Submitted:
01 July 2024
Posted:
02 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
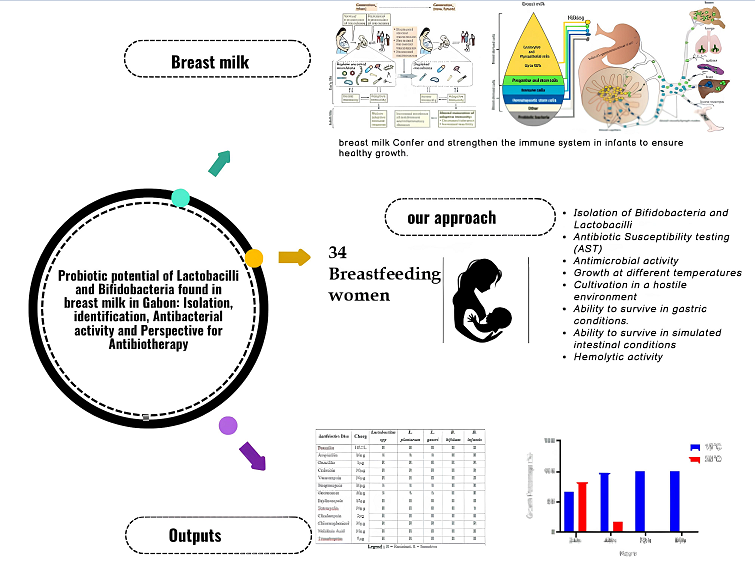
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Socio-Demographic Characteristic of Studied Population
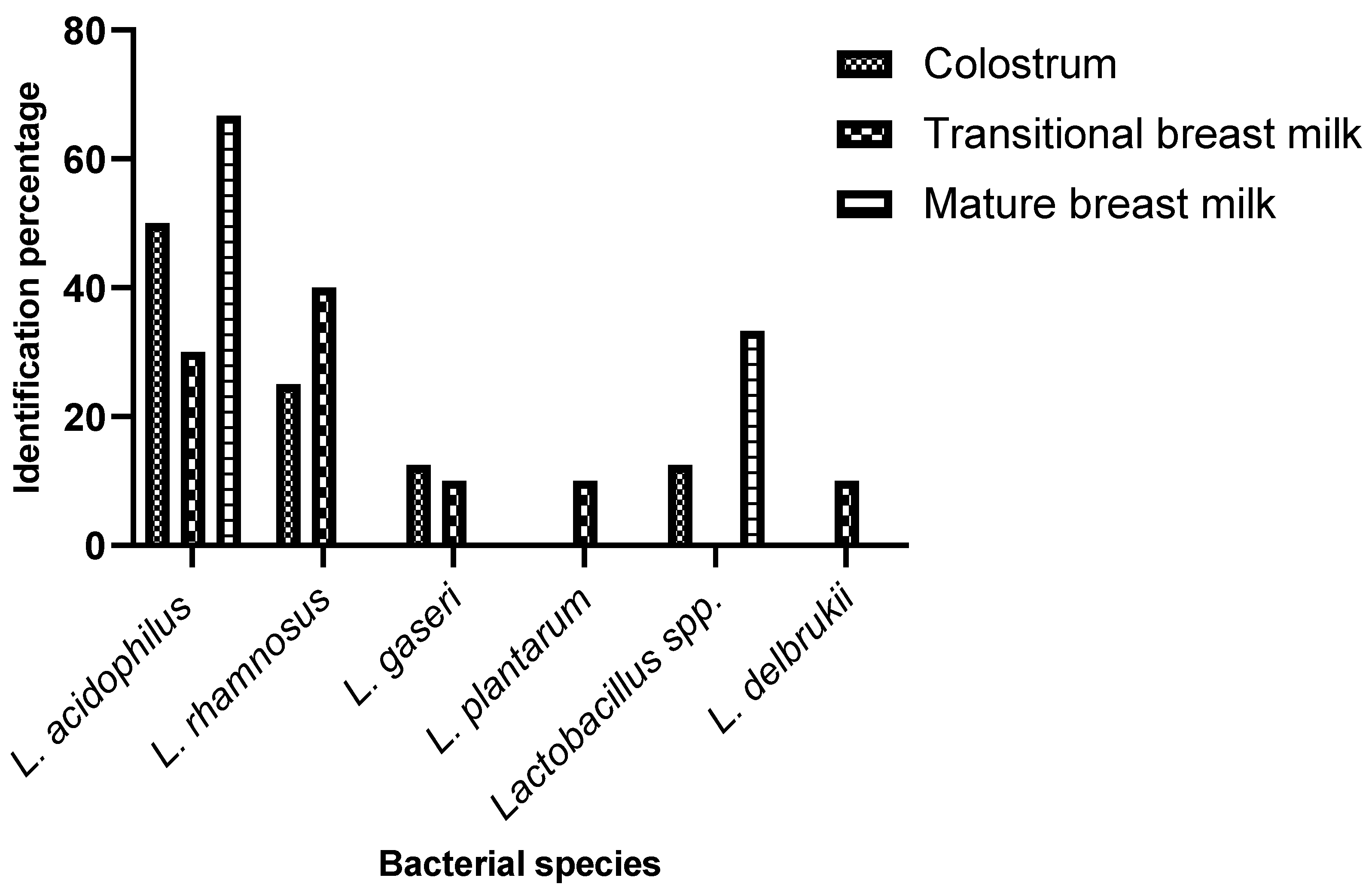
2.2. Isolation and Biochemical and Molecular Identification of Bacterial Species from Milk Samples
2.3. Antimicrobial Sensitivity Testing of Isolated Bacteria
