1. Introduction
Human Papillomavirus is a small DNA virus with a genome of almost 8000 bases of length. The genome is structured into three different regions: an upstream non-coding regulatory region (URR) or Long Control Region (LCR) containing regulatory elements for viral replication and transcription; an early region (E1, E2, E4-E7 genes) encoding E6 and E7 oncogenic proteins and a late region encoding L1 and L2 capsid proteins [
1].
This virus is responsible for the most common sexually transmitted infection worldwide and causes more than 340 000 deaths each year for cervical cancer in women [
2]. More than 200 genotypes are known up to now but just twelve (HPV16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 56, 58, 59) are recognized as carcinogenic for human by the International Agency of Research on Cancer (IARC), and in particular persistent infection of one of these high-risk HPV (hrHPV) genotypes is associated with the increasing risk of cervical pre-cancer and cancer lesion development [
3,
4,
5,
6]. Luckily, most of the infections are cleared spontaneously but some of them persist which may lead to the onset of cervical dysplasia. Different virus-related risk factors have been suggested to be correlated to the persistence such as: infection with specific genotype, high viral load, the over-expression of oncogenic transcripts and also the presence of specific viral lineage variants [
7,
8,
9,
10].
A difference of the complete genome of a specific genotype between 1.0% and 10% defines a distinct lineage and the further classification into sublineages is made if the nucleotide difference between two variants from the same lineage is between 0.5% and 1.0% [
7]. Presently, many mutations have already been published for the different hrHPV genotypes and distinct lineages have been described [
8,
11]. Even if the HPV genome exhibits a very low mutation rate compared to other viruses [
12], there are some specific parts of the genome that should be monitored because directly related to the oncogenesis as the two oncogenes E6 and E7 or involved in the immune system activation such as the L1 gene that encodes for the main surface capsid protein [
5,
13,
14,
15,
16]. Indeed, currently available vaccines are composed of virus-like particles (VLPs) made from L1 protein particles that are characterized by the capacity of self-assembling and inducing the immune system to produce genotype-specific antibodies. This protein has hypervariable immune-dominant regions that show high levels of polymorphism in and among HPV types. The increase of non-synonymous mutations in the L1 protein modifies the original structure of the protein and could lead to a subsequent advantage to escape immune response [
17,
18].
Different studies have already reported the presence of variants, single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and amino acid mutations for some hrHPV genotypes, especially for HPV16 and HPV18, the two genotypes associated with most of the cases of cervical cancer [
19,
20,
21,
22]. Less is reported for less common tumor-associated hrHPV genotypes such as HPV51 [
6,
23,
24,
25]. HPV51 has an worldwide prevalence of 1.1% in women with normal cervical cytology, 8.8% and 5.7% among women with low and high-grade precancerous lesion, respectively, with rates differing depending on the geographical area [
26].
To better understand the presence of variants and genetic variation of HPV51, this study aimed to perform a phylogenetic analysis of the E6, E7 and L1 regions, the study of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and amino acid mutations to detect the hrHPV variants circulating in the women with a recent cervical dysplasia.
2. Results
2.1. Study population
353 patients were enrolled at the baseline at the Colposcopy Centre in Monza and 81 in Sassari. The median age of women was 37 years (Interquartile Range (IQR): 30-45 years) and 45 (IQR:37-51) at Monza (Lombardy Region) and Sassari (Sardinia) colposcopy centers, respectively. Data regarding the cytological results is reported in
Table 1 and classified as follow: HSIL (high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion); ASC-H (atypical squamous cells, cannot exclude HSIL); LSIL (low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion); ASC-US (atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance); AGC (atypical glandular cells); and NILM (negative for intraepithelial lesion or malignancy).
Women found to be HPV-positive at the time of the colposcopy visit were 128 (128/353; 36.3%) and 48 (48/81; 59.3%) at Monza and Sassari colposcopy centers, respectively.
