Submitted:
30 June 2024
Posted:
01 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
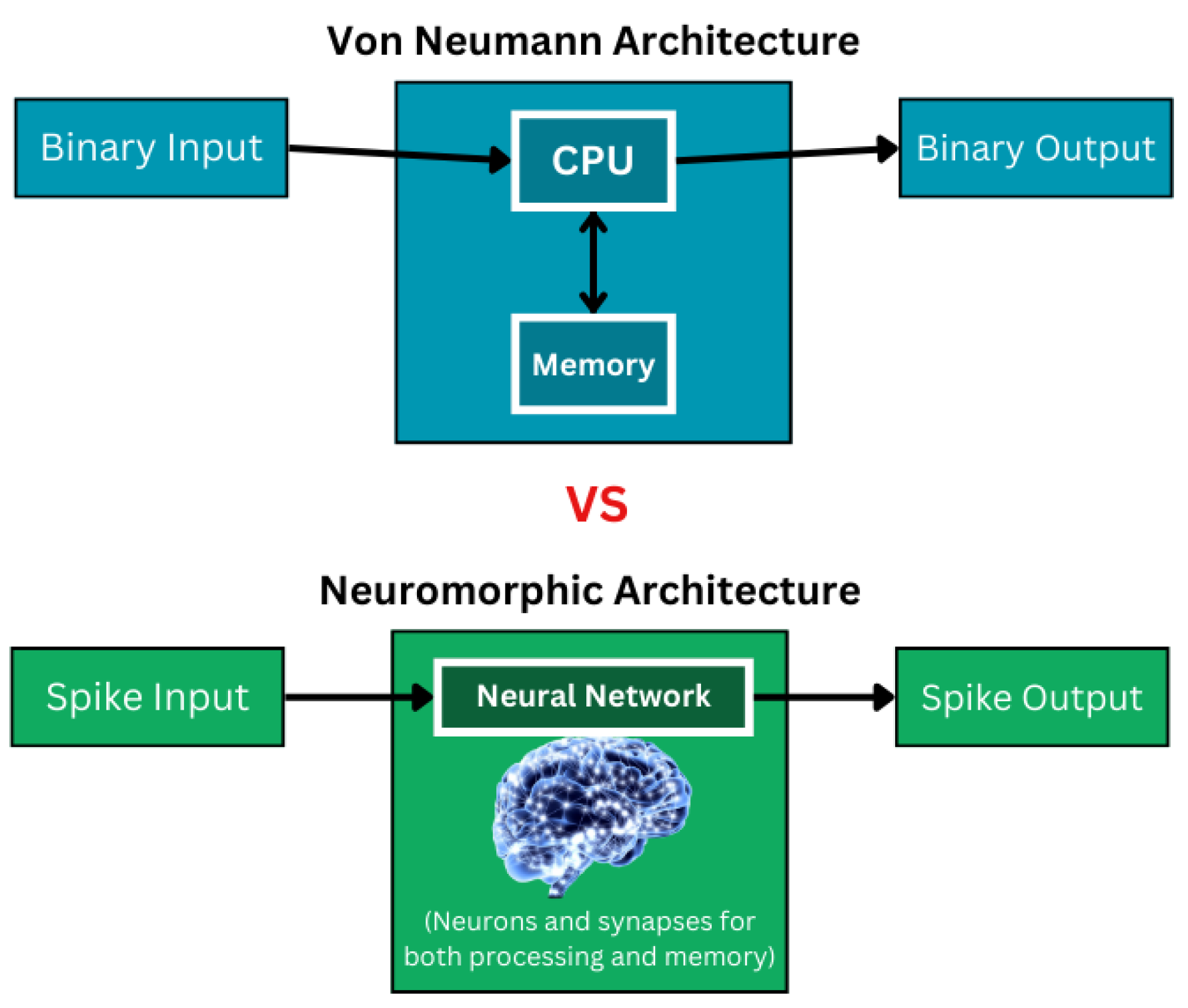
1. Introduction
2. Background
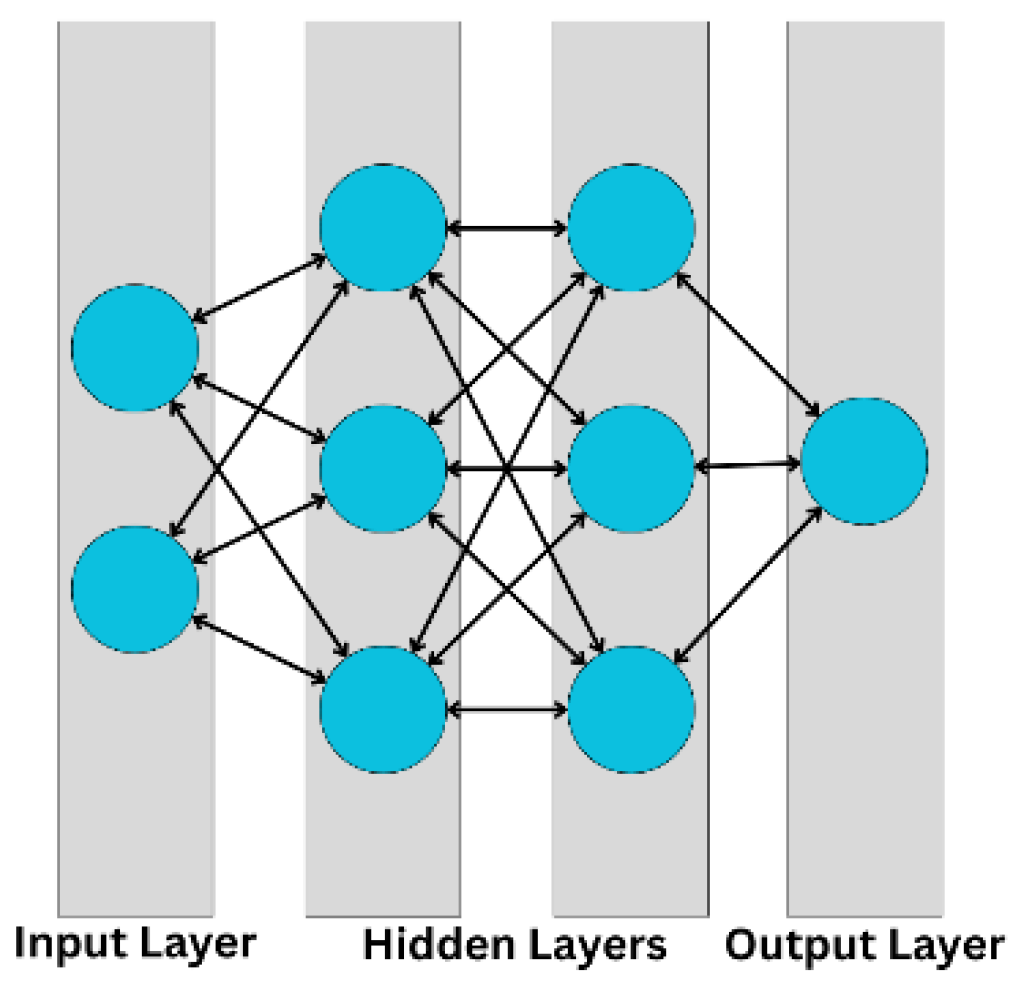
- Connectionism: is described using neural networks (NN) which consist of many simple units (neurons) interconnected together with weights. Determining the appropriate weights results in the NNs ability to learn and solve a given problem [7].
- Parallelism: all neurons work in parallel to each other to simultaneously perform various functions and ensure efficient and successful operation of neural networks [7].
- Asynchrony: to achieve parallelism, synchronization of all neurons is not required as each neuron performs a specified task. Asynchrony reduces the power consumption that would otherwise be required to achieve synchronization [7].
