1. Introduction
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is a frequent complete or incomplete collapse of the upper airway during sleep, resulting in a repetitive decrease in oxygen saturation for more than 10 seconds, elevated respiratory effort, fragmented sleep, nocturnal arousal, and daytime sleepiness [
1]. The polysomnogram (PSG) is the gold standard procedure for diagnoses and follow-up OSA. It is a complex procedure performed by a sleep technician in a highly specialized and equipped sleep laboratory [
2]. An alternative to PSG is the Home Sleep Apnea Testing device (HSAT), which is patient-friendly, has lower costs, and provides easier access to care [
3]. However, The HSAT device does not measure Electroencephalogram (EEG) or arousal; thus, OSA may be missed or underestimated. Also, it does not record the Rapid Eye Movement (REM) stage of sleep, and thus REM-predominant OSA is missed. Senior citizens may find it difficult to fix the sensors, which may dislodge during sleep, resulting in erroneous measurements [
4,
5]. As a result, diagnostic tools in questionnaires have been developed. Their sensitivity was relatively high, but it was not enough to roll out the possibility of OSA. On the contrary, the specificity is low, resulting in more false-positive diagnoses and limiting the application of these tools in clinical practice.
The genioglossus (GG), an upper airway dilator muscle, consistently demonstrates phasic electromyogram (EMG) activity during inspiration [
6]. During sleep, in normal subjects, there is a rise in the upper airway resistance. At sleep onset, the GG activity demonstrates a bigger drop in OSA patients than in normal subjects [
7,
8]. In OSA and during airway occlusion, the GG activity is weakened and becomes less phasic [
9,
10]. At the end of the apnea epoch, the recovery from the airway occlusion is associated with a sudden burst of the GG EMG [
9,
11]. Interestingly, the genioglossus was shown to have augmented EMG activity in obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) patients compared to normal cases during wakefulness [
12,
13]. From a clinical perspective, the accurate analysis of GG fatigue using EMG is critical to explore the hypothesis that GG fatigue contributes to the pathophysiology of obstructive sleep apnea.
In this work, we present a novel design of dental appliances that provides suitable and continuous contact between the sensing surface electrodes and the GG muscle. Few attempts have been made to place electrodes intraorally and measure the EMG of the GG [
