1. Introduction
Motor imagery (MI) is the mental simulation of a motor action without its actual execution [
1]. It is used in neuro-rehabilitation therapies, including Brain-Computer Interface interventions, however, its efficacy is difficult to predict due to the large variability of motor imagery abilities in the general population [
2,
3]. Hypnotizability is a psychophysiological trait measured by standardized scales and associated with several behavioral and brain morpho-functional characteristics [
4], which could assist in screening the best candidates for motor imagery training [
5,
6]. Higher hypnotizability scores are associated with lower differences in the brain activations between actual and imagined sensorimotor conditions [
7,
8], which is defined as stronger functional equivalence (FE) [
9] and indicates the efficacy of imagery better than self-report [
7,
8,
10]. Actual and effective imagined actions also share time duration and autonomic responses, thus possibly accounting for the beneficial effect of motor imagery on motor performance in athletes [
11] and in the rehabilitation of neurological disorders [
5,
6].
Actual and imagined movements have been associated with different EEG patterns during their preparatory, execution, and post-execution phases. Generally, alpha and beta desynchronization is observed during movement preparation and execution phases, whereas beta rebound occurs at the end of the movement [
12,
13]. Similar findings are reported for MI, with a decrease in EEG power (desynchronization) indicating increased cortical activity [
14,
15], and its increase representing the maintenance or inhibition of cortical activity [
14,
16,
17].
The experience of MI is assessed by self-reports, and the difference between the duration of actual and imagined movements is considered a behavioral index of its efficacy. Nonetheless, the correspondence between MI measures is still an object of debate. It has been suggested that MI should be considered from multiple perspectives including self-reports, chronometric indices, EEG activities, electrodermal and cardiac responses [
18].
Efficacious MI requires a correct body schema, influenced by interoception [
19], which is described as the »sense of the body« [
20]. Interoception includes the dimensions of accuracy (IA, measured by the heartbeat counting task and heartbeat-evoked cortical potential (HEP)), sensitivity (IS, measured by self-report questionnaires), and awareness (the correspondence between IA and IS) [
21].
The insular cortex is the brain structure most involved in interoception. It also receives gustatory, auditory, visual, olfactory, and somesthetic information, is involved in the sensory context relevant to voluntary movements [
22], and participates in decision-making, and social and risky behavior [
23].
The body sensations experienced during motor imagery with different emotional content can increase or decrease the functional connectivity between the insula and the dorsomedial frontal cortex [
22]. Additionally, an impaired body schema has been observed in patients with anorexia nervosa [
24], who are also less accurate than control subjects in MI and less successful in the mental rotation of human figures [
25].
Hypnotizability-related brain differences include reduced grey matter volume in the insula [
26,
27]. Highly hypnotizable individuals (highs) exhibit lower interoceptive accuracy [
28,
29] than low hypnotizables (lows), and »more adaptive« interoceptive sensitivity (IS) – that is, the tendency to trust their bodily signals and behave accordingly [
30] - compared to lows and medium hypnotizables (mediums).
Since both the efficacy of MI - indicated by the functional equivalence between actual and imagined perception/action [
7,
8] - and interoceptive sensitivity [
30] differ according to hypnotizability, the study aimed to assess the role of hypnotizability and interoceptive sensitivity in the subjective experience, chronometric variables, and EEG correlates of visual and kinesthetic motor imagery in healthy highs, mediums, and lows.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Participants
Fifty-three right-handed (according to the Edinburgh Handedness Inventory) healthy volunteers of both sexes (age range: 19 – 26 years) were recruited among the students at the University of Pisa. After signing the informed consent approved by the University Bioethics Committee (n.29/2022), the absence of medical, neurological, psychiatric disease, sleep, and attention disorders and current pharmacological therapies was assessed by anamnestic interviews. Then, the participants were administered the Italian version of the Stanford Hypnotic Susceptibility Scale: Form A (SHSS: A, range: 0-12) [
31]. According to the SHSS: A, they were 16 highs (
M +
SD: 9.75 + 1.24; 9 females), 11 mediums (6.00 + .77; 7 females), 26 lows (1.00 + 1.52; 13 females), with mediums representing 70% of the general population and highs and lows each representing 15% [
32]. SHSS scores were significantly different between hypnotizability groups (
F(2, 50) = 224.90,
p < .001) with the highs' scores higher than mediums (
p < .001) and lows (
p < .001), and mediums' scores higher than lows' (
p < .001).
2.2. Experimental Design and Procedure
At least 2 weeks after hypnotic assessment (to prevent expectancy effects), the proneness to be deeply involved in cognitive tasks and interoceptive sensitivity were assessed through the Tellegen Absorption Scale (TAS, [
33]) and the Multidimensional Assessment of Interoceptive Awareness (MAIA, [
34]), respectively.
