Submitted:
02 July 2024
Posted:
03 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
1. Possibilities of De-Escalation (see Figure 1)
1.1‘. Sophisticated’ RT
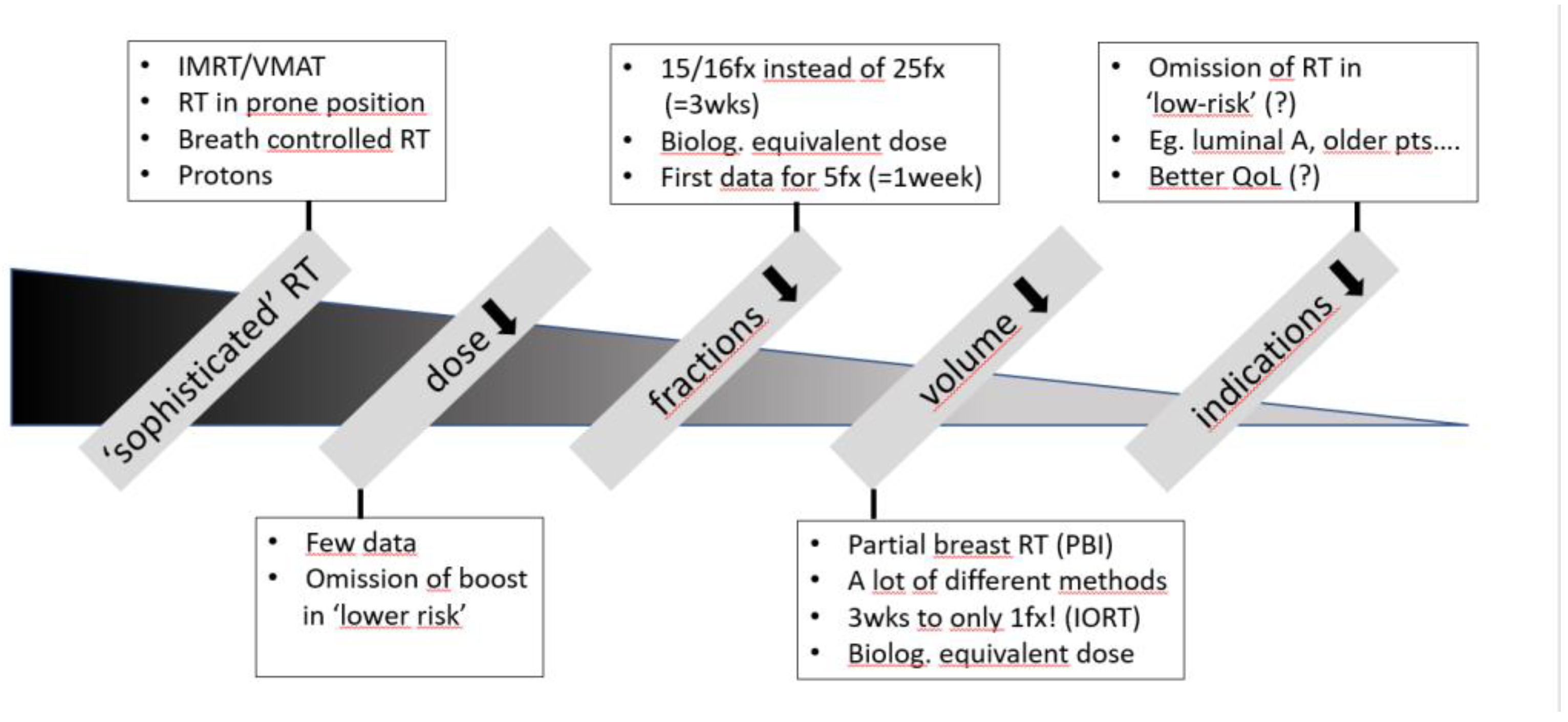
1.2. Dose Reduction
1.3. Reduction in Fractions
1.4. Volume Reduction – Partial Breast Irradiation Only (PBI)
1.5. Reduction of Indication (= Omission of RT)
2. Possibilities of Escalation (see Figure 2)
2.1. Preoperative RT
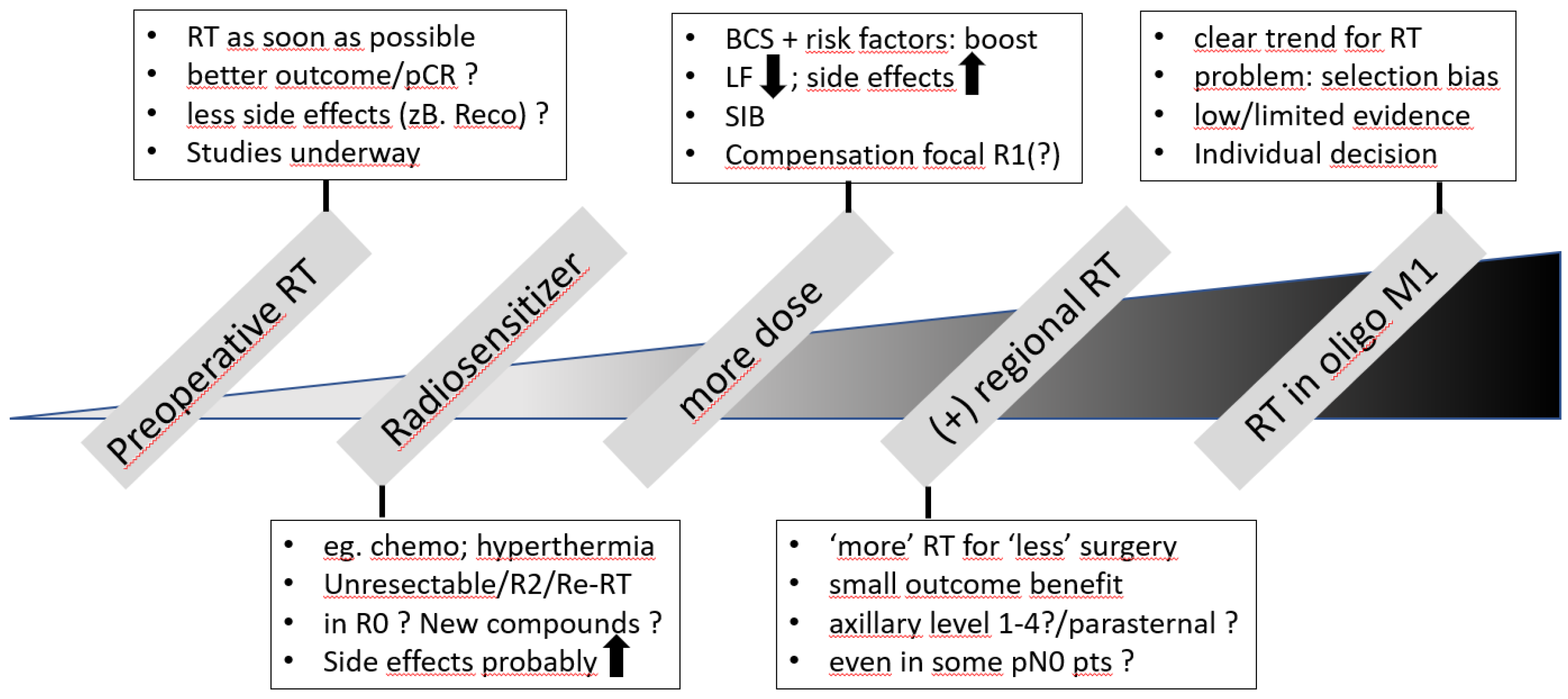
2.2. Radiosensitizer
2.3. Dose Escalation (Boost)
2.4. Additional Regional RT
2.5. RT in Oligometastatic Situations
3. Possibilities for Optimization
3.1. Technical Issues
3.2. Biology-Based Optimization
3.3. Tumor-Response-Based Considerations
Conclusions
References
- Early Breast Cancer Trialists' Collaborative Group (EBCTCG), Darby S., McGale P., Correa C., Taylor C., Arriagada R., Clarke M., Cutter D., Davies C., Ewertz M., Godwin J., et al.: Effect of radiotherapy after breast-conserving surgery on 10-year recurrence and 15-year breast cancer death: meta-analysis of individual patient data for 10,801 women in 17 randomised trials. Lancet. 2011 Nov 12;378(9804):1707-16.
- Shariati S., Behroozian T., Kennedy S., Caini S., Herst P.M., Zhang L., Ding K., Karam I., van den Hurk C., Wolf J.R., et al.: Mepithel film for the prevention and treatment of acute radiation dermatitis in breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Support Care Cancer. 2023 Aug 16; 31(9): 524.
- Prescott R.J., Kunkler I.H., Williams L.J., King C.C., Jack W., van der Pol M., Goh T.T., Lindley R., Cairns J.: A randomised controlled trial of postoperative radiotherapy following breast-conserving surgery in a minimum-risk older population. The PRIME trial. Health Technol Assess. 2007 Aug;11(31):1-149.
- Velikova G., Williams L.J., Willis S., Dixon J.M., Loncaster J., Hatton M., Clarke J., Kunkler I.H., Russell N.S.: MRC SUPREMO trial UK investigators: Quality of life after postmastectomy radiotherapy in patients with intermediate-risk breast cancer (SUPREMO): 2-year follow-up results of a randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2018 Nov;19(11):1516-1529.