14,
15,
16,
17]. However, these appliances are designed to be used clinically. They are ready-made but don’t ensure the comfortable fit and intimate contact needed for the electrodes to the GG muscle to function correctly. The literature lacks a reliable and effective method for placing and maintaining surface electrodes in close contact with the GG muscle to record EMG intraorally. A prototype of a preliminary appliance design was tested to acquire GG EMG from an OSA group and a Control group in wakefulness, and the results were compared with what was previously presented in the literature. The project's ultimate goal will be to have the whole EMG amplifier embedded in the dental appliance so that the device can be used during sleep for a full-night GG EMG monitoring.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Intra-Oral Appliance Fabrication
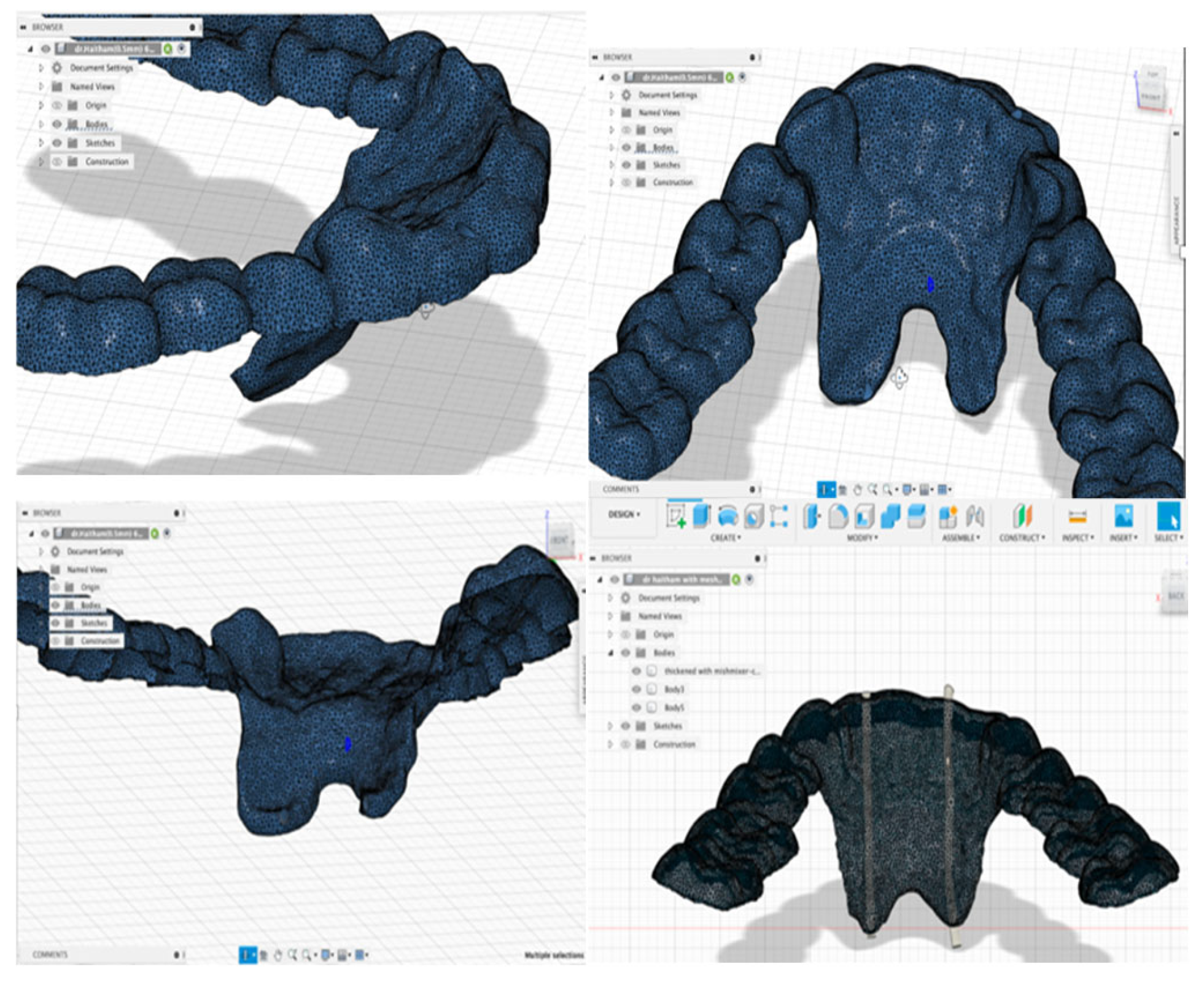
For digital fabrication and designing of the Intra-oral appliance, primary impressions using alginate impression materials were taken for the lower arch of the participants. At the same time, the tongue was relaxed to capture the floor of the mouth in the rest position. After that, the diagnostic casts were scanned using a Lab scanner (KAVO ARTICA auto-scan), and the scanned cast’s stereolithography (STL) files were imported into the ExoCad software. Multiple initial designs for the appliance were designed, printed, and piloted by the authors to determine the most comfortable and effective appliance. The optimization criteria are summarized in
Table 1.
The approved design of the appliance was done with the Bite-splint Module on ExoCad, and it was as follows:
The appliance was extended half the occluso-gingival length of the teeth except in the lingual anterior area, where the electrode will be placed.
The lingual extension was extended to the full depth to the floor of the mouth while the tongue was in the rest position.
The width was 1 mm all around except at the electrode area, where it was 2 mm.
Then, the STL file of the appliance’s primary design was exported to MeshMixer software, where the width of the lingual area was thickened to 2 mm to accommodate the electrodes’ tube placement. After that, the design was exported to Autodesk® Fusion 360® software to design the tubes used for placing and including the electrodes. Autodesk® Fusion 360® is a cloud-based 3D modeling software platform for producing, designing, and editing, utilizing pre-existing features or model fixtures with integrated CAD\CAM software tools.
