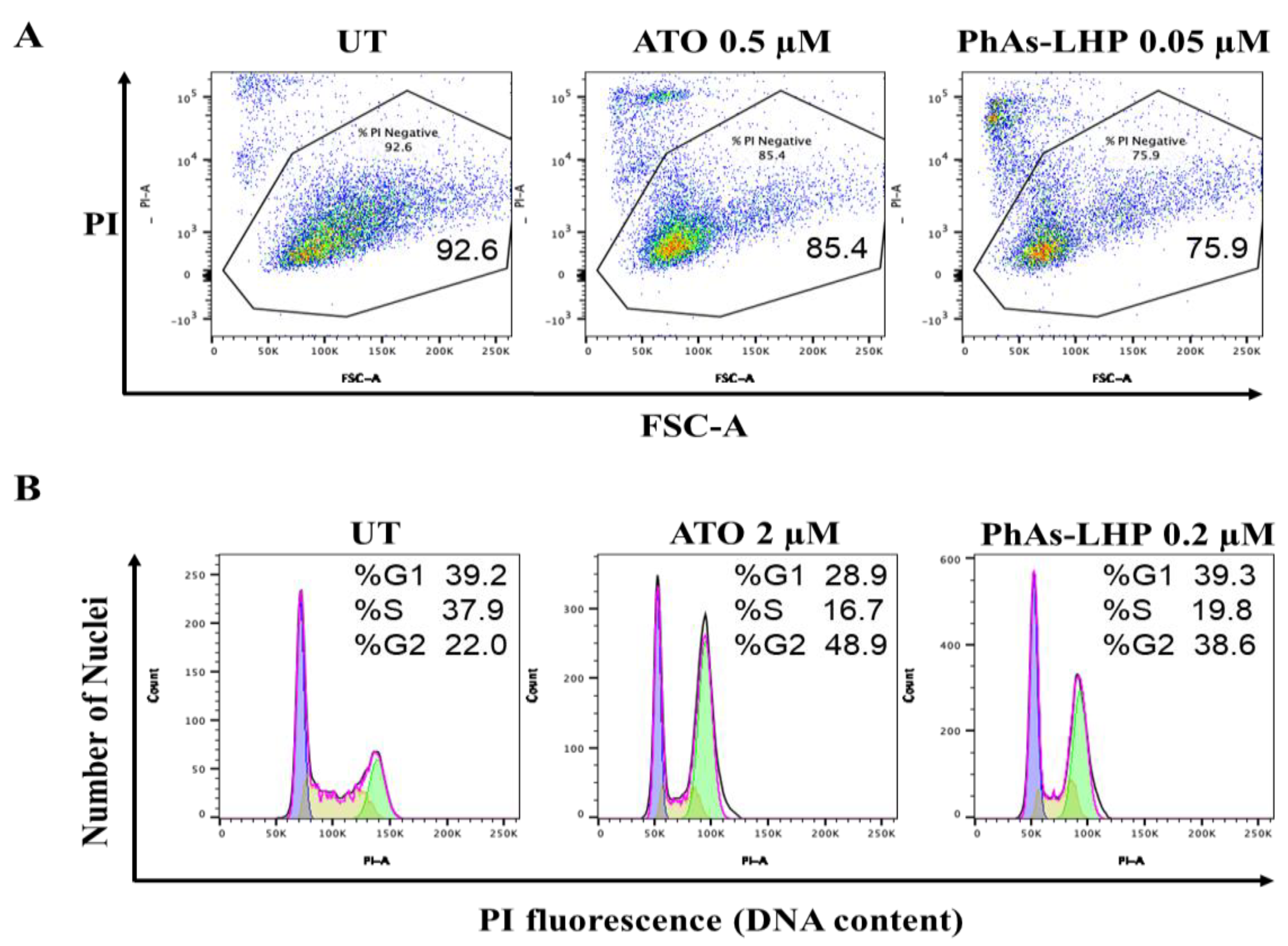
ATO inhibited PC cell growth by stimulation of apoptosis [
14,
19]. The effects of PhAs-LHP on cell cycle and cell death were determined by Flow Cytometry analysis. In MiaPaCa-2 cells, after 48 h treatment, ATO induced about 15% cell death at 0.5 μM while PhAs-LHP (0.05 μM) caused 24% cell death at 10 times lower concentrations than ATO (
Figure 4A). Likewise, after 24-h treatment, ATO (2 μM) and PhAs-LHP (0.2 μM) induced cell cycle arrest at G2/M phase in PANC-1 cells (
Figure 4B). These results demonstrated the intracellular mechanism for the more potent inhibition of this small peptide-linked compound on PC growth compared to ATO (
Figure 3).
