1. Introduction
Human anomaly detection involves real-time analysis and recognition of human behaviors in surveillance videos or images, aiming to identify deviations from typical behavior patterns [
1,
2]. Such anomalies may include activities like falling, climbing, running, and carrying hazardous items. This technology has widespread applications in public safety and intelligent monitoring systems, facilitating prompt identification of security threats and emergencies to effectively mitigate accidents [
3,
4,
5,
6].
With advancements in modeling, mainstream methods for anomaly behavior detection can be categorized into three types: frame reconstruction-based methods, frame prediction-based methods, and end-to-end anomaly score calculation methods [
7,
8,
9,
10,
11,
12,
13,
14]. Frame reconstruction methods leveraging deep learning often rely on Auto-Encoders [
15]. Gong et al. [
16] introduced the Memory-Augmented Autoencoder (MemAE), enhancing reconstruction by incorporating a memory module. MemAE selects the most relevant memory items for reconstruction using the encoded query, ensuring that testing results closely resemble normal samples. This approach aims to minimize the reconstruction error for normal behavior while maximizing it for anomalous behavior. Frame prediction-based methods involve feeding a video segment into a predictor to predict a frame; significant deviations between the predicted and current input frames indicate abnormal behavior [
17,
18]. In [
19], a frame prediction network based on multipath ConvGRU was employed, capable of handling semantically informative objects and areas of various scales, capturing spatial-temporal dependencies in normal videos. To mitigate interference from background noise, a noise tolerance loss was introduced during training. However, samples in a static state may be misclassified as background due to the lack of differences between adjacent action frames, potentially leading to missed detections [
20,
21].
The YOLOv8 model adopts an end-to-end detection approach, enabling real-time object detection with high accuracy across diverse scenes and object types [
22]. Its concise and lightweight architecture makes it suitable for deployment in resource-constrained environments. However, anomaly behavior detection presents challenges such as variations in spatial orientation, size, shape, overlapping backgrounds, and limited detection precision. To address these challenges, this paper proposes an enhanced YOLOv8-based method for anomaly behavior detection, termed YOLO-ABD, integrating small object detection and Group Shuffle Convolution (GSConv) [
23]. The key contributions of this study are summarized as follows:
- 1.
Introducing an end-to-end anomaly behavior detection method that incorporates a small target detection head for identifying anomalies of various scales.Additionally, the method utilizes the SimAM attention mechanism [
24] to mitigate background interference.
- 2.
Incorporating the Group Shuffle Convolution (GSConv) module enhances the model’s accuracy. Furthermore, implementing a shuffling strategy reduces computational complexity, thus achieving the goal of lightweighting the model.
- 3.
The proposed method is trained and validated on public datasets for anomaly behavior detection. Generalization testing in traffic scene detection demonstrates significant performance improvements over existing methods.
2. Related Works
Classical methods for anomaly detection typically involve extracting features from videos or images to identify abnormal behaviors. Motion features are derived from various dimensions such as optical flow maps, heat maps, and depth maps. These motion features can be integrated with trajectory information or motion magnitude to fuse high-level semantic features with low-level details, achieving precise detection of abnormal behaviors [
25,
26,
27,
28]. For instance, Xie et al. [
29] applied spatiotemporal representation learning to identify behaviors such as sleeping and using mobile phones by analyzing college students’ movement trajectories. Banerjee et al. [
30] introduced a deep convolutional network architecture for detecting behavioral patterns of students and teachers in laboratory settings. Guan et al. [
31] employed a 3D-CNN to extract features from optical flow and motion history images, using LSTM networks to capture spatiotemporal features for anomaly detection. These studies highlight the effectiveness of classical approaches in recognizing abnormal behaviors. However, these methods may struggle with detecting diverse abnormal behaviors across different scenarios and can be susceptible to interference from complex backgrounds, which poses challenges for multi-person anomaly detection in complex environments.
Modern anomaly detection methods also incorporate multi-object detection techniques to identify abnormal behaviors [
32,
33,
34,
35,
36]. Researchers apply these approaches to detect abnormal behaviors in individuals or crowds within specific contexts. Object detection frameworks broadly fall into two categories: two-stage and single-stage approaches [
37]. Two-stage algorithms, exemplified by Faster R-CNN, have been used for anomaly detection and classification, enhancing accuracy but requiring substantial computational resources and less suitable for real-time applications, as demonstrated by Mansour et al. [
38] and Hongchao et al. [
39], who proposed enhanced models for identifying hazardous behaviors in factory workers.
In contrast, single-stage algorithms, exemplified by the YOLO series, are also employed for anomaly detection [
40,
41]. For example, in [
42], the YOLOv3 model was used to detect unsafe behaviors at gas stations like smoking and mobile phone usage. Benjumea et al. [
43] modified YOLOv5 to improve its ability to detect small objects in autonomous driving scenarios, while Xiao et al. [
44] applied YOLOv5 to monitor safety in substations. The YOLO series simplifies the detection process, offering efficient computation and faster speeds, making it suitable for practical scenarios.
3. Methodology
3.1. The General Structure of YOLO-ABD
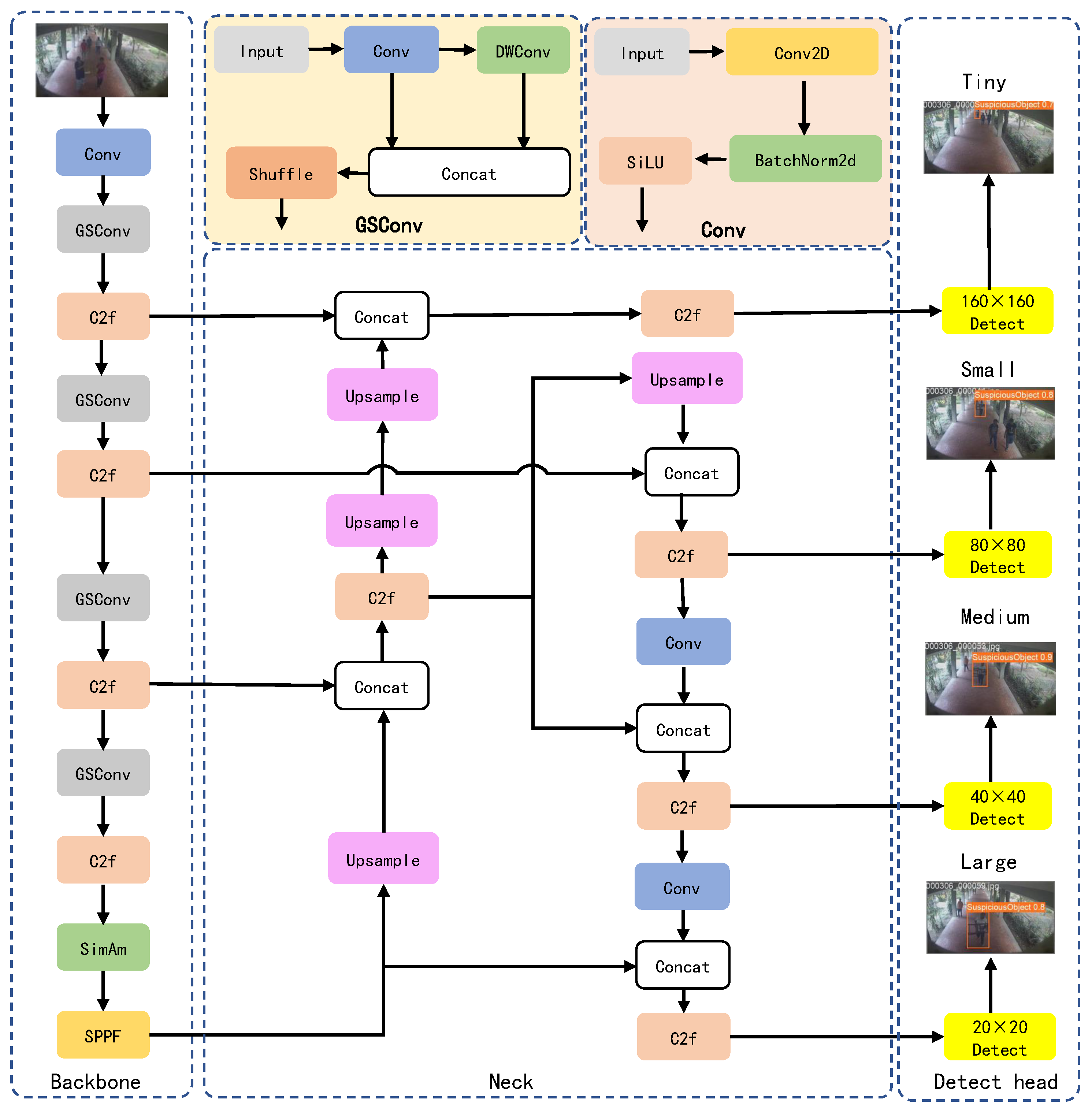
In the network architecture of YOLO-ABD, we adopt YOLOv8n as the base model, enhancing it with a small object detection head and integrating GSConv convolutional blocks along with the SimAm attention mechanism for improvement. The network structure, illustrated in
Figure 1, consists of three main components: the backbone, the neck, and the detection head. In the backbone, GSConv modules replace the original Conv modules of YOLOv8n, while the SimAm attention is integrated before the SPPF module. GSConv maintains implicit channel connections to reduce model complexity while retaining the learning capacity of standard convolutions, thereby enhancing feature extraction for abnormal behavior characterization. The SimAm attention mechanism mitigates background interference while maintaining parameter efficiency, thereby improving accuracy. To further enhance the network’s capability to perceive abnormal behaviors across multiple scales, new pathways and detection heads for small objects are designed within the neck and head sections to prevent overlooking or misclassifying distant pedestrians.