2.4. Evaluation of Probiotic Capacity In Vitro
2.4.1. Antimicrobial Activity
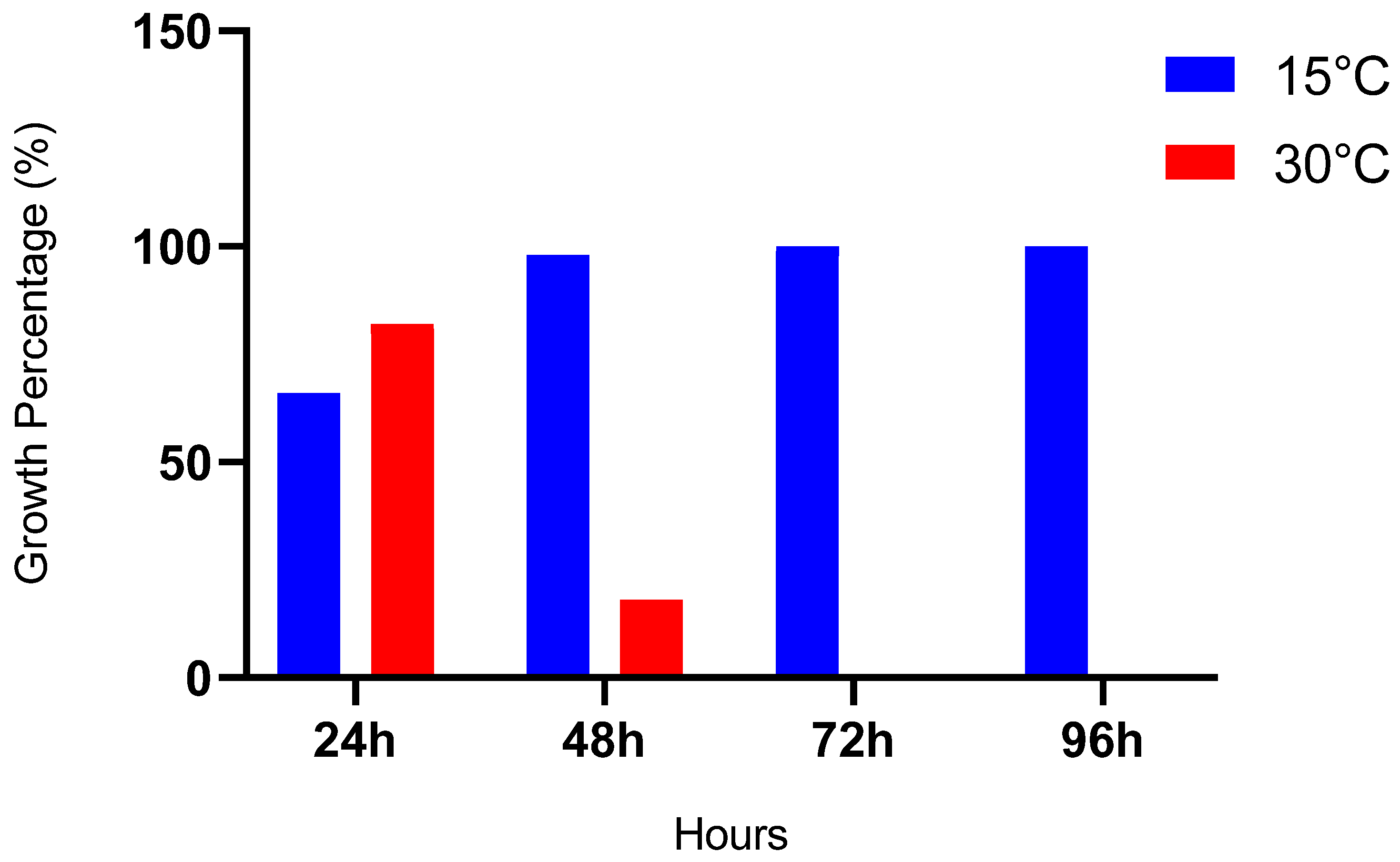
2.4.2. Capacity of Bacteria to Grow in a Range of Temperatures
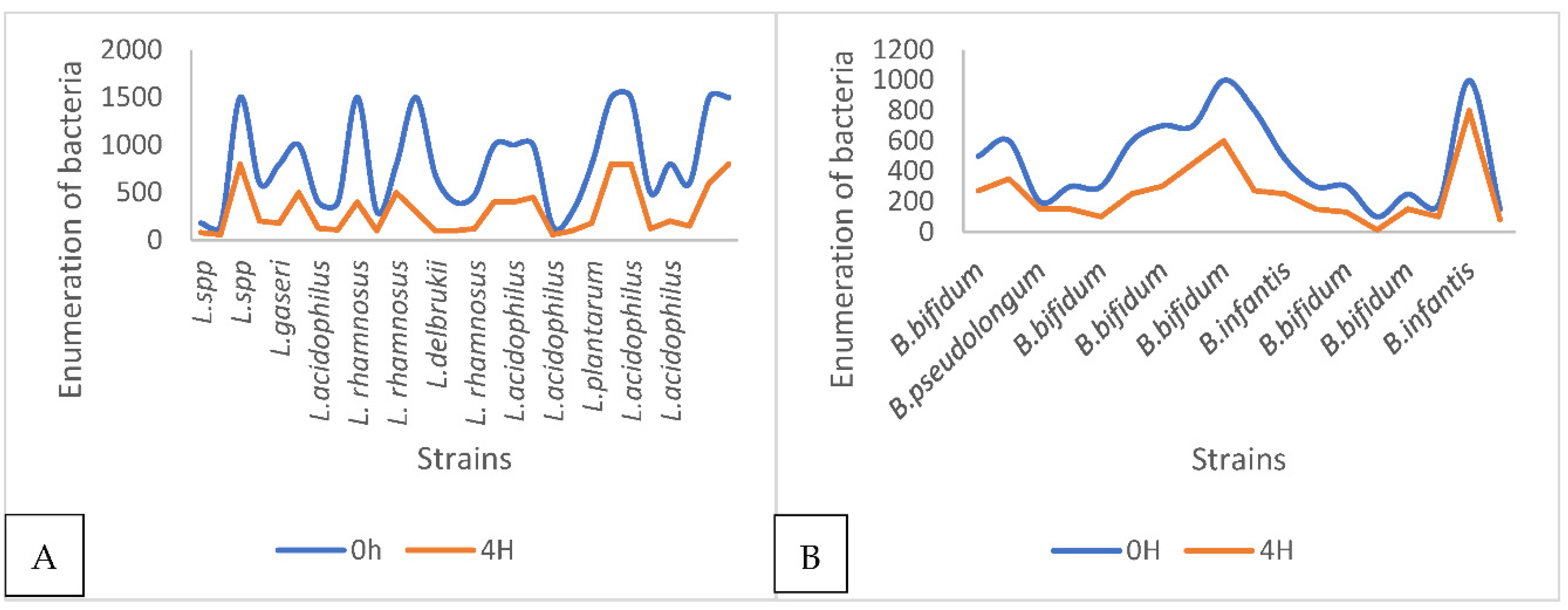
2.4.3. Bacteria's Ability to Grow in a Hostile Environment
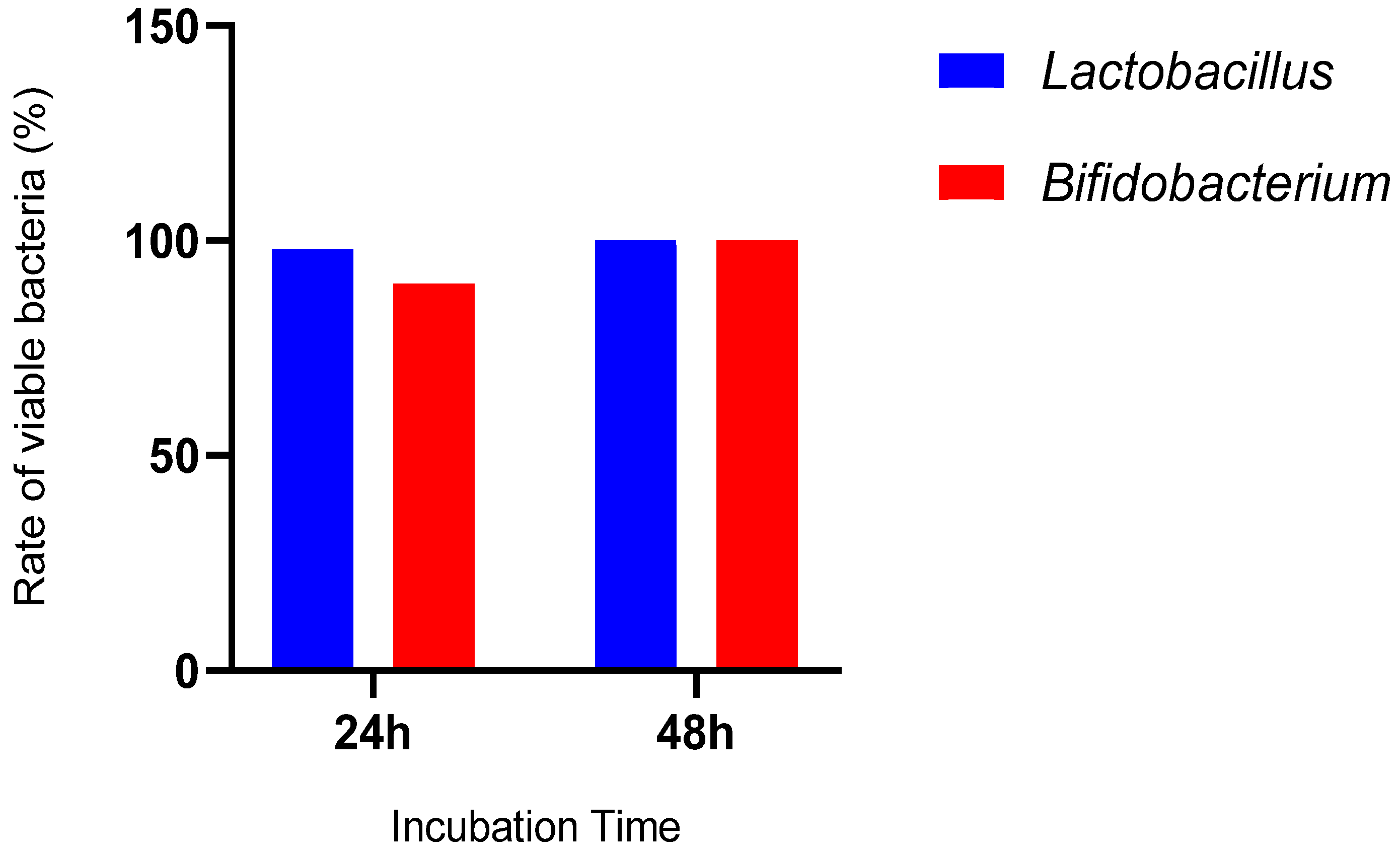
2.4.4. Ability to Survive in Simulated Intestinal Conditions
2.4.5. Ability to Survive in Gastric Conditions in the Presence of Bile Salts
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Biological Material
4.2. Inclusion Criteria
4.3. Methods
4.3.1. Samples Collection
4.3.2. Bacteria Isolation from Breast Milk and Biochemical Identification
4.3.3. Molecular Identification
4.3.4. Antibiotic Susceptibility Testing (AST)
4.3.5. In Vitro Probiotic Capacity of Strains
- Antimicrobial activity
- Growth at different temperatures
- Cultivation in a hostile environment
- Ability to survive in gastric conditions.