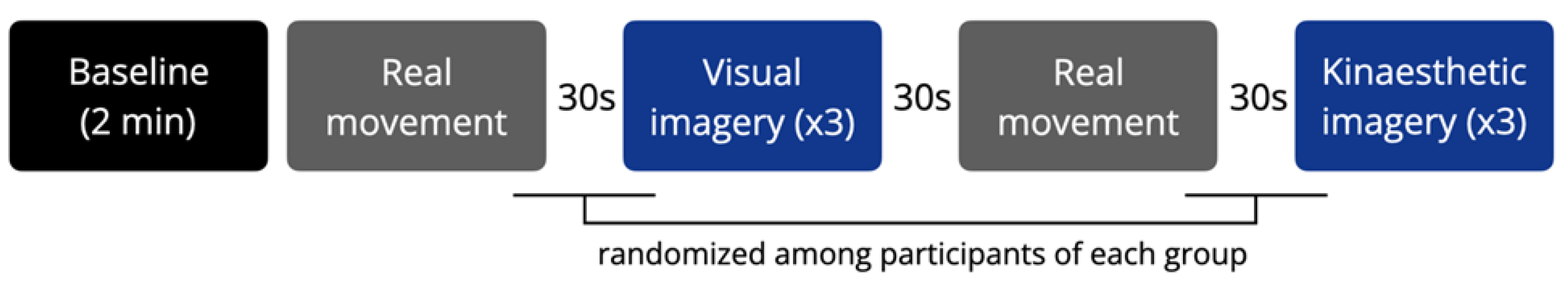
The experiments were conducted on the same day, in a semi-dark and quiet room. Participants sat in a comfortable armchair with their eyes closed. Before the experimental session started, one of the experimenters demonstrated the movement to be performed and later imagined. Subjects were required to perform the movement with the left hand to introduce an additional level of difficulty. They were instructed to minimize body and head movements, except for the movements required in the real movement condition. The experimental session consisted of a 2-minute resting state (baseline), followed by two series of actual and imagined movements performed through two different modalities (visual and kinesthetic). One actual movement (Mv) preceded three repetitions of the same, visually imagined movement (MIv). Another actual movement (Mk) preceded three repetitions of the same, kinesthetically imagined movement (MIk). The movement consisted of ten repetitions of flexion-extension of the left arm, hand, and fingers to touch the thumb. The conditions were interspersed with 30-second rest periods. The imaginative visual and kinesthetic sequences were randomized among subjects of each group (
Figure 1). Each condition was initiated by a vocal command and ended when the experimenter saw that the real movement had ended or when the subject declared that the imagery task had been completed. The duration of each condition was monitored. At the end of each imagery condition, the participants rated the perceived efficacy of imagery (range: 0-10).
Each imagery series was preceded by listening to the script describing the movement. Visual imagery consisted of listening to a script describing the movement through visual images (“Now please imagine doing the same movement you did a few minutes ago. You can clearly see your left arm flexing up to the shoulder while your fingers touch your thumb one by one from the index to the little finger. You can distinctly see your hand approaching your body until your arm touches your shoulder, then your fingers go back touching your thumb from the little finger to the index as your arm extends back to the starting position on the thigh. Please, continue imagining doing this movement ten times at the same pace, with your arm flexing and extending and your fingers touching your thumb from the index to the little finger on the way up, and from the little finger to the index on the way down) and then imagine that movement”. The kinesthetic imagery consisted of listening to a script describing the movement through kinesthetic images (“Now, please imagine repeating the same movement you did a few minutes ago. You can feel the tension growing in your left biceps as it flexes up to the shoulder, while the muscles in your forearm start contracting and your fingers touch your thumb one by one from the index to the little finger. Notice the increasing extension in your triceps as your hand approaches your body, until the arm contacts your shoulder. Then, as your fingers start going back, feel the contraction in your triceps, while your fingers touch your thumb from the little finger to the index and your arm extends back to the starting position on your thigh. Please continue imagining this movement ten times at the same pace, with your bicep and triceps alternating in contraction and relaxation, and your fingers touching your thumb from the index to the little finger on the way up, and from the little finger to the index on the way down”).
2.3. Signals Acquisition and Analysis
Electrocardiogram (ECG) and Electroencephalogram (EEG) were acquired by the g.tec’s multipurpose wireless biosignal acquisition tool g.Nautilus. An EEG cap with 28 electrodes placed in standardized positions according to the modified 10-10 international system was used (FP1, FP2, AF3, AF4, F7, F3, Fz, F4, F8, C3, FC1, FC2, C4, T7, Cz, T8, CP5, CP1, CP2, CP6, P7, P3, Pz, P4, P8, PO3, PO4, Oz) and the reference was set to Cz. Two additional ECG electrodes were placed underneath the right and left clavicle. The sampling rate was set to 500 Hz and all impedances were kept below 30 kΩ.
EEG pre-processing was performed with the EEGLAB toolbox [
35]. Signals were band-pass filtered (band pass: 0.5–45 Hz, two-way least-squares FIR filtering) and visually inspected to reject physiological and non-physiological artifacts. Individual channels showing quality decline (due to instability or loss of contact with the scalp during recordings) were visually identified and replaced with signals obtained via spline interpolation. To remove residual artifacts, values exceeding the range of -70–70 mV were discarded. Retained EEG signals were downsampled to 256 Hz.̲ Signal was then submitted to Independent Component Analysis (ICA, [
36]) to remove ocular, heart, and muscular artifacts in each subject. Artifact components were identified by visual inspection of their time course, power spectrum and scalp maps. For every condition (B, M, MIv, and MIk), the pre-processed EEG signal was subjected to Power Spectral Density (PSD) analysis using Welch's method. PSD estimation was performed with a Hamming window of 4-second length and 50% overlap. For Fz, F3, F4, C3, C4, P3, P4, PO3, PO4, Oz channels, the PSD was integrated over the alpha (8-12 Hz), low beta (13-21 Hz), and high beta (22-30 Hz) frequency bands and then log-transformed. Signals from frontal and central, as well as parietal and occipital electrodes was averaged to obtain two regions (fronto-central (FC) and parieto-occipital (PO)). Heart rate was extracted by an open-source MATLAB toolbox EEG-Beats [
37], which downsamples (128 Hz) and FIR filters (3 Hz high-pass, 20 Hz low-pass) the signal and then uses a divide-and-conquer strategy to identify ECG peaks.