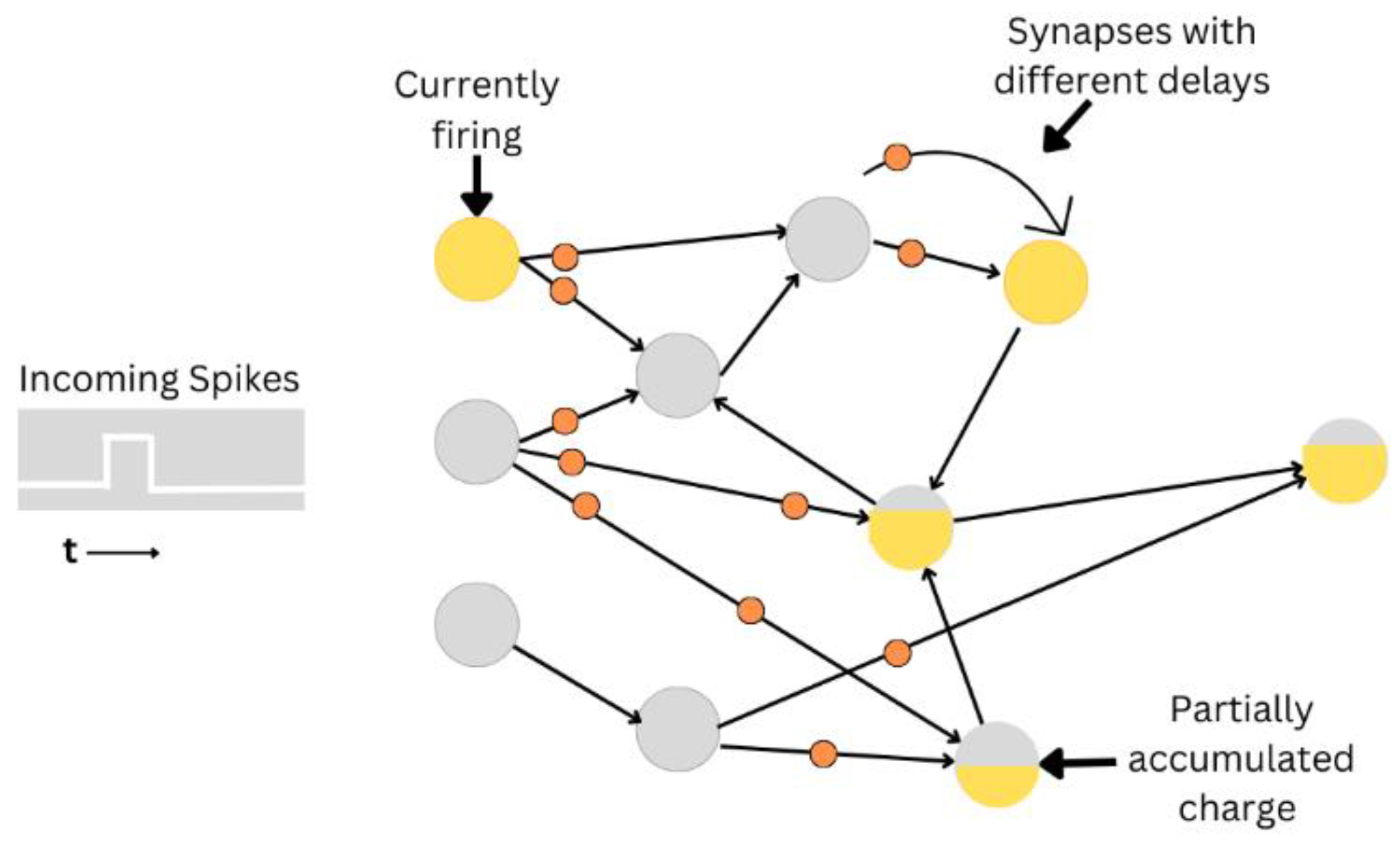
- Impulse nature of information transmission: the information encoded as spikes differs between different pairs of neurons and does not occur instantly. A synapse is therefore characterized by the weight and time delay and provides advantages over traditional neural networks. It is asynchronous, allows the use of dynamic data due to its inclusion of the time component, it is a complex non-linear dynamic system, and the neuron is only activated upon the receival of a spike, reducing the power consumption as its inactive state does not consume a large amount of energy [7].
- On-device learning: it has the ability to learn in a continuous and incremental manner which in turn allows the customization and personalization of smart devices based on the user needs while maintaining privacy through the avoidance of user data transmission to the cloud [7].
