Submitted:
01 July 2024
Posted:
02 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Storage Conditions
2.2. Chemicals, Reagents, and Standards
2.3. Determination of Chemical and Nutritional Properties
2.4. Extraction Process
2.5. Determination of Antioxidant Activity
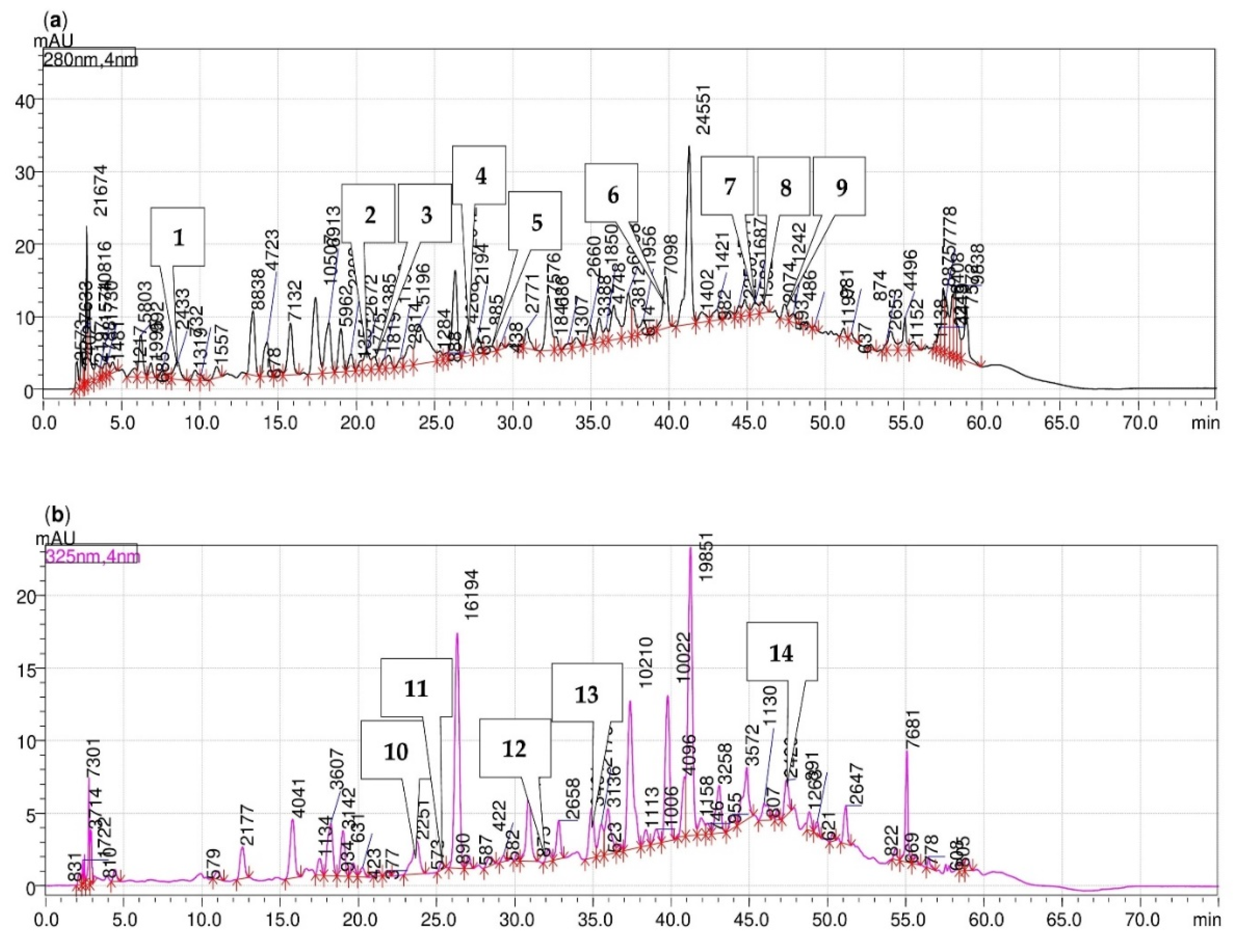
2.6. Determination of Phenolic Acids and Bioflavonoids Profiles - HPLC Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
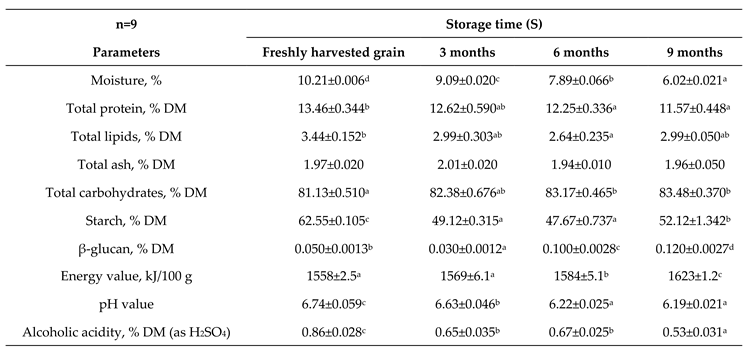
3.1. Physico-Chemical, Chemical and Nutritional Properties
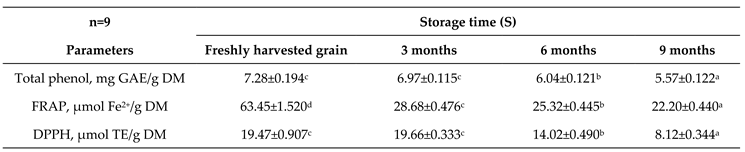
3.2. Potential of Antioxidant Activity and Capacity
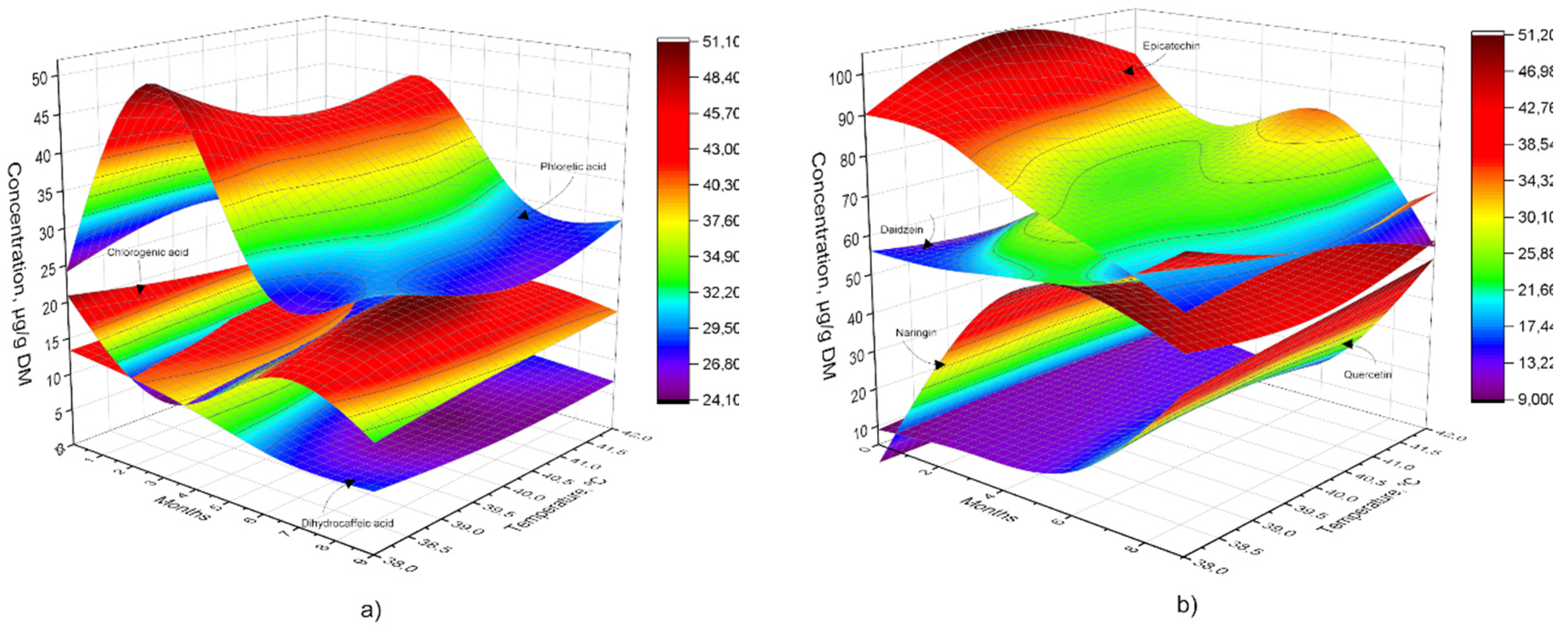
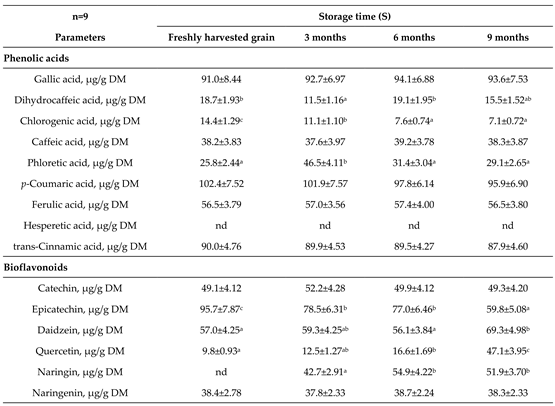
3.3. Phenolic Acids and Bioflavonoids Profiles
4. Discussion
4.1. Physico-Chemical, Chemical and Nutritional Properties
4.2. Potential of Antioxidant Activity and Capacity
4.3. Phenolic Acids and Bioflavonoids Profiles
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgements
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Šteinberga, V.; Muter, O.; Jansone, I.; Alsina, I.; Dubova, L. Effect of buckwheat and potato as forecrops on soil microbial properties in crop rotation. Proc. Latvian Acad. Sci., Section B, 2012; 66, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamaratskaia, G.; Gerhardt, K.; Knicky, M.; Wendin, K. Buckwheat: an underutilized crop with attractive sensory qualities and health benefits. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinski, A.; Zhou, M.; Betekhtin, A. Editorial: Advances in buckwheat research. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1190090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farooq, S.; Rehman, R.Ul.; Pirzadah, T.B.; Malik, B.; Ahmad Dar, F.; Tahir, I. Cultivation, agronomic practices, and growth performance of buckwheat. In Molecular breeding and nutritional aspects of buckwheat; Zhou, M., Kreft, I., Woo, S.H., Chrungoo, N., Wieslander, G., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, Massachusetts, 2016, 23, pp. 299–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ongalbek, D.; Tokul-Olmez, O.; Sahin, B.; Küçükaydın, S.; Aydogmus-Oztürk, F.; Sıcak, Y.; Yeskaliyeva, B.; Oztürk, M. Classification of buckwheat honey produced in Kazakhstan according to their biochemical