1. Introduction
Infections caused by microorganisms represent a significant threat to public health, accounting for more than 400 million life years lost annually worldwide [
1]. The emergence of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) by bacteria and fungi is a major global concern, with significant repercussions on both health systems and the countries’ economies. Tuberculosis (TB) presents significant antimicrobial resistance due to its prolonged treatment regimen, ranging from 6 (susceptible cases) to 9 or more months (multidrug-resistant, MDR cases); as well as associated side effects. These factors have led to problems with adherence and treatment follow-up, increasing the number of MDR-TB and extremely resistant TB (XDR) strains. Although MDR and XDR-TB can be treated with second-line drugs, these are expensive and can lead to adverse effects [
2].
Conventional antimicrobials are facing increasing challenges due to the emergence of resistant strains, driving the need to search for therapeutic alternatives. This effort to find new treatment options has sparked substantial interest in the use of nanotechnology and the incorporation of natural products, given their promising antimicrobial capacity.
One of the most abundant and studied biopolymers is chitosan, which has been widely used in the pharmaceutical field due to its biocompatibility and biodegradability, in addition to showing antimicrobial activity against various microorganisms. In recent years it has been reported by different researchers that nanostructured chitosan exhibits improved physical and chemical properties compared to its pure form, due to its high surface area, porosity and mechanical properties [
3]. It was shown that chitosan nanoparticles (CNP) forms complexes with Mn
2+, Zn
2+, Cu
2+ and Ag
+; process that significantly enhanced its antibacterial activity against
Staphylococcus aureus,
Salmonella enterica serotype Choleraesuis and
Escherichia coli [
4,
7]. Antimicrobial activity of low molecular weight CNP at neutral pH against
Streptoccocus mutans and fungicidal effects are mainly related to the interaction of positively charged chitosan with the negatively charged cell wall or membrane [
8,
9,
10,
11].
Similarly, the antibacterial capacity of chitosan nanoformulations against
Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB) strains functioning as a drug delivery system has been reported to improve both their efficacy and administration [
12,
13]. Furthermore, CNP have been shown to possess intrinsic antimycobacterial properties, suggesting the potential of chitosan as a source compound for future antimycobacterial drug development [
14].
Natural extracts derived from plants, herbs, and other biological sources have long been recognized for their diverse therapeutic properties, including antimicrobial activity. In the last decade, there has been a remarkable increase in the acceptance and interest in therapies that are based on natural products, both in developing and developed countries. because the use of such products is often more economical and has a lower incidence of side effects compared to synthetic drugs [
15,
16].
Allium sativum, popularly known as garlic, has been reported to exhibit various pharmacological properties. According to traditional medical practices of Ayurvedic and Greek medicine, garlic has been recognized as one of the established remedies for tuberculosis [
17]. Furthermore, it has been reported that the whole extract of
Allium sativum exhibits superior antimicrobial activity against Mtb H37Rv strain compared to standard drugs (isoniazid, rifampicin, and ethambutol) which makes it a formidable contender for its further development as an antituberculosis agent [
18].
The active search for therapeutic alternatives involves not only the development of new drugs, but also the optimization of clinical practices, the promotion of infection prevention and awareness of the correct use of antibiotics. In terms of public health, early detection of susceptibilities of isolates to antituberculosis drugs is crucial to ensure timely and effective treatment. Therefore, agile, and effective methods are needed to accurately diagnose and rapidly follow up. The most prevalent conventional methods for assessing MTB susceptibility encompass the ratio method, carried out on media such as Lowenstein-Jensen (LJ) and Middlebrook 7H10-11 agar, which are characterized as complex and lengthy, and the BACTEC 460 TB system, which although faster, requires specialized equipment, resulting in increased costs [
19]. As an alternative option, it has been reported that blood agar is suitable for the growth and incubation of mycobacteria, including those responsible for TB. In addition, its usefulness for culture and susceptibility testing of first-line drugs has been evidenced [
20,
21,
22,
23].
In this study, the antimicrobial potential of CNP with size variations, and aqueous extract and liophylized powder of three Allium species against various microorganisms, including Gram-positive bacteria, Gram-negative bacteria, a fungus, and clinical isolates of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, was investigated to determine whether these materials could be effective in combating infectious diseases. In addition, an innovation to growth media was implemented to improve the efficiency of susceptibility testing for MBT.
2. Materials and Methods
Low molecular weight chitosan (91.7% deacetylated), sodium chloride (NaCl), sodium pentabasic tripolyphosphate (TPP), sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and glacial acetic acid were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich. Mueller-Hinton agar (MHA), Blood agar-based (BAB) and Löwenstein-Jensen (LJ) were obtained from Becton Dickinson. Garlic bulbs were purchased from the local market.
2.1. Synthesis of Chitosan Nanoparticles
CNP were synthesized via ionotropic gelation with TPP. Various NaCl concentrations (100 - 1400 mM) were used to produce nanoparticles of different sizes [
24]. Stock solutions were prepared, consisting of 0.1% low molecular weight chitosan (CS) in 0.01% glacial acetic acid and 0.1% TPP in Milli-Q water. NaCl solutions were prepared at concentrations of 100, 600, 1200, and 1400 mM. To adjust the pH, a 0.1 M NaOH solution was also prepared in Milli-Q water.
To promote nanoparticle formation, the pH of the CS solution was adjusted to 4.7-4.8 by adding 0.1 M NaOH dropwise. Subsequently, 1 mL of NaCl was added to each stock solution (CS and TPP) at the required concentration, and the mixture was agitated for one minute. Then, 3.95 mL of the TPP/NaCl mixture was added dropwise to the CS solution under constant magnetic stirring for five minutes. The samples were placed in glass vials and allowed to stand for 24 hours to reach equilibrium. To remove unreacted material, the samples were purified by dialysis using membrane tubes (MWCO 12-14 kD) against distilled water for 24 hours.
2.2. Physicochemical Properties of CNP
The particle size distribution, polydispersity index (PDI) and Z-potential of the nanoparticles were assessed through Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS) and electrophoretic mobility using the ZetaSizer Nano ZS (Malvern Instruments). Analysis was conducted after 24 hours of equilibration for all samples. Samples were appropriately diluted with deionized water. Each measurement was conducted in triplicate, and the average value of the three samples was recorded. The particle size distribution is represented by a polydispersity index (PDI), ranging from 0 for a completely uniform dispersion to 1 for a highly heterogeneous system. Additionally, changes in nanoparticle size and surface charge were evaluated at pH levels ranging from 2 to 10.