2.2. HPV DNA detection
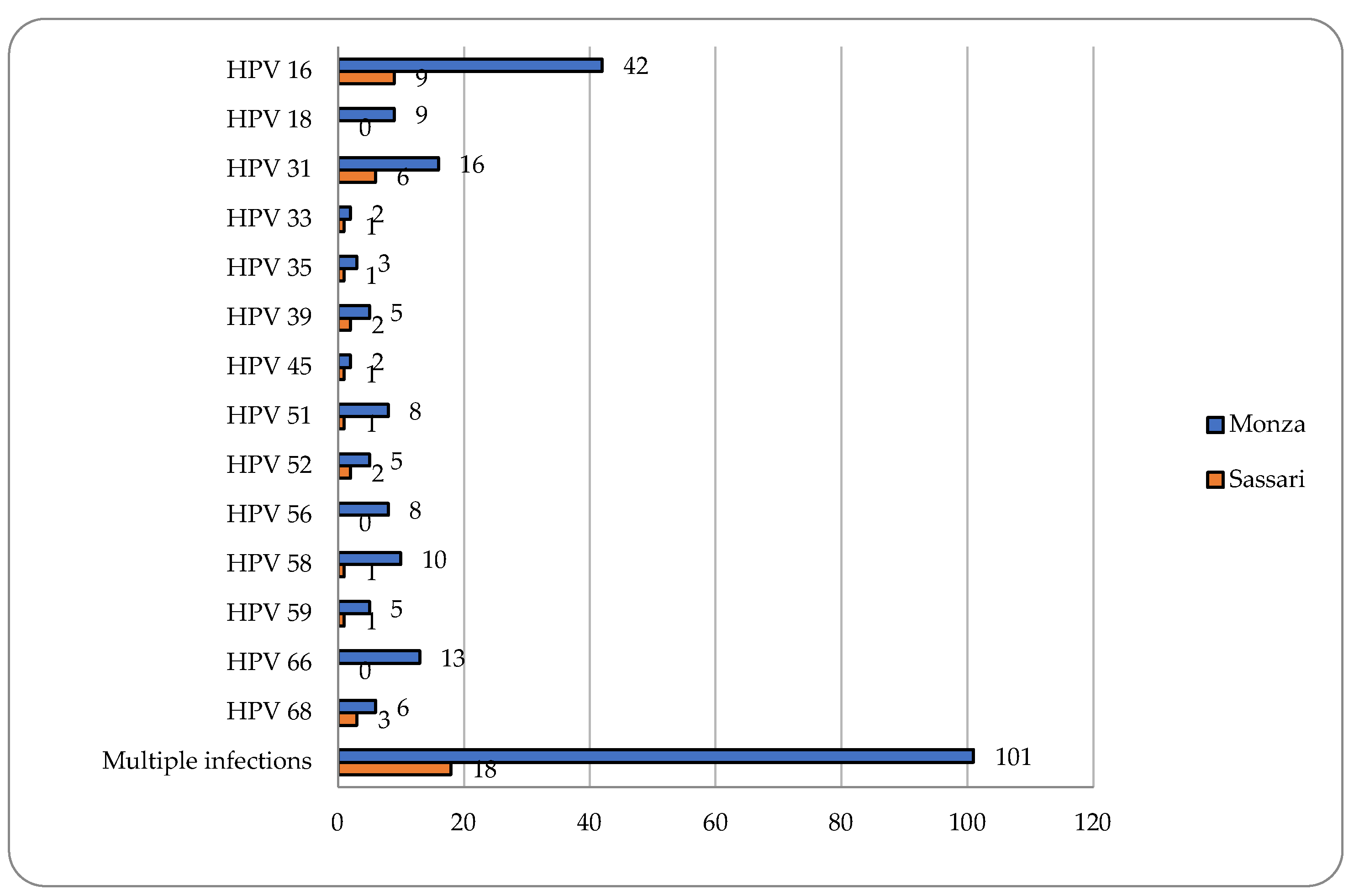
Cervical samples were available for 351 women enrolled in Monza and for all 81 women enrolled in Sassari. A positivity for HPV DNA was observed in 67% (235/351) and 56.8% (46/81) women in Monza and in Sassari, respectively. Multiple hrHPV infections were found to be very frequent in both colposcopy centers (43% and 39.1%) and HPV16 followed by HPV31 resulted the two most common HPV genotypes detected (
Figure 1).
