1. Introduction
Candida albicans is a commensal yeast fungus that is part of the human microbiota and is commonly found in the oral surfaces, gastrointestinal, respiratory, and genitourinary tracts and skin. Under conditions that impair the integrity of the mucocutaneous barrier and/or disturb the host’s protective defense mechanisms, such as, antibiotic-induced dysbiosis, iatrogenic immunosuppression, and/or medical interventions,
C. albicans becomes an opportunistic pathogen, causing everything from superficial mucocutaneous diseases to life-threatening systemic infections [
1,
2].
Candida species are responsible for the majority of human infections caused by pathogenic fungi, with
C. albicans being the most common agent causing of opportunistic infections [
3]. Clinically important infections caused by
C. albicans can be classified as; mucosal and systemic. The main mucocutaneous infections are: vulvovaginal candidiasis (VVC), oropharyngeal candidiasis (OPC), esophageal candidiasis (EPC) and, less frequently, onychomycosis [
1]. Mucosal candidiasis, particularly VVC, can occur in immunocompetent people, although immunocompromised people have a higher risk of suffering greater frequency, severity and/or recurrence; it is reported that CVV can affect 75 million women per year, with recurrences of 5 to 8% [
2].
Systemic or Invasive candidiasis (IC), affects sterile parts of the body, such as the bloodstream (candidemia), and can affect the central nervous system (CNS), liver, spleen, heart and/or kidneys. It can also affect the intra-abdominal compartment, with or without candidemia. IC is associated with high mortality despite the administration of antifungal therapy [
4], it is estimated 1565000 cases and at least 995000 (63.6%) deaths per year [
5,
6].
Currently, the availability of antifungals is limited (polyenes, azoles, echinocandins), despite the significant impact that fungi have on human health. This fact is mainly attributed to the slow development process of new antifungal agents. This slowness is largely due to the complexity of fungal cells, which are eukaryotic, as well as the challenges associated with the permeability of compounds through the fungal cell wall and membrane [
7].
Another problem regarding fungal medications is that a growing resistance to them has been reported; in the case of
C. albicans, tolerance is more evident with fungistatic drugs and has been measured and characterized more widely in isolates treated with fluconazole (FLC) [
8,
9]. Resistance of
C. albicans to FLC, can be caused by mutations or overexpression of
ERG11 (drug target), loss-of-function mutations in
ERG3, blocking the accumulation of toxic sterols, increased drug efflux due to upregulation of ABC transporters, and aneuploidy, such as duplication of the left arm of chromosome 5 [
10,
11].
In line with the problem of new drug discovery, combination antifungal therapy has been considered a promising strategy, since drug combinations offer many advantages, including a reduced risk of the emergence of antifungal resistance, greater antifungal activity at low doses of drug, a shorter duration of treatment and a reduction in drug toxicity [
12].
In a previous study [
13], we evaluated the antifungal efficacy of the palindromic peptide R-1-R: RWQWRWQWR, together with twenty synthetic derivatives and ethanolic extracts of leaves and stems of the plant
Bidens pilosa against clinical isolates sensitive and resistant to antifungals of
C. albicans and
C. auris. Furthermore, we investigated combinations of the peptide, extract and/or FLC, and evaluated the cytotoxicity of peptides and extracts on erythrocytes and fibroblasts. Our findings revealed that the original palindromic peptide, certain derived peptides, and the ethanolic extract of
B. pilosa leaves showed notable activity against some of the strains tested. It is suggested that the antifungal activity of peptide R-1-R could be dependent on the amphipathicity, and in the case of the
B. pilosa extract, the activity could be related to a synergistic effect among the metabolites present in the extract, such as phenylpropanoids and flavonoids, which were previously identified after the characterization of the chemical composition of the extract.
On the other hand, the combination of peptide/FLC or peptide/extract/FLC managed to return
C. albicans 256 and
C. auris 537 from a FLC resistant to FLC-sensitive phenotype, and the combination of the extract with the original palindromic peptide significantly decreased the minimal inhibitory concentrations (MIC) against
C. albicans SC5314,
C. albicans 256,
C. auris 435 and
C. auris. 537 by a factor ranging between 2 and 16. These combinations induced morphological changes in the cells, such as surface deformations. Our results suggested that the combinations of R-1-R/FLC, R-1-R/extract/FLC and R-1-R/
B. pilosa extract presents a promising alternative to improve antifungal activity and at the same time reduce cytotoxicity and costs, becoming a potentially effective strategy to treat diseases related to sensitive or resistant
Candida spp [
13].
The palindromic peptide R-1-R has exhibited a broad-spectrum activity, being effective against Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, different species of
Candida, breast, colon and cervical cancer cells [
14,
15,
16,
17,
18,
19], becoming a molecule that is very promising for the development of new treatments; however, its mechanism of action in fungi has not been studied. The peptide R-1-R, is a synthetic derivative of the minimal motif (RRWQWR) of Bovine Lactoferricin (LfcinB), which, in turn, comes from the hydrolysis of the N-terminal region of a protein named Bovine Lactoferrin (LFB) [
20]; therefore, it is possible that its mode of action is similar to the mechanism of LfcinB and its derived peptides.
LfcinB has a net charge of +8 and amphipathic characteristics so it can interact with plasma membranes through electrostatic (Arginine and Lysine) and hydrophobic (Tryptophan) interactions [
21]. It has also been shown that LfcinB can internalize into the cell [
22], cause changes in ultrastructural features and promote the aggregation of cytoplasmic, which, has been traced to stimulation of ATP synthesis and extracellular secretion, resulting in pore formation in the plasma membrane [
23,
24]. For peptides derived from LFB, it has been seen that the mechanism of action against fungi is also mainly linked to interactions with the cell wall and plasma membrane, observing by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), morphological alteration on the surface, with the appearance of being perforated, leaks of cytoplasmic content and appearance of membrane blebs, along with deep pits [
25] and using confocal microscopy, it has been observed that these peptides can internalize the surface of
C. albicans [
26]. Finally, Chang, et al. [
27], reported LfcinB15, a peptide that also has the minimal LfcinB motif; after incubation with cells of
C. albicans, it is localized on the cell surface and in the vacuoles within the yeast, using several different methods to kill it, including the alteration of the cell membrane, the induction of the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and mitochondrial dysfunction, also, two mitogen-activated protein kinases were identified: Hog1 and Mkc1, which were activated in
C. albicans in response to treatment with the peptide LfcinB15.
To extracts of B.
pilosa, although the broad anti-candida activity has already been proven, its mechanism of action is unknown, the only information about it, is the study reported by Angelini [
28], who, using docking experiments, found a micromolar affinity of caftaric acid, a metabolite presents in a methanolic extract of leaves of
B. pilosa, towards the lanosterol 14α-demethylase, involved in the biosynthesis of ergosterol in fungi.
Due to the limited information regarding the mechanism of action of R-1-R, B. pilosa extract and the combination of these, this study investigated with a proteomic and biological approach, the changes in protein expression alteration of C. albicans SC5314 and C. albicans 256 (FLC-resistant) in response to such treatments.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Susceptibility of C. albicans Mutant Strains to R-1-R and B. Pilosa Extract
In previous studies we reported the antifungal activity of the R-1-R peptide (MIC and minimal fungicidal concentration [MFC] 100 μg/mL) [
17] and the extract of
B. pilosa (MIC and MFC 500 μg/mL) [
13] against the reference strain
C. albicans SC5314 and the fluconazole-resistant isolate,
C. albicans 256 (
Table 1), demonstrating that the resistance mechanism of the clinical isolate
C. albicans 256 (mutation of the
ERG11 gene) does not interfere with the activity of the peptide.
According to other authors [
27], a peptide derived from LfcinB, exhibited several different methods to kill
C. albicans, including disruption of the cell membrane, induction of the generation of ROS and mitochondrial dysfunction, therefore, mutants of these cellular processes were selected to be treated with R-1-R peptide or
B. pilosa extract (
Table 1).
First, two efflux pump mutants (cdr1∆/CDR1 and cdr2∆/CDR2) were evaluated and no changes were observed in the susceptibility to R-1-R (MIC / MFC: 100 μg/mL), however, a slight tolerance to the B. pilosa extract (MIC / MFC: 1000 /2000->2000 μg/mL) was also observed, compared to the wild type strain and the FLC-resistant isolate. FLC was evaluated as a control, as it is a substrate for these efflux pumps, obtaining a significant increase in sensitivity (MIC: < 0.25 μg/mL).
The results were as expected for FLC, however, they varied for the extracted peptide. In a previous study [
13], a synergistic effect with R-1-R/FLC combination, indifference in the extract/FLC combination, and additivity in the R-1-R/extract/FLC combination were obtained. We hypothesized that, considering the increase in FLC efflux due to overexpression of membrane transporters, especially Cdr1p and Cdr2p, which is related to resistance to this antifungal, the synergy occurred, since the peptide was exerting a possibly inhibitory effect on the efflux pumps and thus prevented FLC from being exported out of the yeast. On the contrary, the extract might not be affecting the efflux pumps, hence the indifferent effect. Thus, a change in the sensitivity of the mutants to the peptide and not to the extract was expected. To clarify these results, other tests shown below were carried out.
Consecutively, four Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases (MAPKs) mutants
(hog1∆/HOG1, hog1∆/hog1∆, mkc1∆/MKC1, mkc1∆/mkc1∆) were evaluated and, especially, the homozygous,
hog1∆/hog1∆ and
mkc1∆/mkc1∆, were more sensitive to the peptide R-1-R exhibiting MIC / MFC of 15.5 / 25 μg/mL and 25 / 50 μg/mL, respectively. To the
B. pilosa the effect was opposite, since the four mutant strains were slightly more tolerant (MIC: 500-000 / MFC: 2000->2000 μg/mL). The results of R-1-R against
hog1∆ mutants agree with the results obtained with other peptides such as HsT5, hBD-2 and hBD-3, where increased sensitivity was also seen, suggesting that Hog1p has a role in the cellular response to AMPs [
29,
30]. However, they differ from the results obtained with the LfcinB15 peptide, where the
hog1∆ mutant was more tolerant, although they confirmed the participation of Hog1p by showing an increase in the phosphorylation of this protein when was treated with the peptide [
27], which suggests that the use of strains mutants helps to infer the mode of action of new antifungal molecules, whether their susceptibility increases or decreases. Therefore, we can infer that it is possible that the two MAPKs also respond to the effect of the extract.
2.2. Identification of C. albicans total protei.ns.
On the other hand, seven mutants lacking mitochondrial complex I and IV genes were evaluated (
ali1∆/ALI1, ali1∆/ali1∆, cox4∆/COX4, cox4∆/cox4∆, mci∆/mci∆, orf19.4758∆/orf19.4758∆ and orf19.7590∆/orf19.7590∆), the greatest changes in susceptibility were observed in
ali1∆/ALI1 and cox4∆/COX4, obtaining greater sensitivity to R-1-R (MIC/CMF: 12.5/25 μg/mL) and significant tolerance to the
B. pilosa extract (MIC and MFC: >2000 μg/mL). The results suggest that in response to R-1-R and the extract, the mitochondrial electron transport chain (ETC) is being affected, this due to the change in the susceptibility of
ali1∆/ALI1 (related to mitochondrial complex I assembly) and
cox4∆/COX4 (Putative cytochrome c oxidase) mutants [
31]. Regarding the results obtained with R-1-R, similar to those observed with MAPKs, the Lfcinb15 peptide was more tolerant to the ETC mutants, however they found that the effect was associated with mitochondrial dysfunction [
27].
The haploinsufficient phenotype or aptitude test (deletion of an allele in a diploid, obtaining a mutant strain), is a tool that has been widely studied for
S. cerevisiae and represents a novel opportunity to deepen the knowledge of
C. albicans. It has been observed that, when a new inhibitory compound is tested, the response (hypersensitivity and resistance to the compound; i.e., haploinsufficiency and haplocompetence, respectively) of specific heterozygous strains can provide phenotypic information that reflects the mechanism of action of the compound [
32].
According to the above, the results obtained with the mutant strains reflect that the R-1-R peptide and the
B. pilosa extract, it is suggested that the R-1-R peptide and the
B. pilosa extract exhibit a mechanism of action related to cell wall stress mediated by MAPKs (Hog1p and Mkc1p) [
33] and alteration in mitochondrial respiration due to interruption of ETC.
To investigate in more detail the possible mechanism of action of R-1-R and the combination with B. pilosa extract against C. albicans, changes in the protein expression profile of both FLC-sensitive and -resistant C. albicans were analyzed using label free proteomics after six hours of incubation with R-1-R or the combination.
The reference strain C. albicans SC5314 (antifungal sensitive) was grown in three conditions, basal (without treatment), in the presence of the peptide R-1-R to100 µg/mL, corresponding to the MIC and in the presence of R-1-R in combination with B. pilosa extract, to concentrations where a synergistic effect was previously observed, 25 µg/mL) and 250 µg/mL, respectively.
The clinical isolate
C. albicans 256 (FLC-resistant) was cultured under two conditions, basal (without treatment) and with the peptide R-1-R to the MIC: 100 µg/mL. The MIC values and concentrations of the synergistic or additive effect in the two
C. albicans strains were previously reported by our group [
13].
Four replicates of total cytoplasmic protein extracts of both strains in these conditions were obtained and quantitatively analyzed by the Bradford method and SDS-PAGE. The results indicated consistent protein concentrations for all study samples (
Table S1). Furthermore, the bands were clear and uniform, the proteins were not degraded and the parallelism of each line was good (
Figure S1), indicating that the total protein of
C. albicans, for both SC5314 and 256, met the quality standard of the experiment. The total protein difference obtained between the SC5314 and the resistant strain; and between the untreated and treated strains, this is in accordance with a previous study [
34], where, using the Lowry method, they estimated total proteins for
C. albicans isolates, resistant to antifungals, and found that all strains resistant to FLC and itraconazole had a concentration of proteins higher than the other strains resistant to ketoconazole or Amphotericin B, and that when the yeasts were incubated with the antifungal, there was a decrease in the total protein concentration compared to untreated yeasts. Both studies indicate that there is a difference in the concentration of total protein related to the respective drug resistance, which according to Zaidi, et al. [
34], could be used as a marker for the development of resistance.