2.3. Arsenic-Peptide Suppressed Pancreatic Cancer Growth
To determine the effects of PhAs-LHP on PC growth
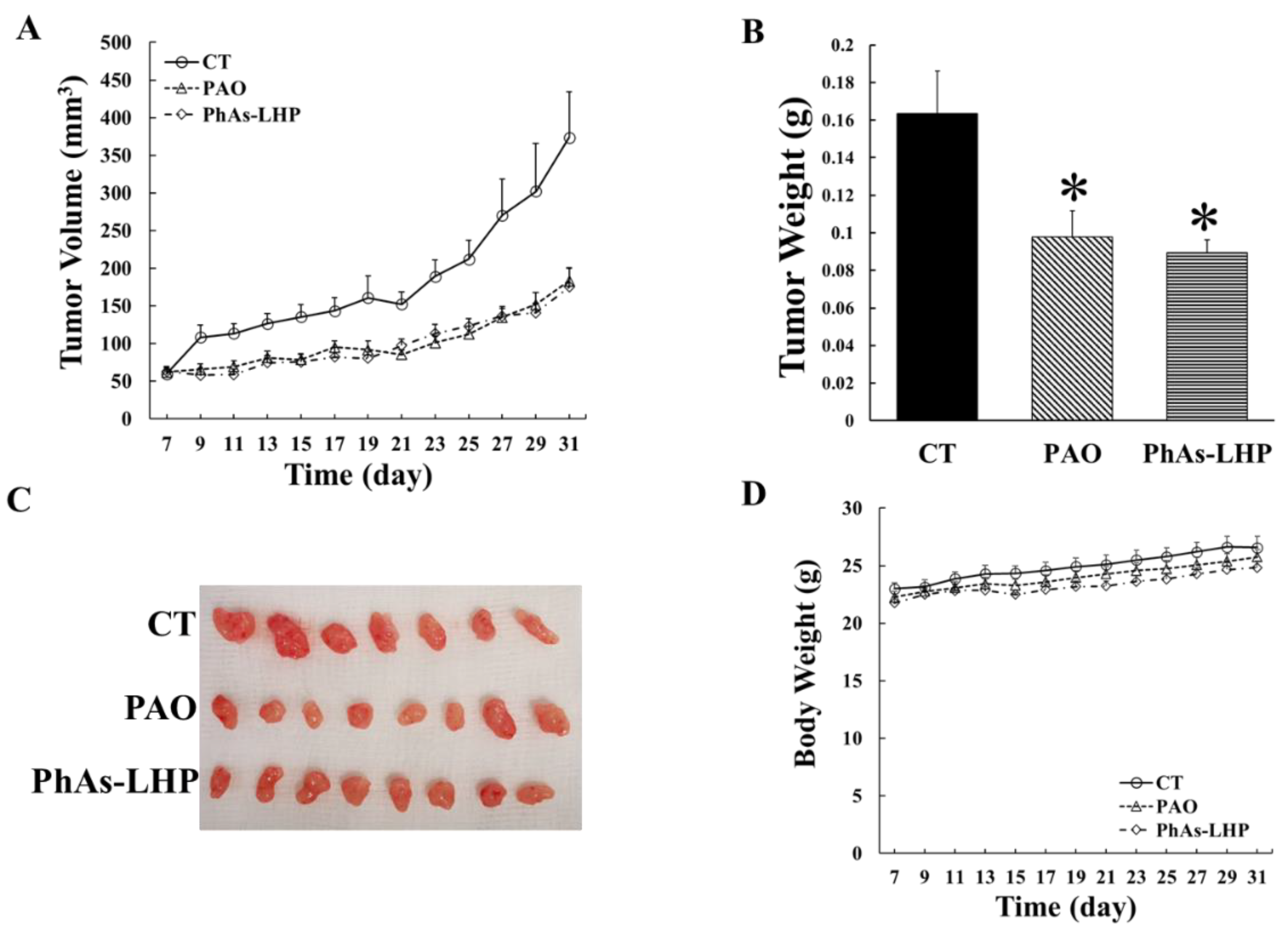
in vivo, human PC cells (MiaPaCa-2) were subcutaneously injected into the flanks of Scid mice which were then treated with phenylarsine oxide (PAO, 50 μg/Kg) or PhAs-LHP (200 μg/Kg) by intraperitoneal injection as described in the Materials and Methods section. The doses of PAO and PhAs-LHP were calculated from the results obtained from the
in vitro assay. PAO was selected as a control because it is the As-containing product produced following the dissociation of LHP from PhAs-LHP. Both PAO and PhAs-LHP significantly suppressed pancreatic tumor growth in Scid mice, as demonstrated by a reduction in tumor volumes (
Figure 5A) during the treatment period and decreased tumor weight at the end of the treatment (
Figure 5B). The mouse body weights were slightly and consistently increased throughout the treatment period (
Figure 5D). There was no significant difference in either tumor volumes or tumor weight between PAO- and PhAs-LHP-treated mice. Although the dose of PhAs-LHP was 4 times greater than the dose of PAO based on weight, the 8-fold greater molecular weight of PhAs-LHP (1368.2 g/mol) compared to PAO (168.0 g/mol) suggests that PhAs-LHP was more potent than PAO, as this effectively equates to half the amount of arsenic in the PhAs-LHP dose administered to the mice. The results showed that PAO and PhAs-LHP suppressed PC growth in Scid mice to a similar degree at the dosages used in this experiment, where the molar concentration of PhAs-LHP was 2 times less than PAO. These results suggested that the peptide-linked arsenic compound suppressed the pancreatic cancer growth
in vivo more potently than PAO.
