1. Introduction
The SiCp/Al composite material is produced by incorporating SiC particles as reinforcement into an aluminum matrix material using advanced manufacturing processes. This material has a high tensile strength, a high stiffness-to-weight ratio, good resistance to wear, and a low coefficient of thermal expansion. It demonstrates great physical qualities and mechanical characteristics. It is extensively employed in the production of lightweight telescopes for accurate optical equipment [
1]. This material is also used in the manufacturing of bomber tail fins and fighter aircraft ventral fins [
2,
3]. Nevertheless, the presence of hard SiC particles in this material often results in significant tool wear and diminished surface quality during mechanical machining. As a result, SiCp/Al is considered a challenging material to machine, which limits its application [
4,
5]. Conventional mechanical machining techniques not only face challenges in meeting the demands of environmentally friendly machining but also fall short in guaranteeing efficient processing and high quality. Hence, doing research on processing technology and specialized machining procedures [
6] is of great significance.
Researchers both domestically and internationally have undertaken thorough investigations on SiCp/Al composite materials. Zhang Huiting and a team of researchers from Xiamen University of Technology conducted a study on the wear characteristics of SiCp/Al composite materials with a high volume percentage. The materials were subjected to the influence of spinning ultrasonic. According to the findings, when subjected to ultrasonic vibration, the primary wear mechanisms of diamond particles are microfracture and abrasion [
7]. Ma Guohong and his team from Taiyuan University of Science and Technology conducted cutting simulations to analyze the cutting process of composite materials. They compared the results of conventional cutting with those of ultrasonic vibration-assisted cutting. The researchers also examined the damage characteristics of SiC particles, the surface morphology, and the subsurface damage of the workpiece. The findings suggest that ultrasonic vibration-assisted cutting is more effective than conventional cutting in improving surface integrity, reducing subsurface damage, and enhancing the surface quality of composite materials [
8]. Researchers from Jinan University, under the leadership of Professor Leng Jinfeng, discovered that the tool life in precision machining of SiCp/Al may be successfully increased by utilizing PCD tools and optimizing cutting settings. To enhance processing performance, it is suggested to utilize elongated and small-scale particles as reinforcements and ensure a homogeneous distribution of these SiC particles within the aluminum matrix [
9]. Wu Yuchao and other researchers from the University of Shanghai for Science and Technology discovered that by utilizing two-dimensional cutting model simulation methods and conducting high-speed linear motor experiments, they were able to effectively examine the mechanism behind the formation of surface damage during the cutting process of SiCp/Al composite materials. The spatial arrangement of SiC particles in relation to the tool’s cutting path will lead to varying degrees of cutting damage; the surface quality of SiCp/Al composite materials will enhance as the cutting velocity increases [
10]. Ben Deng and his colleagues from the School of Mechanical Science and Engineering performed milling experiments on SiCp/Al composite materials utilizing micro PCD equipment. The findings suggest that during the early phases of cutting, adhesive wear is the main type of wear, making up around 57% of the overall wear. As the cutting duration increases, two-body abrasive wear becomes the dominant wear mechanism in the later stages of processing, accounting for 60% of the wear on the tool surface [
11]. Pradyut Kumar Swain and their team from the Aryan Institute of Engineering & Technology performed dry cutting experiments on SiCp/Al composite materials. Through a comparison of the performance of uncoated and coated cemented carbide tools, it was shown that the uncoated cemented carbide inserts saw significant wear, but the coated tools demonstrated a reduced rate of wear at lower temperatures [
12]. Volodymyr Bushlya and his colleagues at Lund University discovered that while machining SiCp/Al composite materials with PCBN tools, a stable built-up edge was formed at low cutting speeds, often resulting in significant adhesion between the tool and the workpiece material. Nevertheless, the lack of a built-up edge at a velocity of 400m/min resulted in swift deterioration of the tool [
13].
Presently, the majority of research investigations on SiCp/Al composite materials, both locally and globally, employ materials with volume fractions that vary from 15% to 36%. There is a scarcity of studies on the milling processes of aluminum-based composites containing medium to high-volume fractions. Furthermore, previous studies have examined the machining mechanisms involved in the cutting process of SiCp/Al composite materials. These studies have emphasized the considerable influence of milling settings on the indicators of tool wear after milling. Several process optimizations have been investigated regarding tool wear in SiCp/Al composite materials. Nevertheless, there is a dearth of comprehensive studies on the systematic prediction and management of tool wear based on production needs, as well as the optimization of milling settings to minimize tool wear and extend tool lifespan in SCCO2-MQL ultrasonic vibration circumstances.
2. Experimental Conditions and Procedures
2.1. Experimental Equipment and Tools
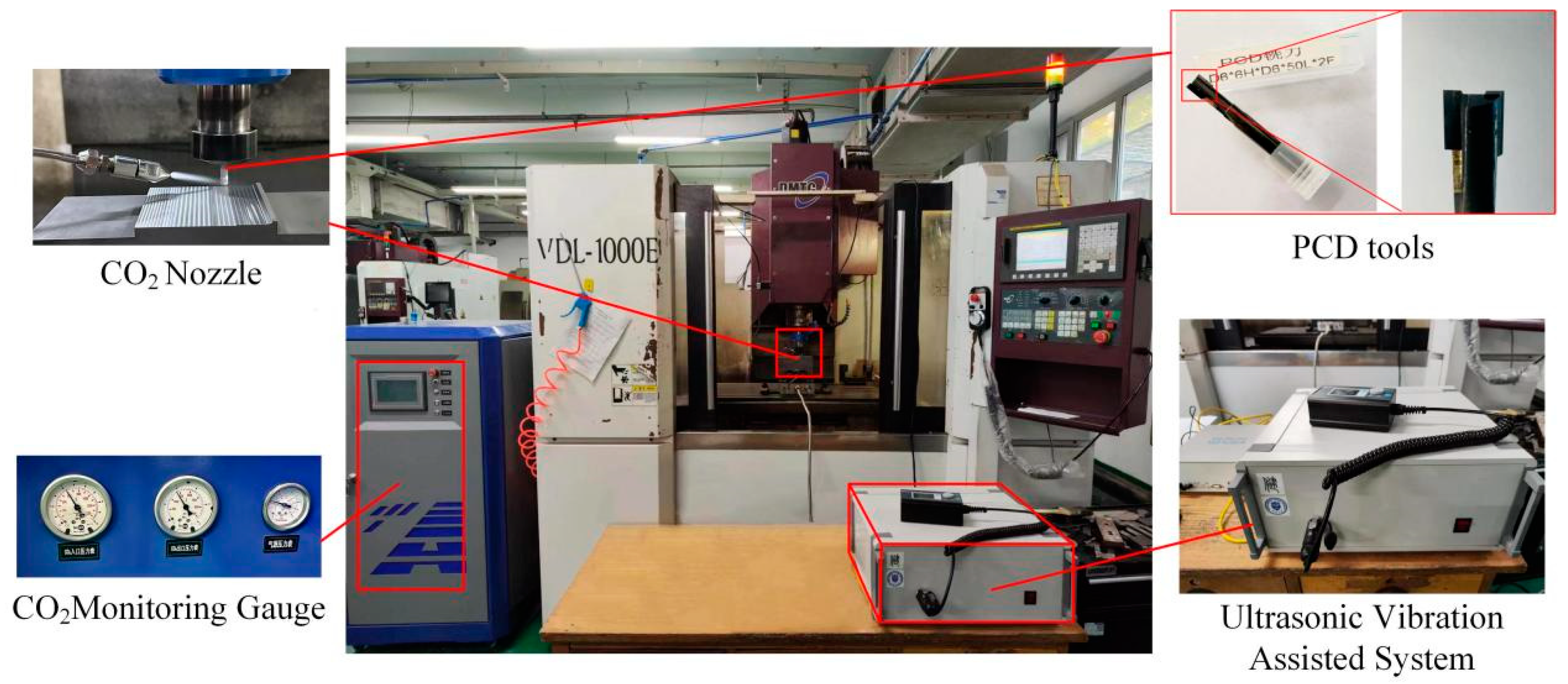
The test employed PCD tools of the D6×6H×D6×50L×2F variant. The experimental material consisted of a composite material made of 6063DL31 aluminum alloy, which contained SiC particles with a volume proportion of 45%. The SiCp/Al composite material was manufactured using a meticulously planned procedure and subsequent stabilization techniques, with its chemical composition provided in
Table 1. The experiment was performed using a VDL-1000 three-axis vertical machining center, as depicted in
Figure 1. Throughout the trial, the Supercritical Carbon Dioxide equipment was connected and placed onto the machine tool. This equipment employed the Cry0lube-i0oW model, a supercritical CO
2 micro lubrication device developed by Dongguan Anlin Mechanical Manufacturing Technology Co., Ltd. The primary measuring devices utilized in the investigation were the VHX-1000 Ultra-Depth Microscope and the inVia-Reflex Raman confocal microscope.
2.2. Experimental Plan
The experimental plan consists of single-factor tests that focus on the cutting velocity
vc, feed per tooth
fz, milling depth
ap, and milling width
ae.
Table 2 displays the experimental parameters. Tool wear was monitored and documented at various milling distances, and accurate measurements of the loss of wear value
VB on the rake face were performed.
Considering that the cutting method used in this study belongs to the domain of precision machining, it is crucial to keep tool wear within a narrow range. Thus, a value of VB=0.09mm is established as the threshold for determining when the tool has become dull.