2.4. Variables
2.4.1. Preliminary Questionnaires Administration
- Absorption (Tellegen Absorption Scale (TAS, [
33]) measuring the level of proneness to be deeply involved in cognitive tasks (range: 0-34)
- Interoceptive sensitivity (Multidimensional Assessment of Interoceptive Awareness (MAIA, Mehling 2012, [
34]), consisting of 8 dimensions (noticing, not distracting, not worrying, attention regulation, emotional awareness, self-regulation, body listening, trusting), with scores ranging from 0 to 5).
2.4.2. Experimental Session
- For physiological assessment: EEG alpha and beta PSD and heart rate (HR) during baseline condition (B), actual movement (M), visual and kinesthetic MI (VI, KI).
- For psychophysiological assessment, visual (ΔV) and kinesthetic (ΔK) imagery duration normalized to movement duration computed as [(actual movement duration – imagined movement duration) / actual movement duration].
- For the subjective experience of MI, self-report of the efficacy of visual (Ve) and kinesthetic (Ke) imagery (range: 0-10).
2.5. Statistical Analysis
To assess hypnotizability group differences, a univariate ANOVA was used for TAS scores, and multivariate ANOVA was applied to MAIA dimensions. Separate repeated measures ANOVAs (2 modalities x 3 groups) were applied to ΔHR, chronometry and efficacy variables. EEG log transformed signals were studied by repeated measures ANOVAs according to the following experimental design: 3 groups (highs, mediums, lows) x 4 conditions (B, M, V, K) x 2 hemispheric sides (left, right) x 2 brain regions (fronto-central, parieto-occipital).
The Greenhouse-Geisser correction was used when sphericity assumption was not met. ANCOVA was applied to test the differences in chronometry, efficacy, and EEG using MAIA dimensions as covariates. Post-hoc comparisons were performed by contrast analysis and paired t-tests. Bonferroni correction for multiple comparisons was applied when necessary. Spearman correlation was used to study associations between chronometric, subjective measures of efficacy of each imagery modality and EEG alpha/ low beta/high beta power spectra. The significance level was set at a = .05.
3. Results
TAS scores were significantly different between hypnotizability groups (F(2, 50) = 6.99, p = .002) with highs’ (p = .006) and mediums' scores (p = .019) higher than lows’, and no difference between highs and mediums. Among MAIA dimensions of interoceptive sensitivity, only noticing differed among hypnotizability groups (F(2, 50) = 3.86, p = .028) with highs' scores > lows' (p = .046).
Repeated measures ANOVA did not reveal a significant group effect for ΔHR. The changes in heart rate between visual imagery and actual movement (ΔHRv) were larger than the changes occurring between kinaesthetic imagery and actual movement (ΔHRk) (
F(1,50) = 28.63,
p < .001).
Table 1 reports the mean values and standard deviations of all the studied variables.
3.1. Motor Imagery, Hypnotizability, and Interoception
3.1.1. Subjective Efficacy (Ve, Ke)
Repeated measures ANOVA (3 groups x 2 MI modalities) revealed significant differences between imagery modalities (K > V,
F(1, 50) = 16.82,
p < .001, η
2 =.252, α =.980) and a significant Modality x Group interaction (
F(2, 50) = 3.918,
p = .026, η
2 =.135, α =. 680). Its decomposition revealed a significant difference between imagery modalities in highs (K > V,
F(1, 15) = 6.79,
p = .020) and mediums (K > V,
F(1, 10) = 7.56,
p = .02) and no difference in lows. The kinesthetic efficacy was greater in mediums than in lows (
p = .046) and did not differ between highs and mediums and between highs and lows. The visual efficacy was similar in all three groups (
Figure 2a). Controlling ANOVA for MAIA dimensions abolished all differences.
3.1.2. Chronometry (ΔV, ΔK)
Repeated measures ANOVA (3 groups x 2 MI modalities) did not reveal significant differences between groups and imagery modalities (
Figure 2b). No difference was disclosed controlling ANOVA for MAIA dimensions.
3.1.3. Correlational Analysis
Chronometric (ΔK, ΔV) and subjective (Ke, Ve) measures of motor imagery did not correlate with each other for both modalities of imagery. Partial correlation controlling for SHSS and MAIA dimensions did not disclose any significant relationship.
3.2. EEG Alpha, and Beta PSD
Based on both the functional equivalence model and on the literature showing lower desynchronization during imagery than during actual movement [
38,
39], we studied the conditions in which K and/or V power spectra were higher or non-significantly different from M, provided the presence of significant differences between B and V/K,
The EEG power spectra of alpha, low and high beta showed significant differences between the baseline (B) and movement (M) conditions at all sites.
Alpha PSD
The significant main effects and interactions are reported in
Table 2.