ingredients and bioactivities by chemometric approach. Food Chem. 2024, 451, 139409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fijen, T.P.M.; Bodegraven, V.; Lucassen, F. Limited honeybee hive placement balances the trade-off between biodiversity conservation and crop yield of buckwheat cultivation. Basic Appl. Ecol. 2022, 65, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; He, C.; Wang, L.; Wang, M. Effect of milling method on the chemical composition and antioxidant capacity of Tartary buckwheat flour. Int. J. Food Sci. Tech. 2018, 53(11), 2457–2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, S.A.; Farooq, S.; Shah, M.A.; Sofi, S.A.; Dar, B.N.; Sunooj, K.V.; Khaneghah, A.M. Recent advancements in the development of multigrain bread. Cereal Chem. 2023, 100(1), 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhao, J.; Mao, Y.; Liu, L.; Li, C.; Wu, H.; Zhao, H.; Wu, Q. Tartary buckwheat rutin: Accumulation, metabolic pathways, regulation mechanisms, and biofortification strategies. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2024, 208, 108503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Q.; Yu, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, L.; Cao, R. Effects of different treatments on composition, physicochemical and biological properties of soluble dietary fiber in buckwheat bran. Food Biosci. 2023, 53, 102517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Cao, F.; Fan, J.; Ouyang, S.; Luo, Q.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, G. Physically modified common buckwheat starch and their physicochemical and structural properties. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 40, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rachman, A.; Chen, L.J.; Brennan, M.; Brennan, C. Effects of addition of buckwheat bran on physicochemical, pasting properties and starch digestion of buckwheat gels. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2020, 246(10), 2111–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, Q.; Bao, J.; Liu, Q. Identification and quantification of polyphenols in hull, bran and endosperm of common buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum) seeds. J. Funct. Foods Part A 2017, 38, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beitāne, I.; Krūmiņa-Zemture, G.; Krūma, Z.; Cinkmanis, I. Phenolics content in buckwheat flour. Proc. Latv. Acad. Sci. Sect. B: Nat. Exact Appl. Sci. 2018, 72, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devrajan, N.; Prakash, P.; Jindal, N. Effect of extrusion cooking on colour (L*, a*, b*) of germinated buckwheat-corn based snacks. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. App. Sci. 2018, Special Issue 7, 3413–3424. [Google Scholar]
- Małgorzata, S.; Georgios, K.; Henryk, Z. Sensory analysis and aroma compounds of buckwheat containing products: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 58(11), 1767–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sofi, S.A.; Ahmed, N.; Farooq, A.; Rafiq, S.; Zargar, S.M.; Kamran, F.; Dar, T.A.; Mir, S.A.; Dar, B.N.; Khaneghah, M.A. Nutritional and bioactive characteristics of buckwheat, and its potential for developing gluten-free products: An updated overview. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 11(5), 2256–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hęś, M.; Szwengiel, A.; Dziedzic, K.; Le Thanh-Blicharz, J.; Kmiecik, D.; Górecka, D. The effect of buckwheat hull extract on lipid oxidation in frozen-stored meat products. J. Food Sci. 2017, 82(4), 882–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atambayeva, Z.; Nurgazezova, A.; Assirzhanova, Z.; Urazbayev, Z.; Kambarova, A.; Dautova, A.; Idyryshev, B.; Sviderskaya, D.; Kaygusuz, M. Nutritional, physicochemical, textural and sensory characterization of horsemeat patties as affected by whole germinated green buckwheat and Its flour. Int. J. Food Prop. 2023, 26(1), 600–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salejda, A.M.; Olender, K.; Zielińska-Dawidziak, M.; Mazur, M.; Szperlik, J.; Miedzianka, J.; Zawiślak, I.; Kolniak-Ostek, J.; Szmaja, A. Frankfurter-type sausage enriched with buckwheat by-product as a source of bioactive compounds. Foods 2022, 11(5), 674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yessengaziyeva, A.; Uzakov, Y.; Chernukha, I.; Kaimbayeva, L.; Kalashinova, L.; Zhantleuov, D. The use of buckwheat flour in the technology of semi-smoked sausage. Potr. S. J. F. Sci. 2023, 17, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Noda, T.; Morishita, T.; Ishiguro, K.; Otsuka, S.; Brunori, A. Present status and future perspectives of breeding for buckwheat quality. Breed. Sci. 2020, 70(1), 48–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Zhuang, H.; Nasiru, M.M.