Submitted:
05 July 2024
Posted:
05 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Grape Pomace
2.3. Grape Pomace Extract Preparation
2.4. Optimisation of Process Parameters Using the Response Surface Methodology
2.4.1. Optimisation of Homogenisation in an Ultrasonic Bath and on Magnetic Stirrer
2.4.2. Optimisation of Spray Drying Conditions
2.5. Microcapsule Characterisation
2.5.1. Encapsulation Efficiency
2.5.2. Moisture Content Determination
2.5.3. Encapsulation Yield
2.5.4. Determination of the Solubility Properties of the Microcapsules
2.5.5. Determination of Density and Compressibility Properties of Microcapsules
2.5.6. Determination of Colour Parameters
3. Results and Discussion
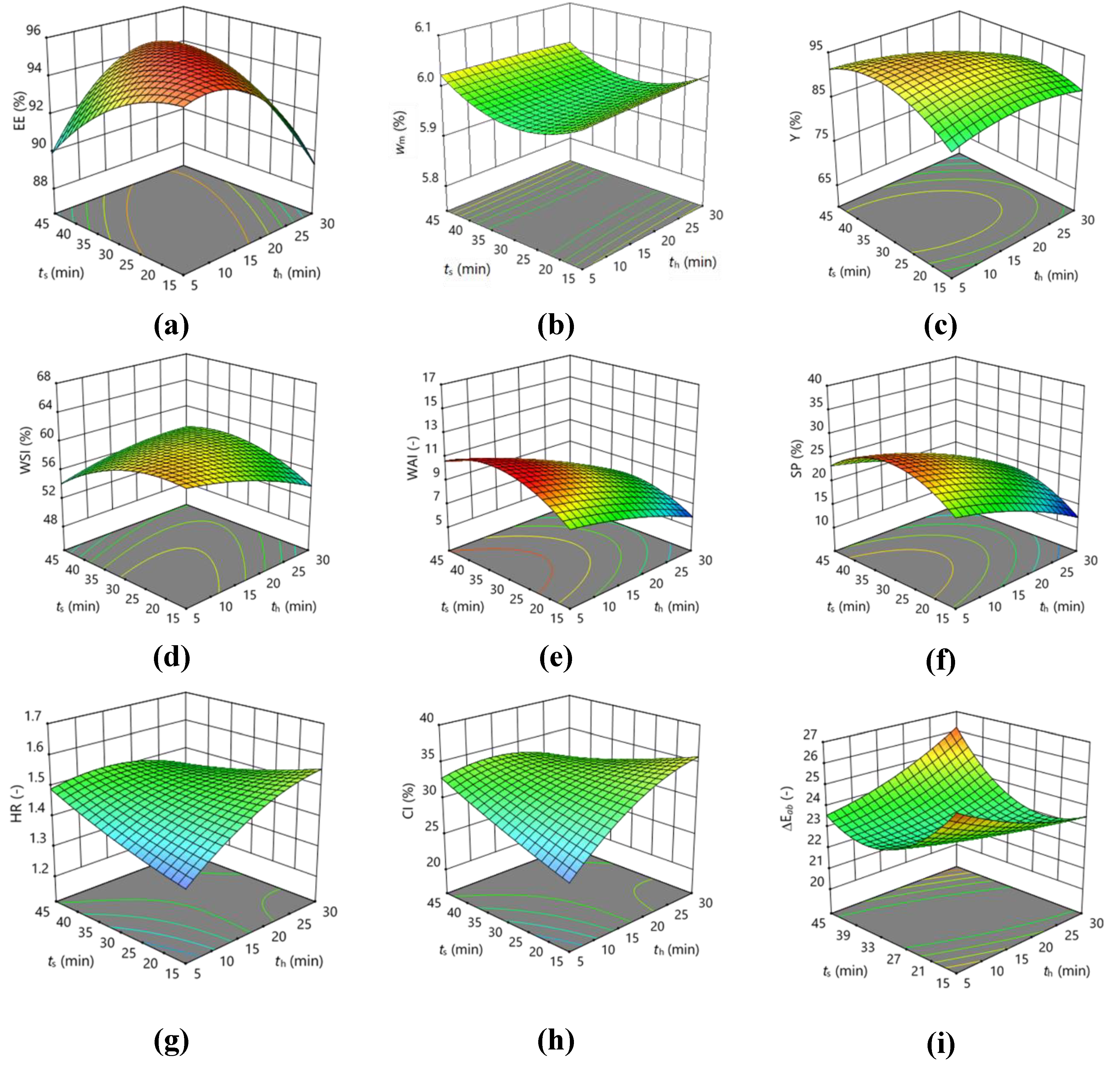
3.1. Optimisation of the Homogenisation of the Encapsulation Mixture in an Ultrasonic Bath
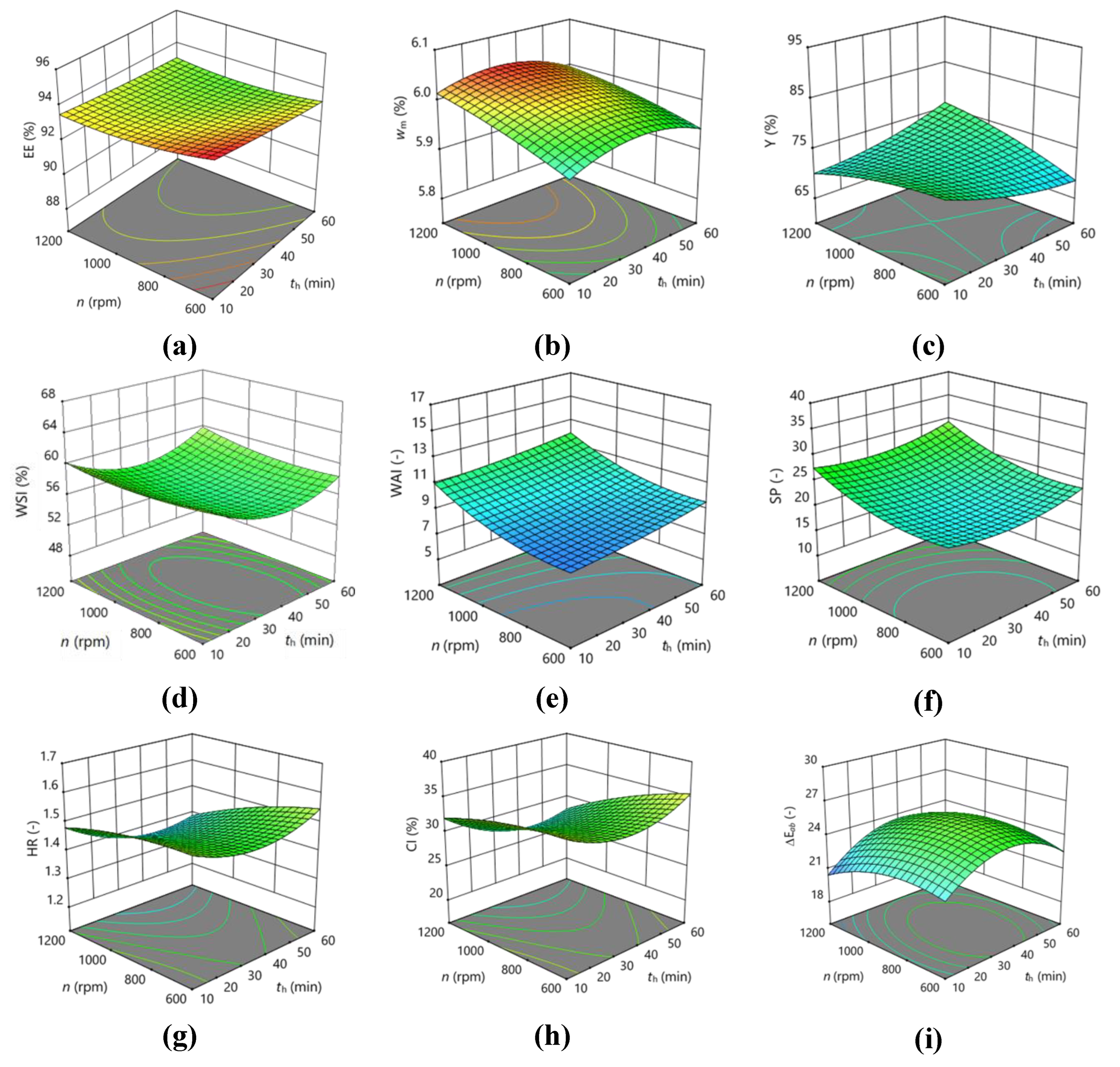
3.2. Optimization of Homogenization of the Feed Mixture on a Magnetic Stirrer
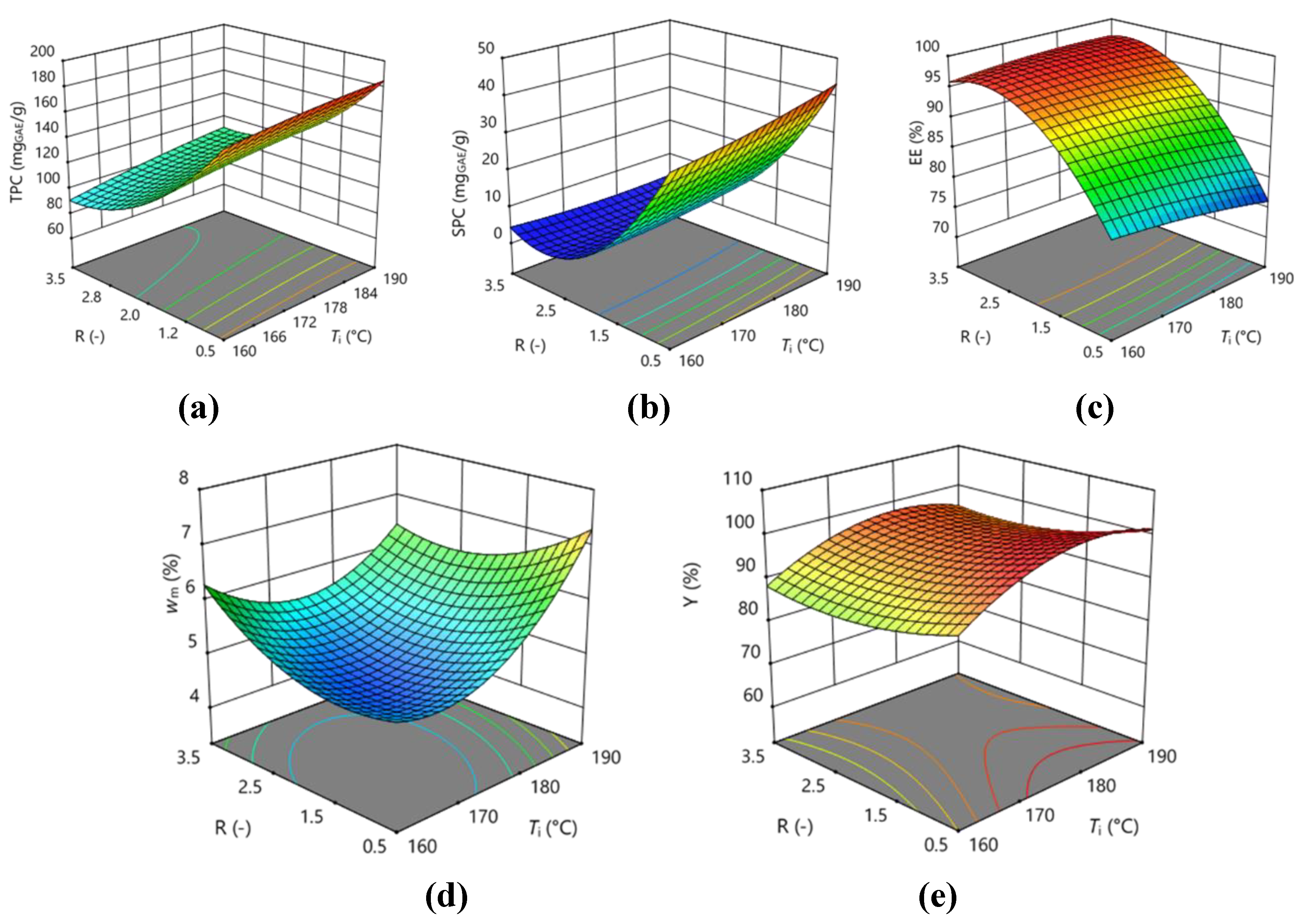
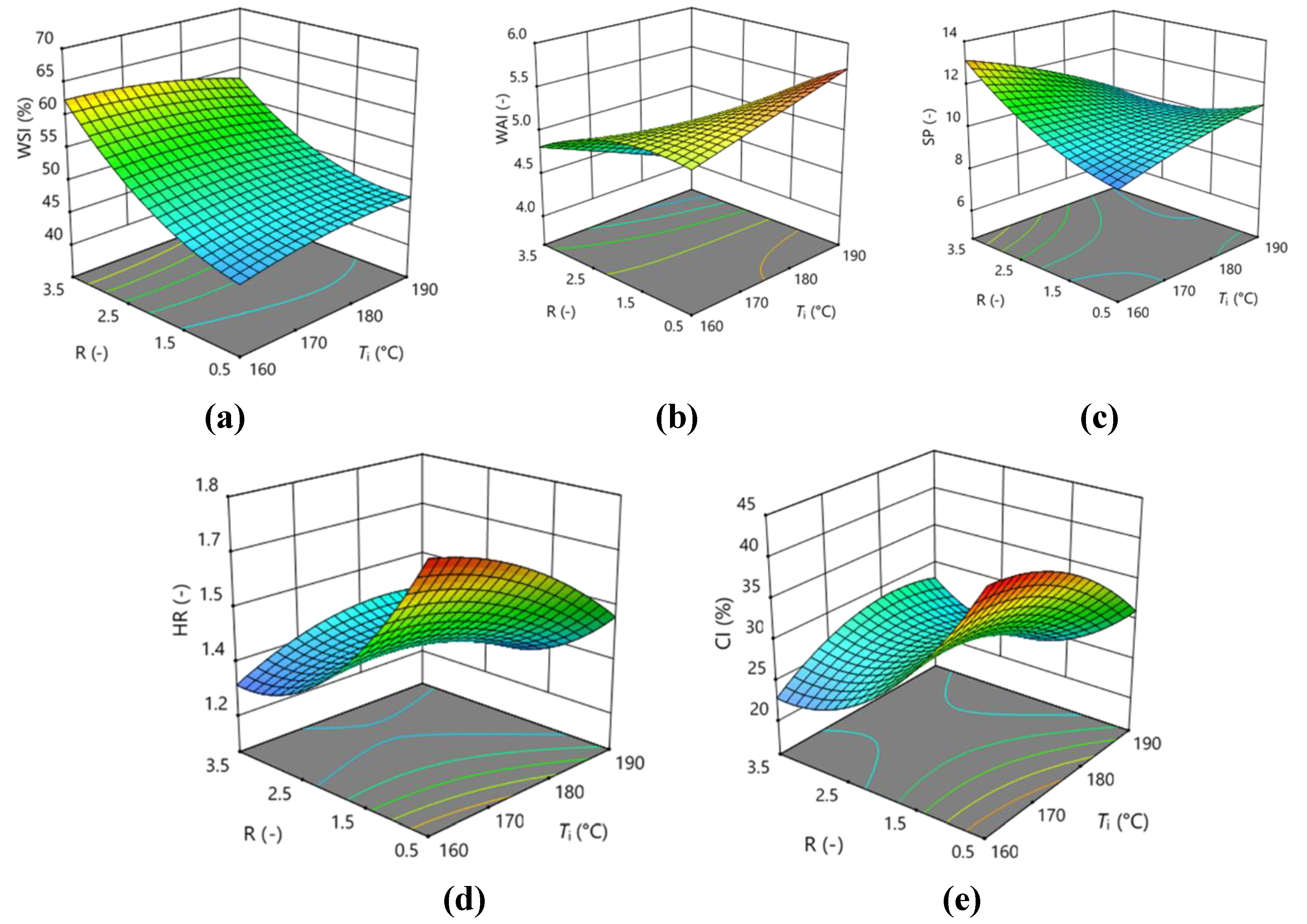
3.3. Optimization of Encapsulation by Spray Drying
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- López-Belchí, M.D.; Caamaño, E.F.; Pascual, G.; Noriega, F.; Fierro-Morales, P.; Romero-Román, M.E.; Jara, P.; Schoebitz, M.; Serra, I.; Moreno, D.A. Spray-Dried Formulations Rich in Malvidin from Tintorera Grape Wastes: Characterization, Stability, and Storage. Processes 2021, 9, 518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moro, K.I.B.; Bender, A.B.B.; da Silva, L.P.; Penna, N.G. Green Extraction Methods and Microencapsulation Technologies of Phenolic Compounds From Grape Pomace: A Review. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2021, 14, 1407–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoukat, A.; Imran, M.; Khan, M.K.; Ahmad, M.H.; Ahmad, R.S.; Ramadan, M.F.; Nadeem, M.; Yasmin, A.; Rahim, M.A.; Khan, M.I. Impact of Spray Drying Operating Conditions on Yield, Secondary Metabolites, Antioxidant Potential and Storage Quality of Grape (Vitis Vinifera L.) Pomace Powder. South Afr. J. Bot. 2024, 169, 383–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, V.B. de; Fujita, A.; Thomazini, M.; da Silva, E.R.; Lucon, J.F.; Genovese, M.I.; Favaro-Trindade, C.S. Functional Properties and Stability of Spray-Dried Pigments from Bordo Grape (Vitis Labrusca) Winemaking Pomace. Food Chem. 2014, 164, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhary, P.; Gupta, A.; Gnansounou, E.; Pandey, A.; Chaturvedi, P. Current Trends and Possibilities for Exploitation of Grape Pomace as a Potential Source for Value Addition. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 278, 116796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pourashouri, P.; Shabanpour, B.; Razavi, S.H.; Jafari, S.M.; Shabani, A.; Aubourg, S.P. Impact of Wall Materials on Physicochemical Properties of Microencapsulated Fish Oil by Spray Drying. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2014, 7, 2354–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El-Kader, A.; Abu Hashish, H. Encapsulation Techniques of Food Bioproduct. Egypt. J. Chem. 2020, 63, 1881–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinović, J.; Lukinac, J.; Jukić, M.; Ambrus, R.; Planinić, M.; Šelo, G.; Klarić, A.