Submitted:
03 July 2024
Posted:
03 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
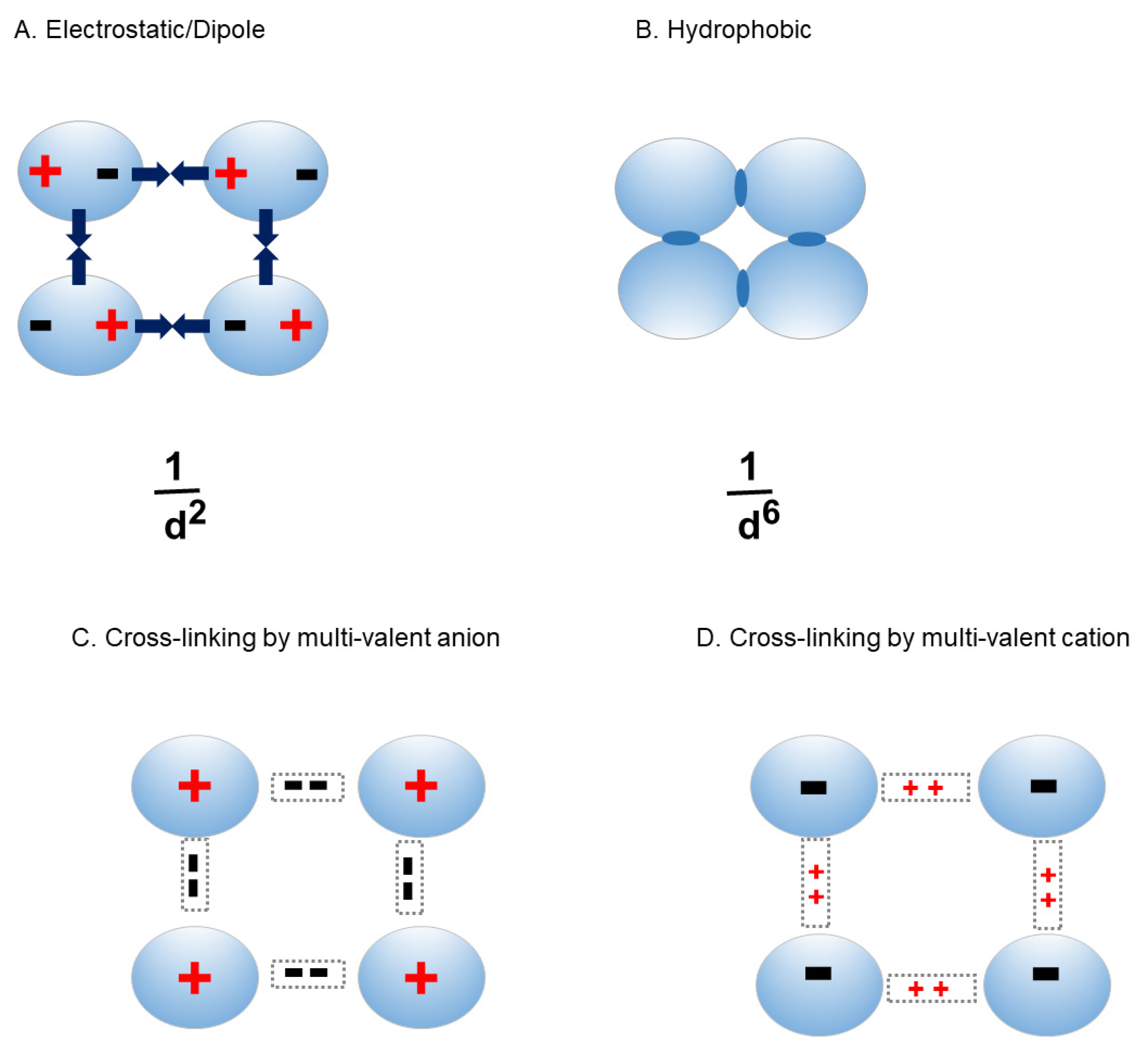
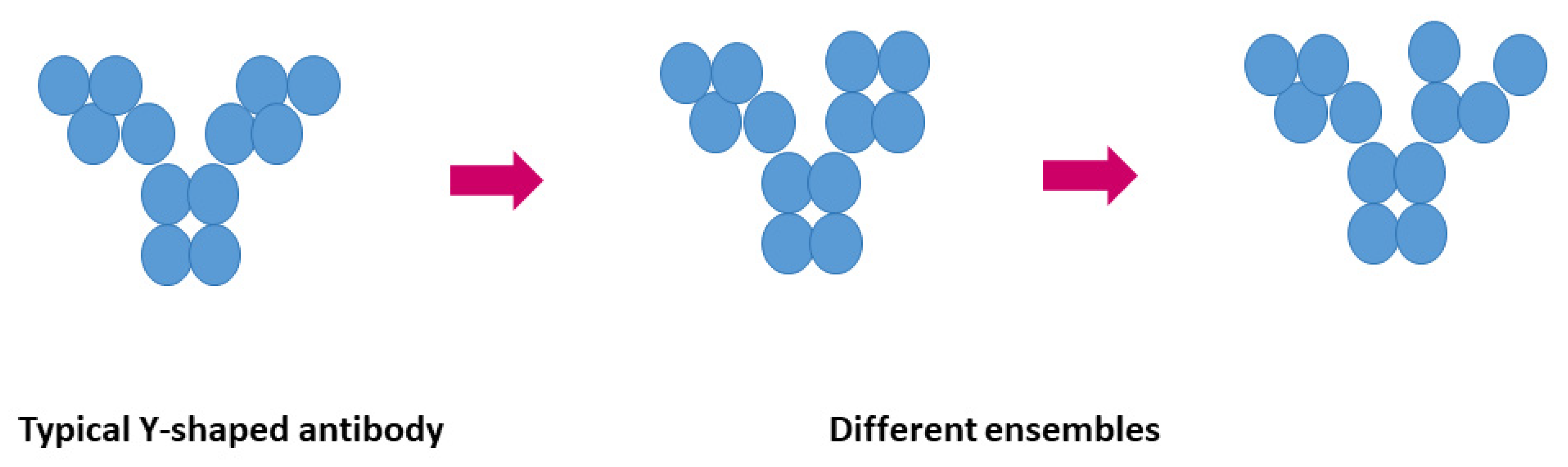
2. Inter-molecular interactions
3. High antibody concentration
3.1. Viscosity
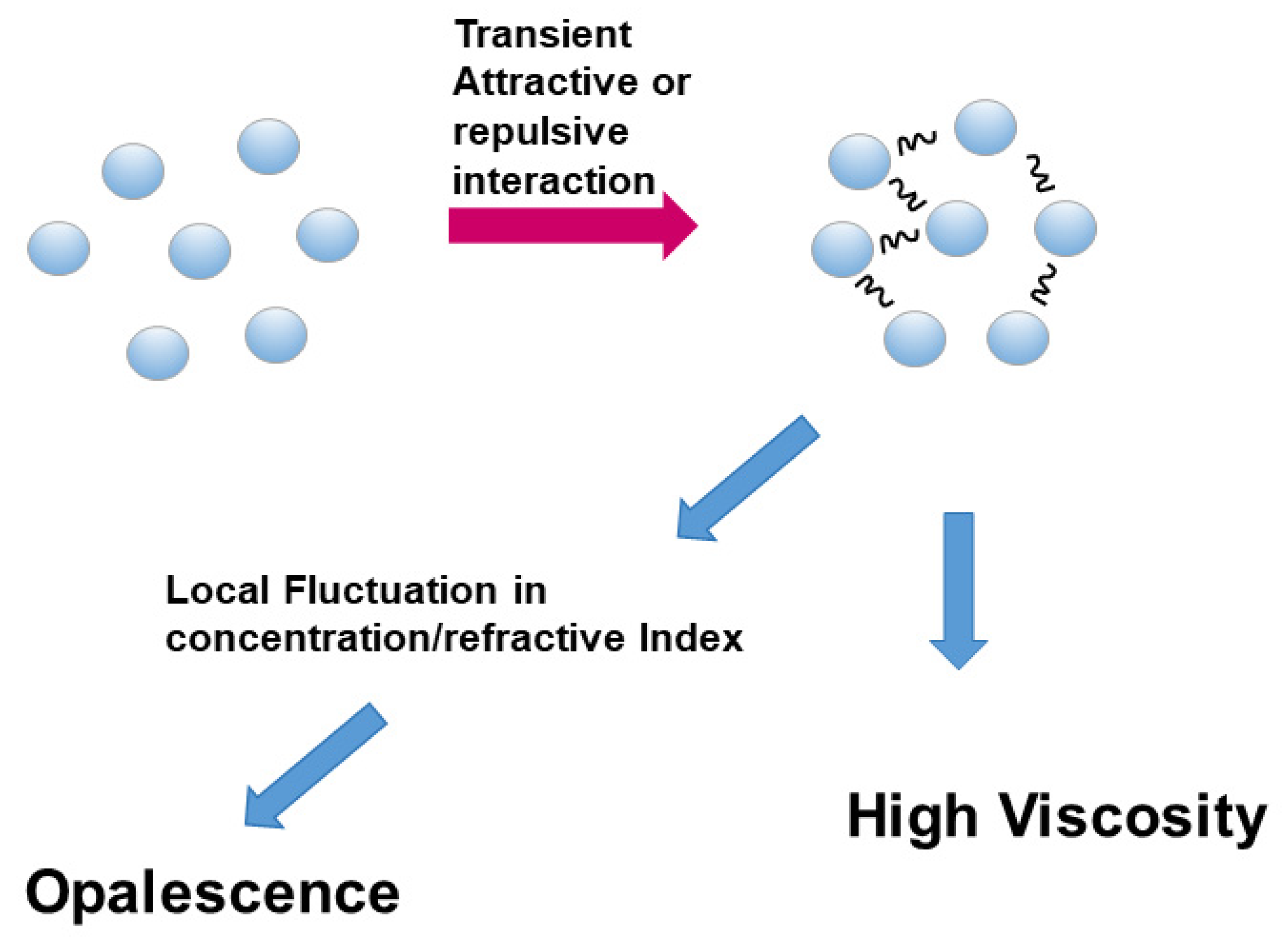
3.2. Opalescence
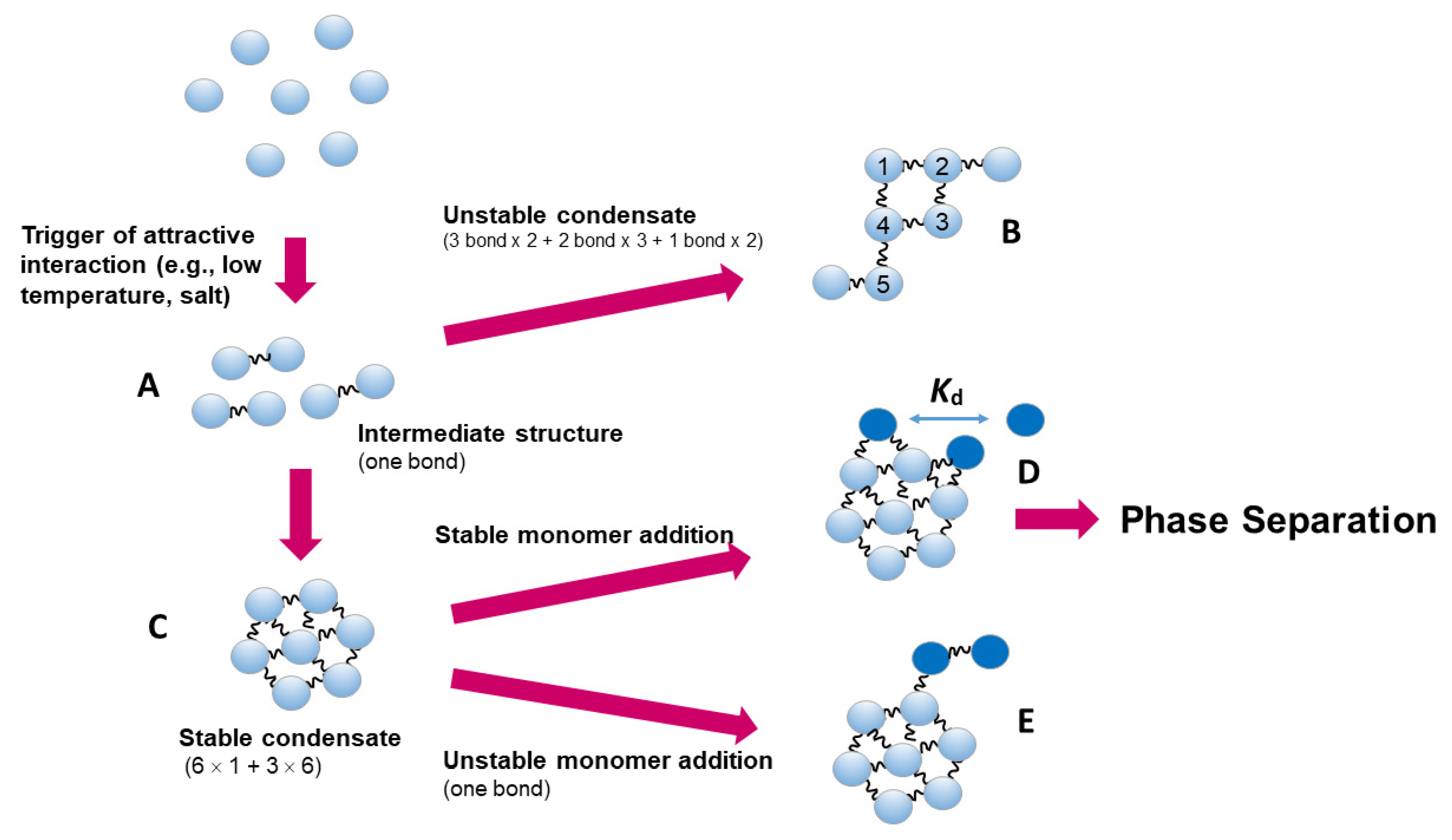
3.3. Liquid-liquid phase separation
3.4. Aggregation and amyloid
3.5. Reversible aggregation
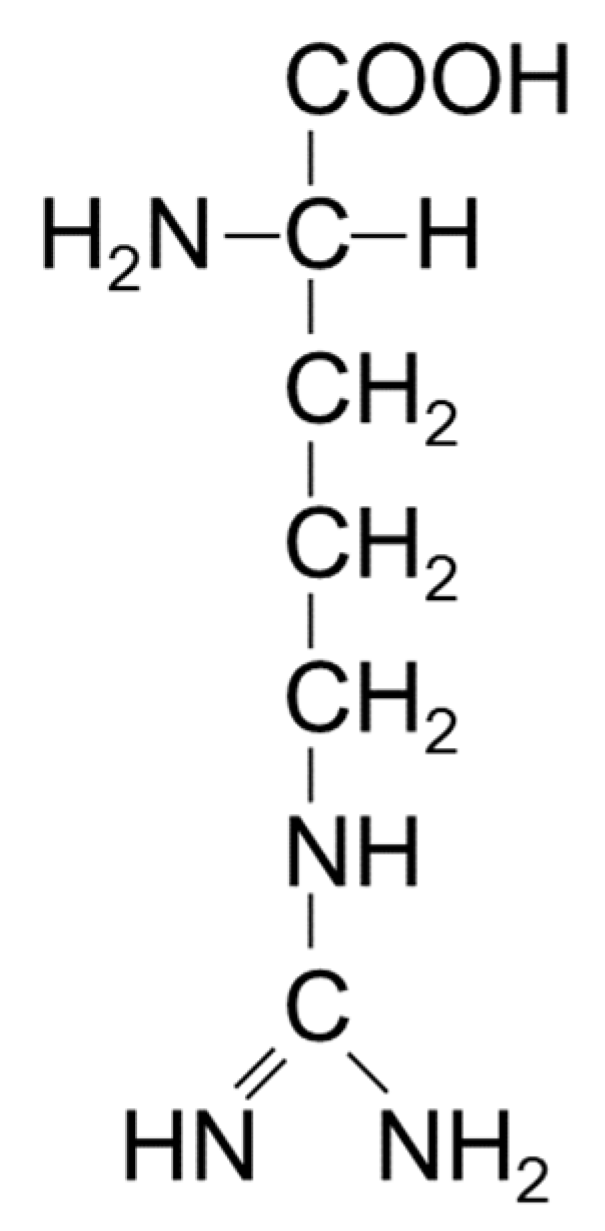
4. The effects of arginine
5. Conclusions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lui, L.H.; van der Walle, C.F.; Brochchini, S.; Velayuolhan, A. Discovering novel small molecule compound for prevention of monoclonal self-association. Antibodies 2022, 11, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Probakaran, P.; Chen, W.; Zhu, Z.; Feng, Y.; Dimitrov, D.S. Antibody aggregation: insights from sequence and structure. Antibodies 2016, 5, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sibanda, N.; Shanmugam, R.K.; Curtis, R. The relationship between protein-protein interactions and liquid-liquid phase separa tion for monoclonal antibodies, Mol. Pharm. 2023, 20, 2662–2674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, J.M.R.; Patapoff, T.W.; Cromwell, M.E.M. Kinetics and thermodynamics of dimer formation and dissociation for a re combinant humanized monoclonal antibody to vascular endothelial growth factor. Biochemistry 1999, 38, 13960–13967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingsbury, J.S.; Saini, A.; Auclair, S.M.; Fu, L.; Lantz, M.M.; Halloran, K.T.; Calero-Rubio, C.; Schwenger, W.; Airiau, C.Y.; Zhang, J.; Gokarn, Y.R. A single molecular descriptor to predict solution behavior of therapeutic antibodies. Sci Adv 2020, 5, eabb0372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhri, A. The role of amino acid sequence in the self-association of therapeutic monoclonal antibodies: Insights frpm co arce-grained modeling. J. Phys. Chem. 2013, B117, 1269–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.; Shire, S.J.; Kalonia, D.S. Factors affecting the viscosity in high concentration solutions of different monoclonal anti bodies. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 99, 4812–4829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmeister, F. Zur Lehre von der wirkung der salze. Arch. Expt. Pathl. Pharmakol. 1888, 24, S12–S23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traube, J. The theory of attraction pressure. J. Phys. Chem. 1910, 14, 471–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traube, J. The attraction pressure. J. Phys. Chem. 1910, 14, 452–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Qi, W.; Schwartz, D.K.; Randolph, T.W.; Carpenter, J.H. The effects of excipients on protein aggregation during agi tation: an interfacial shear rheology study. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 102, 2460–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yancey, P.H.; Clark, M.E.; Hand, S.C.; Bowlus, R.D.; Somero, G.N. Living with water stress: evolution of osmolyte systems. Science 1982, 217, 1214–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerlsma, S.Y. Reversible denaturation of ribonuclease in aqueous solutions as influenced by polyhydric alcohols and some other additives. J. Biol. Chem. 1968, 243, 857–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arakawa, T.; Timasheff, S.N. The stabilization of proteins by osmolytes. Biophys. J. 1985, 47, 411–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanford, C. Protein Denaturation: Part C. Theoretical models for the mechanism of denaturation. Adv. Protein Chem. 1968, 23, 121–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsumoto, K.; Umetsu, M.; Kumagai, I.; Ejima, D.; Philo, J.S.; Arakawa, T. Role of arginine in protein refolding, solubilization, and purification. Biotechnol. Prog. 2004, 20, 1301–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, C.; Iwashita, K.; Shiraki, K. Selective separation method of aggregates from IgG solution by aqueous two-phase system. Protein Expr. Purif. 2019, 161, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asakura, S.; Oosawa, F. On interaction between two bodies immersed in a solution of macromolecules. J. Chem. Phys. 1954, 22, 1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minton, A.P. Excluded volume as a determinant of protein structure and stability. Biophys. J. 1980, 32, 77–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauzmann, W. Structural factors in protein denaturation. J. Cell Physiol. Suppl. 