The morphology of the CNP was examined using a Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscope (FESEM JSM-7800 F Prime). To prepare the sample, 2 μL of a CNP solution with a concentration of 2 mg/mL was applied onto the surface of a 400-mesh copper-carbon grid. Subsequently, 2 μL of uranyl acetate solution (2 mg/mL) was added and left to dry. The sample was then inserted into the sample chamber and analyzed at 25 kV to capture images of the nanoparticles.
Stability studies were conducted on nanoparticle solutions stored in glass vials at 4 - 8°C for 30 days. Size distributions, PDI, and pH were assessed every eight days, with samples equilibrated to room temperature before each analysis.
2.3. Water-Based Extraction of Garlic
To explore the antimicrobial properties of natural extracts, aqueous extractions were carried out on purple, black, and Chinese garlic bulbs (Allium sativum, Allium neapolitanum, and Allium sphaerocephalon, respectively). This involved macerating 5 g of each plant in 50 mL of double-distilled water. To enhance the stability of the active components within the plant, fresh garlic bulbs were first cut into 5 mm cubes and then subjected to lyophilization. Once dried, they were crushed and sieved (315 μm) to obtain a uniform powder.
2.3. Antimicrobial Activity Assays
The disk diffusion method was employed following the CLSI M02-A12 protocol to conduct antimicrobial tests against Escherichia coli (ATCC 25922), Enterococcus faecalis (ATCC 29212), Staphylococcus aureus (ATCC 25923), and Candida albicans (ATCC 14053) strains. Antimicrobial discs were manufacture from filter paper (Whatman No.1) into diameters of 6 and 8 mm and subsequently impregnated with natural extracts. Absorption proceeded until a final concentration of 300 μg per disc was attained.
For the determination of Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) and Minimum Bactericidal Concentration (MBC) of CNP, the broth microdilution method, as outlined in the CLSI M07-A10 protocol was utilized.
Four nanoparticle sizes (134.6, 164.6, 216.2, and 280.0 nm) were tested against three bacteria—S. aureus, E. faecalis, E. coli—and one yeast, Candida albicans. Serial microdilutions ranging from 2.0 μg/mL to 0.0625 μg/mL were performed for each nanoparticle size. Microbial cell suspensions were standardized to the 0.5 McFarland scale.
The MIC was determined as the lowest concentration of CNP at which no visible growth was observed in the well after 24 hours of incubation at 37°C. To determine the MBC, 100 μL of the content from wells showing no visible growth were plated on Mueller-Hinton agar (MHA) plates and incubated for 24 hours at 37°C. The MBC was defined as the lowest concentration that eliminated 99.9% of microbial growth. Each test was conducted in triplicate.