-M.; Perković, G.; Bucić-Kojić, A. Physicochemical Characterization and Evaluation of Gastrointestinal In Vitro Behavior of Alginate-Based Microbeads with Encapsulated Grape Pomace Extracts. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coimbra, P.P.S.; Cardoso, F. de S.N.; Gonçalves, É.C.B. de A. Spray-Drying Wall Materials: Relationship with Bioactive Compounds. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 61, 2809–2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smithers, G.W. Whey and Whey Proteins—From ‘Gutter-to-Gold. ’ Int. Dairy J. 2008, 18, 695–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Božanić, R.; Barukčić Jurina, I.; Lisak Jakopović, K.; Tratnik, L. Possibilities of Whey Utilisation. Austin J. Nutr. Food Sci. 2014, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, Z.; Duley, J.A.; Cowley, D.M.; Reed, S.; Arachchige, B.J.; Bhandari, B.; Shaw, P.N.; Bansal, N. Physicochemical Properties and Whey Proteomes of Camel Milk Powders Produced by Different Concentration and Dehydration Processes. Foods 2022, 11, 727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros, G.K.V.V.; Queiroga, R.C.R.E.; Costa, W.K.A.; Gadelha, C.A.A.; e Lacerda, R.R.; Lacerda, J.T.J.G.; Pinto, L.S.; Braganhol, E.; Teixeira, F.C.; de, S. Barbosa, P.P.; et al. Proteomic of Goat Milk Whey and Its Bacteriostatic and Antitumour Potential. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 113, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerasioti, E.; Stagos, D.; Georgatzi, V.; Bregou, E.; Priftis, A.; Kafantaris, I.; Kouretas, D. Antioxidant Effects of Sheep Whey Protein on Endothelial Cells. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, e6585737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garau, V.; Manis, C.; Scano, P.; Caboni, P. Compositional Characteristics of Mediterranean Buffalo Milk and Whey. Dairy 2021, 2, 469–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Renzo, G.C.; Altieri, G.; Genovese, F. Donkey Milk Powder Production and Properties Compared to Other Milk Powders. Dairy Sci. Technol. 2013, 93, 551–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Liu, X.; Guo, H. The Nutritional Ingredients and Antioxidant Activity of Donkey Milk and Donkey Milk Powder. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2018, 27, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricaurte, L.; Prieto, R.; Perea-Flores, M.J.; Quintanilla-Carvajal, M.X. Influence of Milk Whey on High-Oleic Palm Oil Nanoemulsions: Powder Production, Physical and Release Properties. Food Biophys. 2017, 12, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warncke, M.; Keienburg, S.; Kulozik, U. Cold-Renneted Milk Powders for Cheese Production: Impact of Casein/Whey Protein Ratio and Heat on the Gelling Behavior of Reconstituted Rennet Gels and on the Survival Rate of Integrated Lactic Acid Bacteria. Foods 2021, 10, 1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macwan, S.; Dabhi, B.; Parmar, S.; Aparnathi, K. Whey and Its Utilization. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2016, 5, 134–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchanan, D.; Martindale, W.; Romeih, E.; Hebishy, E. Recent Advances in Whey Processing and Valorisation: Technological and Environmental Perspectives. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 2023, 76, 291–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prazeres, A.R.; Carvalho, F.; Rivas, J. Cheese Whey Management: A Review. J. Environ. Manage. 2012, 110, 48–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, J.S.S.; Yan, S.; Pilli, S.; Kumar, L.; Tyagi, R.D.; Surampalli, R.Y. Cheese Whey: A Potential Resource to Transform into Bioprotein, Functional/Nutritional Proteins and Bioactive Peptides. Biotechnol. Adv. 2015, 33, 756–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jauregi, P.; Guo, Y.; Adeloye, J.B. Whey Proteins-Polyphenols Interactions Can Be Exploited to Reduce Astringency or Increase Solubility and Stability of Bioactives in Foods. Food Res. Int. 2021, 141, 110019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ming, Y.; Chen, L.; Khan, A.; Wang, H.; Wang, C. Effects of Tea Polyphenols on Physicochemical and Antioxidative Properties of Whey Protein Coating. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2020, 29, 1655–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasapoğlu, K.N.; Gültekin-Özgüven, M.; Kruger, J.; Frank, J.; Bayramoğlu, P.; Barla-Demirkoz, A.; Özçelik, B. Effect of Spray Drying on Physicochemical Stability and Antioxidant Capacity of Rosa Pimpinellifolia Fruit Extract-Loaded Liposomes Conjugated with Chitosan or Whey Protein During In Vitro Digestion. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, P.; Gorena, T.; Romero, N.; Sepulveda, E.; Chavez, J.; Saenz, C. Encapsulation of Polyphenols and Anthocyanins from Pomegranate (Punica Granatum) by Spray Drying. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 45, 1386–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calva-Estrada, S.J.; Lugo-Cervantes, E.; Jiménez-Fernández, M. Microencapsulation of Cocoa Liquor Nanoemulsion with Whey Protein Using Spray Drying to Protection of Volatile Compounds and Antioxidant Capacity. J. Microencapsul. 2019, 36, 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damerau, A.; Ogrodowska, D.; Banaszczyk, P.; Dajnowiec, F.; Tańska, M.; Linderborg, K.M. Baltic Herring (Clupea Harengus Membras) Oil Encapsulation by Spray Drying Using a Rice and Whey Protein Blend as a Coating Material. J. Food Eng. 2022, 314, 110769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baba, W.N.; McClements, D.J.; Maqsood, S. Whey Protein–Polyphenol Conjugates and Complexes: Production, Characterization, and Applications. Food Chem. 2021, 365, 130455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, T.H.; Benjakul, S.; Sae-leaw, T.; Balange, A.K.; Maqsood, S. Protein–Polyphenol Conjugates: Antioxidant Property, Functionalities and Their Applications. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 91, 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAOSTAT. Available online: https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QCL (accessed on 26 June 2024).