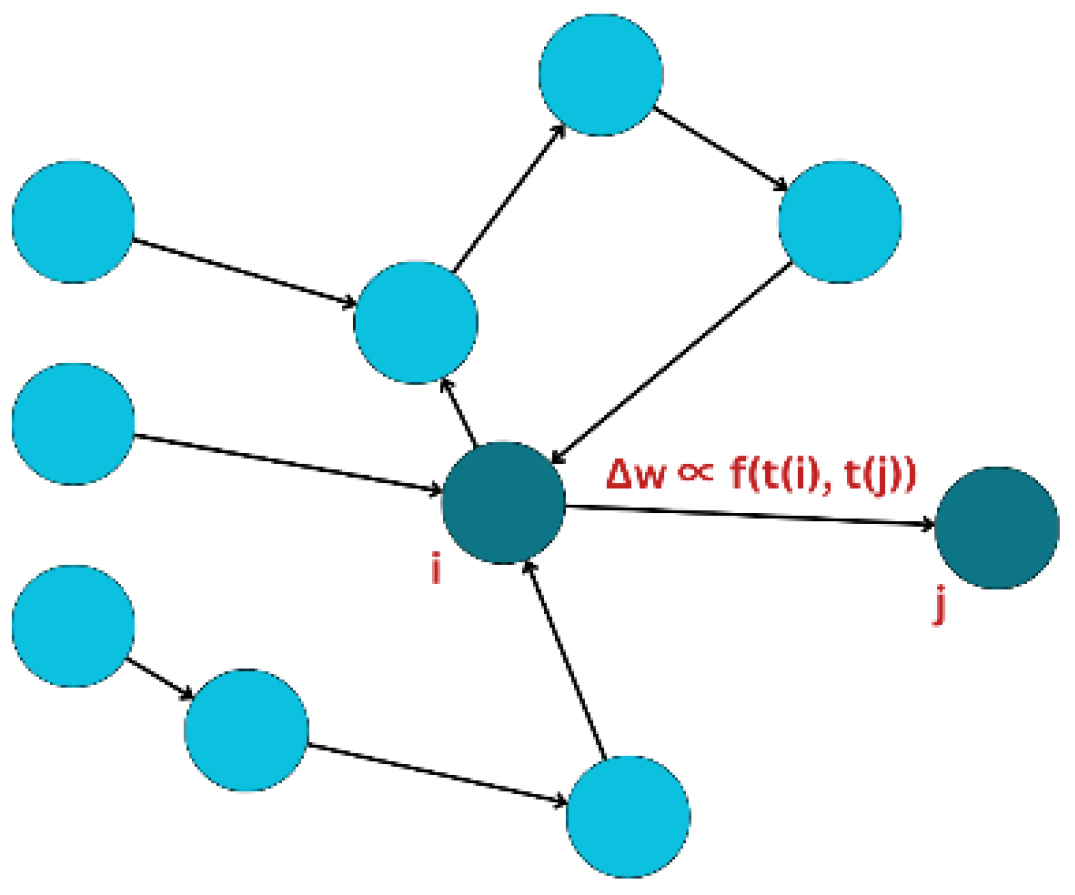
- Local learning: conventional neural networks use backpropagation algorithms which introduce two problems: the weight transport problem and the update locking problem. The weight transport problem is the system’s inability to exchange information about the weight value and the update locking problem is the requirement of forward pass activation values to be stored for backward pass. Local learning is an alternative to backpropagation and uses a Spike timing Dependent Plasticity (STDP) model where the synapses are strengthened upon receival of a spike before the neuron generated the spike or weekend if the spike was received after the neuron generated the spike. As a result, local learning can train any size of network as it does not require large amounts of global data transfer operations [7].