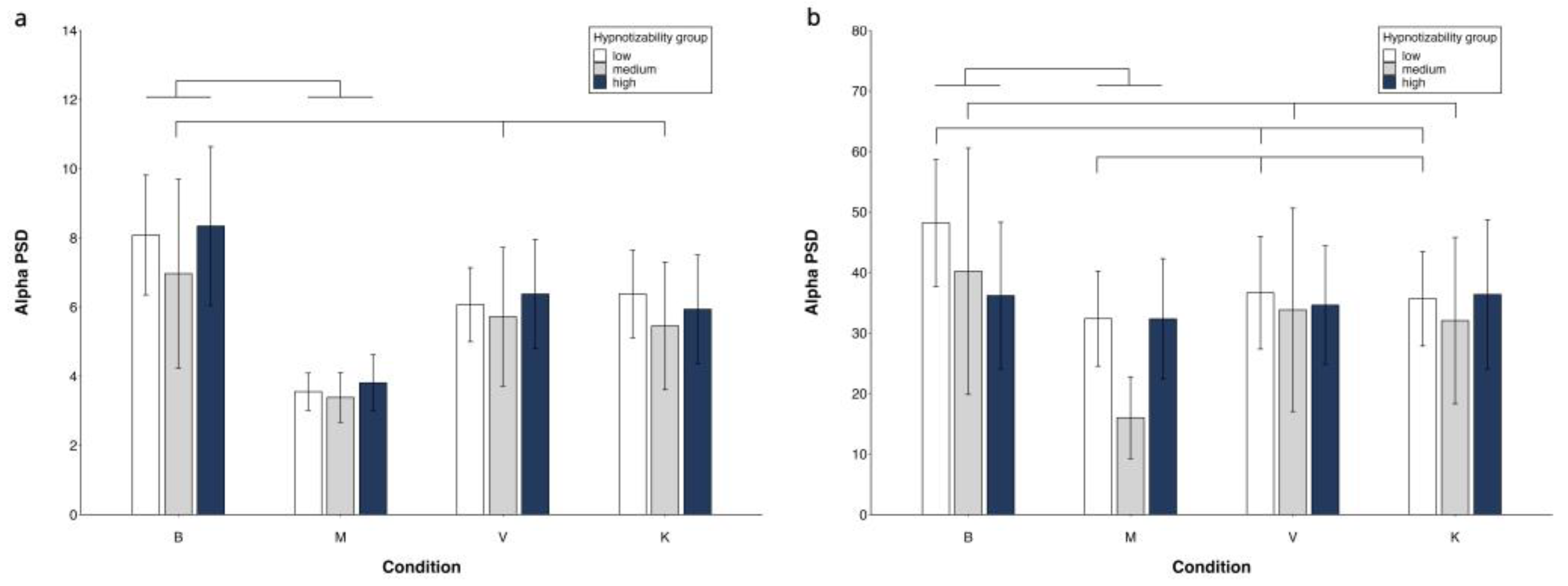
The Side and Condition effects were abolished controlling for MAIA dimensions. The Region effect (F(1, 42) = 6.62, p = .014, η2 = .136 α = .710) and the Region x Condition x Group interaction (F(6, 126) = 3,05, p = .013, η2 = .126 α =.854) survived.
In highs, the decomposition of this interaction revealed significant Region (FC < PO) and Condition effects, which however did not involve differences between B, V, and K (Table A, Suppl. El. Mat.),
In mediums,
Table 2 shows significant Side, Region, and Condition effects consisting also of M = V and M = K (Table A, Suppl. El. Mat.).
In lows, the Region x Condition interaction revealed FC power < PO power in all conditions, B = K = V in FC, and M < K in PO (Table A, Suppl. El. Mat.).
No significant group effect was observed.
Figure 3.
Alpha PSD. Region x Condition x Group interaction. FC region (a) and PO region (b). Mean values and standard errors. Lines indicate significant differences (differences between M and V/K are presented only if V/K are different from B).
Figure 3.
Alpha PSD. Region x Condition x Group interaction. FC region (a) and PO region (b). Mean values and standard errors. Lines indicate significant differences (differences between M and V/K are presented only if V/K are different from B).
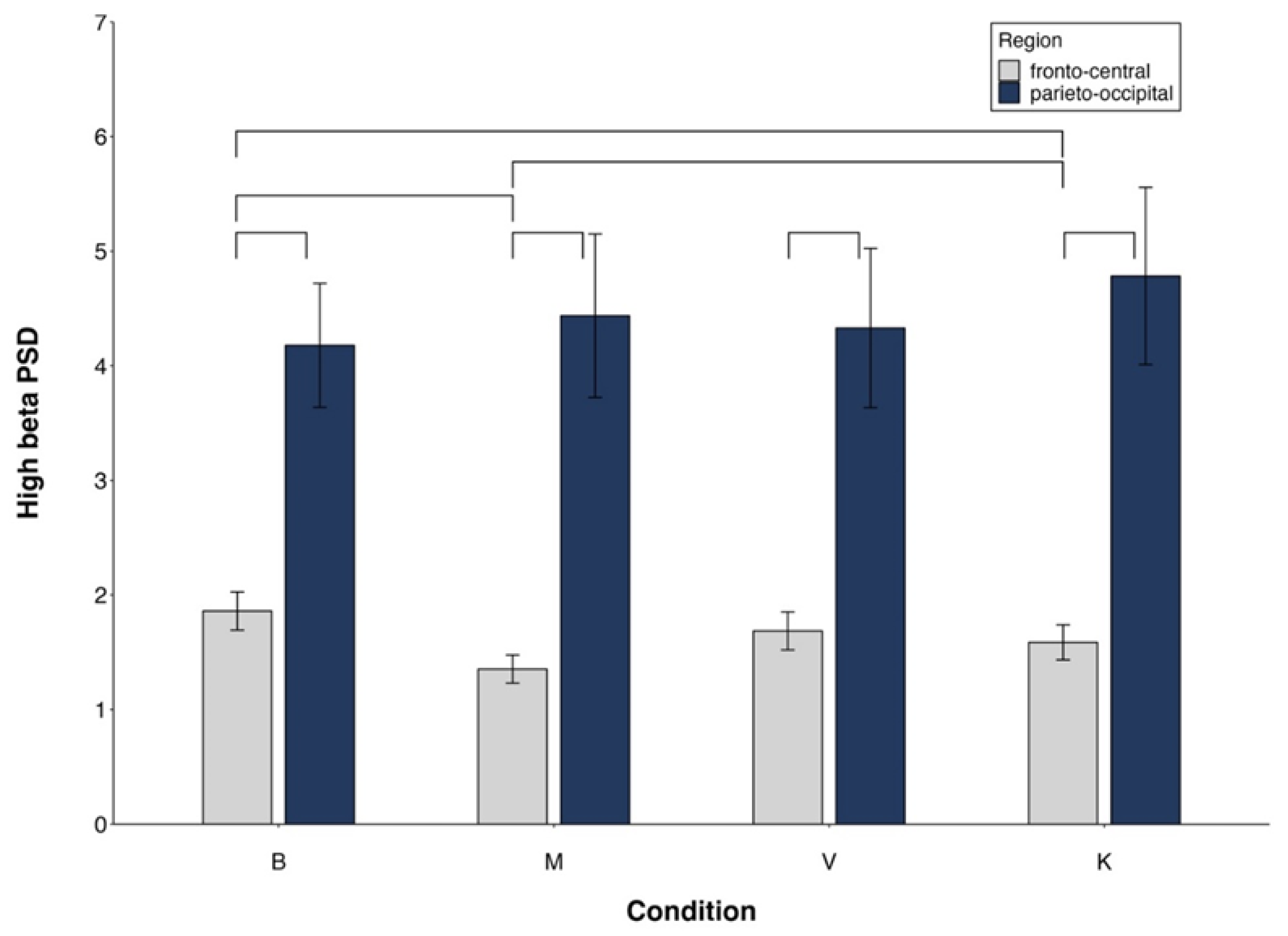
Table 3 shows the main effects and interactions for low and high beta.