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yan, W. Changes in color, myoglobin, and lipid oxidation in beef patties treated by dielectric barrier discharge cold plasma during storage. Meat Sci. 2021, 176, 108456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fotschki, B.; Juśkiewicz, J.; Jurgoński, A.; Amarowicz, R.; Opyd, P.; Bez, J.; Muranyi, I.; Petersen, I.L.; Laparra-Llopis, M. Protein-rich flours from quinoa and buckwheat favourably affect the growth parameters, intestinal microbial activity and plasma lipid profile of rats. Nutrients 2020, 12(9), 2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S.; Ashfaquddin, M.D.; Bhar, K.; Pradhan, N.K.; Anjum, M.D.; Molla, S. Silver hull buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum Moench) is a part of nature that offers best health and honour. Discov. Phytomed. 2021, 8(4), 137–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleurat-Lessard, F. Qualitative reasoning and integrated management of the quality of stored grain: A promising new approach. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2002, 38(3), 191–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGorrin, R.J. Key aroma compounds in oats and oat cereals. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67(50), 13778–13789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huyghebaert, G.; Schoner, F.J. Influence of storage and addition of enzyme on metabolisable energy concentration of wheat 1. Impact of storage and enzyme addition. Arch. Geflügelkd. 1999, 63, 13–20. [Google Scholar]
- Rakić, S.; Janković, S.; Demin, M.; Bucalo, D.; Maslovarić, M. Quality and condition of wheat grain (Triticum spp.) during storage. Biotechnol. Anim. Husb. 2012, 28, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakić, S.; Janković, S.; Krivokapić, M.; Jovanović, R.; Ikanović, J. Grain quality and status of oats (Avena sativa L.) during storage. Biotechnol. Anim. Husb. 2012, 28, 863–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingua, M.S.; Gies, M.; Descalzo, A.M.; Servent, A.; Páez, R.B.; Baroni, M.V.; Blajman, J.E.; Dhuique-Mayer, C. Impact