- Joseph K., Vos L.J., Gabos Z., Pervez N., Chafe S., Tankel K., Warkentin H., Ghosh S., Amanie J., Powell K., et al.: Skin Toxicity in Early Breast Cancer Patients Treated with Field-In-Field Breast Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy versus Helical Inverse Breast Intensity-Modulated Radiotherapy: Results of a Phase III Randomised Controlled Trial. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2021 Jan;33(1):30-39. [CrossRef]
- Yee C., Wang K., Asthana R., Drost L., Lam H., Lee J., Vesprini D., Leung E., DeAngelis C., Chow E.: Radiation-induced Skin Toxicity in Breast Cancer Patients: A Systematic Review of Randomized Trials. Clin Breast Cancer. 2018 Oct;18(5): e825-e840.
- Jagsi R., Griffith K.A., Moran J.M., Ficaro E., Marsh R., Dess R.T., Chung E., Liss A.L., Hayman J.A., Mayo C.S., et al.: A Randomized Comparison of Radiation Therapy Techniques in the Management of Node-Positive Breast Cancer: Primary Outcomes Analysis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2018 Aug 1;101(5):1149-1158. [CrossRef]
- Mulliez T., Veldeman L., Speleers B., Mahjoubi K., Remouchamps V., Van Greveling A., Gilsoul M., Berwouts D., Lievens Y., Van den Broecke R., et al.: Heart dose reduction by prone deep inspiration breath hold in left-sided breast irradiation. Radiother Oncol. 2015 Jan;114(1):79-84. [CrossRef]
- Mulliez T., Veldeman L., van Greveling A., Speleers B., Sadeghi S., Berwouts D., Decoster F., Vercauteren T., De Gersem W., Van den Broecke R., et al.: Hypofractionated whole breast irradiation for patients with large breasts: a randomized trial comparing prone and supine positions. Radiother Oncol. 2013 Aug;108(2):203-8. [CrossRef]
- Bekelman J.E., Lu H., Pugh S., Baker K., Berg C.D., de Gonzalez A.B., Braunstein L.Z., Bosch W., Chauhan C., Ellenberg S., et al., RadComp (Radiotherapy Comparative Effectiveness Consortium): Pragmatic randomised clinical trial of proton versus photon therapy for patients with non-metastatic breast cancer: the Radiotherapy Comparative Effectiveness (RadComp) Consortium trial protocol. BMJ Open. 2019 Oct 15;9(10): e025556.