3.2. Baseline Model
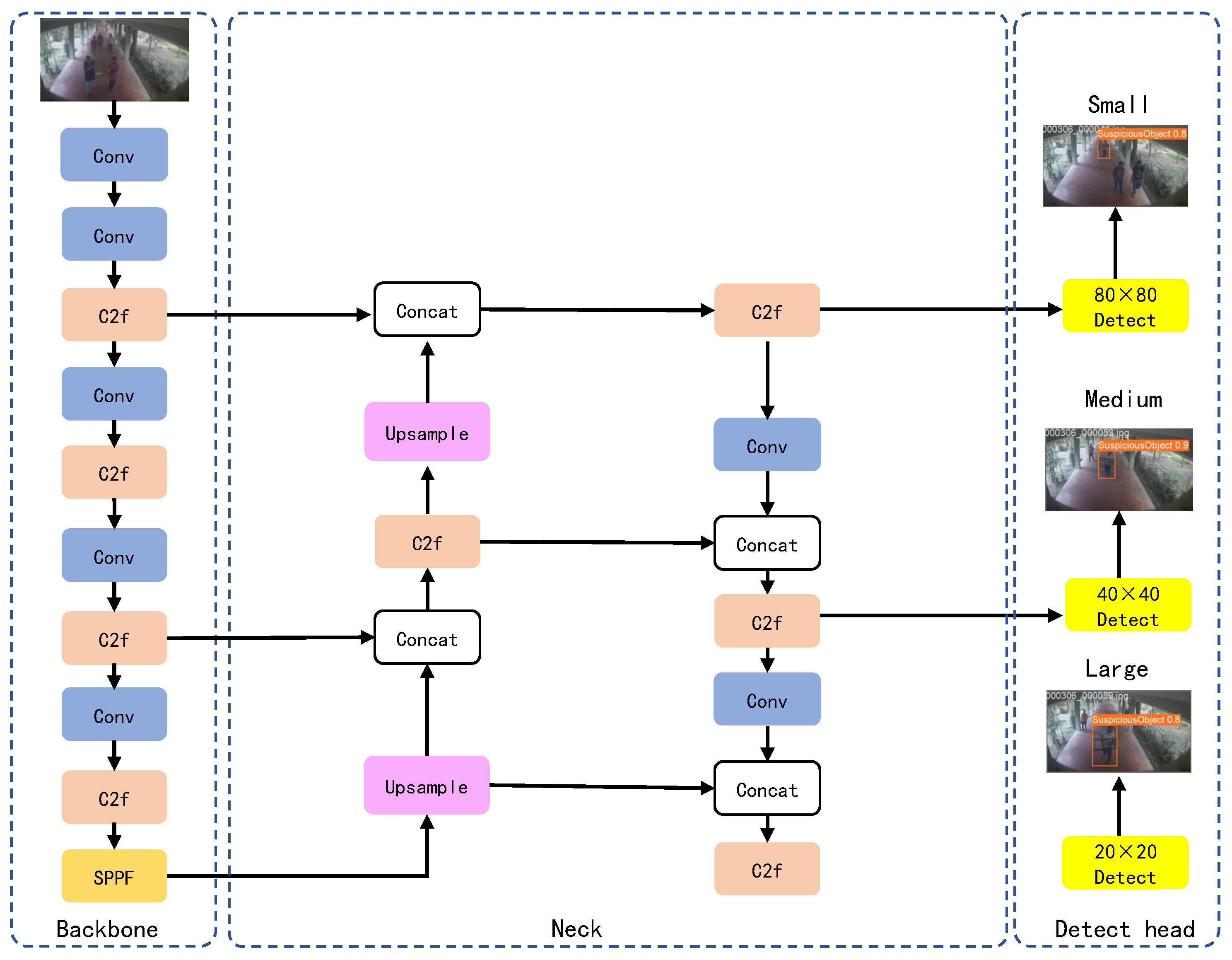
YOLOv8 models are categorized into five versions based on network depth, width, and maximum number of channels: n, s, m, l, and x. Among these, YOLOv8n stands out with the least parameters and floating-point operations, making it highly efficient and suitable for real-time deployment while maintaining high accuracy. This paper adopts YOLOv8n as the baseline model, depicted in
Figure 2. YOLOv8 consists of three main components: Backbone, Neck, and Head. The Backbone includes Conv modules, C2f modules, and an SPPF module, focused on extracting features from input images. Conv modules process images or feature maps, generating new maps with reduced resolution and increased channels. C2f modules excel in deep and multi-scale feature extraction. The Neck integrates multi-scale features through a combination of Feature Pyramid Network (FPN) [
45] and Path Aggregation Network (PAN) [
46], employing techniques like upsampling, channel concatenation, and deep feature extraction. These features are then passed to the Head, which utilizes a decoupled head structure [
47] to separate classification and prediction tasks. This design enables precise object detection regarding size and position using feature maps of varying scales.
3.3. Small Object Detection Head
In the IITB-corridor dataset [
57], distant pedestrians occupy a relatively small portion of the image. When resizing the dataset images to 640×640 pixels, the input image includes numerous small targets. However, after multiple upsampling and pooling operations in the neck network, many detection features associated with small targets are lost, resulting in missed detections. The baseline model includes detection heads sized at 80×80, 40×40, and 20×20. The 80×80 detection head’s receptive field is overly extensive for small targets, causing the baseline model to struggle in accurately detecting abnormal behaviors of distant pedestrians.