2.4. Arsenic-Peptide Enhanced the Inhibitory Effect of Gemcitabine on Pancreatic Cancer Growth
The
in vitro data showed that the combination of ATO and gemcitabine inhibited PC cell proliferation more potently than either compound singly (
Figure 2). To determine if the combination of PhAs-LHP and gemcitabine suppressed PC growth
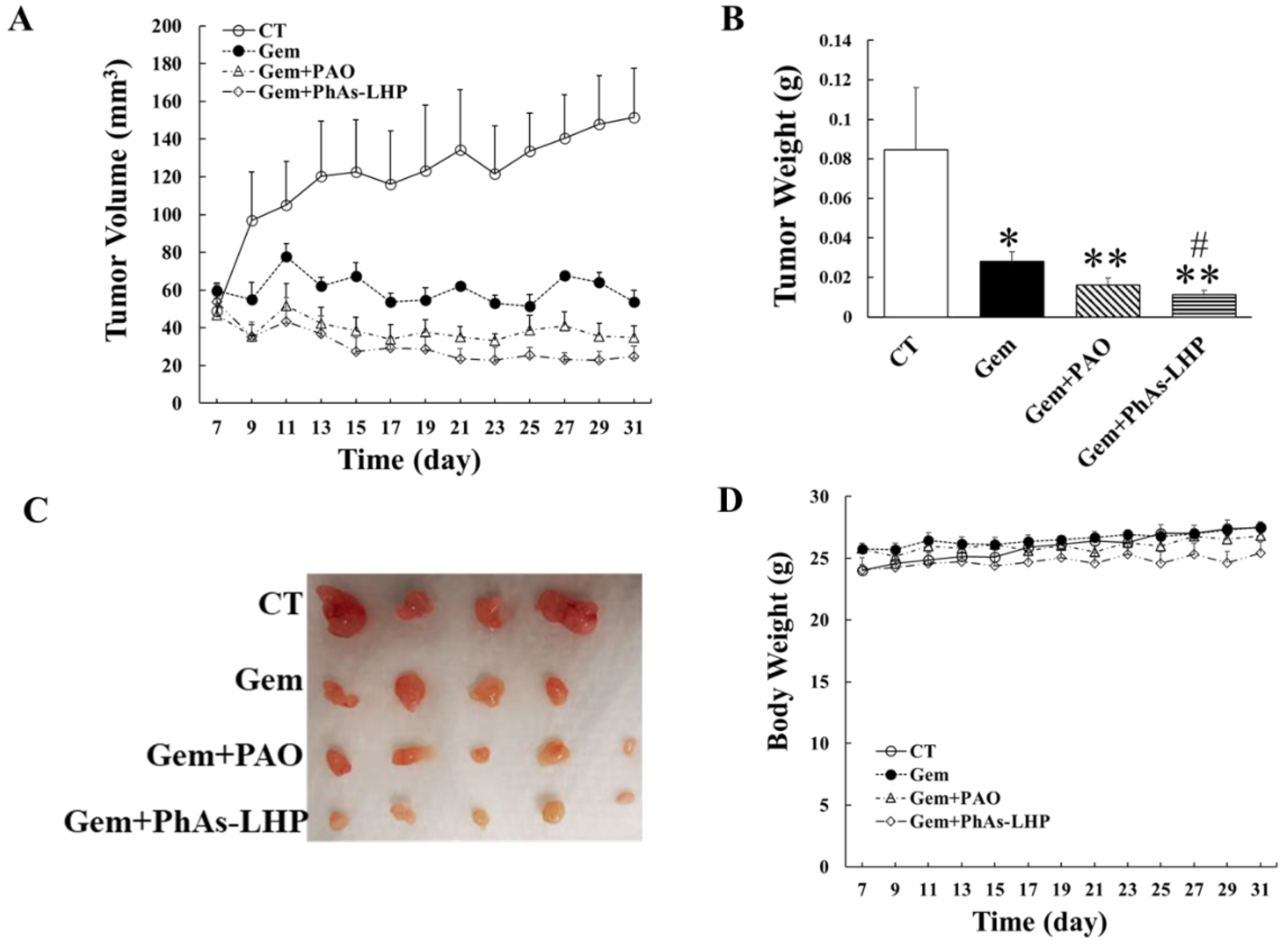
in vivo more effectively than either compound singly, human PC cells (MiaPaCa-2) were subcutaneously injected into the flanks of Scid mice which were then treated with gemcitabine alone (50 mg/Kg), or with gemcitabine (50 mg/Kg) plus PAO (50 μg/Kg) or PhAs-LHP (200 μg/Kg), by intraperitoneal injection as described in the Materials and Methods section. Gemcitabine alone significantly decreased PC growth as shown by reduced tumor volumes (
Figure 6A) and tumor weight (
Figure 6B). The apparent further reduction in tumor volumes and weight by PAO on top of the gemcitabine did not reach statistical significance. However, the peptide-linked arsenic compound, PhAs-LHP further decreased tumor volumes (
Figure 6A) and tumor weight (
Figure 6B) significantly when combined with gemcitabine treatment. No toxicity was observed with PAO, PhAs-LHP or gemcitabine with the dosages used as demonstrated by the absence of any significant decrease in mouse body weight (
Figure 6D). The results showed that PhAs-LHP enhanced the inhibitory effect of gemcitabine on PC growth
in vivo. The tumor volume and weight of gemcitabine plus PhAs-LHP were lower than those of gemcitabine plus PAO though it did not reach statistically significant. However, the molar concentration of PhAs-LHP was 2 times less than the PAO, indicating the more potent inhibition by PhAs-LHP. When comparing the relative tumor growth by taking the tumor volumes measured on Day 7 (when the treatment started) as 100%, the tumor growth of Gem plus PhAs-LHP was significantly slower than of Gem plus PAO on Day 27 (
Figure S2B). In the presence of gemcitabine, the inhibitory effects of both PAO and PhAs-LHP were increased compared to PAO or PhAs-LHP alone respectively (
Figure S2C).
