Submitted:
03 July 2024
Posted:
04 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
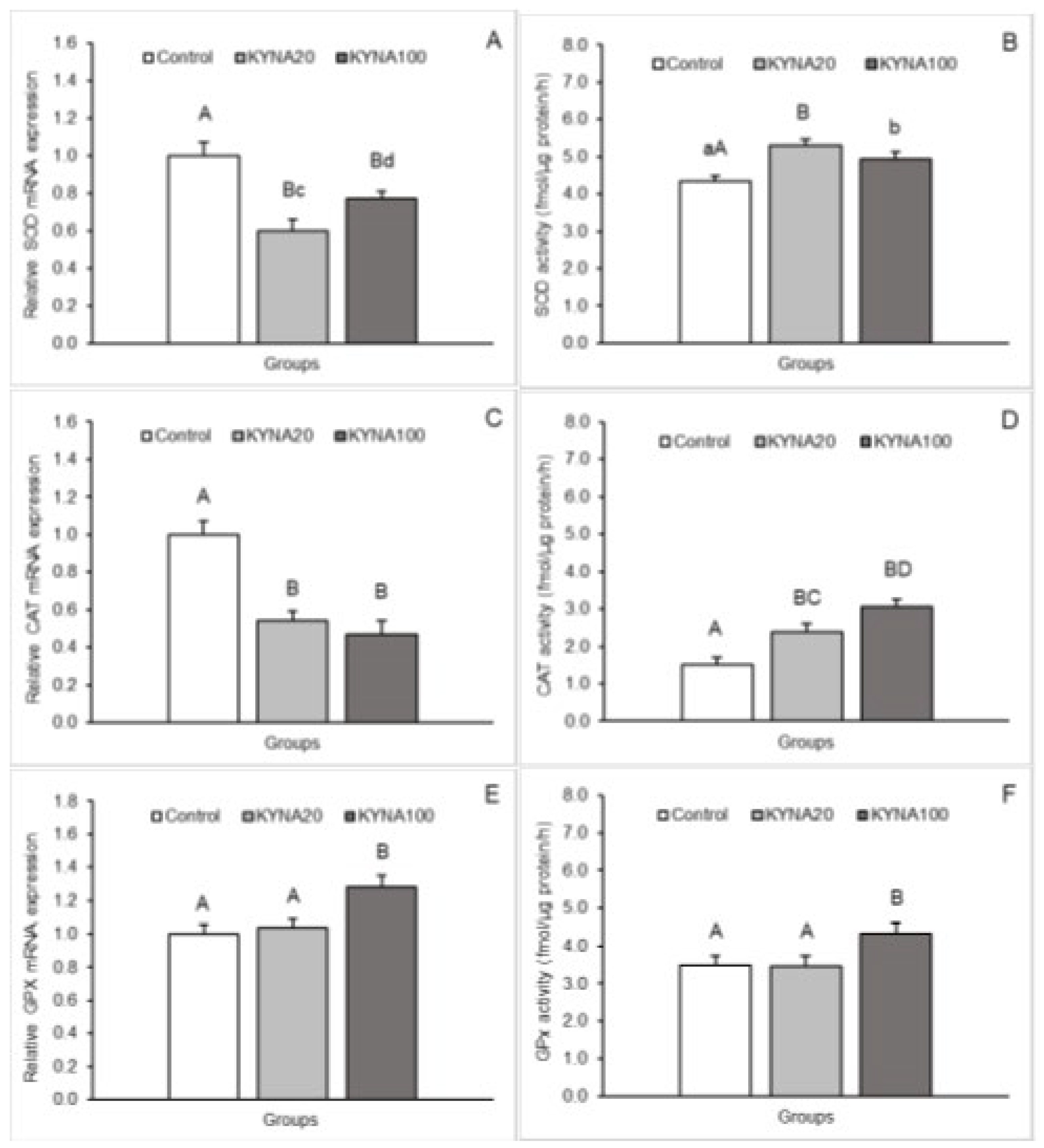
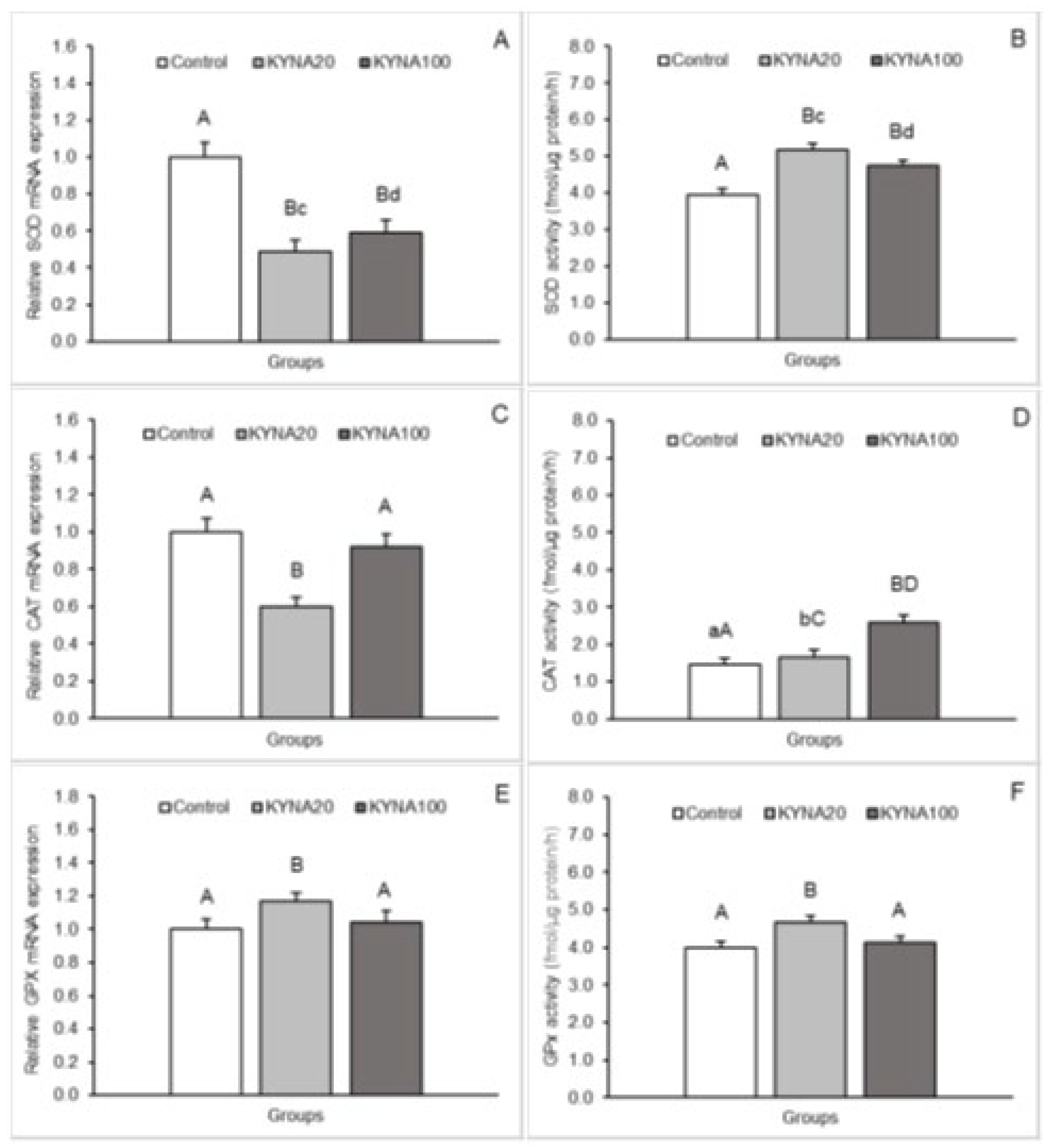
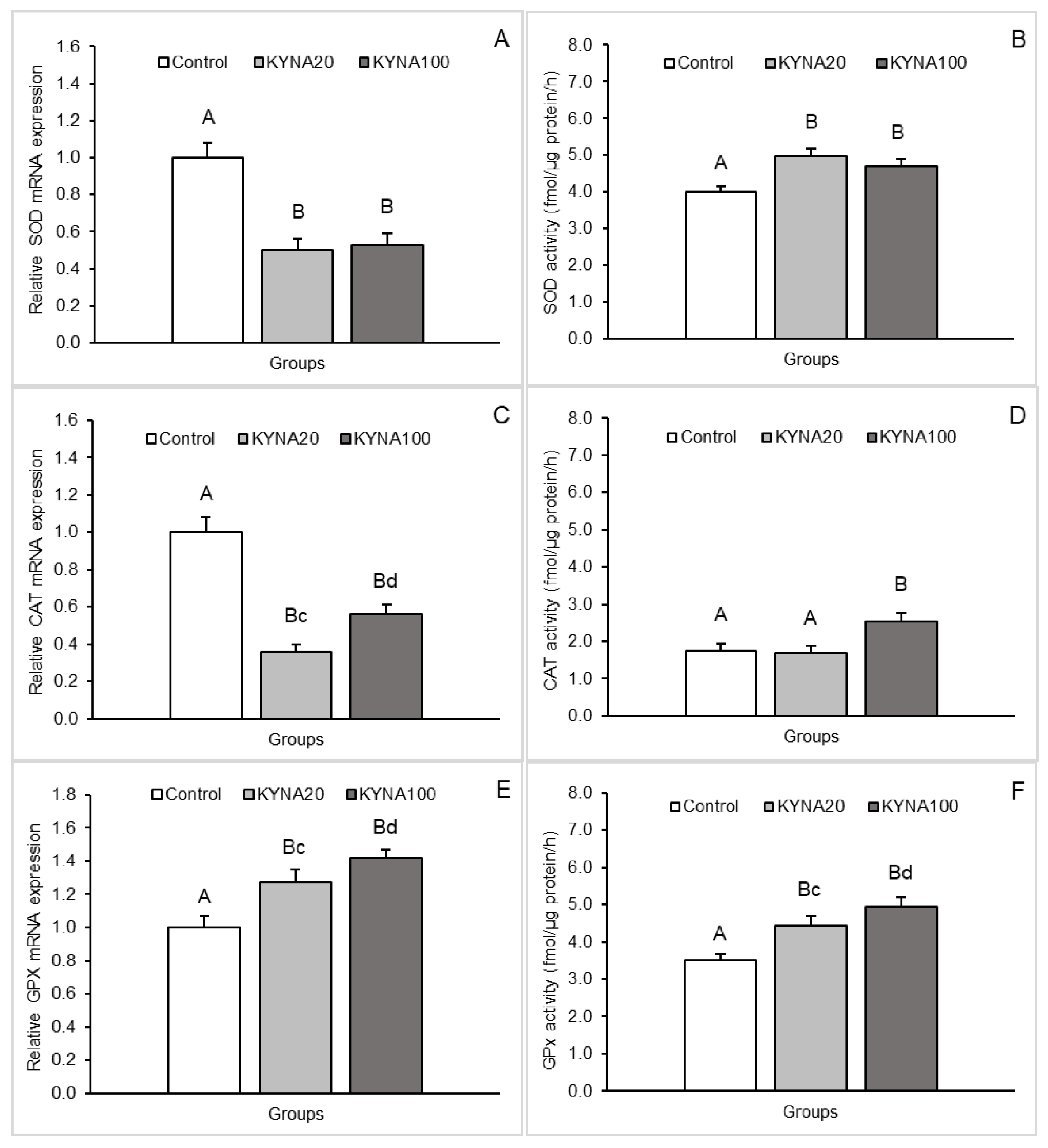
2.1. SOD2, CAT and GPx1 mRNA Expression Levels in the Hypothalamus and Hippocampus
2.2. SOD, CAT and GPx Activities in the Hypothalamus and Hippocampus
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animal Maintenance
4.2. Third Ventricle Cannulation
4.3. Experimental Design and Tissue Collection
4.4. Relative mRNA Abundance
4.5. Determination of the Antioxidant Enzyme Activity
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stone, T.W. Kynurenines in the CNS: from endogenous obscurity to therapeutic importance. Prog. Neurobiol. 2001, 64, 185–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilmas, C.; Pereira, E.F.; Alkondon, M.; Rassoulpour, A.; Schwarcz, R.; Albuquerque, E.X. The brain metabolite kynurenic acid inhibits alpha7 nicotinic receptor activity and increases non-alpha7 nicotinic receptor expression: physiopathological implications. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 7463–7473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozłowska, M.; Kozłowski, P. Kynurenine acid - metabolism and regulation of kynurenine pathway. J. Edu. Health Sport. 2017, 7, 888–895. [Google Scholar]