2.3. Proteomic Analysis of C. albicans SC5314 and 256, after Treatment with R-1-R
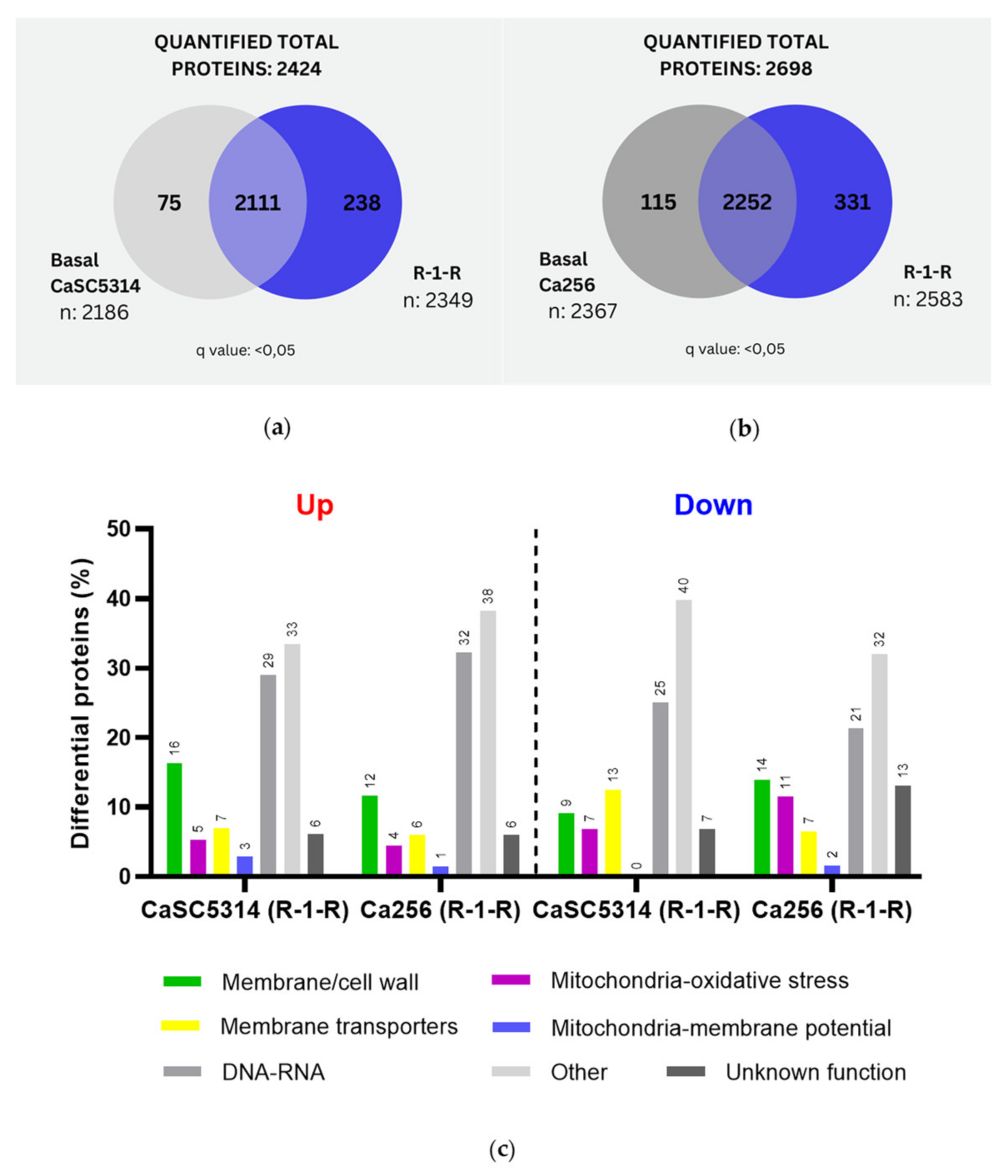
When comparing SC5314 and 256 treated with R-1-R, it was evident that for the 256 resistant strain, more exclusive proteins were obtained both from the basal condition (115 vs 75 proteins) and from the condition treated with R-1-R (331 vs 238 proteins) (
Figure 1a,b). For all comparisons carried out, the proteins taken into account as exclusive and significant were those that presented a q value <0.05. After the differential quantitative analysis of proteins regulated by R-1-R treatment, 245 up-regulated proteins and 88 down-regulated proteins were found in SC5314 (Table A1 and Table A2). In strain 256, 335 up-regulated and 122 down-regulated proteins were obtained (Table A3 and Table A4). This comparison (
Figure 1c) highlights several aspects: (i) there are more up-regulated than down-regulated proteins for both strains, indicating that both the sensitive and resistant strains, in some way seek to compensate for the damage caused by the R-1-R peptide. (ii) and the most abundant regulated proteins for both strains are those related to metabolism and nucleus (21-40%). (iii) Regarding the up-regulated proteins, to SC5314, in order of abundance, we highlight cell wall or membrane proteins (16%), membrane transporters (7%), oxidative stress (5%) and potential mitochondrial membrane (3, with similar trends observed in strain 256 but at lower percentages. Additionally, (iv) down-regulated proteins differed between strains. SC5314 exhibited greater down-regulation in membrane transport proteins (13%), followed by structural membrane or cell wall proteins (9%), and oxidative stress proteins (4%), while mitochondrial membrane potential proteins were unaffected. In contrast, strain 256 showed greater regulation in structural membrane or cell wall proteins (14%), followed by oxidative stress (11%), membrane transporters (7%), and regulation in mitochondrial membrane potential proteins (2%).
After establishing that R-1-R primarily affects critical cellular processes on the cell surface, nucleus, and mitochondria in both strains, a functional annotation enrichment analysis was conducted for all regulated proteins (up and down) under each condition (
Appendix A). Enriched GO categories (Cellular Component, Molecular Function, and Biological Process) are presented in
Appendix B and
Figure 2.
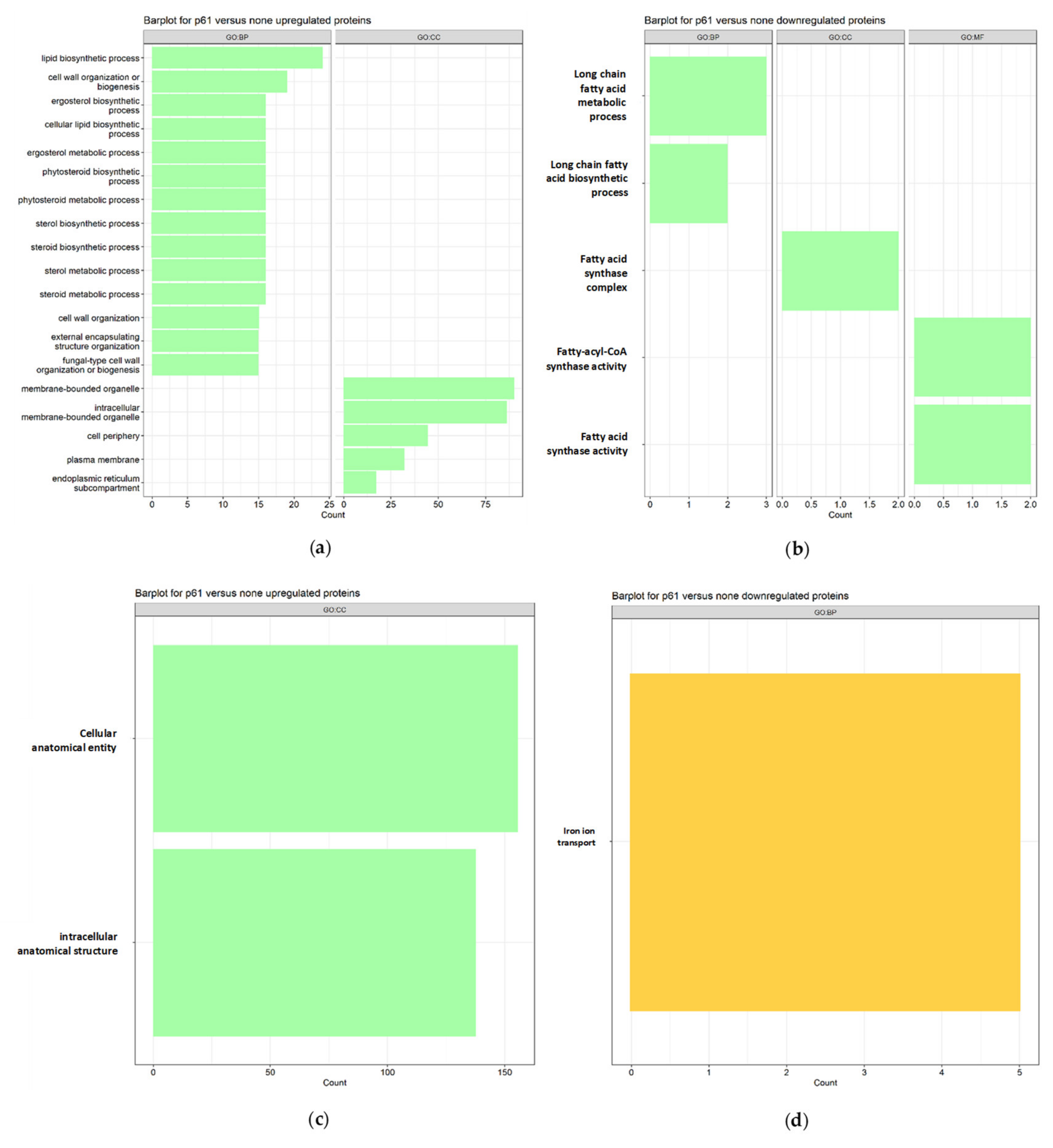
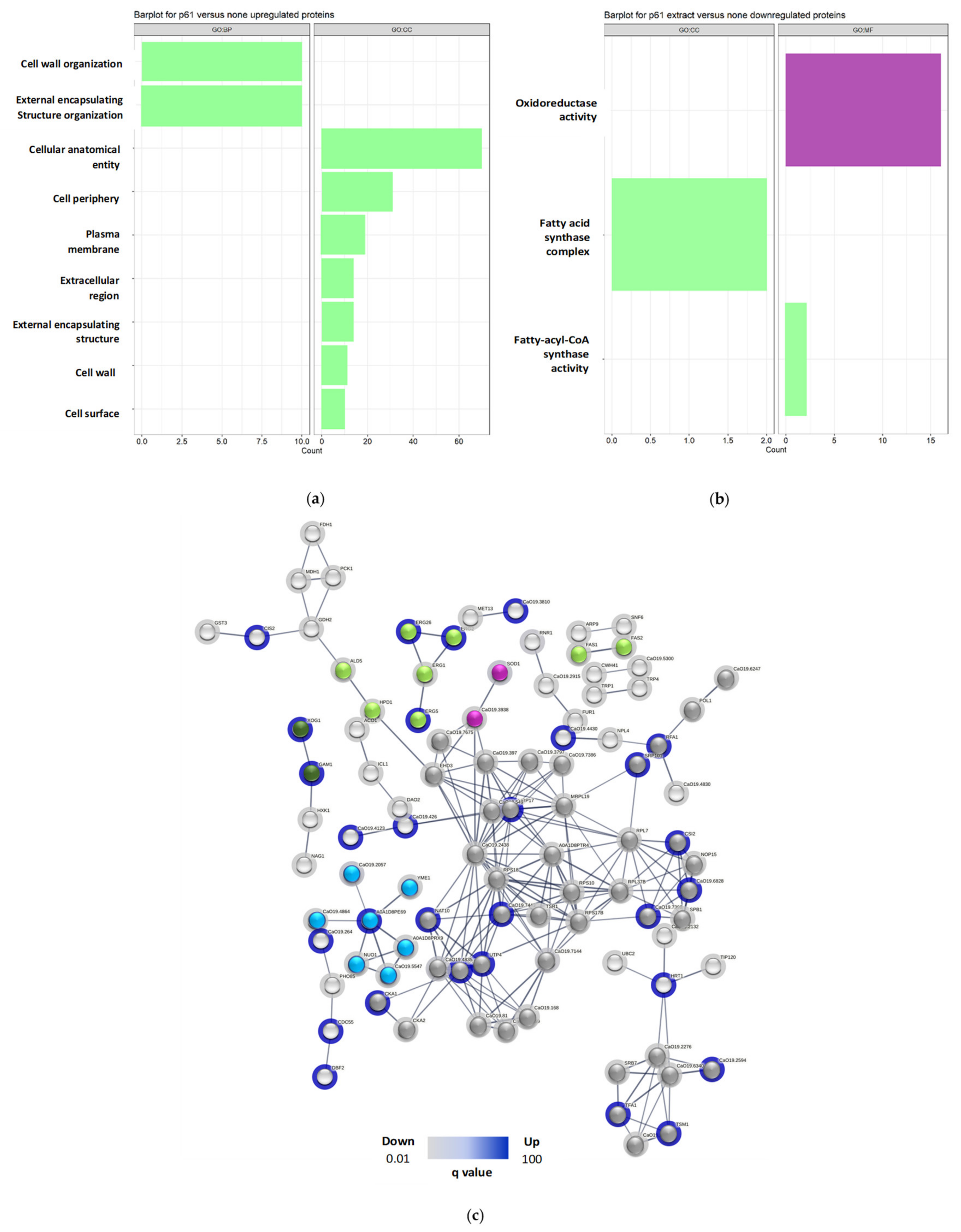
For SC5314 treated with the peptide,
up-regulated proteins (
Figure 2a) enriched 45 terms associated with biological processes (PB), 3 molecular functions (MF), and 12 cellular components (CC), highlighting (green vertical bars) lipid biosynthetic processes, cell wall biogenesis or organization, ergosterol, steroid and phytosteroid biosynthetic and metabolic processes, and external structure/encapsulation organization. Down-regulated proteins (
Figure 2b) enriched 8 terms associated with PB,
3 MF, and 1 CC, focusing on biosynthetic and metabolic processes of long-chain fatty acids.
On the other hand, for 256 treated with R-1-Rup-regulated proteins (
Figure 2c) enriched 110 terms associated with PB, 21 MF, and 27 CC, emphasizing cellular and intracellular anatomical entities, gene expression, metabolic processes of nucleic acids, and ribosome biogenesis. Down-regulated proteins (
Figure 2d) enriched 12 terms in PB, with no associated MF and CC terms, highlighting iron ion transport.