- Ability to survive in simulated intestinal conditions
- Hemolytic activity
4.4. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arboleya, S.; Ruas-Madiedo, P.; Margolles, A.; Solís, G.; Salminen, S.; De los Reyes-Gavilan, C.G.; Gueimonde, M. Characterization and in vitro properties of potentially probiotic Bifidobacterium strains isolated from breast-milk. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2011, 149, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, F.; Yu, R.; Feng, X.; Chen, L.; Zeng, Z.; Khaskheli, G.B.; Ma, H.; Chen, S. Characterization and in vitro properties of potential probiotic Bifidobacterium strains isolated from breast-fed infant feces. Ann. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 1027–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortmann, I.; Marißen, J.; Siller, B.; Spiegler, J.; Humberg, A.; Hanke, K.; Faust, K.; Pagel, J.; Eyvazzadeh, L.; Brenner, K. Lactobacillus acidophilus/Bifidobacterium infantis probiotics are beneficial to extremely low gestational age infants fed human milk. Nutrients 2020, 12, 850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Chen, M.; Duo, L.; Wang, J.; Guo, S.; Sun, H.; Menghe, B.; Zhang, H. Characterization of potentially probiotic lactic acid bacteria and bifidobacteria isolated from human colostrum. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 4013–4025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamyuang, C.; Phoonlapdacha, P.; Chongviriyaphan, N.; Chanput, W.; Nitisinprasert, S.; Nakphaichit, M. Characterization and probiotic properties of Lactobacilli from human breast milk. 3 Biotech 2019, 9, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Łubiech, K.; Twarużek, M. Lactobacillus bacteria in breast milk. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oddi, S.; Huber, P.; Duque, A.R.F.; Vinderola, G.; Sivieri, K. Breast-milk derived potential probiotics as strategy for the management of childhood obesity. Food Res. Int. 2020, 137, 109673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Yi, D.Y. Comprehensive analysis of the effect of probiotic intake by the mother on human breast milk and infant fecal microbiota. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2021, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, F.A.; Mehmood, R.; Hussain, S.; Khan, M.A.; Khan, M.S. Lactobacilli as probiotics and their isolation from different sources. Br. J. Res. 2018, 5, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juharji, H.; Albalawi, K.; Aldwaighri, M.; Almalki, A.; Alshiti, H.; Kattan, W.; Alqarni, M.; Alsulaimani, S.; AlShaikh, T.; Alsulaimani, F. Impact of Breastfeeding on Low Birthweight Infants, Weight Disorders in