3. Experimental Results and Analysis
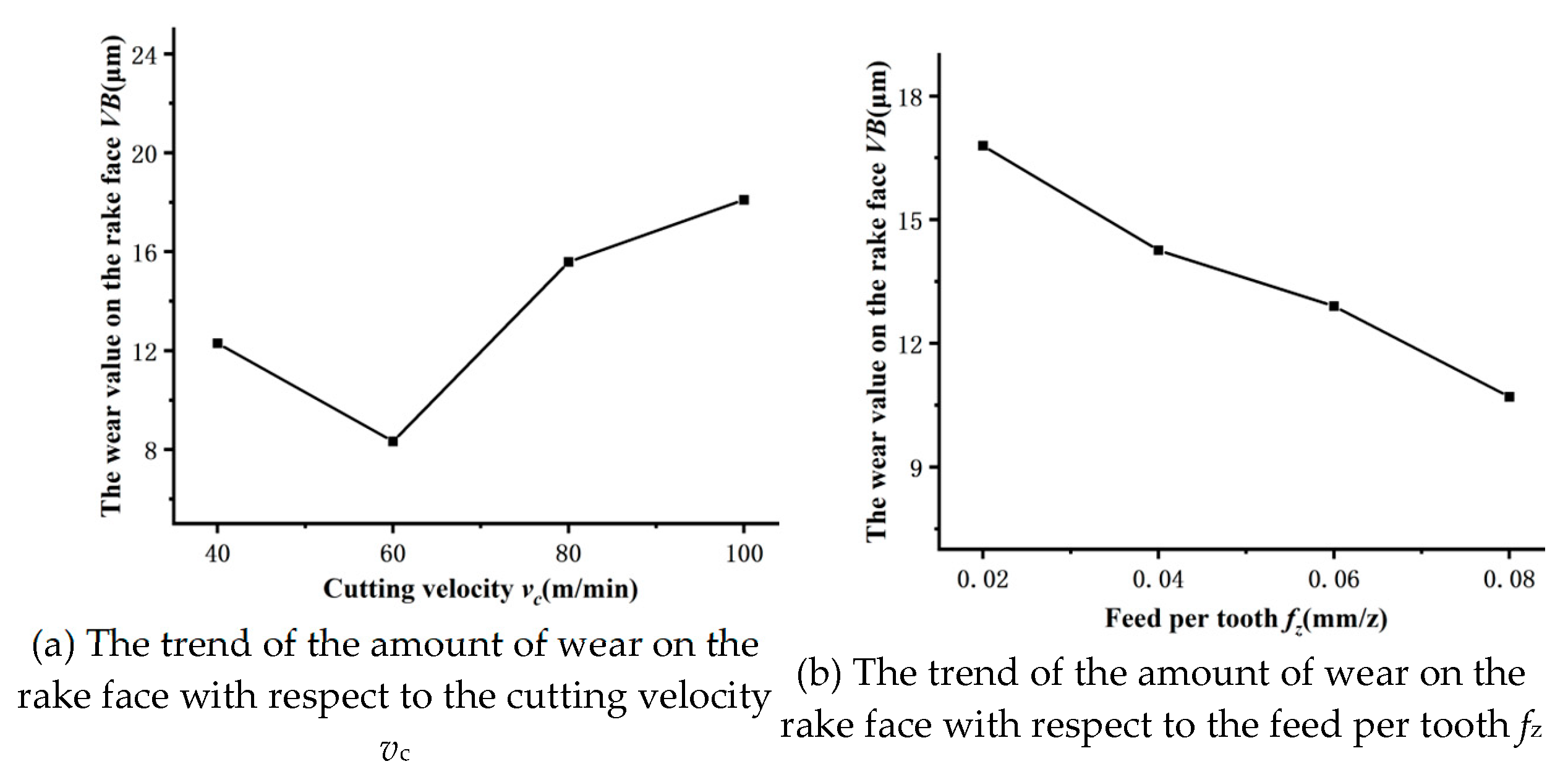
3.1. Impact of Cutting Velocity on Tool Wear
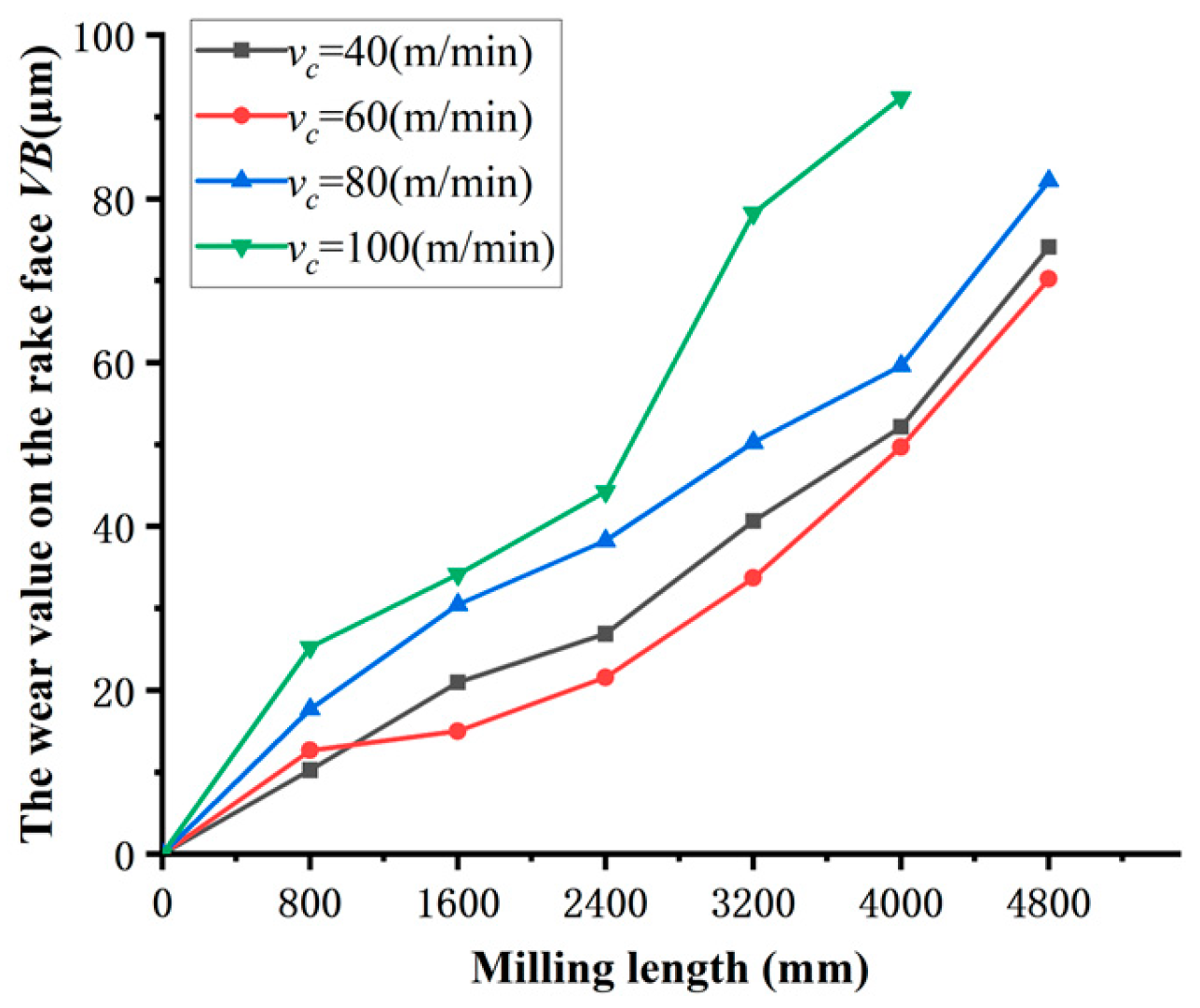
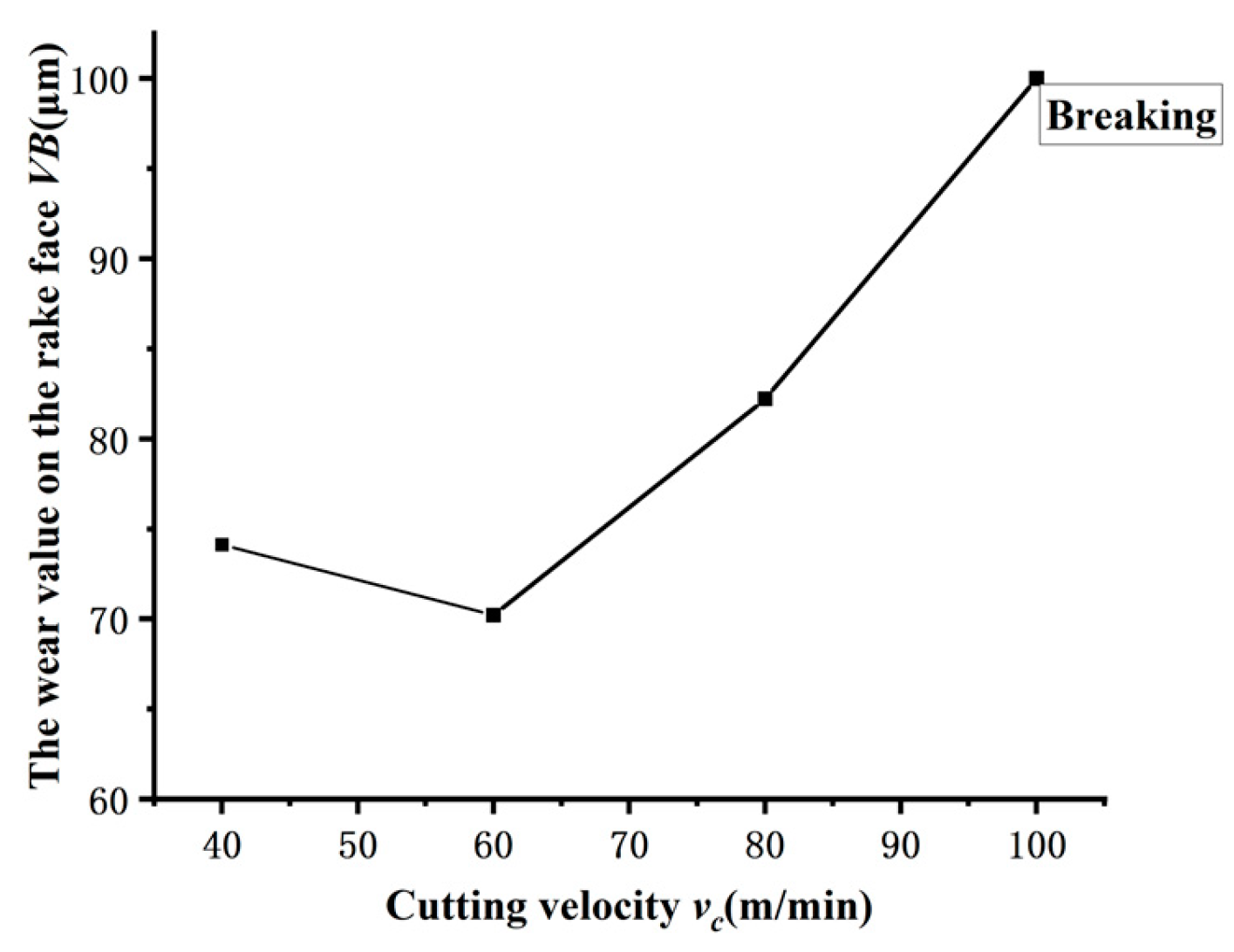
Figure 2 illustrates the impact of cutting velocity v
c on the level of tool wear VB, whereas
Figure 3 displays the amount of tool wear VB at a milling length of L=4800mm. These two graphs demonstrate that when the milling length L and cutting velocity v
c rise, the tool wear amount VB initially decreases and subsequently increases. At a cutting velocity of 60m/min, the tool wear amount VB is minimized. Increasing the cutting velocity v
c from 40m/min to 60m/min results in a decrease in the amount of tool wear VB, suggesting that tool wear progresses relatively slowly at this stage. The reason for this is that when the cutting velocity is reduced at 40m/min, the area of contact between the tool and the chips becomes larger. As a result, it takes more time for the chips to disengage from the tool, leading to a higher degree of tool wear VB compared to the scenario at 60m/min. Nevertheless, when the cutting velocity v
c is raised from 60m/min to 100m/min, there is a noticeable increase in the amount of tool wear VB, particularly on the rake face of the tool. Once the cutting velocity v
c , reaches around 100m/min, the tool wear has already met the requirement for becoming dull. This occurs because, in high-speed cutting operations, the rate at which chips are removed increases. Nevertheless, as a result of the overly rapid cutting velocity, the duration of contact between the chips and the tool diminishes, resulting in inadequate cooling of the chips. The cumulative heat will result in thermal degradation of the tool, intensifying wear.