- Vu, H.T.; Scarlett, C.J.; Vuong, Q.V. Encapsulation of Phenolic-Rich Extract from Banana (Musa Cavendish) Peel. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 57, 2089–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolun, A.; Altintas, Z.; Artik, N. Microencapsulation of Grape Polyphenols Using Maltodextrin and Gum Arabic as Two Alternative Coating Materials: Development and Characterization. J. Biotechnol. 2016, 239, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, G.M.; O’Mahony, J.A.; Kelly, A.L.; O’Callaghan, D.J. Effect of Hydrolyzed Whey Protein on Surface Morphology, Water Sorption, and Glass Transition Temperature of a Model Infant Formula. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 6961–6972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.-W.; Oh, H.-J.; Han, S.-H.; Lim, S. Effects of Hot Air and Freeze Drying Methods on Physicochemical Properties of Citrus “Hallabong” Powders. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2012, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyano-Orozco, L.; Gallardo-Velázquez, T.; Meza-Márquez, O.G.; Osorio-Revilla, G. Microencapsulation of Rambutan Peel Extract by Spray Drying. Foods 2020, 9, 899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalušević, A.M.; Lević, S.M.; Čalija, B.R.; Milić, J.R.; Pavlović, V.B.; Bugarski, B.M.; Nedović, V.A. Effects of Different Carrier Materials on Physicochemical Properties of Microencapsulated Grape Skin Extract. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 54, 3411–3420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, H.C.F.; Tonon, R.V.; Grosso, C.R.F.; Hubinger, M.D. Encapsulation Efficiency and Oxidative Stability of Flaxseed Oil Microencapsulated by Spray Drying Using Different Combinations of Wall Materials. J. Food Eng. 2013, 115, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koç, M.; Koç, B.; Güngör, Ö.; Ertekin, F.K. The Effects of Moisture on Physical Properties of Spray-Dried Egg Powder. Dry. Technol. 2012, 30, 567–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, C.W.; Lim, W.T. Storage Stability of Spray-Dried Papaya (Carica Papaya L. ) Powder Packaged in Aluminium Laminated Polyethylene (ALP) and Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET). 2016, 23, 1887–1894. [Google Scholar]
- Sundararajan, P.; Moser, J.; Williams, L.; Chiang, T.; Riordan, C.; Metzger, M.; Zhang-Plasket, F.; Wang, F.; Collins, J.; Williams, J. Driving Spray Drying towards Better Yield: Tackling a Problem That Sticks Around. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousefi, S.; Emam-Djomeh, Z.; Mousavi, S.M. Effect of Carrier Type and Spray Drying on the Physicochemical Properties of Powdered and Reconstituted Pomegranate Juice (Punica Granatum L.). J. Food Sci. Technol. 2011, 48, 677–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Pharmacopoeia; European treaty series; 7th ed.; Council Of Europe : European Directorate for the Quality of Medicines and Healthcare: Strasbourg, 2010; ISBN 978-92-871-6700-2.
