Submitted:
01 July 2024
Posted:
02 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
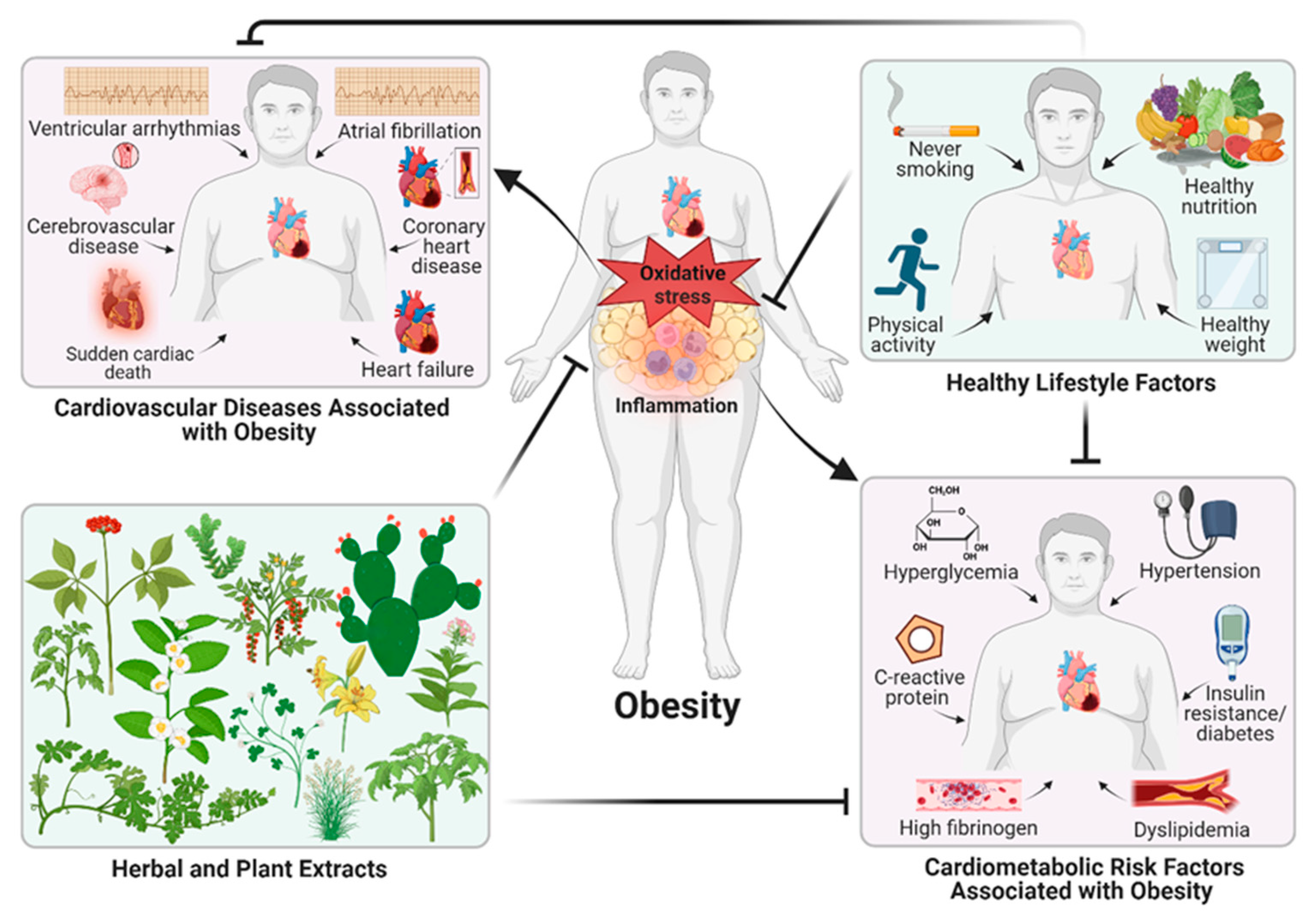
1. Introduction
2. Phytochemical Constituents and Pharmacological Activities of Herbs and Plants with Cardiovascular Protective Effects
2.1. Allium sativum, Family Alliaceae
2.2. Andrographis paniculata (Burm. F.) Wall. Ex Nees (Family: Acanthaceae)
2.3. Aronia melanocarpa (Michx.) Elliott. (Family: Rosaceae)
2.4. Camellia sinensis (Family: Theaceae)
2.5. Caralluma fimbriata (Family: Apocynaceae)
2.6. Cinnamomum zeylanicum (Ceylon cinnamon), Family: Lauraceae
2.7. Citrullus colocynthis (Family: Cucurbitacea)
2.8. Cacao (Theobroma cacao L.), Family: Malvaceae
2.9. Corni Fructus (Cornus ofcinalis Sieb. et Zucc.), Family: Cornaceae
2.10. Cydonia oblonga Miller (Family: Rosaceae)
2.11. Ginkgo biloba (Family: Ginkgoaceae)
2.12. Coffea (genus Coffea), Family: Rubiaceae
2.13. Hibiscus sabdariffa (Roselle), Family: Malvaceae
2.14. Ilex paraguariensis A.St.-Hil. (Mate), Family: Aquifoliaceae
2.15. Moringa oleifera Lam., Family: Moringaceae
2.16. Nigella sativa, Family: Ranunculaceae
2.17. Opuntia ficus indica, Family: Cactaceae
2.18. Platycodon grandiflorus, Family: Campanulaceae
2.19. Punica granatum L., Family: Lythraceae
2.20. Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge, Family: Lamiaceae
2.21. Taraxacum officinale L. (Dandelion), Family: Asteraceae
3. Pathological Processes Involved in Obesity
3.1. Plant and Herb Extracts with Anti-Obesity Activity
4. Adipogenesis and Obesity
4.1. Adipogenesis as a Possible Target Against Obesity
| Name of herbs and plants and Method Extraction | Type of Study | Doses and Duration | Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Allium sativum (Galic) Aged Garlic Extract (15-20% aqueous ethanol) |
Isolated human platelets stimulated with ADP |
1.56 to 25% (v/v) | Inhibited platelet binding to fibrinogen by 40-70.4%, decreased PAC-1 binding to GPIIb/IIIa by 72%, and increased cAMP levels [144] |
| Andrographis paniculata (ethanolic extract) | 4-week-old male C57/BL6 mice with HFD (45% kcal from fat) |
2 g/kg/day, orally for a week | Attenuated cardiac hypertrophy and apoptosis, decreased ANP and BNP proteins, reduced cardiac collagen accumulation and fibrosis, inhibited COX-2, p-IκBα, and NF-κB proteins, reversed cardiac inflammation and myocardial apoptosis [141] |
| Aronia melanocar-pa (Chokeberry), methanol extract | 3T3-L1 adipo-cytes and 5-week-old male C57BL/6J mice with HFD (60% kcal from fat) | In vitro: 7 poly-phe-nols at 10 µM for 8 days. In vivo: 100 or 200mg/kg/day, oral-ly for 8 weeks | Inhibited 3T3-L1 adipocyte differentiation, de-creased body weight, serum TG, and LDL-C levels; and improved insulin sensitivity [152] |
| Aronia melanocarpa (Chokeberry) Polyphenol-rich extract (aqueous extract) |
Human platelets stimulated with ADP |
Platelet adhesion assay (range 0.5-100 µg/mL), thrombin activity (0.5-100 mg/mL), Plasmin activity (2.5, 5, 10, 20, 100 µg/mL) | Reduced ADP-activated platelet adhesion, increased overall potential of clotting and lysis, inhibited thrombin and plasmin amidolytic activity [142] |
| Aronia melanocarpa (Chokeberry), the extract was purchased from Agropharm SA (Poland) |
Patients with metabolic syndrome | 100 mg, three times daily for 2 months |
Reduced TC, LDL-C, and TG levels, inhibited platelet aggregation (less pronounced after 2 months), decreased potential for coagulation and clot formation, beneficial changes in coagulation and fibrinolysis parameters [143] |
| Camellia sinensis (Green tea aqueous extract, GTAE) | 12-week-old male Wistar rats with HFD (50% kcal from fat) |
1.1% and 2.0% GTAE for 8 weeks |
Reduced body weight gain (5.6% decrease at 2.0% GTAE), prevented visceral fat accumulation (17.8% reduction at 2.0% GTAE), lowered atherogenic index (14.3% reduction at both doses), reduced protein digestion (82.6% and 84.3% at 1.1% and 2.0% GTAE, respectively) [123] |
| Caralluma fimbriata (alcohol extract) |
Male Wistar rats (200-220 g) with cafeteria diet |
25, 50, 100 mg/kg/day for 90 days |
Inhibited food intake, prevention of body weight, liver weight, and fat pad mass gains, improved serum lipid and leptin profiles, and protection against atherogenesis [125] |
| Caralluma fimbriata (40% aqueous alcohol) |
Male Wistar rats (170–190 g) with HFD (60 kcal% from fat) |
200 mg/kg/day for 90 days |
Attenuated cardiac lipids and oxidative stress, and improved antioxidant enzyme activities [27] |
| Caralluma fimbriata (dry extract concentrate in gelatin capsules) |
Double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial |
1 g/kg/day for 16 weeks | Reduced waist circumference, calorie intake, maintained body weight, reduced fat mass and BMI, and improved satiety markers [26] |
| Cinnamomum zeylanicum (70% ethylene alcohol) |
3T3-L1 cells and 7-week-old male C57BL/6J mice with a normal diet with 45% fat |
In vitro: 1, 3, 5, 7, 10 µg/mL for 3 days. In vivo: 1% cinnamon extract for 14 weeks |
In vitro: Inhibited lipid accumulation, increased adiponectin and leptin gene expression. In vivo: Reduced lipid synthesis, increased lipolysis, decreased VLDL-C, increased HDL-C, and lowered body fat and fatty tissue accumulation [153] |
| Citrullus colocynthis, hydro-alcoholic extract (80/20, v/v) |
9-week-old male Sprague-Dawley rats with HFD (45% kcal from fat) |
50 mg/kg/day, orally for 16 weeks |
Enhanced bleeding time and tPA levels, decreased PAI-1 and thromboxane B2, inhibited platelet aggregation, reversed HFD-induced increases in fibrinogen and von Willebrand factor, decreased food intake, pancreatic lipase activity, TNF-a, IL-6, and leptin, and increased adiponectin levels [33] |
| Coffea (Green coffee bean extract, GCBE from KPLC group: Montagne, France) |
5-week-old male C57BL/6J mice with HFD (60% Kcal from fat) |
Obesity induction for 4 weeks and then with extract (50, 100, 200 mg/kg/day) for 6 weeks |
Reduced body weight gain, liver weight, and white adipose tissue weights. Increased adiponectin and reduced leptin. GCBE upregulated mRNA levels of PPARα, ATGL, and HSL, and downregulated adipogenesis-related genes like C/EBPα, SREBP-1c, and PPARγ. GCBE increased pAMPK expression [130] |
| Coffea Arabica (aqueous extract) |
Male Wistar rats (160-180 g) with HFD (40% beef tallow) |
Obesity induction for 8 weeks and then with extract (200 mg/kg/day) for 8 weeks |
Decreased body and organ weights, reduced TC, TG, LDL-C, VLDL-C, glucose, and insulin levels, improved HOMA-IR, increased adiponectin, and reduced adipocyte hypertrophy [131] |
| Coffea canephora var. robusta beans (hot water extract) | 8-12-week-old male ApoE-/- mice with HFD (42% kcal from fat) |
At 2 weeks received 220 mg/kg/day for 14 weeks. At 4 weeks received HFD for 12 weeks |
Improved fasting glucose, insulin resistance, serum leptin, urinary catecholamines, and liver triglycerides. Reduced weight gain, adiposity, and inflammatory infiltrate in adipose tissue. Recovered operational taxonomic units (alpha diversity) [146] |
| Combination of Corni Fructus, Dioscoreae Rhizoma, Aurantii Fructus Immaturus, Platycodonis Radix (ethanol extract) |
3T3-L1 adipocytes and 5-week-old male C57BL/6J mice with HFD (60% kcal from fat) |
In vitro: 10, 50, 100 µg/mL for 48 hours. In vivo: Obesity induction for 4 weeks and then with extract (100 mg/kg/day) for 16 weeks |
Inhibited the differentiation of 3T3-L1 adipocytes and expressions of PPAR-γ, C/EBP-α, and lipin-1, increased phosphorylation of AMPK-α, and reduced weight gain in mice [154] |
| Cydonia oblonga (30% ethanol) |
3T3-L1 adipocytes | 0-600 µg/mL for 8 days |
Inhibited intracellular TG accumulation, induced AMPKα phosphorylation, downregulated adipogenic transcription factors (SREBP-1c, PPAR-γ, C/EBP-α), reduced mRNA expression of FAS, ACL, aP2, LPL, and increased mRNA expression of HSL and CPT-1 [44] |
| Cydonia oblonga (aqueous extract) | Male ICR mice (18-22 g) and male Wistar rats (300-350 g) | 20, 40, 80 mg/kg/day, orally for 14 days | Prolonged bleeding and clotting times, reduced pulmonary embolus mortality, increased thrombolysis, shortened ELT, reduced arterial and venous thrombus weights, decreased TXB2 and increased 6-keto-PGF1α levels [46] |
| Ginkgo biloba (extract obtained from Huacheng Biotech Inc. China) |
2-month-old male Wistar rats with HFD (57.3% from fat) |
Obesity induction for 2 months and then with extract (500 mg/kg/day), orally for 2 weeks |
Reduced energy intake, epididymal adipocyte volume, and lipid accumulation. It also reduced Plin 1 and Fasn mRNA and FAS protein levels [129] |
| Ginkgo biloba (unspecified extract) |
Male Sprague-Dawley rats (200-250 g) with acute myocardial infarction |
100 mg/kg/day, orally for 4 and 8 weeks |
Decreased TGF-β1, MMP-2, and MMP-9 mRNA transcription levels, reduced protein levels of type I collagen, MMP-2, and MMP-9, and inhibited myocardial remodeling after AMI [145] |
| Hibiscus sabdariffa (water extract) |
7-9 weeks old male C57BL/6J mice with HFD (60% kcal from fat) | 1, 10, 25 mg/kg/day for 42 days | Inhibited adipogenesis via PI3-K and MAPK pathways, reduced weight gain, improved glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity, normalized LDL-C/HDL-C ratio, reduced inflammatory state in liver, reinforced gut integrity, and prebiotic effects on gut microbiota [147] |
| Hibiscus sabdariffa (hot water extract) |
3T3-L1 adipocytes | 2 mg/ml for 5 days | Inhibited adipocyte differentiation through PI3-K/Akt and ERK pathways, and decreased lipid droplet accumulation [155] |
| Ilex paraguariensis (Yerba mate), water extract |
6-week-old male Swiss strain mice with HFD |
Obesity induction for 8 weeks and then with extract (1 mg/kg) for 8 weeks |
Attenuation of weight gain, decreased adiposity and epididymal fat-pad weight, restored serum levels of cholesterol, TG, LDL-C, and glucose [68] |