Hence, the choice of cutting velocity v
c must take into account both the longevity of the tool and the efficiency of the machining process. To achieve a balance between tool life and processing efficiency, it is advisable to maintain a cutting velocity v
c of around 60m/min. This will help ensure the quality of the machined parts. This supports the conclusion made by experts such as Niu Qiulin and others, who suggested a direct relationship between the amount of tool wear VB and the cutting velocity v
c . As the cutting velocity v
c , increases, the occurrence of tool failure caused by excessive wear on the rake face intensifies [
14].
3.2. The Impact of Feed per Tooth on Tool Wear
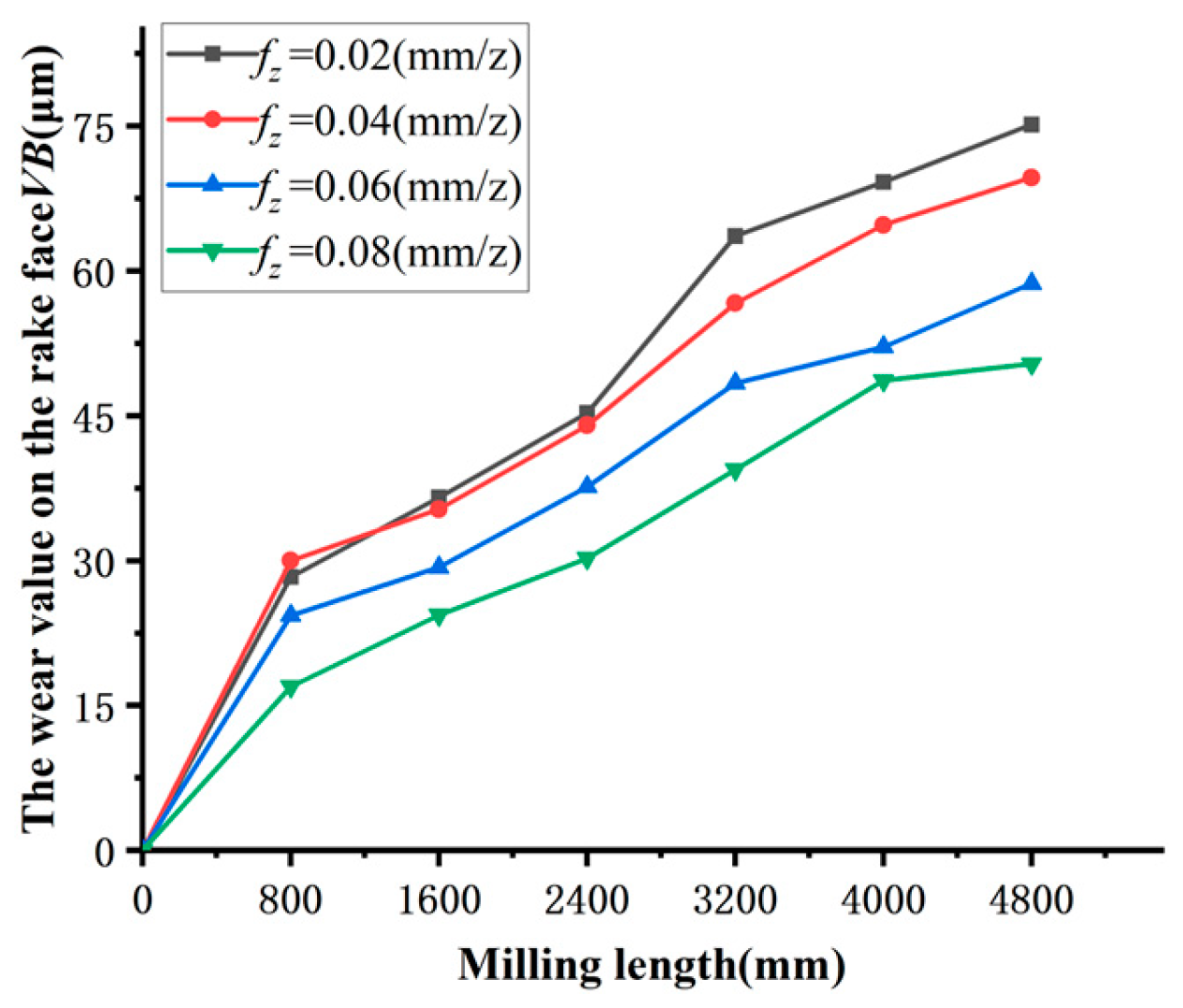
Figure 5 depicts the correlation between the feed per tooth f
z and the amount of tool wear VB on the rake face. Meanwhile,
Figure 6 displays the tool wear amount VB for a milling length of L=4800mm. The graph clearly demonstrates that the feed per tooth f
z has a substantial influence on the amount of tool wear VB. Using a smaller feed per tooth f
z on the milling machine results in a decrease in the feed rate, which in turn increases the duration of contact between the workpiece and the tool. Conversely, a higher value of feed per tooth f
z can shorten the cutting time needed to remove a given amount of material, minimize the abrasive impact of particles on the tool, and expedite the bonding process between the treated surface and the reinforcing particles. This significantly decreases the amount of wear on the tool. Optimizing tool longevity and machining efficiency relies heavily on adjusting the feed per tooth f
z.
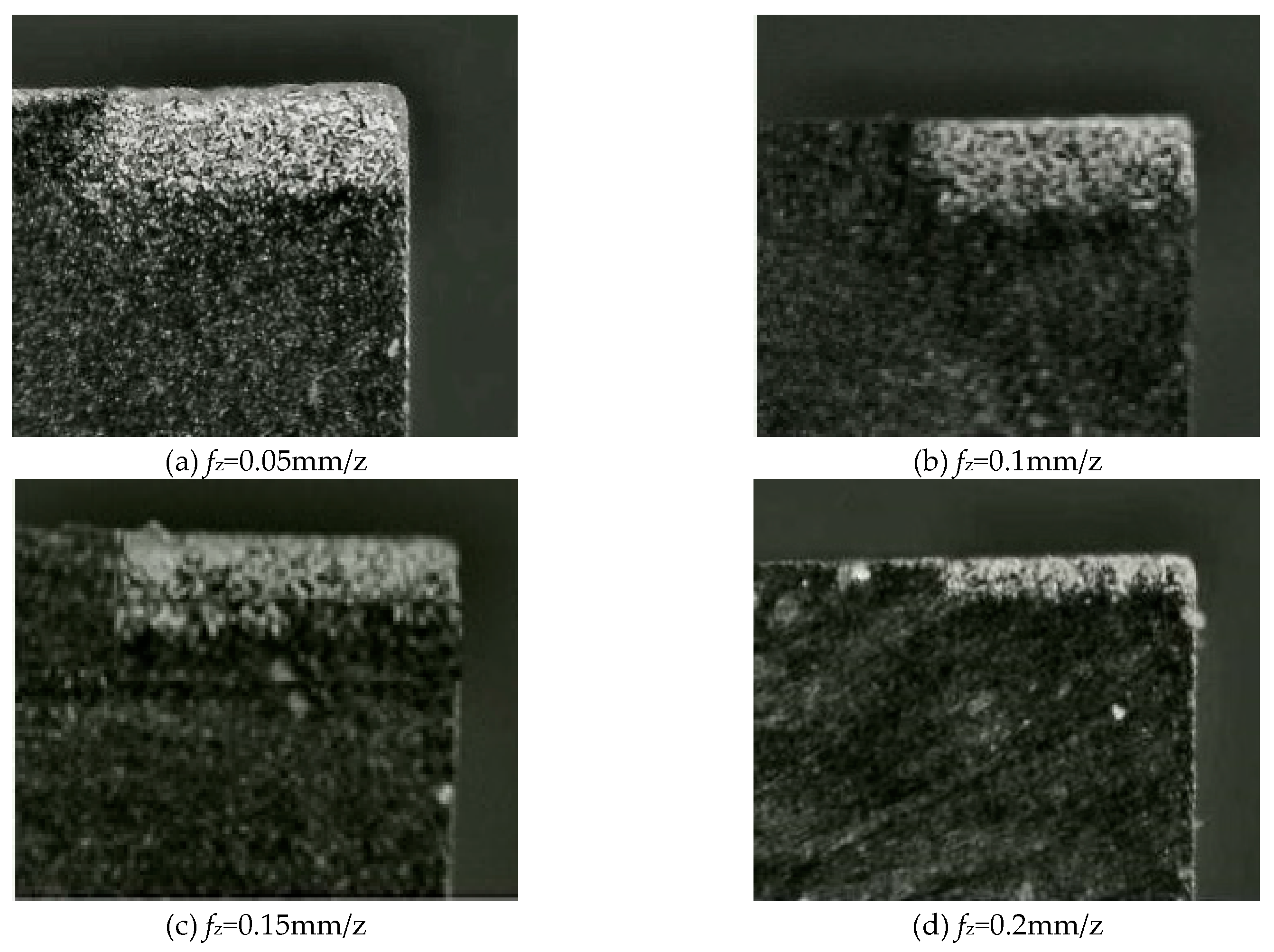
Figure 7 displays the wear patterns on the rake face under various feed per tooth f
z settings. It is evident that the rake face shows varying degrees of wear phenomena, such as little chipping of the tool, under different feed per tooth f
z settings. At a feed per tooth f
z of 0.2mm/z, the tool wear VB value reduces to a minimum, the surface roughness Ra reaches an ideal state, and there are no noticeable traces of damage on the rake face. This conclusion aligns with the research conducted by Lin Jieqiong and other researchers, who suggested that when the feed per tooth f
z grows, the impact of worn tools on the surface roughness Ra diminishes [
15]. Research findings suggest that when using SCCO
2-MQL with ultrasonic vibration, the cutting process can endure for a maximum duration of 50 minutes. This not only prolongs the duration between tool replacements but also effectively reduces the rate of tool deterioration.