1956, 47, 113–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.; Jiang, X.; Chen, Z.; Huang, C.; Qian, F. Quantifyinh protein shape to elucidate its inf;uence on solution viscosity in high-concentration electrolyte solutions. Mol. Pharm. 2024, 21, 1719–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lilyestrom, W.G.; Yadav, S.; Shire, S.J.; Scherer, T.M. Monoclonal antibody self-association, cluster formation, and rheology at high concentrations. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2013, 117, 6373–6384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, J.; Hu, Y.; Esfandiary, R.; Sathish, H.A.; Bishop, S.M.; Joshi, S.B.; Middaugh, C.R.; Volkin, D.B.; Weis, D.D. Charge-mediated Fab-Fc interactions in an IgG1 antibody induce reversible self-association, cluster formation, and elevated viscosity. MABs 2016, 8, 1561–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanai, S.; Liu, J.; Patapoff, T.W.; Shire, S.J. Revsersible self-association of a concentrated monoclonal antibody solution mediated by Fab-Fab interaction that impacts solution viscosity. J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 97, 4219–4227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Izadi, S.; Zarzar, J.; Wu, P.; Oh, A.; Carter, P.J. Variable domain mutational analysis to probe the molecular mechanisms of high viscosit of an IgG1 antibody. MABS 2024, 16, 2304282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S. Effects of arginine in therapeutic protein formulations: a decade review and perspectives. Antib. Ther. 2023, 6, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, T.; Iwashita, K.; Shiraki, K. Viscosity control of protein solution by small solutes: a review. Curr. Protein Pept. Sci. 2018, 19, 746–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, A.Y.; Castellanos, M.M.; Mattison, K.; Kruger, S.; Curtis, J.E. Studying excipient modulated physical stabilioty and viscosity of monoclonal antibody formulations using small angle-light scattering. Mol. Pharm. 