Submitted:
29 June 2024
Posted:
01 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Material & Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Transthoracic Echocardiography
2.3. Decision to CRT-D Implantation
2.4. CRT-D Implantation
2.5. Responder Criteria
- Functional status:
- 1. NYHA-improvement of ≥ I stage 6 months after CRT-D implantation
- Echocardiographic status:
- 2. LVEF-increase of 5% 6 months after CRT-D implantation
- 3. LVEF-increase of 10% 6 months after CRT-D implantation
- Laboratory status:
- 4. proBNP-decrease of ≥ 25% 6 months after CRT-D implantation
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Overall Study Cohort and Baseline Characteristics
3.2. Responder Status and Baseline Characteristics
3.3. Responder Status and Follow-Up Characteristics
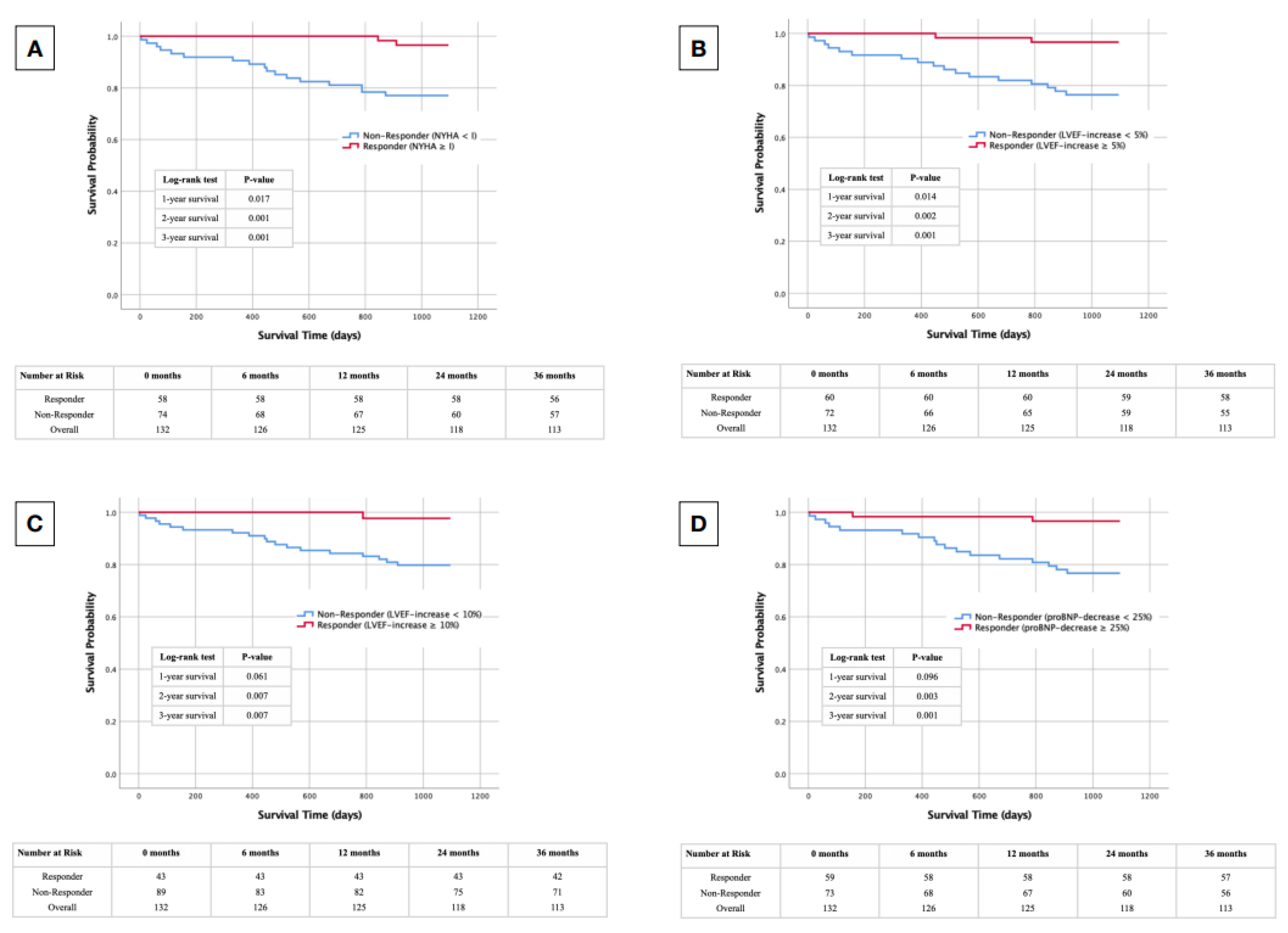
3.4. Responder Status-Dependent Survival after CRT-D Implantation
3.5. Predictive Factors Regarding Responder Status
4. Discussion
4.1. Influence of Right Ventricular Function on CRT-D Implantation
4.2. Influence of Drug-Based HF Therapy on CRT-D Implantation
4.3. Influence of Atrial Fibrillation on CRT-D Implantation
4.4. Influence of Kidney Function on CRT-D Implantation
5. Limitation
- Single-Center Design: The study's reliance on data from a single center may limit the generalizability of the findings. Variations in patient demographics, local practices, and healthcare infrastructure could influence the external validity of the results.
- Retrospective Nature: The retrospective nature of the study design might introduce inherent biases, including selection bias and information bias. The reliance on existing medical records could lead to incomplete or missing data, impacting the comprehensiveness of the analysis.
- Sample Size: The study's sample size, though sufficient for the conducted analyses, might pose limitations when stratifying results based on certain subgroups or rare outcomes. Larger cohorts would enhance the statistical power for subgroup analyses, even if the statistical power was a satisfactory 88.5%.
- Definition of Responder Status: The lack of a universally accepted definition for CRT-D responder status could introduce variability in patient classification. The absence of standardized criteria across studies or clinical guidelines may impact the consistency and comparability of findings.
- Follow-Up Duration: The study's follow-up duration may be limited, particularly if exploring longer-term outcomes. Extended follow-up periods could provide a more comprehensive understanding of the durability of CRT-D response and potential late effects.
- Incomplete Covariate Adjustment: Despite efforts to control for confounding variables, unmeasured or residual confounding may persist. Incomplete adjustment for relevant covariates could influence the accuracy of the observed associations.
- Medication changes: The impact of CRT-D on medication, including potential post-implantation adjustments, is hindered by the probable unavailability of data on medication changes, with this study solely relying on baseline medication documentation.
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Roger V. L. (2021). Epidemiology of Heart Failure: A Contemporary Perspective. Circulation research, 128(10), 1421–1434. [CrossRef]
- Jaffe, L. M., & Morin, D. P. (2014). Cardiac resynchronization therapy: history, present status, and future directions. Ochsner journal, 14(4), 596–607.