of storage on the functional characteristics of a fermented cereal product with probiotic potential, containing fruits and phytosterols. Food Chem. 2022, 370, 130993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 24333:2009. Cereals and cereal products – Sampling. Geneva: International Organization for Standardization.
- Ping-Ping, T.; Yang-Yong, L.; Wen-Jing, Y.; Shuai-Bing, Z.; Yuan-Sen, H. Effect of artificial aging on wheat quality deterioration during storage. J. Stored Prod. Res. 2019, 80, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 712:2009. Cereals and cereal products - Determination of moisture content - Reference method. International Organization for Standardization, Geneva, Switzerland.
- NMKL 160:1998. Fat - Determination in foods. Nordic Committee on food analysis, Oslo, Norway.
- ISO 2171:2023. Cereals, pulses and by-products - Determination of ash yield by incineration. International Organization for Standardization, Geneva, Switzerland.
- ISO 20483:2013. Cereals and pulses - Determination of the nitrogen content and calculation of the crude protein content - Kjeldahl method. International Organization for Standardization, Geneva, Switzerland.
- AOAC 986.25:1988. Proximate analysis of milk-based infant formula. AOAC Official Methods of Analysis, 17th ed., 2000; The Association of Official Analytical Chemists, Arlington, VA, USA.
- CAC/GL 2-1985:2017. Guidelines on Nutrition Labelling. Codex Alimentarius Commission, Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations and World Health Organization, Rome, Geneva.
- ISO 10520:1997. Native starch - Determination of starch content - Ewers polarimetric method. International Organization for Standardization, Geneva, Switzerland.
- AOAC 995.16:1995. β-D-Glucan in Barley and Oats - Streamlined Enzymatic Method. AOAC Official Methods of Analysis, 17th ed., 2000; The Association of Official Analytical Chemists, Arlington, VA, USA.
- AOAC 943.02:1943. PH of flour - Potentiometric method. AOAC Official Methods of Analysis, 17th ed., 2000; The Association of Official Analytical Chemists, Arlington, VA, USA.
- IS 12711:1989 (R2005). Bakery products - Methods of analysis: 14. Determination of alcoholic acidity. Bureau of Indian Standards, New Delhi, India.