The oral appliance was designed with bilateral electrode configurations for GG EMG. An electrode tube was created on either side of the mouth with a 1 mm diameter at the area of the lateral incisors and extended from the incisal tip of the tooth to the floor of the mouth with a minimum 10 mm inter-electrodes distance. The electrodes were referenced to a common ground lead and placed on the cheek to yield a bipolar recording. The design was 3D printed using NextDent® 5100 3D Printer with OrthoFlex material (NextDent). The printed appliance was then cleaned according to the manufacturer’s instructions and light-cured with (NextDent LC-3D Print) for 30 minutes for final polymerization.
Figure 1 demonstrates the 3D finished design.
2.2. Optimum Device Design
Three aspects of the design were piloted by three of the authors of this study, and the results of each aspect were as follows:
Material thickness: at a 2-mm thick appliance, the material flexibility vanished, and it was uncomfortable to wear, but this was the minimum thickness to protect the electrodes and protect them. Therefore, the appliance was printed at 1 mm thickness, but the thickness was increased to 2 mm at the electrode’s areas only.
Peripheral extension: The appliance was printed to cover the teeth all around and extend to the lingual sulcus’s depth. This amount of extension was annoying to the patient. Therefore, the material covered only the occlusal 1/3 of the tooth and only had a full extension at the electrode’s area.
Lingual extension: The appliance's lingual flanges were extended to the full depth of the lingual sulcus in the preliminary design. However, this extension was uncomfortable or even irritating to the participant. Therefore, the extension was reduced to cover the functional depth of the genioglossus muscle.
2.3. EMG Amplifier Design
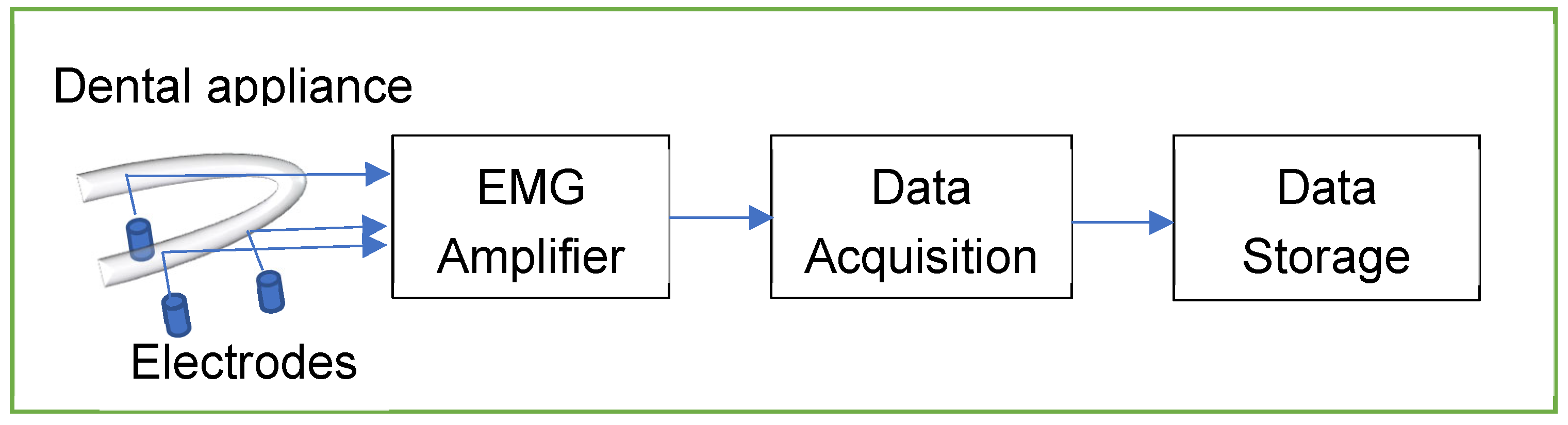
The EMG Amplifier was powered by a 3V lithium battery with a micropower instrumentation amplifier (INT122) from Texas Instruments. Silver-silver chloride electrodes were inserted through the mouthpiece to touch the surface of the genioglossus muscles. In this preliminary version, the amplifier was placed outside the mouth and was connected to the sensing electrodes through electrically isolated wires. The EMG activity was acquired with a data acquisition device from National Instruments (USB-6009-NI), and the data was stored on a laptop for further analysis using MATLAB software.