- Nakai, T., Ikeya, Y., Kogawa, R., Otsuka, N., Wakamatsu, Y., Kurokawa, S., Ohkubo, K., Nagashima, K., & Okumura, Y. (2021). What Are the Expectations for Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy? A Validation of Two Response Definitions. Journal of clinical medicine, 10(3), 514. [CrossRef]
- Bakos, Z., Chatterjee, N. C., Reitan, C., Singh, J. P., & Borgquist, R. (2018). Prediction of clinical outcome in patients treated with cardiac resynchronization therapy - the role of NT-ProBNP and a combined response score. BMC cardiovascular disorders, 18(1), 70. [CrossRef]
- van 't Sant, J., Mast, T. P., Bos, M. M., Ter Horst, I. A., van Everdingen, W. M., Meine, M., & Cramer, M. J. (2016). Echo response and clinical outcome in CRT-D patients. Netherlands heart journal : monthly journal of the Netherlands Society of Cardiology and the Netherlands Heart Foundation, 24(1), 47–55. [CrossRef]
- Allison, J. D., Jr, Biton, Y., & Mela, T. (2022). Determinants of Response to Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy. The Journal of innovations in cardiac rhythm management, 13(5), 4994–5003. [CrossRef]
- Gold, M. R., Rickard, J., Daubert, J. C., Zimmerman, P., & Linde, C. (2021). Redefining the Classifications of Response to Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy: Results From the REVERSE Study. JACC. Clinical electrophysiology, 7(7), 871–880. [CrossRef]
- Rosero, S. Z., Hernandez, N., Goldenberg, I., McNitt, S., Plonsky, B., Zareba, W., Buber, Y., Solomon, S. D., & Kutyifa, V. (2020). Utility of 6-Minute Walk Test to Predict Response to Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy in Patients With Mild Heart Failure. The American journal of cardiology, 132, 79–86. [CrossRef]
- Kuppahally, S. S., Fowler, M. B., Vagelos, R., Wang, P., Al-Ahmad, A., Hsia, H., & Liang, D. (2010). Dyssynchrony Assessment with Tissue Doppler Imaging and Regional Volumetric Analysis by 3D Echocardiography Do Not Predict Long-Term Response to Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy. Cardiology research and practice, 2011, 568918. [CrossRef]
- Zweerink, A., van Everdingen, W. M., Nijveldt, R., Salden, O. A. E., Meine, M., Maass, A. H., Vernooy, K., de Lange, F. J., Vos, M. A., Croisille, P., Clarysse, P., Geelhoed, B., Rienstra, M., van Gelder, I. C., van Rossum, A. C., Cramer, M. J., & Allaart, C. P. (2018). Strain imaging to predict response to cardiac resynchronization therapy: a systematic comparison of strain parameters using multiple imaging techniques. ESC heart failure, 5(6), 1130–1140. [CrossRef]
- Abdellatif, Y. A., Onsy, A. M., Eldemerdash, S. E. H., Rayan, M. M., Abu Shouk, H. M., & Badran, H. A. (2023). Prediction of Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy Response Using Quantitative Gated Myocardial Perfusion Imaging. The Journal of innovations in cardiac rhythm management, 14(1), 5313–5321. [CrossRef]
- Heggermont, W., Auricchio, A., & Vanderheyden, M. (2019). Biomarkers to predict the response to cardiac resynchronization therapy. Europace : European pacing, arrhythmias, and cardiac electrophysiology : journal of the working groups on cardiac pacing, arrhythmias, and cardiac cellular electrophysiology of the European Society of Cardiology, 21(11), 1609–1620. [CrossRef]
- Asgardoon, M. H., Vasheghani-Farahani, A., & Sherafati, A. (2020). Usefulness of Biomarkers for Predicting Response to Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy. Current cardiology reviews, 16(2), 132–140. [CrossRef]
- Yokoyama, Y., Kataoka, N., Nakai, M., Matsuo, A., Fujiwara, A., Wakamiya, A., Ueda, N., Nakajima, K., Kamakura, T., Wada, M., Yamagata, K., Ishibashi, K., Inoue, Y., Miyamoto, K., Nagase, S., Noda, T., Aiba, T., Takahama, H., Izumi, C., Kinugawa, K., … Kusano, K. (2022). A new biomarker of cardiac resynchronization therapy response: cGMP to mature BNP ratio. Journal of cardiology, 79(6), 727–733. [CrossRef]
- Parasuraman, S., Walker, S., Loudon, B. L., Gollop, N. D., Wilson, A. M., Lowery, C., & Frenneaux, M. P. (2016). Assessment of pulmonary artery pressure by echocardiography-A comprehensive review. International journal of cardiology. Heart & vasculature, 12, 45–51. [CrossRef]
- Glikson, M., Nielsen, J. C., Kronborg, M. B., Michowitz, Y., Auricchio, A., Barbash, I. M., Barrabés, J. A., Boriani, G., Braunschweig, F., Brignole, M., Burri, H., Coats, A. J. S., Deharo, J. C., Delgado, V., Diller, G. P., Israel, C. W., Keren, A., Knops, R. E., Kotecha, D., Leclercq, C., … ESC Scientific Document Group (2021). 2021 ESC Guidelines on cardiac pacing and cardiac resynchronization therapy. European heart journal, 42(35), 3427–3520. [CrossRef]