Among women referred to the colposcopy center in Monza, a positivity for HPV51 of 7.4% (26/351) of cervical samples has been demonstrated. 30.8% (8/26) and 69.2% (18/26) were single and multiple infections, respectively. Six women infected with HPV51 were positive at colposcopy and two showed Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia of grade 2 or higher (CIN2+). The positivity for HPV51 among women attending the center in Sassari resulted 13.6% (11/81). All detected infections were hrHPV multiple infections excepted for one infection (
Table 2).
2.3. HPV51 E6 and E7 genetic variation
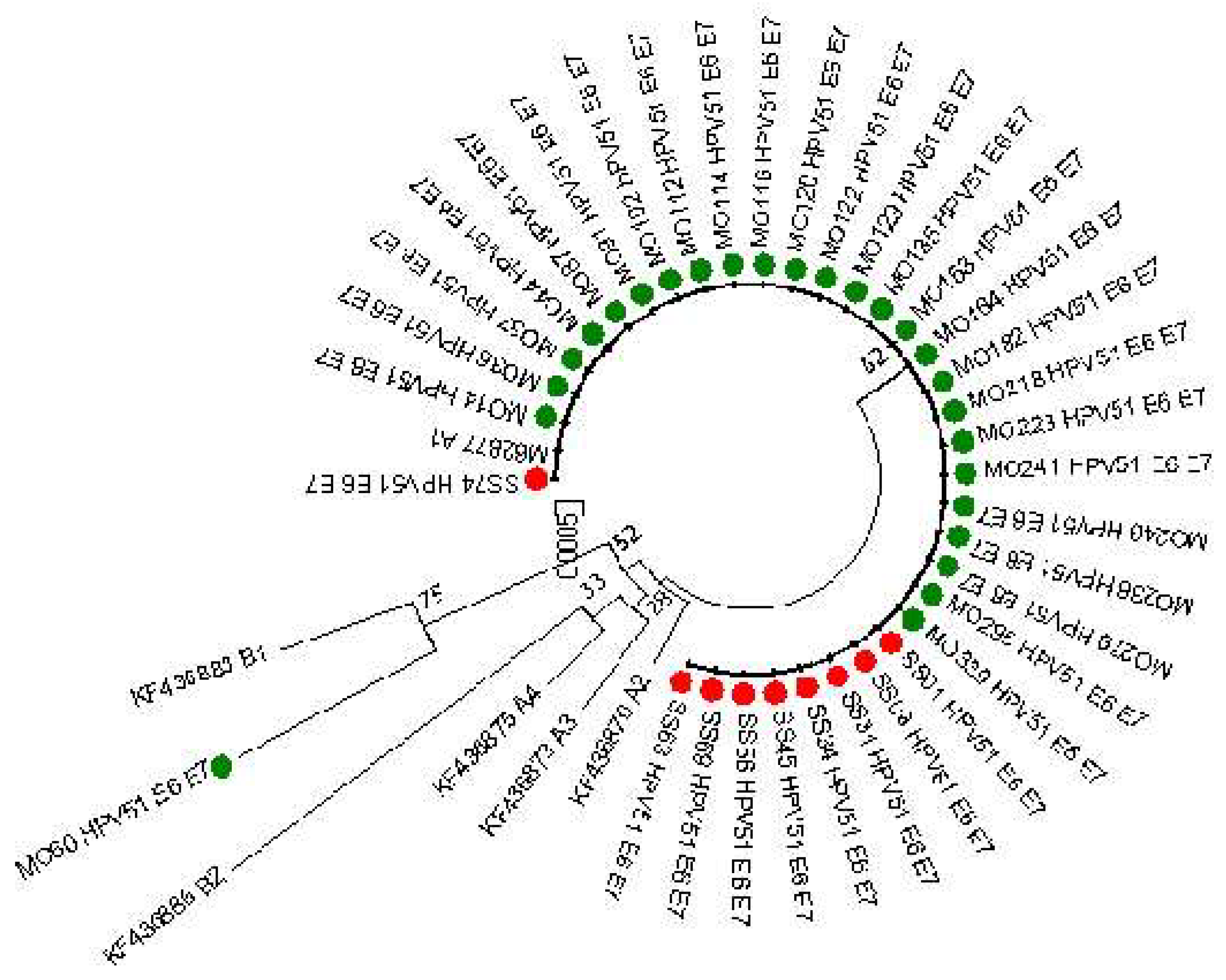
E6 and E7 sequences (769 nucleotides, 151 and 101 aminoacids for E6 and E7, respectively) were obtained from 35 patients (26 from Monza and 9 from Sassari). As reported in
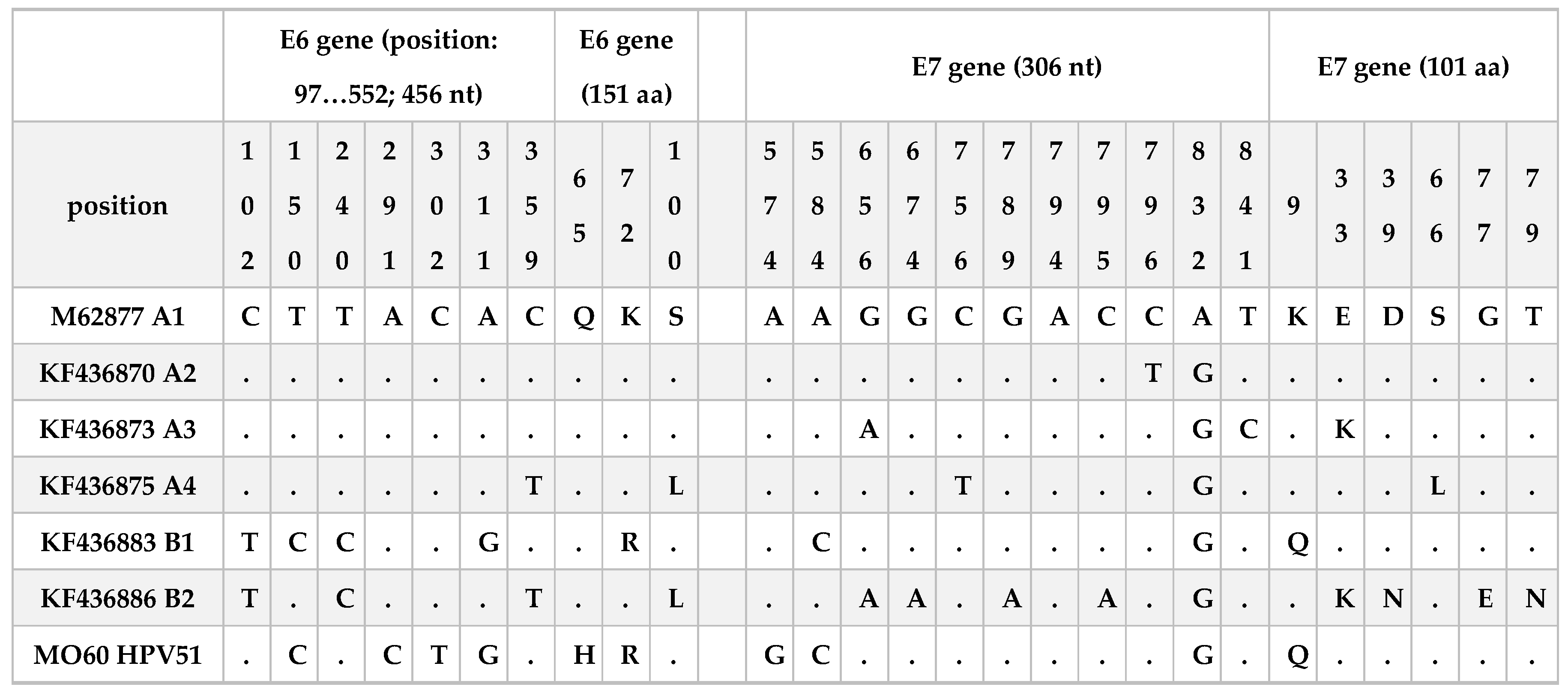
Figure 2 almost all the sequences analyses clustered into lineage A. Only the sequence MO60 resulted similar to the B1 reference sequence but including other mutations reported in
Table 3. This infection was associated with a LSIL cytology result.