Figure 2 shows the process of signal transmission.
2.4. Subject Recruitment and Data Acquisition
To test the comfort of the mouthpiece and stability of the acquired EMG signal, a preliminary study was conducted to compare a group of OSA patients and a control group during wakefulness. This observational study was conducted at King Abdul-Aziz University. The OSA group consisted of eight severe OSA patients who were already diagnosed with OSA after passing a night in the Center of Sleep Medicine at King Abdulaziz University. The control group consisted of nine subjects who didn’t have sleep complaints and passed the Berlin questionnaire [
18] with a low probability of having apnea.
The appliance was checked intra-orally to ensure seating and comfort. The electrodes were then inserted into their corresponding position and attached to the panel. The subjects were instructed to keep their tongues at rest while the signal was acquired for one minute. This defines the Rest state. Afterward, the participants were instructed to push the tongue against the frontal teeth for 10 seconds with steady force while keeping the mouth closed. This defines the Active state.
The acquired GG EMG signals were processed offline using MATLAB®. Each EMG recording was divided into segments of 5 seconds in length, and from each segment, seven signal processing features were computed. These features were mean power, standard deviation, wavelength, mean frequency, zero crossing, slope change account, and sample entropy of the GG EMG. The mean values of the features in the 5-minute segments were then determined. Due to the small sample size, the Mann-Whitney U test was performed to test the difference between the EMG features in OSA and the control group in Rest and Active states.
2.5. Ethical Considerations
Ethical approval was obtained from the Research Ethics Committee at the College of Dentistry at KAU (approval number: 43107153). Before starting the experiments, the participants signed informed consent.
3. Results
3.1. Sample Size and Participants Characteristics
Demographics of the participants in the study are shown in
Table 2:
3.2. EMG Results
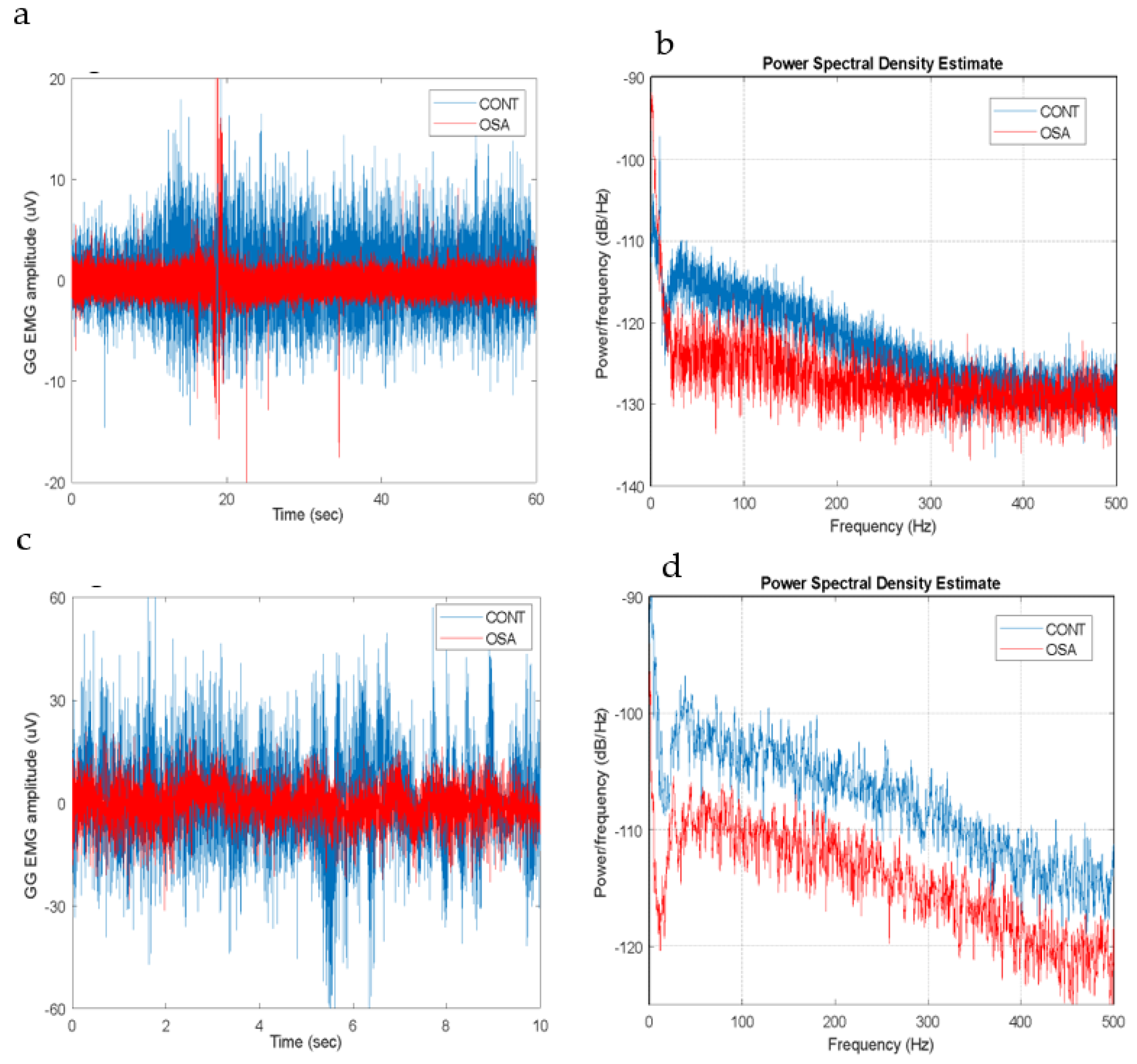
The magnitude of the GG EMG was in the range of a few microvolts, and its frequency bandwidth extended to 450-500 Hz. Both the magnitude and bandwidth increase as the tongue is activated, as shown in
Figure 3.
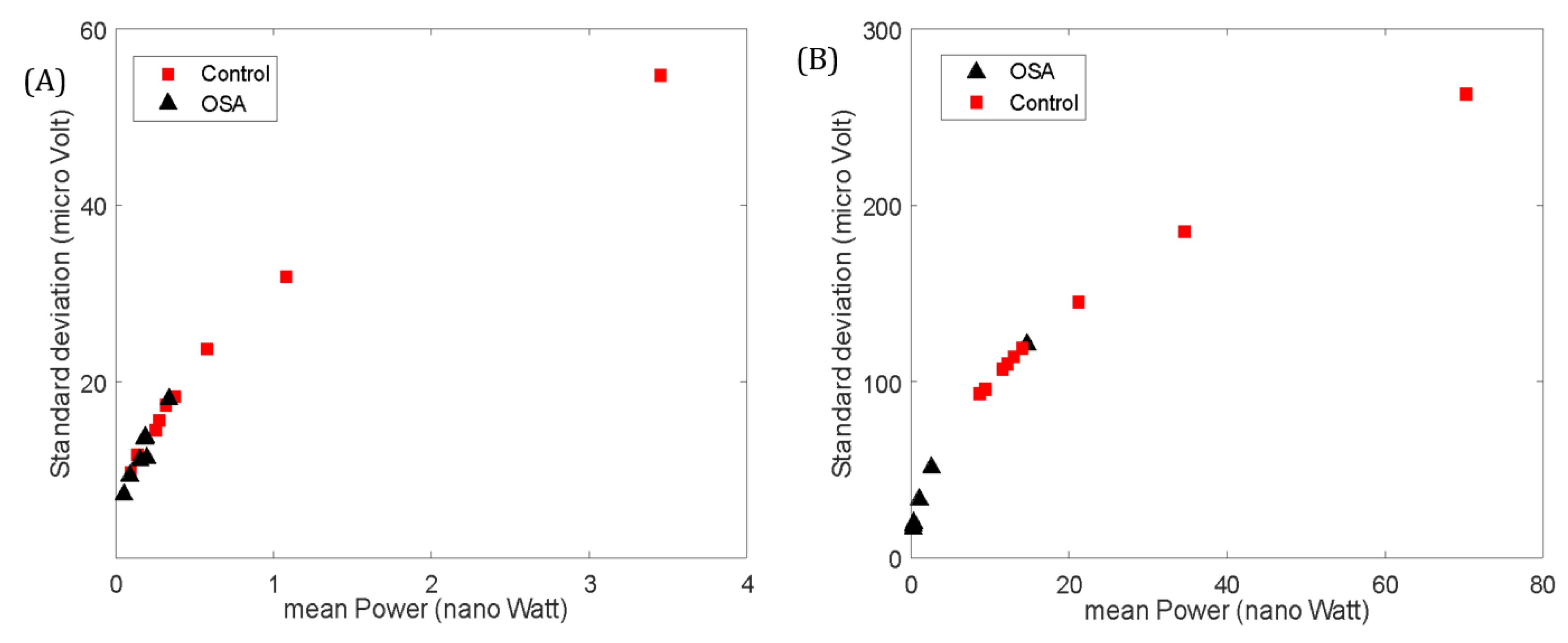
The values of the GG EMG activity showed differences between healthy and OSA patients (
Table 3). The mean power was higher (although not statistically significant) in the control group compared to the OSA group at Rest (p= 0.055). The standard deviation, however, was statistically significant between the two groups at Rest (p < 0.05,
Figure 4-a).