- Daubert, J. C., Ritter, P., Le Breton, H., Gras, D., Leclercq, C., Lazarus, A., Mugica, J., Mabo, P., & Cazeau, S. (1998). Permanent left ventricular pacing with transvenous leads inserted into the coronary veins. Pacing and clinical electrophysiology : PACE, 21(1 Pt 2), 239–245. [CrossRef]
- Sidiropoulos, G., Antoniadis, A., Saplaouras, A., Bazoukis, G., Letsas, Κ. P., Karamitsos, T. D., Giannopoulos, G., & Fragakis, N. (2023). Impact of baseline right ventricular function on the response to cardiac resynchronization therapy - A meta-analysis. Hellenic journal of cardiology : HJC = Hellenike kardiologike epitheorese, 73, 61–68. [CrossRef]
- Ogunyankin, K. O., & Puthumana, J. J. (2010). Effect of cardiac resynchronization therapy on right ventricular function. Current opinion in cardiology, 25(5), 464–468. [CrossRef]
- Alpendurada, F., Guha, K., Sharma, R., Ismail, T. F., Clifford, A., Banya, W., Mohiaddin, R. H., Pennell, D. J., Cowie, M. R., McDonagh, T., & Prasad, S. K. (2011). Right ventricular dysfunction is a predictor of non-response and clinical outcome following cardiac resynchronization therapy. Journal of cardiovascular magnetic resonance : official journal of the Society for Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance, 13(1), 68. [CrossRef]
- Patel, D., Trulock, K., Kumar, A., Kiehl, E., Toro, S., Moennich, L. A., Gorodeski, E., Hussein, A., Cantillon, D., Tarakji, K. G., Niebauer, M., Wazni, O., Varma, N., Wilkoff, B., & Rickard, J. W. (2020). Baseline Right Ventricular Dysfunction Predicts Worse Outcomes in Patients Undergoing Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy Implantation. Journal of cardiac failure, 26(3), 227–232. [CrossRef]
- Abreu, A., Oliveira, M., Silva Cunha, P., Santa Clara, H., Santos, V., Portugal, G., Rio, P., Soares, R., Moura Branco, L., Alves, M., Papoila, A. L., Ferreira, R., Mota Carmo, M., & BETTER-HF investigators (2017). Predictors of response to cardiac resynchronization therapy: A prospective cohort study. Revista portuguesa de cardiologia : orgao oficial da Sociedade Portuguesa de Cardiologia = Portuguese journal of cardiology : an official journal of the Portuguese Society of Cardiology, 36(6), 417–425. [CrossRef]
- Stassen, J., Galloo, X., Hirasawa, K., Chimed, S., Marsan, N. A., Delgado, V., van der Bijl, P., & Bax, J. J. (2022). Right ventricular-pulmonary artery coupling in cardiac resynchronization therapy: evolution and prognosis. ESC heart failure, 9(3), 1597–1607. [CrossRef]
- Aranda, J. M., Jr, Woo, G. W., Schofield, R. S., Handberg, E. M., Hill, J. A., Curtis, A. B., Sears, S. F., Goff, J. S., Pauly, D. F., & Conti, J. B. (2005). Management of heart failure after cardiac resynchronization therapy: integrating advanced heart failure treatment with optimal device function. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 46(12), 2193–2198. [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, S., Hürlimann, D., Starck, C. T., Hindricks, G., Lüscher, T. F., Ruschitzka, F., & Steffel, J. (2014). Treatment with higher dosages of heart failure medication is associated with improved outcome following cardiac resynchronization therapy. European heart journal, 35(16), 1051–1060. [CrossRef]
- Witt, C. T., Kronborg, M. B., Nohr, E. A., Mortensen, P. T., Gerdes, C., & Nielsen, J. C. (2015). Optimization of heart failure medication after cardiac resynchronization therapy and the impact on long-term survival. European heart journal. Cardiovascular pharmacotherapy, 1(3), 182–188. [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, G. A., & Steinberg, J. S. (2012). Managing atrial fibrillation in the CRT-D patient: controversy or consensus?. Heart rhythm, 9(8 Suppl), S51–S59. [CrossRef]
- Hoppe, U. C., Casares, J. M., Eiskjaer, H., Hagemann, A., Cleland, J. G., Freemantle, N., & Erdmann, E. (2006). Effect of cardiac resynchronization on the incidence of atrial fibrillation in patients with severe heart failure. Circulation, 114(1), 18–25. [CrossRef]
- Sieniewicz, B. J., Gould, J., Porter, B., Sidhu, B. S., Teall, T., Webb, J., Carr-White, G., & Rinaldi, C. A. (2019). Understanding non-response to cardiac resynchronisation therapy: common problems and potential solutions. Heart failure reviews, 24(1), 41–54. [CrossRef]
- Elliott, M. K., Mehta, V. S., Martic, D., Sidhu, B. S., Niederer, S., & Rinaldi, C. A. (2021). Atrial fibrillation in cardiac resynchronization therapy. Heart rhythm O2, 2(6Part B), 784–795. [CrossRef]
- Dębska-Kozłowska, A., Warchoł, I., Książczyk, M., & Lubiński, A. (2021). The Significance of Renal Function in Response to Cardiac Resynchronisation Therapy - A Piece of a Much Larger Puzzle. Current vascular pharmacology, 19(4), 403–410. [CrossRef]