The agar proportion method, considered the gold standard for susceptibility testing in MTB, was employed in this assay. The protocol outlined in CLSI M24-A2 was adapted, replacing Middlebrook 7H10 agar with 5% Blood agar-based (BAB). This adjustment offered a faster and more cost-effective approach while preserving the effectiveness of the conventional method and enhancing the diagnostic process.
Tests were performed using clinical strains obtained from the Department of Health in Vulnerable Populations of the Autonomous University of Baja California, identified as part of the M. tuberculosis complex via smear microscopy and culture in Löwenstein-Jensen (LJ) medium.
Four sizes of CNP (116.6, 144.3, 279.1, and 364.4 nm) were tested at concentrations ranging from 100 to 400 μg per quadrant. One quadrant served as a control, containing agar medium without additives to monitor growth. A standardized cell suspension was then inoculated into each quadrant of the agar plate. All experiments were conducted in triplicate.
Growth was observed over a three-week period before colony counting [
25]. Interpretation considered isolates as resistant if the colony count in the nanoparticle quadrant equaled or exceeded 1% of the count in the control quadrant.
3. Results
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of Chitosan Nanoparticles (CNP)
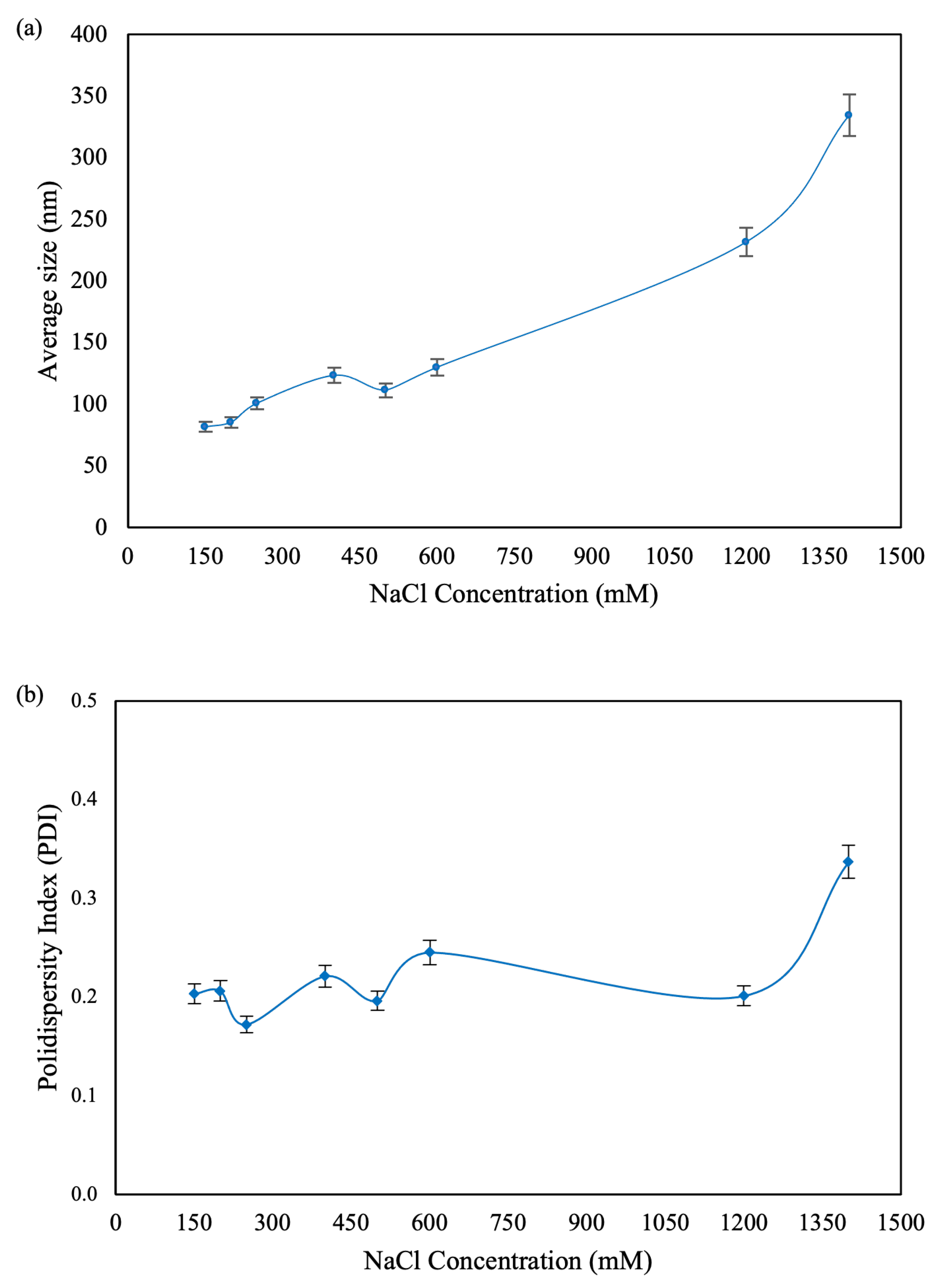
CNP were obtained in different sizes, ranging from approximately 80 to 350 nm. The particle size variation was directly influenced by the concentration of NaCl added during the synthesis process (
Figure 1), consistent with previous studies [
26]. The increase in particle size with higher salt concentrations is attributed to the electrostatic repulsion caused by the added ionic strength from the monovalent salt. This results in an increased frequency of collisions in solution, which in turn leads to coagulation of sodium tripolyphosphate with the chitosan chains, forming aggregates of primary particles as the ionic strength increases [
27].
3.1.1. Effect of pH on Surface Charge and Size of CNP
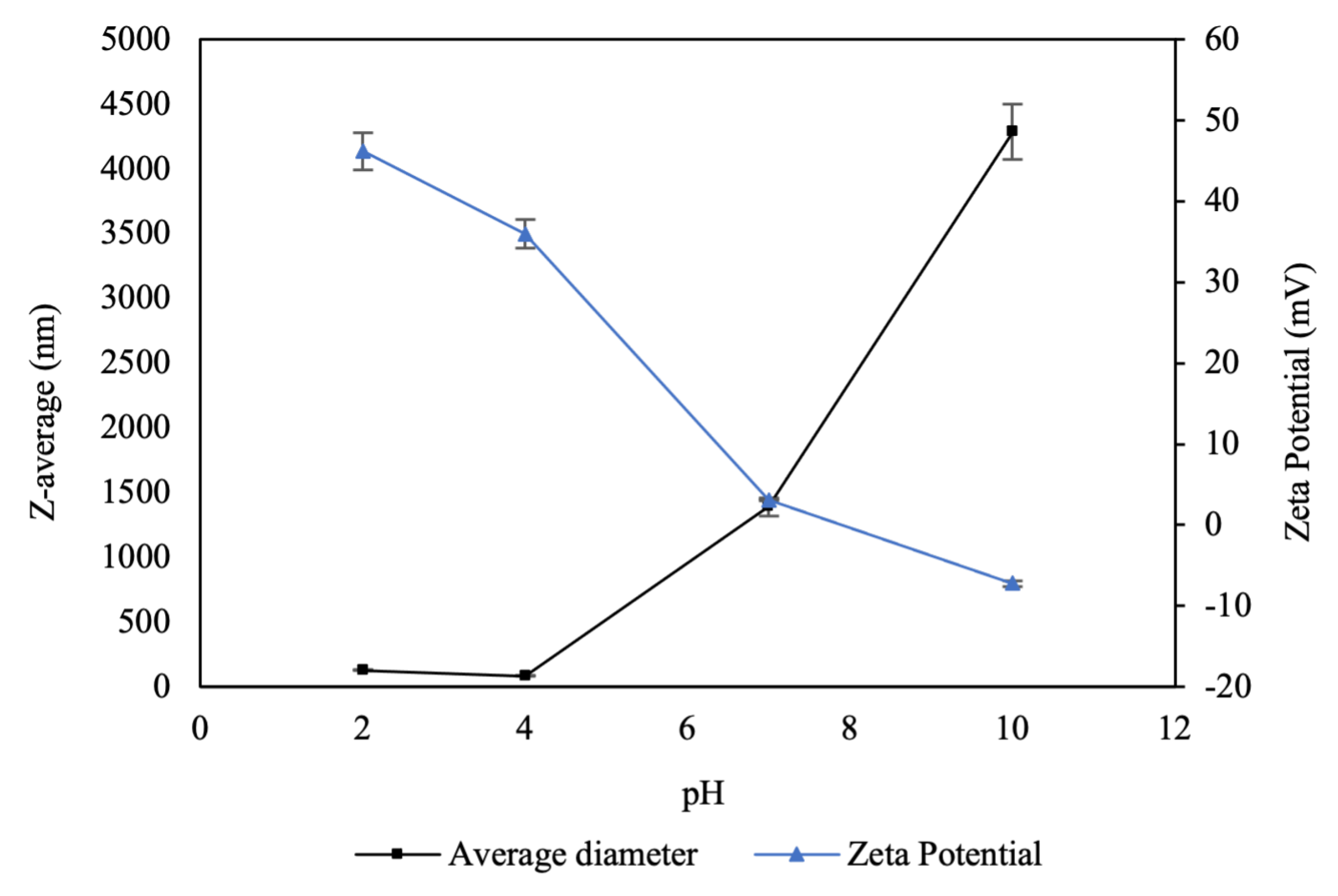
An analysis of CNP exposed to different pH levels was performed to examine changes in surface charge (Z-potential) and hydrodynamic diameter using DLS (
Figure 2). The nanoparticle suspensions exhibited an initial pH of 4. Under these conditions, the Z-potential was positive (40 ± 3 mV), attributable to the protonation of the amino and hydroxyl groups of chitosan in an acidic medium, forming hydrogen bonds [
28].