The mean frequency at Rest was significantly higher in the OSA group (p < 0.01). In the Active state, the power, standard deviation, and wavelength were significantly higher in the control group (p < 0.01,
Figure 4-b). Although no significant differences were found in the mean frequency between the groups, the mean frequency significantly increased for the Control group from Rest to Active (p< 0.05). This was not the case for the OSA group. No significant differences were seen in the entropy, zero crossing or slope change between the two groups in any state.
4. Discussion
In this work, we have designed and tested a prototype of a novel dental appliance that allows the acquisition of GG EMG during wakefulness. The preliminary pilot design consisted of a 2-mm-thick appliance that wrapped the whole teeth and extended 2-mm apical to the gingival margin from the buccal/labial side and up to the floor of the mouth from the lingual side. Piloting this design resulted in extreme discomfort and interfered with tongue movement. In addition, the 2-mm-thick appliance lacked flexibility. Previous reports have stated that participants preferred custom-made flexible splints and appliances over rigid, ready-made ones due to their resilience and ease of adjustment to the oral anatomy [
19,
20]. In addition, these studies also reported that participants preferred thin appliances as they interfered less with oral functions [
21]. Moreover, the manufacturer’s recommendation for the material was to keep a maximum thickness of 1 mm to provide maximum flexibility and resiliency to the limit that does not jeopardize the mechanical properties [
22].
Therefore, the design was adjusted, and its extension was reduced to cover only the occlusal third of the teeth. The lingual extension extends the full depth to the floor of the mouth to be as close as possible to the GG muscle. The thickness was reduced around the appliance to 1 mm thick except at the areas of the electrodes and chip, where it was 2 mm to provide appropriate housing for the electrical parts. This design was also piloted, and the participants reported much more acceptance.
Regarding to the study results, the strength of the GG EMG was higher for the Control group in both Rest and Active states. This contradicts what was previously reported in the literature between the OSA and Control groups in wakefulness [
12,
13]. A reason for this could be that our representation of the signal power is in absolute value, while previously, it was presented as a percentage of the maximum EMG (the max EMG is usually determined during tongue protrusion). The rise in the EMG power in the Active state in our study (which is analogous to protrusion) is much higher in the Control group. This makes the ratio of the Rest power over Active power higher in the OSA group. The mean frequency of the Control was significantly lower in the Rest state, and it significantly increased for this group from Rest to Active state. This is analogous to the shift in the power spectrum when more skeletal muscle fibers are recruited to raise muscular power [
23,
24]. This was not observed in the OSA group, which could be due to the fatigue that these muscles experience [
25,
26]. The variability in the GG EMG (assessed by the standard deviation and wavelength features) was higher in the Control group. This is also related to this group's higher strength of the EMG signal.