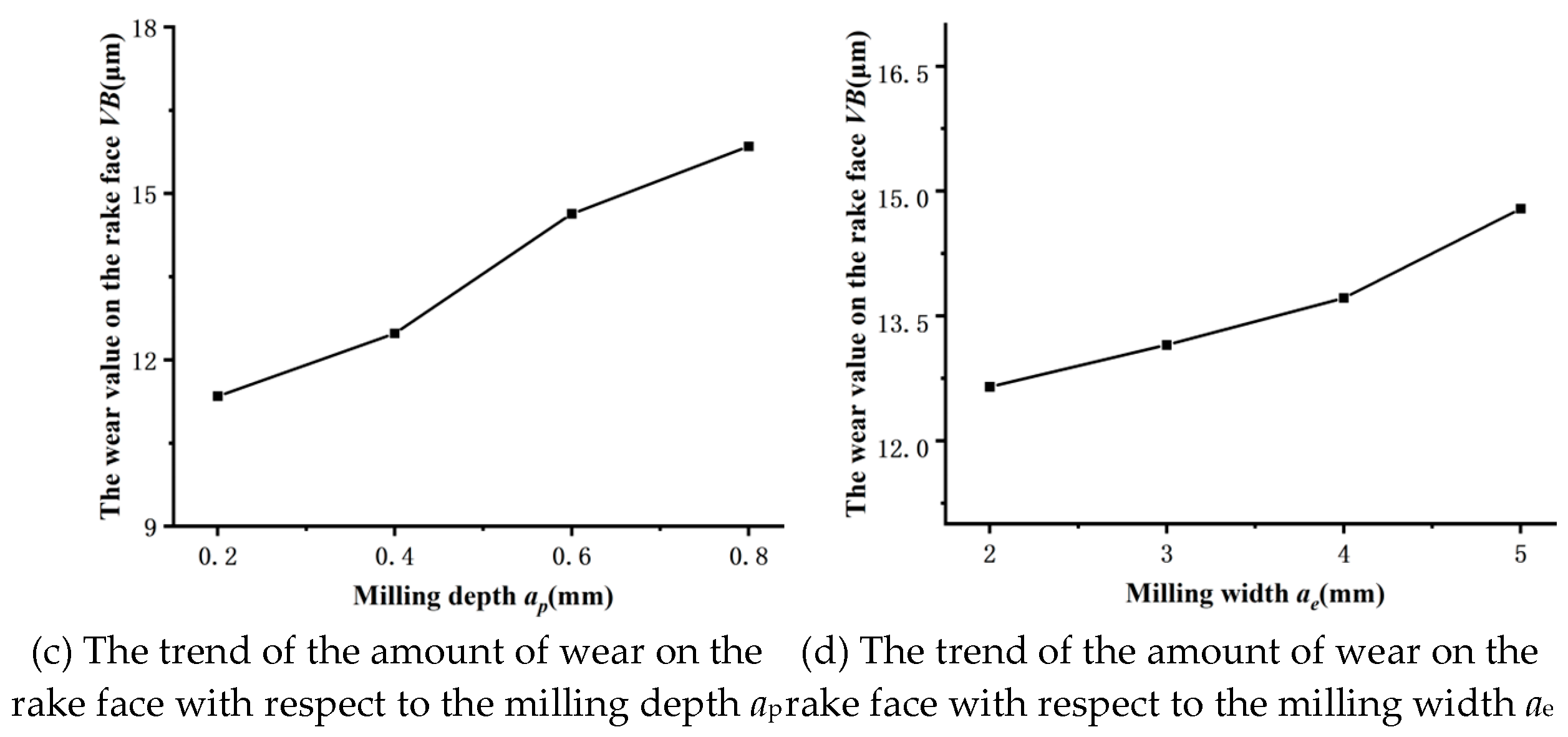
3.3. The Influence of Milling Depth on Tool Wear
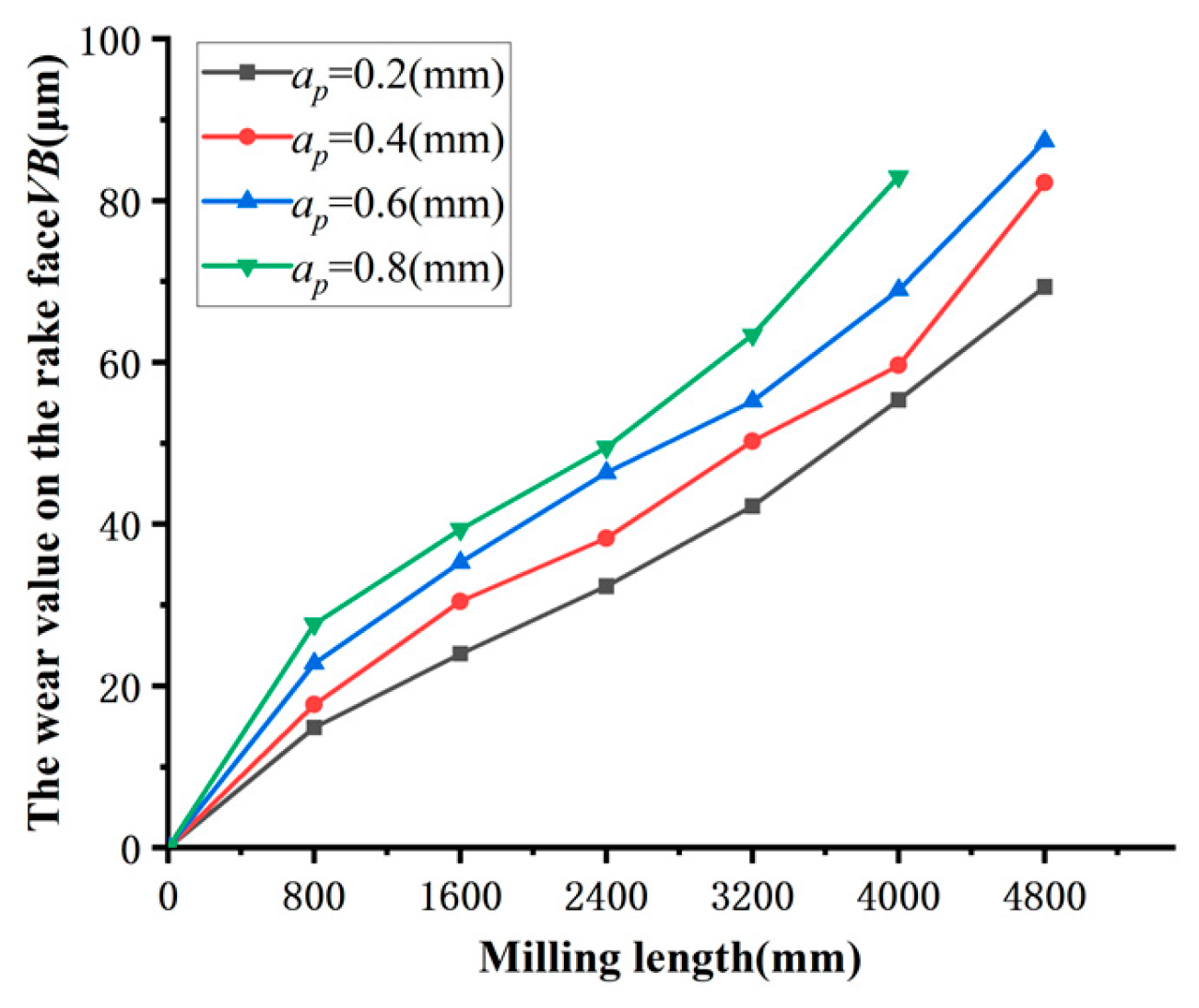
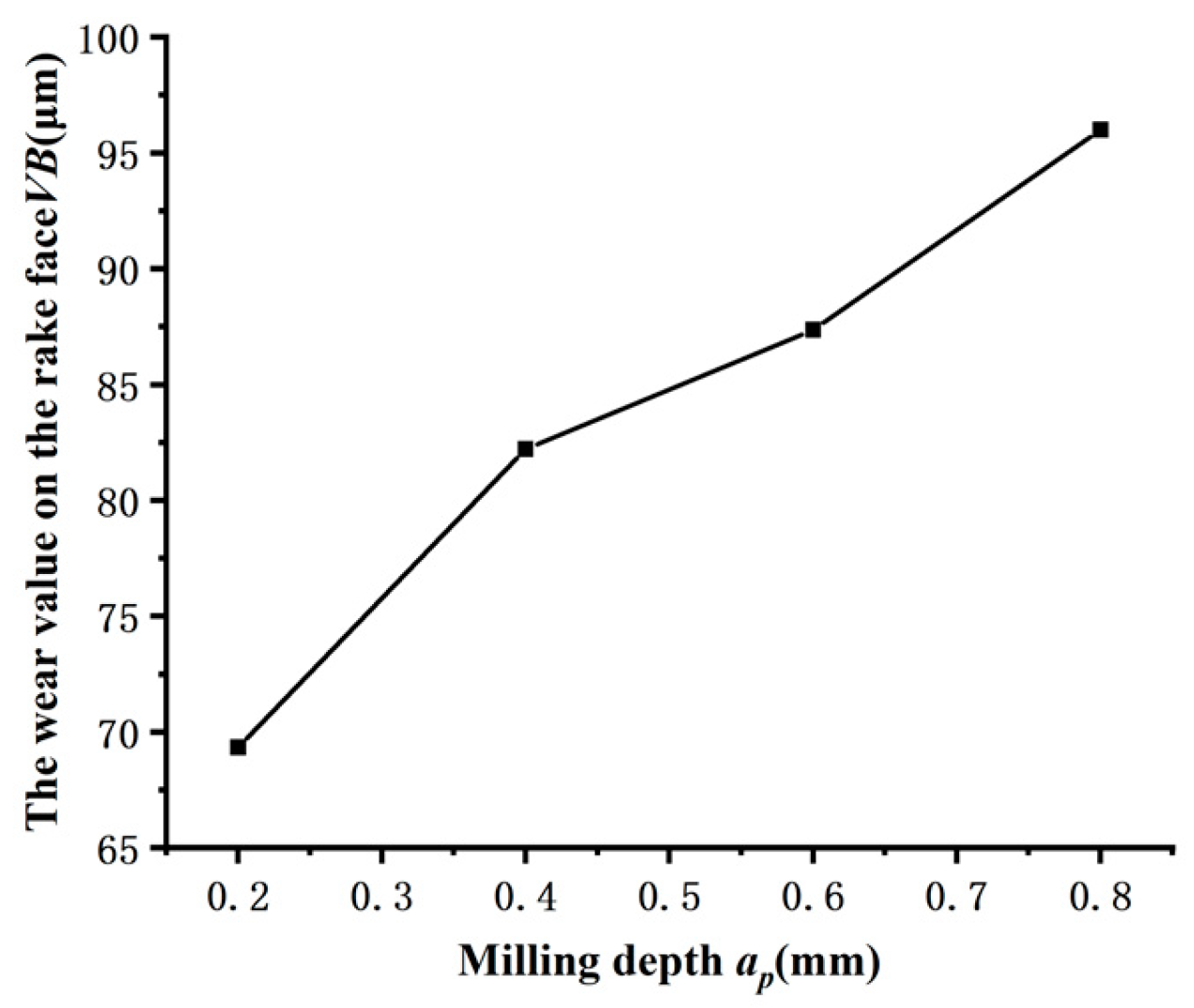
Figure 8 depicts the relationship between the milling depth a
p and the amount of tool wear VB on the rake face. Meanwhile,
Figure 9 displays the amount of tool wear VB for a milling length of L=4800mm. These two graphs demonstrate that when the milling depth a
p grows, the tool wear amount VB value noticeably increases.
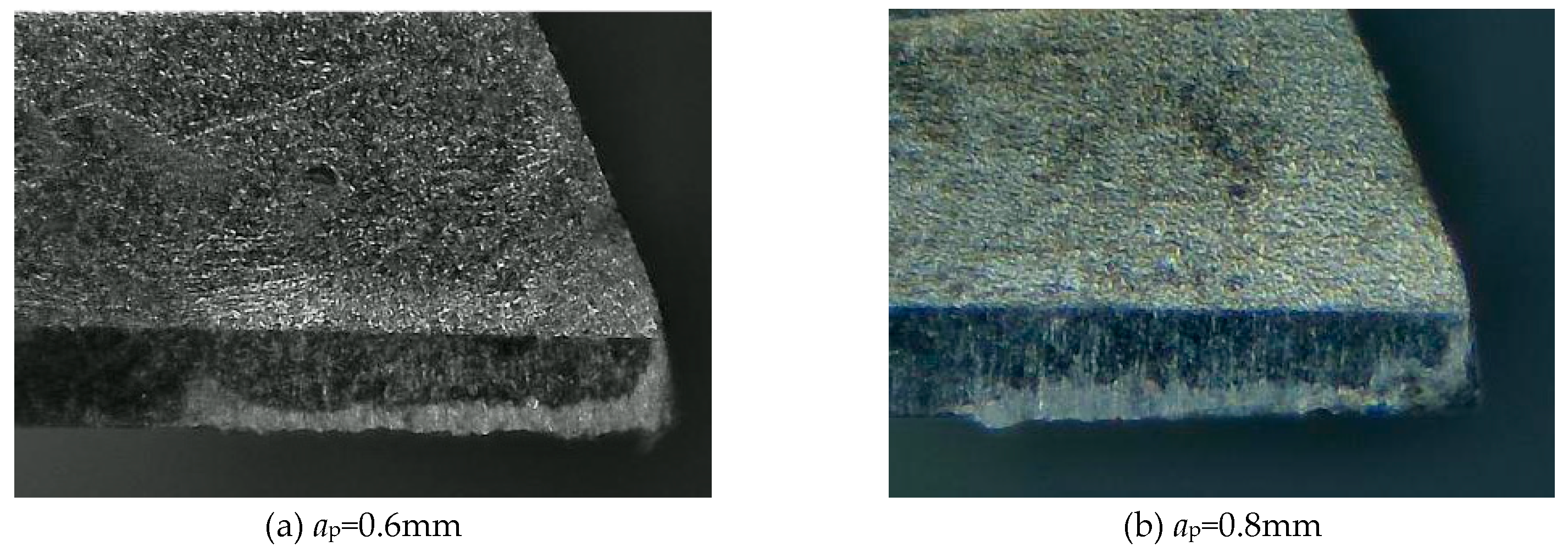
Figure 10 illustrates the variations in damage phenomena and severity on the flank face when the milling depths a
p are adjusted to 0.6mm and 0.8mm, respectively. The escalation of this form of damage can be attributed to the elevation in temperature that occurs during milling, as the milling depth a