Subsequently, an
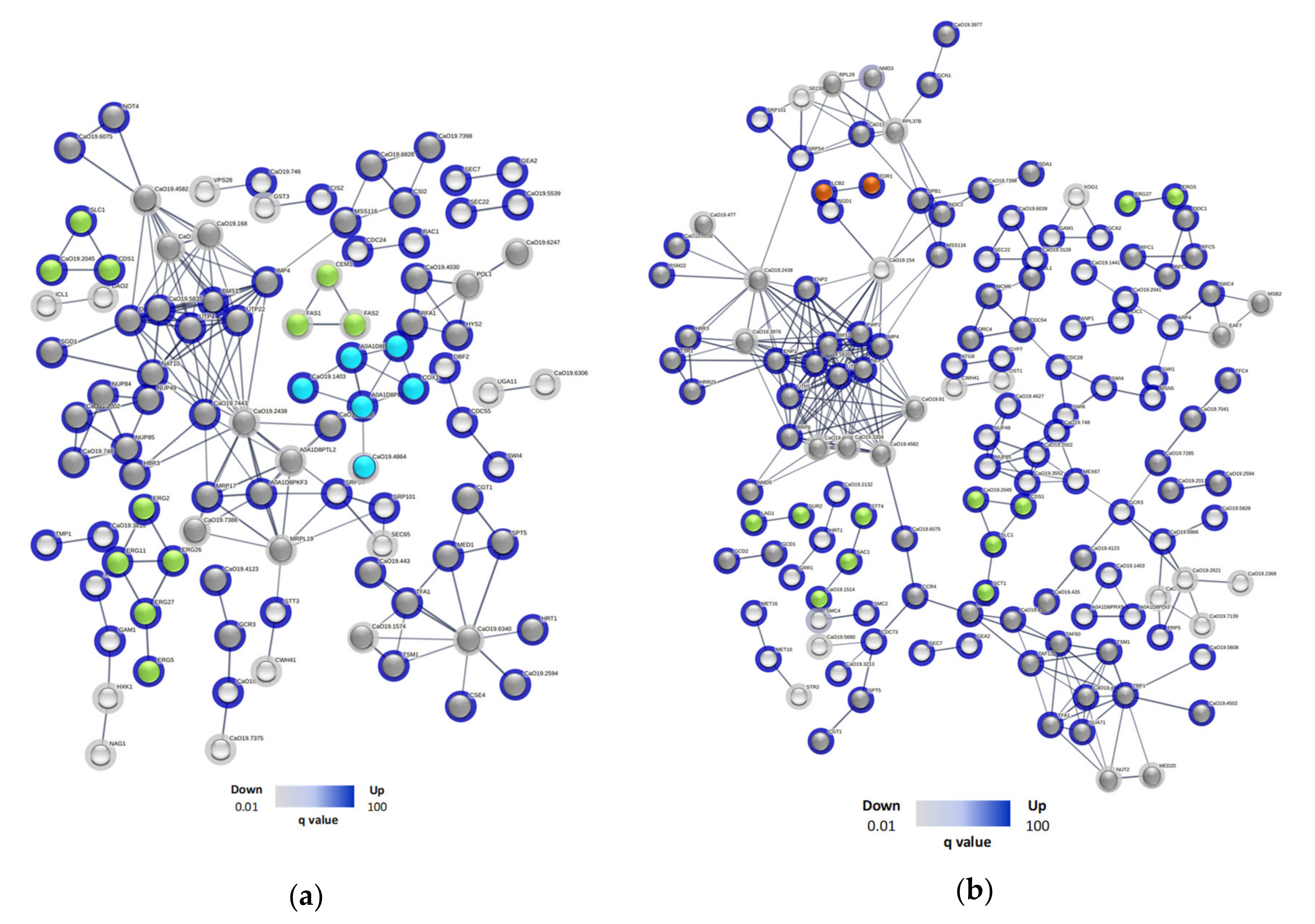
in-silico protein-protein interaction analysis was performed with the Up and Down proteins regulated in SC5314 and 256 treated with R-1-R (
Appendix C). For SC5314 treated with R-1-R (
Figure 3a), 96 proteins were involved and 27 clusters were found. Of these, 4 clusters corresponded to membrane-related pathways, including: glycerophospholipid metabolism (Cds1p, C2_00790cp_a, Slc1p), downregulated and steroid biosynthesis (Erg11p, Erg2p, Erg26p, Erg27p, Erg5p), biosynthesis and metabolism of fatty acids (Cem1p, Fas1p, Fas2p), which were up-regulated. On the other hand, 1 cluster was involved in the pathways of the respiratory chain and mitochondrial internal membrane complex, whose proteins C1_05180cp_a, C1_08080cp_a, Cox1p, C2_09510cp_a, Mas1p, were up-regulated and C1_09980cp_a, down regulated. 8 clusters were related to nucleic acid processes, especially RNA, here two up-regulated proteins stand out (Rfa1p and Hys2p), for participating in nucleotide excision repair, and the cluster formed by.
C4_02090cp_a (down-regulated), C1_00330cp_a, Not4p (up-regulated), involved in RNA degradation. The remaining clusters refer to other metabolic processes.
In the case of 256 (
Figure 3b), 140 proteins were involved and 42 clusters were found. 4 clusters were correlated with cell membrane, including pathways of glycerophospholipid metabolism (Cds1p, C2_00790cp_a, Sct1p, Slc1p), phosphatidylinositol signaling (C2_02000wp_a, Sac1p, Stt4p), steroids (Erg27p, Erg5p) and sphingolipid metabolism (Lag1p , Sur2p), all up-regulated, 17 cluster (71) proteins were related to nucleic acids, highlighting processes such as nucleotide repair (Ddc1p, Rfc1p, Rfc2p, Rfc5p), DNA repair (Eaf7p, Msb2p, Swc4p) and degradation of RNA (Ccr4p, C1_00330cp_a), interestingly two clusters related to autophagy (Lcb2p, Tor1p) and endocytosis (Gea2p, Sec7p) were found, also up-regulated. Finally, 14 clusters (39 proteins) were related to other metabolic processes.
2.4. Important Proteins Regulated in SC5314 and 256 in Response to R-1-R
Table 2 summarizes the most important differentially regulated proteins in each of the biological processes affected by the peptide R-1-R in both SC5314 and/or 256. In cell wall, to both strain SC5314 and 256, most proteins were Up regulated, and were related with biogenesis, regeneration, response to damage, organization, assembly and maintenance of the cell wall, also, adhesion, biofilm and B-glucan biosynthesis. Biosynthesis of mannoproteins proteins, were found exclusively in SC5314 o 256 and only one protein related to chitin remodeling was found in 256.
To the membrane cell, after treating with R-1-R, we found that the main affected pathway was ergosterol biosynthesis in both the sensitive and resistant strains to FLC, and all proteins were up-regulated. It should be noted that in strain 256, Erg11p did not appear when it was treated with the R-1-R peptide, possibly due to the mutation of ERG11, which confers resistance to FLC to this clinical isolate. Fatty acid biosynthesis was also affected in both study strains, with down-regulated and up-regulated proteins.
Transport proteins, a protein that participates in the activation of efflux pumps CDR1, carbohydrate transport proteins, iron and cations transport proteins, were down-regulated in both strains. Exclusively, proteins involved in membrane transport were regulated in SC5314 and 256, where proteins related to ABC transporters, are highlighted, given that, they are involved in resistance to FLC.
In response to oxidative stress, for both study strains, proteins of the Hog1 and Cap1 pathways, and antioxidant proteins were up-regulated. Also, oxidoreductase activity proteins were down. Other differentially regulated proteins, related to similar processes, were found exclusively in SC5314 or 256. A particular case occurred, when evaluating mitochondrial membrane potential, only two protein was found in the two strains, involved in respiratory chain and Cytochrome C activity. The other proteins were exclusive for each strain. To SC5314, all protein had role in respiratory chain and all were up-regulated. To 256, we obtained, Cytochrome C, ETC proteins-complex III and IV. Another interesting discovery was finding in SC5314 and 256, proteins Up regulated related to mitochondrial autophagy, mitophagy, autophagy, and mitochondria and vacuole maintenance.
Finally, proteins related to the nucleus or cellular processes of nucleic acids were mostly up-regulated, this is highlighted for both study strains, ribosomal biogenesis proteins, nuclear export, DNA repair, and RNA degradation. Regarding the down-regulated, they were involved in DNA Replication, ribosome subunit and a MAPK transcription factor in response to the Hog1 signaling pathway. Only two exclusive up-regulated proteins were found in SC5314, both with roles in response to repairing DNA damage due to oxidation. For 256, RNA degradation proteins, replication, and ribosomal biogenesis were up-regulated, while down-regulated proteins were involved in tRNA biosynthesis, nucleocytoplasmic transport, and ribosome biogenesis.
2.5. Effect of the Combination between R-1-R and B. Pilosa Extract against C. albicans SC5314
Once the possible effects of the R-1-R peptide on C. albicans strains, sensitive and resistant to FLC, were analyzed, we proceeded to explore the mechanism of action of the combination between the peptide and an extract of B. pilosa, considering that this combination improves anti-candida activity.
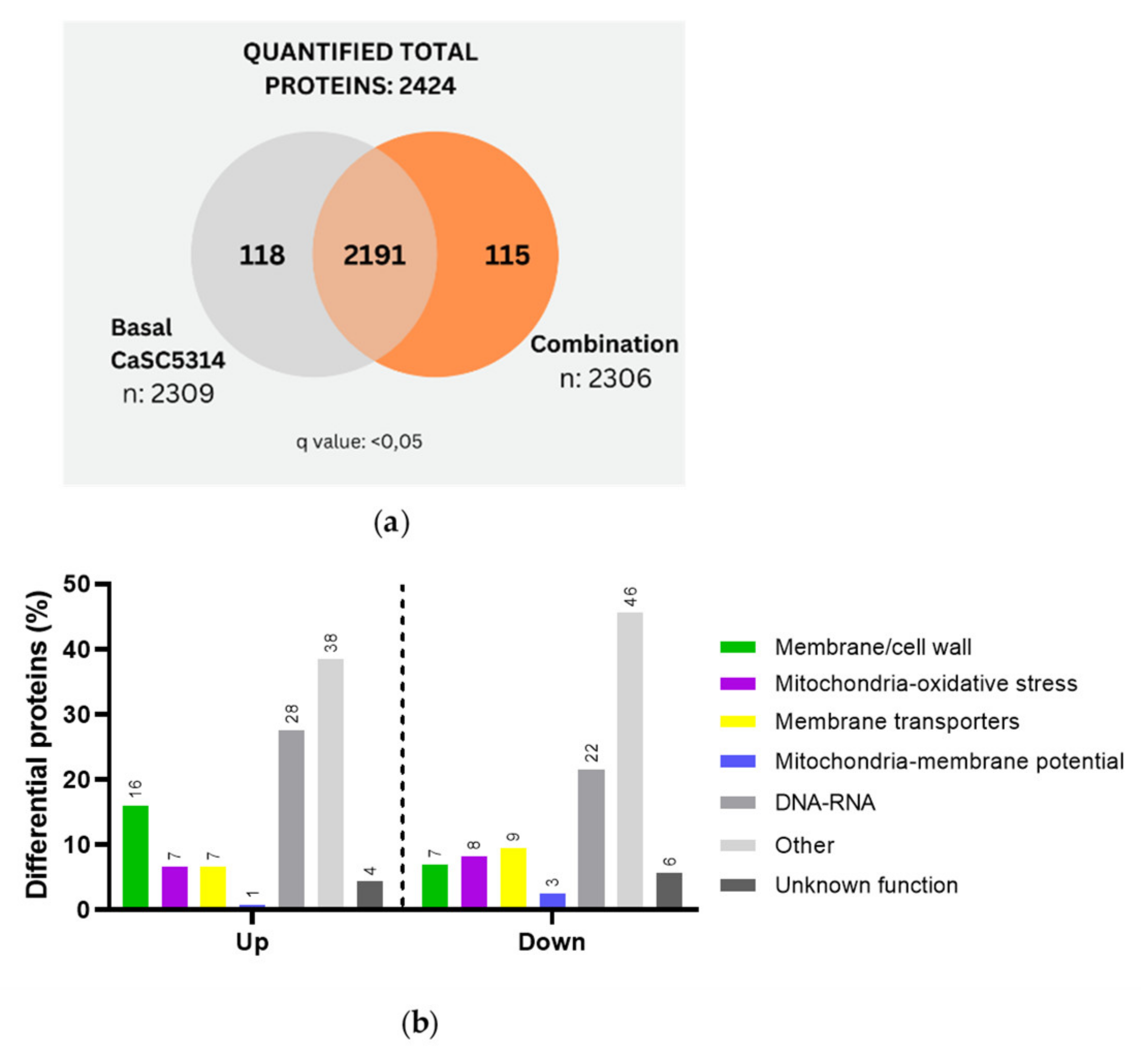
C. albicans SC5314 was then treated with the combination, resulting in 118 proteins exclusive to the untreated strain and 115 proteins exclusive to the combination treatment (
Figure 4a). This number of proteins corresponds to half of those identified when treated solely with the R-1-R peptide (238 proteins) (
Figure 1a). After the differential quantitative analysis, 138 up-regulated proteins and 158 Down-regulated proteins were identified (Table A5-A6). Notably, the regulation of proteins was opposite to the results obtained with the peptide R-1-R, where more proteins had been obtained Up-regulated than Down-regulated (245/88 proteins, respectively). This suggests that the combination suppresses more proteins, possibly indicating greater difficulty for strain SC5314 to mount a compensatory response.