- Goldenberg, I., Moss, A. J., McNitt, S., Barsheshet, A., Gray, D., Andrews, M. L., Brown, M. W., Zareba, W., Sze, E., Solomon, S. D., Pfeffer, M. A., & Multicenter Automatic Defibrillator Implantation Trial--Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy Investigators (2010). Relation between renal function and response to cardiac resynchronization therapy in Multicenter Automatic Defibrillator Implantation Trial--Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy (MADIT-CRT-D). Heart rhythm, 7(12), 1777–1782. [CrossRef]
- Fung, J. W., Szeto, C. C., Chan, J. Y., Zhang, Q., Chan, H. C., Yip, G. W., & Yu, C. M. (2007). Prognostic value of renal function in patients with cardiac resynchronization therapy. International journal of cardiology, 122(1), 10–16. [CrossRef]
- Ter Maaten, J. M., Martens, P., L'hoyes, W., Maass, A. H., Damman, K., Dupont, M., & Mullens, W. (2019). Response to Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy Across Chronic Kidney Disease Stages. Journal of cardiac failure, 25(10), 803–811. [CrossRef]
- Abraham, W. T., Compton, S., Haas, G., Foreman, B., Canby, R. C., Fishel, R., McRae, S., Toledo, G. B., Sarkar, S., Hettrick, D. A., & FAST Study Investigators (2011). Intrathoracic impedance vs daily weight monitoring for predicting worsening heart failure events: results of the Fluid Accumulation Status Trial (FAST). Congestive heart failure (Greenwich, Conn.), 17(2), 51–55. [CrossRef]
| Overall | |
|---|---|
|
Demographics n Male (%) Age (years — mean ± SD) |
132 75.0 65.0 ± 9.5 |
|
Clinical Weight (kg — mean ± SD) Height (m — mean ± SD) BMI (kg/m2 — mean ± SD) BMI < 18.5 kg/m2 (%) BMI 18.5 - 24.9 kg/m2 (%) BMI 25.0 - 29.9 kg/m2 (%) BMI 30.0 - 34.9 kg/m2 (%) BMI 35.0 - 39.9 kg/m2 (%) BMI ≥ 40.0 kg/m2 (%) ICMP (%) NICMP (%) Arterial Hypertension (%) Diabetes mellitus (%) Dyslipidemia (%) CVD (%) CVD – 1 vessel (%) CVD – 2 vessels (%) CVD – 3 vessels (%) Recent MI (%) Recent CABG (%) AF (%) COPD (%) Asthma (%) PAOD (%) Anemia (%) CKD > II (%) Recent Stroke (%) |
83.5 ± 16.9 173.7 ± 8.5 27.6 ± 5.0 2.3 31.8 38.6 18.9 6.8 1.5 35.6 59.1 65.2 39.4 70.5 50.8 21.1 11.4 16.7 33.3 11.4 33.3 12.9 2.3 8.3 3.8 44.7 11.4 |
|
Functional Class NYHA (median ± IQR) NYHA II (%) NYHA III (%) NYHA IV (%) |
3.0 ± 1.0 43.9 53.8 2.3 |
|
Medication ACEI/ARB (%) BB (%) Ivabradine (%) MRA (%) ARNI (%) SGLT2I (%) Loop Diuretics (%) Digoxin/Digitoxin (%) Amiodarone (%) |
67.4 95.5 6.8 72.0 28.8 12.1 72.0 12.1 31.1 |
|
Laboratory Creatinine (mg/dl — median ± IQR) proBNP (ng/l — median ± IQR) |
1.2 ± 0.5 2459.0 ± 3146.5 |
|
ECG LBBB (%) QRS-width (ms — mean ± SD) |
88.6 170.4 ± 28.4 |
|
Echocardiography LVEF (% — mean ± SD) LVEDD (mm — mean ± SD) TAPSE (mm — mean ± SD sPAP (mmHg — mean ± SD) |
27.0 ± 7.6 63.9 ± 8.2 18.4 ± 4.8 45.8 ± 13.2 |
|
Implantation characteristics Primary prevention (%) |
84.8 |
| Functional Status NYHA-improvement ≥ I R NR p |
Echocardiographic Status LVEF-increase ≥ 5% LVEF-increase ≥ 10% R NR p R NR p |
Laboratory Status proBNP-decrease ≥ 25% R NR p |
||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Demographics n Male (%) Age (years — mean ± SD) |
58 69.0 62.0 ± 9.8 |
74 79.7 67.5 ± 8.6 |
0.156 0.001 |
60 65.0 62.1 ± 9.7 |
72 83.3 67.5 ± 8.6 |
0.015 0.001 |
43 67.4 61.4 ± 10.0 |
89 78.7 66.8 ± 8.8 |
0.163 0.002 |
59 64.4 61.6 ± 10.1 |
73 83.6 67.8 ± 8.0 |
0.012 0.000 |
|
Clinical Weight (kg — mean ± SD) Height (m — mean ± SD) BMI (kg/m2 — mean ± SD) BMI < 18.5 kg/m2 (%) BMI 18.5 - 24.9 kg/m2 (%) BMI 25.0 - 29.9 kg/m2 (%) BMI 30.0 - 34.9 kg/m2 (%) BMI 35.0 - 39.9 kg/m2 (%) BMI ≥ 40.0 kg/m2 (%) ICMP (%) NICMP (%) Arterial Hypertension (%) Diabetes mellitus (%) Dyslipidemia (%) CVD (%) CVD - 1 vessel (%) CVD - 2 vessels (%) CVD - 3 vessels (%) Recent MI (%) Recent CABG (%) AF (%) COPD (%) Asthma (%) PAOD (%) Anemia (%) CKD > II (%) Recent Stroke (%) |
85.8 ± 16.8 173.5 ± 7.9 28.5 ± 5.1 3.4 27.6 34.5 25.9 6.9 1.7 32.8 62.1 62.1 34.5 70.7 46.6 25.9 6.9 13.8 24.1 8.6 20.7 8.6 5.2 5.2 0.0 37.9 8.6 |
81.6 ± 16.8 173.9 ± 9.0 26.9 ± 4.8 1.4 35.1 41.8 13.5 6.8 1.4 37.8 56.8 67.6 43.2 70.3 52.7 16.2 17.6 18.9 40.5 13.5 43.2 16.2 0.0 10.8 6.8 50.0 13.5 |
0.129 0.809 0.074 0.673 0.125 0.386 0.072 0.975 0.862 0.545 0.538 0.511 0.307 0.958 0.392 0.199 0.440 0.393 0.047 0.379 0.006 0.196 0.048 0.245 0.044 0.166 0.379 |
86.2 ± 18.9 172.3 ± 8.6 28.9 ± 5.4 3.3 23.3 35.0 25.0 11.7 1.7 30.0 65.0 61.7 36.7 70.0 40.0 23.3 6.7 10.0 23.3 8.3 18.3 8.3 3.3 8.3 3.3 30.0 10.0 |
81.1 ± 14.7 174.9 ± 8.2 26.5 ± 4.3 1.4 38.9 41.7 13.9 2.8 1.4 40.3 54.2 68.1 41.7 70.8 59.6 18.1 18.1 22.2 41.7 13.9 45.8 16.7 1.4 8.3 4.2 56.9 12.5 |
0.083 0.075 0.005 0.877 0.008 0.433 0.105 0.044 0.896 0.219 0.207 0.443 0.558 0.917 0.024 0.505 0.376 0.051 0.026 0.317 0.001 0.155 0.455 1.000 0.803 0.002 0.823 |