- Sparsity: not all neurons are activated to perform a task. Neuromorphic chips have temporal, spatial and structural sparsity. Temporal sparsity is the data sparse in time which is determined by the transmission of only the changed part of a signal. Spatial sparsity is sparsity in data streams resulted by neurons activated only upon reaching a certain threshold value. Structural sparsity refers to the data flow with respect to the network topology, as each neuron has a limited number of connections, and they are not all fully interconnected together [7].
- Analog computing: digital computing is limited due to its high costs. Analog circuits can be used to model the dynamics of the membrane potential and to model synaptic operations. Analog circuits provide a more time and energy efficient alternative.
- In-memory computing: each individual neuron has its own memory or stored state which eliminates the need for transferring intermediate data or the competitive memory access [7].
2.1. Spiking Neural Networks (SNN)
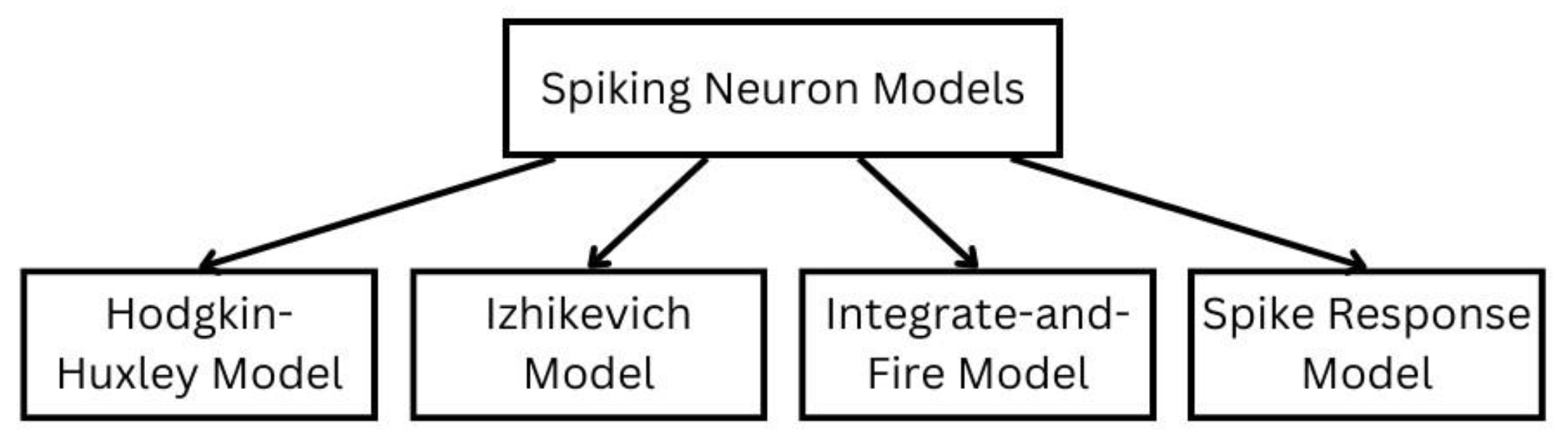
2.2. Spiking Neuron Models
2.3. SNN Testing
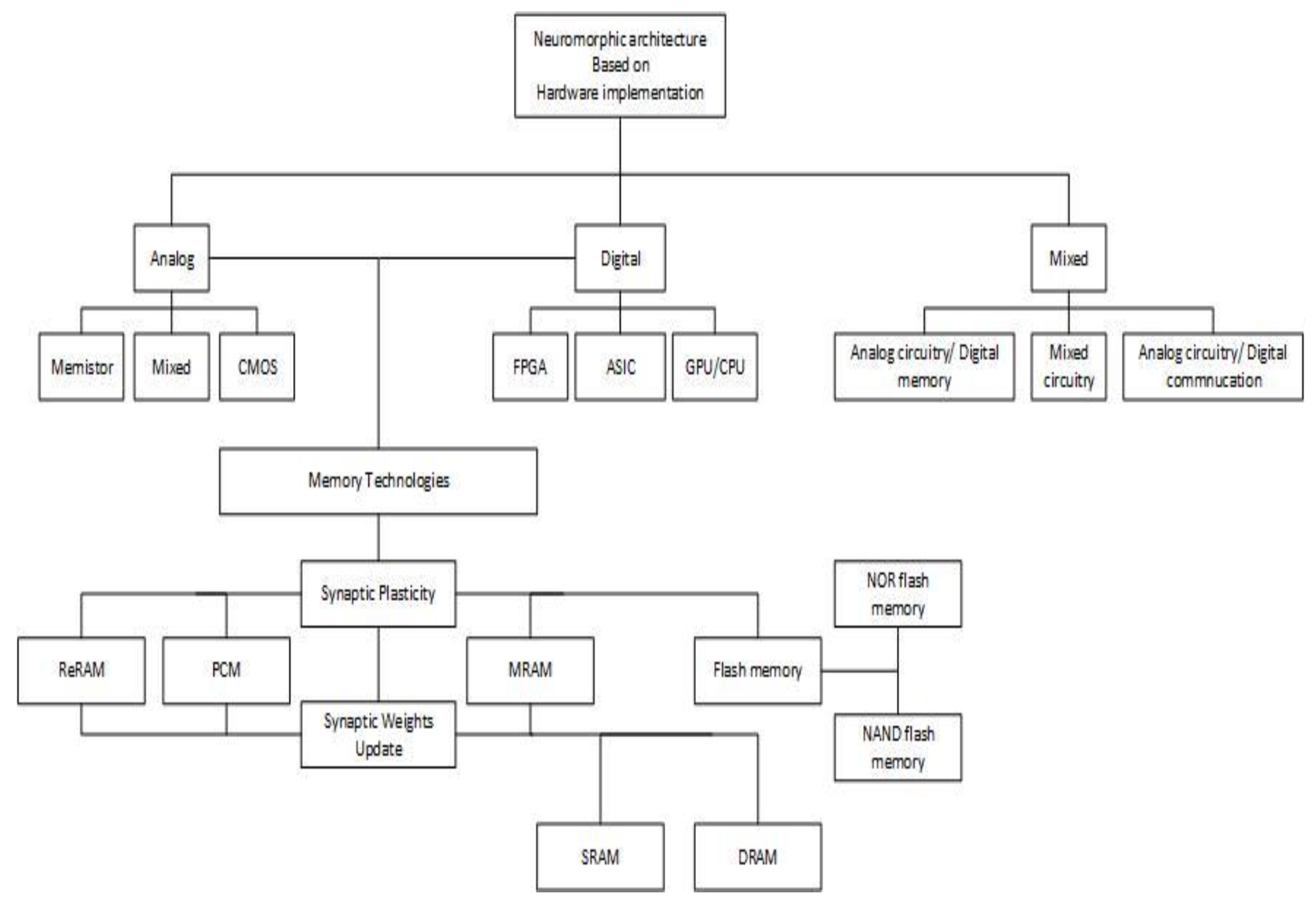
3. Neuromorphic Circuit Design
3.1. Analog Design
3.2. Digital Design
3.3. Mixed Design
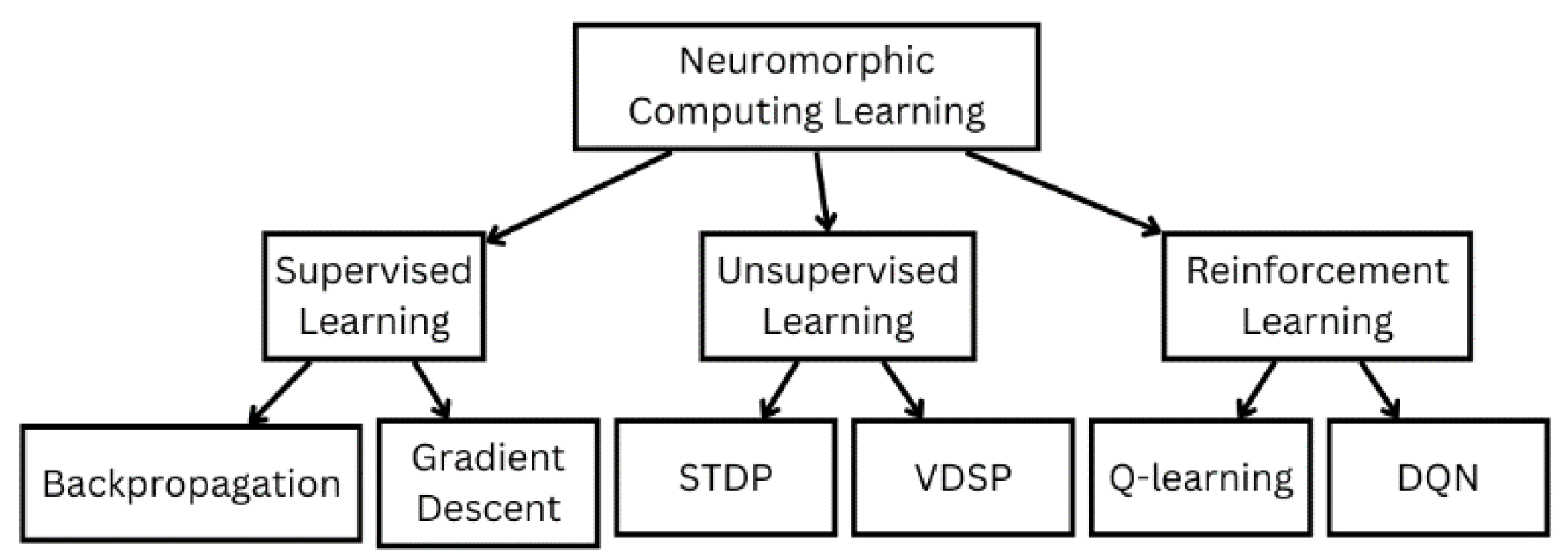
4. Machine Learning Algorithms
4.1. Supervised Learning
4.2. Unsupervised Learning
4.3. Reinforcement Learning
5. Neuromorphic Projects
6. Proposed Method and Future Work
7. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Luo, T.; Wong, W.-F.; Goh, R.S.M.; Do, A.T.; Chen, Z.; Li, H.; Jiang, W.; Yau, W. Achieving Green AI with Energy-Efficient Deep Learning Using Neuromorphic Computing. Commun. ACM 2023, 66, 52–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Wang, X.; Strachan, J.P.; Yang, Y.; Lu, W.D. Dynamical memristors for higher-complexity neuromorphic computing. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2022, 7, 575–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Huang, Y.; Fang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yu, S.; Xu, R. Recent Progress of Neuromorphic Computing Based on Silicon Photonics: Electronic–Photonic Co-Design, Device, and Architecture. Photonics 2022, 9, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuman, C.D.; Kulkarni, S.R.; Parsa, M.; Mitchell, J.P.; Date, P.; Kay, B. Opportunities for neuromorphic computing algorithms and applications. Nat. Comput. Sci. 2022, 2, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byun, K.; Choi, I.; Kwon, S.; Kim, Y.; Kang, D.; Cho, Y.W.; Yoon, S.K.; Kim, S. Recent Advances in Synaptic Nonvolatile Memory Devices and Compensating Architectural and Algorithmic Methods Toward Fully Integrated Neuromorphic Chips. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2022, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javanshir, A.; Nguyen, T.T.; Mahmud, M.A.P.; Kouzani, A.Z. Advancements in Algorithms and Neuromorphic Hardware for Spiking Neural Networks. Neural Comput. 2022, 34, 1289–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanov, D.; Chezhegov, A.; Kiselev, M.; Grunin, A.; Larionov, D. Neuromorphic artificial intelligence systems. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 959626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrestha, A.; Fang, H.; Mei, Z.; Rider, D.P.; Wu, Q.; Qiu, Q. A Survey on Neuromorphic Computing: Models and Hardware. IEEE Circuits Syst. Mag. 2022, 22, 6–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Gao, B.; Tang, J.; Qian, H.; Wu, H. Emerging Memory-Based Chip Development for Neuromorphic Computing: Status, Challenges, and Perspectives. IEEE Electron Devices Mag. 2023, 1, 33–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.; Pan, K.; Jiao, Y.; Sun, B.; Du, C.; Mills, J.P.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, X.; Wei, L.; Zhou, Y.N.; et al. Versatile memristor for memory and neuromorphic computing. Nanoscale Horizons 2022, 7, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Mao, H.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, X.; Fu, C.; Ke, S.; Wan, C.; Wan, Q. CMOS-compatible neuromorphic devices for neuromorphic perception and computing: a review. Int. J. Extreme Manuf. 