p increases. The tool surface is very susceptible to cold welding, resulting in heightened chemical reactivity and diminished material malleability, ultimately causing escalated tool deterioration. This experimental finding suggests that using a milling depth a
p that is too large is not appropriate for cutting activities. This finding aligns with the conclusion put forth by scholars such as Sun Wenlong et al., which states that when the milling depth a
p increases, the milling temperature also increases, resulting in a rise in tool flank wear [
16].
3.4. The Effect of Milling Width on Tool Wear
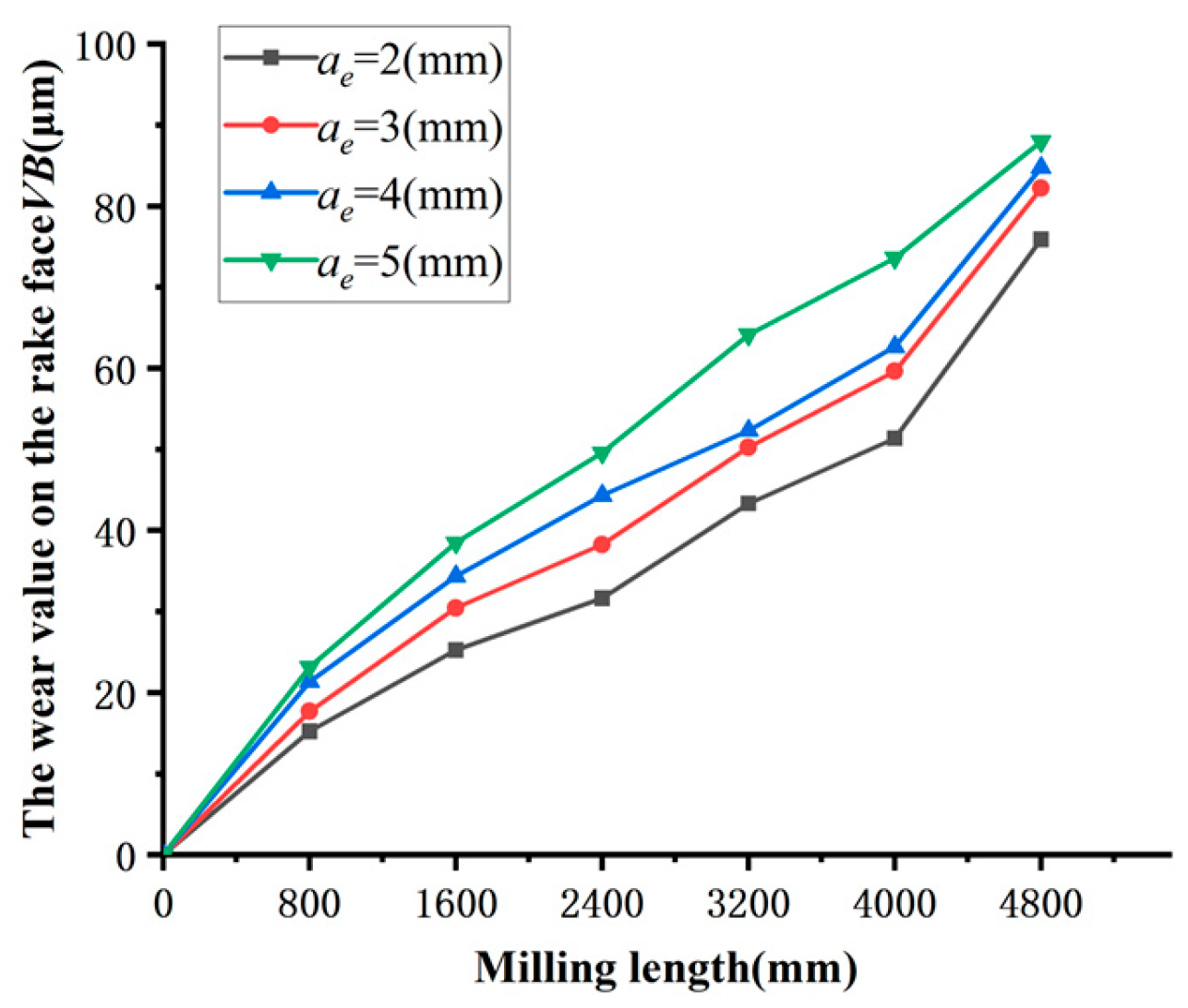
Figure 11 illustrates the impact of milling width a
e on the tool flank wear VB.