- Dang, B.; Zhang, W.G.; Zhang, J.; Yang, X.J.; Xu, H.D. Evaluation of nutritional components, phenolic composition, and antioxidant capacity of highland barley with different grain colors on the Qinghai Tibet plateau. Foods 2022, 11, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Đurović, S.; Nikolić, B.; Luković, N.; Jovanović, J.; Stefanović, A.; Šekuljica, N.; Mijin, D.; Knežević-Jugović, Z. The impact of high-power ultrasound and microwave on the phenolic acid profile and antioxidant activity of the extract from yellow soybean seeds. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2018, 122, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benzie, F.F.I.; Strain, J.J. The ferric reducing ability of plasma (FRAP) as a measure of “antioxidant power”: The FRAP assay. Anal. Biochem. 1996, 239(1), 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakar, M.F.; Mohamed, M.; Rahmat, A.B.; Fry, J.R. Phytochemicals and antioxidant activity of different parts of bambangan (Mangifera pajang) and tarap (Artocarpus odoratissimus). Food Chem. 2009, 113(2), 479–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dapčević, H.T.; Torbica, A.; Hadnađev, M. Rheological properties of wheat flour substitutes/alternative crops assessed by Mixolab. Procedia Food Sci. 2011, 1, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silav-Tuzlu, G.; Tacer-Caba, Z. Influence of chia seed, buckwheat and chestnut flour addition on the overall quality and shelf life of the gluten-free biscuits. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2021, 59(4), 463–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mar’in, V.A.; Vereshchagin, A.L. Effects of humidity and the content of sprouted and spoiled buckwheat grains on the changes of acid number of fat and grain acidity. Foods Raw Materi. 2014, 2(1), 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nalinkumar, A.; Singh, P. An overview of buckwheat (Fagopyrum spp)-An underutilized crop in India-nutritional value and health benefits. Int. J. Med. Res. Health Sci. 2020, 9(7), 39–44. [Google Scholar]
- Kramer, A. Effect of storage on nutritive value of food. J. Food Qual. 2007, 1, 23–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, I.A.; Orsi, D.C.; Gomes, A.J.; Lunardi, C.N. Enzymatic hydrolysis of starch into sugars is influenced by microgel assembly. Biotechnol. Rep. 2019, 22, e00342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Ahmad, F.; Dar, E.A.; Bhat, R.A.; Mushtaq, T.; Shah, F. Buck wheat (Fagopyrum esculentum)-A neglected crop of high altitude cold arid regions of Ladakh: Biology and nutritive value. Int. J. Pure App. Biosci. 2018, 6, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singla, A.; Gupta, O.P.; Sagwal, V.; Kumar, A.; Patwa, N.; Mohan, N.; Ankush; Kumar, D.; Vir, O.; Singh, J.; Kumar, L.; Lal, C.; Singh, G. Beta-glucan as a soluble dietary fiber source: origins, biosynthesis, extraction, purification, structural characteristics, bioavailability, biofunctional attributes, industrial utilization, and global trade. Nutrients 2024, 16, 900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hozová, B.; Kuniak, Ľ.; Moravčíková, P.; Gajdošová, A. Determination of water-insoluble β-d-glucan in the whole-grain cereals and pseudocereals. Czech J. Food Sci. 2007, 25(6), 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jara, P.A.; Schoeninger, V.; Dias, L.M.; Siqueira, V.C.; Lourente, E.R.P. Physicochemical quality characteristics of buckwheat flour. Eng. Agríc. 2021, 42, e20210026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousavi, M.H.; Gharekhani, M.; Alirezalu, K.; Roufegarinejad, L.; Azadmard-Damirchi, S. Production and characterization of nondairy gluten-free fermented beverage based on buckwheat and lentil. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 11, 2197–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mgaya-Kilima, B.; Remberg, S.F.; Chove, B.E.; Wicklund, T. Influence of storage temperature and time on the physicochemical and bioactive properties of roselle-fruit juice blends in plastic bottle. Food Sci. Nutr. 2014, 2(2), 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabikha, M.M.M.; El-Shehawy, Sh.M.M.; Helal, D.M.A. Changes in chemical and nutritional quality during cold storage of some fruit and vegetable juice blends. J. Food Dairy Sci. 2010, 1(4), 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedej, I.J.; Sakač, M.B.; Mišan, A.