- Holt F., Probert J., Darby S.C., Haviland J.S., Coles C.E., Kirby A.M., Liu Z., Dodwell D., Ntentas G., et al.: Proton Beam Therapy for Early Breast Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Clinical Outcomes. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2023 Nov 15;117(4):869-882. Epub 2023 Mar 2. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Offersen B.V., Boersma L.J., Kirkove C., Hol S., Aznar M.C., Biete Sola A., Kirova Y.M., Pignol J-P., Remouchamps V., Verhoeven K., et al.: ESTRO consensus guideline on target volume delineation for elective radiation therapy of early stage breast cancer. Radiother Oncol 2015; 114: 3 – 10. [CrossRef]
- Nelms BE, Robinson G, Markham J, Velasco K, Boyd S, Narayan S, et al.. Variation in external beam treatment plan quality: An inter-institutional study of planners and planning systems. PractRadiatOncol. 2012; 2(4):296–305. [CrossRef]
- Phurailatpam R., Sah M.K., Wadasadawala T., Khan A., Palottukandy J., Gayake U., Jain J., Sarin R., Pathak R., Krishnamurthy R., et al.: Can knowledge based treatment planning of VMAT for post-mastectomy locoregional radiotherapy involving internal mammary chain and supraclavicular fossa improve performance efficiency? Front Oncol. 2023 Apr 3;13:991952. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bartelink, H; Maingon, P; Poortmans, P; Weltens, C; Fourquet, A; Jager, J; Schinagl, D; Oei, B; Rodenhuis, C; Horiot, JC; et al.: Whole-breast irradiation with or without a boost for patients treated with breast-conserving surgery for early breast cancer: 20-year follow-up of a randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16(1), 47–56. [CrossRef]
- Hau E, Browne L, Capp A, Delaney GP, Fox C, Kearsley JH, Millar E, Nasser EH, Papadatos G, Graham PH: The impact of breast cosmetic and functional outcomes on quality of life: long-term results from the St. George and Wollongong randomized breast boost trial. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2013 May;139(1):115-23.
- Coles CE, Griffin CL, Kirby AM, Titley J, Agrawal RK, Alhasso A, Bhattacharya IS, Brunt AM, Ciurlionis L, Chan C, et al.: IMPORT Trialists. Import low Partial-breast radiotherapy after breast conservation surgery for patients with early breast cancer (UK IMPORT LOW trial): 5-year results from a multicentre, randomised, controlled, phase 3, non-inferiority trial. Lancet. 2017 Sep 9;390(10099):1048-1060. [CrossRef]
- www.leitlinienprogramm-onkologie.de/fileadmin/user_upload/Downloads/Leitlinien/Mammakarzinom_4_0/Version_4.4/LL_Mammakarzinom_Langversion_4.4.pdf (accessed on May 17th, 2024).
- Haviland JS, Owen JR, Dewar JA, Agrawal RK, Barrett J, Barrett-Lee PJ, Dobbs HJ, Hopwood P, Lawton PA, Magee BJ, et al.: START Trialists' Group: The UK Standardisation of Breast Radiotherapy (START) trials of radiotherapy hypofractionation for treatment of early breast cancer: 10-year follow-up results of two randomised controlled trials. Lancet Oncol. 2013 Oct;14(11):1086-1094.
- Wang SL, Fang H, Song YW, Wang WH, Hu C, Liu YP, Jin J, Liu XF, Yu ZH, Ren H, et al.: Hypofractionated versus conventional fractionated postmastectomy radiotherapy for patients with high-risk breast cancer: a randomised, non-inferiority, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2019 Mar;20(3):352-360.
- Murray Brunt A, Haviland JS, Wheatley DA, Sydenham MA, Alhasso A, Bloomfield DJ, Chan C, Churn M, Cleator S, Coles CE, et al.: FAST-Forward Trial Management Group: Hypofractionated breast radiotherapy for 1 week versus 3 weeks (FAST-Forward): 5-year efficacy and late normal tissue effects results from a multicentre, non-inferiority, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2020 May 23;395(10237):1613-1626.
- Krug D, Baumann R, Combs SE, Duma MN, Dunst J, Feyer P, Fietkau R, Haase W, Harms W, Hehr T, et al.: Breast Cancer Expert Panel of the German Society of Radiation Oncology (DEGRO). Moderate hypofractionation remains the standard of care for whole-breast radiotherapy in breast cancer: Considerations regarding FAST and FAST-Forward. Strahlenther Onkol. 2021 Apr;197(4):269-280. Epub 2021 Jan 28. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Yadav BS, Dahiya D, Kannan P, Goyal S, Laroiya I, Irrinki S, Singh NR, Sharma R: HYPofractionated Adjuvant RadioTherapy in 1 versus 2 weeks in high-risk patients with breast cancer (HYPART): a non-inferiority, open-label, phase III randomized trial. Trials. 2024 Jan 2;25(1):21.
- Meattini I, Becherini C, Boersma L, Kaidar-Person O, Marta GN, Montero A, Offersen BV, Aznar MC, Belka C, Brunt AM, et al.: European Society for Radiotherapy and Oncology Advisory Committee in Radiation Oncology Practice consensus recommendations on patient selection and dose and fractionation for external beam radiotherapy in early breast cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2022 Jan;23(1):e21-e31. [CrossRef]
- Orecchia R, Veronesi U, Maisonneuve P, Galimberti VE, Lazzari R, Veronesi P, Jereczek-Fossa BA, Cattani F, Sangalli C, Luini A, et al.: ELIOT trial Intraoperative irradiation for early breast cancer (ELIOT): long-term recurrence and survival outcomes from a single-centre, randomised, phase 3 equivalence trial. Lancet Oncol. 2021 May;22(5):597-608. [CrossRef]
- JS Vaidya, M Bulsara, Ml Baum, F Wenz, S Massarut, S Pigorsch, M Alvarado, M Douek, C Saunders, HL Flyger, et al.: Long term survival and local control outcomes from single dose targeted intraoperative radiotherapy during lumpectomy (TARGIT-IORT) for early breast cancer: TARGIT-A randomised clinical trial. BMJ. 2020; 370: m2836. [CrossRef]
- Haussmann J, Budach W, Corradini S, Krug D, Tamaskovics B, Bölke E, Djiepmo-Njanang FJ, Simiantonakis I, Kammers K, Matuschek C: No Difference in Overall Survival and Non-Breast Cancer Deaths after Partial Breast Radiotherapy Compared to Whole Breast Radiotherapy-A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Trials. Cancers (Basel). 2020 Aug 17;12(8):2309.