Low beta showed significantly higher power in the right hemisphere, in the PO region, and during V and K compared to M (Table B, Suppl. El. Mat.).
For high beta, the significant Side x Group interaction revealed a significant Side effect only in mediums (Table B, Suppl. El. Mat.). The significant Region x Condition interaction indicated FC power < PO in all conditions, M < K in FC and no difference between conditions in PO (Table B, Suppl. El. Mat.).
All main effects and interactions described for low and high beta became non-significant controlling for MAIA
Figure 4.
High beta PSD. Region x Condition interaction. Mean values and standard errors. Lines indicate significant differences (differences between M and V/K are presented only if V/K are different from B).
Figure 4.
High beta PSD. Region x Condition interaction. Mean values and standard errors. Lines indicate significant differences (differences between M and V/K are presented only if V/K are different from B).
No significant correlation was observed between EEG alpha / beta PSD and subjective or chronometric variables.
4. Discussion
The study aimed to investigate the role of hypnotizability and interoceptive sensitivity in motor imagery performed through the visual or kinesthetic sensory modality. Findings allow us to report, for the first time, a relevant role of interoceptive sensitivity to the subjective experience of movement imagery and to its cortical correlates, in contrast to chronometric indices. Only alpha and high beta PSD displayed a few hypnotizability-related differences
4.1. Subjective and Behavioral Findings
The findings show that both interoceptive sensitivity and hypnotizability contribute to the difference in the subjective experience of visual and kinesthetic MI among the three groups, but not to their chronometric differences. The absence of correlation between chronometry and subjective experience in both modalities of imagery was not unexpected, owing to hypnotizability-related differences in imagery abilities [
7,
8,
40] and interoceptive characteristics [
30], which might buffer each other differentially in the three groups. Subjective experience and chronometric indices of MI have been described, however, as measures of different components of motor imagery, whose effects may not be necessarily correlated with each other [
41].
The subjective reports of the efficacy of visual imagery did not differ between groups, possibly due to the easiness of this modality of imagery. In a previous study, visual imagery was reported as easier than somesthetic imagery by lows when in standing position [
42], thus possibly buffering the gap with highs, whereas highs and lows reported the same vividness and effort when sited [
43].
Kinaesthetic imagery was reported as more effective than visual imagery by mediums and highs, but not by lows, as earlier observed in standing participants with different hypnotizability [
42] and elite athletes not characterized by hypnotizability [
41]. The proneness to absorption, higher in mediums and highs than in lows, might account for the difference between lows and medium/highs.
As earlier observed in the general population [
41], and in line with the suggested multivariate model of motor imagery [
18], no group difference was found in chronometry, despite the hypnotizability-related differences in the efficacy of kinesthetic imagery.
4.2. EEG Findings
The EEG findings indicate that cortical activities –alpha, low and high beta – were largely sustained by interoceptive sensitivity, as controlling the repeated measures ANOVAs for MAIA dimensions abolished almost all the significant effects. This provides additional insight into the relationship between cognitive functions, such as imagery, and the perception and interpretation of bodily sensations, supporting the concept of embodied cognition [
44].
EEG alpha spectral frequency, whose changes were sustained by interoceptive sensitivity, highlighted three different modes of cortical elaboration of the imagery tasks. In highs, the cortical activities associated with both imagery tasks did not differ from the baseline, despite their subjective and behavioral correlates. This could be a side effect of the distributed rather than nested cortical activity indicated by earlier studies [
7,
8,
42,
45] which reported quite few spectral changes in brain activities during sensory-cognitive imagery tasks in this group. In contrast, mediums, that represent the general population [
32], exhibited the expected desynchronization [
14,
15]. Lows desynchronized only in the parietal-occipital region, suggesting a visual rather than kinesthetic mechanisms of motor imagery, independently of the requested modality. This group, like highs, had the same frontocentral alpha power in baseline and imagery conditions, which could be accounted for by their lower absorption.
Low and high beta changes were sustained by interoceptive sensitivity, too. Low beta changes were as expected, i.e., lower desynchronization during visual and kinesthetic imagery compared to the actual movement, which allows to think that the participants did perform the mental tasks [
46]. High beta was sensitive to both the kinesthetic and visual imagery in frontocentral regions and, counterintuitively, only to the kinesthetic imagery at parieto-occipital sites. Nonetheless, this could be accounted for by the role suggested for beta as a large-scale communication mechanism between sensorimotor areas and other brain regions [
47]. The absence of cortical response to visual imagery suggests that, in line with the subjective experience reported by highs and mediums, kinesthetic motor imagery is more effective than visual motor imagery [
48]. Indeed, the correlates of kinesthetic imagery are more similar to movement, whereas visual correlates better resemble action observation [
16].