In response to increasing pH, the surface charges of the nanoparticles decreased, becoming nearly neutral at pH 7 and acquiring slightly negative charges under alkaline conditions (pH 10), with values ranging from 46.2 to -7.22 mV. Conversely, as pH increased, the sizes of the nanoparticles increased, reaching micrometer levels and increasing drastically with respect to their original size. This phenomenon could be attributed to the neutralization of the positive charges of the chitosan with the addition of NaOH, causing the formation of agglomerates.
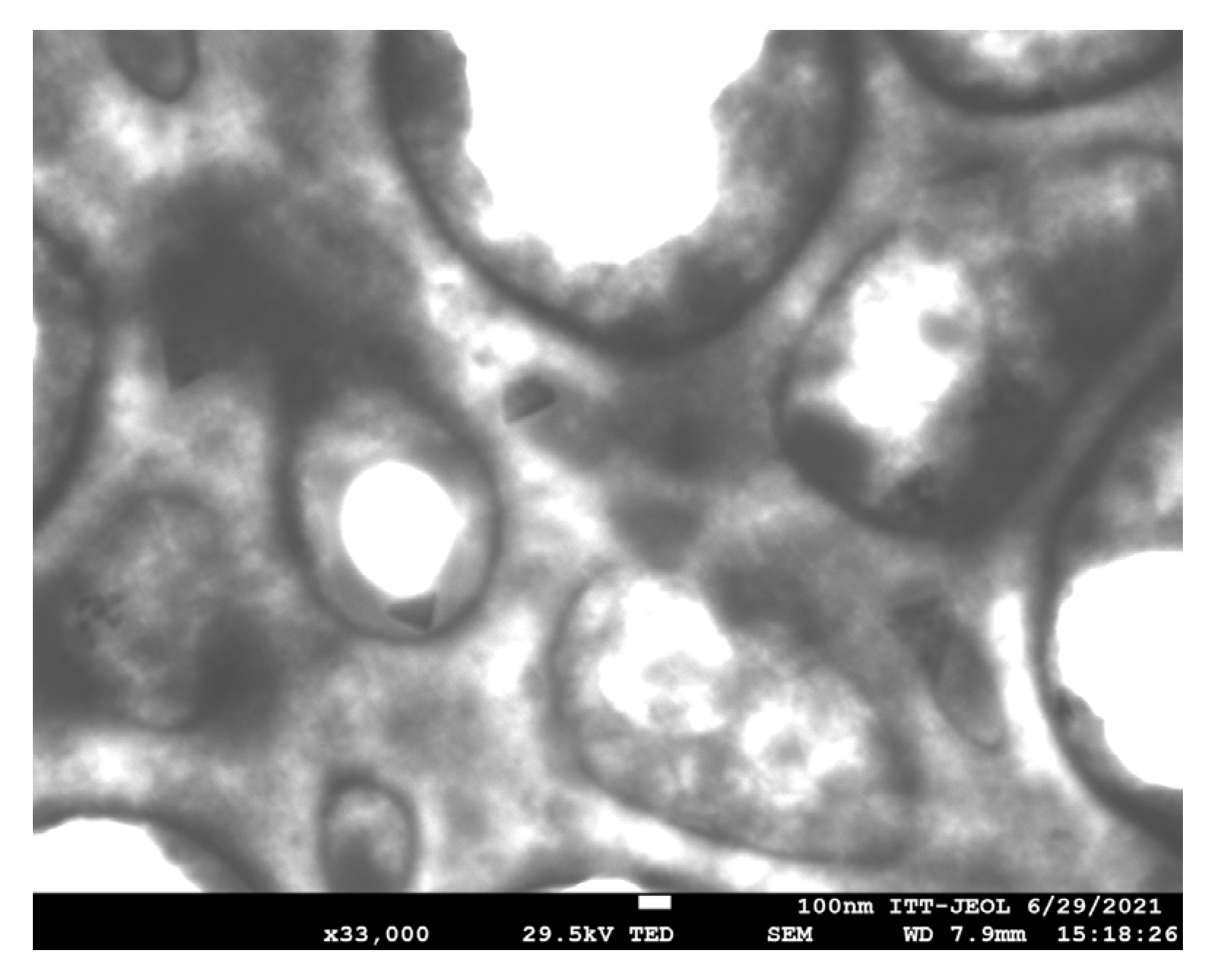
3.1.2. Morphological Analysis of CNP
The morphology of the CNP was examined using field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM). As shown in
Figure 3, the nanoparticles exhibit low density, attributed to ionic crosslinking, which results in the formation of agglomerates.
3.1.3. Stability and Size Variation of Stored Nanoparticles
Each sample was maintained at a pH of 4, which remained unchanged throughout the storage period. The smaller CNP demonstrated good stability, retaining sizes of 87.3 ± 1.1 nm and 146.0 ± 8.0 nm. However, the larger nanoparticles exhibited greater size variation over time, reaching 219.2 ± 10.1 nm and 274.7 ± 20.7 nm after one month of storage under refrigerated conditions (4 - 8°C).
3.2. Antimicrobial Activity
3.2.1. Inhibition Tests of Natural Extracts by Disk Diffusion
The susceptibility of different
Allium species extracts to a range of microorganisms was assessed using the disk diffusion method. Extracts from
Allium neapolitanum (black garlic) and
Allium sativum (purple garlic) demonstrated antimicrobial activity, producing inhibition halos against all tested microorganisms. In contrast, the extract from
Allium sphaerocephalon (Chinese garlic) showed no inhibitory effects (
Table 1).
The antimicrobial activity of
Allium sativum has been documented by several researchers. However, it has been noted that the sulfur compounds, which are primarily responsible for this activity, exhibit limited stability, leading to a decrease in antimicrobial efficacy over time [
29].
To enhance the stability of these active compounds, garlic bulbs were cut into 5 mm cubes and subjected to freeze-drying. The dried garlic was then pulverized and sieved to produce a uniform powder.