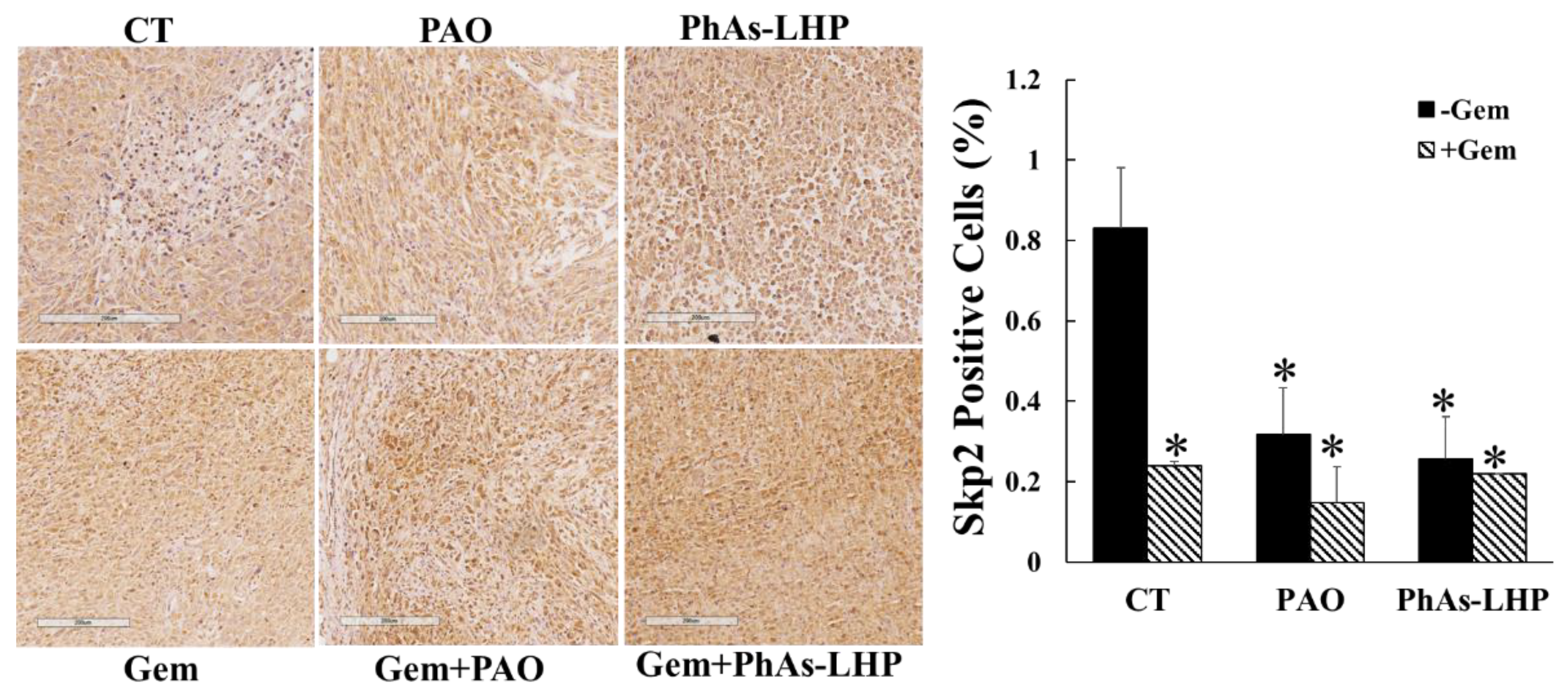
Previous reports have demonstrated that ATO inhibited pancreatic xenografted tumor growth by decreasing proliferation and increasing apoptosis
in vivo [
15,
20], and that ATO suppressed PC cell proliferation and migration by downregulation of S-phase kinase-associated protein 2 (Skp2), a cell cycle regulator[
12]. The
in vivo effect of ATO and its peptide-linked compound on Sky2 expression in xenografted tumors was determined by immunohistochemical staining. The overall levels of Skp2 detected were low. The levels of Skp2 were reduced in the tumors of the mice treated with PAO, PhAs-LHP and gemcitabine respectively (
Figure 7) compared to the non-treatment control. The combination of gemcitabine and PAO or PhAs-LHP did not further reduce the expression of Skp2 compared to single reagent treatments (
Figure 7).
3. Discussion
The observation that, despite its effective inhibition of PC cells
in vitro, ATO has not shown any activity in pancreatic cancer patients with progressive disease after gemcitabine treatment [
10], indicates new approaches are required. To reduce the toxicity and increase the anticancer efficacy of ATO, a peptide-linked arsenic compound was synthesized and its effect was tested on pancreatic cancer growth
in vitro and
in vivo, and compared to the effects of non-peptide-linked ATO. The peptide-linked arsenic compound inhibited pancreatic cancer cell growth more potently with IC
50 values 10 times lower than ATO. More importantly, the peptide-linked arsenic compound inhibited pancreatic cancer growth in mice and enhanced the inhibitory effect of gemcitabine on pancreatic tumour growth.
The peptide-linked compound, PhAs-LHP, induced cell death in MiaPaCa-2 cells at 10 times lower concentrations than ATO (
Figure 4A). Similarly, PhAs-LHP caused G2/M cell cycle arrest of PANC-1 cells at 10 times lower concentrations than ATO (
Figure 4B). These findings provide an intracellular mechanism for the more potent inhibitory effect of PhAs-LHP, compared to ATO, on PC cell growth, and are also consistent with previous reports that ATO induces apoptotic cell death in PC cells via changes in cell cycle [
11,
12].