2023, 5, 042010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- B. Li, D. Zhong, X. Chen, and C. Liu, “Enabling Neuromorphic Computing for Artificial Intelligence with Hardware-Software Co-Design,” Artificial intelligence, Nov. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Christensen, D.V.; Dittmann, R.; Linares-Barranco, B.; Sebastian, A.; Le Gallo, M.; Redaelli, A.; Slesazeck, S.; Mikolajick, T.; Spiga, S.; Menzel, S.; et al. 2022 roadmap on neuromorphic computing and engineering. Neuromorphic Comput. Eng. 2022, 2, 022501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, M.D.; D’angiulli, A.; Dehnavi, M.M.; Chhabra, R. From Brain Models to Robotic Embodied Cognition: How Does Biological Plausibility Inform Neuromorphic Systems? Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ho, N.-M.; Polat, D.Y.; Chen, P.; Wahib, M.; Nguyen, T.T.; Meng, J.; Goh, R.S.M.; Matsuoka, S.; Luo, T.; et al. Simeuro: A Hybrid CPU-GPU Parallel Simulator for Neuromorphic Computing Chips. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst. 2023, 34, 2767–2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, R.; Biswas, C.; Majumder, S. Study of Spiking Neural Network Architecture for Neuromorphic Computing. 2022 IEEE 11th International Conference on Communication Systems and Network Technologies (CSNT), Apr. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spyrou, T.; Stratigopoulos, H.-G. On-Line Testing of Neuromorphic Hardware. May 2023. [CrossRef]
- Frenkel, C.; Bol, D.; Indiveri, G. Bottom-Up and Top-Down Approaches for the Design of Neuromorphic Processing Systems: Tradeoffs and Synergies Between Natural and Artificial Intelligence. Proc. IEEE 2023, 111, 623–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, K.; Wu, Y. Survey of Neuromorphic Computing: A Data Science Perspective. May 2023. [CrossRef]