| Ilex paraguariensis (Yerba mate), water extract |
6-week-old male C57BL/6J mice with HFD (60% kcal from fat) |
Obesity induction for 6 weeks and then with extract (0.5, 1, or 2 g/kg/day) for 4 weeks |
Reduced body weight gain, lower adipose tissue, decreased serum cholesterol, TG, and glucose levels [69] |
| Ilex paraguariensis (Yerba mate), 15% etanol extract |
6-week-old male Sprague-Dawley rats with HFD (40% kcal from fat) |
Daily supplementation of extract, 0.24% (w/w) for 60 days |
Reduced body weight, visceral fat, blood and hepatic lipid levels, improved glucose and insulin levels, enhanced AMPK phosphorylation, increased UCP2 and UCP3 expression [133] |
| Ilex paraguariensis (Yerba mate), water extract |
Early weaned Wistar rats |
1 g/kg BW/day, gavage for 30 days |
Reduced adipose mass (retroperitoneal and epididymal), total body fat, subcutaneous fat, visceral adipocyte area, TG, and hypothalamic NPY content; restored central leptin resistance, hyperphagia, and higher hypothalamic SOCS-3 content [134] |
| Ilex paraguariensis (Yerba mate), water extract (capsules) |
A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial on obese Korean adults |
3 g/day for 12 weeks |
Decreased body fat mass, percent body fat, and WHR [136] |
| Ilex paraguariensis (Yerba mate), water extract |
8-week-old male Wistar rats with HFD (45% kcal from lard fat) |
100 mg/day in 3rd month of age and 200 mg/day in 4th month of age, daily for 2 months |
Reduced hypothalamic IKK phosphorylation and NF-κB p65 expression, increased IκBα and AdipoR1 expression, reduced IL-6 levels, increased IL-10/TNF-α ratio, and reduced low-grade inflammation [140] |
| Ilex paraguariensis (Yerba mate), water extract |
3T3-L1 adipocytes and 8-week-old male Sprague-Dawley rats with HFD (507.6 kcal/100 g) |
In vitro: 10, 50, 100 µg/mL for 7 days. In vivo: 500 mg/kg/day for 8 weeks |
In vitro: Suppressed lipid accumulation, increased AMPK, HSL, CaMKK, LKB1, PKA, C/EBPβ, IRβ, IRS1 (Tyr465), decreased SREBP-1c, FAS, PPARγ, and IRS1 (Ser1101). In vivo: suppressed body weight gain, improved serum cholesterol levels, increased AMPK, PKA, Erk1/Erk2, UCP1, reduced mTOR, S6K, SREBP-1c, ap2, FAS, IL-6, adiponectin, leptin, and Fabp4 [156] |
| Moringa oleifera (70% ethanol extract) |
Male albino rats (100 ± 20 g) with HFD (58% fat) and overweight/obese female patients |
In vivo: Obesity induction for 2 months and then with extract (200 and 400 mg/kg/day) for 1 month; patients: gelatine capsules (400 mg/day) for 8 weeks |
In rats, reduced final weight, adiposity index, glucose, insulin, and HOMA-IR. Increased R-QUICKI, adiponectin, omentin, GLUT-4, and PPAR-α expression. Reduced leptin and vaspin. Suppressed FAS and HMG-CoA reductase. In patients reduced BMI, TC, and LDL-C [74] |
| Moringa oleífera, Moringa oleifera leaf petroleum ether extract (MOPEE) |
3T3-L1 adipocytes and 7-week-old male C57BL/6J mice with HFD (60% kcal from fat) |
In vitro: 0, 50, 100, 200, and 400 µg/ml for 24 hours. In vivo: 0.125, 0.25, 0.5 g/kg/day for 14 weeks |
In vitro: Inhibited adipogenesis in a dose-dependent manner. Downregulated PPARγ, C/EBPα, C/EBPβ, FAS. Upregulated HSL, AMPKα, and ACC phosphorylation. In vivo: Decreased body weight, fat pad weight, and hepatic fat accumulation. Reduced TC, LDL-C, and AST levels. Downregulated PPARγ and FAS. Upregulated ATGL, AMPKα, and ACC phosphorylation [75] |
| Moringa oleifera (methanol extract from leaves) |
3-month-old male Wistar rats with HFD |
200 and 400 mg/kg/day for 12 weeks |
Alleviated serum biochemical abnormalities, balanced antioxidant status, and reestablished normal heart histology [139] |
| Opuntia streptacantha and Opuntia ficus-indica. Opuntia young cladode powders |
3T3-F442A adipocytes and 6-week-old male Sprague-Dawley rats with HFD (60% kcal from fat) |
In vitro: 1, 10, 100 μg/mL for 10 days. In vivo: 0.5% w/w for 8 weeks | In vitro: Impaired adipocyte differentiation and decreased TG, and reduced glucose uptake. In vivo: Slightly reduced body weight gain, liver and abdominal fat weights. Increased TG excretion in feces [157] |
| Platycodon grandiflorus (ethanol extract) |
Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial on overweight or moderately obese adults |
571 mg, 1142 mg, 2855 mg (in tablets) per day for 12 weeks |
Decreased body fat mass and body fat percentage, reduced total abdominal and subcutaneous fat areas, increased muscle mass [137] |
| Platycodon grandifloras (water extract) | 3T3-L1 preadipocytes and 8-week-old male Sprague-Dawley rats with HFD (59.8% kcal from fat) | In vitro: various concentrations (10-50 mg/mL). In vivo: 150 mg/kg/day for 7 weeks |
Inhibited 3T3-L1 preadipocyte differentiation and fat accumulation. Decreased pancreatic lipase activity. In vivo: Reduced plasma TC) and TG levels, decreased body weight and subcutaneous adipose tissue weight, reduced size of subcutaneous adipocytes, repressed up-regulation of FABP mRNA in subcutaneous adipose tissue [158] |
| Punica granatum (Pomegranate), ethanol:water 70:30 | 6-week-old male C57BL/6 mice with HFD (45% of total fat) |
g/kg/3 days per week for 12-14 weeks |
Increased energy expenditure, reduced chronic inflammation and insulin resistance, promoted browning and thermogenesis in adipose tissue, reduced inflammatory markers, increased the reductive potential [95] |
| Salvia miltiorrhiza (75% etanol extract) |
8-9-week-old male Sprague-Dawley rats with HFD (45% kcal from fat) | 0.675, 1.35, 2.70 g/kg/day for 8 weeks | Reduced body weight, body fat index, serum lipid level, hepatic lipid accumulation, and adipocyte vacuolation. Improved gut integrity and lipid metabolism, altered gut microbiota composition [101] |
| Taraxacum officinale (95% ethanol extract) |
Porcine pancreatic lipase and 7-week-old male ICR mice |
In vitro: 50-250 µg/ml. In vivo: 400 mg/kg single dose for 240 min |
In vitro: inhibited pancreatic lipase activity. In vivo: decreased plasma TG levels and reduced AUC of plasma TG response curve [104] |
| Taraxacum officinale (leaf and root extracts in ethanol 60%) |
3T3-L1 adipocytes | 300-600 μg/μL for 6 days |
Inhibited adipocyte differentiation, reduced lipid and TG accumulation, regulated expression of genes and long non-coding RNAs involved in adipogenesis and lipid metabolism [105] |
| Theobroma cacao (aqueous extract) |
Wistar rats (250 ± 20 g) with HFD (45% kcal) and 20% fructose |
Obesity induction for 5 weeks and then with 100%, 10%, 1% pellet for 5 weeks |
Decreased body weight by 39%, systolic blood pressure by 27%, triglycerides by 55%, TC by 24%, LDL-C by 37%, and TG/HDL-C ratio by 54% [37] |
5. Plant and Herb Extracts Targeting Dyslipidemia and Adipokines in Obesity
6. Plant and Herb Extracts Against to Insulin Resistance, Hyperglycemia, and Diabetes
7. Plant and Herb Extracts with Anti-Hypertensive Effects
8. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gutiérrez-Cuevas, J.; Santos, A.; Armendariz-Borunda, J. Pathophysiological Molecular Mechanisms of Obesity: A Link between MAFLD and NASH with Cardiovascular Diseases. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karri, S.; Sharma, S.; Hatware, K.; Patil, K. Natural Anti-Obesity Agents and Their Therapeutic Role in Management of Obesity: A Future Trend Perspective. Biomedicine and Pharmacotherapy 2019, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez-cuevas, J.; Sandoval-rodriguez, A.; Meza-rios, A.; Monroy-ramírez, H.C.; Galicia-moreno, M.; García-bañuelos, J.; Santos, A.; Armendariz-borunda, J. Molecular Mechanisms of Obesity-linked Cardiac Dysfunction: An Up-date on Current Knowledge. Cells 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuster, D. Obesity and the Development of Type 2 Diabetes: The Effects of Fatty Tissue Inflammation. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaughlin, T.; Lamendola, C.; Liu, A.; Abbasi, F. Preferential Fat Deposition in Subcutaneous versus Visceral Depots Is Associated with Insulin Sensitivity. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 2011, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konige, M.; Wang, H.; Sztalryd, C. Role of Adipose Specific Lipid Droplet Proteins in Maintaining Whole Body Energy Homeostasis. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis 2014, 1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garin-Shkolnik, T.; Rudich, A.; Hotamisligil, G.S.; Rubinstein, M. FABP4 Attenuates PPARγ and Adipogenesis and Is Inversely Correlated with PPARγ in Adipose Tissues. Diabetes 2014, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, H.K.; Taylor, A.G. Biomarkers and Potential Mechanisms of Obesity-Induced Oxidant Stress in Humans. Int J Obes 2006, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csige, I.; Ujvárosy, D.; Szabó, Z.; Lorincz, I.; Paragh, G.; Harangi, M.; Somodi, S.; Santulli, G. The Impact of Obesity on the Cardiovascular System. J Diabetes Res 2018, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi-Sunyer, X. The Medical Risks of Obesity. Postgrad Med 2009, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, P.; Kawar, B.; El Nahas, M. Obesity and Diabetes in the Developing World — A Growing Challenge. New England Journal of Medicine 2007, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdi Beshir, S.; Ahmed Elnour, A.; Soorya, A.; Parveen Mohamed, A.; Sir Loon Goh, S.; Hussain, N.; Al Haddad, A.H.I.; Hussain, F.; Yousif Khidir, I.; Abdelnassir, Z. A Narrative Review of Approved and Emerging Anti-Obesity Medications. Saudi Pharmaceutical Journal 2023, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.G.; Park, C.Y. Anti-Obesity Drugs: A Review about Their Effects and Safety. Diabetes Metab J 2012, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, M.S.; Ahmed, N. Antiglycation Properties of Aged Garlic Extract: Possible Role in Prevention of Diabetic Complications. In Proceedings of the Journal of Nutrition; 2006; Vol. 136.