Infants, and Child Development. Cureus 2022, 14, e32894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez Arreola, A.; Solís Pacheco, J.R.; Lacroix, M.; Balcazar López, E.; Navarro Hernández, R.E.; Sandoval Garcia, F.; Gutiérrez Padilla, J.A.; García Morales, E.G.; Aguilar-Uscanga, B.R. In vivo assessment and characterization of lactic acid bacteria with probiotic profile isolated from human milk powder. Nutr. Hosp. 2020, 38, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lokossou, G.A.G.; Kouakanou, L.; Schumacher, A.; Zenclussen, A.C. Human Breast Milk: From Food to Active Immune Response With Disease Protection in Infants and Mothers. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javed, G.A.; Arshad, N.; Munir, A.; Khan, S.Y.; Rasheed, S.; Hussain, I. Signature probiotic and pharmacological attributes of lactic acid bacteria isolated from human breast milk. Int. Dairy J. 2022, 127, 105297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, K.E.; Ryan, C.A.; Dempsey, E.M.; Ross, R.P.; Stanton, C. Breast milk, a source of beneficial microbes and associated benefits for infant health. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunyakti, A.; Asan-Ozusaglam, M. Lactobacillus gasseri from human milk with probiotic potential and some technological properties. LWT 2019, 109, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakwinska, O.; Moine, D.; Delley, M.; Combremont, S.; Rezzonico, E.; Descombes, P.; Vinyes-Pares, G.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, P.; Thakkar, S.K. Microbiota in breast milk of Chinese lactating mothers. PLoS One 2016, 11, e0160856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvamani, S., Dailin, D. J., Gupta, V. K., Wahid, M., Keat, H. C., Natasya, K. H., ... & El Enshasy, H. A. An insight into probiotics bio-route: translocation from the mother’s gut to the mammary gland. Applied Sciences 2021, 11(16), 7247. [CrossRef]
- Chong, H.-Y.; Tan, L.T.-H.; Law, J.W.-F.; Hong, K.-W.; Ratnasingam, V.; Ab Mutalib, N.-S.; Lee, L.-H.; Letchumanan, V. Exploring the potential of human milk and formula milk on infants’ gut and health. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moossavi, S.; Azad, M.B. Origins of human milk microbiota: new evidence and arising questions. GutMicrobes 2020, 12, 1667722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, F.; Eshaghi, M.; Razavi, S.; Sarokhalil, D.D.; Talebi, M.; Pourshafie, M.R. Characterization of bacteriocin production in Lactobacillus spp. isolated from mother’s milk. Microb. Pathog. 