- Whelan TJ, Julian JA, Berrang TS, Kim DH, Germain I, Nichol AM, Akra M, Lavertu S, Germain F, Fyles A, et al.: External beam accelerated partial breast irradiation versus whole breast irradiation after breast conserving surgery in women with ductal carcinoma in situ and node-negative breast cancer (RAPID): a randomised controlled trial. RAPID Trial Investigators. Lancet. 2019 Dec 14;394(10215):2165-2172. [CrossRef]
- Kunkler IH, Williams LJ, Jack WJL, Cameron DA, Dixon JM. Breast-Conserving Surgery with or without Irradiation in Early Breast Cancer. N Engl J Med. 2023 Feb 16;388(7):585-594. [CrossRef]
- Overgaard M, Hansen PS, Overgaard J, Rose C, Andersson M, Bach F, Kjaer M, Gadeberg CC, Mouridsen HT, Jensen MB, Zedeler K. Postoperative radiotherapy in high-risk premenopausal women with breast cancer who receive adjuvant chemotherapy. Danish Breast Cancer Cooperative Group 82b Trial. N Engl J Med. 1997 Oct 2;337(14):949-55. [CrossRef]
- Overgaard M, Jensen MB, Overgaard J, Hansen PS, Rose C, Andersson M, Kamby C, Kjaer M, Gadeberg CC, Rasmussen BB, et al.: Postoperative radiotherapy in high-risk postmenopausal breast-cancer patients given adjuvant tamoxifen: Danish Breast Cancer Cooperative Group DBCG 82c randomised trial. Lancet. 1999 May 15;353(9165):1641-8. [CrossRef]
- Overgaard M, Nielsen HM, Tramm T, Højris I, Grantzau TL, Alsner J, Offersen BV, Overgaard J; DBCG Radiotherapy Group. Postmastectomy radiotherapy in high-risk breast cancer patients given adjuvant systemic therapy. A 30-year long-term report from the Danish breast cancer cooperative group DBCG 82bc trial. Radiother Oncol. 2022 May;170:4-13. Epub 2022 Mar 11. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/breast.pdf (accessed on June 27th, 2024).
- Kunkler IH, Canney P, van Tienhoven G, Russell NS; MRC/EORTC (BIG 2-04) SUPREMO Trial Management Group. Elucidating the role of chest wall irradiation in 'intermediate-risk' breast cancer: the MRC/EORTC SUPREMO trial. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2008 Feb;20(1):31-4. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matuschek C, Nestle-Kraemling C, Haussmann J, et al. Long-term cosmetic outcome after preoperative radio−/chemotherapy in locally advanced breast cancer patients. Strahlenther Onkol. 2019; 195:615–28. [CrossRef]
- www.gbg.de/en/trials/neorad (accessed on May 26th, 2024).
- O'Donnell JPM, Murphy D, Ryan ÉJ, Gasior SA, Sugrue R, O'Neill BL, Boland MR, Lowery AJ, Kerin MJ, McInerney NM. Optimal reconstructive strategies in the setting of post-mastectomy radiotherapy - A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2021 Nov;47(11):2797-2806. [CrossRef]
- L Admojo, P Chidley, YH Lin, F Foroudi, S Jassal, SW Loh, G Chew, E Bevington, SL Ng, A Hyett, T Leech, WM Ooi, Chionh, M Chao; Comparing Radiotherapy (RT) Late Toxicities to the Reconstructed DIEP Flap in Breast Cancer Patients Treated with Neoadjuvant RT (NART) vs. Post-Mastectomy RT (PMRT); Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phy, Volume 114, Issue 3, Suppl., S145, November 01, 2022.
- Civil YA, Jonker LW, Groot Koerkamp MPM, Duvivier KM, de Vries R, Oei AL, Slotman BJ, van der Velde S, van den Bongard HJGD. Preoperative Partial Breast Irradiation in Patients with Low-Risk Breast Cancer: A Systematic Review of Literature. Ann Surg Oncol. 2023 Jun;30(6):3263-3279. [CrossRef]
- Meattini I, Francolini G, Di Cataldo V, Visani L, Becherini C, Scoccimarro E, Salvestrini V, Bellini C, Masi L, Doro R, Di Naro F, Loi M, Salvatore G, Simontacchi G, Greto D, Bernini M, Nori J, Orzalesi L, Bianchi S, Mangoni M, Livi L. Preoperative robotic radiosurgery for early breast cancer: Results of the phase II ROCK trial (NCT03520894). Clin Transl Radiat Oncol. 2022 Sep 22;37:94-100. [CrossRef]
- EL Jones, JR Oleson, LR Prosnitz, TV Samulski, Z Vujaskovic, D Yu, LL Sanders, MW Dewhirst: Randomized Trial of Hyperthermia and Radiation for Superficial Tumors. J Clin Oncol. 2005 May 1;23(13):3079-85. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim DY, Youn JC, Park MS, Lee S, Choi SW, Ryu KH, Kim LS, Shim MS, Lee JJ, Han S. Cardiovascular outcome of breast cancer patients with concomitant radiotherapy and chemotherapy: A 10-year multicenter cohort study. J Cardiol. 2019 Aug;74(2):175-181. [CrossRef]
- Montero A, Ciérvide R. Preoperative Radio(Chemo)Therapy in Breast Cancer: Time to Switch the Perspective? Curr Oncol. 2022 Dec 12;29(12):9767-9787. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Breast Cancer Study of Preoperative Pembrolizumab + Radiation - Full Text View - ClinicalTrials.gov (accessed on June 2nd, 2024).