- Turski, M.P.; Turska, M.; Zgrajka, W.; Kuc, D.; Turski, W.A. Presence of kynurenic acid in food and honeybee products. Amino Acids 2009, 36, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukui, S.; Schwarcz, R.; Rapoport, S.I.; Takada, Y.; Smith, Q.R. Blood-brain barrier transport of kynurenines: implications for brain synthesis and metabolism. J. Neurochem. 1991, 56, 2007–2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, F.; Schmidt, W.; Okuno, E.; Kido, R.; Köhler, C.; Schwarcz, R. Localization of kynurenine aminotransferase immunoreactivity in the rat hippocampus. J. Comp. Neurol. 1992, 321, 477–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wejksza, K.; Rzeski, W.; Okuno, E.; Kandefer-Szerszeń, M.; Albrecht, J. Turski, W.A. Demonstration of kynurenine aminotransferases I and II and characterization of kynurenic acid synthesis in oligodendrocyte cell line (OLN-93). Neurochem. Res. 2005, 30, 963–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannazza, G.; Chiarugi, A.; Parenti, C.; Zanoli, P.; Baraldi, M. Changes in kynurenic, anthranilic, and quinolinic acid concentrations in rat brain tissue during development. Neurochem. Res. 2001, 26, 511–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceresoli-Borroni, G.; Schwarcz, R. Perinatal kynurenine pathway metabolism in the normal and asphyctic rat brain. Amino Acids. 2000, 19, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notarangelo, F.M.; Pocivavsek, A. Elevated kynurenine pathway metabolism during neurodevelopment: Implications for brain and behavior. Neuropharmacology 2017, 112, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, F.; Eid, T.; Schwarcz, R. Neuronal damage after the injection of aminooxyacetic acid into the rat entorhinal cortex: a silver impregnation study. Neuroscience 1998, 82, 1165–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carpenedo, R.; Pittaluga, A.; Cozzi, A.; Attucci, S.; Galli, A.; Raiteri, M.; Moroni, F. Presynaptic kynurenate-sensitive receptors inhibit glutamate release. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2001, 13, 2141–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zmarowski, A.; Wu, H.Q.; Brooks, J.M.; Potter, M.C.; Pellicciari, R.; Schwarcz, R.; Bruno, J.P. Astrocyte-derived kynurenic acid modulates basal and evoked cortical acetylcholine release. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 529–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rassoulpour, A.; Wu, H.Q.; Ferré, S.; Schwarcz, R. Nanomolar concentrations of kynurenic acid reduce extracellular dopamine levels in the striatum. J. Neurochem. 2005, 93, 762–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amori, L.; Wu, H.Q.; Marinozzi, M.; Pellicciari, R.; Guidetti, P.; Schwarcz, R. Specific inhibition of kynurenate synthesis enhances extracellular dopamine levels in the rodent striatum. Neuroscience 2009, 159, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beggiato, S.; Tanganelli, S.; Fuxe, K.; Antonelli, T.; Schwarcz, R.; Ferraro, L. Endogenous kynurenic acid regulates extracellular GABA levels in the rat prefrontal cortex. Neuropharmacology 2014, 82, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardeland, R.; Zsizsik, B.K. Kynurenic acid as a free radical scavenger: measurements of educt and product fluorescence and of light emission from an excited intermediate state. In: Hardeland R, ed. Biological rhythms and antioxidative protection. Göttingen: Cuvillier. 1997, p. 153-160.