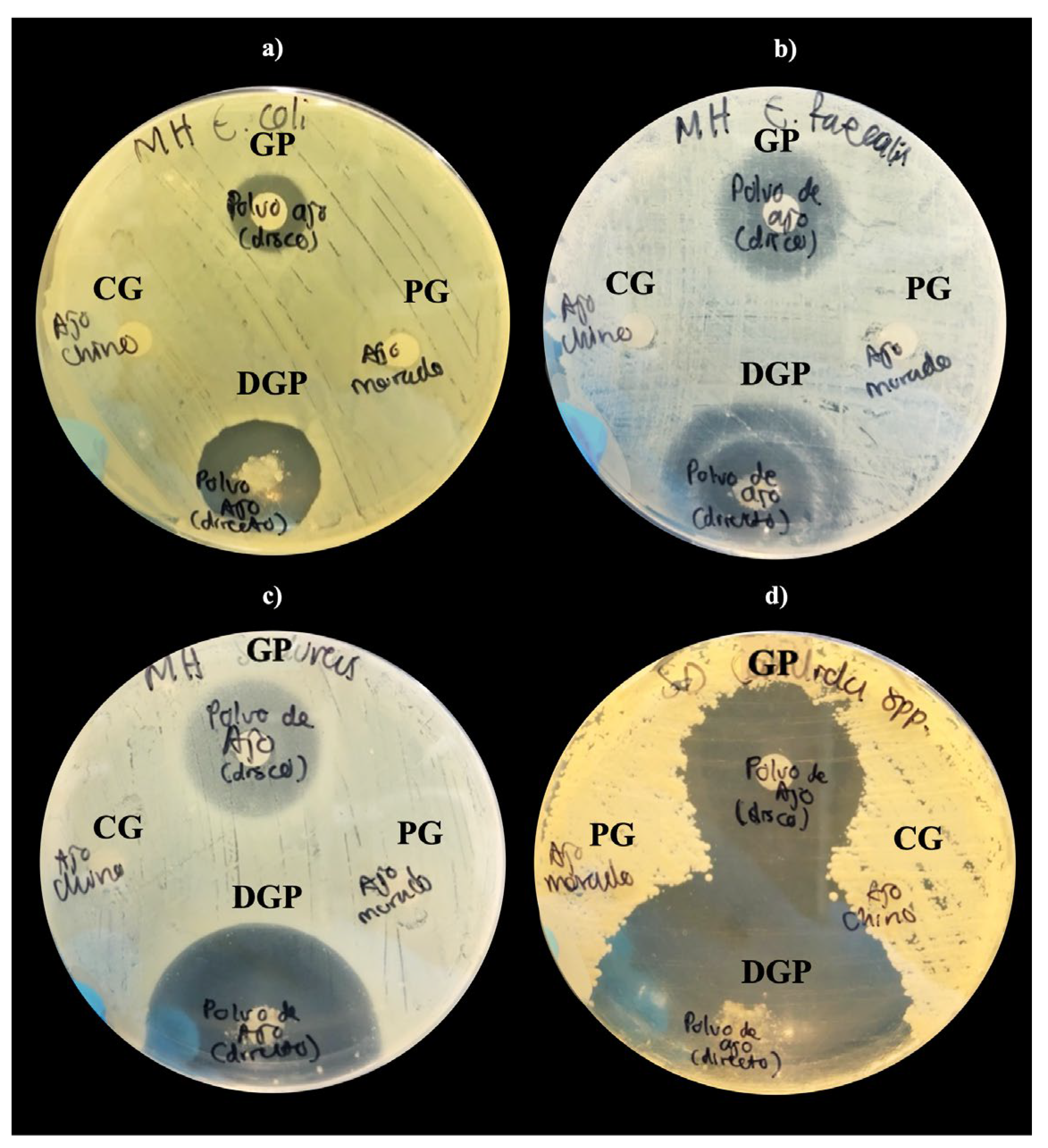
After obtaining the garlic powder, additional inhibition tests were conducted to verify that the antimicrobial activity remained effective following freezing and lyophilization. The inhibition zones produced were larger in diameter and achieved with a lower concentration compared to the aqueous extract (
Figure 4). The most significant inhibition zone was observed against
Candida albicans, measuring 25 mm in diameter (
Table 2).
In the case of
Enterococcus faecalis, the Eagle effect was observed (
Figure 3, b), which describes a paradoxical reduction in microbial death when concentrations exceed the optimal bactericidal concentration of the antibiotic. This phenomenon could present challenges in the therapeutic application of the compound [
30].
3.2.2. Antimicrobial Activity of CNP Assessed by Broth Dilution Method
The antimicrobial efficacy of nanoparticles against various microorganisms was evaluated using the broth microdilution method with four nanoparticle sizes.
Table 3 presents the MIC and BMC results for each microorganism.
Among the tested nanoparticles, those measuring 280 nm exhibited the highest antimicrobial activity against E. faecalis, with a MIC of 0.125 μg/mL and a CMB of 0.25 μg/mL. In contrast, C. albicans displayed the highest resistance, exhibiting growth across all dilutions tested against the 280 nm nanoparticles.
Proposed mechanisms of action for chitosan against various bacterial and fungal groups primarily focus on its polycationic nature and interactions with cell membranes. Under acidic conditions (pH < 6.5), cationic chitosan binds to phospholipids on the cell surface, disrupting essential bacterial functions [
31,
32,
33].