Subsequent categorization based on their function revealed that among the up-regulated proteins (
Figure 4b), the distribution was similar to that seen with R-1-R treatment (
Figure 1c). The highest regulation was observed in metabolism and nucleus-related proteins (38% and 28%, respectively), followed by membrane/cell wall proteins (16%), mitochondria/oxidative stress, and membrane transporters (7%), with mitochondrial membrane potential proteins accounting for 1%. In contrast, the down-regulated proteins showed a notable difference compared to R-1-R treatment. Here, more proteins were associated with other metabolic processes (48%), which warrants further investigation in future studies. Additionally, membrane potential proteins were affected (3%), a phenomenon not observed with peptide treatment alone (0%).
Regarding GO analysis of SC5314 treated with the combination, up-regulated proteins (
Figure 5a) were enriched in 14 terms associated with PB and 7 with cellular component CC. Notably, the enriched terms included organization processes of the external encapsulating structure and cell wall organization. In contrast, treatment with the peptide affected both the cell wall and cell membrane processes but not the external region (
Figure 2b)
For down-regulated proteins (
Figure 5b), 24 terms associated with PB, 6 MF and 3 CC were enriched, highlighting the oxidoreductase activity and the fatty acid synthase complex, crucial in fatty acid biosynthesis. Similar terms were observed with R-1-R treatment, specifically related to fatty acids.
Finally, in the
in-silico analysis of protein-protein interaction in SC5314 treated with the combination, (
Figure 5c), 97 proteins were involved, and 27 clusters were found. 3 clusters were correlated with cell membrane, including processes such as ergosterol biosynthesis [Erg1p (down), Erg2p, Erg26p, Erg5p (Up)], fatty acid beta oxidation [Ald5p, Hpd1p (Down)] and fatty acid biosynthesis [Fas1p, Fas2p (Down)]. 1 cluster (Gam1p, Xog1p (Up)) was related to the cell wall. One cluster (C5_04530wp_a, Sod1p) was related to oxidative stress, where the superoxide dismutase pathway was down-regulated, indicating reduced antioxidant activity. Furthermore, a cluster was related to complex I of the mitochondrial respiratory chain, where Cr_01300wp_a, C2_00700wp_a, C1_09980cp_a, C6_02740wp_a, Nuo1p, Yme1p were Up-regulated, and only C1_08080cp_a was Down-regulated. 6 cluster contained 44 proteins involved in processes with nucleic acids and 14 cluster that includes 33 proteins that are related to other metabolic processes. For this analysis, we highlighted the cell wall and oxidative stress clusters that were not seen in the protein interaction when the same strain was treated with the R-1-R peptide.
2.6. Important Proteins up or Down Regulated for SC5314 in Response to the Combination
Important proteins exclusively regulated by the combination, absent when SC5314 was treated with R-1-R alone, were selected for further analysis. A smaller subset of proteins was chosen (
Table 3).
At the cell wall level, treatment of SC5314 with the combination resulted in up-regulated GPI anchor and cytoskeleton proteins. Down-regulated proteins included cytoskeletal proteins, a chitinase, and a cell wall integrity protein. In the cell membrane, down-regulated proteins included one involved in ergosterol biosynthesis and a sterol transfer protein. Regarding membrane transporters, one protein involved in cation transport was up-regulated, while those down-regulated were associated with carbohydrate transport and MDR1 transporters.
Concerning oxidative stress response proteins, only two proteins were up-regulated, one associated with the HOG1 pathway. Down-regulated proteins included those involved in oxidative stress, oxidoreductases, and antioxidant activity. An up-regulated protein from complex III of the ETC was identified, while down-regulated proteins included those from complexes I and II of the ETC. Another protein was also associated with ETC and the last one was related to ATP synthesis.
In processes related to nucleic acids, all proteins were down-regulated, including those involved in ribosome function, rRNA maturation, and nucleocytoplasmic transport.
Overall, although similar processes or cellular organelles were affected by R-1-R peptide and the combination, the latter notably resulted in a higher proportion of down-regulated proteins. Also, a notable characteristic is the predominantly down-regulated expression of proteins observed with the combination. This highlights the significant role of the B. pilosa extract in enhancing the peptide’s anti-fungal efficacy, resulting in a more pronounced lethal effect.
The results of this proteomic study preliminarily indicate that, like LF, Lfcin or other LfcinB peptides [
27,
35], the R-1-R peptide affects the cell wall and membrane, generating oxidative stress and altering the mitochondrial membrane potential. Besides, it was observed that R-1-R affects the function of membrane transporters. Moreover, the observed effects on different functional protein groups were consistent irrespective of whether the strain was sensitive or resistant to FLC, except for mitochondrial membrane potential damage.
To further explore the effects on cell wall and membrane, efflux pumps, oxidative stress, and mitochondrial respiration, complementary studies were conducted based on results from mutant strains and proteomic approaches.
2.7. Scanning Transmission Electron Microscopy (STEM)
The changes in the ultrastructure observed by STEM, in
C. albicans SC5314, treated for 2 h with the R-1-R peptide (
Figure 6b,c) compared to the untreated control (
Figure 6a), included the presence of microbodies in the cytoplasm and apparent cell wall thickening. Treatment with
B. pilosa extract also resulted in the presence of cytoplasmic microbodies and irregularities in the cell wall (
Figure 6d), along with nuclear swelling and irregularities, without microbodies (
Figure 6e). Combination treatment resulted in swollen nuclei, indicative of potential cell bursting, and expulsion of cytoplasmic contents with cell wall rupture (
Figure 6f–i), demonstrating a synergistic effect. R-1-R was used at 25 µg/mL, and
B. pilosa extract at 250 µg/mL.
Observation of
C. albicans 256 by STEM showed that the untreated strain (
Figure 7a,b) had a thicker cell wall compared to
C. albicans SC5314 (
Figure 6a). This difference may be influenced by the FLC resistance exhibited by this strain. In contrast to
C. albicans SC5314, treatment with R-1-R (
Figure 7c,d), extract (
Figure 7e,f), and combination (
Figure 7g,h) resulted in disorganized cytoplasm with granular appearance, surrounded by filaments, and with retracted and irregular cell membranes and walls. These changes were more pronounced with the combination.
The observed irregularities in the cell wall of
C. albicans SC5314 and
C. albicans 256 due to all three treatments are consistent with a previous study [
13], where SEM was used to observe cell membrane retraction and wall alterations in the same strains treated with R-1-R, extract, and their combination.
Regarding the changes seen inside the yeast, this study represents the first observation of effects induced by the peptide, extract, and their combination. However, consistent with previous studies on other antifungal molecules, the presence of microbodies suggests apoptosis-related cell death [
36]. Additionally, the disorganized cytoplasm with a granular appearance is suggestive of necrosis [
37].
2.8. Alteration of the Activity of Efflux Pumps
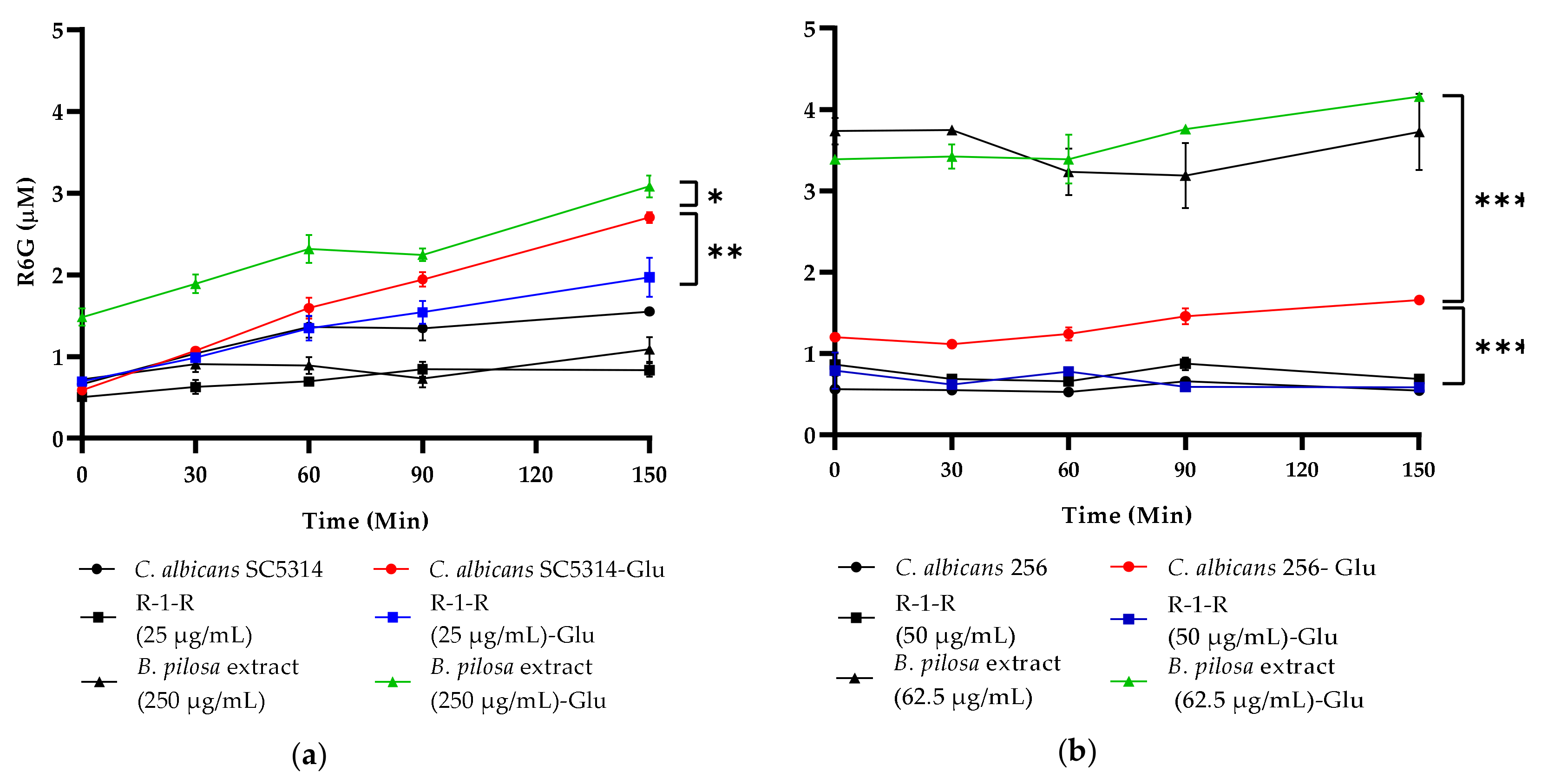
The accumulation of Rhodamine 6G (R6G) in growing
C. albicans cells inversely correlates with the expression level of the ABC transporter Candida drug resistance 1 (CDR1) mRNA. The measurement of released R6G is used to determine the activity of these R6G-dependent pumps ATP [
38].
Figure 8 illustrates that treatment of
C. albicans SC5314 with R-1-R (sub-MIC 25 µg/mL) significantly decreased R6G release, while treatment with
B. pilosa extract (250 µg/mL) increased its release, suggesting that the peptide may inhibit efflux pump activity, whereas the
B. pilosa extract enhances it. Similar effects were observed for the FLC-resistant strain
C. albicans 256 (
Figure 8b). Controls without glucose showed no R6G release, as expected.
The efflux transporters Cdr1, activated by ATP and proton flow, are overexpressed and associated with FLC resistance. Previous studies have evaluated the antifungal activity of FLC combined with LF, Lfcin, or related peptides, demonstrating synergistic effects [
35,
39,
40]. It has been suggested that LF and derivatives can inhibit these transporters by dissipating the proton gradient across the cell membrane and inhibiting glucose uptake. However, further investigations are warranted. The results of this study confirm the ability of peptides derived from LfcinB to inhibit efflux pumps in
C. albicans.
2.9. Induction of Cellular ROS Generation
Increasingly, it is evident that several species of fungi increase the production of ROS upon contact with antifungal drugs (azoles, polyenes, and echinocandins) [
41] and PAMs [
42,
43,
44], including peptides derived from LfcinB [
27]. In several studies it has been reported that the origin of ROS in these cases is the mitochondria, favoring the fungicidal capacity of drugs and being part of drug-induced programmed cell death (PCD). However, it is not clear whether ROS is a primary consequence of the antifungal mechanism of action or a secondary consequence of PCD. It is also believed that the induction of ROS may promote tolerance to antimycotic drugs as part of adaptive evolution to them [
41].