2018, 118, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amadoro, C.; Rossi, F.; Pallotta, M.L.; Gasperi, M.; Colavita, G. Traditional dairy products can supply beneficial microorganisms able to survive in the gastrointestinal tract. LWT 2018, 93, 376–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokryazdan, P.; Faseleh Jahromi, M.; Liang, J.B.; Ho, Y.W. Probiotics: From Isolation to Application. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2017, 36, 666–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Alessandro, M.; Parolin, C.; Patrignani, S.; Sottile, G.; Antonazzo, P.; Vitali, B.; Lanciotti, R.; Patrignani, F. Human Breast Milk: A Source of Potential Probiotic Candidates. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolopoulou, G.; Tsironi, T.; Halvatsiotis, P.; Petropoulou, E.; Genaris, N.; Vougiouklaki, D.; Antonopoulos, D.; Thomas, A.; Tsilia, A.; Batrinou, A. Analysis of the Major Probiotics in Healthy Women’s Breast Milk by Realtime PCR. Factors Affecting the Presence of Those Bacteria. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 9400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajoka, M.S.R.; Mehwish, H.M.; Siddiq, M.; Haobin, Z.; Zhu, J.; Yan, L.; Shao, D.; Xu, X.; Shi, J. Identification, characterization, and probiotic potential of Lactobacillus rhamnosus isolated from human milk. LWT 2017, 84, 271–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zacarías, M.F.; Binetti, A.; Laco, M.; Reinheimer, J.; Vinderola, G. Preliminary technological and potential probiotic characterisation of bifidobacteria isolated from breast milk for use in dairy products. Int. Dairy J. 2011, 21, 548–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehanna, N.S.; Tawfik, N.F.; Salem, M.M.; Effat, B.A.; Gad El-Rab, D.A. Assessment of potential probiotic bacteria isolated from breast milk. Middle-East J. Sci. Res. 2013, 14, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza Rodrigues, J.Z.; Passos, M.R.; de Macêdo Neres, N.S.; Almeida, R.S.; Pita, L.S.; Santos, I.A.; Silveira, P.H.S.; Reis, M.M.; Santos, I.P.; Ricardo, L. de O.N. Antimicrobial activity of Lactobacillus fermentum TcUESC01 against Streptococcus mutans UA159. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 142, 104063. [CrossRef]
- Talhi-Mekhici, M.; Cornu, B.; Talhi-Mehaya, R.; Sahraoui, D.; Dib, W.; Yazi, L.A.; Zemmour, A.; Nadjia, S.-O.; Kacem, M.; Vander Wauven, C. Phenotypic and Genotypic Identification of Bacteria from Women Breast-Milk and the Feces of their Childs in the Western Region of Algeria. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 2017, 11, 1767–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thongaram, T.; Hoeflinger, J.L.; Chow, J.; Miller, M.J. Human milk oligosaccharide consumption by probiotic and human-associated bifidobacteria and lactobacilli. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 7825–7833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tušar, T.; Žerdoner, K.; Bogovič Matijašić, B.; Paveljšek, D.; Benedik, E.; Bratanič, B.; Fidler, N.; Rogelj, I. Cultivable bacteria from milk from Slovenian breastfeeding mothers. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2014, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blessing, E.N.; Chukwuemeka, I.S.; Ukeachu, C.D.; Onuawuchi, U.G. Antibacterial properties of probiotics bacterial isolated from human breast milk. World News Nat. Sci. 2020, 29, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toscano, M.; De Grandi, R.; Grossi, E.; Drago, L. Role of the human breast milk-associated microbiota on the newborns’ immune system: a mini review. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 296917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisano, M.B.; Viale, S.; Conti, S.; Fadda, M.E.; Deplano, M.; Melis, M.P.; Deiana, M.; Cosentino, S. Preliminary evaluation of probiotic properties of Lactobacillus strains isolated from Sardinian dairy products. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014. [CrossRef]
- Manini, F.; Casiraghi, M.C.; Poutanen, K.; Brasca, M.; Erba, D.; Plumed-Ferrer, C. Characterization of lactic acid bacteria isolated from wheat bran sourdough. LWT 2016, 66, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadadji, M. Caractérisation Microbiologique et Biochimique des Bifidobactéries isolées à partir des selles de nourrissons: Etude des critères Technologiques et Thérapeutiques. 2007. [CrossRef]
- Abhijit, C.; Nur, H.; Nure, J.; Mostazir, F.; Morsaline, B.; Monzur, M.A. Screening of Lactobacillus spp. From Buffalo Yoghurt for Probiotic and Antibacterial Activity. J. Bacteriol. Parasitol. 2012, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahri, F.; Lejeune, A.; Dubois-Dauphin, R.; El Mejdoub, T.; Boulahrouf, A.; Thonart, P. Characterization of Lactobacillus strains isolated from Algerian children faeces for their probiotic properties. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2014, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
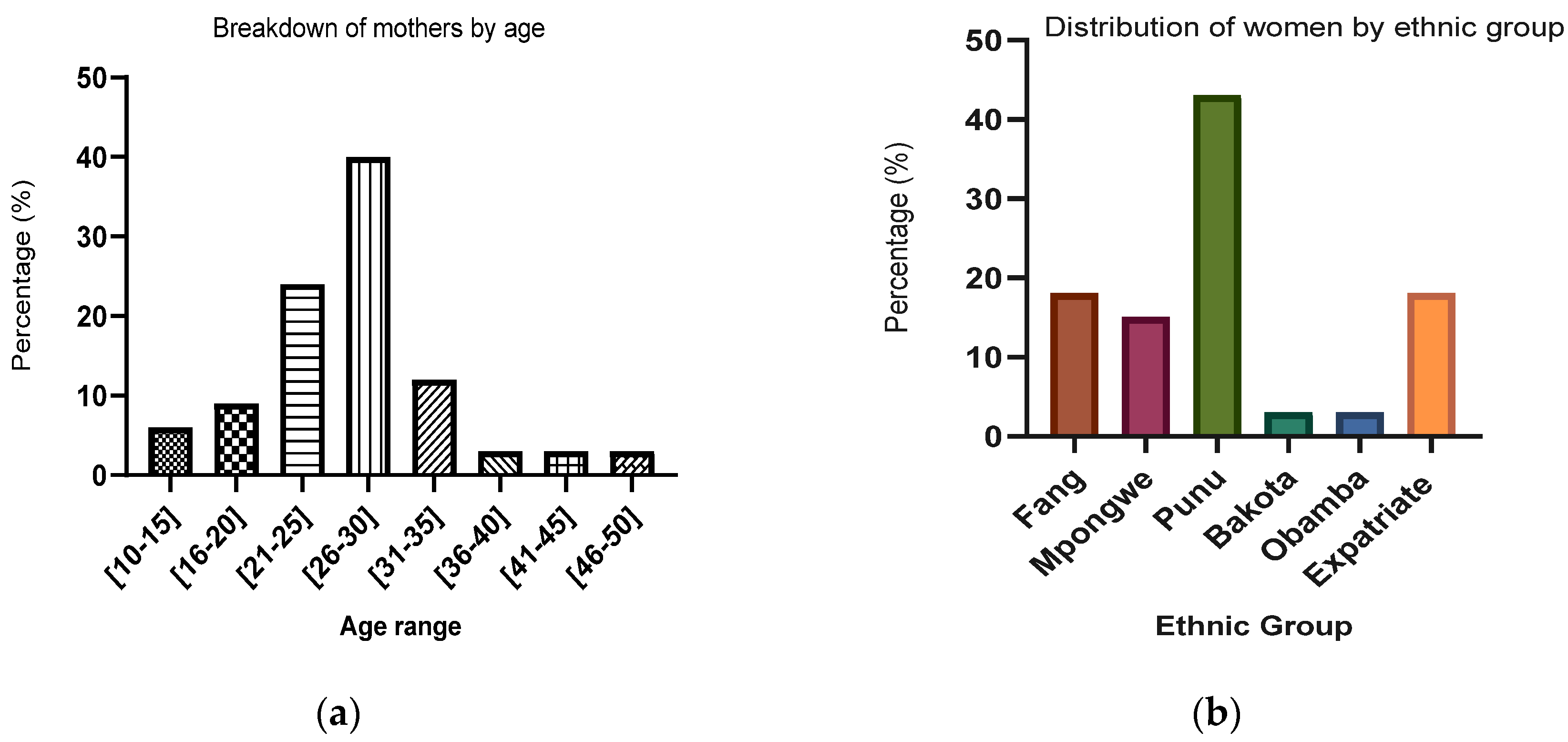
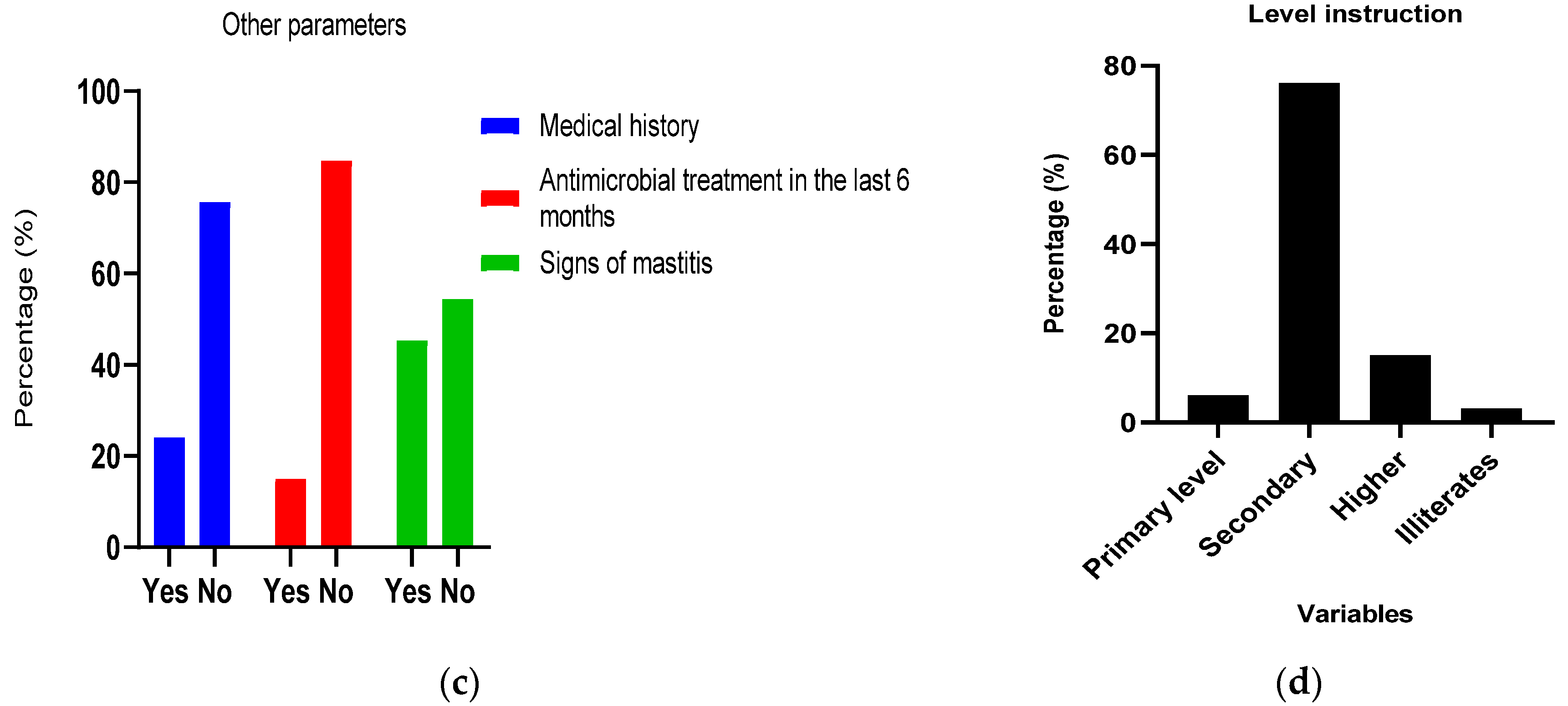
| Parameters | Good Knowledge % | Bad Knowledge % |
|---|---|---|
| Composition of breast milk | 50 | 50 |
| Digestion of breast milk | 80 | 20 |
| Antibodies in breast milk | 90 | 10 |
| Allergies | 40 | 60 |
| Protective role of breast milk | 65 | 35 |
| Benefits of breast milk for babies | 90 | 10 |
| Improvement of the immune system | 50 | 50 |
| Duration of exclusive breastfeeding | 66.66 | 33.33 |
| Lactobacillus | Bifidobacteria | |||||
| Colostrum n=9 |