- Garg, N.; Balafrej, I.; Stewart, T.C.; Portal, J.-M.; Bocquet, M.; Querlioz, D.; Drouin, D.; Rouat, J.; Beilliard, Y.; Alibart, F. Voltage-dependent synaptic plasticity: Unsupervised probabilistic Hebbian plasticity rule based on neurons membrane potential. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 983950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wunderlich, T.; Kungl, A.F.; Müller, E.; Hartel, A.; Stradmann, Y.; Aamir, S.A.; Grübl, A.; Heimbrecht, A.; Schreiber, K.; Stöckel, D.; et al. Demonstrating Advantages of Neuromorphic Computation: A Pilot Study. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Nakajima, K.; Krisnanda, T.; Fujii, K.; Liew, T.C.H. Quantum Neuromorphic Computing with Reservoir Computing Networks. Adv. Quantum Technol. 2021, 4, 2100053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, A.; Ramanathan, S.; Grollier, J.; Kent, A.D.; Rozenberg, M.J.; Schuller, I.K.; Shpyrko, O.G.; Dynes, R.C.; Fainman, Y.; Frano, A.; et al. Quantum materials for energy-efficient neuromorphic computing: Opportunities and challenges. APL Mater. 2022, 10, 070904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
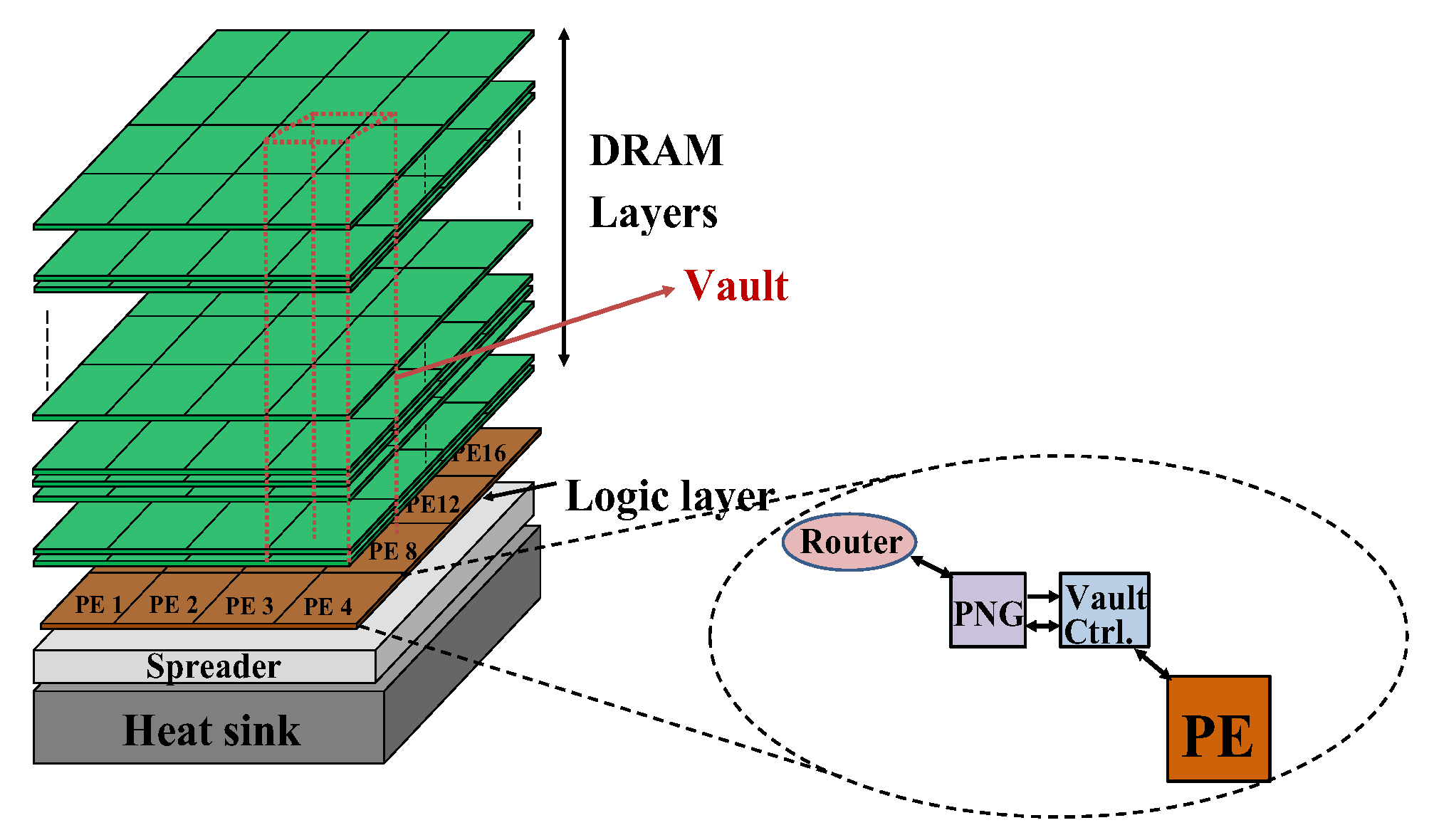
- Asad and, F. Mohammadi, “NeuroTower: A 3D Neuromorphic Architecture with Low-Power TSVs,” Lecture notes in networks and systems, pp. 227–236, Oct. 2022. [CrossRef]
- Panzeri, S.; Janotte, E.; Pequeño-Zurro, A.; Bonato, J.; Bartolozzi, C. Constraints on the design of neuromorphic circuits set by the properties of neural population codes. Neuromorphic Comput. Eng. 2023, 3, 012001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartolozzi, C.; Indiveri, G.; Donati, E. Embodied neuromorphic intelligence. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Wang, Z.; Cui, X.; Cao, J.; Wang, Y. An Efficient Neuromorphic Implementation of Temporal Coding-Based On-Chip STDP Learning. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II: Express Briefs 2023, 70, 4241–4245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, M.; Shibayama, Y.; Nakashima, Y. Neuromorphic chip integrated with a large-scale integration circuit and amorphous-metal-oxide semiconductor thin-film synapse devices. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asad, A.; Kaur, R.; Mohammadi, F. A Survey on Memory Subsystems for Deep Neural Network Accelerators. Futur. Internet 2022, 14, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R. Kaur, A. Asad, and F. Mohammadi, “A Comprehensive Review on Processing-in-Memory Architectures for Deep Neural Networks,” Jun. 2024. [CrossRef]