- Neo-adjuvant Chemotherapy Combined With Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy to the Primary Tumour +/- Durvalumab, +/- Oleclumab in Luminal B Breast Cancer: - Full Text View - ClinicalTrials.gov (accessed on June 2nd, 2024).
- Converting HR+ Breast Cancer Into an Individualized Vaccine - Full Text View - ClinicalTrials.gov (accessed on June 2nd, 2024).
- Meattini I, Becherini C, Caini S, Coles CE, Cortes J, Curigliano G, de Azambuja E, Isacke CM, Harbeck N, Kaidar-Person O, Marangoni E, Offersen BV, Rugo HS, Salvestrini V, Visani L, Morandi A, Lambertini M, Poortmans P, Livi L; Consensus Panellist Group. International multidisciplinary consensus on the integration of radiotherapy with new systemic treatments for breast cancer: European Society for Radiotherapy and Oncology (ESTRO)-endorsed recommendations. Lancet Oncol. 2024 Feb;25(2):e73-e83. [CrossRef]
- Koide Y, Nagai N, Adachi S, Ito M, Kawamura M, Ito M, Ito F, Shindo Y, Aoyama T, Shimizu H, et al.: Impact of concurrent antibody-drug conjugates and radiotherapy on symptomatic radiation necrosis in breast cancer patients with brain metastases: a multicenter retrospective study. J Neurooncol. 2024 Jul;168(3):415-423. Epub 2024 Apr 22. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chua BH, Link EK, Kunkler IH, Whelan TJ, Westenberg AH, Gruber G, Bryant G, Ahern V, Purohit K, Graham PH, et al.: BIG 3–07/TROG 07.01 trial investigators. Radiation doses and fractionation schedules in non-low-risk ductal carcinoma in situ in the breast (BIG 3-07/TROG 07.01): a randomised, factorial, multicentre, open-label, phase 3 study. Lancet. 2022 Aug 6;400(10350):431-440. [CrossRef]
- S Bosma, E van Werkhoven, H Bartelink, A Fourquet, C Hurkmans, J Maduro, E Rutgers, L Scheijmans, D Schinagl, M Stam, et al.: Young boost randomized phase III trial of high vs low boost radiation in young breast cancer patients: 10-years results. EBCC-14; Milano March 22th-24th, 2024. Abstract no: 4LBA. [CrossRef]
- Schmitt M, Menoux I, Chambrelant I, Hild C, Petit T, Mathelin C, Noël G. Adjuvant hypofractionated radiotherapy with simultaneous integrated boost after breast-conserving surgery: A systematic literature review. Transl Oncol. 2022 Aug;22:101456. [CrossRef]
- Coles CE, Haviland JS, Kirby AM, Griffin CL, Sydenham MA, Titley JC, Bhattacharya I, Brunt AM, Chan HYC, Donovan EM, et al.: IMPORT Trial Management Group. Dose-escalated simultaneous integrated boost radiotherapy in early breast cancer (IMPORT HIGH): a multicentre, phase 3, non-inferiority, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2023 Jun 24;401(10394):2124-2137. [CrossRef]
- J Dunst, D Krug, A Schreiber, AD Boicev, J Zimmer, R Laubach, N Weidner, SE Dinges, M Hipp, R Schneider, et al.: Patient Reported Experience with Treatment Modalities and Safety of Adjuvant Breast Radiotherapy - First Results of the Randomized HYPOSIB - Study. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys, Volume 108, Issue 3 Suppl., S13, November 01, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Vicini FA, Winter K, Freedman GM, et al: NRG RTOG 1005: A phase III trial of hypo fractionated whole breast irradiation with concurrent boost vs. Conventional whole breast irradiation plus sequential boost following lumpectomy for high risk early-stage breast cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 114:S1, 2022 (3 suppl) 194. [CrossRef]
- Garcia Zanuguera C, Gadea Quintero J, Curbelo Artiles AG, Mateu Castell L, Maturana JEM, Ortiz Gonzalez I, Alastuey I, Pardo J. Safety and feasibility of simultaneous integrated boost in extreme 1-week hypofractionated radiotherapy for early breast cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys, Volume 114, Issue 3, Suppl. E28-E29, 2022.
- Chatterjee S, Chakraborty S: Hypofractionated radiation therapy comparing a standard radiotherapy schedule (over 3 weeks) with a novel 1-week schedule in adjuvant breast cancer: An open-label randomized controlled study (HYPORT-Adjuvant)-study protocol for a multicentre, randomized phase III trial. Trials 21:819, 2020.
- Hypofractionated LocoRegional Radiotherapy in Breast Cancer (RHEAL). https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04228991 (accessed on May 26th, 2024).
- www.targit.org.uk (accessed on May 26th, 2024).
- Vos EL, Siesling S, Baaijens MHA, Verhoef C, Jager A, Voogd AC, Koppert LB: Omitting re-excision for focally positive margins after breast-conserving surgery does not impair disease-free and overall survival. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2017 Jul;164(1):157-167.
- Budach W, Bölke E, Kammers K, Gerber PA, Nestle-Krämling C, Matuschek C: Adjuvant radiation therapy of regional lymph nodes in breast cancer - a meta-analysis of randomized trials - an update. Radiat Oncol. 2015 Dec 21; 10:258.
- Early Breast Cancer Trialists' Collaborative Group (EBCTCG). Radiotherapy to regional nodes in early breast cancer: an individual patient data meta-analysis of 14 324 women in 16 trials. Lancet. 2023 Nov 25;402(10416):1991-2003. [CrossRef]
- Haussmann J, Budach W, Tamaskovics B, Bölke E, Corradini S, Djiepmo-Njanang FJ, Kammers K, Matuschek C: Which target volume should be considered when irradiating the regional nodes in breast cancer? Results of a network-meta-analysis. Radiat Oncol. 2019 Jun 11;14(1):102. [CrossRef]
- Kim YB, Byun HK, Kim DY, Ahn SJ, Lee HS, Park W, Kim SS, Kim JH, Lee KC, Lee IJ, et al.: Effect of Elective Internal Mammary Node Irradiation on Disease-Free Survival in Women With Node-Positive Breast Cancer: A Randomized Phase 3 Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2022 Jan 1;8(1):96-105.