Consistent with the
in vitro findings, the peptide-linked compound PhAs-LHP supressed xenografted PC growth in Scid mice more potently than the non-peptide-linked arsenic (as PAO), with 2 times lower molar concentration (
Figure 5), and further enhanced the inhibitory effect of gemcitabine on PC growth
in vivo (
Figure 6). PAO alone did not significantly increase the inhibition of gemcitabine on PC growth
in vivo (
Figure 6), although ATO was shown to promote the inhibitory effect of gemcitabine in a similar xenografted PC growth model where a higher dosage of ATO was used [
12]. The difference between the data presented here and the previous report [
12] may be due to the different concentrations of ATO (5 mg/Kg [
12]) or PAO (50 μg/Kg) used in the experiments. The fact that PhAs-LHP, at 2 times lower molar concentrations than PAO, enhanced the inhibitory effect of gemcitabine on PC growth
in vivo while PAO did not increase the inhibitory effect of gemcitabine significantly, indicates that PhAs-LHP sensitises PC response to gemcitabine more potently. Thus, the peptide-linked arsenic compound acts more effectively alone and in combination with gemcitabine to suppress PC growth.
The toxicity of ATO has limited its clinical application, contributing to the failure in clinical trials of ATO as a cancer treatment. A low dosage used in a clinical trial in PC patients did not benefit patients at all [
10]. The peptide-linked arsenic compound PhAs-LHP, demonstrated anti-cancer effects on pancreatic cancer
in vitro (
Figure 3 and
Figure 4, Table 2) and
in vivo (
Figure 5 and
Figure 6) at a much lower concentration than ATO, indicating more potent anti-cancer effects of this peptide-linked arsenic compound with reduced toxicity. The results here show that due to the targeting properties imparted by linking the peptide to arsenic, a significant reduction in tumour growth can be obtained with substantially less administration of arsenic, which in turn should reduce indiscriminate toxicity. These observations imply a potential clinical application of this peptide-linked arsenic compound on its own or in combination with gemcitabine.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture and Reagents
The human pancreatic cancer (PC) cell lines PANC-1 and MiaPaCa-2 were purchased from the American Type Culture Collection. The murine pancreatic cancer cell lines KPCWT942 and TB33117 were isolated and characterized from KPC mice as described previously [
21]. Phenasen, ATO was provided by Phebra Pty. Ltd. (Lane Cove West, NSW, Australia). PhAs-LHP was prepared as previously published [
7]. PF-3758309 was purchased from Active Biochemical Co. (Maplewood, NJ) and gemcitabine was obtained from Sigma-Aldrich (Sydney, Australia). Phenylarsine oxide (PAO) was purified by HPLC before use by us. LHP was obtained from Peptide 2.0 (Chantilly, VA). Cells were cultured in Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium (DMEM) supplemented with 5% fetal bovine serum (FBS) obtained from Hyclone Laboratories(Melbourne, Australia) in a 37 °C incubator with a humidified atmosphere of 5% CO
2.
4.2. Cell Proliferation Assay
Human and murine PC cells were incubated in 5% FBS in DMEM with different concentrations of ATO and PhAs-LHP for the periods indicated in the Results section. For the combination of ATO with gemcitabine or PF-3758309, the cells were pre-incubated with gemcitabine or PF-3758309 for 24 h, followed by incubation with different concentrations of the ATO for 24 h. Cell proliferation was then measured by MTT assay.
4.3. Measurements of Cell Death and Cell Cycle
Cell death and cell cycle were assayed using propidium iodide (PI) and flow cytometry. Cells were treated with ATO or PhAs-LHP with the concentrations indicated in the text for 48 h for measuring cell death or 24 h for determining cell cycle arrest. All floating and adhering cells were then trypsinized and washed two times with cold phosphate-buffered saline (PBS). For cell death assays, cells were harvested and resuspended in PBS containing 1 μg/mL PI. For cell cycle analysis, cells were harvested and resuspended in PBS containing 0.1% Triton X-100, 50 μg/mL PI, and 10 μg/mL RNaseA (Thermo Scientific), and then incubated at 37 °C for 15 min. Samples were processed with the FACSymphony A3 flow cytometer (BD Biosciences) and the acquired data was analysed with the FlowJo software (BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA).
4.4. Mouse Study
All mouse experiments were approved by the Austin Health Animal Ethics Committee (A2019/05654). Experimental mice were housed in the BioResource Facility at Austin Health and monitored according to health criteria. Human PC cells MiaPaCa-2 (5x106 cells/100 μl culture medium) were subcutaneously injected into the flanks of 6-week-old, male Scid mice. When a tumor reached 50 mm3 (approximately 7 days), phenylarsine oxide (PAO, 50 μg/Kg) or PhAs-LHP (200 μg/Kg) was given by intraperitoneal injection every other day for 4 weeks. The control mice were given the same volume of saline. For combined treatment with gemcitabine, gemcitabine was given by intraperitoneal injection every four days for 4 weeks. There were 4 to 8 mice per group. Tumor growth was determined by tumor volume measured with callipers every other day and by tumor weight measured at the end of each experiment.