Figure 12 shows the VB value of tool wear for a milling length of 4800.
Figure 11 and
Figure 12 demonstrate that as the milling width a
e increases, the rate of tool wear VB increases at a rather slow pace. The effect of the milling width a
e on the tool wear VB value is not significant within a narrow fluctuation range. According to this trend analysis, we can deduce that the milling width a
e and milling depth a
p have comparable effects on tool wear VB, both in terms of amplitude and trend. Based on the findings of this experiment, it is recommended to refrain from employing overly wide milling widths during the milling procedure.
3.5. Analysis of Tool Wear Mechanism
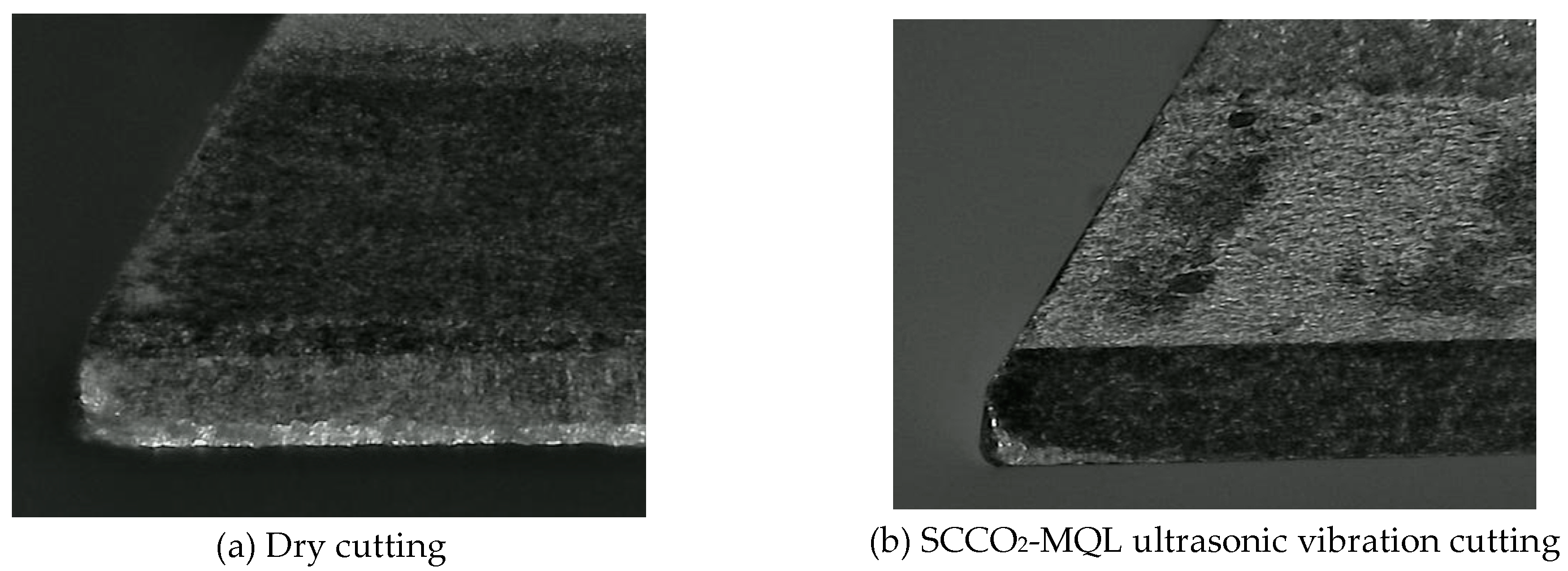
3.5.1. Grain Abrasion
During the cutting process, grain abrasion inevitably occurs, so when cutting SiCp/Al composite materials, grain abrasion is one of the main reasons for tool wear [
17].
Figure 13 illustrates the grain abrasion of the tool under different milling conditions. By comparing (a) and (b) in
Figure 13, it can be observed that under the conditions of SCCO
2-MQL with ultrasonic vibration, the wear pattern on the rake face of the tool is more ideal compared to dry cutting, and the grain abrasion is also less pronounced. The experiments indicate that the SCCO
2-MQL ultrasonic vibration technology, with its excellent low-temperature cooling effect, performs remarkably well in suppressing high temperatures at the cutting point, thereby effectively improving the condition of grain-abrasion. This finding is consistent with the conclusion drawn by Liang Xu and other scholars in their research on titanium alloy milling comparing dry cutting with SCCO
2-MQL ultrasonic vibration technology.
3.5.2. Adhesive Wear
Figure 14 displays SEM pictures of tool wear under varying cutting circumstances, specifically in (a) and (b). The presence of trace elements including carbon, aluminum, silicon, copper, and oxygen on the tool was validated using Energy Dispersive Spectrum (EDS) analysis. This is shown in (c) of
Figure 14, and specific data regarding the elemental content can be found in
Table 3. Upon analyzing the data, it is clear that the elemental content in the bond material is lower under the SCCO
2-MQL ultrasonic vibration cutting environment compared to dry cutting. This suggests that SCCO
2-MQL ultrasonic vibration can effectively reduce tool adhesive wear.
3.5.3. Breaking and Spalling
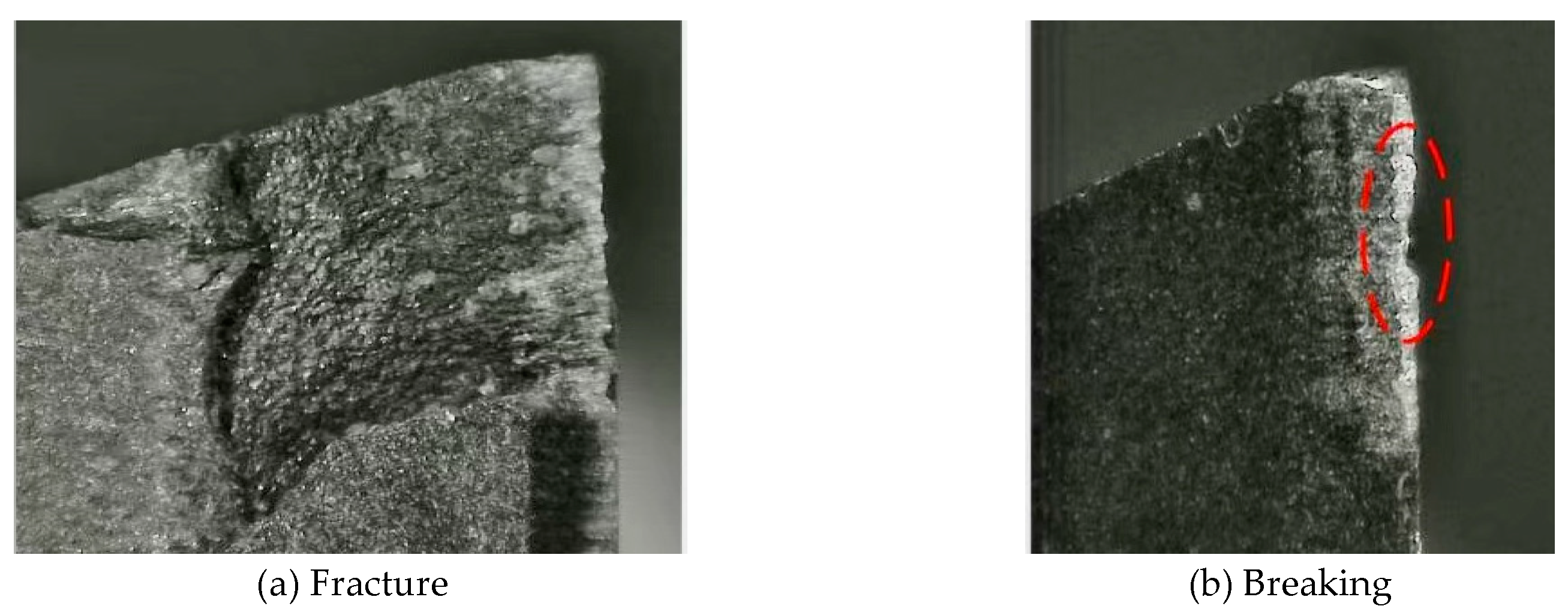
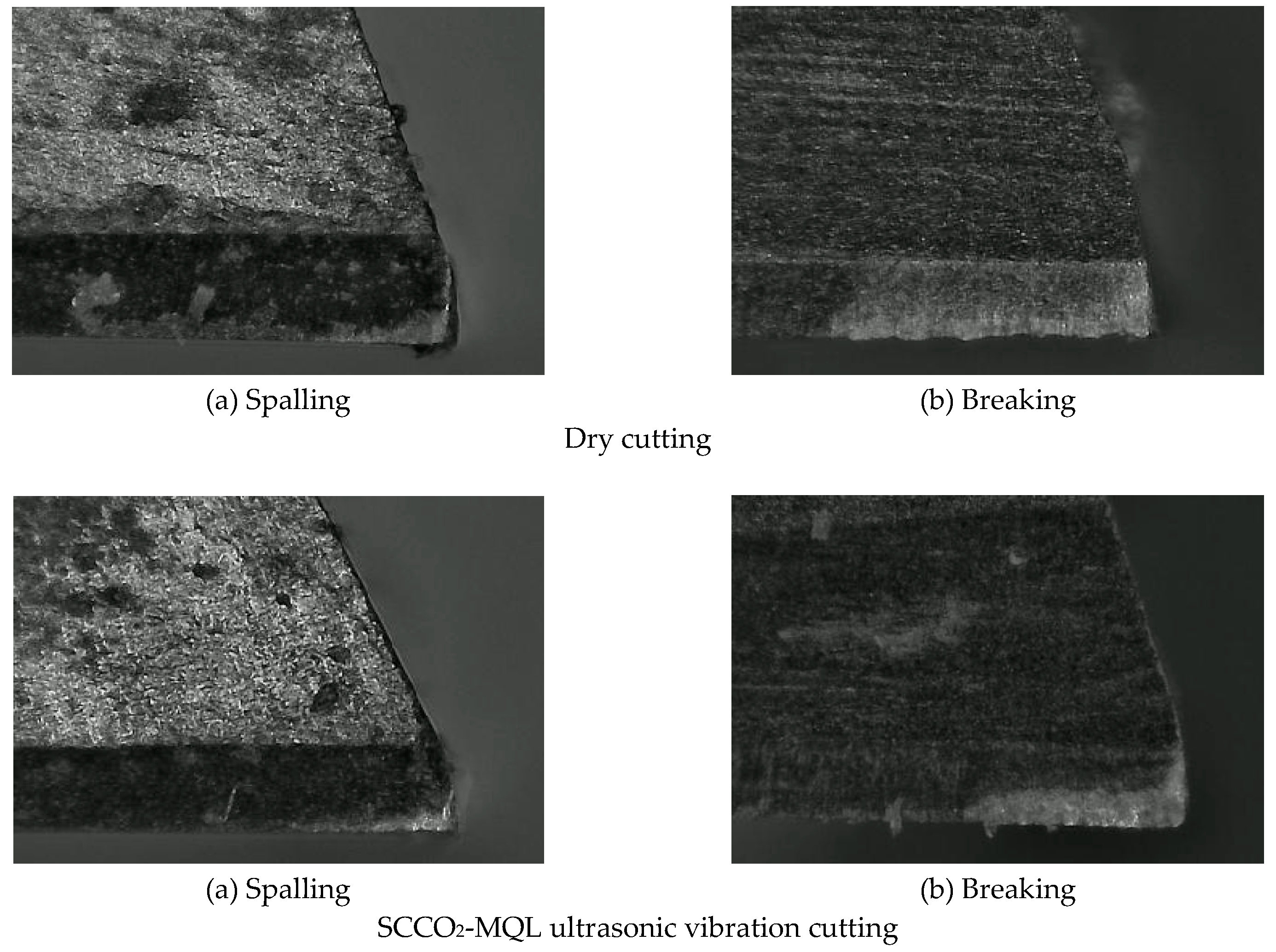
Figure 15 clearly demonstrates that the cutting edge of the PCD tool exhibits signs of fracturing and chipping. Research investigation reveals that the PCD tool constantly undergoes cracking and spalling during the machining process, with varying degrees of damage. When using SCCO
2-MQL ultrasonic vibration, the tools show substantial advantages compared to dry cutting environments, such as reduced incidences of breaking and spalling damage. The benefits of the SCCO
2-MQL ultrasonic vibration technology are due to its complex and versatile mechanics. By utilizing supercritical carbon dioxide minimum quantity lubrication, it is possible to efficiently cool the cutting zone, hence decreasing heat buildup and consequently reducing the temperatures of both the tool and workpiece. This leads to a decrease in the rate of tool wear. Ultrasonic vibration improves lubrication efficacy by facilitating the even distribution of lubricants in the cutting zone, resulting in a more stable lubricating layer. This reduces frictional resistance during cutting and effectively safeguards the tool’s surface. Moreover, when subjected to ultrasonic vibration, the chips undergo easy fragmentation and dispersion, resulting in reduced accumulation in the contact area between the tool and the workpiece. This, in turn, leads to decreased friction in the cutting zone and mitigates interactions between the tool, workpiece, and chips. Consequently, there is a decrease in mechanical stress and thermal shocks. This helps to reduce the rate of tool wear, enhancing resistance to breakage and spalling.
4. Prediction Model and Parameter Optimization of Tool Wear in SiCp/Al Composite
4.1. Orthogonal Experimental Design and Result Analysis
The orthogonal experiment involved the comprehensive specification of the variables cutting velocity
vc, feed per tooth
fz, milling depth
ap, and milling width
ae. The findings of the orthogonal experiment may be seen in
Table 4.
The ideal combination of components was identified by completing a range analysis of the experimental data, as presented in
Table 5. According to the findings of the range analysis, it was deduced that the cutting velocity
vc and feed per tooth
fz are the primary factors that have a major impact on tool wear. When conducting milling operations, it is crucial to carefully consider the settings of these two parameters. By employing the mean range values, curves were graphed, as shown in
Figure 16. In general, the average range values roughly correspond to the observed trends of milling parameters in single-factor trials.
4.2. Development of Tool Wear Model
Through an analysis of the law of tool wear, the key parameters that have an impact on the amount of tool wear, known as VB, were determined. The parameters that need to be considered are the cutting velocity v
c, feed per tooth f
z, milling depth a
p, and milling width a
e. An empirical mathematical model was developed to establish a relationship between the amount of tool wear VB and the milling process parameters, based on the principles of metal cutting. The formula is as stated:
The formula utilizes CVB as the inherent coefficient of the empirical formula, with b1, b2, b3, and b4 serving as correction coefficients.
The predictive model for tool wear in the SCCO
2-MQL ultrasonic vibration environment was developed using Matlab. Presented below is the model that predicts the wear of the tool:
Utilizing SPSS software to perform an F-test in order to evaluate the statistical significance of the predictive model created earlier and its coefficients. At a significance level of α=0.05, which is equivalent to a 5% significance level, the crucial F-value is 3.36 as determined by the F-distribution table. Given that our computed F-statistic exceeds the critical value of 3.36, F > F0.05(4, 11) = 3.36, we can confidently assert that the multivariate linear regression model developed in this experiment possesses statistical significance. This validates the robustness of the tool wear prediction model.
Although the empirical model used to predict tool wear has statistical significance as a whole, it is important to note that not all independent factors have a significant influence on VB. In order to further examine the impact of each regression coefficient, it is necessary to do individual significance tests for each of them [
19]. For the purpose of this investigation, we utilized the t-test approach, employing calculations based on the following formula.
When performing t-tests in
SPSS, a significance level of α= 0.05 was selected. The significance level for the
t-test is obtained using the formula t
(α/2)(n-p)= t
0.025(11)=2.2010, as shown in the table. The results of the regression coefficient tests in
Table 6 indicate that
β1 is larger than
β2,
β2 is larger than
β3, and
β3 is larger than 2.2010, which is also larger than
β4. The analysis reveals that the cutting velocity
vc and feed per tooth
fz exert a more substantial influence on the projected values than the milling width
ae and milling depth
ap. Furthermore, the milling width
ae has a negligible impact on the model. This method aligns well with the maximum deviation obtained from the orthogonal experiment, indicating the importance of the coefficients in the tool wear prediction model.
4.3. Establishment of Multi-Objective Optimization Function and Optimization of Milling Parameters
The objective of the model is to minimize the degradation of tools while simultaneously maximizing the pace at which metal is removed. Genetic algorithms are used to optimize milling parameters in order to approximate or achieve the predefined objective function. The expression is as stated:
In this experiment, parameters matching the milling properties of SiCp/Al composite material were carefully determined and adjusted using Matlab software. The optimal milling parameters were successfully achieved by feeding the goal function and restrictions into Matlab and running the specially constructed genetic algorithm program.
During the critical phase of solving the optimization model, it is imperative to precisely establish the computational bounds, which refer to the constraint conditions. The parameter optimization bounds in this scenario were established using experimental data and encompassed the following constraint conditions: The cutting velocity vc, must fall within the range of 40 to 100 m/min. The feed per tooth fz, is limited to a range of 0.02 to 0.08 mm/z. The milling depth ap, must be between 0.2 and 0.8 mm. Lastly, the milling width ae, is restricted to a range of 2 to 5 mm. The utilization of Matlab software facilitated a thorough study, yielding the most favorable combination of milling parameters: a cutting velocity vc of 60.0064 m/min, a feed per tooth fz of 0.07978 mm/z, a milling depth ap of 0.202239 mm, and a milling width ae of 2.047596 mm.
5. Conclusions
The investigation of high-speed milling parameters for SiCp/Al composite materials using SCCO2-MQL ultrasonic vibration technology revealed that the cutting velocity vc reaches its lowest value for tool wear VB at 60m/min. However, once surpassing this threshold, wear intensifies, resulting in significant deterioration on both the front and posterior tool surfaces. As the feed per tooth fz grows, the tool wear VB reduces. This effect is particularly pronounced when the feed per tooth is 0.2mm/z, resulting in decreased tool wear VB and optimal surface roughness Ra. Augmenting the milling depth ap and milling width ap results in an escalation of tool wear VB, particularly when the milling depth ap surpasses 0.6mm, causing a substantial intensification of tool wear. The research findings suggest that by optimizing milling parameters under SCCO2-MQL ultrasonic vibration conditions, it is possible to effectively decrease tool wear, prolong tool lifespan, and enhance processing quality. Under these circumstances, it is efficient in minimizing tool wear, such as fractures and chipping, reducing grain erosion and sticking, thereby greatly improving tool longevity. Hence, it is advisable to refrain from employing overly elevated cutting velocity and milling depths while conducting the milling procedure in order to guarantee optimal processing efficiency and superior workpiece quality.
The study utilized the orthogonal experimental approach, which methodically explored different parameter combinations through a restricted number of tests. As a result, the study determined that cutting velocity vc and feed per tooth fz were the main parameters that influenced tool wear. A predictive model for tool wear was developed utilizing range analysis and multiple linear regression approaches, based on experimental data. The tool wear predictive model was analyzed using F-tests and t-tests, which demonstrated that the model can accurately predict tool wear. The prediction accuracy is influenced by two important parameters: cutting velocity vc and feed per tooth fz. The optimization of milling settings was accomplished by combining the global search capabilities of genetic algorithms with the programming advantages of Matlab. By performing iterations that involve encoding, selection, crossover, and mutation processes, the most effective combination of milling parameters has been successfully determined: vc=60.0064m/min, fz=0.07978mm/z, ap=0.202239mm, ae=2.047596mm.
Author Contributions
Writing – review and editing, Huiping Zhang; Writing – original draft preparation, Bowen Wang; Investigation, Resources, Liqiang Qu; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant nos.52275417).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- HaiJiao Yu, XinGui Zhou, ChangRui Zhang. Research Progress of SiC Reflecting Mirror[J]. New Technology & New Process, 2006, (5): 26-30.