| Property | TrueNorth | Loihi |
| In-memory Computation | Near-memory | Near-memory |
| Signal | Spikes | Spikes |
| Size neurons/synapses | 1M/256M | 128K/128M |
| On-device learning | No | STDP |
| Analog | No | No |
| Event-based | Yes | Yes |
| nm | 28 | 14 |
| Features | First industrial neuromorphic chip without training (IBM) | First neuromorphic chip with training (Intel) |
| Property | Loihi2 | Tianjic |
| In-memory Computation | Near-memory | Near-memory |
| Signal | Real numbers, Spikes | Real numbers, Spikes |
| Size neurons/synapses | 120K/1M | 40K/10M |
| On-device learning | STDP | No |
| Analog | No | No |
| Event-based | Yes | Yes |
| nm | 7 | 28 |
| Features | Non-binary spikes, neurons can be programmed | Hybrid chip |
| Property | SpiNNaker | Brain-ScaleS |
| In-memory Computation | Near-memory | Yes |
| Signal | Real numbers, Spikes | Real numbers, Spikes |
| Size neurons/synapses | - | 512/130K |
| On-device learning | STDP | STDP |
| Analog | No | Yes |
| Event-based | No | Yes |
| nm | 22 | 65 |
| Features | Scalable computer for SNN simulation | Analog neurons, large size |
| Property | GrAIOne | Akida |
| In-memory Computation | Near-memory | Near-memory |
| Signal | Real numbers, Spikes | Spikes |
| Size neurons/synapses | 200K/- | 1.2M/10B |
| On-device learning | No | STDP |
| Analog | No | No |
| Event-based | Yes | Yes |
| nm | 28 | 28 |
| Features | NeuronFlow architecture, effective support of sparse computations | Incremental, one-shot and continuous learning for CNN |
| Property | Memristor (IBM) | |
| In-memory Computation | Yes | |
| Signal | Spikes | |
| Size neurons/synapses | 512/64K | |
| On-device learning | Yes | |
| Analog | Yes | |
| Event-based | Yes | |
| nm | 50 | |
| Features | Allows each synaptic cell to operate asynchronously |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