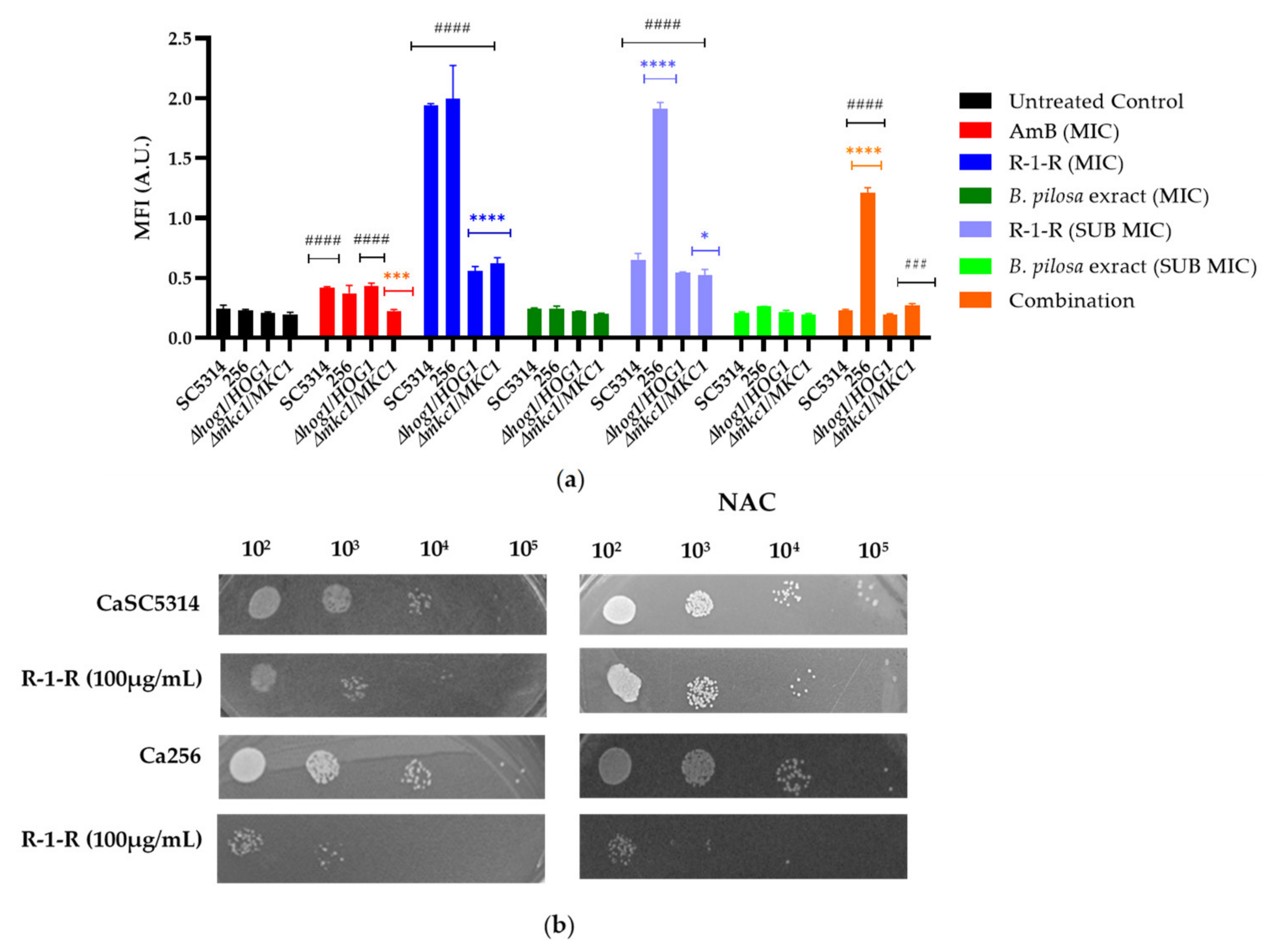
In the current study, intracellular ROS accumulation was measured after 2 h of treatment (
Figure 9a). Firstly, it is evident that both the positive control (AmB) and the R-1-R peptide generated an increase in ROS production in SC5314; the increase was dependent on the concentration. These results are consistent with those obtained with the peptide Lfcinb15 [
27]. In strain 256, the increase in ROS was significantly more pronounced, even at sub-inhibitory concentrations. This marked accumulation of ROS in strain 256 has been previously reported, suggesting that although the absence of ergosterol in this strain is not specifically related to FLC resistance, mutations in ergosterol biosynthesis genes may lead to an abnormal membrane structure and functionality. Consequently, these mutations could affect tolerance to oxidative stress [
45].
In the case of the extract (
Figure 9a), no significant increase in ROS was observed. However, based on the results from
Table 1 with the mutant strains, it is evident that oxidative stress is being generated, which may be masked by the polyphenolic effects of the
B. pilosa extract, known for its antioxidant activity [
46]. When the reference strain and the FLC-resistant strain were treated with the combination, an increase in ROS was observed only in strain 256. This suggests that in SC5314, the extract could be exhibiting an antioxidant effect against the ROS generated by the R-1-R peptide. However, in strain 256, the antioxidant effect of the extract is insufficient, as the ROS generated by the peptide exceeds that observed in the FLC-susceptible strain.
Acknowledging the role of Hog1p and Mkc1p and the results obtained with the Lfcib15 peptide in response to oxidative stress, two heterozygous mutant strains were exposed to the peptide, extract, and combination (
Figure 9a). The most significant results were observed with the R-1-R peptide at 100 µg/mL, where the accumulation of ROS decreased significantly in both mutant strains. H
2O
2 is a known ROS inducer; under its action, Hog1 phosphorylates Mkc1. However, cells lacking Mkc1 are not sensitive to oxidative stress [
48], suggesting in this study that the sensitivity observed in the Mkc1 mutant strain in the presence of the R-1-R peptide is more related to oxidative stress than to cellular wall. Although Hog1 correlates with oxidative stress, it has been found not to be specific to this pathway. These findings could possibly explain why the mutant strains of these two kinases generate an amount of ROS similar to that of the WT strain, indicating that they are competent in responding to oxidative stress, possibly through activation of the Cap1 pathway [
49].
ROS in high quantities leads to oxidative stress, damaging vital components of cells and causing cell death [
49,
50]. Subsequently, a ROS-scavenging agent, N-acetylcysteine (NAC) 60 mM, was used to confirm that fluorescence increased due to ROS and to correlate the antifungal activity of R-1-R with ROS. When NAC was added to the two strains pretreated with R-1-R and the combination, no increase in fluorescence was evident (Data not shown), confirming the relationship between fluorescence and ROS. Conversely, when the strains were treated with R-1-R and NAC (
Figure 9b), an increase in cell viability was exhibited for SC5314, similar to the LfcinB15 peptide [
27].
These results suggest that the ROS induced by R-1-R are directly related to the candidacidal activity of the peptide. While the initial mechanism involves the cell membrane, as previously stated, it is hypothesized that as an effector mechanism, the generation of ROS damages vital cellular components in yeast, promoting cell death. This phenomenon has been documented for antifungals such as itraconazole against
C. albicans and Amphotericin B against
Aspergillus fumigatus [
42].
Moreover, after pretreatment with NAC, strain 256 remained susceptible to the peptide, confirming that the FLC-resistant strain has a disadvantage in tolerance to the peptide compared with the sensitive strain. This difference is possibly due to the mutation present in the ergosterol pathway, which induces mitochondrial dysfunction as confirmed in the following experiment
2.10. Decreased Mitochondrial Membrane Potential
It is believed that the main source of ROS in fungal cells, following the action of antifungals, is mitochondria, when superoxide is formed after the leakage of electrons from respiratory complexes I and III, in the ETC, most of this superoxide is converted to hydrogen peroxide thanks to mitochondrial superoxide dismutases (SOD). Superoxide and hydrogen peroxide can remain within the mitochondria or diffuse into the cytosol, where they are neutralized by cytosolic SOD and catalases, respectively [
41]. Excessive production of ROS causes alterations in ETC, mitochondrial membrane potential (ΔΨm), and ATP generation leading to mitochondrial dysfunction [
49].
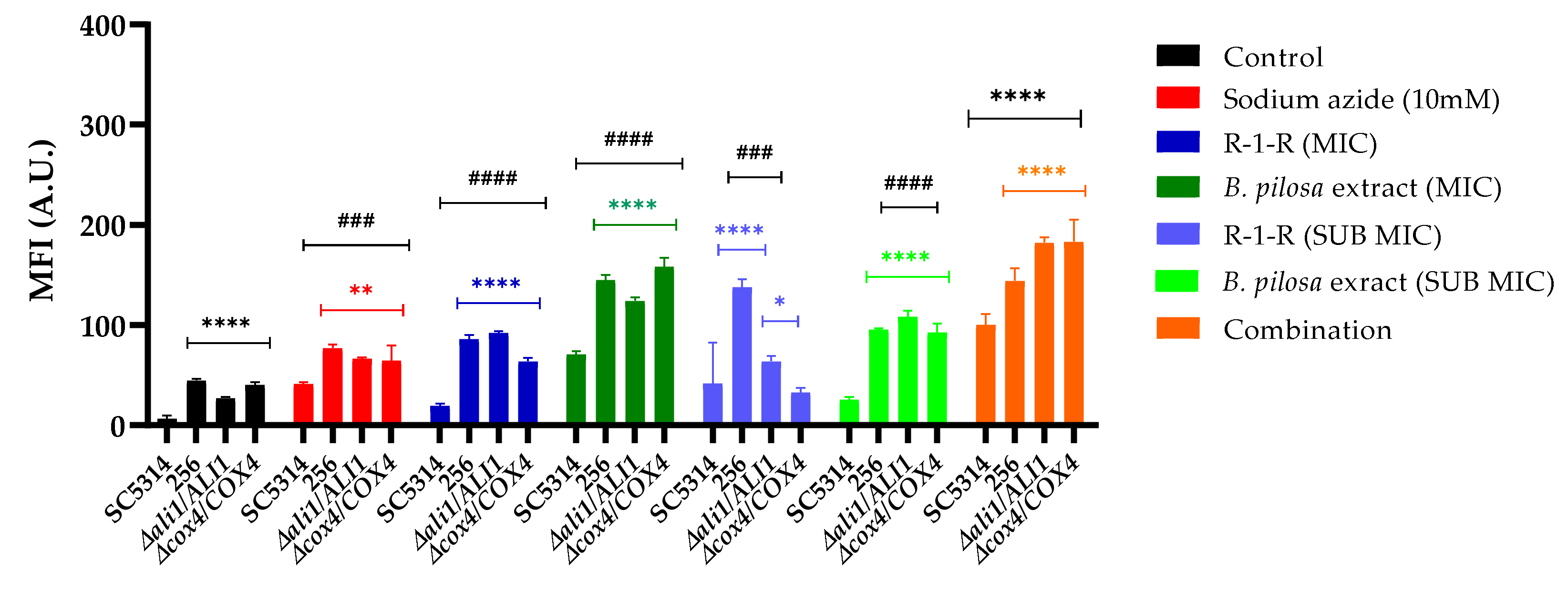
Given that the R-1-R peptide induces ROS accumulation, and it is presumed that the extract and their combination do so as well, we measured the ΔΨm of C. albicans SC5314, 256, and mutant strains following exposure to these treatments. This was achieved using the fluorescent dye rhodamine 123 (Rho 123), where an increase in fluorescence intensity indicates mitochondrial membrane depolarization.
Several observations were made (
Figure 10): Firstly, for the group of untreated strains, it was observed that compared to SC5314, the FLC-resistant strain and the two mutant strains exhibited an increase in the MFI, that is, at baseline they already present a low mitochondrial dysfunction; For the 256 strain, it is possible that this effect is related to the alteration in the membrane due to resistance to FLC, and for the
Ali1 and
Cox4 mutant strains, this occurs since they are ETC-deficient mutants. This finding corresponds with the proteomic analysis, suggesting that in the resistant strain, a greater percentage of downregulated proteins related to mitochondrial membrane potential were detected. Conversely, the WT strain treated with the peptide exhibited no downregulated proteins.
Subsequently, it was observed that for SC5314, as expected, the positive control, sodium azide, increased fluorescence. With the R-1-R peptide, the increase in MFI was modest, while with the extract, a significant increase was observed depending on the concentration, and with the combination, the MFI was significantly higher, even exceeding that of the positive control and the extract alone. This indicates that although mitochondrial dysfunction occurs in all cases, this effect is more pronounced with the extract and the combination. These results are consistent with the increased MFI observed for a peptide derived from LfcinB [
27]. For strain 256, regardless of the treatment concentration evaluated, fluorescence was significantly higher than for SC5314, indicating that this strain indeed shows greater susceptibility to mitochondrial dysfunction.
To further investigate the functionality of mitochondria in this study, two heterozygous mutant strains (
ali1Δ/ALI1 and
cox4Δ/COX4) from ETC I and IV complexes were evaluated. In each case, an increase in MFI was noted compared to the WT. As shown in
Figure 10, the amount of Rho 123 incorporated and the fluorescence intensity increased in both mutants when treated with
B. Pilosa extract, indicating compromised mitochondrial membrane integrity compared to mutants treated with R-1-R, which exhibited lower mitochondrial membrane potential. These findings are consistent with a previous investigation within our group, involving the same mutant strains treated with varying concentrations of piperine isolated from a natural extract [
45]. Notably, the dynamics of Rho 123 accumulation in the mitochondria of
ali1Δ/ALI1 and
cox4Δ/COX4 cells differed from those treated with the combination, which exhibited the highest mitochondrial membrane potential. Taken together, these results suggest that both compounds induce increased depolarization of the mitochondrial membrane, where
Ali1 and
Cox4 may play a significant role in the action of
B. pilosa, whereas susceptibility to R-1-R in fungi may be determined by different mechanisms.
3. Discussion
It has been described that the main antifungal mechanism of PAMs is directed at the cell surface, affecting the cell wall or membrane, intracellular targets (nucleic acids, proteins, etc.) [
38,
39]. For LfcinB peptides, it has been seen that the anti-Candida activity is due to damage to the cell surface, inducing the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and mitochondrial dysfunction [
27].