- Liu J W, Cheng K, Ding H. An Investigation of Surface Defect Formation in Micro Milling the 45% SiCp/Al Composite[J]. Procedia CIRP, 2016, 45(6): 211-214. [CrossRef]
- Min Li, AiQin Wang, JingPei Xie. The present research situation and progress of SiC particle-reinforced aluminum matrix composites[J]. Powder Metallurgy Industry,2015,25(03):55-60. [CrossRef]
- Weinert K A. Consideration of Tool Wear Mechanism When Machining Metal Matrix Composites (MMC)[J]. Annals of the CIRP, 2008, 42(1): 95-98. [CrossRef]
- Ernest G. Wolff. An Introduction to Metal Matrix Composites[J]. Materials Research Bulletin, 1995, 30(12). [CrossRef]
- DaoJun Lv. Research on SiCp/Al Composite Machining Technology[J]. Electro-Mechanical Engineering, 2011, 27(05): 29-32. [CrossRef]
- HuiTing Zha, PingFa Feng, JianFu Zhang. Wear characteristics of cutting tools in ultrasonic vibration-assisted scratching high volume fraction SiC particle reinforced aluminum matrix composites[J]. Journal of Jilin University, Changchun, China, 2019, 49(02): 458-465. [CrossRef]
- GuoHong Ma, JiaLi Zhang, Fan Yan. Finite element analysis of cutting process and surface formation of SiCp/Al composites under conventional and ultrasonic vibration assisted conditions[J]. Manufacturing Technology & Machine Tool, 2024(04): 51-56. [CrossRef]
- JinFeng Leng, GaoHui Wu. Status of Research on Machinability of SiCp/Al Composites[J]. Aerospace Materials & Technology, 2007, (02): 6-9.
- YuChao Wu, MiaoXian Guo, WeiCheng Guo. Surface Damage Formation Mechanism of SiCp/Al Composites Based on 2D Cutting[J]. Surface Technology, 2024, 53(08): 145-155. [CrossRef]
- Deng B, Peng F, Zhou L. A Comprehensive Study on Flank Wear Progression of Polycrystalline Diamond Micro-tool During Micro End-milling of SiCp/Al Composites[J]. Wear, 2020, 456-457. [CrossRef]
- Pradyut Kumar Swain, Kasinath Das Mohapatra, Pratyush Kumar Swain. Investigations, Analysis and Performance Comparison of Uncoated CNMG 120408 TTR and Coated 12040822 Carbide Tools during Dry Turning of Al-SiCp Nano Composites[J]. Materials Today: Proceedings, 2020, 26: 2. [CrossRef]
- Volodymyr Bushlya, Filip Lenrick, Oleksandr Gutnichenko. Performance and Wear Mechanisms of Novel Superhard Diamond and Boron Nitride Based Tools in Machining Al-SiCp Metal Matrix Composite[J]. Wear, 2017, 376-377. [CrossRef]
- QiuLin Niu, LingYan Tang, DaoHui Xiang. Study on tool wear of cemented carbide coated tool in milling of SiCp/Al composites[J]. Journal of Henan Polytechnic University(Natural Science), Jiaozuo, China, 2018, 37(04): 90-93+111. [CrossRef]
- JieQiong Lin, Ru Jia, Yan Zhou. PCD tool wear in cutting SiCp/6005Al composites[J]. Diamond & Abrasives Engineering, 2023, 43(03): 322-331. [CrossRef]
- WenLong Sun, WenTian Shi, YuDe Liu. Study on Tool Wear of Aramid Fiber Reinforced Plastic Composites in Micromilling[J]. Tool Engineering, 2021, 55(10): 35-40. [CrossRef]
- ZhanQiang Liu, Xing Ai. Wear Characteristics of Cutting Tools in High Speed Machining[J]. Tribology, 2002, 22(6): 468-471. [CrossRef]
- Xu Liang, ChongYan Cai, QingLong An. Cooling and Lubrication Performance of SCCO2 Mixed Oil Film with Water Droplets in TC4 Milling[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2020, 31(03): 328-335. [CrossRef]
- MengHua Gao, ChenLi Tao, Lei Shi. Data Analysis and Test of an Uniform Design Experiment Based SAS[J]. Journal of Ordnance Engineering College, 2015, 27(01): 6-9. [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
Experimental site equipment.
Figure 1.
Experimental site equipment.
Figure 2.
The curve of the variation of tool wear amount VB.
Figure 2.
The curve of the variation of tool wear amount VB.
Figure 3.
The curve showing tool wear amount VB for a milling length of L=4800mm.
Figure 3.
The curve showing tool wear amount VB for a milling length of L=4800mm.
Figure 4.
The tool shape after wear.
Figure 4.
The tool shape after wear.
Figure 5.
The curve of the variation of tool wear amount VB.
Figure 5.
The curve of the variation of tool wear amount VB.
Figure 6.
The curve showing tool wear amount VB for a milling length of L=4800mm.
Figure 6.
The curve showing tool wear amount VB for a milling length of L=4800mm.
Figure 7.
The wear morphology of the rake face under different feed per tooth fz.
Figure 7.
The wear morphology of the rake face under different feed per tooth fz.
Figure 8.
The cuEzrve of the variation of tool wear amount VB.
Figure 8.
The cuEzrve of the variation of tool wear amount VB.
Figure 9.
The curve showing tool wear amount VB for a milling length of L=4800mm.
Figure 9.
The curve showing tool wear amount VB for a milling length of L=4800mm.
Figure 10.
The tool wear condition at milling depths of 0.6mm and 0.8mm.
Figure 10.
The tool wear condition at milling depths of 0.6mm and 0.8mm.
Figure 11.
The curve of the variation of tool wear amount VB.
Figure 11.
The curve of the variation of tool wear amount VB.
Figure 12.
The curve showing tool wear amount VB for a milling length of L=4800mm.
Figure 12.
The curve showing tool wear amount VB for a milling length of L=4800mm.
Figure 13.
Tool wear diagram under different machining conditions.
Figure 13.
Tool wear diagram under different machining conditions.
Figure 14.
Adhesive wear image on the tool’s back surface.
Figure 14.
Adhesive wear image on the tool’s back surface.
Figure 15.
Spalling and breaking on the rake face.
Figure 15.
Spalling and breaking on the rake face.
Figure 16.
The trend chart of parameters.
Figure 16.
The trend chart of parameters.
Table 1.
Composition Percentage of Materials.
Table 1.
Composition Percentage of Materials.
| Types of Elements |
Weight Percentage(%) |
Atomic Percentage(%) |
| Carbon |
9.43 |
19.59 |
| Magnesium |
0.51 |
0.47 |
| Aluminum |
43.13 |
34.7 |
| Silicon |
45.13 |
44.34 |
| Copper |
1.80 |
0.9 |
Table 2.
Experimental Parameters.
Table 2.
Experimental Parameters.
| Number |
vc(m/min) |
fz(mm/z) |
ap(mm) |
ae(mm) |
| 1 |
40 |
0.02 |
0.2 |
2 |
| 2 |
60 |
0.04 |
0.4 |
3 |
| 3 |
80 |
0.06 |
0.6 |
4 |
| 4 |
100 |
0.08 |
0.8 |
5 |
Table 3.
The Percentage Content of Elements in the Bond Material on the Rake Face.
Table 3.
The Percentage Content of Elements in the Bond Material on the Rake Face.
| Cutting environment |
C(%) |
Cu(%) |
Mg(%) |
Si(%) |
O(%) |
Al(%) |
| Dry cutting |
8.35 |
0.02 |
00.68 |
18.36 |
5.96 |
26.67 |
| SCCO2-MQL ultrasonic vibration |
6.01 |
0.04 |
00.21 |
14.23 |
3.99 |
18.14 |
Table 4.
Orthogonal Experimental Results.
Table 4.
Orthogonal Experimental Results.
| Number |
vc(m/min) |
fz(mm/z) |
ap(mm) |
ae(mm) |
VB(μm) |
| 1 |
40 |
0.02 |
0.2 |
2 |
12.69 |
| 2 |
40 |
0.04 |
0.4 |
3 |
10.01 |
| 3 |
40 |
0.06 |
0.6 |
4 |
12.47 |
| 4 |
40 |
0.08 |
0.8 |
5 |
14.01 |
| 5 |
60 |
0.02 |
0.4 |
4 |
11.69 |
| 6 |
60 |
0.04 |
0.2 |
5 |
7.99 |
| 7 |
60 |
0.06 |
0.8 |
2 |
7.21 |
| 8 |
60 |
0.08 |
0.6 |
3 |
6.42 |
| 9 |
80 |
0.02 |
0.6 |
5 |
19.63 |
| 10 |
80 |
0.04 |
0.8 |
4 |
19.01 |
| 11 |
80 |
0.06 |
0.2 |
3 |
13.01 |
| 12 |
80 |
0.08 |
0.4 |
2 |
10.68 |
| 13 |
100 |
0.02 |
0.8 |
3 |
23.16 |
| 14 |
100 |
0.04 |
0.6 |
2 |
20.01 |
| 15 |
100 |
0.06 |
0.4 |
5 |
17.52 |
| 16 |
100 |
0.08 |
0.2 |
4 |
11.69 |
Table 5.
Range Analysis.
| |
Parameters |
vc (m/min) |
fz (mm/z) |
ap (mm) |
ae (mm) |
| Mean value |
|
|
12.295 |
16.7925 |
11.345 |
12.6475 |
|
8.3275 |
14.255 |
12.475 |
13.15 |
|
15.5825 |
12.5525 |
14.6325 |
13.715 |
|
18.095 |
10.7 |
15.8475 |
14.7875 |
| R |
9.7675 |
6.0925 |
4.5025 |
2.14 |
| |
vc>fz>ap>ae
|
Table 6.
Model Coefficient Test.
Table 6.
Model Coefficient Test.
| Independent Variables |
β1
|
β2 |
β3 |
β4 |
Significance of Regression Coefficients |
| |vc| |
|fz| |
|ap| |
|ae| |
| VB |
3.512 |
2.846 |
2.232 |
0.995 |
β1>β2>β3>2.2010>β4
|
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).