- Kaidar-Person O, Fortpied C, Hol S, Weltens C, Kirkove C, Budach V, Peignaux-Casasnovas K, van der Leij F, Vonk E, Valli M, eta l.: EORTC Radiation Oncology and Breast Cancer Groups. The association of internal mammary and medial supraclavicular lymph node radiation technique with clinical outcomes: Results from the EORTC 22922/10925 randomised trial. Radiother Oncol. 2022 Jul;172:99-110. [CrossRef]
- Giuliano AE, Ballman KV, McCall L, Beitsch PD, Brennan MB, Kelemen PR, Ollila DW, Hansen NM, Whitworth PW, Blumencranz PW, et al.: Effect of Axillary Dissection vs No Axillary Dissection on 10-Year Overall Survival Among Women With Invasive Breast Cancer and Sentinel Node Metastasis: The ACOSOG Z0011 (Alliance) Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA. 2017 Sep 12;318(10):918-926. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bartels SAL, Donker M, Poncet C, Sauvé N, Straver ME, van de Velde CJH, Mansel RE, Blanken C, Orzalesi L, Klinkenbijl JHG, et al.: Radiotherapy or Surgery of the Axilla After a Positive Sentinel Node in Breast Cancer: 10-Year Results of the Randomized Controlled EORTC 10981-22023 AMAROS Trial. J Clin Oncol. 2023 Apr 20;41(12):2159-2165. Epub 2022 Nov 16. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sávolt Á, Péley G, Polgár C, Udvarhelyi N, Rubovszky G, Kovács E, Győrffy B, Kásler M, Mátrai Z. Eight-year follow up result of the OTOASOR trial: The Optimal Treatment Of the Axilla - Surgery Or Radiotherapy after positive sentinel lymph node biopsy in early-stage breast cancer: A randomized, single centre, phase III, non-inferiority trial. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2017 Apr;43(4):672-679. Epub 2017 Jan 16. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haussmann J, Matuschek C, Bölke E, Orth K, Ghadjar P, Budach W: The Role of Local Treatment in Oligometastatic and Oligoprogressive Cancer. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 2019 Dec 13;116(50):849-856.
- Chmura SJ, Winter KA, Woodward WA, Borges VF, Kamel J, et al. NRG-BR002: a phase IIR/III trial of standard of care systemic therapy with or without stereotactic body radiotherapy (SBRT) and/or surgical resection (SR) for newly oligometastatic breast cancer (NCT02364557). Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol. 2022; 40 (abstr).1007. [CrossRef]
- Ng J, Pennell R, Formenti SC. The initial experience of MRI-guided precision prone breast irradiation with daily adaptive planning in treating early stage breast cancer patients. Front Oncol. 2022;12:1048512. [CrossRef]
- Liu X, Li Z, Yin Y. Clinical application of MR-Linac in tumor radiotherapy: a systematic review. Radiat Oncol. 2023;18:52. [CrossRef]
- Matuschek C., Bolke E., Haussmann J., Mohrmann S., Nestle-Kramling C., Gerber P.A., et al. The benefit of adjuvant radiotherapy after breast conserving surgery in older patients with low risk breast cancer- a meta-analysis of randomized trials. Radiat Oncol. 2017;12(1):60. [CrossRef]
- Sjöström M, Chang SL, Fishbane N, Davicioni E, Zhao SG, Hartman L, Holmberg E, Feng FY, Speers CW, Pierce LJ, et al.: Clinicogenomic Radiotherapy Classifier Predicting the Need for Intensified Locoregional Treatment After Breast-Conserving Surgery for Early-Stage Breast Cancer. .J Clin Oncol. 2019 Dec 10;37(35):3340-3349. [CrossRef]
- Whelan TJ, Smith S, Parpia S, Fyles AW, Bane A, Liu FF, Rakovitch E, Chang L, Stevens C, Bowen J, et al.: LUMINA Study Investigators. Omitting Radiotherapy after Breast-Conserving Surgery in Luminal A Breast Cancer. N Engl J Med. 2023 Aug 17;389(7):612-619. [CrossRef]
- Jagsi R, Griffith KA, Harris EE, Wright JL, Recht A, Taghian AG, Lee L, Moran MS, Small W Jr, Johnstone C, et al.: Omission of Radiotherapy After Breast-Conserving Surgery for Women With Breast Cancer With Low Clinical and Genomic Risk: 5-Year Outcomes of IDEA. J Clin Oncol. 2024 Feb 1;42(4):390-398. [CrossRef]
- LZ Braunstein, J Wong, DA Dillon, YH Chen, P Catalano, O Cahlon, MB El-Tamer, R Jimenez, A Khan, C Perez, et al.: Preliminary report of the PRECISION Trial (Profiling Early Breast Cancer for Radiotherapy Omission): A Phase II Study of Breast-Conserving Surgery Without Adjuvant Radiotherapy for Favorable-Risk Breast Cancer [abstract]. In: Proceedings of the 2022 San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium; 2022 Dec 6-10; San Antonio, TX. Philadelphia (PA): AACR; Cancer Res 2023;83(5 Suppl):Abstract nr OT1-12-02. [CrossRef]
- Kirwan, C.C.; Coles, C.E.; Bliss, J.; Kirwan, C.; Kilburn, L.; Fox, L.; Cheang, M.; Griffin, C.; Francis, A.; Kirby, A.; et al. It’s PRIMETIME. Postoperative Avoidance of Radiotherapy: Biomarker Selection of Women at Very Low Risk of Local Recurrence. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 28, 594–596. [CrossRef]
- Offersen, B.; Al-Rawi, S.; Bechmann, T.; Kamby, C.; Mathiessen, L.; Nielsen, H.; Nielsen, M.; Stenbygaard, L.; Jensen, M.; Alsner, J. The DBCG RT NATURAL trial: Accelerated partial breast irradiation versus no irradiation for early stage breast cancer, a clinically controlled randomized phase III trial. In Proceedings of the Danske Kræftforskningsdage, Odense, Denmark, 30–31 August 2018.