It is also important to note that the BMI and age do not match between the OSA and the control group, which might have affected the results. In addition, the tests were done only during wakefulness. These findings, however, encourage further investigations that include new wearable versions of the amplifier, which can be tested at home for acquiring the GG EMG on different days and multiple times during the day in wakefulness. Comparison between the GG EMG and the polysomnography (the gold standard) during sleep will be considered with the amplifier fully embedded in the mouthpiece, which is the ultimate goal of our research work.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, this study aims to develop an oral appliance that can be used at home to place surface electrodes in close contact with the GG muscle during sleep to record the EMG signals for the purpose of detection (or screening) of OSA.
Multiple prototypes were developed and tested; the best design in terms of results and comfortability was the one that covered half the occluso-gingival length of the teeth buccal and extended up to the floor of the mouth lingually. The most suitable material thickness was 1 mm all over except over the electrode areas. OrthoFlex (NextDent) resinous material was used to fabricate the appliance. It has suitable strength, resiliency, and flexibility to house the electrical components and provides comfortable seating in the patient’s mouth.
EMG features are numerous, and multiple features were recorded in this clinical trial. The mean power, standard deviation, and wavelength were significantly higher in the control group compared to the OSA group during the active state. Also, monitoring changes in the GG EMG spectrum might help in understanding the effect of fatigue on GG muscle. However, these results were recorded during wakefulness, and the results may differ during sleep.
Future research should focus on embedding the miniaturized chip and electrodes within the device to form a single, easy-to-use appliance for home use with a larger sample size and testing the device during sleep.
6. Patents
This section is not mandatory but may be added if there are patents resulting from the work reported in this manuscript.
Author Contributions
Thamer Marghalani: Contributed to conception, design, and critically revised the manuscript. Haitham Alangari: Contributed to conception, design, data acquisition, and interpretation. Performed all statistical analyses and critically revised the manuscript. Ruwaa Salamah: Contributed to conception, design, data acquisition, and interpretation; drafted and critically revised the manuscript. All authors gave their final approval and agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Funding
This research was funded by Khalifa University (KU) and King Abdulaziz University (KAU) Joint Research Program Award No. KAUKUJRP-1B-2021.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Institutional Review Board at the College of Dentistry at KAU (approval number: 43107153 and date of approval 17/4/2022).
Acknowledgments
This publication is based upon work supported by the Khalifa University (KU) and King Abdulaziz University (KAU) Joint Research Program Award No. KAUKUJRP-1B-2021.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Mohammadieh, A.; Sutherland, K.; Cistulli, P.A. Sleep disordered breathing: management update. Internal Medicine Journal 2017, 47, 1241–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rundo, J.V.; Downey, R. Polysomnography. Handbook of Clinical Neurology 2019, 160, 381–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosen, C.L.; Auckley, D.; Benca, R.; Foldvary-Schaefer, N.; Iber, C.; Kapur, V.; Rueschman, M.; Zee, P.; Redline, S. A Multisite Randomized Trial of Portable Sleep Studies and Positive Airway Pressure Autotitration Versus Laboratory-Based Polysomnography for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Obstructive Sleep Apnea: The HomePAP Study. Sleep 2012, 35, 757–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zancanella, E.; do Prado, L.F.; de Carvalho, L.B.; Machado Júnior, A.J.; Crespo, A.N.; do Prado, G.F. Home sleep apnea testing: an accuracy study. Sleep Breath 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapur, V.K.; Auckley, D.H.; Chowdhuri, S.; Kuhlmann, D.C.; Mehra, R. Clinical Practice Guideline for Diagnostic Testing for Adult Obstructive Sleep Apnea: An American Academy of Sleep Medicine Clinical Practice Guideline. Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine 2017, 13, 479–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tangel, D.J.; Mezzanotte, W.S.; White, D.P. Influence of sleep on tensor palatini EMG and upper airway resistance in normal men. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1991, 70, 2574–2581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, D.P. Sleep-related breathing disorder.2. Pathophysiology of obstructive sleep apnoea. Thorax 1995, 50, 797–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fogel, R.B.; Trinder, J.; White, D.P.; Malhotra, A.; Raneri, J.; Schory, K.; Kleverlaan, D.; Pierce, R.J. The effect of sleep onset on upper airway muscle activity in patients with sleep apnoea versus controls. J Physiol 2005, 564, 549–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remmers, J.E.; deGroot, W.J.; Sauerland, E.K.; Anch, A.M. Pathogenesis of upper airway occlusion during sleep. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol 1978, 44, 931–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praud, J.P.; D'Allest, A.M.; Delaperche, M.F.; Bobin, S.; Gaultier, C. Diaphragmatic and genioglossus electromyographic activity at the onset and at the end of obstructive apnea in children with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Pediatr Res 1988, 23, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, R.B.; Gleeson, K. Respiratory arousal from sleep: mechanisms and significance. Sleep 1997, 20, 654–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mezzanotte, W.S.; Tangel, D.J.; White, D.P. Waking genioglossal electromyogram in sleep apnea patients versus normal controls (a neuromuscular compensatory mechanism). The Journal of clinical investigation 1992, 89, 1571–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fogel, R.B.; Malhotra, A.; Pillar, G.; Edwards, J.K.; Beauregard, J.; Shea, S.A.; White, D.P. Genioglossal activation in patients with obstructive sleep apnea versus control subjects. Mechanisms of muscle control. American journal of respiratory and critical care medicine 2001, 164, 2025–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhao, D.; Yin, G.; Li, J.; Cao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ye, J. Analysis of the myoelectric characteristics of genioglossus in REM sleep and its improvement by CPAP treatment in OSA patients. Sleep & breathing = Schlaf & Atmung 2020, 24, 471–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O'Connor, C.M.; Lowery, M.M.; Doherty, L.S.; McHugh, M.; O'Muircheartaigh, C.; Cullen, J.; Nolan, P.; McNicholas, W.T.; O'Malley, M.J. Improved surface EMG electrode for measuring genioglossus muscle activity. Respiratory Physiology and Neurobiology 2007, 159, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johal, A.; Gill, G.; Ferman, A.; McLaughlin, K. The effect of mandibular advancement appliances on awake upper airway and masticatory muscle activity in patients with obstructive sleep apnoea. Clinical physiology and functional imaging 2007, 27, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doble, E.A.; Leiter, J.C.; Knuth, S.L.; Daubenspeck, J.A.; Bartlett, D.J. A noninvasive intraoral electromyographic electrode for genioglossus muscle. Journal of applied physiology (Bethesda, Md. : 1985) 1985, 58, 1378–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Netzer, N.C.; Stoohs, R.A.; Netzer, C.M.; Clark, K.; Strohl, K.P. Using the Berlin Questionnaire to identify patients at risk for the sleep apnea syndrome. Annals of internal medicine 1999, 131, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, E.; Anderson, G.; Schulte, J. A randomized clinical trial of intraoral soft splints and palliative treatment for masticatory muscle pain. J Orofac Pain 1995, 9, 192–199. [Google Scholar]
- Chi, H.H. Properly fitted custom-made mouthguards. Compend Contin Educ Dent 2007, 28, 36–40. [Google Scholar]
- Gawlak, D.; Mierzwinska-Nastalska, E.; Manka-Malara, K.; Kaminski, T. Assessment of custom and standard, self-adapted mouthguards in terms of comfort and users subjective impressions of their protective function. Dent Traumatol 2015, 31, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flex, N. NextDent ortho flex manufacturer instructions for use. Available online: https://nextdent.com/products/nextdent-ortho-flex/ (accessed on 7 June 2022).
- Bilodeau, M.; Arsenault, A.B.; Gravel, D.; Bourbonnais, D. Influence of gender on the EMG power spectrum during an increasing force level. J Electromyogr Kinesiol 1992, 2, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilodeau, M.; Arsenault, A.B.; Gravel, D.; Bourbonnais, D. The influence of an increase in the level of force on the EMG power spectrum of elbow extensors. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol 1990, 61, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moxham, J.; Edwards, R.H.; Aubier, M.; De Troyer, A.; Farkas, G.; Macklem, P.T.; Roussos, C. Changes in EMG power spectrum (high-to-low ratio) with force fatigue in humans. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol 1982, 53, 1094–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merletti, R.; Knaflitz, M.; De Luca, C.J. Myoelectric manifestations of fatigue in voluntary and electrically elicited contractions. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1990, 69, 1810–1820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).