2.4. HPV51 L1 mutations and selective pressure analysis
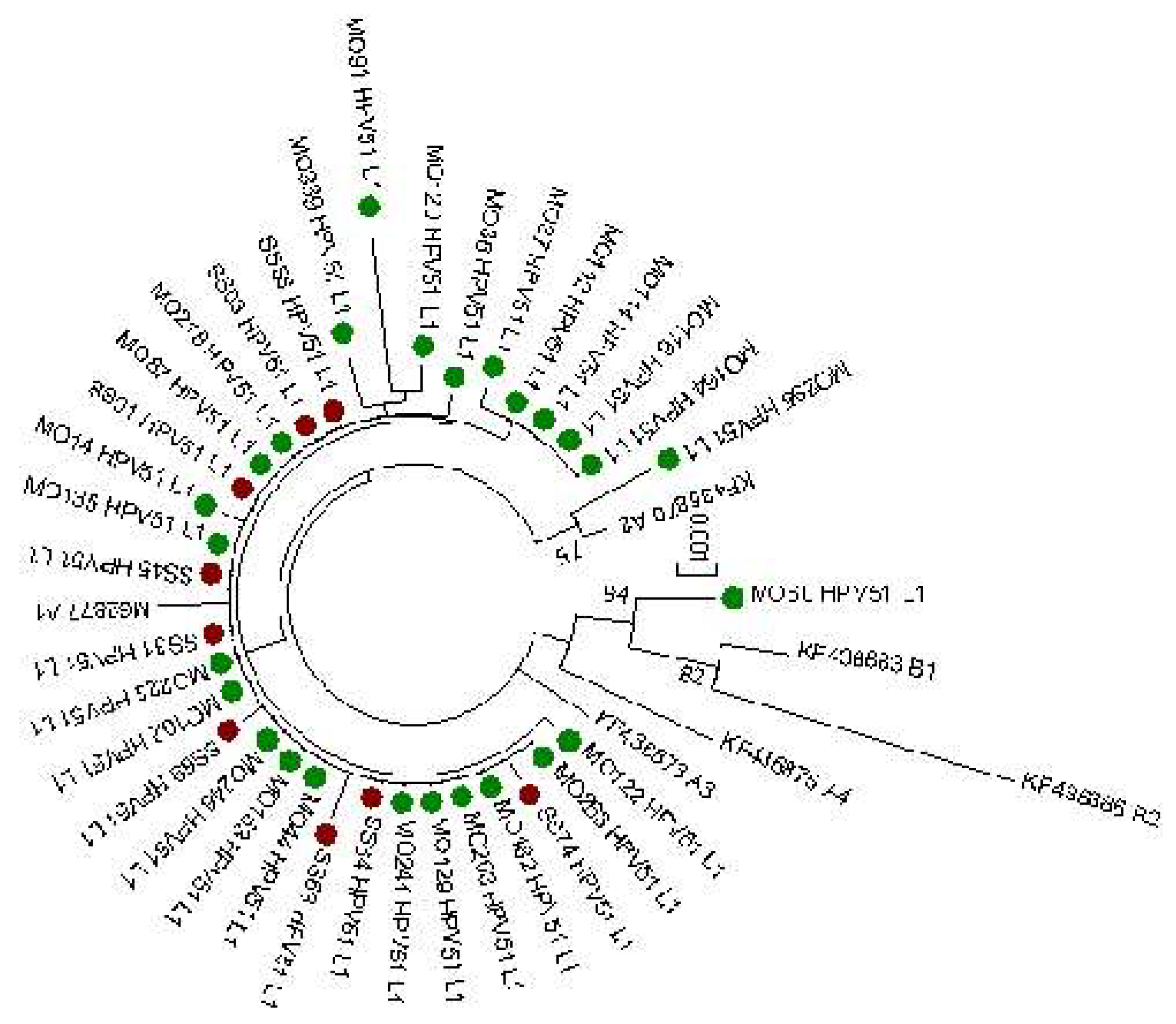
L1 sequences (1515 bp) obtained from the same 35 cervical samples were also evaluated. The phylogenetic tree of L1 sequences is reported in
Figure 3 and confirmed the results observed from E6 and E7 lineage analysis that 34 out 35 sequences clustered into A lineage. On the contrary, a greater variability was observed in the L1 gene compared to E6 and E7. Tables reporting specific nucleotide and amino acid mutations detected are reported in
Supplementary Tables S1 and S2. 37 nucleotide polymorphism sites were identified (14 non-synonymous and 13 synonymous mutations) compared to the M62777 reference sequence. All sequences have shown the presence of 3 nucleotide polymorphisms T6311G, A6312T and G6313A that are related to the two aminoacidic mutations V264G and G265S. The other most common nucleotide mutation found was A6167G detected in 7 analyzed sequences. No significant correlation was found between the detected mutation and the clinical data (
Supplementary Table S3). No sites under diversifying positive selection at p≤0.1 were defined using FEL analysis.