To address this issue, we enhanced the baseline model by introducing a 160×160 small target detection head. The structural diagram for this new detection head is depicted in
Figure 1. Minimal modifications were made to the original model structure as shown in
Figure 1 for clarity. The initially upsampled feature map in the neck layer, originally sized at 40×40, undergoes two additional upsampling steps to produce a detailed 160×160 feature map rich in small target information. This feature map is then concatenated with the 160×160 feature map from the second layer of the backbone network, enhancing the model’s capability to detect small target behaviors at the 160×160 scale. Finally, this refined feature map is fed into the detection head layer, creating a new small target detection head that effectively reduces missed and false detections of abnormal behaviors across various scales.
3.4. GSConv Module
Currently, lightweight network design heavily relies on Depth-wise Separable Convolution (DSConv) to reduce model parameters and floating-point operations [
48,
49,
50]. DSConv conducts convolutions independently across three channels, which minimizes redundant feature information but also fully separates the channel information of input data, thereby reducing the model’s feature extraction capability compared to dense channel convolutions, such as standard convolutions. To address this limitation, Zhang et al. [
51] introduced "ShuffleNet," which employs pointwise group convolution and channel shuffle operations to significantly decrease computational cost while maintaining accuracy. GhostNet [
52] generates multiple feature maps through a series of low-cost linear transformations, effectively revealing intrinsic feature information.
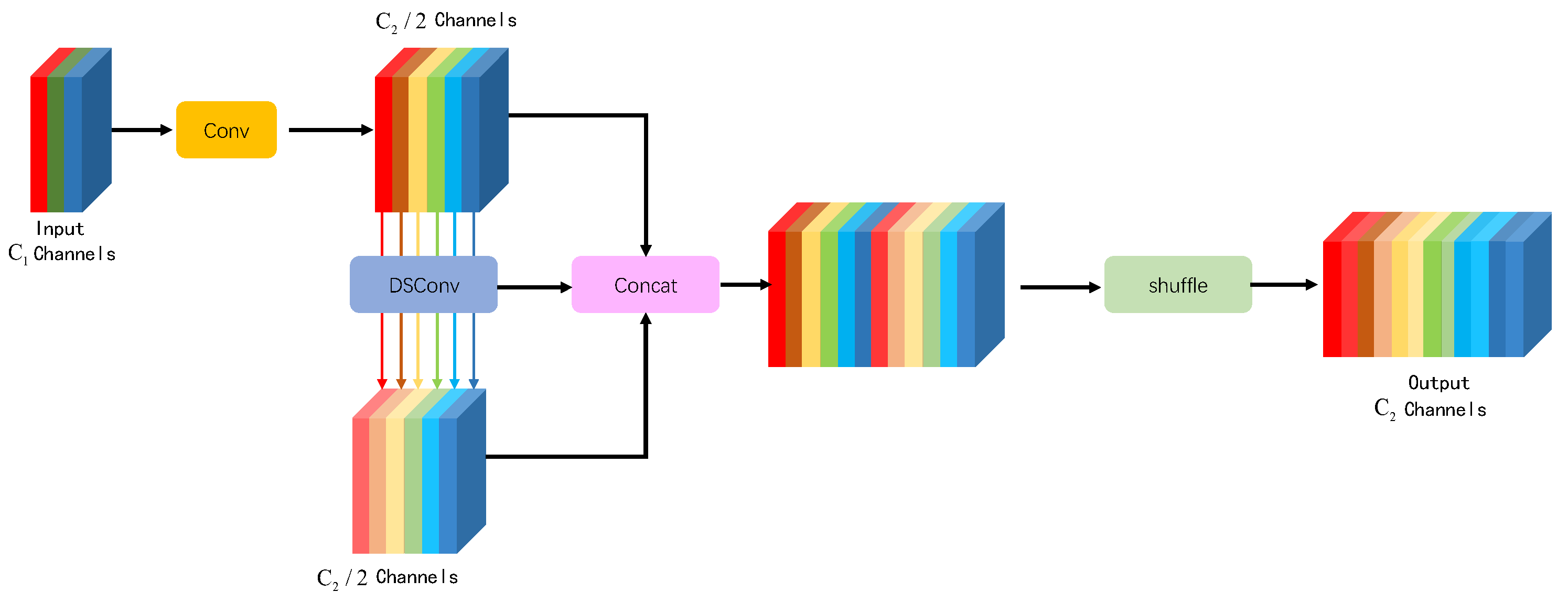
Li et al. [
23] introduced GSConv as an alternative to standard convolutions, offering a computational cost approximately 60%-70% lower while retaining comparable learning capability. Illustrated in
Figure 3, GSConv initially applies a standard convolution to the input feature map with
channels, resulting in an intermediate feature map with
/2 channels. Subsequently, this intermediate feature map undergoes Depth-wise Separable Convolution (DSConv) to produce another intermediate feature map, also with
/2 channels. Finally, the two intermediate feature maps are concatenated and shuffled to yield an output feature map with
channels. This approach mitigates information loss that can occur with DSConv’s channel separation, while maintaining an output similar to that of standard convolution. The time complexity formulas for standard convolution (SC), Depth-wise Separable Convolution (DSC), and GSConv are shown in equations (
1), (
2), and (
3) respectively:
In the above formulas, W and H represent the width and height of the output feature map, and are the sizes of the convolution kernels, is the number of input feature channels, and is the number of output feature channels.
3.5. SimAm Attention Module
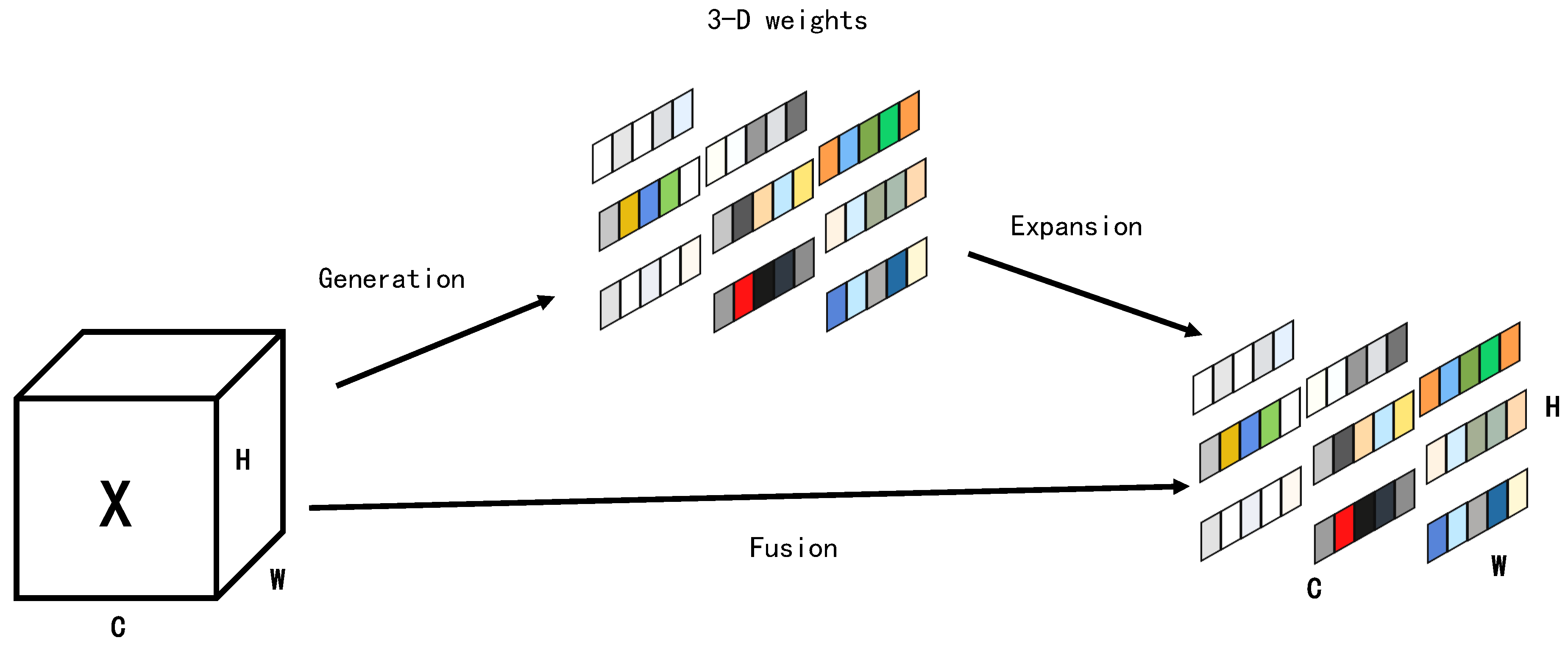
To enhance the model’s capability in detecting abnormal behaviors and mitigate interference from complex backgrounds, this paper introduces SimAm, a parameter-free attention mechanism. SimAm, rooted in neural network theory, distinguishes itself from existing attention mechanisms [
53,
54], which typically focus on either the channel or spatial domain. Unlike CBAM [
55] and GAM [
56], which extract features from both channel and spatial dimensions and merge them into a hybrid attention mechanism, SimAm integrates spatial, channel, and feature dimensions to generate 3D weights. This comprehensive approach enhances the model’s ability to perceive changes in pedestrian movement.