- Ji, J.; Fitzpatrick, J.; Cronin, K.; Fenelon, M.A.; Miao, S. The Effects of Fluidised Bed and High Shear Mixer Granulation Processes on Water Adsorption and Flow Properties of Milk Protein Isolate Powder. J. Food Eng. 2017, 192, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, S.M.; Ghalegi Ghalenoei, M.; Dehnad, D. Influence of Spray Drying on Water Solubility Index, Apparent Density, and Anthocyanin Content of Pomegranate Juice Powder. Powder Technol. 2017, 311, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koç, M.; Güngör, Ö.; Zungur, A.; Yalçın, B.; Selek, İ.; Ertekin, F.K.; Ötles, S. Microencapsulation of Extra Virgin Olive Oil by Spray Drying: Effect of Wall Materials Composition, Process Conditions, and Emulsification Method. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2015, 8, 301–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koc, B.; Yilmazer, M.S.; Balkır, P.; Ertekin, F.K. Spray Drying of Yogurt: Optimization of Process Conditions for Improving Viability and Other Quality Attributes. Dry. Technol. 2010, 28, 495–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roccia, P.; Martínez, M.L.; Llabot, J.M.; Ribotta, P.D. Influence of Spray-Drying Operating Conditions on Sunflower Oil Powder Qualities. Powder Technol. 2014, 254, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziaee, A.; Albadarin, A.B.; Padrela, L.; Femmer, T.; O’Reilly, E.; Walker, G. Spray Drying of Pharmaceuticals and Biopharmaceuticals: Critical Parameters and Experimental Process Optimization Approaches. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 127, 300–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pino, J.A.; Aragüez-Fortes, Y.; Bringas-Lantigua, M. Optimization of Spray-Drying Process for Concentrated Orange Juice. Acta Aliment. 2018, 47, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, T.; de Paz, E.; Navarro, I.; Rodríguez-Rojo, S.; Matías, A.; Duarte, C.; Sanz-Buenhombre, M.; Cocero, M.J. Spray Drying Formulation of Polyphenols-Rich Grape Marc Extract: Evaluation of Operating Conditions and Different Natural Carriers. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2016, 9, 2046–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, T.; Cocero, M.J.; Rodríguez-Rojo, S. Storage Stability and Simulated Gastrointestinal Release of Spray Dried Grape Marc Phenolics. Food Bioprod. Process. 2018, 112, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siacor, F.D.C.; Lim, K.J.A.; Cabajar, A.A.; Lobarbio, C.F.Y.; Lacks, D.J.; Taboada, E.B. Physicochemical Properties of Spray-Dried Mango Phenolic Compounds Extracts. J. Agric. Food Res. 2020, 2, 100048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Independent variable | Variable levels | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| - 1 | 0 | 1 | ||
| Homogenisation temperature (Th, °C) | X1 | 30 | 40 | 50 |
| Homogenisation time (th, min) | X2 | 5 | 17.5 | 30 |
| Stabilisation time (ts, min) | X3 | 15 | 30 | 45 |
| Independent variable | Variable levels | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| - 1 | 0 | 1 | ||
| Homogenisation temperature (Th, °C) | X1 | 25 | 37.5 | 50 |
| Homogenisation time (th, min) | X2 | 10 | 35 | 60 |
| Mixing speed (n, rpm) | X3 | 600 | 900 | 1200 |
| Independent variable | Variable levels | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| - 1 | 0 | 1 | ||
| Inlet air temperature (Ti, °C) | X1 | 160 | 175 | 190 |
| Proportion of GW (R, -) | X2 | 0.5 | 2 | 3.5 |
| Feed flow (Q, mL/min) | X3 | 6 | 8 | 10 |
| Run |
Th (°C) |
th (min) |
ts (min) |
TPC (mgGAE/gdb) | SPC (mgGAE/gdb) |