For high beta mediums exhibited hemispheric differences consisting of larger left than right desynchronization. In baseline conditions, highs have been reported to have higher cortical activity than lows in the frontal left region [
49,
50], and it is possible that in the present study the bilateral activations reported for mental imagery [
51] have buffered the hemispheric difference in highs and not disclosed any difference in lows. Nonetheless, the mediums’ pre-eminent left activation could suggest a mechanism like highs’. As a matter of fact, few studies have enrolled mediums, thus information about their difference from highs and lows is scarce [
52].
Like previously reported [
18], and in line with the several discrepancies observed in behavioral and neural correlates of imagined and executed actions [
38], no significant correlations were observed between subjective, chronometric and EEG correlates of the studied tasks. Regarding EEG, the debate should also consider the substantial absence of reliable indicators of covert cortical activities [
53] and the different styles of information processing observed in participants with different hypnotizability [
7,
8,
42]. Different methods of EEG signal analysis may likely provide further information. Furthermore, we might argue that the temporal equivalence between actual and imagined movements, which is expressed by the chronometric index, is not necessarily an index of performance accuracy and imagery vividness. This prompts the urge to find a reliable behavioral index that reflects cortical activity.
5. Limitations and Conclusions
Limitations of the study are the absence of reports about how much participants imagined through the requested sensory modality, and the distribution of the participant's hypnotizability, which was not in line with the hypnotizability distribution observed in the general population that includes 15% of highs and lows and 70% of mediums [
32]. A strength of the study is its protocol, which involved a complex flexion-extension movement of the entire arm, rather than partially automatic, sequential movements limited to hands or fingers [
54]. Moreover, the participants were seated rather than lying down [
55,
56], which was more suitable for performing the studied movement. Finally, the similar EEG correlates of visual and kinesthetic imagery could be accounted for by the fact that the two modalities of imagery were not exclusively used when participants were invited to use one of them, in line with earlier findings of imaging studies [
57,
58].
In conclusion, despite the above limitations at our best knowledge this is the first report of the major role of interoceptive sensitivity in the cortical activities associated with motor imagery. This finding can be relevant to neurorehabilitation training and to the improvement of sports performance by imagery training. In a general perspective, it highlights the close relationship between interoception and cognitive activities extending to motor imagery the important role of the insula [
23], thus shedding further light on the concept of embodied cognition [
44].
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org., Table A; Table B.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.L.S. EM, ZZ; methodology, E.L.S., E.M., Z.Z.; formal analysis, E.L.S., E.M., Z.Z.; investigation, E.M., Z.Z.; resources, E.L.S.; data curation, E.M., Z.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, E.L.S., E.M., Z.Z.; writing—review and editing, E.L.S., E.M., Z.Z.; visualization, E.M., Z.Z.; supervision, E.L.S.; funding acquisition, E.L.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Pisa University (Ateneo, 2019).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Bioethical Committee of the University of Pisa (protocol code 29/2022, June 29, 2022) for studies involving humans.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The original data presented in the study are openly available in Supplementary Materials.
Acknowledgments
This article was produced by Eleonora Malloggi while attending the Ph.D. program in Space Science and Technology at the University of Trento, Cycle XXXVIII, with the support of a scholarship financed by the Ministerial Decree no. 352 of 9 April 2022, and by Žan Zelič while attending the PhD program in Space Science and Technology at the University of Trento, Cycle XXXIX, with the support of a scholarship financed by the Ministerial Decree no. 118 of March 2, 2023, based on the NRRP—funded by the European Union—NextGenerationEU—Mission 4 “Education and Research”, Component 1 “Enhancement of the offer of educational services: from nurseries to universities”—Investment 4.1 “Extension of the number of research doctorates and innovative doctorates for public administration and cultural heritage”.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Jeannerod, M.; Decety, J. Mental motor imagery: A window into the representational stages of action. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 1995, 5, 727–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeunet, C.; N’Kaoua, B.; Lotte, F. Advances in user-training for mental-imagery-based BCI control. In Progress in Brain Research, Elsevier, 2016; Volume 228, pp. 3–35.
- Saha, S.; Baumert, M. Intra- and Inter-subject Variability in EEG-Based Sensorimotor Brain Computer Interface: A Review. Front Comput Neurosci. 2020, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santarcangelo, E. L. Physiological Correlates of Hypnotizability. In The Routledge International Handbook of Clinical Hypnosis; Linden, J. H., De Benedittis, G., Sugarman, L. I., Varga, K., Eds.; Taylor & Francis, 2024: pp. 313-330.
- Fontanelli, L.; Spina, V.; Chisari, C.; Siciliano, G.; Santarcangelo, E. L. Is Hypnotic Assessment Relevant to Neurology? Neurol. Sci. 2022, 43, 4655–4661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malloggi, E.; Santarcangelo, E.L. Physiological Correlates of Hypnotizability: Hypnotic Behaviour and Prognostic Role in Medicine. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibáñez-Marcelo, E.; Campioni, L.; Phinyomark, A.; Petri, G.; Santarcangelo, E.L. Topology Highlights Mesoscopic Functional Equivalence between Imagery and Perception: The Case of Hypnotizability. NeuroImage 2019, 200, 437–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibáñez-Marcelo, E.; Campioni, L.; Manzoni, D.; Santarcangelo, E.L.; Petri, G. Spectral and Topological Analyses of the Cortical Representation of the Head Position: Does Hypnotizability Matter? Brain Behav. 2019, 9, e01277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decety, J. Do Imagined and Executed Actions Share the Same Neural Substrate? Cogn. Brain Res. 1996, 3, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srzich, A.J.; Byblow, W.D.; Stinear, J.W.; Cirillo, J.; Anson, J.G. Can Motor Imagery and Hypnotic Susceptibility Explain Conversion Disorder with Motor Symptoms? Neuropsychologia 2016, 89, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collet, C.; Guillot, A. Autonomic Nervous System Activities during Imagined Movements. In The Neurophysiological Foundations of Mental and Motor Imagery; Guillot, A., Collet, C., Eds.; Oxford University Press: New York, 2010; pp. 95–108.