Transitional breast milk n=12 |
Mature breast milk n=7 |
Colostrum n=5 |
Transitionall breast milk n=10 |
Mature breast Milk n=6 |
|
| L. acidophilus | 50% | 30% | 66,70% | - | - | - |
| L. rhamnosus | 25% | 40% | - | - | - | - |
| L. gaseri | 12,5% | 10% | - | - | - | - |
| Lactobacillus spp | 12,5% | - | 33,33% | - | - | - |
| L. plantarum | - | 10% | - | - | - | - |
| L. delbrukii | - | 10% | - | - | - | - |
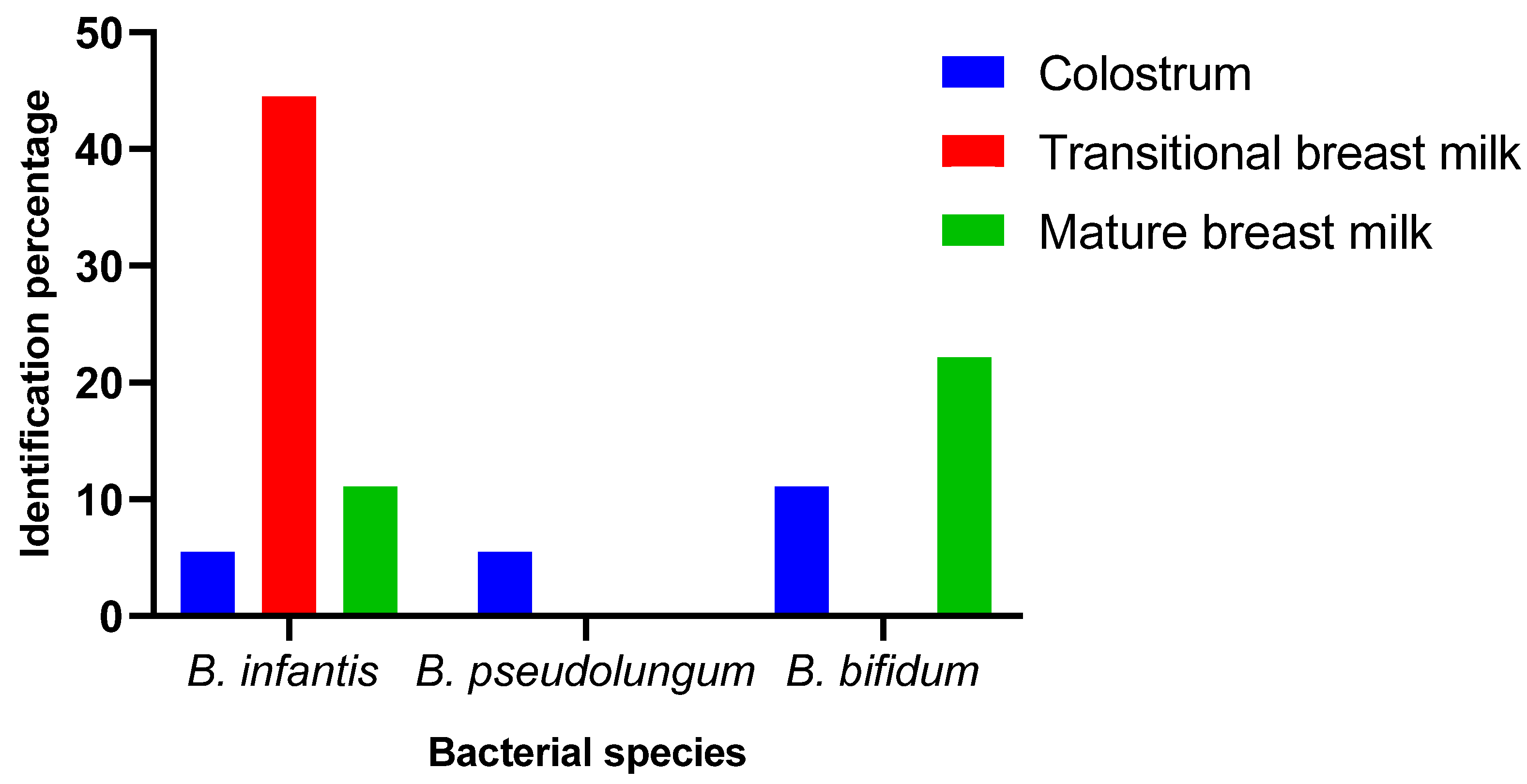
| B. infantis | - | - | - | 5,5% | 44,5% | 11,1% |
| B. pseudolungum | - | - | - | 5,5% | - | - |
| B. bifidum | - | - | - | 11,1% | - | 22,2% |
| Antibiotics Disc | Charge | Lactobacillusspp |
L. plantarum |
L. gaseri |
B. bifidum |
B. infantis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Penicilin | 10U/L | R | R | R | R | R |
| Ampicillin | 10µg | S | S | S | R | R |
| Oxacillin | 1µg | R | R | R | R | R |
| Cefoxitin | 30µg | R | R | R | R | R |
| Vancomycin | 30µg | R | R | R | R | R |
| Streptomycin | 10µg | S | S | S | R | R |
| Gentamicin | 10µg | S | S | S | R | R |
| Erythromycin | 15µg | R | R | R | R | R |
| Tetracyclin | 30µg | R | R | R | R | S |
| Clindamycin | 2µg | R | R | R | R | R |
| Chloramphenicol | 30µg | R | R | R | R | R |
| Nalidixic Acid | 30µg | R | R | R | R | R |
| Trimetroprim | 5µg | R | R | R | R | R |
| Inhibition diameter (mm) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Bacteria Strains | P1=Salmonella typhimurium | P2=Staphylococcus aureus |
Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 |
| L. gaseri | 8 | 8 | 8 |
| CFS L. gaseri | 0 | 6 | 0 |
| Lactobacillus spp | 8 | 8 | 8 |
| CFS Lactobacillus. spp | 0 | 6 | 0 |
| L. plantarum | 8 | 10 | 8 |
| CFS L. plantarum | 0 | 7 | 0 |
| B. infantis | 10 | 10 | 10 |
| CFS B. infantis | 0 | 6 | 0 |
| B. bifidum | 11 | 12 | 10 |
| CFS B. bifidum | 0 | 7 | 0 |
| Bacterial species | Primers | Sequences (5’ to 3’) | Size (pb) |
|---|---|---|---|
| All Lactobacillus | IDL03R | CCACCTTCCTCCGGTTTGTCA | - |
| All Lactobacillus | IDL04F | AGGGTGAAGTCGTAACAAGTAGCC | - |
| Lactobacillus casei | IDL11F | TGGTCGGCAGAGTAACTGTTGTCG | 727 |
| Lactobacillus acidophilus | IDL22R | AACTATCGCTTACGCTACCACTTTGC | 606 |
| Lactobacillus delbrueckii | IDL31F | CTGTGCTACACCTAGAGATAGGTGG | 184 |
| Lactobacillus gasseri | IDL42R | ATTTCAAGTTGAGTCTCTCTCTC | 272 |
| Lactobacillus reuteri | IDL52F | ACCTGATTGACGATGGATCACCAGT | 1105 |
| Lactobacillus plantarum | IDL62R | CTAGTGGTAACAGTTGATTAAAACTGC | 428 |
| Lactobacillus rhamnosus | IDL73R | GCCAACAAGCTATGTGTTCGCTTGC | 448 |
| Bifidobacterium | lm26-f | GATTCTGGCTCAGGATGAACG | - |
| Bifidobacterium | lm3-r | CGGGTGCTCCCACTTTCATG | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