- EXamining PErsonalised Radiation Therapy for Low-risk Early Breast Cancer (EXPERT), NCT02889874. [Internet] https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT02889874. (accessed on May 26th, 2024).
- White JR, Anderson SJ, Harris EE, et al. NRG-BR007: a phase III trial evaluating de-escalation of breast radiation (DEBRA) following breast-conserving surgery (BCS) of stage 1, hormone receptor1, HER2-, RS 18 breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 2022;40(16_suppl). TPS613-TPS613. [Internet] https://clin.larvol.com/abstract-detail/SABCS%202022/60536546.
- Meattini, I.; Poortmans, P.M.P.; Marrazzo, L.; Desideri, I.; Brain, E.; Hamaker, M.; Lambertini, M.; Miccinesi, G.; Russell, N.; Saieva, C.; et al. Exclusive endocrine therapy or partial breast irradiation for women aged ≥70 years with luminal A-like early stage breast cancer (NCT04134598-EUROPA): Proof of concept of a randomized controlled trial comparing health related quality of life by patient reported outcome measures. J. Geriatr. Oncol. 2021, 12, 182–189. [CrossRef]
- Savard MF, Alzahrani MJ, Saunders D, Chang L, Arnaout A, Ng TL, Brackstone M, Vandermeer L, Hsu T, Awan AA, Cole K, Larocque G, Clemons M. Experiences and Perceptions of Older Adults with Lower-Risk Hormone Receptor-Positive Breast Cancer about Adjuvant Radiotherapy and Endocrine Therapy: A Patient Survey. Curr Oncol. 2021 Dec 8;28(6):5215-5226. [CrossRef]
- A Morris, DA Hanes, H Kaplan; Long Term Outcomes of Radiation (RT)-Monotherapy vs. Combined RT + Endocrine Therapy (RT+ET) in Low-Risk Early-Stage Breast Cancer Patients 70 Years or Older after Breast-Conserving Surgery (BCS). Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys Volume 117, Issue 2, Suppl., S5-S6; October 01, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Mann GB, Skandarajah AR, Zdenkowski N, Hughes J, Park A, Petrie D, Saxby K, Grimmond SM, Murugasu A, Spillane AJ, et al.: Postoperative radiotherapy omission in selected patients with early breast cancer following preoperative breast MRI (PROSPECT): primary results of a prospective two-arm study. Lancet. 2024 Jan 20;403(10423):261-270. Epub 2023 Dec 5. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jagsi R, Chadha M, Moni J, Ballman K, Laurie F, Buchholz TA, Giuliano A, Haffty BG. Radiation field design in the ACOSOG Z0011 (Alliance) Trial. J Clin Oncol. 2014 Nov 10;32(32):3600-6. Epub 2014 Aug 18. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Katz MS, McCall L, Ballman K, Jagsi R, Haffty BG, Giuliano AE. Correction to: Nomogram-based estimate of axillary nodal involvement in ACOSOG Z0011 (Alliance): validation and association with radiation protocol variations. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2021 Feb;185(3):891. doi: 10.1007/s10549-020-05980-0. Erratum for: Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2020 Apr;180(2):429-436. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henke G, Knauer M, Ribi K, Hayoz S, Gérard MA, Ruhstaller T, Zwahlen DR, Muenst S, Ackerknecht M, Hawle H, et al.: Tailored axillary surgery with or without axillary lymph node dissection followed by radiotherapy in patients with clinically node-positive breast cancer (TAXIS): study protocol for a multicenter, randomized phase-III trial. Trials. 2018 Dec 4;19(1):667. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Algara López M, Rodríguez García E, Beato Tortajada I, Martínez Arcelus FJ, Salinas Ramos J, Rodríguez Garrido JR, Sanz Latiesas X, Soler Rodríguez A, Juan Rijo G, Flaquer García A. OPTimizing Irradiation through Molecular Assessment of Lymph node (OPTIMAL): a randomized open label trial. Radiat Oncol. 2020 Oct 2;15(1):229. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Tinterri C, Gentile D, Gatzemeier W, Sagona A, Barbieri E, Testori A, Errico V, Bottini A, Marrazzo E, Dani C, et al.: SINODAR-ONE Collaborative Group. Preservation of Axillary Lymph Nodes Compared with Complete Dissection in T1-2 Breast Cancer Patients Presenting One or Two Metastatic Sentinel Lymph Nodes: The SINODAR-ONE Multicenter Randomized Clinical Trial. Ann Surg Oncol. 2022 Sep;29(9):5732-5744. Epub 2022 May 12. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Boniface J, Filtenborg Tvedskov T, Rydén L, Szulkin R, Reimer T, Kuehn T, Kontos M, Gentilini OD, Olofsson Bagge R, Sund M, et al.: SENOMAC Trialists’ Group; SENOMAC Trialists' Group. Omitting Axillary Dissection in Breast Cancer with Sentinel-Node Metastases. N Engl J Med. 2024 Apr 4;390(13):1163-1175. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Wild SR, van Roozendaal LM, de Wilt JHW, van Dalen T, van der Hage JA, van Duijnhoven FH, Simons JM, Schipper RJ, de Munck L, van Kuijk SMJ, et al.: De-escalation of axillary treatment in the event of a positive sentinel lymph node biopsy in cT1-2 N0 breast cancer treated with mastectomy: nationwide registry study (BOOG 2013-07). Br J Surg. 2024 Apr 3;111(4):znae077. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Alkner S, de Boniface J, Lundstedt D, Mjaaland I, Ryden L, Vikstrom J, Bendahl PO, Holmberg E, Sackey H, Wieslander E, et al.: Protocol for the T-REX-trial: tailored regional external beam radiotherapy in clinically node-negative breast cancer patients with 1-2 sentinel node macrometastases - an open, multicentre, randomised non-inferiority phase 3 trial. BMJ Open. 2023 Sep 26;13(9):e075543. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Regional Radiotherapy in Biomarker Low-Risk Node Positive and T3N0 Breast Cancer; https://clinicaltrials.goc/study/NCT03488693 (accessed on May 17th, 2024).