BD (g/cm3) |
TD (g/cm3) |
L* (−) |
a* (−) |
b* (−) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 30 | 30.0 | 30 | 119.07 ± 1.95 | 13.29 ± 0.66 | 0.11 ± 0.00 | 0.16 ± 0.00 | 65.98 ± 2.05 | 8.01 ± 0.28 | 3.62 ± 0.12 |
| 2 | 50 | 17.5 | 15 | 106.49 ± 1.99 | 7.82 ± 0.66 | 0.08 ± 0.00 | 0.13 ± 0.00 | 67.33 ± 1.93 | 8.24 ± 0.20 | 3.64 ± 0.22 |
| 3 | 50 | 17.5 | 45 | 113.46 ±1.92 | 9.43 ± 0.15 | 0.08 ± 0.00 | 0.11 ± 0.00 | 67.47 ± 4.20 | 7.76 ± 0.33 | 3.57 ± 0.21 |
| 4 | 40 | 5.0 | 45 | 115.12 ± 2.55 | 11.86 ± 0.67 | 0.08 ± 0.00 | 0.11 ± 0.00 | 63.36 ± 1.28 | 7.74 ± 0.18 | 3.28 ± 0.05 |
| 5 | 30 | 5.0 | 30 | 114.47 ± 1.16 | 9.98 ± 0.35 | 0.08 ± 0.00 | 0.11 ± 0.00 | 66.59 ± 0.85 | 8.33 ± 0.08 | 3.33 ± 0.05 |
| 6 | 40 | 17.5 | 30 | 159.29 ± 2.46 | 7.86 ± 0.80 | 0.08 ± 0.00 | 0.12 ± 0.00 | 63.91 ± 3.11 | 8.50 ± 0.16 | 3.59 ± 0.09 |
| 7 | 40 | 17.5 | 30 | 155.93 ± 1.74 | 7.28 ± 0.20 | 0.07 ± 0.00 | 0.11 ± 0.00 | 64.21 ± 3.14 | 8.42 ± 0.11 | 3.41 ± 0.13 |
| 8 | 50 | 5.0 | 30 | 137.01 ± 1.63 | 8.56 ± 0.57 | 0.07 ± 0.00 | 0.11 ± 0.00 | 66.81 ± 1.31 | 7.51 ± 0.14 | 3.22 ± 0.07 |
| 9 | 40 | 5.0 | 15 | 169.21 ± 2.28 | 9.25 ± 0.72 | 0.08 ± 0.00 | 0.11 ± 0.00 | 60.66 ± 0.64 | 7.40 ± 0.05 | 2.88 ± 0.09 |
| 10 | 30 | 17.5 | 45 | 157.06 ± 1.62 | 9.25 ± 0.74 | 0.07 ± 0.00 | 0.11 ± 0.00 | 62.44 ± 4.65 | 8.61 ± 0.76 | 3.69 ± 0.34 |
| 11 | 50 | 30.0 | 30 | 115.50 ± 3.76 | 7.11 ± 0.69 | 0.08 ± 0.00 | 0.13 ± 0.00 | 66.74 ± 1.87 | 7.05 ± 0.14 | 3.68 ± 0.05 |
| 12 | 30 | 17.5 | 15 | 119.53 ± 0.90 | 8.11 ± 0.75 | 0.06 ± 0.00 | 0.10 ± 0.00 | 62.41 ± 0.71 | 7.07 ± 0.05 | 3.42 ± 0.04 |
| 13 | 40 | 17.5 | 30 | 147.63 ± 2.31 | 7.2 ± 1.29 | 0.08 ± 0.00 | 0.11 ± 0.00 | 64.80 ± 2.68 | 6.90 ± 0.25 | 3.41 ± 0.07 |
| 14 | 40 | 30.0 | 45 | 122.13 ± 1.32 | 7.34 ± 0.95 | 0.07 ± 0.00 | 0.11 ± 0.00 | 59.01 ± 2.21 | 6.73 ± 0.06 | 3.24 ± 0.04 |
| 15 | 40 | 30.0 | 15 | 115.66 ± 1.80 | 12.00 ± 0.46 | 0.07 ± 0.00 | 0.11 ± 0.00 | 62.55 ± 2.18 | 8.25 ± 0.19 | 4.31 ± 0.15 |
| Response | Estimated coefficients of coded factors ¥ | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | A | B | C | AB | AC | BC | A2 | B2 | C2 | |
| EE | 95.173 | 0.5638 | -0.3725 | -0.0663 | 0.6300 | -0.4675 | 2.3000 ** | -1.1429 | -2.1004 | -1.1129 |
| wm | 5.970 | 0.0363 | 0.0013 | 0.0050 | -0.0175 | -0.0100 | -0.0050 | -0.0263 | -0.0013 | 0.0463 |
| Y | 93.773 | 2.7325 | -2.0263 | -0.0688 | -0.2625 | -0.8125 | -2.4400 | -3.2317 | -2.1342 | -4.6042 |
| WSI | 59.203 | -0.4488 | -0.8388 | -0.6825 | -2.3775 | 0.7050 | 2.2100 | -2.3704 | -0.8654 | -2.0879 |
| WAI | 10.167 | 0.088 | -1.9613 ** | 0.4425 | -0.3700 | -1.1125 ** | -0.3375 | -0.2408 | -0.4108 | -1.7833 ** |
| SP | 24.977 | 0.2850 | -4.9650 ** | 0.6350 | -2.1825 ** | -2.2425 ** | 0.2525 | -1.5496 | -1.3646 | -5.4996 ** |
| HR | 1.490 | -0.0175 | 0.0425 | 0.0100 | -0.0050 | -0.0550 | -0.0650 | 0.0275 | -0.0425 | 0.0125 |
| CI | 32.907 | -0.6875 | 2.0138 | 0.5638 | -0.2025 | -2.1625 | -3.1400 | 1.3192 | -1.9733 | 0.2767 |
| ΔEab | 22.813 | -1.0125** | 0.1075 | 0.1375 | -0.1325 | -0.1875 | 1.1925 ** | -1.9929 ** | 0.3621 | 1.5971 |
| Dependent variable | Predicted value | Experimentally determined value |
Deviation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| EE (%) | 95.17 | 93.88 | 1.36 |
| wm (%db) | 5.97 | 5.88 | 1.51 |
| Y (%) | 93.77 | 91.90 | 1.99 |
| WSI (%) | 59.20 | 55.77 | 5.79 |
| WAI (-) | 10.17 | 9.32 | 8.36 |
| SP (-) | 24.98 | 21.06 | 15.69 |
| HR (-) | 1.49 | 1.48 | 0.67 |
| CI (%) | 33 | 35 | 6 |
| ΔEab (-) | 22.81 | 22.88 | 0.31 |
| Run |
Th (°C) |
th (min) |
n (rpm) |
TPC (mgGAE/gdb) | SPC (mgGAE/gdb) |