3.2.3. Antimycobacterial Activity of CNP Assessed by Agar Proportion Method
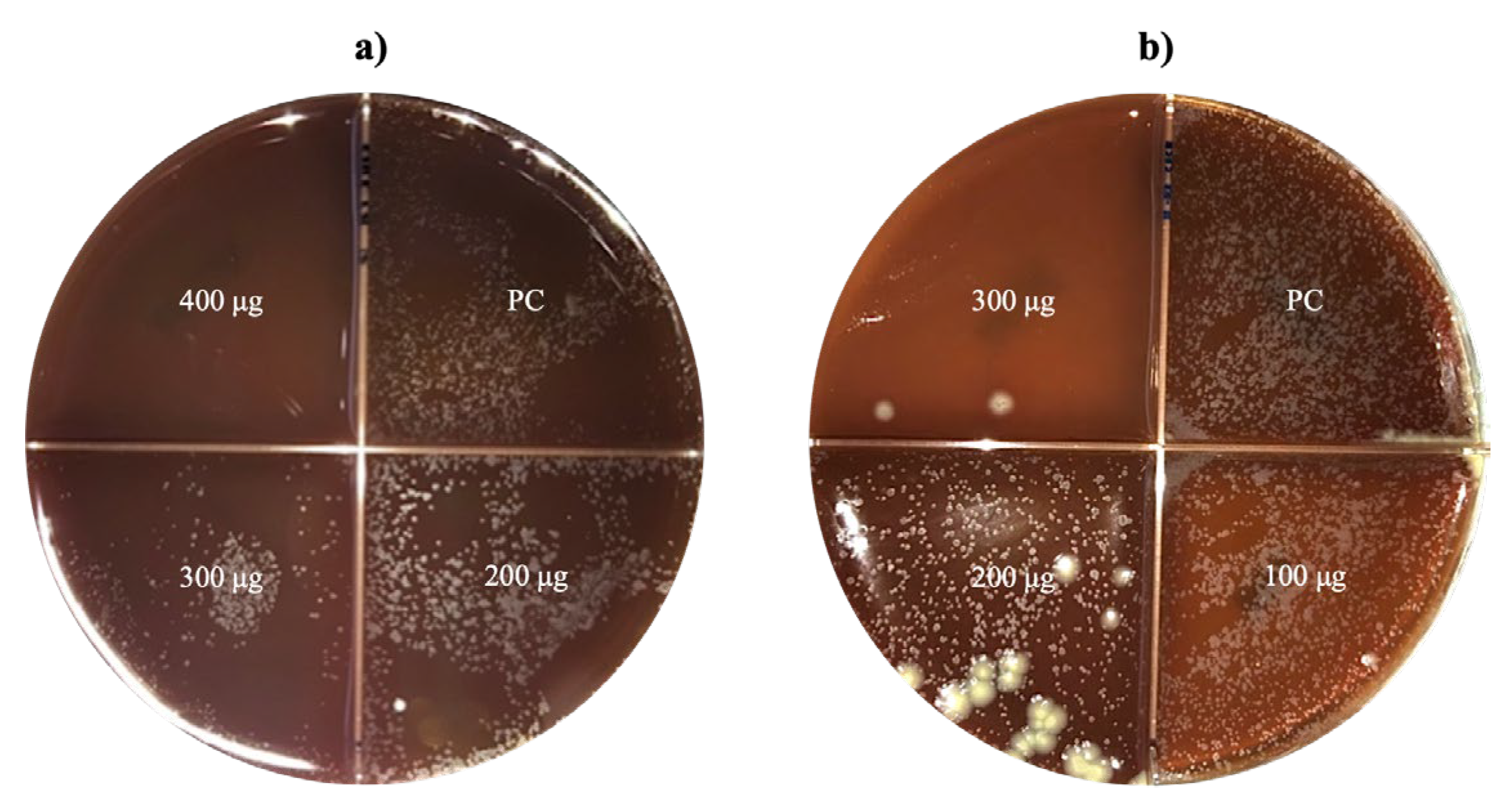
Mycobacterial growth was successful in the BAB medium, allowing the counting and identification of MTB colonies. Results were classified as sensitive when no growth occurred and resistant when growth was present in the quadrant containing nanoparticles.
MTB showed susceptibility to two nanoparticle sizes: CNP100 (116.6 nm) at 300 μg and CNP1400 (364.4 nm) at 400 μg, both of which completely inhibited growth (
Figure 5). The remaining nanoparticle sizes demonstrated no inhibitory effects on mycobacteria at any concentration (
Table 4).
Table 3.
Critical concentrations of CNP against M. tuberculosis clinical strain.
Table 3.
Critical concentrations of CNP against M. tuberculosis clinical strain.
| CNP |
Size (nm) |
Nanoparticle concentration (μg)
|
| 100 |
200 |
300 |
400 |
| CNP100 |
116.6 |
R |
R |
S |
NT |
| CNP600 |
144.3 |
NT |
R |
R |
R |
| CNP1200 |
279.1 |
R |
R |
R |
NT |
| CNP1400 |
364.4 |
NT |
R |
R |
S |
3.3. Morphological Comparison of Clinical Strain Colonies of MTB
When cultured on LJ medium, clinical isolates of MTB displayed distinct morphological variations. Some colonies exhibited typical growth characteristics with rough, yellowish-white appearance, while others displayed smooth, monolayer growth (
Figure 6).
This occurrence has been documented previously and attributed to the absence of glycolipid trehalose 6,6-dimycolate (TDM) in the bacillus cell wall. TDM typically imparts a rough texture to colonies and its absence is linked to reduced virulence of the mycobacterium. The potentially heterogeneous population of intracellular bacilli exploits this lower virulence state to sustain long-term coexistence within the human host [
34,
35].
4. Discussion
The antimicrobial activity of CNP against various microorganisms, as demonstrated by its MIC and BMC values, aligns with previous studies highlighting the efficacy of CNP due to its polycationic nature. This property allows CNP to interact with microbial cell membranes, altering their integrity and leading to inhibition or eradication of the pathogens evaluated [
31,
32,
33].
The observed variation in antimicrobial efficacy among different CNP sizes underscores the importance of nanoparticle size in determining their effectiveness. Smaller nanoparticles, such as CNP100, exhibited greater potency against certain bacteria and fungi compared to larger sizes. This could be attributed to better penetration and interaction at the cellular level, enhancing their bactericidal or fungicidal effects [
36]. However, larger nanoparticles, such as CNP1400, were able to inhibit MTB growth. This may be attributed to a larger surface area and charge density for interacting with microbial membranes [
37]. This size-dependent effectiveness suggests that nanoparticle optimization could play a crucial role in maximizing antimicrobial efficacy.
Moreover, exploration of the antimicrobial properties of
Allium sativum, revealed significant potential mainly against the yeast
C. albicans. Its antimicrobial properties have been widely documented, and its efficacy is attributed to the presence of sulfur compounds, mainly allicin [
17]. Our findings corroborate these reports, demonstrating that both aqueous extracts and garlic powder exhibit substantial antimicrobial activity against several microorganisms.