4.5. Immunohistochemical Staining
Tumor tissues from the mouse study were formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded and cut into a 4 μM slide. For immunohistochemical staining (IHC), antigen was retrieved by boiling the samples in citrate buffer (10 mM citric acid, pH6, Sigma-Aldrich, Castle Hill NSW, Australia) for 30 min, followed by incubation with hydrogen peroxidase blocker for 15 min and then with 5% normal goat serum for 30 min at room temperature for endogenous peroxidase quenching and protein blocking, respectively. Subsequently, the samples were incubated with an anti-Skp2 antibody (1:400, Bioss, USA ) at 4 °C overnight, followed by staining with EnVision kit (Dako, Botany, Australia) and haematoxylin (Sigma-Aldrich). The images of all slides were captured and scanned with Aperio AT2 digital pathology scanner (Leica Biosystems, Melbourne, Australia). The samples were analysed using QuPath version 0.4.3. The percentage of positively stained cells was calculated.
4.6. Statistical Analysis
All values are expressed as mean ± standard error. The in vitro data are from three independent experiments each in triplicate. The in vivo data were collated according to the number of tumor samples. Data were analysed by one-way ANOVA (SPSS, IBM, New York, NY). Differences between two means with P < 0.05 were considered significant.
5. Conclusions
The peptide-linked arsenic compound suppressed pancreatic cancer more potently than the non-peptide-linked arsenic by inhibiting PC cell growth in vitro with IC50 values 10 times lower than ATO, and by reducing PC growth in vivo at a molar concentration 2 times lower than PAO. Furthermore, at a 2 times lower arsenic concentration, a peptide-linked arsenic acid enhanced gemcitabine’s inhibition of PC. These results imply the potential clinical application of this peptide-linked arsenic compound in cancer treatment with reduced dosage and increased effectiveness.
6. Patents
There are 14-15 patents/provisional patents on this drug worldwide, inventors are C. Dillon and J. Carrall.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org.
Author Contributions
HH: MN and GB designed the study. HH performed mouse experiments and overall data analysis; HH & CD performed cell-based assays; LD did the flow cytometry assay and analyzed the data; JC, and CD were responsible for the design and production of the arsenic-peptide compounds; ME was responsible for the production of ATO (Phenasen) and was involved in the conceptual design of the study.
Funding: This reseach was supported by Phebra Pty. Ltd. and by the Pancare Foundation (
https://www.pancare.org.au).
Institutional Review Board Statement
All mouse experiments were approved by the Austin Health Animal Ethics Committee (A2019/05654).
Informed Consent Statement
not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available.
Acknowledgments
Dr. Hong He is supported by the Henry Baldwin Cancer Research Trust Fund.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A: Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin 2019, 69(1):7-34. [CrossRef]
- Ryan DP, Hong TS, Bardeesy N: Pancreatic adenocarcinoma. N Engl J Med 2014, 371(11):1039-1049. [CrossRef]
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A: Cancer Statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin 2017, 67(1):7-30. [CrossRef]
- Oettle H: Progress in the knowledge and treatment of advanced pancreatic cancer: from benchside to bedside. Cancer Treat Rev 2014, 40(9):1039-1047. [CrossRef]
- Von Hoff DD, Ervin T, Arena FP, Chiorean EG, Infante J, Moore M, Seay T, Tjulandin SA, Ma WW, Saleh MN et al: Increased survival in pancreatic cancer with nab-paclitaxel plus gemcitabine. The New England journal of medicine 2013, 369(18):1691-1703. [CrossRef]
- Zhang Y, Hochster H, Stein S, Lacy J: Gemcitabine plus nab-paclitaxel for advanced pancreatic cancer after first-line FOLFIRINOX: single institution retrospective review of efficacy and toxicity. Exp Hematol Oncol 2015, 4:29. [CrossRef]
- Carrall JA, Lie W, Lambert JM, Harris HH, Lai B, Dillon CT: Optimizing Arsenic Therapy by Selectively Targeting Leukemia Cells. J Med Chem 2023, 66(17):12101-12114. [CrossRef]
- Wang QQ, Jiang Y, Naranmandura H: Therapeutic strategy of arsenic trioxide in the fight against cancers and other diseases. Metallomics 2020, 12(3):326-336. [CrossRef]
- Lin CC, Hsu C, Hsu CH, Hsu WL, Cheng AL, Yang CH: Arsenic trioxide in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: a phase II trial. Invest New Drugs 2007, 25(1):77-84. [CrossRef]
- Kindler HL, Aklilu M, Nattam S, Vokes EE: Arsenic trioxide in patients with adenocarcinoma of the pancreas refractory to gemcitabine: a phase II trial of the University of Chicago Phase II Consortium. Am J Clin Oncol 2008, 31(6):553-556. [CrossRef]
- Li X, Ding X, Adrian TE: Arsenic trioxide induces apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells via changes in cell cycle, caspase activation, and GADD expression. Pancreas 2003, 27(2):174-179.
- Gao J, Wang G, Wu J, Zuo Y, Zhang J, Chen J: Arsenic trioxide inhibits Skp2 expression to increase chemosensitivity to gemcitabine in pancreatic cancer cells. Am J Transl Res 2019, 11(2):991-997.