Figure 4 illustrates the generation of these 3D weights.
In visual neuroscience, the activity of an active neuron can induce spatial suppression in the surrounding neurons. SimAm utilizes this concept by prioritizing neurons that induce spatial suppression. The priority of each neuron is determined by an energy function, represented by Equation (
4).
In the formula,
t and
represent the target neuron and other neurons of a single channel in the input features, respectively. Here,
i is the index in the spatial dimension, and
denotes the number of neurons in that single channel. The weight and bias of the target neuron, denoted as
and
respectively, are computed using the formulas shown in (
5) and (
6):
In the formula,
and
,When ensuring that all pixels within a single channel follow the same distribution, the minimum energy function can be obtained:
In the formula (
7),
and
represent the mean and variance of all neurons except t. A smaller
indicates higher importance, and the importance calculation is
. Scaling the energy of neurons for feature refinement within each neuron yields the final feature map, as shown in formula (
8):
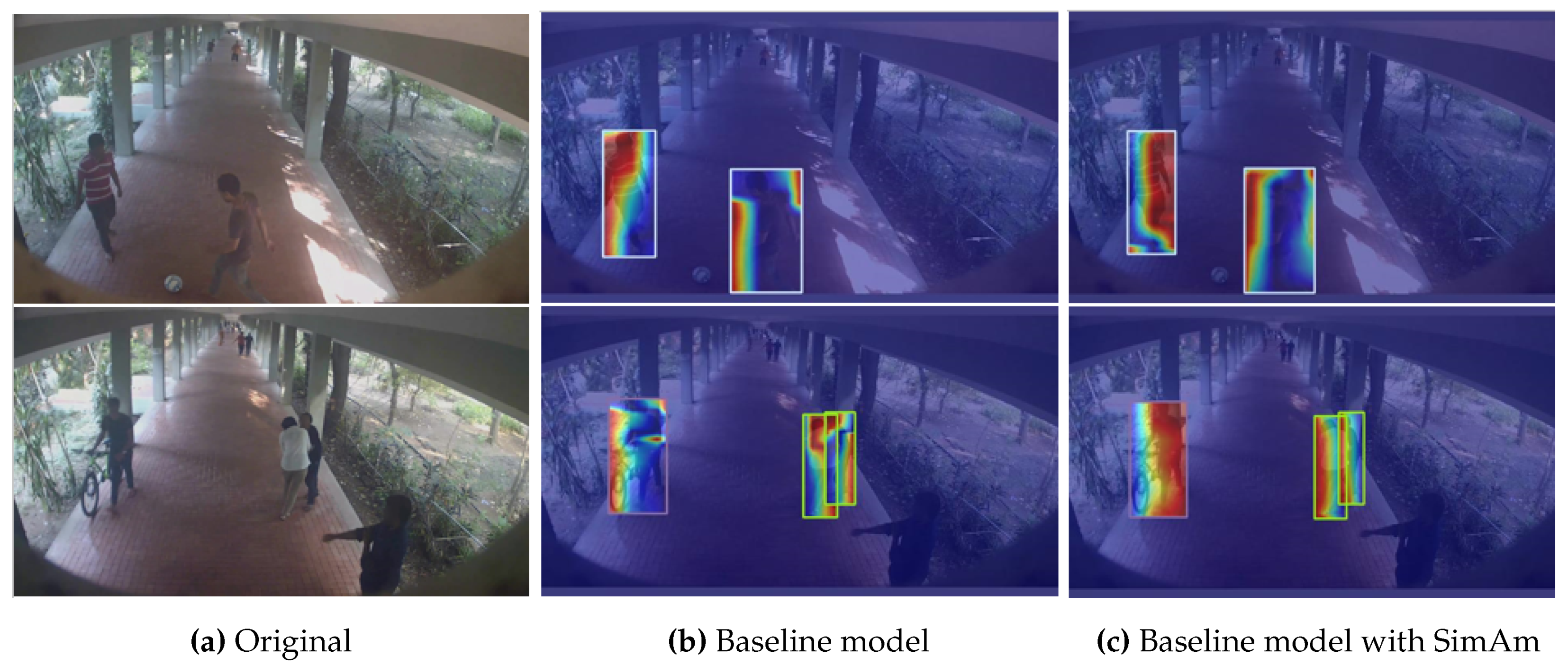
To assess the effectiveness of the SimAm attention module, two images showcasing abnormal behaviors were selected from the IITB-Corridor dataset. Feature extraction was conducted using both the baseline model and the SimAm-enhanced model, followed by visualization of the resulting feature heatmaps, as shown in
Figure 5. Integrating SimAm aligns the model’s attention towards the human body more closely with human brain attention patterns, thereby reducing interference from complex backgrounds. Thus, the inclusion of SimAm enhances the baseline model’s ability to detect abnormal behaviors.
4. Experiments
4.1. Dataset
The IITB-Corridor dataset [
57] was curated to investigate abnormal human activities within the corridors of the Indian Institute of Technology Bombay. These videos were captured by fixed cameras overlooking pedestrian corridors on the Mumbai campus. The dataset encompasses a variety of both normal and abnormal behaviors. Normal activities typically include walking and standing, while abnormal behaviors consist of activities such as running and fighting. Some abnormal behaviors occurred naturally in the videos, while others were intentionally staged by the dataset authors. These anomalies varied from individual to group-level occurrences, occasionally encountering challenges such as personnel overlap and shadow occlusion.
To manage the extensive collection of abnormal and non-abnormal video frames in the IITB-Corridor dataset, abnormal frames were sampled at a rate of 3 frames per second from each video depicting abnormal behavior. Subsequently, all abnormal behaviors were annotated using the labelImg annotation tool, as illustrated in
Table 1.
The adjusted dataset consists of 18,674 video frame images, covering 8 categories of abnormal behaviors: Bag Exchange, Cycling, Suspicious Object, Running, Fighting, Hiding, Playing With Ball, and Protest, with representative abnormal frame images shown in
Figure 6. In this paper, the first three letters of each category denote a specific class (e.g., "Bag" corresponds to "Bag Exchange"). To facilitate model training and validation, the dataset was divided into training and validation sets in an 8:2 ratio.