Č.; Mandić, A.I. Antioxidant activity of wheat and buckwheat flours. Proc. Nat. Sci. 2010, 118, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djordjevic, T.M.; Šiler-Marinkovic, S.S.; Dimitrijevic-Brankovic, S.I. Antioxidant activity and total phenolic content in some cereals and legumes. Int. J. Food Prop. 2011, 14(1), 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Liu, S.; Yao, L.; Wang, L.; Li, C. Free and bound phenolics of buckwheat varieties: HPLC characterization, antioxidant activity, and inhibitory potency towards α-glucosidase with molecular docking analysis. Antioxidants 2019, 8(12), 606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Starowicz, M.; Zieliński, H. Changes in the antioxidant capacity and polyphenols content of rye--buckwheat cakes fortified with spices during their long-term Storage. Ital. J. Food Sci. 2019, 31(2), 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estivi, L.; Pellegrino, L.; Hogenboom, J.A.; Brandolini, A.; Hidalgo, A. Antioxidants of amaranth, quinoa and buckwheat wholemeals and heat-damage development in pseudocereal-enriched einkorn water biscuits. Molecules 2022, 27, 7541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieites-Álvarez, Y.; Reigosa, M.J.; Sánchez-Moreiras, A.M. A decade of advances in the study of buckwheat for organic farming and agroecology (2013-2023). Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1354672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zieliński, H.; Wiczkowski, W.; Topolska, J.; Piskuła, M.K.; Wronkowska, M. Bioaccessibility of phenolic acids and flavonoids from buckwheat biscuits prepared from flours fermented by lactic acid bacteria. Molecules 2022, 27(19), 6628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Škrobot, D.; Mišan, A.; Sakač, M.; Mandić, A.; Pestorić, M.; Belović, M. Preliminary results of the effect of storage on functional properties of buckwheat. J. Proc. Energ. Agric. 2017, 21(4), 201–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Pasquale, I.; Verni, M.; Verardo, V.; Gómez-Caravaca, A.M.; Rizzello, C.G. Nutritional and functional advantages of the use of fermented black chickpea flour for semolina-pasta fortification. Foods 2021, 10, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchanan, M.S.; Carroll, A.R.; Edser, A.; Parisot, J.; Addepalli, R.; Quinn, R.J. Tyrosine kinase inhibitors from the rainforest tree Polyscias murrayi. Phytochemistry 2005, 66(4), 481–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Rensburg, C.J.; Erasmus, E.; Loots, D.T.; Oosthuizen, W.; Jerling, J.C.; Kruger, H.S.; Louw, R.; Brits, M.; van der Westhuizen, F.H. Rosa roxburghii supplementation in a controlled feeding study increases plasma antioxidant capacity and glutathione redox state. Eur. J. Nutr. 2005, 44, 452–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sytar, O.; Cai, Z.; Brestic, M.; Kumar, A.; Prasad, M.N.V.; Taran, N.; Smetanska, I. Foliar applied nickel on buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum) induced phenolic compounds as potential antioxidants. CLEAN 2013, 41(11), 1129–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horbowicz, M.; Chrzanowski, G.; Koczkodaj, D.; Mitrus, J. The effect of methyl jasmonate vapors on content of phenolic compounds in seedlings of common buckwheat (Fagopyrum esculentum Moench). Acta Soc. Bot. Pol. 2011, 80(1), 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinova, J.; Vrchotova, N. The influence of organic and conventional crop management, variety and year on the yield and flavonoid level in common buckwheat groats. Food Chem. 2011, 127(2), 602–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutz, M.; Martínez, A.; Martínez,E.A. A. Daidzein and Genistein contents in seeds of quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa Willd.) from local ecotypes grown in arid Chile. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 49, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huda, M.N.; Lu, S.; Jahan, T.; Ding, M.; Jha, R.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, W.; Georgiev, M.I.; Park, S.U.; Zhou, M. Treasure from garden: Bioactive compounds of buckwheat. Food Chem. 2021, 335, 127653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
 |
 |
 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