- Han JB, Sang F, Chang JJ, Hua YQ, Shi WD, Tang LH, Liu LM: Arsenic trioxide inhibits viability of pancreatic cancer stem cells in culture and in a xenograft model via binding to SHH-Gli. Onco Targets Ther 2013, 6:1129-1138. [CrossRef]
- Lang M, Wang X, Wang H, Dong J, Lan C, Hao J, Huang C, Li X, Yu M, Yang Y et al: Arsenic trioxide plus PX-478 achieves effective treatment in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Cancer letters 2016, 378(2):87-96. [CrossRef]
- Yu S, Wu N, Zhu J, Liu Y, Han J: Pyrrolidine Dithiocarbamate Facilitates Arsenic Trioxide Against Pancreatic Cancer via Perturbing Ubiquitin-Proteasome Pathway. Cancer Manag Res 2020, 12:13149-13159. [CrossRef]
- Nishimura S, Takahashi S, Kamikatahira H, Kuroki Y, Jaalouk DE, O'Brien S, Koivunen E, Arap W, Pasqualini R, Nakayama H, Kuniyasu A: Combinatorial targeting of the macropinocytotic pathway in leukemia and lymphoma cells. J Biol Chem 2008, 283(17):11752-11762. [CrossRef]
- Liu H, Qian F: Exploiting macropinocytosis for drug delivery into KRAS mutant cancer. Theranostics 2022, 12(3):1321-1332. [CrossRef]
- Wang K, Huynh N, Wang X, Pajic M, Parkin A, Man J, Baldwin GS, Nikfarjam M, He H: PAK inhibition by PF-3758309 enhanced the sensitivity of multiple chemotherapeutic reagents in patient-derived pancreatic cancer cell lines. Am J Transl Res 2019, 11(6):3353-3364.
- Xu C, Wang X, Zhou Y, Chen FX, Wang H, Li K, Fan H, Tang X, Jiang G, Zhang J: Synergy between arsenic trioxide and JQ1 on autophagy in pancreatic cancer. Oncogene 2019, 38(47):7249-7265. [CrossRef]
- Tian Z, Tan Y, Lin X, Su M, Pan L, Lin L, Ou G, Chen Y: Arsenic trioxide sensitizes pancreatic cancer cells to gemcitabine through downregulation of the TIMP1/PI3K/AKT/mTOR axis. Transl Res 2023, 255:66-76. [CrossRef]
- Wang K, Zhan Y, Huynh N, Dumesny C, Wang X, Asadi K, Herrmann D, Timpson P, Yang Y, Walsh K et al: Inhibition of PAK1 suppresses pancreatic cancer by stimulation of anti-tumour immunity through down-regulation of PD-L1. Cancer letters 2020, 472:8-18. [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
ATO inhibited pancreatic cancer cell growth. Human (MiaPaCa-2 (A) and PANC-1 (B)) and murine (KPCWT942 (C) and TB33117 (D)) pancreatic cancer (PC) cells were incubated with ATO for 24, 48 and 72 h. Cell proliferation was measured by the MTT assay as described in the Materials and Methods. The values of control cells without treatment with ATO were defined as 100%. The results were representatives from three independent experiments.
Figure 1.
ATO inhibited pancreatic cancer cell growth. Human (MiaPaCa-2 (A) and PANC-1 (B)) and murine (KPCWT942 (C) and TB33117 (D)) pancreatic cancer (PC) cells were incubated with ATO for 24, 48 and 72 h. Cell proliferation was measured by the MTT assay as described in the Materials and Methods. The values of control cells without treatment with ATO were defined as 100%. The results were representatives from three independent experiments.
Figure 2.
The inhibitory effect of ATO on pancreatic cancer cell proliferation was enhanced by pre-treatment with gemcitabine or PF-3758309. Human (MiaPaCa-2 (A) and PANC-1 (B)) and murine (TB33117 (C) and KPCWT942 (D)) pancreatic cancer (PC) cells were pre-treated with gemcitabine (Gem) and PF-3758309 (PF) at concentrations indicated in the figures for 24 h, followed by 48 h treatment with arsenic trioxide (ATO). Cell proliferation was measured by MTT assay. The values of control cells without any treatment were defined as 100%. The results were summarized from three independent experiments. *, P<0.05, **, P<0.01, compared to the non-treated control; #, P<0.05, compared to Gem-pre-treatment only; $, P<0.05, compared to PF-pre-treatment only.
Figure 2.
The inhibitory effect of ATO on pancreatic cancer cell proliferation was enhanced by pre-treatment with gemcitabine or PF-3758309. Human (MiaPaCa-2 (A) and PANC-1 (B)) and murine (TB33117 (C) and KPCWT942 (D)) pancreatic cancer (PC) cells were pre-treated with gemcitabine (Gem) and PF-3758309 (PF) at concentrations indicated in the figures for 24 h, followed by 48 h treatment with arsenic trioxide (ATO). Cell proliferation was measured by MTT assay. The values of control cells without any treatment were defined as 100%. The results were summarized from three independent experiments. *, P<0.05, **, P<0.01, compared to the non-treated control; #, P<0.05, compared to Gem-pre-treatment only; $, P<0.05, compared to PF-pre-treatment only.
Figure 3.
PhAs-LHP inhibited pancreatic cancer cell growth more potently.Human (MiaPaCa-2 (A) and PANC-1 (B)) and murine TB33117 (C) pancreatic cancer (PC) cells were incubated with ATO, PhAs-LHP, or the peptide LHP for 48 h. Cell proliferation was measured by MTT assay. The values of control cells without any treatment were defined as 100%. The results were summarized from at least three independent experiments.
Figure 3.