3. Discussion
HPV is well known to be the common sexually transmitted pathogen but luckily only few infections tend to persist and cause pre-cancerous and cancerous lesions. The main cause associated with the persistence is related to the HPV genotype that is infecting the cervix [
13]. The IARC has classified 12 hrHPV genotypes as carcinogenic for humans with HPV16 and HPV18 the most common related to cervical and other cancers [
19,
22]. However, even among these two genotypes infections the majority are transient and spontaneously resolve suggesting that other co-factors are necessary to support viral persistence. Some studies have suggested that possible virus-related co-factors could also be high viral loads, the over-expression of E6 and E7 oncogenic transcripts and the presence of specific viral lineage variants [
8]. Although different studies have previously reported the different viral variants distributions for HPV16 and HPV18 [
27,
28,
29,
30,
31], less is known regarding the other hrHPV genotypes such as HPV51 [
8,
23,
25,
32,
33]. In our study we found a prevalence of 7.3% and 13.6% in Monza and Sassari respectively, and most of these infections were found as co-infections with other high-risk HPV genotypes and associated with ≤CIN2 lesions. These results are in keeping with other data reported in literature regarding the HPV51 prevalence and the low risk associated with in cervical lesion development related to infection with this specific hrHPV type [
26]. Even if the results obtained are limited, the higher HPV51 prevalence detected in Sardinia compared to Lombardy have confirmed the data reported in a previous study conducted by Piana and colleagues [
34].
From the analysis of HPV51 sequences obtained from the E6 and E7 oncogenes, we have observed that most of the sequences were equal to the reference (M62777) and the phylogenetic analysis confirmed that almost all were clustered into A lineage. These results confirmed what also reported by Xu and colleagues [
32] that E6 and E7 oncogenes are highly conserved. In the present work, we found only one sequence with mutations in both genes. In particular, 4 nucleotide polymorphisms were observed in the E6 gene (T150C, A291C, C302T, A311G) two of them associated with an aminoacidic change Q65H and K75R. Regarding E7 three nucleotide mutations were observed (A574G, A584C and A832G), one of them was a non-synonymous mutation associated to the aminoacidic change K9Q. T150C, A311G and A584C are mutations in common with KF436883 reference sequence and associated to the B1 sub-lineage. The A832G mutation was also described among sequences of two other studies conducted in China [
25,
32]. The analysis of the L1 sequence obtained from the same samples shows the presence of higher rates of nucleotide mutations (A6167G, T6311G, A6312T, G6313A, G6570A, A6580C, A6551G, A6681G, T6708C, A6784C, T6798C, A6807G, A6882G) compared to other samples analyzed in this study. This infection was related to a LSIL cytological result and a negative colposcopy visit. A significant risk of CIN3+ associated with HPV51 variant B compared to variant A was previously reported by Schiffman and colleagues [
8]. Unfortunately, we do not have information regarding the clinical evolution of this infection to make some hypotheses regarding the association of these mutations to the clinical data. Regarding the L1 aminoacidic mutations, all HPV51 analysed sequences showed the presence of V264L, G265S mutations compared to the reference sequence. These changes together with I52L and T354P were previously reported in literature [
25,
32,