- Zsizsik, B.K.; Hardeland, R. A putative mechanism of kynurenic acid oxidation by free radicals: scavenging of two hydroxyl radicals and superoxide anion, release of •NO and CO2. In: Hardeland R, ed. Actions and redox properties of melatonin and other aromatic amino acid metabolites. Göttingen: Cuvillier; 2001, p. 164-167.
- Lugo-Huitrón, R.; Blanco-Ayala, T.; Ugalde-Muñiz, P.; Carrillo-Mora, P.; Pedraza-Chaverrí, J.; Silva-Adaya, D.; Maldonado, P.D.; Torres, I.; Pinzón, E.; Ortiz-Islas, E.; López, T.; García, E.; Pineda, B.; Torres-Ramos, M.; Santamaría, A.; La Cruz, V.P. On the antioxidant properties of kynurenic acid: Free radical scavenging activity and inhibition of oxidative stress. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2011, 33, 538–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Felice, A.; Ricceri, L.; Venerosi, A.; Chiarotti, F.; Calamandrei, G. Multifactorial origin of neurodevelopmental disorders: approaches to understanding complex etiologies. Toxics 2015, 3, 89–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deska, M. Activity of antioxidant enzymes under induced oxidative stress. J. Ecol. Engineer. 2020, 21, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahl, H.L.; Baererle, P.A. Oxygen and the control of gene expression. BioEssays 1994, 16, 497–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, R.J.; Chesrown, S.E.; Kuo, S.; Monnier, J.M.; Nick, H.S. Cytokine-inducible enhancer with promoter activity in both the rat and human manganese-superoxide dismutase genes. Biochem. J. 2000, 347, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sampath, D.; Perez-Polo, R. Regulation of antioxidant enzyme expression by NGF. Neurochem. Res. 1997, 22, 351–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antolin, I.; Rodriguez, C.; Sainz, R.M.; Mayo, J.C.; Uría, H.; Kotler, M.L.; Rodríguez-Colunga, M.J.; Tolivia, D.; Menéndez-Peláez, A. Neurohormone melatonin prevents cell damage: effect on gene expression for antioxidant enzymes. FASEB J. 1996, 10, 882–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czerska, M.; Mikołajewska, K.; Zieliński, M.; Gromadzińska, J.; Wąsowicz, W. Today’s oxidative stress markers. Medycyna Pracy (in Polish). 2015, 66, 393–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moroni, F.; Cozzi, A.; Sili, M.; Mannaioni, G. Kynurenic acid: a metabolite with multiple actions and multiple targets in brain and periphery. J. Neural Transm. 2012, 119, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, S.J.; Mitchell, N.L. The translational benefits of sheep as large animal models of human neurological disorders. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 831838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Praag H, Schinder AF, Christie BR, Toni N, Palmer TD, Gage FH. Functional neurogenesis in the adult hippocampus. Nature 2002, 415, 1030–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cadanes, E.; Davies, K.J. Mitochondrial free radical generation, oxidative stress, and aging. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2000, 29, 222–230. [Google Scholar]
- Espinet, C.; Gonzalo, H.; Fleitas, C.; Menal, M.J.; Egea, J. Oxidative stress and neurodegenerative diseases: A neurotrophic approach. Cur. Drug Targ. 2015, 16, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roszkowicz-Ostrowska, K.; Młotkowska, P.; Kowalczyk, P.; Marciniak, E.; Barszcz, M.; Misztal, T. Central stimulatory effect of kynurenic acid on BDNF-TrkB signaling and BER enzymatic activity in the hippocampal CA1 field in sheep. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, T.W. Development and therapeutic potential of kynurenic acid and kynurenine derivatives for neuroprotection. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2000, 21, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bratovcic, A. Antioxidant enzymes and their role in preventing cell damage. Acta Sci. Nutrition. Health 2020, 4, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inal, M.E.; Kanbak, G.; Sunal, E. Antioxidant enzyme activities and malondialdehyde levels related to aging. Clin. Chim. Acta 2001, 305, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, R.; Wood, T.R.; Nance, E. Superoxide dismutase reduces monosodium glutamate-induced injury in an organotypic whole hemisphere brain slice model of excitotoxicity. J. Biol. Eng. 2020, 14, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niedzielska, E.; Smaga, I.; Gawlik, M.; Moniczewski, A.; Stankowicz, P.; Pera, J.; Filip, M. Oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 53, 4094–4125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.H.; Cha, M.; Lee, B.H. Neuroprotective Effect of Antioxidants in the Brain. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Fernandez, S.; Bobo-Jimenez, V.; Requejo-Aguilar, R.; Gonzalez-Fernandez, S.; Resch, M.; Carabias-Carrasco, M.; Ros, J.; Almeida, A.; Bolaños, J.P. Hippocampal neurons require a large pool of glutathione to sustain dendrite integrity and cognitive function. Redox Biology 2018, 19, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silver Ferreira, F.; Schmitz, F.; Marques, E.P.; Siebert, C.; Wyse, A.T.S. Intrastriatal quinolinic acid administration impairs redox homeostasis and induces inflammatory changes: Prevention by kynurenic acid. Neurotox. Res. 2020, 38, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramírez Ortega, D.; Ugalde Muñiz, P.E.; Blanco Ayala, T.; Vázquez Cervantes, G.I.; Lugo Huitrón, R.; Pineda, B.; González Esquivel, D.F.; Pérez de la Cruz, G.; Pedraza Chaverrí, J.; Sánchez Chapul, L.; Gomez-Manzo, S.; Perez de la Cruz, V. On the antioxidant properties of L-kynurenine: An efficient ROS scavenger and enhancer of rat brain antioxidant defense. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bratek-Gerej, E.; Ziembowicz, A.; Godlewski, J.; Salinska, E. The mechanism of the neuroprotective effect of kynurenic acid in the experimental model of neonatal hypoxia–ischemia: The link to oxidative stress. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Liu, S.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, M.; Peng, J.; Chen, Q. Effects of dietary superoxide dismutase on growth performance, antioxidant capacity and digestive enzyme activity of yellow-feather broilers during the early breeding period (1-28d). J. Anim. Feed Sci. 2022, 31, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubos, E.; Loscalzo, J.; Handy, D.E. Glutathione peroxidase-1 in health and disease: from molecular mechanisms to therapeutic opportunities. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2011, 15, 1957–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dabrowski, W.; Kwiecien, J.M.; Rola, R.; Klapec, M.; Stanisz, G.; Kotlinska-Hasiec, E.; Oakden, W.; Janik, R.; Coote, M.; Frey, B.N.; Turski, W.A. Prolonged subdural infusion of kynurenic acid is associated with dose-dependent myelin damage in the rat spinal cord. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langner, E.; Lemieszek, M.K.; Kwiecień, J.M.; Rajtar, G.; Rzeski, W.; Turski, W.A. Kynurenic acid induces impairment ofoligodendrocyte viability: On the role of glutamatergic mechanisms. Neurochem. Res. 2017, 42, 838–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarcz, R.; Stone, T.W. The kynurenine pathway and the brain: challenges, controversies and promises. Neuropharmacology 2017, 112, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Simonavicius, N.; Wu, X.; Swaminath, G.; Reagan, J.; Tian, H.; Ling, L. Kynurenic acid as a ligand for orphan G protein-coupled receptor GPR35. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 22021–22028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkondon, M.; Pereira, E.F.; Todd, S.W.; Randall, W.R.; Lane, M.V.; Albuquerque, E.X. Functional G-protein-coupled receptor 35 is expressed by neurons in the CA1 field of the hippocampus. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2015, 93, 506–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngo, V.; Duennwald, M.L. Nrf2 and oxidative stress: A general Overview of mechanisms and implications in human disease. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strzetelski, J. IZ PIB–INRA Feeding recommendations for ruminants and feed tables. Kraków, Poland 2014 (in Polish).