- Qi WX, Cao L, Zheng S, Xu C, Cai R, Xu H, Cai G, Chen J. IMNI PRECISION trial protocol: a phase II, open-label, non-inferior randomized controlled trial of tailoring omission of internal mammary node irradiation for early-stage breast cancer. BMC Cancer. 2022 Dec 27;22(1):1356. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Xie SJ, Wang RJ, Wu SG, Zhang FX. 21-gene recurrence score in predicting the outcome of postoperative radiotherapy in T1-2N1 luminal breast cancer after breast-conserving surgery. Breast. 2024 Apr;74:103679. Epub 2024 Feb 12. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Krug D, Baumann R, Budach W, Duma MN, Dunst J, Feyer P, Fietkau R, Haase W, Harms W, Hehr T, et al.: Commercially Available Gene Expression Assays as Predictive Tools for Adjuvant Radiotherapy? A Critical Review. Breast Care (Basel). 2020 Apr;15(2):118-126. Epub 2020 Jan 24. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Gerber B, Schneeweiss A, Möbus V, Golatta M, Tesch H, Krug D, Hanusch C, Denkert C, Lübbe K, Heil J, et al.: Pathological Response in the Breast and Axillary Lymph Nodes after Neoadjuvant Systemic Treatment in Patients with Initially Node-Positive Breast Cancer Correlates with Disease Free Survival: An Exploratory Analysis of the GeparOcto Trial. Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jan 20;14(3):521. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Montero Á, Ciérvide R, Poortmans P. When Can We Avoid Postmastectomy Radiation Following Primary Systemic Therapy? Curr Oncol Rep. 2019 Oct 29;21(12):95. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Wild SR, de Munck L, Simons JM, Verloop J, van Dalen T, Elkhuizen PHM, et al. De-escalation of radiotherapy after primary chemotherapy in cT1-2N1 breast cancer (RAPCHEM; BOOG 2010-03): 5-year follow-up results of a Dutch, prospective, registry study. Lancet Oncol. 2022;23(9): 1201–1210.
- Boersma L.J., Verloop J., Voogd A.C., Elkhuizen P.H.M., Houben R., van Leeuwen A.E., et al. Radiotherapy after primary CHEMotherapy (RAPCHEM): practice variation in a Dutch registration study (BOOG 2010-03) Radiother Oncol. 2020;145:201–208.
- Goyal, A.; Cramp, S.; Marshall, A.; Wheatley, D.; Hammonds, N.; Puri, S.; Homer, T.; Vale, L.; Butt, R.; Mir, R.; et al. Abstract OT1-04-01: ATNEC: A Multi-Centre, Randomised Trial Investigating Whether Axillary Treatment Can Be Avoided in T1-3N1M0 Breast Cancer Patients with No Residual Cancer in the Lymph Glands after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy (Clinicaltrials.Gov: Nct04109079). Cancer Res. 2022, 82, OT1-04-01. [CrossRef]
- Mamounas, E.P. GS02-07 Loco-Regional Irradiation in Patients with Biopsy-Proven Axillary Node Involvement at Presentation Who Become Pathologically Node-Negative after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy: Primary Outcomes of NRG Oncology/NSABP B-51/RTOG 1304. In Proceedings of the 2023 San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium, San Antonio, TX, USA, 7 December 2023.
- Leon-Ferre R.A., Jonas S.F., Salgado R., Loi S., de Jong V., Carter J.M., Nielsen T.O., Leung S., Riaz N., Chia S., et al.: International Immuno-Oncology Biomarker Working Group. Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. JAMA. 2024 Apr 2;331(13):1135-1144. [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chen F, Zhou P, Ren G, Lee EKW, Liu Q, Shen Y, Wang Y, El Helali A, Jin JY, Fu P, et al.: Interpretable deep learning insights: Unveiling the role of 1 Gy volume on lymphopenia after radiotherapy in breast cancer. Radiother Oncol. 2024 May 19;197:110333. Epub ahead of print. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NRG-BR008 (“HERO”): A Phase III Randomized Trial Seeking to Optimize Use of Radiotherapy in Patients with Early-Stage, Low Risk, HER2-Positive Breast Cancer (nrgoncology.org) (accessed on June 27th, 2024).
| Trial | Phase 3 | n | Main selection criteria | Therapy | F-up | Recurrence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LUMINA [74] | no | 500 | 55+ yrs; T1N0; R0(1mm) ; G1-2; Ki-67 -13.25% | ET | 5 yrs | at 5 yrs : 2.3% |
| IDEA [75] | no | 200 | 50-69 yrs; T1N0 R0(2mm); Oncotype RS: -18 | ET | minimum 57mo | overall: 4% |
| PRECISION [76] | no | 690 | 50-75 yrs ; T1N0 ; R0 ; G1-2; PAM50 Luminal A | ET | median 27mo | at 2 yrs: 0.3% |
| PRIMETIME [77] | no | 1623 | 60+ yrs; T1N0; R0(1mm); G1-2; IHC4+C | ET | closed 03/22 | n.a. |
| NATURAL [78] | yes | 926 | 60+ yrs; T1N0; R0(2mm); G1-2 | ET vs ET+PBI | accruing | n.a. |
| EXPERT [79] | yes | 1170 | 50+ yrs; T1N0; R0; G1-2; PAM50 ROR-60 | ET vs ET+WBRT | accruing | n.a. |
| DEBRA [80] | yes | 1670 | 50-70 yrs; T1N0; R0; Oncotype RS -18 | ET vs ET+WBRT | accruing | n.a. |
| EUROPA [81] | yes | 926 | 70+ yrs; T1N0; R0; G1-2 (G3 if T1a/b); Ki67 -20% | ET vs RT(PBI/WBRT) | accruing | n.a. (endpoint : 2 yrs-HRQoL) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