87.0 ± 19.1 172.4 ± 8.6 29.2 ± 5.7 4.7 20.9 34.8 23.3 14.0 2.3 30.2 69.8 60.5 32.6 62.8 37.2 23.3 7.0 9.3 20.9 11.6 11.6 11.6 4.7 9.3 2.3 23.3 7.0 |
81.7 ± 15.5 174.3 ± 8.4 26.8 ± 4.4 1.1 37.1 40.4 16.9 3.4 1.1 38.2 53.9 67.4 42.7 74.2 57.3 19.1 14.6 20.2 39.3 11.2 43.8 13.5 1.1 7.9 4.5 55.1 13.5 |
0.095 0.227 0.020 0.489 0.013 0.538 0.379 0.024 0.596 0.370 0.083 0.432 0.264 0.180 0.030 0.623 0.358 0.103 0.036 0.947 0.000 0.766 0.202 0.779 0.541 0.001 0.270 |
86.2 ± 18.7 172.7 ± 8.5 28.8 ± 5.5 3.4 27.1 32.2 23.7 10.2 3.4 28.8 64.4 71.2 42.4 69.5 44.1 27.1 5.1 11.9 27.1 8.5 18.6 10.2 3.4 6.8 3.4 37.3 8.5 |
81.2 ± 15.1 174.6 ± 8.4 26.6 ± 4.3 1.4 35.6 43.8 15.1 4.1 0.0 41.1 54.8 60.3 37.0 71.2 56.2 15.1 17.8 20.5 38.4 13.7 45.2 15.1 1.4 9.6 4.1 50.7 13.7 |
0.094 0.204 0.011 0.806 0.047 0.172 0.207 0.170 0.113 0.143 0.264 0.191 0.529 0.827 0.167 0.104 0.062 0.161 0.173 0.347 0.001 0.403 0.439 0.561 0.829 0.124 0.347 |
|
Functional Class NYHA (median ± IQR) NYHA II (%) NYHA III (%) NYHA IV (%) |
3.0 ± 1.0 37.9 56.9 5.2 |
3.0 ± 1.0 48.6 51.4 0.0 |
0.131 0.218 0.431 0.048 |
3.0 ± 1.0 45.0 53.3 1.7 |
3.0 ± 1.0 44.4 52.8 2.8 |
0.775 0.823 0.949 0.670 |
3.0 ± 1.0 41.9 55.8 2.3 |
3.0 ± 1.0 44.9 52.9 2.2 |
0.744 0.738 0.656 0.977 |
3.0 ± 1.0 40.7 55.9 3.4 |
3.0 ± 1.0 46.6 52.0 1.4 |
0.435 0.497 0.548 0.439 |
|
Medication ACEI/ARB (%) BB (%) Ivabradine (%) MRA (%) ARNI (%) SGLT2I (%) Loop Diuretics (%) Digoxin/Digitoxin (%) Amiodarone (%) |
62.1 96.6 3.4 72.4 34.5 15.5 63.8 6.9 19.0 |
71.6 94.6 9.5 71.6 24.3 9.5 78.4 16.2 40.5 |
0.245 0.592 0.174 0.920 0.201 0.290 0.064 0.103 0.008 |
66.7 95.0 10.0 73.3 33.3 20.0 61.7 11.7 13.3 |
68.1 95.8 4.2 70.8 25.0 5.6 80.6 12.5 45.8 |
0.865 0.819 0.186 0.750 0.292 0.011 0.016 0.884 0.000 |
67.4 95.3 11.6 74.4 27.9 16.3 60.5 7.0 9.3 |
67.4 95.5 4.5 70.8 29.2 10.1 77.5 14.6 41.6 |
0.998 0.968 0.128 0.663 0.877 0.309 0.041 0.208 0.000 |
57.6 96.6 5.1 81.4 40.7 18.6 57.6 8.5 18.6 |
75.3 94.5 8.2 64.4 19.2 6.8 83.6 15.1 41.1 |
0.031 0.567 0.478 0.031 0.007 0.039 0.001 0.248 0.006 |
|
Laboratory Creatinine (mg/dl — median ± IQR) proBNP (ng/l — median ± IQR) |
1.1 ± 0.5 1179.5 ± 2347.3 |
1.3 ± 0.6 2612.5 ± 3469.8 |
0.005 0.000 |
1.0 ± 0.3 1179.5 ± 2222.3 |
1.4 ± 0.6 2747.5 ± 3833.8 |
0.000 0.000 |
1.0 ± 0.3 1215.0 ± 2398.0 |
1.3 ± 0.6 2041.0 ± 3536.5 |
0.000 0.004 |
1.0 ± 0.4 1555.0 ± 2742.0 |
1.3 ± 0.5 1925.0 ± 3286.0 |
0.000 0.130 |
|
ECG LBBB (%) QRS-width (ms — mean ± SD) |
94.8 167.3 ± 24.2 |
83.8 172.09 ± 31.2 |
0.047 0.255 |
91.7 168.1 ± 23.4 |
86.1 172.4 ± 32.0 |
0.317 0.371 |
93.0 169.0 ± 23.6 |
86.5 171.1 ± 30.5 |
0.270 0.667 |
91.5 172.1 ± 30.5 |
86.3 169.0 ± 26.6 |
0.347 0.539 |
|
Echocardiography LVEF (% — mean ± SD) LVEDD (mm — mean ± SD) TAPSE (mm — mean ± SD sPAP (mmHg — mean ± SD) |
26.3 ± 6.4 64.9 ± 8.5 20.0 ± 4.6 42.7 ± 10.0 |
27.5 ± 8.5 63.1 ± 7.9 17.1 ± 4.6 47.9 ± 14.6 |
0.335 0.242 0.011 0.108 |
25.7 ± 7.6 63.9 ± 9.0 20.5 ± 4.0 46.0 ± 11.6 |
28.0 ± 7.6 63.9 ± 7.6 17.0 ± 4.9 45.7 ± 13.9 |
0.092 0.983 0.002 0.928 |
24.9 ± 6.9 63.9 ± 9.5 20.4 ± 3.8 45.8 ± 12.5 |
27.9 ± 7.8 63.9 ± 7.6 17.7 ± 5.0 45.8 ± 13.5 |
0.033 0.958 0.035 0.998 |
26.5 ± 6.6 64.1 ± 7.6 18.9 ± 4.6 42.7 ± 10.3 |
27.4 ± 8.4 63.8 ± 8.7 17.9 ± 5.0 47.6 ± 14.4 |
0.497 0.817 0.372 0.128 |
|
Implantation characteristics Primary prevention (%) |
93.1 |
78.4 |
0.019 |
88.3 |
81.9 |
0.308 |
88.4 |
83.1 |
0.433 |
88.1 |
82.2 |
0.344 |
| Functional Status NYHA-improvement ≥ I R NR p |
Echocardiographic Status LVEF-increase ≥ 5% LVEF-increase ≥ 10% R NR p R NR p |
Laboratory Status proBNP-decrease ≥ 25% R NR p |
||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Functional Class NYHA 6 months postoperative (median ± IQR) |
2.0 ± 1.0 |
2.5 ± 1.0 |
0.000 |
2.0 ± 0.5 |
2.5 ±1.0 |
0.000 |
1.5 ± 1.0 |
2.5 ± 1.0 |
0.000 |
2.0 ± 0.5 |
2.5 ± 1.0 |
0.005 |
|
Laboratory Creatinine 6 months postoperative (mg/dl — median ± IQR) proBNP 6 months postoperative (ng/l — median ± IQR) |
1.0 ± 0.4 629.0 ± 1493.0 |
1.3 ± 0.8 2270.5 ± 4582.0 |
0.005 0.000 |
1.0 ± 0.3 573.0 ± 2058.0 |
1.4 ± 0.9 2623.5 ± 4814.0 |
0.000 0.000 |
1.0 ± 0.4 573.0 ± 1577.0 |
1.3 ± 0.7 2158.5 ± 3947.8 |
0.000 0.000 |
1.0 ± 0.3 489.5 ± 965.0 |
1.4 ± 0.7 3374.0 ± 4047.0 |
0.000 0.000 |
|
ECG QRS-width postoperative (ms — mean ± SD) |
153.1 ± 26.0 |
165.4 ± 29.8 |
0.014 |
154.8 ± 29.0 |
164.4 ± 28.0 |
0.057 |
153.8 ± 26.9 |
163.0 ± 29.3 |
0.088 |
154.6 ± 28.6 |
164.3 ± 28.3 |
0.054 |
|
CRT-D Analysis Shock releases up to 3 years postoperative (%) nsVT up to 3 years postoperative (%) sVT up to 3 years postoperative (%) |
22.4 53.4 34.5 |
25.7 54.1 32.4 |
0.601 0.810 0.890 |
28.3 53.3 30.0 |
20.8 54.2 36.1 |
0.362 0.786 0.391 |
20.9 48.8 25.6 |
25.8 56.2 37.1 |
0.493 0.352 0.161 |
16.9 62.7 25.4 |