The street-view-gdogo dataset [
58] contains images captured by fixed traffic cameras positioned along urban roads in Turkey. Through manual annotation, common objects encountered in urban street traffic, such as Person, Car, Bus, Motorbike, and Bicycle, were categorized into 5 classes. The dataset comprises a total of 6,685 images, which were divided into training, validation, and test sets at a ratio of 8:1:1.
4.2. Training Setting
The experiment on abnormal behavior detection was conducted on the Ubuntu 20.04 operating system, utilizing Python 3.8 as the programming language, CUDA 12.2, and PyTorch 1.9.0 for developing the deep learning framework. The hardware configuration included an NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3080 GPU with 10GB of memory and an Intel Xeon Silver 4210R CPU with 128GB of memory. Experimental parameters were set as follows: a batch size of 16, training for 200 epochs, employing the Adam optimizer with an initial learning rate of 0.01, and weight decay set to 0.0005. Image preprocessing involved resizing images to dimensions of 640x640 pixels.
4.2.1. Evaluating Indicator
To evaluate the practical performance of YOLO-ABD, the experiments employ established model evaluation metrics from the object detection domain. These metrics include Precision, Recall, Average Precision (AP), mean Average Precision (mAP), Giga Floating-Point Operations Per Second (GFLOPs), and Frames Per Second (FPS). Precision measures the ratio of correctly identified positive samples to all samples classified as positive by the model, while Recall evaluates the ratio of correctly identified positive samples to all actual positive samples. The definitions of Precision and Recall are as follows:
TP represents true positives, indicating the number of positive samples correctly predicted as positive by the model; FP represents false positives, indicating the number of negative samples incorrectly predicted as positive by the model; FN denotes false negatives, indicating the number of positive samples incorrectly predicted as negative by the model. The Precision-Recall (PR) curve illustrates the relationship between recall (x-axis) and precision (y-axis) across various thresholds. AP represents the area under the PR curve for each class, while mAP denotes the average AP value across all classes. The calculation formulas are as follows:
mAP@50 denotes the mean average precision at an IoU threshold of 0.5, while mAP@50:95 signifies the mean average precision across IoU thresholds ranging from 0.5 to 0.95. GFLOPS quantifies the computational efficiency of the model, representing the number of billion floating-point operations the model can execute per second. Frames Per Second (FPS) represents the number of images the model can process per second, providing insights into the model’s real-time performance and detection speed. These metrics collectively offer comprehensive insights into the effectiveness and efficiency of the model in practical scenarios.
4.2.2. Result Analysis
To validate the performance improvement of YOLO-ABD, comparative experiments were conducted on the IITB-Corridor dataset to evaluate various object detection models. Key evaluation metrics such as AP, mAP@50, and GFLOPs were used to assess model performance and compare it with several state-of-the-art methods. Each category of abnormal behavior is represented by the first three letters: "Bag" for "Bag Exchange", "Cyc" for "Cycling", "Sus" for "Suspicious Object", "Run" for "Running", "Fig" for "Fighting", "Hid" for "Hiding", "Pla" for "Playing With Ball", and "Pro" for "Protest". The experimental results are summarized in
Table 2, offering a comprehensive comparison of model performances.
All models were trained from scratch to ensure fairness, without employing pre-training methods. Analysis of the experimental results indicates that YOLO-ABD achieves superior detection performance on the IITB-Corridor dataset, with an mAP@50 score of 89.3%. YOLO-ABD shows a performance improvement of 6.8 percentage points compared to the early-stage two-stage object detection method Faster R-CNN [
59]. Significant advancements are observed compared to the YOLO series, particularly in the "Cyc" and "Run" categories. Compared to YOLOv3 , YOLO-ABD demonstrates superior performance across most categories, notably in "Run", "Pla", and "Pro", with a 2.6 percentage point increase in mAP@50. Compared to YOLOv5s and YOLOv5n models , YOLO-ABD achieves higher accuracy across all categories, with mAP@50 scores improving by 8.1 and 12.9 percentage points, respectively. When compared to YOLOv6s and YOLOv6n models, YOLO-ABD notably enhances accuracy in the "Pro" category, with mAP@50 scores increasing by 4.8 and 8.1 percentage points, respectively. Against the latest YOLOv8s and YOLOv8n models , YOLO-ABD surpasses them in nearly all categories, particularly in "Run", "Pla", and "Pro", with significant improvements in accuracy and mAP@50 scores. Overall, YOLO-ABD exhibits substantial performance advantages, achieving higher mAP@50 values while maintaining a lightweight nature akin to the YOLO series, highlighting significant advancements.
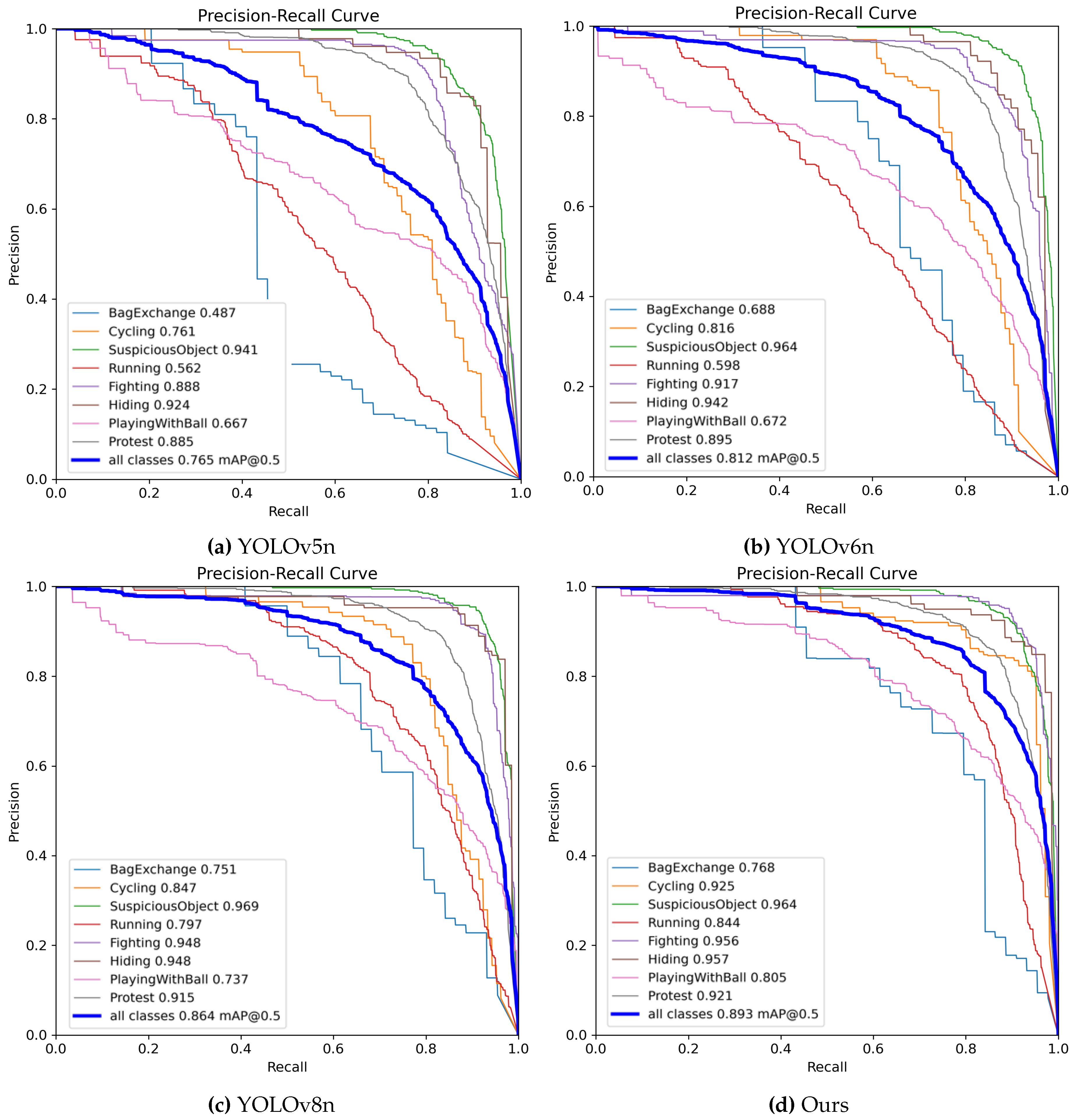
The PR curves shown in
Figure 7 provide a visual comparison between our proposed method and YOLO variants with similar computational complexity on the IITB-Corridor dataset. Our method exhibits a smoother curve, positioned closer to the top-right corner, indicating superior precision and recall performance. This demonstrates a more balanced detection capability, with notable improvements across various classes, particularly evident in the "BagExchange" category. These findings underscore the enhanced effectiveness of our proposed method in detecting abnormal behaviors, validating its superiority over existing YOLO variants.