Previously, we found that the R-1-R peptide caused disruption on the cell surface with permeabilization. In contrast, the
B. pilosa extract was not able to exert this effect. However, when the combination was evaluated, permeabilization of the cell surface was observed in both antifungal sensitive and FLC-resistant
C. albicans [
13].Taking into account the results and the general mechanism of action that has been proposed for LfcinB on electrostatic and hydrophobic interactions in cell membranes [
20], our hypothesis is that the R-1-R peptide binds to the cell surface causing permeabilization, i.e., being an initiator of candidacidal activity, allowing the entry of other molecules such as FLC [
53] or
B. pilosa extract into the yeast, which act in an effector phase of the antifungal activity.
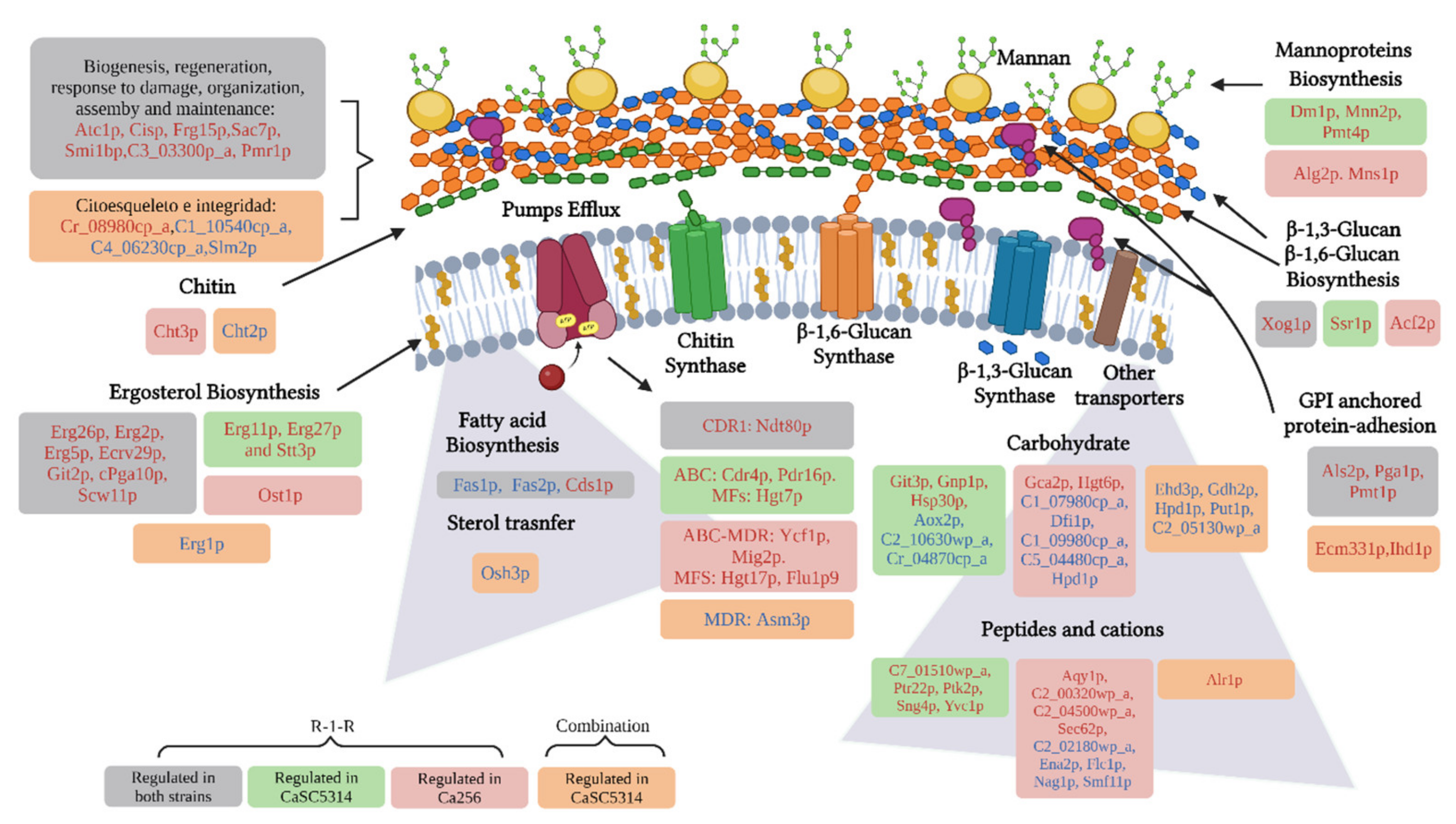
Additionally, the proteomic approach allowed us to observe that important processes of both the cell wall and membrane are affected by the R-1-R peptide (
Figure 11). For example, biosynthesis of mannoproteins, glucans, chitin, GPI-anchored proteins, ergosterol, and other fatty acids were affected independent of the antifungal resistance phenotype. Likewise, it was evident how most of these damages are preserved when treated with the combination and where it is additionally seen that it is possible that the extract intensifies the damage by also affecting the integrity of the cytoskeleton.
It is important to highlight that the cell wall is a dynamic structure, with great plasticity to allow different cell morphologies, molecular remodeling and changes in the composition of the cell wall as a result of adaptation to the surrounding environment ant this is composed mainly of chitin, β-glucan and mannoproteins [
52], where the most abundant proteins are GPI (anchor binding sequences) (88%), followed by PIR-cell wall proteins [
33]. On the other hand, cell membranes have a fundamental role in maintaining cellular integrity, being a highly selective permeability barrier between intra and extracellular media, and are also a binding point for the cytoskeleton and are mainly composed of lipids and proteins [
53]. The main lipids in fungal membranes are glycerophospholipids, lysolipids, sphingolipids and sterols, and the exact composition depends on the fungal species and strains [
42]; the most abundant sterol in fungal membranes is ergosterol, for
C. albicans, this comprises more than 50% of all sterols [
54,
55]. The cell membrane, in addition to being important in virulence and resistance to antifungals, it is possible that, together with the cell wall, they are involved in the response to oxidative stress [
41]. Due to the importance of the cell wall and membrane components, these are putative targets for the discovery and development of new drugs [
52].
Another target in the
C. albicans membrane for the R-1-R peptide and the
B. pilosa extract consists of transport proteins. In this study we confirmed that the R-1-R peptide acts by decreasing the activity of ABC-type efflux pumps. CDR1/CDR2 (
Figure 8), however this effect is not directly related to candidacidal activity, since no changes in susceptibility are evident in the mutant strains
cdr1∆/CDR1 and
cdr2∆/CDR2 (
Table 1). In the case of the
B. pilosa extract, it is suggested that it could activate efflux pumps (
Table 1,
Figure 8), possibly due to basal glucose content in this crude extract. However, additional experiments are necessary to confirm this effect.
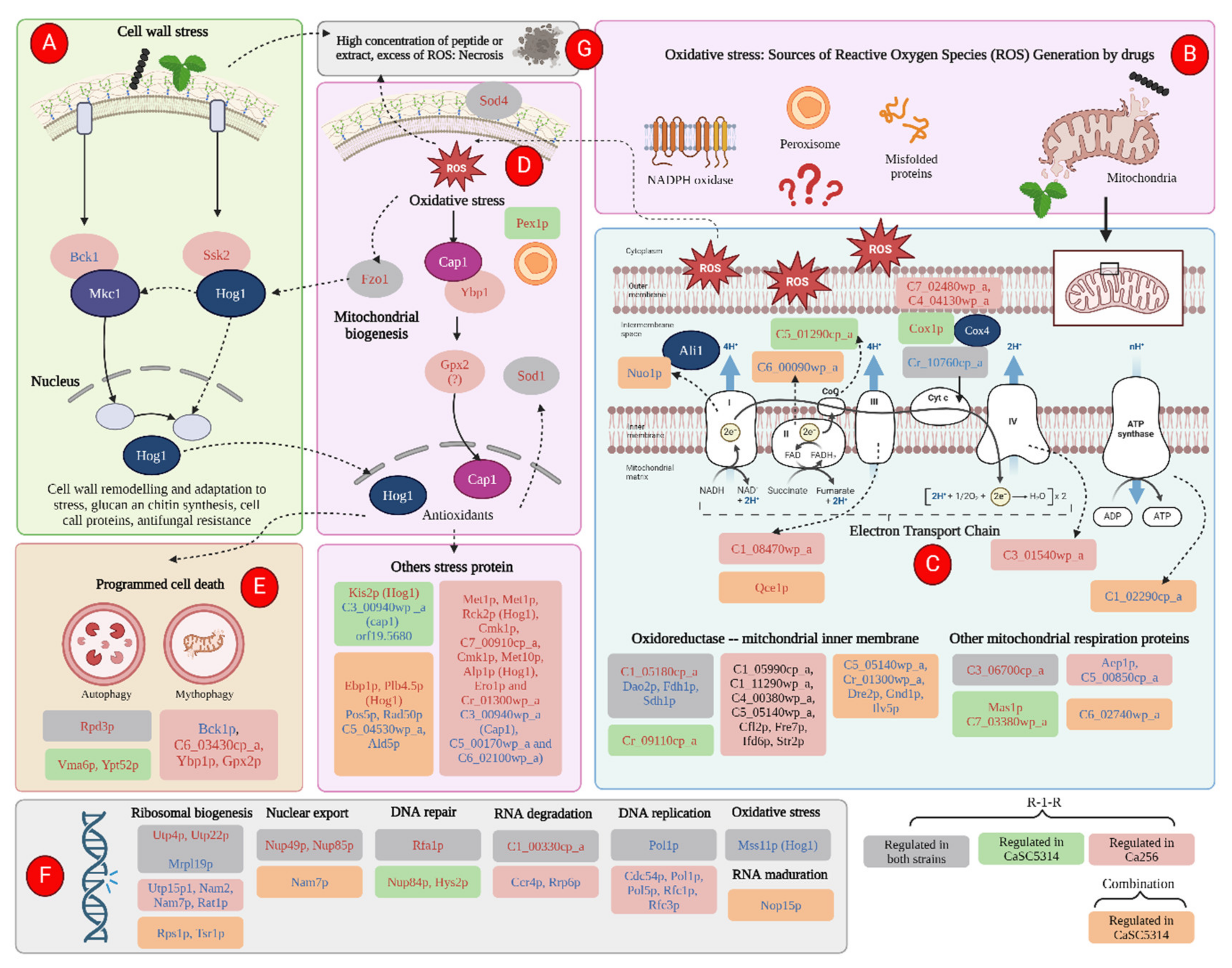
Damage to the cell wall can generate stress in the yeast, triggering responses to regenerate the damage caused by an external agent [
33,
57]. This is evidenced by the upregulation of cell wall biogenesis proteins in both study strains (
Figure 11). The response to cell wall stress was confirmed after using mutant strains and the proteomic study, where it was evident that with the R-1-R peptide, the mutant strains of MAPKs, Mkc1, (specific for wall stress cellular [
33]) and Hog1, (core protein responsive to different types of stress [
48]), were highly more susceptible to R-1-R. On the other hand, in the 256 strain, when it was treated with the R-1-R peptide, the proteins Bck1 (important in the MAPKs pathway, upstream of Mck1) and Ssk2 (upstream of Hog1) [
33], were down and up regulated, respectively (
Figure 12a).
Just as R-1-R and the
B. pilosa extract cause disruption in the cell wall and membrane, they can also exert this effect on the mitochondrial membrane (
Figure 12b), an important source of ROS, affecting the transport of electrons in the chain. respiratory and generating mitochondrial dysfunction, as has been observed for commercial antifungals [
42].
R-1-R, and to a greater extent, the extract of
B. Pilosa, and their combination generate a notable mitochondrial dysfunction, as evidenced by the depolarization of the mitochondrial membrane (
Figure 10). This effect was also observed with the Ali1 and Cox4 mutant strains, which were more sensitive or resistant to the peptide or extract respectively. According to
Figure 12c, we can see how, due to the action of R-1-R, there is regulation of proteins related, mainly, to cytochrome C, in both study strains, with enzyme Q and complexes III and IV of the ETC. The combination, for its part, exerts an effect on complexes I to III and even on the last stage of ATP synthesis. Thus, it is possible to suggest that damage at the level of the ETC may be generating an excessive release of ROS, which is causing oxidative stress in the yeast.
As widely recognized, excessive ROS can oxidize important cellular molecules such as DNA, lipids, and proteins. If this damage is severe, it can lead to cell death through necrosis, as observed in some cells treated with the extract or combination in SC5314 (
Figure 6e,f) or with all treatments in 256 (
Figure 7). However, prior to necrosis and as part of the adaptation to oxidative stress generated by the immune response of the host,
C. albicans exhibits responses against oxidative stress in which Hog1p and Cap1p play important roles [
48,
58]
The proteomic approach revealed that parallel to the Hog1 pathway, another oxidative stress pathway was being activated, the pathway dependent on Cap1p (
Figure 12d), where it is observed that two proteins downstream of Cap1p, Ypb1p and Gpx2p [
47], were up regulated. Additionally, for both study strains, upregulation of antioxidant proteins such as Sod1 and Sod4, and a stress response protein located in peroxisomes, was evident.
The 2,7-Dichorofluorescein Diacetate fluorescent probe assay allowed confirmation of oxidative stress, after the increase in the accumulation of intracellular ROS (
Figure 9), caused by the peptide R-1-R. This presence of ROS was associated with the candidacidal effect of the peptide. as pretreatment with an antioxidant increased the tolerance of SC5314 to R-1-R. Regarding the
B. pilosa extract, studies are needed to confirm the masking of the increase in ROS, caused by the antioxidant metabolites present in the extract, an effect that is replicated for the combination.