30.1 46.6 39.7 |
0.064 0.091 0.064 |
|
Echocardiography LVEF 6 months postoperative (% — mean ± SD) LVEDD 6 months postoperative (mm — mean ± SD) TAPSE 6 months postoperative (mm — mean ± SD) sPAP 6 months postoperative (mmHg — mean ± SD) TAPSE/sPAP 6 months postoperative (mean ± SD) |
35.8 ± 10.2 63.4 ± 8.4 19.6 ± 3.1 35.4 ± 7.7 0.6 ± 0.1 |
28.2 ± 8.1 61.5 ± 10.7 16.6 ± 4.2 44.3 ± 14.2 0.4 ± 0.1 |
0.001 0.489 0.027 0.027 0.000 |
36.9 ± 8.9 62.8 ± 10.0 19.7 ± 3.5 36.4 ± 8.9 0.5 ± 0.2 |
26.5 ± 7.8 62.2 ± 9.1 16.1 ± 3.8 44.5 ± 14.4 0.4 ± 0.2 |
0.000 0.811 0.007 0.054 0.041 |
38.6 ± 8.3 61.5 ± 10.7 19.8 ± 3.6 35.5 ± 9.0 0.6 ± 0.2 |
27.6 ± 8.3 63.0 ± 9.0 17.0 ± 4.0 42.9 ± 13.5 0.4 ± 0.2 |
0.000 0.606 0.065 0.145 0.030 |
34.3 ± 9.5 61.1 ± 6.3 18.6 ± 3.9 36.6 ± 8.9 0.5 ± 0.2 |
29.5 ± 9.7 64.1 ± 12.1 17.2 ± 4.1 44.6 ± 14.4 0.4 ± 0.2 |
0.043 0.281 0.322 0.050 0.160 |
| Cox Regression Analysis | Univariate | Multivariable | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | p-value | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | p-value | |
| 1-year survival | ||||
| Responder NYHA ≥ I | 54.232 (0.119 — 24780.897) | 0.201 | ||
| Responder LVEF ≥ 5% | 57.265 (0.128 — 25544.830) | 0.128 | ||
| Responder LVEF ≥ 10% | 38.426 (0.053 — 27604.409) | 0.277 | ||
| Responder proBNP | 5.037 (0.606 — 41.843) | 0.134 | ||
| Responder NYHA + LVEF ≥ 5% | 38.426 (0.053 — 27604.409) | 0.277 | ||
| Responder NYHA + LVEF ≥ 10% | 31.401 (0.021 — 46570.928) | 0.355 | ||
| Responder NYHA + proBNP | 34.276 (0.034 — 34616.859) | 0.317 | ||
| Responder LVEF ≥ 5% + proBNP | 35.565 (0.040 — 31656.799) | 0.303 | ||
| Responder LVEF ≥ 10% + proBNP | 30.879 (0.019 — 50147.546) | 0.363 | ||
| 2-year survival | ||||
| Responder NYHA ≥ I | 56.829 (0.758 — 4260.552) | 0.067 | ||
| Responder LVEF ≥ 5% | 11.831 (1.547 — 90.457) | 0.017 | 7.044 (0.896 — 55.342) | 0.063 |
| Responder LVEF ≥ 10% | 39.429 (0.392 — 3965.835) | 0.118 | ||
| Responder proBNP | 11.352 (1.485 — 86.790) | 0.019 | 6.605 (0.841 — 51.892) | 0.073 |
| Responder NYHA + LVEF ≥ 5% | 39.429 (0.392 — 3965.835) | 0.118 | ||
| Responder NYHA + LVEF ≥ 10% | 31.912 (0.193 — 5275.549) | 0.184 | ||
| Responder NYHA + proBNP | 34.972 (0.276 — 4437.930) | 0.150 | ||
| Responder LVEF ≥ 5% + proBNP | 36.351 (0.312 — 4230.689) | 0.139 | ||
| Responder LVEF ≥ 10% + proBNP | 31.358 (0.178 — 5519.271) | 0.192 | ||
| 3-year survival | ||||
| Responder NYHA ≥ I | 7.595 (1.754 — 32.889) | 0.007 | 3.015 (0.622 — 14.605) | 0.170 |
| Responder LVEF ≥ 5% | 7.958 (1.838 — 34.356) | 0.006 | 5.066 (1.135 — 22.606) | 0.033 |
| Responder LVEF ≥ 10% | 9.649 (1.288 — 72.294) | 0.027 | 2.226 (0.135 — 36.836) | 0.576 |
| Responder proBNP | 7.651 (1.767 — 33.124) | 0.006 | 4.768 (1.068 — 21.278) | 0.041 |
| Responder NYHA + LVEF ≥ 5% | 40.225 (0.787 — 2056.868) | 0.066 | ||
| Responder NYHA + LVEF ≥ 10% | 32.311 (0.417 — 2505.555) | 0.117 | ||
| Responder NYHA + proBNP | 35.520 (0.572 — 2205.141) | 0.090 | ||
| Responder LVEF ≥ 5% + proBNP | 8.330 (1.112 — 62.406) | 0.039 | 0.281 (0.009 — 8.673) | 0.468 |
| Responder LVEF ≥ 10% + proBNP | 6.036 (0.806 — 45.223) | 0.080 | ||
| CRT-Responder: NYHA ≥ I Binary Logistic Regression | Univariate | Multivariable | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | p-value | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | p-value | |
| Gender (male) | 0.565 (0.255 — 1.250) | 0.159 | ||
| Age | 0.536 (0.365 — 0.788) | 0.001 | 0.553 (0.306 — 0.997) | 0.049 |
| Weight | 1.296 (0.910 — 1.845) | 0.151 | ||
| Height | 0.958 (0.678 — 1.354) | 0.807 | ||
| BMI | 1.380 (0.966 — 1.971) | 0.077 | ||
| ICMP | 0.800 (0.389 — 1.648) | 0.546 | ||
| NICMP | 1.247 (0.618 — 2.516) | 0.538 | ||
| Arterial Hypertension | 0.785 (0.382 — 1.613) | 0.511 | ||
| Diabetes mellitus | 0.691 (0.339 — 1.406) | 0.307 | ||
| Dyslipidemia | 1.020 (0.480 — 2.168) | 0.958 | ||
| Cardiovascular Disease (all) | 0.740 (0.372 — 1.475) | 0.393 | ||
| CVD – 1 vessel | 1.744 (0.742 — 4.098) | 0.202 | ||
| CVD – 2 vessels | 0.523 (0.171 — 1.602) | 0.257 | ||
| CVD – 3 vessels | 0.663 (0.257 — 1.710) | 0.395 | ||
| Recent MI | 0.467 (0.218 — 0.998) | 0.049 | 0.217 (0.063 — 0.743) | 0.015 |
| Recent CABG | 0.604 (0.194 — 1.876) | 0.383 | ||
| AF | 0.342 (0.156 — 0.750) | 0.007 | 0.611 (0.178 — 2.091) | 0.432 |
| COPD | 0.487 (0.161 — 1.473) | 0.203 | ||
| Asthma | 0.000 (0.000 — .) | 0.999 | ||
| PAOD | 0.450 (0.114 — 1.779) | 0.255 | ||
| Anemia | 0.000 (0.000 — .) | 0.999 | ||
| CKD > II | 0.611 (0.304 — 1.230) | 0.167 | ||
| Recent Stroke | 0.604 (0.194 — 1.876) | 0.383 | ||
| NYHA (preoperative) | 1.747 (0.909 — 3.354) | 0.094 | ||
| ACEI/ARB | 0.648 (0.312 — 1.349) | 0.246 | ||
| BB | 1.600 (0.283 — 9.056) | 0.595 | ||