- Imaizumi, V.M.; Laurindo, L.F.; Manzan, B.; Guiguer, E.L.; Oshiiwa, M.; Otoboni, A.M.M.B.; Araujo, A.C.; Tofano, R.J.; Barbalho, S.M. Garlic: A Systematic Review of the Effects on Cardiovascular Diseases. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 2023, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, X.J.; Wang, P.Q.; Li, S.J.; Li, X.K.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Wang, J. Garlic for Hypertension: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Phytomedicine 2015, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, S.; Masamoto, K.; Sumiyoshi, H.; Harada, H. Acute Toxicity Test of Garlic Extract. Journal of Toxicological Sciences 1984, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fardiyah, Q.; Ersam, T.; Suyanta; Slamet, A.; Suprapto; Kurniawan, F. New Potential and Characterization of Andrographis Paniculata L. Ness Plant Extracts as Photoprotective Agent. Arabian Journal of Chemistry 2020, 13. [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.K.; Chin, K.Y.; Ima-Nirwana, S. A Review on the Molecular Basis Underlying the Protective Effects of Andrographis Paniculata and Andrographolide against Myocardial Injury. Drug Des Devel Ther 2021, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulling, S.E.; Rawel, H.M. Chokeberry (Aronia Melanocarpa) - A Review on the Characteristic Components and Potential Health Effects. Planta Med 2008, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banjari, I.; Misir, A.; Šavikin, K.; Jokić, S.; Molnar, M.; De Zoysa, H.K.S.; Waisundara, V.Y. Antidiabetic Effects of Aronia Melanocarpa and Its Other Therapeutic Properties. Front Nutr 2017, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurikova, T.; Mlcek, J.; Skrovankova, S.; Sumczynski, D.; Sochor, J.; Hlavacova, I.; Snopek, L.; Orsavova, J. Fruits of Black Chokeberry Aronia Melanocarpa in the Prevention of Chronic Diseases. Molecules 2017, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brimson, J.M.; Prasanth, M.I.; Kumaree, K.K.; Thitilertdecha, P.; Malar, D.S.; Tencomnao, T.; Prasansuklab, A. Tea Plant (Camellia Sinensis): A Current Update on Use in Diabetes, Obesity, and Cardiovascular Disease. Nutrients 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinh, T.C.; Thi Phuong, T.N.; Minh, L.B.; Minh Thuc, V.T.; Bac, N.D.; Van Tien, N.; Pham, V.H.; Show, P.L.; Tao, Y.; Nhu Ngoc, V.T.; et al. The Effects of Green Tea on Lipid Metabolism and Its Potential Applications for Obesity and Related Metabolic Disorders - An Existing Update. Diabetes and Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research and Reviews 2019, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anwar, R.; Rabail, R.; Rakha, A.; Bryla, M.; Roszko, M.; Aadil, R.M.; Kieliszek, M. Delving the Role of Caralluma Fimbriata: An Edible Wild Plant to Mitigate the Biomarkers of Metabolic Syndrome. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2022, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, A.; Briskey, D.; dos Reis, C.; Mallard, A.R. The Effect of an Orally-Dosed Caralluma Fimbriata Extract on Appetite Control and Body Composition in Overweight Adults. Sci Rep 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gujjala, S.; Putakala, M.; Bongu, S.B.R.; Ramaswamy, R.; Desireddy, S. Preventive Effect of Caralluma Fimbriata against High-Fat Diet Induced Injury to Heart by Modulation of Tissue Lipids, Oxidative Stress and Histological Changes in Wistar Rats. Arch Physiol Biochem 2022, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, P.V.; Gan, S.H. Cinnamon: A Multifaceted Medicinal Plant. Evidence-based Complementary and Alternative Medicine 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roussel, A.M.; Hininger, I.; Benaraba, R.; Ziegenfuss, T.N.; Anderson, R.A. Antioxidant Effects of a Cinnamon Extract in People with Impaired Fasting Glucose That Are Overweight or Obese. J Am Coll Nutr 2009, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beejmohun, V.; Peytavy-Izard, M.; Mignon, C.; Muscente-Paque, D.; Deplanque, X.; Ripoll, C.; Chapal, N. Acute Effect of Ceylon Cinnamon Extract on Postprandial Glycemia: Alpha-Amylase Inhibition, Starch Tolerance Test in Rats, and Randomized Crossover Clinical Trial in Healthy Volunteers. BMC Complement Altern Med 2014, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Qin, M.; Chen, R.; Jia, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Chen, G.; Wang, A.; Ling, B.; Rong, W. Citrullus Colocynthis (L.) Schrad.: A Promising Pharmaceutical Resource for Multiple Diseases. Molecules 2023, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafarizadeh, A.; Raeisi, S.A.; Ghassab-Abdollahi, N.; Yarani, R.; Araj-Khodaei, M.; Mirghafourvand, M. Effect of Citrullus Colocynthis on Glycemic Factors and Lipid Profile in Type II Diabetic Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J Diabetes Metab Disord 2022, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhawiti, N.M. Antiplatelets and Profibrinolytic Activity of Citrullus Colocynthis in Control and High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Rats: Mechanisms of Action. Arch Physiol Biochem 2018, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahimi, R.; Amin, G.; Ardekani, M.R.S. A Review on Citrullus Colocynthis Schrad.: From Traditional Iranian Medicine to Modern Phytotherapy. Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine 2012, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davinelli, S.; Corbi, G.; Righetti, S.; Sears, B.; Olarte, H.H.; Grassi, D.; Scapagnini, G. Cardioprotection by Cocoa Polyphenols and ω-3 Fatty Acids: A Disease-Prevention Perspective on Aging-Associated Cardiovascular Risk. J Med Food 2018, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibero-Baraibar, I.; Suárez, M.; Arola-Arnal, A.; Zulet, M.A.; Martinez, J.A. Cocoa Extract Intake for 4 Weeks Reduces Postprandial Systolic Blood Pressure Response of Obese Subjects, Even after Following an Energy-Restricted Diet. Food Nutr Res 2016, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hidalgo, I.; Ortiz, A.; Sanchez-Pardo, M.; Garduño-Siciliano, L.; Hernández-Ortega, M.; Villarreal, F.; Meaney, E.; Najera, N.; Ceballos, G.M. Obesity and Cardiovascular Risk Improvement Using Cacao By-Products in a Diet-Induced Obesity Murine Model. J Med Food 2019, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Feng, Z.L.; Chen, H.B.; Wang, F.S.; Lu, J.H. Corni Fructus: A Review of Chemical Constituents and Pharmacological Activities. Chinese Medicine (United Kingdom) 2018, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Liu, Y.; An, Z.; Ni, J. Active Components and Pharmacological Effects of Cornus Officinalis: Literature Review. Front Pharmacol 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.H.; Cho, E.J.; Yokozawa, T. Protection against Hypercholesterolemia by Corni Fructus Extract and Its Related Protective Mechanism. J Med Food 2009, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Kim, K.S.; Lee, T.J.; Kim, Y.C. Antidiabetic Effects of Corni Fructus Extract on Blood Glucose and Insulin Resistance in Db/Db Mice. Toxicol Res 2009, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amerizadeh, A.; Vaseghi, G.; Esmaeilian, N.; Asgary, S. Cardiovascular Effects of Cydonia Oblonga Miller (Quince). Evidence-based Complementary and Alternative Medicine 2022, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojdyło, A.; Oszmiański, J.; Bielicki, P. Polyphenolic Composition, Antioxidant Activity, and Polyphenol Oxidase (PPO) Activity of Quince (Cydonia Oblonga Miller) Varieties. J Agric Food Chem 2013, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.S.; Jung, J.I.; Hwang, J.S.; Hwang, M.O.; Kim, E.J. Cydonia Oblonga Miller Fruit Extract Exerts an Anti-Obesity Effect in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes by Activating the AMPK Signaling Pathway. Nutr Res Pract 2023, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umar, A.; Iskandar, G.; Aikemu, A.; Yiming, W.; Zhou, W.; Berké, B.; Begaud, B.; Moore, N. Effects of Cydonia Oblonga Miller Leaf and Fruit Flavonoids on Blood Lipids and Anti-Oxydant Potential in Hyperlipidemia Rats. J Ethnopharmacol 2015, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Abdurahman, A.; Umar, A.; Iskander, G.; Abdusalam, E.; Berké, B.; Bégaud, B.; Moore, N. Effects of Cydonia Oblonga Miller Extracts on Blood Hemostasis, Coagulation and Fibrinolysis in Mice, and Experimental Thrombosis in Rats. J Ethnopharmacol 2014, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, H.; Martins, F.G. Cardiovascular Activity of Ginkgo Biloba—An Insight from Healthy Subjects. Biology (Basel) 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohanta, T.K.; Tamboli, Y.; Zubaidha, P.K. Phytochemical and Medicinal Importance of Ginkgo Biloba L. Nat Prod Res 2014, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Y.; Zhu, F.; Pan, M.; Liu, Q.; Wang, P. Pharmacokinetic, Metabolism, and Metabolomic Strategies Provide Deep Insight Into the Underlying Mechanism of Ginkgo Biloba Flavonoids in the Treatment of Cardiovascular Disease. Front Nutr 2022, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Silva Pinto, M.; Kwon, Y.I.; Apostolidis, E.; Lajolo, F.M.; Genovese, M.I.; Shetty, K. Potential of Ginkgo Biloba L. Leaves in the Management of Hyperglycemia and Hypertension Using in Vitro Models. Bioresour Technol 2009, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.; Yoon, J.W.; Kang, S.M.; Choi, S.H.; Cho, B.J.; Kim, M.; Park, H.S.; Cho, H.J.; Shin, H.; Kim, Y.B.; et al. Egb761, a Ginkgo Biloba Extract, Is Effective against Atherosclerosis in Vitro, and in a Rat Model of Type 2 Diabetes. PLoS One 2011, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Zaher, A.O.; Farghaly, H.S.M.; El-Refaiy, A.E.M.; Abd-Eldayem, A.M. Protective Effect of the Standardized Extract of Ginkgo Biloba (EGb761) against Hypertension with Hypercholesterolemia-Induced Renal Injury in Rats: Insights in the Underlying Mechanisms. Biomedicine and Pharmacotherapy 2017, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manach, C.; Scalbert, A.; Morand, C.; Rémésy, C.; Jiménez, L. Polyphenols: Food Sources and Bioavailability. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2004, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunes, F.M.; Coimbra, M.A. Chemical Characterization of Galactomannans and Arabinogalactans from Two Arabica Coffee Infusions as Affected by the Degree of Roast. J Agric Food Chem 2002, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blum, J.; Lemaire, B.; Lafay, S. Effect of a Green Decaffeinated Coffee Extract on Glycaemia. Nutrafoods 2007, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Asbaghi, O.; Kashkooli, S.; Mardani, M.; Rezaei kelishadi, M.; Fry, H.; Kazemi, M.; Kaviani, M. Effect of Green Coffee Bean Extract Supplementation on Liver Function and Inflammatory Biomarkers: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials. Complement Ther Clin Pract 2021, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozuma, K.; Tsuchiya, S.; Kohori, J.; Hase, T.; Tokimitsu, I. Antihypertensive Effect of Green Coffee Bean Extract on Mildly Hypertensive Subjects. Hypertension Research 2005, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asbaghi, O.; Sadeghian, M.; Nasiri, M.; Khodadost, M.; Shokri, A.; Panahande, B.; Pirouzi, A.; Sadeghi, O. The Effects of Green Coffee Extract Supplementation on Glycemic Indices and Lipid Profile in Adults: A Systematic Review and Dose-Response Meta-Analysis of Clinical Trials. Nutr J 2020, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sapian, S.; Ibrahim Mze, A.A.; Jubaidi, F.F.; Mohd Nor, N.A.; Taib, I.S.; Abd Hamid, Z.; Zainalabidin, S.; Mohamad Anuar, N.N.; Katas, H.; Latip, J.; et al. Therapeutic Potential of Hibiscus Sabdariffa Linn. in Attenuating Cardiovascular Risk Factors. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da-Costa-Rocha, I.; Bonnlaender, B.; Sievers, H.; Pischel, I.; Heinrich, M. Hibiscus Sabdariffa L. - A Phytochemical and Pharmacological Review. Food Chem 2014, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurrola-Díaz, C.M.; García-López, P.M.; Sánchez-Enríquez, S.; Troyo-Sanromán, R.; Andrade-González, I.; Gómez-Leyva, J.F. Effects of Hibiscus Sabdariffa Extract Powder and Preventive Treatment (Diet) on the Lipid Profiles of Patients with Metabolic Syndrome (MeSy). Phytomedicine 2010, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janson, B.; Prasomthong, J.; Malakul, W.; Boonsong, T.; Tunsophon, S. Hibiscus Sabdariffa L. Calyx Extract Prevents the Adipogenesis of 3T3-L1 Adipocytes, and Obesity-Related Insulin Resistance in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Rats. Biomedicine and Pharmacotherapy 2021, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ademiluyi, A.O.; Oboh, G. Aqueous Extracts of Roselle (Hibiscus Sabdariffa Linn.) Varieties Inhibit α-Amylase and α-Glucosidase Activities in Vitro. J Med Food 2013, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsayed, A.M.A.; Zhang, B.L.; Bredeloux, P.; Boudesocque-Delaye, L.; Yu, A.; Peineau, N.; Enguehard-Gueiffier, C.; Ahmed, E.M.; Pasqualin, C.; Maupoil, V. Aqueous Fraction from Hibiscus Sabdariffa Relaxes Mesenteric Arteries of Normotensive and Hypertensive Rats through Calcium Current Reduction and Possibly Potassium Channels Modulation. Nutrients 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Vasconcellos, A.C.; Frazzon, J.; Zapata Noreña, C.P. Phenolic Compounds Present in Yerba Mate Potentially Increase Human Health: A Critical Review. Plant Foods for Human Nutrition 2022, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paluch, E.; Okińczyc, P.; Zwyrzykowska-Wodzińska, A.; Szperlik, J.; Żarowska, B.; Duda-Madej, A.; Babelewski˛, P.; Włodarczyk, M.; Wojtasik, W.; Kupczyński, R.; et al. Composition and Antimicrobial Activity of Ilex Leaves Water Extracts. Molecules 2021, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, T.W.; Miranda, J.; Teixeira, L.; Aiastui, A.; Matheu, A.; Gambero, A.; Portillo, M.P.; Ribeiro, M.L. Yerba Mate Stimulates Mitochondrial Biogenesis and Thermogenesis in High-Fat-Diet-Induced Obese Mice. Mol Nutr Food Res 2018, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arçari, D.P.; Bartchewsky, W.; Dos Santos, T.W.; Oliveira, K.A.; Funck, A.; Pedrazzoli, J.; De Souza, M.F.F.; Saad, M.J.; Bastos, D.H.M.; Gambero, A.; et al. Antiobesity Effects of Yerba Maté Extract (Ilex Paraguariensis) in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice. Obesity 2009, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Y.-R.; Lee, H.-Y.; Kim, J.-H.; Moon, D.-I.; Seo, M.-Y.; Park, S.-H.; Choi, K.-H.; Kim, C.-R.; Kim, S.-H.; Oh, J.-H.; et al. Anti-Obesity and Anti-Diabetic Effects of Yerba Mate ( Ilex Paraguariensis ) in C57BL/6J Mice Fed a High-Fat Diet. Lab Anim Res 2012, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, G.A.; Stefanuto, A.; Boaventura, B.C.B.; De Morais, E.C.; Da Cavalcante, L.S.; De Andrade, F.; Wazlawik, E.; Di Pietro, P.F.; Maraschin, M.; Da Silva, E.L. Mate Tea (Ilex Paraguariensis) Improves Glycemic and Lipid Profiles of Type 2 Diabetes and Pre-Diabetes Individuals: A Pilot Study. J Am Coll Nutr 2011, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González Arbeláez, L.F.; Fantinelli, J.C.; Ciocci Pardo, A.; Caldiz, C.I.; Ríos, J.L.; Schinella, G.R.; Mosca, S.M. Effect of an Ilex Paraguariensis (Yerba Mate) Extract on Infarct Size in Isolated Rat Hearts: The Mechanisms Involved. Food Funct 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azlan, U.K.; Mediani, A.; Rohani, E.R.; Tong, X.; Han, R.; Misnan, N.M.; Jam, F.A.; Bunawan, H.; Sarian, M.N.; Hamezah, H.S. A Comprehensive Review with Updated Future Perspectives on the Ethnomedicinal and Pharmacological Aspects of Moringa Oleifera. Molecules 2022, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbikay, M. Therapeutic Potential of Moringa Oleifera Leaves in Chronic Hyperglycemia and Dyslipidemia: A Review. Front Pharmacol 2012, 3 MAR. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezzat, S.M.; El Bishbishy, M.H.; Aborehab, N.M.; Salama, M.M.; Hasheesh, A.; Motaal, A.A.; Rashad, H.; Metwally, F.M. Upregulation of MC4R and PPAR-α Expression Mediates the Anti-Obesity Activity of Moringa Oleifera Lam. in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity in Rats. J Ethnopharmacol 2020, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, W.W.; Luo, X.F.; Dai, T.Y.; Peng, L.; Song, S.; Li, L.F.; Tao, L.; Shi, C.Y.; et al. Moringa Oleifera Leaf Petroleum Ether Extract Inhibits Lipogenesis by Activating the AMPK Signaling Pathway. Front Pharmacol 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghasi, S.; Nwobodo, E.; Ofili, J.O. Hypocholesterolemic Effects of Crude Extract of Leaf of Moringa Oleifera Lam in High-Fat Diet Fed Wistar Rats. J Ethnopharmacol 2000, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Martínez, S.; Díaz-Prieto, L.E.; Castro, I.V.; Jurado, C.; Iturmendi, N.; Martín-Ridaura, M.C.; Calle, N.; Dueñas, M.; Picón, M.J.; Marcos, A.; et al. Moringa Oleifera Leaf Supplementation as a Glycemic Control Strategy in Subjects with Prediabetes. Nutrients 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asgary, S.; Sahebkar, A.; Goli-Malekabadi, N. Ameliorative Effects of Nigella Sativa on Dyslipidemia. J Endocrinol Invest 2015, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derosa, G.; D’Angelo, A.; Maffioli, P.; Cucinella, L.; Nappi, R.E. The Use of Nigella Sativa in Cardiometabolic Diseases. Biomedicines 2024, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehkordi, F.R.; Kamkhah, A.F. Antihypertensive Effect of Nigella Sativa Seed Extract in Patients with Mild Hypertension. Fundam Clin Pharmacol 2008, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madrigal-Santillán, E.; Portillo-Reyes, J.; Madrigal-Bujaidar, E.; Sánchez-Gutiérrez, M.; Izquierdo-Vega, J.A.; Izquierdo-Vega, J.; Delgado-Olivares, L.; Vargas-Mendoza, N.; Álvarez-González, I.; Morales-González, Á.; et al. Opuntia Spp. in Human Health: A Comprehensive Summary on Its Pharmacological, Therapeutic and Preventive Properties. Part 2. Plants 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, E.Y.; Ezzat, M.I.; El Hefnawy, H.M.; Abdel-Sattar, E. An Overview and Update on the Chemical Composition and Potential Health Benefits of Opuntia Ficus-Indica (L.) Miller. J Food Biochem 2022, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padilla-Camberos, E.; Flores-Fernandez, J.M.; Fernandez-Flores, O.; Gutierrez-Mercado, Y.; Carmona-De La Luz, J.; Sandoval-Salas, F.; Mendez-Carreto, C.; Allen, K. Hypocholesterolemic Effect and in Vitro Pancreatic Lipase Inhibitory Activity of an Opuntia Ficus-Indica Extract. Biomed Res Int 2015, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Romero, P.; Pichardo-Ontiveros, E.; Avila-Nava, A.; Vázquez-Manjarrez, N.; Tovar, A.R.; Pedraza-Chaverri, J.; Torres, N. The Effect of Nopal (Opuntia Ficus Indica) on Postprandial Blood Glucose, Incretins, and Antioxidant Activity in Mexican Patients with Type 2 Diabetes after Consumption of Two Different Composition Breakfasts. J Acad Nutr Diet 2014, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butterweck, V.; Semlin, L.; Feistel, B.; Pischel, I.; Bauer, K.; Verspohl, E.J. Comparative Evaluation of Two Different Opuntia Ficus-Indica Extracts for Blood Sugar Lowering Effects in Rats. Phytotherapy Research 2011, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Yang, D.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, N.; Li, M.; Liu, Y. Platycodon Grandiflorus - An Ethnopharmacological, Phytochemical and Pharmacological Review. J Ethnopharmacol 2015, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, M.Y.; Bo, A.; Yang, M.; Xu, J.F.; Jiang, L.L.; Zhou, B.C.; Li, M.H. The Pharmacological Effects and Health Benefits of Platycodon Grandiflorus - A Medicine Food Homology Species. Foods 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, K.A.; Hwang, Y.J.; Im, P.R.; Hwang, H.J.; Song, J.; Kim, Y.J. Platycodon Grandiflorum Extract Reduces High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity Through Regulation of Adipogenesis and Lipogenesis Pathways in Mice. J Med Food 2019, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, M.J.; Kim, S.H.; Park, J.W.; Lee, Y.J.; Ham, S.S. Platycodon Grandiflorum Root Attenuates Vascular Endothelial Cell Injury by Oxidized Low-Density Lipoprotein and Prevents High-Fat Diet-Induced Dyslipidemia in Mice by up-Regulating Antioxidant Proteins. Nutrition Research 2012, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, Y.M.; Kim, S.K.; Kang, J.S.; Lee, B.C. Platycodon Grandiflorum Modifies Adipokines and the Glucose Uptake in High-Fat Diet in Mice and L6 Muscle Cells. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology 2012, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.C.; Lin, C.H.; Yao, H.T.; Kuo, W.W.; Shen, C.Y.; Yeh, Y.L.; Ho, T.J.; Padma, V.V.; Lin, Y.C.; Huang, C.Y.; et al. Platycodon Grandiflorum (PG) Reverses Angiotensin II-Induced Apoptosis by Repressing IGF-IIR Expression. J Ethnopharmacol 2017, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, C.; Zhang, W.; Li, J.; Du, L.; Lv, O.; Zhao, S.; Li, J. Beneficial Effects of Pomegranate on Lipid Metabolism in Metabolic Disorders. Mol Nutr Food Res 2019, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maphetu, N.; Unuofin, J.O.; Masuku, N.P.; Olisah, C.; Lebelo, S.L. Medicinal Uses, Pharmacological Activities, Phytochemistry, and the Molecular Mechanisms of Punica Granatum L. (Pomegranate) Plant Extracts: A Review. Biomedicine and Pharmacotherapy 2022, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokgalaboni, K.; Dlamini, S.; Phoswa, W.N.; Modjadji, P.; Lebelo, S.L. The Impact of Punica Granatum Linn and Its Derivatives on Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Endothelial Function in Diabetes Mellitus: Evidence from Preclinical and Clinical Studies. Antioxidants 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reguero, M.; Gómez de Cedrón, M.; Sierra-Ramírez, A.; Fernández-Marcos, P.J.; Reglero, G.; Quintela, J.C.; Ramírez de Molina, A. Pomegranate Extract Augments Energy Expenditure Counteracting the Metabolic Stress Associated with High-Fat-Diet-Induced Obesity. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wen, S.; Kota, B.P.; Peng, G.; Li, G.Q.; Yamahara, J.; Roufogalis, B.D. Punica Granatum Flower Extract, a Potent α-Glucosidase Inhibitor, Improves Postprandial Hyperglycemia in Zucker Diabetic Fatty Rats. J Ethnopharmacol 2005, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, R.L.; Dellacqua, L.O.; Delgado, N.T.B.; Rouver, W.N.; Podratz, P.L.; Lima, L.C.F.; Piccin, M.P.C.; Meyrelles, S.S.; Mauad, H.; Graceli, J.B.; et al. Pomegranate Peel Extract Attenuates Oxidative Stress by Decreasing Coronary Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE) Activity in Hypertensive Female Rats. Journal of Toxicology and Environmental Health - Part A: Current Issues 2016, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Q.; Zhu, R.; Tian, Y.; Chen, B.; Li, R.; Li, L.; Wang, L.; Che, Y.; Zhao, D.; Mo, F.; et al. Salvia Miltiorrhiza in Diabetes: A Review of Its Pharmacology, Phytochemistry, and Safety. Phytomedicine 2019, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Fu, L.; Nile, S.H.; Zhang, J.; Kai, G. Salvia Miltiorrhiza in Treating Cardiovascular Diseases: A Review on Its Pharmacological and Clinical Applications. Front Pharmacol 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, S.; Huo, D.; Wang, S.; Qian, Q. Inhibition of Glucose-Induced Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Expression by Salvia Miltiorrhiza Hydrophilic Extract in Human Microvascular Endothelial Cells: Evidence for Mitochondrial Oxidative Stress. J Ethnopharmacol 2011, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, Z.L.; Zhang, X.; Ge, W.; Zhong, Y.B.; Wang, H.Y.; Zuo, Z.Y.; Liu, D.Y. Salvia Miltiorrhiza Extract May Exert an Anti-Obesity Effect in Rats with High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity by Modulating Gut Microbiome and Lipid Metabolism. World J Gastroenterol 2022, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kania-Dobrowolska, M.; Baraniak, J. Dandelion (Taraxacum Officinale L.) as a Source of Biologically Active Compounds Supporting the Therapy of Co-Existing Diseases in Metabolic Syndrome. Foods 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olas, B. New Perspectives on the Effect of Dandelion, Its Food Products and Other Preparations on the Cardiovascular System and Its Diseases. Nutrients 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Kang, M.-J.; Kim, M.-J.; Kim, M.-E.; Song, J.-H.; Lee, Y.-M.; Kim, J.-I. Pancreatic Lipase Inhibitory Activity of Taraxacum Officinale in Vitro and in Vivo. Nutr Res Pract 2008, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Castejón, M.; García-Carrasco, B.; Fernández-Dacosta, R.; Dávalos, A.; Rodriguez-Casado, A. Reduction of Adipogenesis and Lipid Accumulation by Taraxacum Officinale (Dandelion) Extracts in 3T3L1 Adipocytes: An in Vitro Study. Phytotherapy Research 2014, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aremu, O.O.; Oyedeji, A.O.; Oyedeji, O.O.; Nkeh-Chungag, B.N.; Sewani Rusike, C.R. In Vitro and in Vivo Antioxidant Properties of Taraxacum Officinale in Nω-Nitro-L-Arginine Methyl Ester (L-NAME)-Induced Hypertensive Rats. Antioxidants 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murtaza, I.; Laila, O.; Drabu, I.; Ahmad, A.; Charifi, W.; Popescu, S.M.; Mansoor, S. Nutritional Profiling, Phytochemical Composition and Antidiabetic Potential of Taraxacum Officinale, an Underutilized Herb. Molecules 2022, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, J.; Gavrilova, O.; Pack, S.; Jou, W.; Mullen, S.; Sumner, A.E.; Cushman, S.W.; Periwal, V. Hypertrophy and/or Hyperplasia: Dynamics of Adipose Tissue Growth. PLoS Comput Biol 2009, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stich, V.; Berlan, M. Physiological Regulation of NEFA Availability: Lipolysis Pathway. Proceedings of the Nutrition Society 2004, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frühbeck, G.; Méndez-Giménez, L.; Fernández-Formoso, J.A.; Fernández, S.; Rodríguez, A. Regulation of Adipocyte Lipolysis. Nutr Res Rev 2014, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafontan, M.; Langin, D. Lipolysis and Lipid Mobilization in Human Adipose Tissue. Prog Lipid Res 2009, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manna, P.; Jain, S.K. Obesity, Oxidative Stress, Adipose Tissue Dysfunction, and the Associated Health Risks: Causes and Therapeutic Strategies. Metab Syndr Relat Disord 2015, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahima, R.S.; Flier, J.S. Adipose Tissue as an Endocrine Organ. Trends Endocrinol Metab 2000, 11, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macdougall, C.E.; Wood, E.G.; Loschko, J.; Scagliotti, V.; Cassidy, F.C.; Robinson, M.E.; Feldhahn, N.; Castellano, L.; Voisin, M.B.; Marelli-Berg, F.; et al. Visceral Adipose Tissue Immune Homeostasis Is Regulated by the Crosstalk between Adipocytes and Dendritic Cell Subsets. Cell Metab 2018, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotoh, K.; Inoue, M.; Masaki, T.; Chiba, S.; Shimasaki, T.; Ando, H.; Fujiwara, K.; Katsuragi, I.; Kakuma, T.; Seike, M.; et al. A Novel Anti-Inflammatory Role for Spleen-Derived Interleukin-10 in Obesity-Induced Inflammation in White Adipose Tissue and Liver. Diabetes 2012, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, H.; Karin, M.; Bai, H.; Cai, D. Hypothalamic IKKbeta/NF-KappaB and ER Stress Link Overnutrition to Energy Imbalance and Obesity. Cell 2008, 135, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milanski, M.; Degasperi, G.; Coope, A.; Morari, J.; Denis, R.; Cintra, D.E.; Tsukumo, D.M.L.; Anhe, G.; Amaral, M.E.; Takahashi, H.K.; et al. Saturated Fatty Acids Produce an Inflammatory Response Predominantly through the Activation of TLR4 Signaling in Hypothalamus: Implications for the Pathogenesis of Obesity. Journal of Neuroscience 2009, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barale, C.; Russo, I. Influence of Cardiometabolic Risk Factors on Platelet Function. Int J Mol Sci 2020, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivamaruthi, B.S.; Kesika, P.; Suganthy, N.; Chaiyasut, C. A Review on Role of Microbiome in Obesity and Antiobesity Properties of Probiotic Supplements. Biomed Res Int 2019, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborti, C.K. New-Found Link between Microbiota and Obesity. World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crespy, V.; Williamson, G. A Review of the Health Effects of Green Tea Catechins in in Vivo Animal Models. In Proceedings of the Journal of Nutrition; 2004; Vol. 134.
- Lin, J.K.; Lin-Shiau, S.Y. Mechanisms of Hypolipidemic and Anti-Obesity Effects of Tea and Tea Polyphenols. Mol Nutr Food Res 2006, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajerska, J.; Wozniewicz, M.; Jeszka, J.; Drzymala-Czyz, S.; Walkowiak, J. Green Tea Aqueous Extract Reduces Visceral Fat and Decreases Protein Availability in Rats Fed with a High-Fat Diet. Nutrition Research 2011, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basu, A.; Sanchez, K.; Leyva, M.J.; Wu, M.; Betts, N.M.; Aston, C.E.; Lyons, T.J. Green Tea Supplementation Affects Body Weight, Lipids, and Lipid Peroxidation in Obese Subjects with Metabolic Syndrome. J Am Coll Nutr 2010, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamalakkannan, S.; Rajendran, R.; Venkatesh, R. V.; Clayton, P.; Akbarsha, M.A. Antiobesogenic and Antiatherosclerotic Properties of Caralluma Fimbriata Extract. J Nutr Metab 2010, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banin, R.M.; Hirata, B.K.S.; Andrade, I.S.; Zemdegs, J.C.S.; Clemente, A.P.G.; Dornellas, A.P.S.; Boldarine, V.T.; Estadella, D.; Albuquerque, K.T.; Oyama, L.M.; et al. Beneficial Effects of Ginkgo Biloba Extract on Insulin Signaling Cascade, Dyslipidemia, and Body Adiposity of Diet-Induced Obese Rats. Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research 2014, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirata, B.K.S.; Banin, R.M.; Dornellas, A.P.S.; De Andrade, I.S.; Zemdegs, J.C.S.; Caperuto, L.C.; Oyama, L.M.; Ribeiro, E.B.; Telles, M.M. Ginkgo Biloba Extract Improves Insulin Signaling and Attenuates Inflammation in Retroperitoneal Adipose Tissue Depot of Obese Rats. Mediators Inflamm 2015, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banin, R.M.; de Andrade, I.S.; Cerutti, S.M.; Oyama, L.M.; Telles, M.M.; Ribeiro, E.B. Ginkgo Biloba Extract (GbE) Stimulates the Hypothalamic Serotonergic System and Attenuates Obesity in Ovariectomized Rats. Front Pharmacol 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirata, B.K.S.; Cruz, M.M.; De Sá, R.D.C.C.; Farias, T.S.M.; Machado, M.M.F.; Bueno, A.A.; Alonso-Vale, M.I.C.; Telles, M.M. Potential Anti-Obesogenic Effects of Ginkgo Biloba Observed in Epididymal White Adipose Tissue of Obese Rats. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, B.K.; Park, S.B.; Lee, D.R.; Lee, H.J.; Jin, Y.Y.; Yang, S.H.; Suh, J.W. Green Coffee Bean Extract Improves Obesity by Decreasing Body Fat in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice. Asian Pac J Trop Med 2016, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seliem, E.M.; Azab, M.E.; Ismail, R.S.; Nafeaa, A.A.; Alotaibi, B.S.; Negm, W.A. Green Coffee Bean Extract Normalize Obesity-Induced Alterations of Metabolic Parameters in Rats by Upregulating Adiponectin and GLUT4 Levels and Reducing RBP-4 and HOMA-IR. Life 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pamplona Mosimann, A.L.; Wilhelm-Filho, D.; Da Silva, E.L. Aqueous Extract of Ilex Paraguariensis Attenuates the Progression of Atherosclerosis in Cholesterol-Fed Rabbits. BioFactors 2006, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, J.; Choi, Y.; Park, T. Ilex Paraguariensis Extract Ameliorates Obesity Induced by High-Fat Diet: Potential Role of AMPK in the Visceral Adipose Tissue. Arch Biochem Biophys 2008, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, N.D.S.; Franco, J.G.; Peixoto-Silva, N.; Maia, L.A.; Kaezer, A.; Felzenszwalb, I.; De Oliveira, E.; De Moura, E.G.; Lisboa, P.C. Ilex Paraguariensis (Yerba Mate) Improves Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders in Obese Rats Primed by Early Weaning. Eur J Nutr 2014, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gugliucci, A.; Bastos, D.H.M.; Schulze, J.; Souza, M.F.F. Caffeic and Chlorogenic Acids in Ilex Paraguariensis Extracts Are the Main Inhibitors of AGE Generation by Methylglyoxal in Model Proteins. Fitoterapia 2009, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.Y.; Oh, M.R.; Kim, M.G.; Chae, H.J.; Chae, S.W. Anti-Obesity Effects of Yerba Mate (Ilex Paraguariensis): A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. BMC Complement Altern Med 2015, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.J.; Kwon, E.Y.; Kim, J.W.; Lee, Y.; Ryu, R.; Yun, J.; Kim, M.; Choi, M.S. Intervention Study on the Efficacy and Safety of Platycodon Grandiflorus Ethanol Extract in Overweight or Moderately Obese Adults: A Single-Center, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reguero, M.; de Cedrón, M.G.; Reglero, G.; Quintela, J.C.; de Molina, A.R. Natural Extracts to Augment Energy Expenditure as a Complementary Approach to Tackle Obesity and Associated Metabolic Alterations. Biomolecules 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabrouki, L.; Rjeibi, I.; Taleb, J.; Zourgui, L. Cardiac Ameliorative Effect of Moringa Oleifera Leaf Extract in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity in Rat Model. Biomed Res Int 2020, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, G.D.; Lira, F.S.; Rosa, J.C.; Caris, A. V.; Pinheiro, F.; Ribeiro, E.B.; Oller do Nascimento, C.M.; Oyama, L.M. Yerba Mate Extract (Ilex Paraguariensis) Attenuates Both Central and Peripheral Inflammatory Effects of Diet-Induced Obesity in Rats. Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry 2013, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, Y.L.; Shibu, M.A.; Lii, C.K.; Viswanadha, V.P.; Lin, Y.L.; Lai, C.H.; Chen, Y.F.; Lin, K.H.; Kuo, W.W.; Huang, C.Y. Andrographis Paniculata Extract Attenuates Pathological Cardiac Hypertrophy and Apoptosis in High-Fat Diet Fed Mice. J Ethnopharmacol 2016, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikora, J.; Markowicz-Piasecka, M.; Broncel, M.; Mikiciuk-Olasik, E. Extract of Aronia Melanocarpa-Modified Hemostasis: In Vitro Studies. Eur J Nutr 2014, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikora, J.; Broncel, M.; Markowicz, M.; Chałubiński, M.; Wojdan, K.; Mikiciuk-Olasik, E. Short-Term Supplementation with Aronia Melanocarpa Extract Improves Platelet Aggregation, Clotting, and Fibrinolysis in Patients with Metabolic Syndrome. Eur J Nutr 2012, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allison, G.L.; Lowe, G.M.; Rahman, K. Aged Garlic Extract Inhibits Platelet Activation by Increasing Intracellular CAMP and Reducing the Interaction of GPIIb/IIIa Receptor with Fibrinogen. Life Sci 2012, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Luo, Z.; Liu, X.; Fu, L.; Xu, Y.; Wu, L.; Shen, X. Effect of Ginkgo Biloba Extract on Experimental Cardiac Remodeling. BMC Complement Altern Med 2015, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caro-Gómez, E.; Sierra, J.A.; Escobar, J.S.; Álvarez-Quintero, R.; Naranjo, M.; Medina, S.; Velásquez-Mejía, E.P.; Tabares-Guevara, J.H.; Jaramillo, J.C.; León-Varela, Y.M.; et al. Green Coffee Extract Improves Cardiometabolic Parameters and Modulates Gut Microbiota in High-Fat-Diet-Fed ApoE -/- Mice. Nutrients 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diez-Echave, P.; Vezza, T.; Rodríguez-Nogales, A.; Ruiz-Malagón, A.J.; Hidalgo-García, L.; Garrido-Mesa, J.; Molina-Tijeras, J.A.; Romero, M.; Robles-Vera, I.; Pimentel-Moral, S.; et al. The Prebiotic Properties of Hibiscus Sabdariffa Extract Contribute to the Beneficial Effects in Diet-Induced Obesity in Mice. Food Research International 2020, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evseeva, M.N.; Balashova, M.S.; Kulebyakin, K.Y.; Rubtsov, Y.P. Adipocyte Biology from the Perspective of in Vivo Research: Review of Key Transcription Factors. Int J Mol Sci 2022, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Mao, S.; Chen, S.; Zhang, W.; Liu, C. Ppars-Orchestrated Metabolic Homeostasis in the Adipose Tissue. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savova, M.S.; Mihaylova, L. V.; Tews, D.; Wabitsch, M.; Georgiev, M.I. Targeting PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway in Obesity. Biomedicine and Pharmacotherapy 2023, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, B.; Serpell, C.J.; Fong, I.L.; Wong, E.H. Molecular Mechanisms of Adipogenesis: The Anti-Adipogenic Role of AMP-Activated Protein Kinase. Front Mol Biosci 2020, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.H.; Jegal, J.; Kim, Y.N.; Heo, J.D.; Rho, J.R.; Yang, M.H.; Jeong, E.J. Chokeberry Extract and Its Active Polyphenols Suppress Adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes and Modulates Fat Accumulation and Insulin Resistance in Diet-Induced Obese Mice. Nutrients 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, J.; Ahn, S.H.; Zhou, X.; Lim, Y.J.; Hong, S.; Kim, H.S. Effects of Cinnamon (Cinnamomum Zeylanicum) Extract on Adipocyte Differentiation in 3T3-L1 Cells and Lipid Accumulation in Mice Fed a High-Fat Diet. Nutrients 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.L.; Jeon, Y.D.; Park, J.; Rim, H.K.; Jeong, M.Y.; Lim, H.; Ko, S.G.; Jang, H.J.; Lee, B.C.; Lee, K.T.; et al. Corni Fructus Containing Formulation Attenuates Weight Gain in Mice with Diet-Induced Obesity and Regulates Adipogenesis through AMPK. Evidence-based Complementary and Alternative Medicine 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.K.; So, H.; Youn, M.J.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, Y.; Park, C.; Kim, S.J.; Ha, Y.A.; Chai, K.Y.; Kim, S.M.; et al. Hibiscus Sabdariffa L. Water Extract Inhibits the Adipocyte Differentiation through the PI3-K and MAPK Pathway. J Ethnopharmacol 2007, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, M.; Gao, M.; Hayashi, M.; Kobayashi, Y.; Yang, J.; Liu, T. Ilex Paraguariensis A.St.-Hil. Improves Lipid Metabolism in High-Fat Diet-Fed Obese Rats and Suppresses Intracellular Lipid Accumulation in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes via the AMPK-Dependent and Insulin Signaling Pathways. Food Nutr Res 2024, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Héliès-Toussaint, C.; Fouché, E.; Naud, N.; Blas-Y-Estrada, F.; del Socorro Santos-Diaz, M.; Nègre-Salvayre, A.; Barba de la Rosa, A.P.; Guéraud, F. Opuntia Cladode Powders Inhibit Adipogenesis in 3 T3-F442A Adipocytes and a High-Fat-Diet Rat Model by Modifying Metabolic Parameters and Favouring Faecal Fat Excretion. BMC Complement Med Ther 2020, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.S.; Yoon, Y.; Ahn, H.S. Platycodon Grandiflorum Extract Represses Up-Regulated Adipocyte Fatty Acid Binding Protein Triggered by a High Fat Feeding in Obese Rats. World J Gastroenterol 2007, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezenwaka, C.E.; Okoye, O.; Esonwune, C.; Onuoha, P.; Dioka, C.; Osuji, C.; Oguejiofor, C.; Meludu, S. High Prevalence of Abdominal Obesity Increases the Risk of the Metabolic Syndrome in Nigerian Type 2 Diabetes Patients: Using the International Diabetes Federation Worldwide Definition. Metab Syndr Relat Disord 2014, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Joo, H.; Kim, C.T.; Kim, I.H.; Kim, Y. High Hydrostatic Pressure Extract of Garlic Increases the HDL Cholesterol Level via Up-Regulation of Apolipoprotein A-I Gene Expression in Rats Fed a High-Fat Diet. Lipids Health Dis 2012, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannel, W.B. Prevalence and Natural History of Electrocardiographic Left Ventricular Hypertrophy. Am J Med 1983, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, M.C.L.; Lima, L.N.; Cota, L.H.T.; Costa, M.B.; Orsi, P.M.E.; Espíndola, R.P.; Albanez, A. V.; Rosa, B.B.; Carvalho, M.G.S.; Garcia, J.A.D. Effect of Camellia Sinensis Teas on Left Ventricular Hypertrophy and Insulin Resistance in Dyslipidemic Mice. Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research 2020, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamani, M.; Kelishadi, M.R.; Ashtary-Larky, D.; Amirani, N.; Goudarzi, K.; Torki, I.A.; Bagheri, R.; Ghanavati, M.; Asbaghi, O. The Effects of Green Tea Supplementation on Cardiovascular Risk Factors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front Nutr 2023, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balzan, S.; Hernandes, A.; Reichert, C.L.; Donaduzzi, C.; Pires, V.A.; Gasparotto, A.; Cardozo, E.L. Lipid-Lowering Effects of Standardized Extracts of Ilex Paraguariensis in High-Fat-Diet Rats. Fitoterapia 2013, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Long, Y.; Jiang, X.; Liu, Z.; Wang, D.; Zhao, Y.; Li, D.; Sun, B. liang Beneficial Effects of Yerba Mate Tea (Ilex Paraguariensis) on Hyperlipidemia in High-Fat-Fed Hamsters. Exp Gerontol 2013, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boaventura, B.C.B.; Di Pietro, P.F.; Stefanuto, A.; Klein, G.A.; de Morais, E.C.; de Andrade, F.; Wazlawik, E.; da Silva, E.L. Association of Mate Tea (Ilex Paraguariensis) Intake and Dietary Intervention and Effects on Oxidative Stress Biomarkers of Dyslipidemic Subjects. Nutrition 2012, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masson, W.; Barbagelata, L.; Lobo, M.; Nogueira, J.P.; Corral, P.; Lavalle-Cobo, A. Effect of Yerba Mate (Ilex Paraguariensis) on Lipid Levels: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Plant Foods for Human Nutrition 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandrasekaran, P.; Weiskirchen, R. The Role of Obesity in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus—An Overview. Int J Mol Sci 2024, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudhakara, G.; Mallaiah, P.; Sreenivasulu, N.; Sasi Bhusana Rao, B.; Rajendran, R.; Saralakumari, D. Beneficial Effects of Hydro-Alcoholic Extract of Caralluma Fimbriata against High-Fat Diet-Induced Insulin Resistance and Oxidative Stress in Wistar Male Rats. J Physiol Biochem 2014, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drissi, F.; Lahfa, F.; Gonzalez, T.; Peiretti, F.; Tanti, J.F.; Haddad, M.; Fabre, N.; Govers, R. A Citrullus Colocynthis Fruit Extract Acutely Enhances Insulin-Induced GLUT4 Translocation and Glucose Uptake in Adipocytes by Increasing PKB Phosphorylation. J Ethnopharmacol 2021, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Kim, B.H.; Kim, Y.C. Antioxidative Action of Corni Fructus Aqueous Extract on Kidneys of Diabetic Mice. Toxicol Res 2011, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalili-Moghadam, S.; Hedayati, M.; Golzarand, M.; Mirmiran, P. Effects of Green Coffee Aqueous Extract Supplementation on Glycemic Indices, Lipid Profile, CRP, and Malondialdehyde in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Front Nutr 2023, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.H.; Chyau, C.C.; Chan, K.C.; Chan, T.H.; Wang, C.J.; Huang, C.N. Hibiscus Sabdariffa Polyphenolic Extract Inhibits Hyperglycemia, Hyperlipidemia, and Glycation-Oxidative Stress While Improving Insulin Resistance. J Agric Food Chem 2011, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leem, K.H.; Kim, M.G.; Hahm, Y.T.; Kim, H.K. Hypoglycemic Effect of Opuntia Ficus-Indica Var. Saboten Is Due to Enhanced Peripheral Glucose Uptake through Activation of AMPK/P38 MAPK Pathway. Nutrients 2016, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, J.E.; Do Carmo, J.M.; Da Silva, A.A.; Wang, Z.; Hall, M.E. Obesity-Induced Hypertension: Interaction of Neurohumoral and Renal Mechanisms. Circ Res 2015, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shariq, O.A.; Mckenzie, T.J. Obesity-Related Hypertension: A Review of Pathophysiology, Management, and the Role of Metabolic Surgery. Gland Surg 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valls, R.M.; Companys, J.; Calderón-Pérez, L.; Salamanca, P.; Pla-Pagà, L.; Sandoval-Ramírez, B.A.; Bueno, A.; Puzo, J.; Crescenti, A.; Del Bas, J.M.; et al. Effects of an Optimized Aged Garlic Extract on Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors in Moderate Hypercholesterolemic Subjects: A Randomized, Crossover, Double-Blind, Sustainedand Controlled Study. Nutrients 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.Y.; Tan, B. Hypotensive Activity of Aqueous Extract of Andrographis Paniculata in Rats. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 1996, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, J.; Hires, C.; Baker, C.; Keenan, L.; Bush, M. Daily Supplementation with Aronia Melanocarpa (Chokeberry) Reduces Blood Pressure and Cholesterol: A Meta Analysis of Controlled Clinical Trials. J Diet Suppl 2021, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonello, M.; Montemurro, D.; Bolognesi, M.; Di Pascoli, M.; Piva, A.; Grego, F.; Sticchi, D.; Giuliani, L.; Garbisa, S.; Rossi, G.P. Prevention of Hypertension, Cardiovascular Damage and Endothelial Dysfunction with Green Tea Extracts. Am J Hypertens 2007, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onakpoya, I.; Spencer, E.; Heneghan, C.; Thompson, M. The Effect of Green Tea on Blood Pressure and Lipid Profile: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials. Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases 2014, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogueira, L. de P.; Nogueira Neto, J.F.; Klein, M.R.S.T.; Sanjuliani, A.F. Short-Term Effects of Green Tea on Blood Pressure, Endothelial Function, and Metabolic Profile in Obese Prehypertensive Women: A Crossover Randomized Clinical Trial. J Am Coll Nutr 2017, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Yuan, X.; Sun, C.; Sun, Y.; Yang, M.; Feng, S.; Yao, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, G.; Li, F. Preparation of a New Component Group of Ginkgo Biloba Leaves and Investigation of the Antihypertensive Effects in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Biomedicine and Pharmacotherapy 2022, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inuwa, I.; Ali, B.H.; Al-Lawati, I.; Beegam, S.; Ziada, A.; Blunden, G. Long-Term Ingestion of Hibiscus Sabdariffa Calyx Extract Enhances Myocardial Capillarization in the Spontaneously Hypertensive Rat. Exp Biol Med 2012, 237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nwachukwu, D.C.; Aneke, E.I.; Obika, L.F.; Nwachukwu, N.Z. Effects of Aqueous Extract of Hibiscus Sabdariffa on the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System of Nigerians with Mild to Moderate Essential Hypertension: A Comparative Study with Lisinopril. Indian J Pharmacol 2015, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abubakar, S.M.; Ukeyima, M.T.; Spencer, J.P.E.; Lovegrove, J.A. Acute Effects of Hibiscus Sabdariffa Calyces on Postprandial Blood Pressure, Vascular Function, Blood Lipids, Biomarkers of Insulin Resistance and Inflammation in Humans. Nutrients 2019, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ignat, M.V.; Coldea, T.E.; Salanță, L.C.; Mudura, E. Plants of the Spontaneous Flora with Beneficial Action in the Management of Diabetes, Hepatic Disorders, and Cardiovascular Disease. Plants 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cesare, M.; McGhie, D.V.; Perel, P.; Mwangi, J.; Taylor, S.; Pervan, B.; Kabudula, C.; Narula, J.; Bixby, H.; Pineiro, D.; et al. The Heart of the World. Glob Heart 2024, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Name of herbs and plants and Method Extraction | Type of Study | Doses and Duration | Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Allium sativum (garlic), high hydrostatic pressure extract | 5-week-old male Sprague-Dawley rats with HFD (45% kcal from fat) |
2% (w/w) of extract for 5 weeks | Decreased in plasma TG and LDL-C levels, increased in HDL-C levels, reduced hepatic TG and TC levels, upregulated hepatic apoA-I, ABCA1, and LCAT gene expression [160] |
| Camellia sinensis, teas (green, red, and white) |
3-month-old male LDLr-/- mice with HFD (20% fat with 1.25% cholesterol, and 0.5% cholic acid) |
25 mg/kg body weight daily for 60 days | Prevented left ventricular hypertrophy, partially prevented hyperlipidemia and insulin resistance, and reduced CRP levels [162] |
| Camellia sinensis, green tea extract (GTE) |
Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials |
Varied dosages, some ≥1000 mg/day, others <1000 mg/day, and durations with subgroup analyses based on ≥12 weeks vs. <12 weeks |
Significant reduced total cholesterol (TC) and LDL-C. Decreased fasting blood sugar, and HbA1c. Small increased HDL-C. Reduced diastolic blood pressure [163] |
| Corni Fructus, extract produced by Tsumura Juntendo Inc. (Tokyo, Japan) |
5-week-old male Wistar rats with a high cholesterol diet (1% cholesterol and 0.5% cholic acid) |
50, 100, and 200 mg/kg/day for 10 days | Lowered blood pressure and serum cholesterol levels. Decreased atherogenic index, increased cholesterol and bile acid excretion. Reduced lipid peroxidation, up-regulated SREBP-2 and PPARα expression, and enhanced fatty acid oxidation [40] |
| Cydonia oblonga (ethanol extract) | Male Sprague Dawley rats (240 ± 20 g) induced with hyperlipidemia | Hyperlipidemia induction for 21 days and then with 40, 80, 160 mg/kg/day for 4 weeks |
Reduced serum TC, TG, LDL-C, ALT, AST, increased HDL-C, reduced MDA, improved SOD and GSH-Px activity in hepatic tissues [45] |
| Ilex paraguariensis (Yerba mate), hydroethanolic extract and n-butanolic fraction | 8-week-old male Wistar rats with HFD (60% kcal from fat) with cholesterol (2%) and cholic acid (0.2%) |
Hyperlipidemia induction for 30 days and then with 200, 400, 800 mg/kg/day for 30 days | Reduced serum TG, cholesterol, and atherogenic index [164] |
| Ilex paraguariensis (Yerba mate), aqueous extract | A systematic review and meta-analysis |
Various doses in included studies | No significant change in TC, LDL-C, HDL-C, and TG levels [167] |
| Ilex paraguariensis (Yerba mate), aqueous extract |
8-week-old male Syrian golden hamsters with HFD (15% lard and 0.2% cholesterol) |
Hyperlipidemia induction for 4 weeks and then with 1%, 2%, and 4% w/v for 4 weeks |
Decreased body weight gain, lowered serum lipid levels, increased antioxidant enzyme activity, improved lipoprotein lipase (LPL) and hepatic lipase (HL) activities, and upregulated PPARα and LDL-C receptor mRNA expression. Reduced SREBP-1c and acetyl CoA carboxylase mRNA expression [165] |
| Ilex paraguariensis (Yerba mate), aqueous extract |
Randomized clinical trial with dyslipidemic individuals | 1 L/day (20 mg/mL) for 90 days | Increased serum antioxidant capacity and GSH, and decreased LDL-C [166] |
| Moringa oleífera (aqueous extract) | Male Wistar rats with HFD (3% fat) | 1 mg/g for 30 days | Decreased cholesterol levels in serum, liver, and kidney. Increased serum albumin [76] |
| Nigella sativa, seed powder, seed oil, and seed (methanolic extract) |
Systematic review of experimental and clinical studies |
Variable treatment time of seed powder (100 mg-20 g daily), seed oil (20-800 mg daily), and seed extract (6, 9, 14, and 21 g/kg) | Reduced TC, LDL-C, and TG. No significant effect on HDL-C [78] |
| Opuntia ficus-indica (aqueous extract) |
Triton-induced hypercholesterolemia in male Balb-c mice |
500 mg/kg in a single administration for 16 hours plus fasting for 8 hours | Significantly decreased cholesterol levels. Inhibited pancreatic lipase with IC50 = 588.5 μg/mL [83] |
| Platycodon grandiflorus (water extract) |
9-week-old male C57BL/6J mice with HFD |
1 g/kg/day for 8 weeks | Reduced body weight gain by 7.5%, improved plasma lipid profiles, decreased leptin, increased adiponectin, downregulated lipogenic gene expression, increased lipolysis gene expression, and inhibited adipogenic transcription factors [88] |
| Platycodon grandiflorus (70% ethanol extract) |
5-week-old male C57BL/6J mice with HFD (40% of fat) |
Dyslipidemia induction for 5 weeks and then with 25 and 75 mg/kg/day for 4 weeks |
Reduced plasma and hepatic lipid levels, upregulated antioxidant proteins, inhibited oxLDL-C-induced cell death and lactate dehydrogenase release, exhibited antioxidant activity in vitro and in vivo [89] |
| Platycodon grandiflorus, extract (water, 50% ethanol, and 80% ethanol) |
L6 muscle cells and 9-weeks-old male ICR mice with HFD (60% kcal from fat) |
1% and 5% extract in diet for 6 weeks | Reduced food intake, body weight, epididymal fat weight, adipocyte size,and blood glucose levels. Maintained serum adiponectin, resistin, leptin, fructosamine, and triglycerides. Upregulated adiponectin mRNA, downregulated TNF-a and leptin mRNA in WAT. In L6 muscle cells increased insulin-stimulated glucose uptake [90] |
| Name of herbs and plants and Method Extraction | Type of Study | Doses and Duration | Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Caralluma fimbriata (hydro-alcoholic extract) |
Male Wistar rats with HFD (60% of fat) |
200 mg/kg/day for 90 days |
Reduced hyperglycemia, hyperinsulinemia, hyperleptinemia, hypertriglyceridemia, oxidative stress, and improved insulin sensitivity [169] |
| Ceylon Cinnamon (hydro-alcoholic extract) |
Pancreatic alpha-amylase activity. 7-week-old male Wistar Han IGS rats. A randomized, placebo-controlled, cross-over clinical trial in healthy subjects |
In vitro: 0-100 µg/ml. In vivo: 6.25, 12.5, 25, 50, 100 mg/kg for 5 weeks. Humans: 1 g of extract (two 500 mg capsules), single dose post-meal |
In vitro: Inhibited pancreatic alpha-amylase (IC50 = 25 μg/mL). In vivo: Reduced glycemic response to starch. Human: Lowered postprandial glycemia by 14.8% (0-120 min) and 21.2% (0-60 min) without increasing insulin secretion [30] |
| Citrullus colocynthis (petroleum ether, water or 80% methanol, ethyl acetate and n-butanol, crude aqueous extracts) | 3T3-L1 adipocytes | 4, 20, or 100 μg/ml for 24, 48, and 96 hours |
Enhanced insulin-induced GLUT4 translocation and glucose uptake, and increased insulin-induced PKB phosphorylation [170]. |
| Citrullus colocynthis (Tablets, Capsules, or Oral Drops) |
Randomized Controlled Clinical Trials | Different doses for 30 to 60 days |
No significant effect on FBS, HbA1c, LDL-C, TC, and TG. Increased HDL-C levels [32] |
| Corni fructus (water extract) | 7-week-old male C57BUKsJ-db/db mice and C57BL/6 mice | 500 mg/kg/day for 8 weeks | Reduced blood glucose levels, improved insulin resistance, and increased glucose utilization [41] |
| Corni fructus (aqueous extract) |
7-week-old male C57BL/KsJ-db/db mice | 500 mg/kg/day for 8 weeks |
Reduced oxidative stress, increased SOD activity, decreased XO, CAT, and GST activities. Lower mRNA expression of eNOS in kidneys [171] |
| Ginkgo biloba (aqueous and 12% ethanol extracts) |
α-amylase and α-glucosidase activities |
10, 25 and 50 mg/ml of Ginkgo leaf extract |
Aqueous extracts had higher total phenolic content but only ethanolic extracts inhibited ACE, strong correlation between total phenolics and α-glucosidase inhibitory activity, and to a lesser degree positive correlation between total phenolics and α-amylase inhibitory activity [50] |
| Ginkgo biloba (EGb761) | RAoSMCs and HUVECs. 5-week-old male Otsuka Long-Evans Tokushima Fatty rats and 5-week-old male ApoE-/- mice |
Obesity and insulin resistance induction for 24 weeks (rats). 2 months all mice with HFD (42% fat, 1.25% cholesterol). All animals with 100 mg/kg and 200 mg/kg for 6 weeks (rats), and for 2 months (mice) |
Reduced intima-media ratio. Induced greater apoptosis in rats, improved glucose homeostasis and increased circulating adiponectin levels, decreased plasma hsCRP concentrations. In vitro: Decreased VSMC proliferation and migration, Increased caspase-3 activity and DNA fragmentation, decreased monocyte adhesion and ICAM-1/VCAM-1 levels. Kaempferol and quercetin: Reduced VSMC migration and increased caspase activity, and protected against atherosclerosis [51] |
| Green Coffee (Coffea), aqueous extract) |
A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial |
400 mg (capsules) twice per day for 10 weeks |
Decreased SBP, TG, hs-CRP, increased HDL-C, and marginally significant reduction in FBG. No significant changes in DBP, LDL-C, TC, insulin levels, HOMA-IR, and MDA [172] |