BD (g/cm3) |
TD (g/cm3) |
L* (−) |
a* (−) |
b* (−) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 37.5 | 10 | 1200 | 134.70 ± 4.34 | 8.86 ± 0.53 | 0.06 ± 0.00 | 0.08 ± 0.00 | 61.77 ± 0.38 | 6.95 ± 0.03 | 2.72 ± 0.04 |
| 2 | 50 | 35 | 600 | 121.54 ± 2.39 | 8.30 ± 0.92 | 0.05 ± 0.00 | 0.07 ± 0.00 | 61.66 ± 1.36 | 6.67 ± 0.13 | 2.45 ± 0.06 |
| 3 | 50 | 60 | 900 | 147.75 ± 3.39 | 8.04 ± 0.92 | 0.06 ± 0.00 | 0.08 ± 0.00 | 55.35 ± 0.08 | 6.05 ± 0.01 | 2.36 ± 0.03 |
| 4 | 50 | 10 | 900 | 123.44 ± 9.81 | 8.51 ± 0.27 | 0.05 ± 0.00 | 0.07 ± 0.00 | 63.50 ± 1.29 | 6.94 ± 0.75 | 2.78 ± 0.17 |
| 5 | 37.5 | 35 | 900 | 123.43 ± 9.75 | 7.28 ± 0.79 | 0.07 ± 0.00 | 0.11 ± 0.00 | 69.60 ± 0.46 | 8.03 ± 0.03 | 3.06 ± 0.06 |
| 6 | 37.5 | 60 | 1200 | 130.92 ± 9.92 | 10.07 ± 0.33 | 0.06 ± 0.00 | 0.08 ± 0.00 | 64.52 ± 0.41 | 7.57 ± 0.07 | 2.97 ± 0.02 |
| 7 | 50 | 35 | 1200 | 138.83 ± 4.03 | 9.60 ± 0.35 | 0.08 ± 0.00 | 0.10 ± 0.00 | 66.72 ± 0.31 | 7.53 ± 0.12 | 3.22 ± 0.06 |
| 8 | 37.5 | 35 | 900 | 124.73 ± 2.61 | 7.42 ± 0.33 | 0.07 ± 0.00 | 0.11 ± 0.00 | 69.26 ± 0.68 | 8.41 ± 0.14 | 3.36 ± 0.21 |
| 9 | 25 | 35 | 1200 | 136.52 ± 2.79 | 8.51 ± 1.11 | 0.08 ± 0.00 | 0.11 ± 0.00 | 67.10 ± 1.77 | 6.13 ± 0.04 | 4.08 ± 0.06 |
| 10 | 37.5 | 10 | 600 | 132.08 ± 3.86 | 8.42 ± 0.69 | 0.07 ± 0.00 | 0.10 ± 0.00 | 67.28 ± 1.70 | 8.18 ± 0.18 | 3.52 ± 0.06 |
| 11 | 25 | 60 | 900 | 136.44 ± 6.68 | 8.95 ± 1.64 | 0.09 ± 0.00 | 0.13 ± 0.00 | 57.95 ± 0.48 | 7.51 ± 0.04 | 2.63 ± 0.03 |
| 12 | 37.5 | 60 | 600 | 113.31 ± 1.09 | 9.78 ± 0.20 | 0.06 ± 0.00 | 0.09 ± 0.00 | 59.76 ± 1.36 | 7.04 ± 0.22 | 2.15 ± 0.06 |
| 13 | 25 | 10 | 900 | 131.26 ± 3.93 | 8.29 ± 0.78 | 0.07 ± 0.00 | 0.10 ± 0.00 | 58.90 ± 0.93 | 7.23 ± 0.09 | 2.52 ± 0.06 |
| 14 | 37.5 | 35 | 900 | 124.78 ± 3.20 | 7.38 ± 0.26 | 0.07 ± 0.00 | 0.11 ± 0.00 | 69.42 ± 0.83 | 8.19 ± 0.20 | 3.14 ± 0.06 |
| 15 | 25 | 35 | 600 | 138.07 ± 3.70 | 9.29 ± 0.77 | 0.08 ± 0.00 | 0.13 ± 0.00 | 61.72 ± 0.16 | 8.67 ± 0.07 | 3.56 ± 0.08 |
| Response | Estimated coefficients of coded factors ¥ | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | A | B | C | AB | AC | BC | A2 | B2 | C2 | |
| EE | 93.2033 | 0.04375 | -0.27625 | -0.1725 | -0.3325 | -0.275 | 0.155 | -0.140417 | 0.0595833 | 0.317083 |
| wm | 6.01333 | -0.025 | -0.00375 | 0.03125 | -0.0375 | 0.0125 | -0.005 | -0.0191667 | -0.0316667 | -0.00667 |
| Y | 72.4867 | 5.1125 | -0.1575 | 0.5575 | -3.5425 | 2.3125 | 3.2625 | 4.27042 | 1.20542 | -1.00458 |
| WSI | 56.14 | 1.40875 | -0.57625 | 0.305 | -2.895 | -0.1825 | 0.4325 | -2.3425 | 2.9425 | 0.79 |
| WAI | 9.37333 | 1.3625 | 0.5375 | 1.2625 | 0.9925 | 0.9075 | -0.0775 | 1.18208 | 0.147083 | 0.732063 |
| SP | 21.91 | 3.84 | 0.81 | 2.795 | 0.6275 | 1.9225 | 0.1025 | 1.30125 | 1.74625 | 2.07625 |
| HR | 1.45 | -0.055 | -0.02125 | -0.05375 | 0.0675 | -0.0325 | -0.025 | -0.03 | 0.0575 | -0.0175 |
| CI | 30.72 | -2.53625 | -0.84375 | -2.5825 | 2.885 | -1.7175 | -1.1425 | -1.5475 | 2.6475 | -0.7 |
| ΔEab | 25.32 | -0.9675 | 0.495 | -0.5725 | 0.78 | 0.25 | 0.365 | -0.0025 | -2.3025 | -1.1225 |
| Dependent variable | Predicted value | Experimentally determined value |
Deviation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| EE (%) | 94.70 | 91.45 | 3.40 |
| wm (%db) | 5.92 | 5.96 | 0.70 |
| Y (%) | 86.16 | 81.11 | 5.90 |
| WSI (%) | 62.72 | 52.46 | 16.40 |
| WAI (-) | 9.02 | 9.76 | 8.20 |
| SP (-) | 24.82 | 20.54 | 17.20 |
| HR (-) | 1.42 | 1.42 | 0.00 |
| CI (%) | 32 | 30 | 6 |
| ΔEab (-) | 20.34 | 22.79 | 12.00 |
| Run |
Ti (°C) |
R (–) |
Q (mL/min) |
BD (g/cm3) |
TD (g/cm3) |
L* (−) |
a* (−) |