| Ivabradine | 0.342 (0.068 — 1.712) | 0.192 | ||
| MRA | 1.040 (0.483 — 2.238) | 0.920 | ||
| ARNI | 1.637 (0.767 — 3.496) | 0.203 | ||
| SGLT2I | 1.758 (0.613 — 5.045) | 0.294 | ||
| Loop Diuretics | 0.486 (0.225 — 1.050) | 0.066 | ||
| Digoxin/Digitoxin | 0.383 (0.117 — 1.257) | 0.113 | ||
| Amiodarone | 0.343 (0.154 — 0.767) | 0.009 | 1.012 (0.257 — 3.979) | 0.986 |
| Creatinine (baseline) | 0.571 (0.366 — 0.889) | 0.013 | 1.057 (0.457 — 2.441) | 0.897 |
| proBNP (baseline) | 0.503 (0.287 — 0.882) | 0.016 | 0.508 (0.230 — 1.122) | 0.094 |
| LBBB | 3.548 (0.951 — 13.233) | 0.059 | ||
| QRS-width (preoperative) | 0.819 (0.576 — 1.166) | 0.268 | ||
| LVEF (preoperative) | 0.846 (0.596 — 1.200) | 0.349 | ||
| LVEDD (preoperative) | 1.255 (0.858 — 1.834) | 0.241 | ||
| TAPSE (preoperative) | 1.951 (1.135 — 3.355) | 0.016 | 1.832 (1.014 — 3.311) | 0.045 |
| sPAP (preoperative) | 0.650 (0.382 — 1.107) | 0.113 | ||
| TAPSE/sPAP (preoperative) | 1.870 (0.935 — 3.741) | 0.077 | ||
| Primary Prevention | 3.724 (1.171 — 11.840) | 0.026 | 2.368 (0.368 — 15.237) | 0.364 |
| CRT-Responder: LVEF ≥ 5% Binary Logistic Regression | Univariate | Multivariable | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | p-value | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | p-value | |
| Gender (male) | 0.371 (0.164 — 0.840) | 0.017 | 0.282 (0.041 — 1.947) | 0.199 |
| Age | 0.541 (0.368 — 0.794) | 0.002 | 1.377 (0.627 — 3.023) | 0.425 |
| Weight | 1.366 (0.957 — 1.952) | 0.086 | ||
| Height | 0.725 (0.508 — 1.036) | 0.077 | ||
| BMI | 1.701 (1.168 — 2.479) | 0.006 | 1.177 (0.467 — 2.971) | 0.730 |
| ICMP | 0.635 (0.308 — 1.313) | 0.221 | ||
| NICMP | 1.571 (0.777 — 3.179) | 0.209 | ||
| Arterial Hypertension | 0.755 (0.368 — 1.549) | 0.444 | ||
| Diabetes mellitus | 0.811 (0.401 — 1.638) | 0.558 | ||
| Dyslipidemia | 0.961 (0.454 — 2.035) | 0.917 | ||
| Cardiovascular Disease (all) | 0.450 (0.223 — 0.904) | 0.025 | 0.358 (0.090 — 1.418) | 0.143 |
| CVD – 1 vessel | 1.334 (0.571 — 3.119) | 0.505 | ||
| CVD – 2 vessels | 0.488 (0.159 — 1.493) | 0.208 | ||
| CVD – 3 vessels | 0.375 (0.136 — 1.031) | 0.057 | ||
| Recent MI | 0.426 (0.199 — 0.911) | 0.028 | 0.480 (0.066 — 3.483) | 0.468 |
| Recent CABG | 0.564 (0.181 — 1.750) | 0.321 | ||
| AF | 0.265 (0.119 —0.591) | 0.001 | 0.459 (0.095 — 2.212) | 0.332 |
| COPD | 0.455 (0.150 — 1.373) | 0.162 | ||
| Asthma | 2.448 (0.217 — 27.682) | 0.469 | ||
| PAOD | 1.000 (0.290 — 3.454) | 1.000 | ||
| Anemia | 0.793 (0.128 — 4.909) | 0.803 | ||
| CKD > II | 0.324 (0.157 — 0.668) | 0.002 | 0.734 (0.110 — 4.888) | 0.749 |
| Recent Stroke | 0.778 (0.260 — 2.325) | 0.653 | ||
| NYHA (preoperative) | 0.899 (0.475 — 1.703) | 0.745 | ||
| ACEI/ARB | 0.939 (0.452 — 1.949) | 0.865 | ||
| BB | 0.826 (0.161 — 4.251) | 0.819 | ||
| Ivabradine | 2.556 (0.611 — 10.689) | 0.199 | ||
| MRA | 1.132 (0.527 — 2.434) | 0.750 | ||
| ARNI | 1.500 (0.704 — 3.197) | 0.294 | ||
| SGLT2I | 4.250 (1.292 — 13.975) | 0.017 | 9.013 (1.614 — 50.313) | 0.012 |
| Loop Diuretics | 0.388 (0.178 — 0.849) | 0.018 | 0.326 (0.079 — 1.340) | 0.120 |
| Digoxin/Digitoxin | 0.925 (0.323 — 2.650) | 0.884 | ||
| Amiodarone | 0.182 (0.076 — 0.437) | < 0.001 | 0.395 (0.059 — 2.645) | 0.339 |
| Creatinine (baseline) | 0.318 (0.179 — 0.563) | < 0.001 | 0.155 (0.047 — 0.505) | 0.002 |
| proBNP (baseline) | 0.392 (0.206 — 0.747) | 0.004 | 0.690 (0.140 — 3.409) | 0.649 |
| LBBB | 1.774 (0.571 — 5.510) | 0.321 | ||
| QRS-width (preoperative) | 0.855 (0.603 — 1.213) | 0.381 | ||
| LVEF (preoperative) | 0.737 (0.516 — 1.053) | 0.094 | ||
| LVEDD (preoperative) | 1.004 (0.693 — 1.456) | 0.983 | ||
| TAPSE (preoperative) | 2.263 (1.274 — 4.021) | 0.005 | 2.858 (1.305 — 6.259) | 0.009 |
| sPAP (preoperative) | 1.024 (0.618 — 1.696) | 0.926 | ||
| TAPSE/sPAP (preoperative) | 1.334 (0.654 — 2.722) | 0.428 | ||
| Primary Prevention | 1.668 (0.619 — 4.494) | 0.311 | ||
| CRT-Responder: LVEF ≥ 10% Binary Logistic Regression | Univariate | Multivariable | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | p-value | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | p-value | |
| Gender (male) | 0.562 (0.249 — 1.270) | 0.166 | ||
| Age | 0.555 (0.376 — 0.820) | 0.003 | 1.098 (0.399 — 3.016) | 0.857 |
| Weight | 1.369 (0.944 — 1.986) | 0.098 | ||
| Height | 0.796 (0.550 — 1.152) | 0.226 | ||
| BMI | 1.627 (1.110 — 2.385) | 0.013 | 0.907 (0.366 — 2.248) | 0.832 |
| ICMP | 0.701 (0.322 — 1.527) | 0.371 | ||
| NICMP | 1.971 (0.910 — 4.269) | 0.085 | ||
| Arterial Hypertension | 0.739 (0.347 — 1.573) | 0.433 | ||
| Diabetes mellitus | 0.648 (0.302 — 1.391) | 0.265 | ||
| Dyslipidemia | 0.588 (0.270 — 1.282) | 0.182 | ||
| Cardiovascular Disease (all) | 0.442 (0.209 — 0.932) | 0.032 | 0.462 (0.067 — 3.175) | 0.432 |