- Leriche, R.B.; Jackson, N.A.; Peterson, K.; Aspandiar, Z.; Hufnagel, V.; Swann, N.C. Reduced Sensorimotor Beta Dynamics Could Represent a "Slowed Movement State" in Healthy Individuals. Neuropsychologia 2022, 172, 108276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borra, D.; Fantozzi, S.; Bisi, M. C.; Magosso, E. Modulations of Cortical Power and Connectivity in Alpha and Beta Bands during the Preparation of Reaching Movements. Sensors (Basel) 2023, 23, 3530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steriade, M.; Llinás, R.R. The Functional States of the Thalamus and the Associated Neuronal Interplay. Physiol. Rev. 1988, 68, 649–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Opri, E.; Cernera, S.; Okun, M. S.; Foote, K.D.; Gunduz, A. The Functional Role of Thalamocortical Coupling in the Human Motor Network. J. Neurosci. 2019, 39, 8124–8134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuper, C.; Scherer, R.; Reiner, M.; Pfurtscheller, G. Imagery of Motor Actions: Differential Effects of Kinesthetic and Visual-Motor Mode of Imagery in Single-Trial EEG. Brain Res. Cogn. Brain Res. 2005, 25, 668–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engel, A.K.; Fries, P. Beta-Band Oscillations--Signalling the Status Quo? Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2010, 20, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collet, C.; Guillot, A.; Lebon, F.; MacIntyre, T.; Moran, A. Measuring Motor Imagery Using Psychometric, Behavioral, and Psychophysiological Tools. Exerc. Sport Sci. Rev. 2011, 39, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raimo, S.; Di Vita, A.; Boccia, M.; Iona, T.; Cropano, M.; Gaita, M.; Guariglia, C.; Grossi, D.; Palermo, L. The Body across the Lifespan: On the Relation between Interoceptive Sensibility and High-Order Body Representations. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craig, A.D. How Do You Feel? Interoception: The Sense of the Physiological Condition of the Body. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2002, 3, 655–666. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Garfinkel, S.N.; Seth, A. K.; Barrett, A. B.; Suzuki, K.; Critchley, H. D. Knowing Your Own Heart: Distinguishing Interoceptive Accuracy from Interoceptive Awareness. Biol. Psychol. 2015, 104, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tinaz, S.; Para, K.; Vives-Rodriguez, A.; Martinez-Kaigi, V.; Nalamada, K.; Sezgin, M.; Scheinost, D.; Hampson, M.; Louis, E. D.; Constable, R.T. Insula as the Interface Between Body Awareness and Movement: A Neurofeedback-Guided Kinesthetic Motor Imagery Study in Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Deng, H.; Xiao, X. The Insular Cortex: An Interface Between Sensation, Emotion and Cognition. Neurosci. Bull. 2024. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beckmann, N.; Baumann, P.; Herpertz, S.; Trojan, J.; Diers, M. How the Unconscious Mind Controls Body Movements: Body Schema Distortion in Anorexia Nervosa. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2021, 54, 578–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meregalli, V.; Tenconi, E.; Madan, C.R.; Somà, E.; Meneguzzo, P.; Ceccato, E.; Zuanon, S.; Sala, A.; Favaro, A.; Collantoni, E. Beyond Body Image: What Body Schema and Motor Imagery Can Tell Us About the Way Patients with Anorexia Nervosa Experience Their Body. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2023, 77, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landry, M.; Lifshitz, M.; Raz, A. Brain Correlates of Hypnosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analytic Exploration. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2017, 81, 75–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Picerni, E.; Santarcangelo, E.; Laricchiuta, D.; Cutuli, D.; Petrosini, L.; Spalletta, G.; Piras, F. Cerebellar Structural Variations in Subjects with Different Hypnotizability. Cerebellum 2019, 18, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosati, A.; Belcari, I.; Santarcangelo, E. L.; Sebastiani, L. Interoceptive Accuracy as a Function of Hypnotizability. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Hypn. 2021, 69, 441–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giusti, G.; Zelič, Ž.; Callara, A.L.; Sebastiani, L.; Santarcangelo, E.L. Interoception as a Function of Hypnotizability during Rest and a Heartbeat Counting Task. Psychophysiology 2024, 61, e14535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diolaiuti, F.; Huber, A.; Ciaramella, A.; Santarcangelo, E.L.; Sebastiani, L. Hypnotisability-Related Interoceptive Awareness and Inhibitory/Activating Emotional Traits. Arch. Ital. Biol. 2019, 157, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weitzenhoffer, A.M.; Hilgard, E.R. Stanford Hypnotic Susceptibility Scale: Forms A and B; Consulting Psychologists Press: 1959.