Comparison of the actual detection results between the baseline model and our proposed model, shown in
Figure 8 and
Figure 9 respectively, reveals significant differences. The baseline model YOLOv8n demonstrates noticeable missed detections on the IITB-Corridor dataset, particularly in scenarios involving crowded and overlapping individuals. In contrast, our proposed model exhibits enhanced accuracy, effectively detecting abnormal targets even under challenging conditions. This improvement is reflected in the higher accuracy and precision of the detection boxes for individuals. Upon analysis of the results depicted in
Figure 8 and
Figure 9, our proposed model demonstrates superior performance in detecting abnormal behaviors such as "Cycling," "SuspiciousObject," "Protest," and "Fighting" compared to the baseline model. Notably, it accurately identifies the "Protest" abnormal behavior, which the baseline model fails to detect, without any missed detections, highlighting the efficacy of our approach. In summary, these findings validate the advanced and effective performance of our proposed model.
4.2.3. Generalization Study
To evaluate the generalization performance of YOLO-ABD in object detection tasks, this study utilized the street-view-gdogo traffic object detection dataset for testing and compared it with several contemporary advanced object detection models. The experimental results, summarized in
Table 3, demonstrate the performance of our model across five classes: Bicycle, Bus, Car, Motorbike, and Person. Our model achieved notable accuracy rates of 93.5%, 95.4%, 97%, 89.9%, and 88.1% for these respective classes. Comparative analysis with the baseline model YOLOv8n reveals that our model consistently outperforms in most categories, with a significant 2.6% increase observed in the Person class. These findings highlight the effectiveness and robust generalization capabilities of our model across diverse scenarios.
4.2.4. Ablation Study
To validate the effectiveness of YOLO-ABD and assess the contributions of SimAm, GSConv, and small object detection heads to the model’s accuracy and computational efficiency, eight sets of comparative experiments were conducted. YOLOv8n served as the baseline model, and experiments were performed on the IITB-Corridor dataset with images resized to 640x640 pixels. The findings are summarized in
Table 4.
From the experimental findings, it is evident that integrating the SimAm module alone improved the model’s mAP50 metric by 0.3 percentage points. The SimAm module enhances performance without adding parameters, thus avoiding increased model complexity or computational cost, and has negligible impact on floating-point operations.
Introducing the GSConv module alone improved the model’s mAP50 and mAP50-90 metrics on the dataset by 1.1 and 0.7 percentage points, respectively, while reducing floating-point operations by 0.4 GFLOPs. Adding the small object detection head alone enhanced the model’s mAP50 and mAP50-90 metrics by 0.4 and 0.3 percentage points, respectively. However, integrating the small object detection path increased floating-point operations from 8.1 to 11.8 GFLOPs, slightly reducing detection speed though still suitable for real-time applications.
Combining pairs of the three modules significantly improved both mAP50 and mAP50-90 metrics. Simultaneously adding the small object detection head and GSConv module increased the mAP50 metric to 89% and the mAP50-90 metric to 59.2%, while keeping additional floating-point operations minimal. Integrating all three modules seamlessly merged with the baseline model, maximizing efficiency and resulting in improvements of 2.9 and 3.2 percentage points in mAP50 and mAP50-90 metrics, respectively. Although integrating the small object detection head increased floating-point operations, the GSConv module effectively reduced the baseline model’s overall floating-point operations.
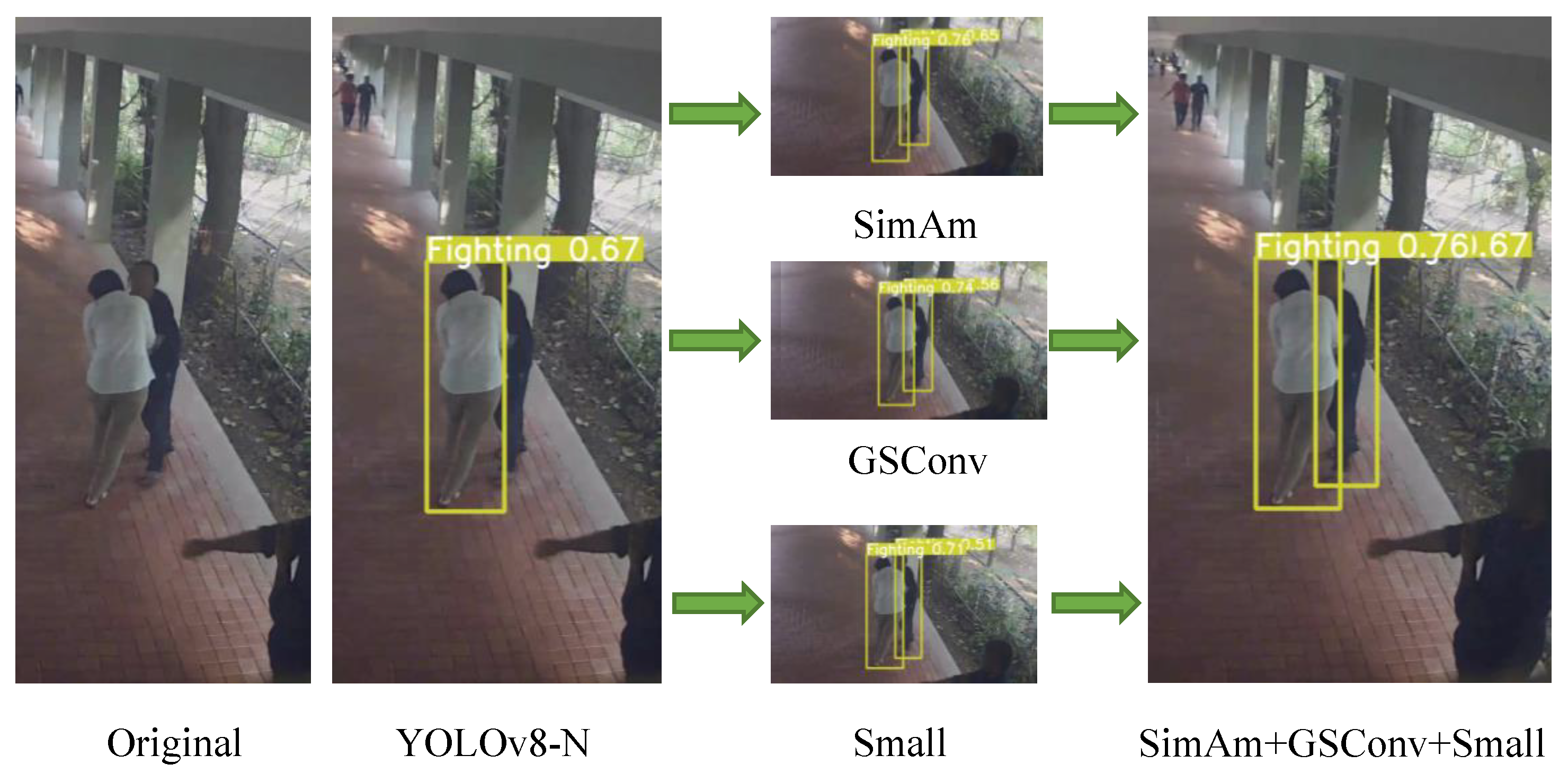
Ablation experiments were conducted by individually integrating different modules based on the baseline model, followed by anomaly behavior testing and comparative diagram generation, as depicted in
Figure 10. These diagrams illustrate that while individual integration of SimAm, GSConv, and the small object detection head each improves performance over the original YOLOv8n model, their simultaneous integration yields substantial enhancements in anomaly behavior detection performance.