b* (−) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 170 | 20 | 2.0 | 0.06 ± 0.00 | 0.08 ± 0.00 | 62.75 ± 1.06 | 6.12 ± 0.05 | 4.49 ± 0.09 |
| 2 | 180 | 20 | 3.5 | 0.07 ± 0.00 | 0.08 ± 0.00 | 61.56 ± 2.16 | 8.62 ± 0.15 | 4.84 ± 0.08 |
| 3 | 170 | 25 | 0.5 | 0.07 ± 0.00 | 0.10 ± 0.00 | 63.63 ± 1.19 | 8.92 ± 0.13 | 3.61 ± 1.08 |
| 4 | 180 | 15 | 2.0 | 0.08 ± 0.00 | 0.10 ± 0.00 | 65.28 ± 0.97 | 7.73 ± 0.17 | 4.34 ± 0.03 |
| 5 | 170 | 20 | 2.0 | 0.13 ± 0.00 | 0.20 ± 0.00 | 58.04 ± 2.21 | 13.54 ± 0.48 | 4.95 ± 0.11 |
| 6 | 160 | 15 | 2.0 | 0.06 ± 0.00 | 0.09 ± 0.00 | 59.30 ± 1.49 | 8.16 ± 0.17 | 7.44 ± 0.26 |
| 7 | 180 | 20 | 0.5 | 0.15 ± 0.00 | 0.25 ± 0.00 | 53.61 ± 2.03 | 11.28 ± 0.27 | 4.69 ± 0.09 |
| 8 | 170 | 20 | 2.0 | 0.13 ± 0.00 | 0.22 ± 0.00 | 49.36 ± 0.92 | 14.32 ± 0.62 | 4.73 ± 0.06 |
| 9 | 180 | 25 | 2.0 | 0.08 ± 0.00 | 0.11 ± 0.00 | 62.35 ± 2.07 | 8.08 ± 0.09 | 4.59 ± 0.16 |
| 10 | 170 | 15 | 3.5 | 0.08 ± 0.00 | 0.11 ± 0.00 | 62.60 ± 1.65 | 7.11 ± 0.21 | 4.19 ± 0.11 |
| 11 | 160 | 20 | 0.5 | 0.08 ± 0.00 | 0.10 ± 0.00 | 61.31 ± 2.51 | 7.48 ± 0.08 | 4.04 ± 0.16 |
| 12 | 170 | 25 | 3.5 | 0.07 ± 0.00 | 0.10 ± 0.00 | 62.72 ± 1.15 | 9.19 ± 0.55 | 4.14 ± 0.10 |
| 13 | 170 | 15 | 0.5 | 0.08 ± 0.00 | 0.11 ± 0.00 | 59.74 ± 3.18 | 9.39 ± 0.54 | 4.38 ± 0.22 |
| 14 | 160 | 25 | 2.0 | 0.07 ± 0.00 | 0.10 ± 0.00 | 62.79 ± 1.64 | 8.96 ± 0.20 | 4.29 ± 0.10 |
| 15 | 160 | 20 | 3.5 | 0.11 ± 0.00 | 0.20 ± 0.00 | 51.35 ± 0.70 | 13.96 ± 0.11 | 4.03 ± 0.08 |
| Response | Estimated coefficients of coded factors ¥ | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | A | B | C | AB | AC | BC | A2 | B2 | C2 | |
| TPC | 120.37 | 8.1025 | -38.7138** | -13.2038 | 1.9525 | 12.3775 | 8.99 | -1.68 | 21.3375 | -5.4325 |
| SPC | 6.49 | 1.87 | -17.5113** | -2.59125** | -2.265 | 0.33 | 3.3425** | 0.83125 | 14.2738** | -0.13625 |
| EE | 94.61 | -0.7538 | 9.075** | 0.62125 | 1.3475 | 0.625 | -0.8125 | -0.52 | -6.7125** | -0.695 |
| wm | 4.9267 | 0.5588** | 0.0575 | 0.40625** | -0.4925 | -2.49·10-17 | -0.1925 | 0.8442** | 0.5367 | 0.17917 |
| Y | 97.137 | 3.8075 | -2.5988 | -2.47125 | -0.4975 | 7.3075 | 0.16 | -5.69083 | 2.97667 | -4.0533 |
| WSI | 51.23 | -0.41375 | 7.01** | -0.35625 | -1.5925 | -2.32 | -2.2825 | -0.93 | 3.1225 | 4.71 |
| WAI | 5.1333 | -0.0575 | -0.5025** | -0.07 | -0.315** | 0.42** | -0.045 | -0.00167 | -0.1767** | -0.10167 |
| SP | 10.537 | -0.3825 | 0.66875 | -0.33875 | -1.1425 | 0.3425 | -0.87 | -0.19083 | 0.601667 | 0.831667 |
| HR | 1.4 | -0.0488** | -0.1413** | 0.0175 | 0.105** | 0.0075 | 0.0225 | -0.0525** | 0.1375** | -0.005 |
| CI | 28.57 | -1.9363** | -6.1063** | 1.09 | 4.515** | 0.6275 | 1.0775 | -2.975** | 6** | -0.2625 |
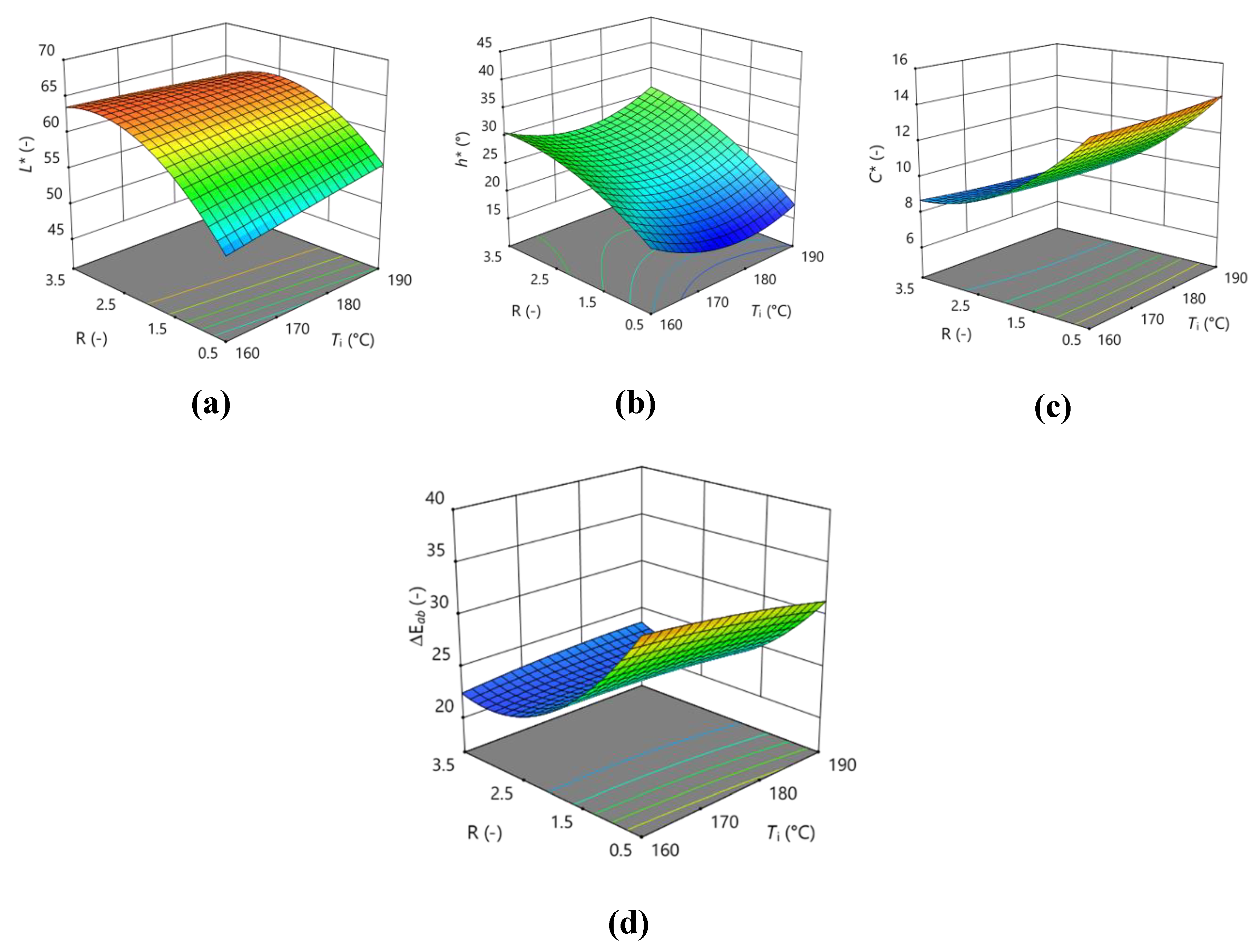
| L* | 63.0467 | 0.60625 | 4.58125** | -0.4125 | -1.3125 | 1.04 | -1 | -0.09708 | -4.58708** | -1.47958 |
| h* | 23.91 | -0.675 | 5.95875** | 1.74875 | 0.99 | -4.33 | -0.8425 | 3.78625 | -2.48125 | 3.81875 |
| C* | 9.89 | -0.0875 | -2.825** | -0.155 | -0.2 | -0.425 | 0.455 | 0.1025 | 1.2675 | 0.0525 |
| ΔEab | 23.847 | -0.4175 | -4.91** | 0.0175 | 0.975 | -0.36 | 1.115 | -0.2833 | 4.35167** | 0.70167 |
| Dependent variable | Predicted value | Experimentally determinate value |
Deviation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| EE (%) | 96.95 | 95.47 | 1.53 |
| wm (%db) | 4.89 | 4.98 | 1.81 |
| Y (%) | 96.67 | 96.10 | 0.59 |
| WSI (%) | 57.94 | 57.47 | 0.81 |
| WAI (-) | 4.98 | 4.37 | 12.25 |
| SP (-) | 11.93 | 10.28 | 13.83 |
| HR (-) | 1.35 | 1.36 | 0.74 |
| CI (%) | 26 | 26 | 0 |
| ΔEab (-) | 24.48 | 23.73 | 3.06 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