The improved stability of the active compounds and the antimicrobial efficacy of garlic, achieved by freeze-drying, ensures the preservation of the natural product, offering a viable alternative to conventional antimicrobial agents.
The combination of Allium sativum extracts and CNP presents a promising avenue for the development of novel antimicrobial agents, thus addressing the pressing problem of antimicrobial resistance. Furthermore, the natural origin of these compounds aligns with the growing demand for sustainable and environmentally friendly antimicrobial solutions.
However, to take full advantage of the therapeutic potential of these natural products, comprehensive cytotoxicity studies and in vivo evaluations are essential to ensure the safety and efficacy of these compounds in clinical settings.
Regarding the morphological variations observed among clinical isolates of MTB, they are consistent with previous reports associating morphology with strain virulence [
34]. Rough colonies, related to the presence of the glycolipid trehalose 6,6-dimicolate (TDM) in the cell wall, indicate greater virulence and robust survival of the pathogen. In contrast, smooth colonies without TDM suggest a less virulent state, linked to lower pathogenicity and persistence in the host.
Understanding these morphological variations is crucial to unveil MTB adaptive strategies within the host environment. The heterogeneous MTB population with different virulence states could take advantage of the less virulent phenotype to evade immune detection and establish prolonged infections in human hosts. This adaptive strategy brings out the complex interplay between MTB and the host immune response, which influences disease progression and treatment outcomes [
38].
Future research could explore the genetic and molecular mechanisms behind morphological variations in MTB colonies. Examining the pathways that regulate TDM biosynthesis and its impact on virulence could reveal new therapeutic targets for tuberculosis. In addition, analyzing the relationship between colony morphology on disease severity and response to treatment could provide valuable information for personalized treatment strategies.
In summary, the study reinforces the antimicrobial potential of CNP and Allium sativum, highlighting their ability to act against a variety of pathogenic microorganisms. These findings pave the way for future research aimed at optimizing natural antimicrobial agents, ultimately contributing to the development of safe, effective and sustainable treatments for infectious diseases.
5. Conclusions
CNP and Allium sativum demonstrated significant efficacy against a spectrum of microorganisms, encompassing Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, fungi, and even the challenging pathogen Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Particularly noteworthy was the extract of Allium sativum which showed remarkable efficacy against Candida albicans, suggesting avenues for future research into its therapeutic applications against opportunistic infections.
Further research into optimizing formulations could lead to development of valuable alternatives or supplements to conventional antimicrobial therapies. However, it is important to emphasize the need for cytotoxicity studies and in vivo evaluations to assess the safety of these compounds in clinical applications.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.R.C.M., J.M.C.B. and N.A.C.M.; methodology, J.O.F. and J.R.C.M.; software, J.O.F.; validation, N.A.C.M.; formal analysis, J.O.F.; investigation, J.M.C.B. and A.S.M.; resources, A.S.M.; data curation, J.O.F..; writing—original draft preparation, J.O.F.; writing—review and editing, J.M.C.B., A.S.M., N.A.C.M. and H.J.S.P.; visualization, J.R.C.M.; supervision, J.M.C.B..; project administration, A.S.M.; funding acquisition, J.R.C.M., A.S.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Internal Call for Research Projects UABC, grant number 4295 and The APC was funded by Autonomous University of Baja California (UABC).
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
Thanks to Dr. Ignacio Rivero from Instituto Tecnológico de Tijuana, TNM for STEM.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Fitzpatrick, M.C.; Bauch, C.T.; Townsend, J.P.; Galvani, A.P. Modelling Microbial Infection to Address Global Health Challenges. Nat. Microbiol. 2019 410 2019, 4, 1612–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, C.J.; Ikuta, K.S.; Sharara, F.; Swetschinski, L.; Robles Aguilar, G.; Gray, A.; Han, C.; Bisignano, C.; Rao, P.; Wool, E.; et al. Global Burden of Bacterial Antimicrobial Resistance in 2019: A Systematic Analysis. Lancet 2022, 399, 629–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, S.K.; Mishra, A.K.; Arotiba, O.A.; Mamba, B.B. Chitosan-Based Nanomaterials: A State-of-the-Art Review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 59, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Tayyar, N.A.; Youssef, A.M.; Al-hindi, R. Antimicrobial Food Packaging Based on Sustainable Bio-Based Materials for Reducing Foodborne Pathogens: A Review. Food Chem. 2020, 310, 125915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, W.L.; Niu, S.S.; Xu, Y.L.; Xu, Z.R.; Fan, C.L. Antibacterial Activity of Chitosan Tripolyphosphate Nanoparticles Loaded with Various Metal Ions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 75, 385–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Du, Y.; Liu, H. Preparation, Characterization and Antimicrobial Activity of Chitosan-Zn Complex. Carbohydr. Polym. 2004, 56, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.; Sun, W.; Qian, W.; Ye, Y.; Ma, X. The Synthesis of Chitosan-Based Silver Nanoparticles and Their Antibacterial Activity. Carbohydr. Res. 2009, 344, 2375–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Paz, L.E.C.; Resin, A.; Howard, K.A.; Sutherland, D.S.; Wejse, P.L. Antimicrobial Effect of Chitosan Nanoparticles on Streptococcus Mutans Biofilms. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 3892–3895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, W.-H.; Deng, F.-S.; Chang, C.-J.; Lin, C.-H. Synergistic Antifungal Activity of Chitosan with Fluconazole against Candida Albicans, Candida Tropicalis, and Fluconazole-Resistant Strains. Mol. 2020, Vol. 25, Page 5114 2020, 25, 5114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Moya, F.; Suarez-Fernandez, M.; Lopez-Llorca, L.V. Molecular Mechanisms of Chitosan Interactions with Fungi and Plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, Vol. 20, Page 332 2019, 20, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma-Guerrero, J.; Lopez-Jimenez, J.A.; Pérez-Berná, A.J.; Huang, I.-C.; Jansson, H.-B.; Salinas, J.; Villalaín, J.; Read, N.D.; Lopez-Llorca, L. V. Membrane Fluidity Determines Sensitivity of Filamentous Fungi to Chitosan. Mol. Microbiol. 2010, 75, 1021–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, T.; Rath, G.; Goyal, A.K. Inhalable Chitosan Nanoparticles as Antitubercular Drug Carriers for an Effective Treatment of Tuberculosis. Artif. Cells, Nanomedicine, Biotechnol. 2015, 44, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scolari, I.R.; Páez, P.L.; Sánchez-Borzone, M.E.; Granero, G.E. Promising Chitosan-Coated Alginate-Tween 80 Nanoparticles as Rifampicin Coadministered Ascorbic Acid Delivery Carrier Against Mycobacterium Tuberculosis. AAPS PharmSciTech 2019, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wardani, G.; Mahmiah, *!!! REPLACE !!!*; Sudjarwo, S.A. In Vitro Antibacterial Activity of Chitosan Nanoparticles against Mycobacterium Tuberculosis. Pharmacogn. J. 2018, 10, 162–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekor, M. The Growing Use of Herbal Medicines: Issues Relating to Adverse Reactions and Challenges in Monitoring Safety. Front. Pharmacol. 2013, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dias, D.A.; Urban, S.; Roessner, U. A Historical Overview of Natural Products in Drug Discovery. Metabolites 2012, 2, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viswanathan, V.; Phadatare, A.; Mukne, A. Antimycobacterial and Antibacterial Activity of Allium Sativum Bulbs. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 76, 256. [Google Scholar]
- Nair, S.S.; Gaikwad, S.S.; Kulkarni, S.P.; Mukne, A.P. Allium Sativum Constituents Exhibit Anti-Tubercular Activity In Vitro and in RAW 264.7 Mouse Macrophage Cells Infected with Mycobacterium Tuberculosis H37Rv. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2017, 13, S209–S215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Global Tuberculosis Programme Technical Manual for Drug Susceptibility Testing of Medicines Used in the Treatment of Tuberculosis. 2018.