5. Conclusions
This study introduces YOLO-ABD, a lightweight anomaly detection method based on the YOLOv8n baseline network. YOLO-ABD addresses the challenge of insufficient detection performance for small objects by incorporating a dedicated small target detection head. Additionally, it integrates the GSConv module to optimize channel connections while minimizing computational costs. The inclusion of the SimAM attention mechanism further aids in mitigating background interference. Experimental results on the IITB-Corridor dataset demonstrate that YOLO-ABD achieves mAP50 and mAP50-95 scores of 89.3% and 60.6%, respectively, without requiring pre-training on additional data. Comparative analysis with other object detection algorithms, such as Faster-RCNN, YOLOv3, YOLOv5s, YOLOv5n, YOLOv6s, YOLOv6n, YOLOv8s, and YOLOv8n, illustrates that YOLO-ABD strikes an optimal balance between speed and accuracy. It effectively reduces missed detections and false alarms caused by background interference and occlusion, achieving a favorable integration of accuracy and lightweight design. Results on the street-view-gdogo dataset underscore YOLO-ABD’s robust generalization capabilities.
This research presents an anomaly detection approach rooted in supervised learning. Given the scarcity of anomaly behavior data, substantial manual annotation is required during initial experimentation, leading to extensive data processing and significant workload. Future research directions could explore the adoption of unsupervised or semi-supervised learning methodologies to reduce the reliance of anomaly detection models on annotated data.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.H. and K.L.; methodology, C.H. and K.L.; software, K.L.; validation, K.L.; formal analysis, C.H.; investigation, K.L.; resources, K.L.; data curation, K.L.; writing—original draft preparation, K.L.; writing—review and editing, C.H.; visualization, K.L.; supervision, C.H.; project administration, C.H.; funding acquisition, Y.W. and R.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the Scientific Research and Innovation Team Program of Sichuan University of Science and Technology under Grant SUSE652A006.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express their heartfelt gratitude to those people who have helped with this manuscript and to the reviewers for their comments on the manuscript..
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Pang, G.; Shen, C.; Cao, L.; Hengel, A. V. D. Deep learning for anomaly detection: A review. ACM Comput. Surv. 2021, 54(2), 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassif, A. B.; Talib, M. A.; Nasir, Q.; Dakalbab, F. M. Machine learning for anomaly detection: A systematic review. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 78658–78700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ristea, N. C.; Madan, N.; Ionescu, R. T.; Nasrollahi, K.; Khan, F. S.; Moeslund, T. B. Self-supervised predictive convolutional attentive block for anomaly detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, LA, USA, 18-24 June 2022; pp. 13576–13586. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Chang, H.; Ma, B.; Shan, S. Diversity-measurable anomaly detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, BC, Canada, 17-24 June 2023; pp. 12147–12156. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, B.; Wang, X.; Bao, Q.; Jia, B.; Li, X.; Wang, Y. An unsafe behavior detection method based on improved YOLO framework. Electronics 2022, 11(12), 1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Yu, C.; Chen, B.; Zhao, Y. YOLO-GP: A Multi-Scale Dangerous Behavior Detection Model Based on YOLOv8. Symmetry 2024, 16(6), 730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravanbakhsh, M.; Nabi, M.; Sangineto, E.; Marcenaro, L.; Regazzoni, C.; Sebe, N. Abnormal event detection in videos using generative adversarial nets. In 2017 IEEE international conference on image processing (ICIP), Beijing, China, 17-20 September 2017; pp. 1577–1581.
- Lv, H.; Chen, C.; Cui, Z.; Xu, C.; Li, Y.; Yang, J. Learning normal dynamics in videos with meta prototype network. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, TN, USA, 20-25 June 2021; pp. 15425–15434. [Google Scholar]
- Yajing, L.; Zhongjian, D. Abnormal behavior detection in crowd scene using YOLO and Conv-AE. In 2021 33rd Chinese Control and Decision Conference (CCDC), Kunming, China, 22-24 May 2021; pp. 1720–1725.
- Dong, F.; Zhang, Y.; Nie, X. Dual discriminator generative adversarial network for video anomaly detection. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 88170–88176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kim, H. G.; Ro, Y. M. BMAN: Bidirectional multi-scale aggregation networks for abnormal event detection. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2019, 29, 2395–2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullah, W.; Hussain, T.; Ullah, F. U. M.; Lee, M. Y.; Baik, S. W. TransCNN: Hybrid CNN and transformer mechanism for surveillance anomaly detection. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2023, 123, 106173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, G.; Yan, C.; Shen, C.; Hengel, A. V. D.; Bai, X. Self-trained deep ordinal regression for end-to-end video anomaly detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, WA, USA, 13-19 June 2020; pp. 12173–12182. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, Y.; Tang, Z.; Alzahrani, B.; Alotaibi, R.; Alharthi, R.; Zhao, M.; Mahmood, A. An end-to-end human abnormal behavior recognition framework for crowds with mentally disordered individuals. IEEE J. Biomed. Health. Inf. 2021, 26(8), 3618–3625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Guo, W. Auto-encoders in deep learning—a review with new perspectives. Mathematics 2023, 11(8), 1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, D.; Liu, L.; Le, V.; Saha, B.; Mansour, M. R.; Venkatesh, S.; Hengel, A. V. D. Memorizing normality to detect anomaly: Memory-augmented deep autoencoder for unsupervised anomaly detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision, Seoul, Korea (South), 27 October 2019 - 02 November 2019; pp. 1705–1714.
- Luo, W.; Liu, W.; Lian, D.; Gao, S. Future frame prediction network for video anomaly detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 44(11), 7505–7520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Fang, J.; Xu, H.; Xue, J. Video frame prediction by deep multi-branch mask network. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2020, 31(4), 1283–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Che, Z.; Jiang, B.; Xiao, N.; Yang, K.; Tang, J.; Qi, Q. Robust unsupervised video anomaly detection by multipath frame prediction. IEEE Trans. Neural Networks Learn. Syst. 2022, 33(6), 2301–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Li, H.; Zhang, G. Future frame prediction based on generative assistant discriminative network for anomaly detection. Appl. Intell. 2023, 53(1), 542–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straka, Z.; Svoboda, T.; Hoffmann, M. PreCNet: Next-frame video prediction based on predictive coding. IEEE Trans. Neural Networks Learn. Syst. 2023, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, M. YOLOv1 to v8: Unveiling Each Variant–A Comprehensive Review of YOLO. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 42816–42833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, J.; Wei, H.; Liu, Z.; Zhan, Z.; Ren, Q. Slim-neck by GSConv: A better design paradigm of detector architectures for autonomous vehicles. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2206.02424. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, R. Y.; Li, L.; Xie, X. Simam: A simple, parameter-free attention module for convolutional neural networks.In International conference on machine learning, Maryland, USA, 18-24 Jul 2021; pp. 11863–11874.