Furthermore, it was evident that as a survival mechanism, the two study strains triggered programmed cell death signals, which evidenced the upregulation of proteins present in autophagy and mitophagy (
Figure 12e). Additionally, it was observed that at the nucleic acid level, for both strains, DNA preparation proteins (due to oxidative stress) and ribosomal biogenesis are being regulated (
Figure 12f). Finally, it can be suggested that, in cases where damage due to cell wall stress or oxidative stress was severe, a necrotic process was triggered (
Figure 12g).
Figure 1.
Venn diagram of the total and exclusive proteins obtained after treatment with R-1-R in (a) SC5314 (b) 256. (c) Up and Down proteins regulated in SC5314 and 256 treated with R-1-R, grouped according to their biological function.
Figure 1.
Venn diagram of the total and exclusive proteins obtained after treatment with R-1-R in (a) SC5314 (b) 256. (c) Up and Down proteins regulated in SC5314 and 256 treated with R-1-R, grouped according to their biological function.
Figure 2.
Barplot of functional analyzes for (a) Up and (b) Down regulated proteins for strain SC5314, and (c) Up and (d) Down regulated proteins in strain 256 treated with R-1-R. The green bars represent terms associated with membrane or cell wall, yellow bars represent terms associated with membrane transporters, dark gray bars, terms associated with the nucleus or DNA/RNA and light gray bars are the terms associated with other cellular processes.
Figure 2.
Barplot of functional analyzes for (a) Up and (b) Down regulated proteins for strain SC5314, and (c) Up and (d) Down regulated proteins in strain 256 treated with R-1-R. The green bars represent terms associated with membrane or cell wall, yellow bars represent terms associated with membrane transporters, dark gray bars, terms associated with the nucleus or DNA/RNA and light gray bars are the terms associated with other cellular processes.
Figure 3.
Protein-protein interaction network of Up and Down proteins regulated in (a) SC5314 and (b) 256 after treatment with R-1-R. The nodes of the network are proteins identified by gene name, while the lines are edges that represent functional associations based on different types of evidence. The haloes of the nodes, in blue, belong to up-regulated proteins, and the gray halos, to down regulated ones. The colors in the nodes represent biological processes, such as: membrane (green), nucleic acids (dark gray), mitochondrial membrane potential (light blue) autophagy and endocytosis (orange) and others (light gray).
Figure 3.
Protein-protein interaction network of Up and Down proteins regulated in (a) SC5314 and (b) 256 after treatment with R-1-R. The nodes of the network are proteins identified by gene name, while the lines are edges that represent functional associations based on different types of evidence. The haloes of the nodes, in blue, belong to up-regulated proteins, and the gray halos, to down regulated ones. The colors in the nodes represent biological processes, such as: membrane (green), nucleic acids (dark gray), mitochondrial membrane potential (light blue) autophagy and endocytosis (orange) and others (light gray).
Figure 4.
(a) Venn diagram of the total and exclusive proteins obtained in SC5314, after treatment with the combination between R-1-R and B. pilosa extract. (b) Up and Down proteins regulated in SC5314 treated with the combination, grouped according to their biological function.
Figure 4.
(a) Venn diagram of the total and exclusive proteins obtained in SC5314, after treatment with the combination between R-1-R and B. pilosa extract. (b) Up and Down proteins regulated in SC5314 treated with the combination, grouped according to their biological function.
Figure 5.
Barplot of functional analyzes for (a) Up and (b) Down regulated proteins for strain SC5314, treated with combination. (c) Protein-protein interaction network of SC5314 treated with the combination. The nodes of the network are proteins identified by gene name; the lines are edges that represent functional associations based on different types of evidence. The haloes of the nodes, in blue, belong to up-regulated proteins, and the gray halos, to down regulated ones. The colors in the nodes represent biological processes, such as: membrane (green), oxidative stress (lilac), mitochondrial respiration (blue), nuclide acids (dark gray), others (light gray).
Figure 5.
Barplot of functional analyzes for (a) Up and (b) Down regulated proteins for strain SC5314, treated with combination. (c) Protein-protein interaction network of SC5314 treated with the combination. The nodes of the network are proteins identified by gene name; the lines are edges that represent functional associations based on different types of evidence. The haloes of the nodes, in blue, belong to up-regulated proteins, and the gray halos, to down regulated ones. The colors in the nodes represent biological processes, such as: membrane (green), oxidative stress (lilac), mitochondrial respiration (blue), nuclide acids (dark gray), others (light gray).
Figure 6.
STEM images of C. albicans SC5314, without treatment (a) after 2 h of incubation with R-1-R (b-c), B. pilosa extract (d-e) and combination of peptide and extract (f-i) where there was synergistic effect. R-1-R (25 µg/mL) and extract B. pilosa (250 µg/mL).
Figure 6.
STEM images of C. albicans SC5314, without treatment (a) after 2 h of incubation with R-1-R (b-c), B. pilosa extract (d-e) and combination of peptide and extract (f-i) where there was synergistic effect. R-1-R (25 µg/mL) and extract B. pilosa (250 µg/mL).
Figure 7.
STEM images of C. albicans 256, without treatment (a-b) after 2 h of incubation with R-1-R (c-d), B. pilosa extract (e-f) and combination of peptide and extract (g-h) where there was synergistic effect. R-1-R (50 µg/mL) and extract B. pilosa (62.25 µg/mL).
Figure 7.
STEM images of C. albicans 256, without treatment (a-b) after 2 h of incubation with R-1-R (c-d), B. pilosa extract (e-f) and combination of peptide and extract (g-h) where there was synergistic effect. R-1-R (50 µg/mL) and extract B. pilosa (62.25 µg/mL).
Figure 8.
Rhodamine 6G (R6G) efflux over time among (a) C. albicans SC5314 and (b) C. albicans 256s. Colored lines indicate the concentration of R6G released after the addition of 20 mM glucose (Glu), black lines correspond to the controls without Glu. Data are means ± SD from three experiments. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. ****p≤ 0.0001.
Figure 8.
Rhodamine 6G (R6G) efflux over time among (a) C. albicans SC5314 and (b) C. albicans 256s. Colored lines indicate the concentration of R6G released after the addition of 20 mM glucose (Glu), black lines correspond to the controls without Glu. Data are means ± SD from three experiments. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. ****p≤ 0.0001.
Figure 9.
(a) ROS accumulation on C. albicans. ROS production was assessed staining with H2DCFDA; Cells were pretreated with concentrations of R-1-R, (SC5314 and mutant strains: MIC: 100 µg/mL, SUB MIC: 25 µg/mL, 256: MIC: 100 µg/mL, SUB MIC: 50 µg/mL), extract (SC5314 and mutant strains: MIC: 500 µg/mL, SUB MIC: 250 µg/mL, 256: MIC: 500 µg/mL, SUB MIC: 62.5 µg/mL) and Amphotericin B (SC5314 and mutant strains: 4 µg/mL and 256: 64 µg/mL) was used as positive control. MFI, mean fluorescence intensity; A.U, arbitrary units. The results obtainable as means ± SD from three experiments. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. ****p≤ 0.0001 compared with SC5314 in each group treated, #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001. ####p≤ 0.0001 compared with SC5314 without treatment. (b) The effect of ROS scavenger, NAC, on the candidacidal activity of R-1-R (100 µg/mL) was also examined.
Figure 9.
(a) ROS accumulation on C. albicans. ROS production was assessed staining with H2DCFDA; Cells were pretreated with concentrations of R-1-R, (SC5314 and mutant strains: MIC: 100 µg/mL, SUB MIC: 25 µg/mL, 256: MIC: 100 µg/mL, SUB MIC: 50 µg/mL), extract (SC5314 and mutant strains: MIC: 500 µg/mL, SUB MIC: 250 µg/mL, 256: MIC: 500 µg/mL, SUB MIC: 62.5 µg/mL) and Amphotericin B (SC5314 and mutant strains: 4 µg/mL and 256: 64 µg/mL) was used as positive control. MFI, mean fluorescence intensity; A.U, arbitrary units. The results obtainable as means ± SD from three experiments. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. ****p≤ 0.0001 compared with SC5314 in each group treated, #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001. ####p≤ 0.0001 compared with SC5314 without treatment. (b) The effect of ROS scavenger, NAC, on the candidacidal activity of R-1-R (100 µg/mL) was also examined.
Figure 10.
Mitochondrial membrane potential was measurement by rhodamine 123 staining. Cells were treated with R-1-R, (SC5314 and mutant strains: MIC: 100 µg/mL, SUB MIC: 25 µg/mL, 256: MIC: 100 µg/mL, SUB MIC: 50 µg/mL), extract (SC5314 and mutant strains: MIC: 500 µg/mL, SUB MIC: 250 µg/mL, 256: MIC: 500 µg/mL, SUB MIC: 62.5 µg/mL) and Sodium azide (NaN3) 5 mM was used as positive control. MFI, mean fluorescence intensity; A.U, arbitrary units. The results obtainable as means ± SD from three experiments. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. ****p≤ 0.0001 compared with SC5314 in each group treated, #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001. ####p≤ 0.0001 compared with SC5314 without treatment.
Figure 10.
Mitochondrial membrane potential was measurement by rhodamine 123 staining. Cells were treated with R-1-R, (SC5314 and mutant strains: MIC: 100 µg/mL, SUB MIC: 25 µg/mL, 256: MIC: 100 µg/mL, SUB MIC: 50 µg/mL), extract (SC5314 and mutant strains: MIC: 500 µg/mL, SUB MIC: 250 µg/mL, 256: MIC: 500 µg/mL, SUB MIC: 62.5 µg/mL) and Sodium azide (NaN3) 5 mM was used as positive control. MFI, mean fluorescence intensity; A.U, arbitrary units. The results obtainable as means ± SD from three experiments. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. ****p≤ 0.0001 compared with SC5314 in each group treated, #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001. ####p≤ 0.0001 compared with SC5314 without treatment.
Figure 11.
Scheme of the Up-regulated (red letters) and Down-regulated (blue letters) proteins by the action of the R-1-R peptide and its combination (orange bubbles) with an extract of B. pilosa against the cell wall and membrane of both strains of C. albicans SC5314 and C. albicans 256 (gray bubbles), or exclusively in each strain [C. albicans SC5314 (Green burbles) and C. albicans 256 (red burbles)].
Figure 11.
Scheme of the Up-regulated (red letters) and Down-regulated (blue letters) proteins by the action of the R-1-R peptide and its combination (orange bubbles) with an extract of B. pilosa against the cell wall and membrane of both strains of C. albicans SC5314 and C. albicans 256 (gray bubbles), or exclusively in each strain [C. albicans SC5314 (Green burbles) and C. albicans 256 (red burbles)].
Figure 12.
Scheme of the Up-regulated (red letters) and Down-regulated (blue letters) proteins by the action of the R-1-R peptide and its combination (orange bubbles) with an extract of B. pilosa against both strains (gray bubbles) of C. albicans SC5314 (Green burbles) and C. albicans 256 (red burbles), or exclusively in each strain.
Figure 12.
Scheme of the Up-regulated (red letters) and Down-regulated (blue letters) proteins by the action of the R-1-R peptide and its combination (orange bubbles) with an extract of B. pilosa against both strains (gray bubbles) of C. albicans SC5314 (Green burbles) and C. albicans 256 (red burbles), or exclusively in each strain.
Table 1.
MICs and MFCs of R-1-R and extract of B. pilosa against C. albicans mutants.
Table 1.
MICs and MFCs of R-1-R and extract of B. pilosa against C. albicans mutants.
| orf19 |
Description1 |
Strain |
R-1-R |
B. pilosa Extract |
FLC |
| CMI/CMF (μg/mL) |
| Wild Type |
C. albicans ATCC SC5314 |
100/100 |
500/500 |
1 |
| Oral clinical isolated. FLC-resistant |
C. albicans 256 PUJ-HUSI |
100/100 |
500/500 |
64 |
| orf19.6000 |
Multidrug transporter of ABC superfamily; transports phospholipids in an in-to-out direction |
cdr1∆/CDR1 |
100/100 |
1000/2000 |
<0,25 |
| orf19.5958 |
Multidrug transporter, ATP-binding cassette (ABC) superfamily; transports phospholipids, in-to-out direction; overexpressed in azole-resistant isolates |
cdr2∆/CDR2 |
100/100 |
1000/>2000 |
<0,25 |
| orf19.895 |
MAP kinase of osmotic-, heavy metal-, and core stress response; role in regulation of glycerol, D-arabitol of response to stress |
hog1∆/HOG1 |
50/100 |
1000/2000 |
4 |
| hog1∆/hog1∆ |
12.5/25 |
500/2000 |
ND |
| orf19.7523 |
MAP kinase, role in cell wall structure/maintenance, caspofungin response; phosphorylated on surface contact, membrane perturbation, or cell wall stress |
mkc1∆/MKC1 |
50/100 |
1000/2000 |
2 |
| mkc1∆/mkc1∆ |
25/50 |
1000/>2000 |
ND |
| orf19.1710 |
Putative NADH-ubiquinone oxidoreductase; plasma membrane-localized; protein decreases in stationary phase |
ali1∆/ALI1 |
12,5/25 |
>2000/>2000 |
<0,5 |
| ali1∆/ali1∆ |
50/100 |
500/500 |
ND |
| orf19.1471 |
Putative cytochrome c oxidase subunit IV; Mig1-regulated |
cox4∆/COX4 |
12,5/25 |
>2000/>2000 |
<0,5 |
| cox4∆/cox4∆ |
50/200 |
500/2000 |
ND |
| orf19.2570 |
Putative NADH-ubiquinone dehydrogenase |
mci∆/mci∆ |
100/200 |
500/2000 |
ND |
| orf19.4758 |
Putative reductase or dehydrogenase |
orf19.4758∆/orf19.4758∆ |
100/200 |
500/1000 |
ND |
| orf19.7590 |
Putative NADH-ubiquinone oxidoreductase; identified in detergent-resistant membrane fraction (possible lipid raft component) |
orf19.7590∆/orf19.7590∆ |
100/100 |
500/500 |
ND |
Table 2.