- Welento, J.; Szteyn, S.; Milart, Z. Observations on the stereotaxic configuration of the hypothalamus nuclei in the sheep. Anat. Anz. 1969, 124, 1–27. [Google Scholar]
- Traczyk, W.; Przekop, F. Methods of investigation of the function of the hypothalamus and hypophysis in chronic experiments in sheep. Acta Physiol. Pol. 1963, 14, 227–236. [Google Scholar]
- Ciechanowska, M.; Łapot, M.; Malewski, T.; Misztal, T.; Mateusiak, K.; Przekop, F. Effect of stress on the expression of GnRH gene and GnRH receptor (GnRH-R) genes in the preoptic area-hypothalamus and GnRH-R gene in the stalk/median eminence and anterior pituitary gland in the ewes during follicular phase of the estrous cycle. Acta Neurobiol. Exp. 2007, 67, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, J.I.; Sudheimer, K.D.; Davis, K.K.; , Kerndt, G.M.; Winn, B.M. The sheep brain atlas. Michigan State University, Brain Biodiversity Bank. Available online: http://brains.anatomy.msu.edu/brains/sheep/index.html (accessed on 5 March 2021).
- Pfaffl, M.W.; Horgan, G.; Dempfle, L. Relative expression software tool (REST) for group-wise comparison and statistical analysis of relative expression results in real-time PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfaffl, M.W.; Tichopad, A.; Prgomet, C.; Neuvians, T.P. Determination of stable housekeeping genes, differentially regulated target genes and sample integrity: BestKeeper – Excel-based tool using pairwise correlations. Biotechnol. Lett. 2004, 26, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fridovich, I. Oxygen radicals, hydrogen peroxide and oxygen toxicity. In Free Radicals in Biology, Pryor W.A., Ed., New York, Academic Press, 1976, 239.
- Aebi, H. Methods Enzymol; Bergmeyer, H.U., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, London, 1984; Volume 105, pp. 121–126. [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins, J.; Tudhope, GR. Glutathione peroxidase in human red cells in health and disease. Br. J. Haematol. 1973, 25, 563–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Gene | Primers (5’ – 3’) | Genbank Acc. No. | Amplicon size |
|---|---|---|---|
| SOD2 | F: GCAAGGAACAACAGGTCTTATCC R: ACTTGGTGTAAGGCTGACGG |
NM_001280703.1 | 181 |
| CAT | F: GAGCCCACCTGCAAAGTTCT R: CTCCTACTGGATTACCGGCG |
XM_004016396.6 | 148 |
| GPx1 | F: TGTCGTACTCGGCTTCCC R: AGCGGATGCGCCTTCTCG |
XM_004018462.1 | 163 |
| GAPDH | F: GGGTCATCATCTCTGCACCT R: GGTCATAAGTCCCTCCACGA |
NM_001190390.1 | 131 |
| PPIC | F: TGGAAAAGTCGTGCCCAAGA R: TGCTTATACCACCAGTGCCA |
XM_004008676.1 | 158 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