- Cheoi, K. J. Temporal saliency-based suspicious behavior pattern detection. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10(3), 1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smoliński, A.; Forczmański, P.; Nowosielski, A. Processing and Integration of Multimodal Image Data Supporting the Detection of Behaviors Related to Reduced Concentration Level of Motor Vehicle Users. Electronics 2024, 13(13), 2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, B.; Guo, H.; Zheng, G. Mining Abnormal Patterns in Moving Target Trajectories Based on Multi-Attribute Classification. Mathematics 2024, 12(13), 1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.; Sun, W.; Fang, Y.; Ye, N.; Yang, S.; Wu, J. A Model for Detecting Abnormal Elevator Passenger Behavior Based on Video Classification. Electronics 2024, 13(13), 2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Y. Abnormal Behavior Recognition in Classroom Pose Estimation of College Students Based on Spatiotemporal Representation Learning. Trait. Signal 2021, 38(1), 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Ashwin, T. S.; Guddeti, R. M. R. Multimodal behavior analysis in computer-enabled laboratories using nonverbal cues. Signal Image Video Proces. 2020, 14(8), 1617–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Hu, W.; Hu, X. Abnormal behavior recognition using 3D-CNN combined with LSTM. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2021, 80(12), 18787–18801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashmi, M.; Ashwin, T. S.; Guddeti, R. M. R. Surveillance video analysis for student action recognition and localization inside computer laboratories of a smart campus. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2021, 80(2), 2907–2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lentzas, A.; Vrakas, D. Non-intrusive human activity recognition and abnormal behavior detection on elderly people: A review. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2020, 53(3), 1975–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lina, W.; Ding, J. Behavior detection method of OpenPose combined with Yolo network. In 2020 International Conference on Communications, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 03-05 July 2020; pp. 326–330.
- Ganagavalli, K.; Santhi, V. YOLO-based anomaly activity detection system for human behavior analysis and crime mitigation. Signal Image Video Process. 2024, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Zheng, L.; Peng, Y.; Jiang, R. A survey of research on crowd abnormal behavior detection algorithm based on YOLO network. In 2022 2nd international conference on consumer electronics and computer engineering (ICCECE), Guangzhou, China, 14-16 January 2022; pp. 783–786.
- Maity, M.; Banerjee, S.; Chaudhuri, S. S. Faster r-cnn and yolo based vehicle detection: A survey. In 2021 5th international conference on computing methodologies and communication (ICCMC), Erode, India, 08-10 April 2021; pp. 1442–1447.
- Mansour, R. F.; Escorcia-Gutierrez, J.; Gamarra, M.; Villanueva, J. A.; Leal, N. Intelligent video anomaly detection and classification using faster RCNN with deep reinforcement learning model. Image Vis. Comput. 2021, 112, 104229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hongchao, S.; Hu, Y.; Guoqing, Z.; Chuyue, Z. Behavior Identification based on Improved Two-Stream Convolutional Networks and Faster RCNN. In 2021 33rd Chinese Control and Decision Conference (CCDC), Kunming, China, 22-24 May 2021; pp. 1771–1776.
- Chen, N.; Man, Y.; Sun, Y. Abnormal cockpit pilot driving behavior detection using YOLOv4 fused attention mechanism. Electronics 2022, 11(16), 2538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhou, G.; Jiang, H. Student behavior detection in the classroom based on improved YOLOv8. Sensors 2023, 23, 8385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jie, C. H. A. N. G.; Guowei, Z. H. A. N. G.; Wenjiang, C. H. E. N.; Diping, Y. U. A. N.; Yongsheng, W. A. N. G. Gas station unsafe behavior detection based on YOLO-V3 algorithm. China Saf. Sci. J. 2023, 33(2), 31–37. [Google Scholar]
- Benjumea, A.; Teeti, I.; Cuzzolin, F.; Bradley, A. YOLO-Z: Improving small object detection in YOLOv5 for autonomous vehicles. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2112.11798. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, W.; Sun, M.; Shen, X.; Luo, Z. Monitoring the Abnormal Human Behaviors in Substations based on Probabilistic Behaviours Prediction and YOLO-V5. In 2022 7th Asia Conference on Power and Electrical Engineering (ACPEE), Hangzhou, China, 15-17 April 2022; pp. 943–948.
- Lin, T. Y.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Hariharan, B.; Belongie, S. Feature pyramid networks for object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, HI, USA, 21-26 July 2017; pp. 2117–2125. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Qi, L.; Qin, H.; Shi, J.; Jia, J. Path aggregation network for instance segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, UT, USA, 18-23 June 2018; pp. 8759–8768. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Jin, Y.; Ke, H.; Zhang, X. DDH-YOLOv5: improved YOLOv5 based on Double IoU-aware Decoupled Head for object detection. J. Real-Time Image Process. 2022, 19(6), 1023–1033.
- Gennari, M.; Fawcett, R.; Prisacariu, V.A. DSConv: Efficient Convolution Operator. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1901.01928. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.; Teodorescu, R.; Agrawal, G. Fused DSConv: Optimizing sparse CNN inference for execution on edge devices. In 2021 IEEE/ACM 21st International Symposium on Cluster, Cloud and Internet Computing (CCGrid), Melbourne, Australia, 10-13 May 2021; pp. 545–554.
- Alalwan, N.; Abozeid, A.; ElHabshy, A. A.; Alzahrani, A. Efficient 3D deep learning model for medical image semantic segmentation. Alex. Eng. J. 2021, 60(1), 1231–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhou, X.; Lin, M.; Sun, J. Shufflenet: An extremely efficient convolutional neural network for mobile devices. In Proceedings of the IEEE conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, UT, USA, 18-23 June 2018; pp. 6848–6856. [Google Scholar]
- Han, K.; Wang, Y.; Tian, Q.; Guo, J.; Xu, C.; Xu, C. Ghostnet: More features from cheap operations. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, WA, USA, 13-19 June 2020; pp. 1580–1589. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, X.; Xie, Y.; Wei, X. S.; Zhao, B. R.; Chen, Z. M.; Tan, X. Delving deep into spatial pooling for squeeze-and-excitation networks. Pattern Recognit. 2022, 121, 108159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaderberg, M.; Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Spatial transformer networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2015, 28, 2017–2025. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J.Y.; Kweon, I.S. Cbam: Convolutional block attention module. In Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 3–19. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Shao, Z.; Hoffmann, N. Global attention mechanism: Retain information to enhance channel-spatial interactions. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2112.05561. [Google Scholar]
- Rodrigues, R.; Bhargava, N.; Velmurugan, R.; Chaudhuri, S. Multi-timescale trajectory prediction for abnormal human activity detection. 2020 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), CO, USA, 01-05 March 2020; pp. 2626–2634.
- FSMVU. Street View Dataset. https://universe.roboflow.com/fsmvu/street-view-gdogo, 2023. visited on 2023-09-05.
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster r-cnn: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2016, 39, 1137–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).