| Hibiscus sabdariffa, (polyphenolic extract by methanol) | 8-week-old male Sprague-Dawley rats with HFD and STZ |
Type 2 diabetes induction: HFD for 7 weeks and then HFD and STZ for 2 weeks. Doses 100 mg/kg and 200 mg/kg for 7 weeks | Reduced hyperglycemia, hyperinsulinemia, serum TG, cholesterol, and LDL-C/HDL-C ratio. Decreased plasma AGE formation and lipid peroxidation. Inhibited CTGF and RAGE expression in aortic regions. Improved weight loss in diabetic rats [173] |
| Hibiscus sabdariffa (aqueous extract) | α-amylase and α-glucosidase activities | Red and white varieties; IC50 values: 25.2 µg/mL (red) and 47.4 µg/mL (white) for α-glucosidase inhibition; 90.5 µg/mL (white) and 187.9 µg/mL (red) for α-amylase inhibition |
Both varieties inhibited α-amylase and α-glucosidase activities, red variety exhibited higher α-glucosidase inhibitory activity, while the white variety showed higher α-amylase inhibitory activity, strong antioxidant properties, particularly in the red variety [63] |
| Hibiscus sabdariffa (aqueous extract) | 3T3-L1 cells and male Sprague Dawley rats (100-120 g) with HFD | In vitro: 0.1, 0.5, 1 mg/ml. In vivo: 250 and 500 mg/kg/day for 8 weeks | Reduced body weight, food intake, lipid profiles, inflammatory cytokines, lipid peroxidation, serum leptin, insulin, and duodenal glucose absorption. Increased glucose uptake in adipose tissue and muscle, downregulated adipogenic gene expression [62] |
| Ilex paraguariensis (Yerba mate), aqueous extract |
T2DM and pre-diabetes subjects | 330 mL of roasted mate tea 3 times a day for 60 days | T2DM: Significant decrease in fasting glucose, HbA1c, and LDL-C. Pre-diabetes: Significant decrease in LDL-C, non-HDL-C, and TG. Improved glycemic control and lipid profile, reduced risk of coronary disease [70] |
| Moringa oleifera (dry leaf powder) | A double-blind, randomized, placebo controlled, parallel group clinical trial |
2400 mg/day (6 capsules/day) for 12 weeks |
Significant decrease FBG and HbA1c. No significant changes in microbiota, hepatic and renal function markers, or appetite-controlling hormones [77] |
| Opuntia ficus-indica var. saboten (hot water extract) | α-Glucosidase activity. L6 muscle cells. 5-week-old male C57BL/6J db/db mice and their non-diabetic heterozygous littermates (db/-), and 9-week-old male ICR mice |
α-Glucosidase activity (1, 5, 10 mg/ml). L6 muscle cells (1-200 µg/ml). db/db mice (1 and 2 g/kg BW) and db/- mice (1 g/kg BW) for 4 weeks | Inhibited α-glucosidase activity and intestinal glucose absorption. In L6 muscle cells, increased glucose uptake, stimulated AMPK and p38 MAPK phosphorylation, and increased GLUT4. In db/db mice, improved hyperglycemia, hyperinsulinemia, glucose tolerance, and regenerated β-cells [174] |
| Opuntia ficus-indica (cladodes and stem/fruit skin-blend ratio 75/25) hot water extract | Wistar rats either sex weighing 250–350 g |
0.176-176 mg/kg for 180 min and glucose (i.p., 2 g/kg in 5 mL) 30 min after extracts administration | Both extracts lowered blood glucose levels (in doses as low as 6 mg/kg). The blend increased basal plasma insulin levels [85] |
| Punica granatum (methanolic extract) | α-glucosidase activity assay. Zucker diabetic fatty (ZDF) rats and Zucker lean (ZL) rats (14-15 weeks old) |
α-glucosidase activity (200 µl of extract for 5 min). 500 mg/kg body weight, oral in 5% acacia once daily for 2 weeks | Lowered plasma glucose levels in non-fasted ZDF rats, inhibited postprandial hyperglycemia, potent inhibitory effect on α-glucosidase activity (IC50: 1.8 µg/ml) [96] |
| Salvia miltiorrhiza (water extract) | HMEC-1 cells | 10 µg/ml of extract in 30 mM glucose condition for 48 hours | Decreased VEGF mRNA and ROS formation induced by high glucose, and UCP-2 siRNA abolished these effects [100] |
| Salvia miltiorrhiza (different extracts) | Review of preclinical and clinical studies on diabetes and complication |
Not applicable | SM exhibits anti-diabetic activities, including anti-inflammation, anti-oxidation, anti-fibrosis, and anti-apoptosis. Key pathways involved are Wnt/β-catenin, TSP-1/TGF-β1/STAT3, JNK/PI3K/Akt, and others. Main compounds include salvianolic acids and diterpenoid tanshinones [98] |
| Taraxacum officinale (aqueous extract) | α-amylase and α-glucosidase activities |
1, 10, 20, 30 mg/mL | Shade-dried leaves demonstrated potent antidiabetic activity via inhibiting α-amylase and α-glucosidase in a dose-dependent manner [107] |
| Name of herbs and plants and Method Extraction | Type of Study | Doses and Duration | Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Allium sativum (aged black garlic extract) |
Randomized, crossover, double-blind, sustained, and controlled study; individuals with moderate hypercholesterolemia |
250 mg (1.25 mg SAC)/tablet/day ABG for 6 weeks, with 3 weeks of washout |
Significantly decreased DBP, particularly in men with a baseline DBP higher than 75 mm Hg, and improved cardiovascular risk factors [177] |
| Andrographis paniculata (aqueous extract) |
Male SHR and WKY rats, aged 14-15 weeks |
2.8, 1.4, 0.7 g/kg for 13 days |
Lowered SBP in SHR and WKY rats, reduced plasma ACE activity and kidney TBA level in SHR. No significant effect on lung ACE activity [178] |
| Aronia melanocarpa (chokeberry), berry extracts | Meta-analysis of controlled clinical trials; included randomized, placebo-controlled trials |
Daily supplementation for an average of 6-8 weeks | Significantly reduces systolic blood pressure and TC, with stronger effects in adults over the age of 50 years [179] |
| Camellia sinensis (Green tea), green tea extract (GTE) |
Crossover, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial |
3 capsules daily, each containing 500 mg of GTE (260 mg polyphenols per capsule), for 4 weeks with a 2-week washout period between treatments | Significant decrease SBP at 24 hours, daytime, and nighttime in obese prehypertensive women. No significant changes in DBP or other metabolic parameters [182] |
| Camellia sinensis (Green Tea), green tea extract (GTE) | 13-week-old male Sprague-Dawley rats | High dose (700 g/kg/day) or low dose (350 g/kg/day) Ang II dose for 13 days, 6 mg/mL GTE in drinking water | GTE prevented hypertension, left ventricular hypertrophy, vascular remodeling, and endothelial dysfunction induced by high Ang II dose. It blunted increases in oxidative stress markers [180] |
| Camellia sinensis (Green tea), green tea extract (GTE) |
A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials |
Various doses and durations across multiple studies | Green tea epigallocatechins have ACE inhibitor properties. Green tea lowers blood pressure by suppressing NADPH oxidase activity and reducing reactive oxygen species. Some meta-analyses reported beneficial effects on blood vessel dilation and lipid profile [181]. |
| Cocoa (flavanols-rich cocoa extract) | Clinical trial, crossover, randomized, double-blind |
1.4 g of cocoa extract (415 mg flavanols) daily for 4 weeks | Reduced postprandial SBP after daily cocoa extract intake within an energy-restricted diet [36] |
| Ginkgo biloba (Standardized leaf extract, EGb761) |
Male adult Wistar rats (120-160 g), hypertension inducedby L-NAME and hypercholesterolemia induced by 1% cholesterol diet |
100 mg/kg/day orally for 12 weeks | Reduced systolic, diastolic, and mean arterial BP. Improved serum lipid profile, protected against renal injury, reduced renal oxidative stress, nitrosative stress, and inflammation. Decreased renal TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β, and iNOS protein expressions, and increased eNOS protein expression [52] |
| Ginkgo biloba (new component group of Ginkgo biloba leaves, GBLCG), 50% ethanol extract |
Male Wistar rats and spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHRs), 200 ± 20 g |
4.4, 2.2, and 1.1 mg/kg for 120 days | Reduced blood pressure and improved myocardial hypertrophy by promoting NO synthesis and release in endothelial cells, reducing oxidative stress, inhibiting platelet aggregation, and promoting lesion circulation. The hypotensive activity of GBLCG (4.4 mg/kg) was better than Ginkgo biloba extract [183] |
| Coffea (green coffee bean extract, GCE) hot-water extract | Healthy male volunteers (aged 30 to 50 years), with mild hypertension |
46 mg, 93 mg, or 185 mg of GCE daily for 28 days |
Dose-dependent reduction in SBP. Reduction in DBP was also observed [57] |
| Hibiscus sabdariffa (dried calyx and hibiscus anthocyanins), water extract |
12-week-old male SHR | 10%, 15%, and 20% Hibiscus sabdariffa for 10 weeks. 50, 100, and 200 mg/kg red anthocyanin by oral gavage for 5 days |
Hibiscus sabdariffa reduced SBP, DBP, and LV mass; increased myocardial capillary surface area and length density. Red anthocyanin did not significantly reduce the SBP and DBP [184] |
| Hibiscus sabdariffa (aqueous extract) | Wistar, Wistar-Kyoto (WKY), and SHR of about 16 weeks old |
SHR (EC50 = 0.83 ± 0.08 mg/mL), WKY (EC50 = 0.46 ± 0.04 mg/mL), and Wistar rats (EC50 = 0.44 ± 0.08 mg/mL) | Concentration-dependent relaxant effect on mesenteric arteries and reduced L-type calcium current [64] |
| Hibiscus sabdariffa calyces (HSC), aqueous extract of calyces | A randomized, controlled, single-blinded, acute, cross-over trial | 7.5 g HSC in 250 mL Buxton water, at time 0 min followed by a medium fat lunch at 120 min in a random order separated by a two-week washout period | Significant increase in % flow mediated dilatation, non-significant decrease in SBP and DBP, non-significant increase in urinary and plasma NOx, reduced response of serum glucose, plasma insulin, serum triacylglycerol, and CRP levels. Significant improvement in systemic antioxidant response. No significant changes in arterial stiffness [186] |
| Hibiscus sabdariffa (aqueous extract) | Double-blind randomized controlled trial |
150 mg/kg daily for 4 weeks |
Reduced plasma aldosterone, serum ACE, and increased plasma renin activity [185] |
| Nigella sativa (seed), boiled water extract |
Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Healthy male volunteers with mild hypertension | 100 mg and 200 mg twice a day for 8 weeks | Significant reduction in SBP and DBP in a dose-dependent manner. Reduced TC and LDL-C levels [80] |
| Platycodon grandifloras (roots) (aqueous extract) | H9c2 myoblasts. SHRs and WKYs rats (about 300 g) |
1.25, 2.5, 5 µg/µL for in vitro. 100 and 200 mg/kg/day for 50 days for in vivo | Suppressed Ang II-induced IGF-IIR signaling, reduced cardiomyocyte apoptosis, decreased SBP and DBP in SHRs [91] |
| Punica granatum (pomegranate peel), ethanol (95°GL) extract |
Female SHRs (4 and 28 weeks old) | 25 mg/100 g rat for 30 days |
Reduced SBP, coronary ACE activity, oxidative stress, and vascular remodeling in hypertensive female rats [97] |
| Taraxacum officinale (leaves and roots), 70% ethanol extract | ABTS and FRAP. L-NAME-induced hypertensive Wistar rats (150 g to 200 g), both sexes | 500 mg/kg/day for 21 days | Leaves possessed higher polyphenol and flavonoid, free radical scavenging activity, and total antioxidant capacities. Leaves and roots extract significantly increased total antioxidant capacities (kidney and brain tissues) and reduced MDA levels (heart tissue) [106] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