PhAs-LHP inhibited pancreatic cancer cell growth more potently.Human (MiaPaCa-2 (A) and PANC-1 (B)) and murine TB33117 (C) pancreatic cancer (PC) cells were incubated with ATO, PhAs-LHP, or the peptide LHP for 48 h. Cell proliferation was measured by MTT assay. The values of control cells without any treatment were defined as 100%. The results were summarized from at least three independent experiments.
Figure 4.
PhAs-LHP induced cell death and cell cycle arrest more potently than ATO. MiaPaCa-2 cells were treated with ATO (0.5 μM) or PhAs-LHP (0.05 μM) for 48 h (A). PANC-1 cells were treated with ATO (2 μM) or PhAs-LHP (0.2 μM) for 24 h (B). Both MiaPaCa-2 and PANC-1 cells were then stained with propidium iodide (PI) and subjected to Flow cytometry analysis. Numbers indicate the percent of PI-negative cells of a total of 10,000 cells analyzed per condition (A).
Figure 4.
PhAs-LHP induced cell death and cell cycle arrest more potently than ATO. MiaPaCa-2 cells were treated with ATO (0.5 μM) or PhAs-LHP (0.05 μM) for 48 h (A). PANC-1 cells were treated with ATO (2 μM) or PhAs-LHP (0.2 μM) for 24 h (B). Both MiaPaCa-2 and PANC-1 cells were then stained with propidium iodide (PI) and subjected to Flow cytometry analysis. Numbers indicate the percent of PI-negative cells of a total of 10,000 cells analyzed per condition (A).
Figure 5.
PhAs-LHP suppressed pancreatic cancer growth in Sicd mice. MiaPaCa-2 human pancreatic cancer cells (5x106 cells) were subcutaneously injected into the flank of a Scid mouse. When the tumor size reached >50 mm3, PAO (50 μg/Kg) or PhAs-LHP (200 μg/Kg) were given by intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection every other day for the time periods indicated in (A). Tumor volume and weight were measured as described in the Materials and Methods. There were 7, 8, 8 mice in control, PAO and PhAs-LHP groups respectively as indicated in (C). *, P<0.05, compared to control.
Figure 5.
PhAs-LHP suppressed pancreatic cancer growth in Sicd mice. MiaPaCa-2 human pancreatic cancer cells (5x106 cells) were subcutaneously injected into the flank of a Scid mouse. When the tumor size reached >50 mm3, PAO (50 μg/Kg) or PhAs-LHP (200 μg/Kg) were given by intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection every other day for the time periods indicated in (A). Tumor volume and weight were measured as described in the Materials and Methods. There were 7, 8, 8 mice in control, PAO and PhAs-LHP groups respectively as indicated in (C). *, P<0.05, compared to control.
Figure 6.
PhAs-LHP enhanced the inhibitory effect of gemcitabine on pancreatic cancer growth in Scid mice. Human pancreatic cancer cell, MiaPaCa-2 (5x106 cells) were subcutaneously injected into the flank of a Scid mouse. When tumor size reached >50 mm3, gemcitabine (Gem, 50 mg/Kg), Gem plus PAO (50 μg/Kg) or PhAs-LHP (200 μg/Kg) were given by intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection for the time periods indicated in (A). Gem was given every 4 days. PAO and PhAs-LHP were given every other day. Tumor volume and weight were measured as described in the Materials and Methods. There were 4, 4, 5, and 5 mice in control, Gem, Gem+PAO and Gem+PhAs-LHP, respectively as indicated in (C). *, P<0.05, **, P<0.01, compared to control; #, P<0.05, compared to Gem alone.
Figure 6.
PhAs-LHP enhanced the inhibitory effect of gemcitabine on pancreatic cancer growth in Scid mice. Human pancreatic cancer cell, MiaPaCa-2 (5x106 cells) were subcutaneously injected into the flank of a Scid mouse. When tumor size reached >50 mm3, gemcitabine (Gem, 50 mg/Kg), Gem plus PAO (50 μg/Kg) or PhAs-LHP (200 μg/Kg) were given by intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection for the time periods indicated in (A). Gem was given every 4 days. PAO and PhAs-LHP were given every other day. Tumor volume and weight were measured as described in the Materials and Methods. There were 4, 4, 5, and 5 mice in control, Gem, Gem+PAO and Gem+PhAs-LHP, respectively as indicated in (C). *, P<0.05, **, P<0.01, compared to control; #, P<0.05, compared to Gem alone.
Figure 7.
The expression of Skp2 was reduced by PAO, PhAs-LHP and gemcitabine. Tumor tissues from the experiments shown in
Figure 5 and
Figure 6. were immunohistochemically stained by Skp2. The expression of Skp2 was decreased in the tumors of mice treated with PAO, PhAs-LHP and gemcitabine. The combination of gemcitabine with PAO or PhAs-LHP did not further decrease the levels of Skp2. *, p<0.05 compared to the un-treated control. CT, control; Gem, gemcitabine. .
Figure 7.
The expression of Skp2 was reduced by PAO, PhAs-LHP and gemcitabine. Tumor tissues from the experiments shown in
Figure 5 and
Figure 6. were immunohistochemically stained by Skp2. The expression of Skp2 was decreased in the tumors of mice treated with PAO, PhAs-LHP and gemcitabine. The combination of gemcitabine with PAO or PhAs-LHP did not further decrease the levels of Skp2. *, p<0.05 compared to the un-treated control. CT, control; Gem, gemcitabine. .
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).