Functional categories of C. albicans SC5314 and C. albicans 256 proteins regulated by R-1-R.
Table 2.
Functional categories of C. albicans SC5314 and C. albicans 256 proteins regulated by R-1-R.
|
C. albicans SC5314 |
C. albicans 256 |
| Systemic name |
Function |
Regulation type |
Systemic name |
Function |
Regulation type |
| Cell wall |
Cell wall |
| C1_11270wp_a |
|
Up |
Acf2p |
endo-1,3-beta-glucanase |
Up |
| Dpm1p |
Mannoproteins biosynthesis |
Up |
Ada2p |
integrity |
Up |
| Gda1p |
cell wall, and cell surface charge |
Up |
Alg2p |
Mannoproteins biosynthesis |
Up |
| Mnn2p |
Mannoproteins biosynthesis |
Up |
C2_08580wp_b |
|
Up |
| Pmt4p |
Mannoproteins biosynthesis |
Up |
C2_10740cp_a |
integrity |
Up |
| Rbe1p |
regulator of cell wall dynamics |
Up |
Cht3p |
chitin |
Up |
| Sim1p |
maintenance |
Up |
CHrr25p |
stress |
Up |
| Spf1p |
formation |
Up |
Mns1p |
Mannoproteins biosynthesis |
Up |
| Ssr1p |
Beta-glucan |
Up |
Cwt1p |
Up |
| Atc1p |
formation |
Up |
Rom2p |
biogenesis |
Up |
| Als2p |
regeneration |
Up |
Sac1p |
integrity
integrity |
Up |
| Cis2p |
biogenesis |
Up |
Bck1p |
Down |
| Fgr15p |
damage response |
Up |
Evp1p |
organization |
Down |
| Sac7p |
organization |
Up |
Pde2p |
Down |
| Smi1bp |
assembly |
Up |
Msb2p |
cell wall stress |
Down |
| C3_03300cp_a |
|
Up |
C1_10540cp_a |
cytoskeleton |
Up |
| Pmr1p |
maintenance |
Up |
Cr_08980cp_a |
Up |
| Xog1p |
Exo-1,3-beta-glucanase-chitin |
Up |
C5_04890cp_a |
Down |
| Ecm15p |
organization |
Down |
Nce102p |
cytoskeleton-actin |
Down |
| Rhb1p |
integrity |
Down |
|
|
|
| Cell membrane |
Cell membrane |
| Erg11p |
Ergosterol biosynthesis |
Up |
Dnf1p |
sphingolipid translocation |
Up |
| Erg27p |
Up |
Sct1p |
phospholipid biosynthesis |
Up |
| Stt3p |
Up |
Stt4p |
kinase |
Up |
| Erg26p |
Ergosterol biosynthesis |
Up |
C1_03690wp_a |
Ergosterol biosynthesis |
Up |
| Erg2p |
Up |
Cht3p |
Biosynthesis+C39:C44 ergosterol |
Up |
| Erg5p |
Up |
Sld1p |
Ergosterol biosynthesis |
Up |
| Ecrv29p |
Up |
Ost1p |
Down |
| Git2p |
Up |
C1_02270cp_a |
fatty acid catabolism |
Down |
| cPga10p |
Up |
Ece1p |
integrity |
Down |
| Scw11p |
Up |
|
|
|
| C6_03240wp_a |
Down |
|
|
|
| C3_00570cp_a |
phosphoprotein |
Up |
|
|
|
| Cds1p |
phospholipid biosynthesis |
Up |
|
|
|
| Ino1p |
inositol-3-phosphate |
Up |
|
|
|
| Osh2p |
sterol transfer |
Up |
|
|
|
| C2_05290cp_a |
Component fatty acids |
Up |
|
|
|
| C2_10010cp_a |
|
Up |
|
|
|
| C5_05440cp_a |
phospholipid binding |
Up |
|
|
|
| Cdc24p |
Up |
|
|
|
| C5_01420wp_a |
|
Up |
|
|
|
| Fmp45p |
|
Up |
|
|
|
| Rac1p |
G-protein of RAC subfamily |
Up |
|
|
|
| Slc1p |
glycerolipid biosynthesis |
Up |
|
|
|
| Fas1p |
Biosynthesis fatty acids |
Down |
|
|
|
| Fas2p |
Down |
|
|
|
| Icl1p |
Catabolism fatty acids |
Down |
|
|
|
| Mitochondria-oxidative stress |
Mitochondria-oxidative stress |
| C5_01290cp_a |
Coenzyme Q-biosynthesis
oxidoreductase |
Up |
Met1p |
oxidative stress - Hog1 |
Up |
| Cr_09110cp_a |
Up |
Rck2p |
Up |
| Kis2p |
oxidative stress-Hog1 |
Up |
Ssk2p |
Up |
| Mas1p |
Mitochondrial respiration
peroxisome |
Up |
C7_00910cp_a |
oxidative stress -Cap1 |
Up |
| Pex1p |
Up |
Cr_01300wp_a |
oxidative stress |
Up |
| C1_05180cp_a |
oxidative stress-Cap1 |
Up |
Cmk1p |
Up |
| Fzo1p |
oxidative stress-Hog1 |
Up |
Met10p |
Reductase- Hog1-induced |
Up |
| C1_05180cp_a |
oxidoreductase
antioxidant |
Up |
Alp1p |
Up |
| Cr_09110cp_a |
oxidoreductase activity
oxidative stress
response to ROS |
Up |
Ero1p |
Oxidoreductases-Homeostasis |
Up |
| Sur2p |
Up |
C5_00170wp_a |
oxidative stress |
Down |
| Sod1p |
oxidoreductase activity
oxidative stress |
Up |
C6_02100wp_a |
Down |
| Sod4p |
Up |
C1_05990cp_a |
Oxidoreductases |
Down |
| C3_00940wp_a |
oxidoreductase activity |
Down |
C1_11290wp_a |
Down |
| C5_00170wp_a |
Down |
C4_00380wp_a |
Down |
| C5_02690wp_a |
oxidoreductase activity |
Down |
C5_05140wp_a |
Down |
| Dao2p |
Down |
Cfl2p |
Down |
| Fdh1p |
Down |
Fre7p |
Down |
| Sdh1p |
Down |
Ifd6p |
Down |
| |
|
|
Str2p |
Down |
| |
|
|
C3_00940wp_a |
oxidative stress -Cap1 |
Down |
| Mitochondria-Membrane Potential |
Mitochondria-Membrane Potential |
| Cox1p |
|
Up |
C7_02480wp_a |
Respiration-Cytochrome C |
Up |
| C3_06700cp_a |
respiratory chain |
Up |
C4_04130wp_a |
Up |
| C7_03380wp_a |
|
Up |
C1_08470wp_a |
Mitochondrial respiration -complex III |
Up |
| C3_00620cp_a |
respiratory chain-
Cytochrome C |
Up |
C3_01540wp_a |
Mitochondrial respiration-complex IV |
Up |
| C5_02740wp_a |
|
Up |
C5_02590cp_b |
Respiration |
Up |
| Cr_10760cp_a |
Cytochrome C |
Down |
Mss116p |
Up |
| |
|
|
Aep1p |
Down |
| |
|
|
C5_00850cp_a |
Down |
| Transport |
Transport |
| Cdr4p |
ABC transporters |
Up |
Ycf1p |
ABC-MDR transporters |
Up |
| Pdr16p |
activates CDR1/CDR2 |
Up |
Mig2p |
Up |
| Ndt80p |
activates CDR1 |
Up |
Hgt17p |
MFS transporters |
Up |
| Hgt7p |
MFS transporters |
Up |
Flu1p |
Up |
| Git3p |
carbohydrate transport |
Up |
Gca2p |
Carbohydrate transport |
Up |
| Gnp1p |
Up |
Hgt6p |
Up |
| Hsp30p |
Up |
C1_07980cp_a |
Down |
| Hgt19p |
carbohydrate transport |
Up |
Dfi1p |
Down |
| Hgt19p |
Up |
C1_09980cp_a |
Down |
| Aox2p |
carbohydrate transport |
Down |
C5_04480cp_a |
Down |
| C2_10630wp_a |
Down |
Hpd1p |
Down |
| Cr_04870cp_a |
Down |
Aqy1p |
water canal |
Up |
| C1_09980cp_a |
carbohydrate transport |
Down |
C2_00320wp_a |
|
Up |
| C5_04480cp_a |
Down |
C2_04500wp_a |
ion |
Up |
| Sfc1p |
Down |
Sec62p |
proteins |
Up |
| C7_01510wp_a |
|
Up |
C2_02180wp_a |
metals |
Down |
| Ptr22p |
peptides |
Up |
Ena2p |
potassium ion |
Down |
| Ptk2p |
|
Up |
Smf11p |
metals |
Down |
| Sng4p |
|
Up |
|
|
|
| C7_03590cp_a |
antiport |
Up |
|
|
|
| Ftr1p |
Fe ion |
Up |
|
|
|
| Ftr2p |
Fe ion |
Up |
|
|
|
| Pho84p |
Cations |
Up |
|
|
|
| Vrg4p |
|
Up |
|
|
|
| Flc1p |
FAD |
Down |
|
|
|
| Yvc1p |
Calcium |
Down |
|
|
|
| Nag1p |
|
Down |
|
|
|
| Vacuole-Mitochondrial connection |
Mitochondria-cell death |
| Vma6p |
mitochondria binding complex |
Up |
Bck1p |
mitophagy |
Down |
| Ypt52p |
Up |
C6_03430cp_a |
autophagy-mitochondria |
Up |
| Rpd3p |
autophagy-mitochondria |
Up |
Ybp1p |
Up |
| |
|
|
Gpx2p |
Up |
| DNA-RNA |
DNA-RNA |
| Nup84p |
repair DNA damage due to oxidation |
Up |
Ccr4p |
RNA degradation |
Up |
| Hys2p |
Up |
Rrp6p |
Up |
| Utp4p |
Ribosome biogenesis |
Up |
Cdc54p |
replication |
Up |
| Utp22p |
Up |
Pol1p |
Up |
| Nup49p |
|
Up |
Pol5p |
Up |
| Nup85p |
nuclear export |
Up |
Rfc1p |
Up |
| Rfa1p |
DNA damage repair |
Up |
Rfc3p |
Up |
| C1_00330cp_a |
RNA degradation |
Up |
Utp15p1 |
ribosome biogenesis |
Up |
| Pol1p |
DNA Replication |
Down |
Nam2 |
tRNA biosynthesis |
Down |
| Mrpl19p |
ribosome subunit |
Down |
Nam7p |
nucleocytoplasmic transport |
Down |
| Mss11p |
Transcription factor- MAPK signaling pathway (HOG1) |
Down |
Rat1p |
ribosome biogenesis |
Down |
Table 3.
Functional categories of C. albicans SC5314 proteins regulated by the combination between R-1-R and B. pilosa extract.
Table 3.
Functional categories of C. albicans SC5314 proteins regulated by the combination between R-1-R and B. pilosa extract.
| Systemic name |
Function |
Regulation type |
| Cell wall |
| Ecm331p |
Cell surface-GPI anchor |
Up |
| Ihd1p |
Up |
| Cr_08980cp_a |
Cytoskeleton-organization |
Up |
| C1_10540cp_a |
Cytoskeleton-actin |
Down |
| C4_06230cp_a |
Down |
| Slm2p |
Down |
| Cht2p |
chitinase |
Down |
| Ada2p |
wall integrity |
Down |
| Membrane cell |
| Erg1p |
Ergosterol biosynthesis |
Down |
| Osh3p |
sterol transfer |
Down |
| Mitochondria-oxidative stress |
| Ebp1p |
Oxidative stress |
Up |
| Plb4.5p |
Oxidative stress-HOG1 |
Up |
| Pos5p |
Oxidative stress |
Down |
| Rad50p |
Down |
| C5_05140wp_a |
Oxidoreductases-mitochondrial matrix |
Down |
| Cr_01300wp_a |
Oxidoreductases-mitochondrial inner membrane |
Down |
| Dre2p, Gnd1p |
Oxidoreductases-redox homeostasis |
Down |
| Ilv5p |
Oxidoreductases |
Down |
| C5_04530wp_a |
Antioxidant activity |
Down |
| Ald5p |
Antioxidant activity-degradation of fatty acids |
Down |
| Mitochondria-Membrane Potential |
| Qce1p |
expression of complex III of the respiratory chain |
Up |
| Nuo1p |
complex I of the respiratory chain |
Down |
| C6_00090wp_a |
complex II of the respiratory chain |
Down |
| C6_02740wp_a |
electron transport |
Down |
| C1_02290cp_a |
ATP synthesis |
Down |
| Transporters |
| Alr1p |
Cation transport |
Up |
| Ehd3p |
carbohydrate transport |
Down |
| Gdh2p |
Down |
| Hpd1p |
Down |
| Put1p |
Down |
| C2_05130wp_a |
Carbohydrate transport-oxidoreductase |
Down |
| Asm3p |
MDR1 transporters |
Down |
| DNA-RNA |
| Rps1p |
ribosome |
Down |
| Tsr1p |
Down |
| Nop15p |
rRNA maturation |
Down |
| Nam7p |
nucleocytoplasmic transport |
Down |