- Coban, A.Y. Blood Agar Validation for Susceptibility Testing of Isoniazid, Rifampicin, Ethambutol, and Streptomycin to Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Isolates. PLoS One 2013, 8, e55370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coban, A.Y.; Bilgin, K.; Uzun, M.; Akgunes, A.; Yusof, A.; Durupinar, B. Comparative Study for Determination of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Susceptibility to First- and Second-Line Antituberculosis Drugs by the Etest Using 7H11, Blood, and Chocolate Agar. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 4095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satana, D.; Coban, A.Y.; Uzun, M. Testing Susceptibility of Multidrug-Resistant Mycobacterium Tuberculosis to Second-Line Drugs by Use of Blood Agar. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 4291–4293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yildiz, C.; Ulger, M.; Aslan, G. Isoniazid Susceptibilities of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis on Blood Agar. apbs.mersin.edu.tr 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Sawtarie, N.; Cai, Y.; Lapitsky, Y. Preparation of Chitosan/Tripolyphosphate Nanoparticles with Highly Tunable Size and Low Polydispersity. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 2017, 157, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satti, L.; Ikram, A.; Coban, A.Y.; Martin, A. Rapid Direct Testing of Susceptibility of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis to Isoniazid and Rifampin on Nutrient and Blood Agar in Resource-Starved Settings. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawtarie, N.; Cai, Y.; Lapitsky, Y. Preparation of Chitosan / Tripolyphosphate Nanoparticles with Highly-Tunable Size and Low Polydispersity. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Lapitsky, Y. Salt-Assisted Mechanistic Analysis of Chitosan/Tripolyphosphate Micro- and Nanogel Formation. Biomacromolecules 2012, 13, 3868–3876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, A. Taranjit Preparation of Chitosan Nanoparticles: A Study of Influencing Factors. In Proceedings of the AIP Conference Proceedings; 2011; Vol. 1393, pp. 299–300. [Google Scholar]
- Phadatare, A.G.; Viswanathan, V.; Mukne, A. Novel Strategies for Optimized Delivery of Select Components of Allium Sativum. Pharmacognosy Res. 2014, 6, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasetyoputri, A.; Jarrad, A.M.; Cooper, M.A.; Blaskovich, M.A.T. The Eagle Effect and Antibiotic-Induced Persistence: Two Sides of the Same Coin? Trends Microbiol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garg, U.; Chauhan, S.; Nagaich, U.; Jain, N. Current Advances in Chitosan Nanoparticles Based Drug Delivery and Targeting. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2019, 9, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, M.; Chen, X.G.; Xing, K.; Park, H.J. Antimicrobial Properties of Chitosan and Mode of Action: A State of the Art Review. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2010, 144, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raafat, D.; Von Bargen, K.; Haas, A.; Sahl, H.G. Insights into the Mode of Action of Chitosan as an Antibacterial Compound. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 3764–3773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giovannini, D.; Cappelli, G.; Jiang, L.; Castilletti, C.; Colone, A.; Serafino, A.; Wannenes, F.; Giacò, L.; Quintiliani, G.; Fraziano, M.; et al. A New Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Smooth Colony Reduces Growth inside Human Macrophages and Represses PDIM Operon Gene Expression. Does an Heterogeneous Population Exist in Intracellular Mycobacteria? Microb. Pathog. 2012, 53, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, K.; Yang, Z. Comparison of Ambient Air Survival of Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Clinical Strains Associated with Different Epidemiological Phenotypes. Int. J. Mycobacteriology 2014, 3, 211–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egorov, A.R.; Kirichuk, A.A.; Rubanik, V. V.; Rubanik, V. V.; Tskhovrebov, A.G.; Kritchenkov, A.S. Chitosan and Its Derivatives: Preparation and Antibacterial Properties. Materials (Basel). 2023, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sankar, A.; Ramesh, S.; Rajeshkumar, S.; Arun, N. Anti Microbial Activity of Chitosan Nanoparticles with Chlorhexidine- An In Vitro Study. J. Popul. Ther. Clin. Pharmacol. 2023, 30, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanabalan, R.D.; Lee, L.J.; Lee, T.Y.; Chong, P.P.; Hassan, L.; Ismail, R.; Chin, V.K. Human Tuberculosis and Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Complex: A Review on Genetic Diversity, Pathogenesis and Omics Approaches in Host Biomarkers Discovery. Microbiol. Res. 2021, 246, 126674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).