2019, 16, 4319–4338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, N.; Takai, E.; Arakawa, T.; Shiraki, K. Arginine and lysine reduce the high viscosity of serum albumin solutions for pharmaceutical injection. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2014, 117, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, N.; Takai, E.; m Arakawa, T.; Shiraki, K. Specific decrease in solution viscosity of antibodies by arginine for therapeutic formulations. Mol. Pharm. 2014, 11, 1889–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pindrus, M.A.; Shire, S.J.; Yadav, S.; Kalonia, D.S. Challenges in determining intrinsic viscosity under low ionic strength. Phar Res. 2017, 34, 836–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishinami, S.; Yoshizawa, S.; Arakawa, T.; Shiraki, K. Allantoin and hydantoin as new protein aggregation suppressors. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 114, 497–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, G.B.; Shah, V.; Sanches, P.; Patel, M.; Casey. R.; Jamieson, C.; Burley, G.A.; Lewis, W.J.; Rattray, Z. Enhancing viscosity control in antibody formulations: A framework for the biophysical screening of mutations targeting solvent-accessible hydrophobic and electrostatic patches. Molecules 2004, 23, 2345–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malkowski, E.K.; Chen, H.T.; Wang, T.; Wu, L.; Huang, J.; Mock, M.; Underhill, P.; Pelegri-O’Day, E.; Maglalang, E.; Winters, D.; Tessier, P.M. Reduction of monoclonal antibody viscosity using interpretable machine learning. MABS 2024, 16, 2303781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arakawa, T.; Tomioka, Y.; Kurosawa, Y.; Akuta, T. Elucidating the mechanism of additive effects at high concentrations on hydrophobic interaction chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A. 2023, 1702, 464091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapenna, A.; Dagallier, C.; Huille, S.; Tribet, C. Poly(glutamic acid)-based viscosity reducers for concentrated formulations of a monclonal IgG antibody. Mol. Pharm. 2024, 21, 982–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salinas, B.A.; Satishi, H.A.; Bishop, S.M.; Hann, N.; Carpenter, J.H.; Randolph, T.W. Understanding and modulating opalescence and viscosity in a monoclonal antibody formulation. J. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 99, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakauchi, Y.; Nishinami, S.; Murakami, Y.; Ogura, T.; Kano, H.; Shiraki, K. Opalescence arising from network assembly in antibody solution. Mol. Pharm. 2022, 19, 1160–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oki, S.; Nishinami, S.; Shiraki, K. Arginine suppresses opalescence and liquid-liquid phase separation in IgG solutions. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 118, 1708–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oki, S.; Nishinami, S.; Nakauchi, Y.; Ogura, T.; Shiraki, K. Arginine and its derivatives suppress the opalescence of an antibody solution. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 111, 1126–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, F.J.; Kisilevsky, R. Immunoglobulin light chains, glycosaminoglycans, and amyloid. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2000, 57, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-Alvarado, M. Amyloid formation in light chain amyloidosis. Curr. Top Med. Chem. 2012, 12, 2523–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, P.W.; Raffen, R.; Hanson, D.K.; Deng, Y.L.; Berrios-Hammond, M.; Westholm, F.A.; Murphy, C.; Eulitz, M.; Wetzel, R.; Solomon, A.; et al. Recombinant immunglobulin variable domains generated from synthetic genes provide a system for in vitro characterization of light-chain amyloid proteins. Protein Sci. 1995, 4, 421–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minakata, E.N.; Popiel, H.A.; Tada, M.; Takahashi, T.; Yamane, H.; Saitoh, Y.; Takahashi, Y.; Ozawa, D.; Takeda, A.; Takeuchi, T.; et al. Arginine is a disease modifier for polyQ disease models that stabilize polyQ protein conformation. Brain 2020, 143, 1811–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, U.; Hariprasad, G.; Ethayathulla, A.S.; Manral, P.; Das, T.K.; Pasha, S.; Mann, A.; Gangull, M.; Verma, A.K.; Bhat, R.; et al. Inhibition of protein aggregation: supramolecular assemblies of arginine hold the key. PLoS One 2007, 