| CVD – 1 vessel | 1.248 (0.516 — 3.020) | 0.624 | ||
| CVD – 2 vessels | 0.427 (0.115 — 1.587) | 0.204 | ||
| CVD – 3 vessels | 0.393 (0.124 — 1.245) | 0.112 | ||
| Recent MI | 0.408 (0.175 — 0.955) | 0.039 | 0.091 (0.012 — 0.667) | 0.018 |
| Recent CABG | 1.039 (0.332 — 3.254) | 0.947 | ||
| AF | 0.169 (0.061 — 0.469) | 0.001 | 0.028 (0.002 — 0.314) | 0.004 |
| COPD | 0.844 (0.277 — 2.570) | 0.766 | ||
| Asthma | 4.293 (0.378 — 48.706) | 0.240 | ||
| PAOD | 1.201 (0.332 — 4.348) | 0.780 | ||
| Anemia | 0.606 (0.055 — 4.669) | 0.548 | ||
| CKD > II | 0.247 (0.109 — 0.563) | 0.001 | 0.403 (0.052 — 3.160) | 0.387 |
| Recent Stroke | 0.481 (0.128 — 1.804) | 0.278 | ||
| NYHA (preoperative) | 1.116 (0.567 — 2.197 | 0.751 | ||
| ACEI/ARB | 1.001 (0.460 — 2.177) | 0.998 | ||
| BB | 0.965 (0.170 — 5.484) | 0.968 | ||
| Ivabradine | 2.796 (0.711 — 10.996) | 0.141 | ||
| MRA | 1.201 (0.527 — 2.735) | 0.663 | ||
| ARNI | 0.938 (0.418 — 2.104) | 0.877 | ||
| SGLT2I | 1.728 (0.597 — 5.005) | 0.313 | ||
| Loop Diuretics | 0.443 (0.202 — 0.975) | 0.043 | 0.230 (0.040 — 1.319) | 0.099 |
| Digoxin/Digitoxin | 0.438 (0.118 — 1.629) | 0.218 | ||
| Amiodarone | 0.144 (0.047 — 0.438) | 0.001 | 0.177 (0.019 — 1.695) | 0.133 |
| Creatinine (baseline) | 0.313 (0.164 — 0597) | < 0.001 | 0.315 (0.075 — 1.328) | 0.116 |
| proBNP (baseline) | 0.492 (0.256 — 0.946) | 0.034 | 0.424 (0.038 — 4.686) | 0.484 |
| LBBB | 2.078 (0.554 — 7.791) | 0.278 | ||
| QRS-width (preoperative) | 0.928 (0.641 — 1.342) | 0.691 | ||
| LVEF (preoperative) | 0.656 (0.442 — 0.973) | 0.036 | 0.497 (0.194 — 1.276) | 0.146 |
| LVEDD (preoperative) | 0.989 (0.665 —1.471) | 0.957 | ||
| TAPSE (preoperative) | 1.772 (1.021 — 3.075) | 0.042 | 1.088 (0.399 — 2.969) | 0.869 |
| sPAP (preoperative) | 0.999 (0.577 — 1.730) | 0.998 | ||
| TAPSE/sPAP (preoperative) | 1.626 (0.725 — 3.646) | 0.238 | ||
| Primary Prevention | 1.541 (0.521 — 4.559) | 0.435 | ||
| CRT-Responder: proBNP Binary Logistic Regression | Univariate | Multivariable | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | p-value | Hazard Ratio (95% CI) | p-value | |
| Gender (male) | 0.356 (0.157 — 0.806) | 0.013 | 0.637 (0.221 — 1.832) | 0.403 |
| Age | 0.481 (0.322 — 0.717) | < 0.001 | 0.677 (0.432 — 1.061) | 0.089 |
| Weight | 1.353 (0.947 — 1.931) | 0.096 | ||
| Height | 0.797 (0.561 — 1.132) | 0.204 | ||
| BMI | 1.596 (1.103 — 2.309) | 0.013 | 1.545 (1.023 — 2.332) | 0.039 |
| ICMP | 0.580 (0.279 — 1.205) | 0.145 | ||
| NICMP | 1.493 (0.738 — 3.020) | 0.265 | ||
| Arterial Hypertension | 1.628 (1.628 — 3.389) | 0.192 | ||
| Diabetes mellitus | 1.253 (0.621 — 2.527) | 0.529 | ||
| Dyslipidemia | 0.920 (0.434 — 1.949) | 0.827 | ||
| Cardiovascular Disease (all) | 0.615 (0.308 — 1.228) | 0.168 | ||
| CVD – 1 vessel | 2.030 (0.857 — 4.805) | 0.107 | ||
| CVD – 2 vessels | 0.239 (0.065 — 0.884) | 0.032 | 0.379 (0.083 — 1.729) | 0.210 |
| CVD – 3 vessels | 0.503 (0.190 — 1.330) | 0.166 | ||
| Recent MI | 0.598 (0.284 — 1.257) | 0.175 | ||
| Recent CABG | 0.583 (0.188 — 1.812) | 0.351 | ||
| AF | 0.278 (0.125 — 0.619) | 0.002 | 0.369 (0.149 — 0.918) | 0.032 |
| COPD | 0.638 (0.221 — 1.842) | 0.406 | ||
| Asthma | 2.526 (0.223 — 28.567) | 0.454 | ||
| PAOD | 0.686 (0.191 — 2.465) | 0.563 | ||
| Anemia | 0.819 (0.132 — 5.068) | 0.830 | ||
| CKD > II | 0.579 (0.287 — 1.164) | 0.125 | ||
| Recent Stroke | 0.583 (0.188 — 1.812) | 0.351 | ||
| NYHA (preoperative) | 1.317 (0.693 — 2.501) | 0.401 | ||
| ACEI/ARB | 0.445 (0.212 — 0.934) | 0.062 | ||
| BB | 1.652 (0.292 — 9.350) | 0.570 | ||
| Ivabradine | 0.598 (0.143 — 2.501) | 0.481 | ||
| MRA | 2.414 (1.072 — 5.435) | 0.033 | 1.860 (0.674 — 5.134) | 0.231 |
| ARNI | 2.890 (1.324 — 6.308) | 0.008 | 2.717 (1.110 — 6.649) | 0.029 |
| SGLT2I | 3.117 (1.017 — 9.551) | 0.047 | 1.373 (0.357 — 5.284) | 0.645 |
| Loop Diuretics | 0.268 (0.119 — 0.599) | 0.001 | 0.509 (0.200 — 1.299) | 0.158 |
| Digoxin/Digitoxin | 0.522 (0.171 — 1.597) | 0.254 | ||
| Amiodarone | 0.328 (0.147 — 0.734) | 0.007 | 0.497 (0.188 — 1.319) | 0.161 |
| Creatinine (baseline) | 0.376 (0.220 — 0.641) | < 0.001 | 0.455 (0.248 — 0.834) | 0.011 |
| proBNP (baseline) | 0.883 (0.615 — 1.266) | 0.498 | ||
| LBBB | 1.714 (0.552 — 5.325) | 0.351 | ||
| QRS-width (preoperative) | 1.116 (0.789 — 1.577) | 0.536 | ||
| LVEF (preoperative) | 0.886 (0.626 — 1.254) | 0.494 | ||
| LVEDD (preoperative) | 1.045 (0.722 — 1.513) | 0.815 | ||
| TAPSE (preoperative) | 1.245 (0.772 — 2.008) | 0.368 | ||
| sPAP (preoperative) | 0.659 (0.383 — 1.134) | 0.132 | ||
| TAPSE/sPAP (preoperative) | 1.452 (0.752 — 2.806) | 0.267 | ||
| Primary Prevention | 0.621 (0.231 — 1.674) | 0.347 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