- De Pascalis, V.; Bellusci, A.; Russo, P.M. Italian Norms for the Stanford Hypnotic Susceptibility Scale, Form C. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Hypn. 2000, 48, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tellegen, A.; Atkinson, G. Openness to Absorbing and Self-Altering Experiences (“Absorption”), a Trait Related to Hypnotic Susceptibility. J. Abnorm. Psychol. 1974, 83, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehling, W.E.; Price, C.; Daubenmier, J.J.; Acree, M.; Bartmess, E.; Stewart, A. The Multidimensional Assessment of Interoceptive Awareness (MAIA). PLoS One 2012, 7, e48230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delorme, A.; Makeig, S. EEGLAB: An Open Source Toolbox for Analysis of Single-Trial EEG Dynamics Including Independent Component Analysis. J. Neurosci. Methods 2004, 134, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makeig, S.; Bell, A.J.; Jung, T.-P.; Sejnowski, T.J. Independent Component Analysis of Electroencephalographic Data. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 8; Touretzky, D., Mozer, M. C., Hasselmo, M., Eds.; MIT Press: 1995; pp 145–151.
- Thanapaisal, S.; Mosher, S.; Trejo, B.; Robbins, K.A. EEG-Beats: Automated Analysis of Heart Rate Variability (HRV) from EEG-EKG. BioRxiv 2020.
- Glover, S.; Bibby, E.; Tuomi, E. Executive Functions in Motor Imagery: Support for the Motor-Cognitive Model over the Functional Equivalence Model. Exp. Brain Res. 2020, 238, 931–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glover, S.; Baran, M. The Motor-Cognitive Model of Motor Imagery: Evidence from Timing Errors in Simulated Reaching and Grasping. J. Exp. Psychol. Hum. Percept. Perform. 2017, 43, 1359–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santarcangelo, E.L.; Scattina, E.; Carli, G.; Ghelarducci, B.; Orsini, P.; Manzoni, D. Can Imagery Become Reality? Exp. Brain Res. 2010, 206, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, S.E.; Guillot, A.; Di Rienzo, F.; Cumming, J. Comparing Self-Report and Mental Chronometry Measures of Motor Imagery Ability. Eur. J. Sport Sci. 2015, 15, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carli, G.; Cavallaro, F.I.; Rendo, C.A.; Santarcangelo, E.L. Imagery of Different Sensory Modalities: Hypnotizability and Body Sway. Exp. Brain Res. 2007, 179, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavallaro, F.I.; Cacace, I.; Del Testa, M.; Andre, P.; Carli, G.; De Pascalis, V.; Rocchi, R.; Santarcangelo, E.L. Hypnotizability-Related EEG Alpha and Theta Activities during Visual and Somesthetic Imageries. Neurosci. Lett. 2010, 470, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapiro, L. Embodied Cognition; 2nd ed.; Routledge/Taylor & Francis Group: 2019.
- Ruggirello, S.; Campioni, L.; Piermanni, S.; Sebastiani, L.; Santarcangelo, E.L. Does Hypnotic Assessment Predict the Functional Equivalence between Motor Imagery and Action? Brain Cogn. 2019, 136, 103598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Lubbe, R.; Sobierajewicz, J.; Jongsma, M.L.A.; Verwey, W.B.; Przekoracka-Krawczyk, A. Frontal Brain Areas Are More Involved during Motor Imagery than during Motor Execution/Preparation of a Response Sequence. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2021, 164, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilavik, B.E.; Zaepffel, M.; Brovelli, A.; MacKay, W.A.; Riehle, A. The Ups and Downs of β Oscillations in Sensorimotor Cortex. Exp. Neurol. 2013, 245, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.J.; Jeon, E.J.; Kim, J.S.; Chung, C.K. Characterization of Kinesthetic Motor Imagery Compared with Visual Motor Imageries. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 3751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruzelier, J.H. Frontal Functions, Connectivity and Neural Efficiency Underpinning Hypnosis and Hypnotic Susceptibility. Contemp. Hypn. 2006, 23, 15–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naish, P.L. Hypnosis and Hemispheric Asymmetry. Conscious. Cogn. 2010, 19, 230–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amemiya, K.; Ishizu, T.; Ayabe, T.; Kojima, S. Effects of Motor Imagery on Intermanual Transfer: A Near-Infrared Spectroscopy and Behavioural Study. Brain Res. 2010, 1343, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, M.P.; Jamieson, G.A.; Lutz, A.; Mazzoni, G.; McGeown, W.J.; Santarcangelo, E.L.; Demertzi, A.; De Pascalis, V.; Bányai, É.I.; Rominger, C.; Vuilleumier, P.; Faymonville, M.E.; Terhune, D.B. New directions in hypnosis research: strategies for advancing the cognitive and clinical neuroscience of hypnosis. Neuroscience of Consciousness 2017, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, M.J.; Fecchio, M.; Bodien, Y.G.; Edlow, B.L. Covert cortical processing: a diagnosis in search of a definition. Neuroscience of Consciousness. 2024. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.; Chen, S.; Jia, J. Sensorimotor Rhythm-Based Brain–Computer Interfaces for Motor Tasks Used in Hand Upper Extremity Rehabilitation after Stroke: A Systematic Review. Brain Sci. 2022, 13, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Lange, F.P.; Helmich, R.C.; Toni, I. Posture Influences Motor Imagery: An fMRI Study. NeuroImage 2006, 33, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saimpont, A.; Malouin, F.; Tousignant, B.; Jackson, P.L. The Influence of Body Configuration on Motor Imagery of Walking in Younger and Older Adults. Neuroscience 2012, 222, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filgueiras, A.; Quintas Conde, E.F.; Hall, C.R. The Neural Basis of Kinesthetic and Visual Imagery in Sports: An ALE Meta-Analysis. Brain Imaging Behav. 2018, 12, 1513–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridderinkhof, K.R.; Brass, M. How Kinesthetic Motor Imagery Works: A Predictive-Processing Theory of Visualization in Sports and Motor Expertise. J. Physiol.-Paris 2015, 109, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).