11, e1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, J.M.R.; Patapoff, T.W.; Cromwell, M.E.M. Kinetics and thermodynamics of dimer formation and dissociation for a recombinant humanized monoclonal antibody to vascular endothelial growth factor. Biochemistry 1999, 38, 13960–13967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirano, A.; Tokunaga, H.; Tokunaga, M.; Arakawa, T.; Shiraki, K. The solubility of nucleobases in aqueous arginine solutions. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2010, 197, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mozgovics, M.; Fischer, A.; Brocard, C.; Jungbauer, A.; Lingg, N. L-Arginine sulfate reduces irreversible protein binding in immobilized metal affinity chromatography. J. Chromatogr. A. 2023, 1706, 464246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maity, H.; Karkaria, C.; Davagnino, J. Mapping of solution components, pH changes, protein stability and the elimination of protein precipitation during freeze-thawing of fibroblast growth factor 20. Int. J. Pharm. 2009, 378, 122–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, L.; Stucchi, R.; Konstantoulea, K.; van de Kamp, G.; Kos, R.; Geerts, W.J.C.; van Bezouwen, L.S.; Förster, F.G.; Altelaar, M.; Hoogenraad, C.C.; et al. Arginine π-stacking drives binding to fibrils of the Alzheimer protein Tau. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Prabakaran, P.; Chen, W.; Zhu, Z.; Feng, Y.; Dimitrov, D.S. Antibody aggregation: insights from sequence and structure. Antibodies (Basel) 2016, 5, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manikwar, P.; Majumdar, R.; Hickey, J.M.; Thakkar, S.V.; Samra, H.S.; Sathish, H.A.; Bishop, S.M.; Middaugh, C.R.; Weiss, D.D.; Volkin, D.B. Correlating excipient effects on conformational and storage stability of an IgG monoclonal antibody with local dynamics as measured by hydrogen/deuterium-exchange mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 102, 2136–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lilyestrom, W.G.; Shire, S.J.; Scherer, T.M. Influence of the cosolute environment on IgG solution structure analyzed by small-angle X-ray scattering. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2012, 116, 9611–9618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.N.; Uversky, V.N. Biological importance of arginine: A comprehensive review of the roles in structure, disorder, and functionality of peptides and proteins. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024, 257, 128646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arakawa, T.; Philo, J.S.; Tsumoto, K.; Yumioka, R.; Ejima, D. Elution of antibodies from a Protein-A column by aqueous arginine solutions. Protein Expr. Purifi. 2004, 36, 244–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arakawa, T.; Tomioka, Y.; Nakagawa, M.; Sakuma, C.; Kurosawa, Y.; Ejima, D.; Tsumoto, K.; Akuta, T. Non-affinity purification of antibodies. Antibodies (Basel) 2023, 12, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshizawa, S.; Arakawa, T.; Shiraki, K. Thermal aggregation of human immunoglobulin G in arginine solutions: Contrasting effects of stabilizers and destabilizers. Int. J. Biol. Macomol. 2017, 104, 650–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshizawa, S.; Oki, S.; Arakawa, T.; Shiraki, K. Trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO) is a counteracting solute of benzyl alcohol for multi-dose formulation of immunoglobulin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 107, 984–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svilenov, H.L.; Kulakova, A.; Zalar, M.; Golovanov, A.P.; Harris, P.; Winter, G. Orthogonal techniques to study the effect of pH, sucrose, and arginine salts on monoclonal antibody physical stability and aggregation during long-term storage. J Pharm Sci. 2020, 109, 584–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hada, S.; Burlakoti, U.; Kim, K.H.; Han, J.S.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, N.A.; Jeong, S.H. ; A comprehensive evaluation of arginine and its derivatives as protein formulation stabilizers. Int J Pharm. 2023, 647, 123545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arakawa, T.; Akuta, T. Mechanistic insight into poly-reactivity of immune antibodies upon acid denaturation or arginine mutation in antigen-binding regions. Antibodies (Basel) 2023, 12, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