35]. No difference in viral variants was observed among the two Italian regions. Even if this study reported the analysis of few HPV51 sequences, to the best of our knowledge, no other data regarding HPV51 viral variants circulating in Italy have been previously reported. This study contributes to implement sequence data related to the molecular epidemiology of HPV51, but additional analysis on a larger number of sequences and associated clinical data is necessary to better understand the role of HPV variants in cervical lesions development.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study population and sample collection
Women with a recent diagnosis of cervical dysplasia and attending the Colposcopy Clinic of IRCSS San Gerardo dei Tintori, (Monza, Lombary, Italy) and of Coordinamento Consultori Familiari, ASSL Sassari (Sardinia) were enrolled after signing the inform consent. A cervical specimen using the L-shaped Endocervical/Esocervical FLOQSwab® (Copan Spa, Italy) was collected from each woman during the colposcopy examination and resuspended into 20 ml of ThinPrep® PreservCyt® Solution (HOLOGIC™). Clinical data regarding cytology, biopsy and conization were also collected. Pap test was repeated in case of it has been performed over 6 months before the date of the colposcopy and biopsy examination or conization treatment was performed depending on colposcopy result. Cytological findings were classified according to the 2001 Bethesda System [
28,
36] as follow: HSIL (High grade squamous intraepithelial lesion); ASCH (Atypical squamous cells, cannot exclude HSIL); LSIL (Low grade squamous intraepithelial lesion); ASCUS (Atypical squamous cells of un-determined significance); AGC (Atypical glandular cells); NILM (negative for intraepithelial lesion or malignancy). Histological finding was reported as Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia grade 1, 2 or 3 (CIN 1, 2 or 3), squamous cell carcinoma, adenocarcinoma or adenosquamous carcinoma [
37]. All samples were transported and tested at the Clinical Microbiology Laboratory of the Department of Medicine and Surgery, University of Milano-Bicocca.
4.2. DNA extraction and HPV detection
After arriving to the laboratory, samples were shaken vigorously for 30 seconds and aliquoted in cryovials. One aliquot was used for nucleic acids extraction. The STARMag 96x4 Universal Cartridge Kit (Seegene, Korea) on Microlab Nimbus was used for the extraction starting from 200 µl of sample and using an elution volume of 100 µl. HPV detection and genotyping was performed using a commercial kit, Anyplex™II HR HPV Detection, (Seegene, Korea) able to identify 14 hr-HPV (16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 56, 58, 59, 66 and 68) using CFX96 thermocycler (Bio-Rad). DNA detection was performed with 5 μl DNA in 20 μl per reaction. Data recording and interpretation were performed with the Seegene Viewer software, according to the manufacturer's instructions. Viral variants analysis was conducted from cervical samples of women resulted positive for HPV51.
4.3. PCR Amplification and Sequencing
Previously described PCR protocols were used to obtain amplicons of E6, E7 and L1 genes of HPV 51 [
25]. HPV DNA amplification was performed in a 50 μL reaction mix containing GoTaq® Long PCR MasterMix (Promega, Madison, WI, USA), 0.75 μM of primer (forward and reverse) and 5 μL of the template sample. Amplicons were visualized on 2% agarose gel. Nucleotide sequences were obtained through the Sanger sequencing method.
4.4. Phylogenetic Analysis
Sequences were aligned using ClustalW software and Phylogenetic analysis was performed using a distance-based neighbour joining method (NJ) [
38] and Kimura two-parameter model [
39] implemented in the MEGA version 7 program [
40]. Reference sequences of lineages A1 (M62877), A2 (KF436870), A3 (KF436873), A4 (KF436875), B1 (KF436883), and B2 (KF436886) were obtained from Papilloma Episteme (PaVE,
https://pave.niaid.nih.gov). The reliability of the observed clades was proved with internal node bootstrap values (after 1000 replicates). All sequences were submitted to the NCBI database and their accession numbers in GenBank are from (to be defined).
4.5. L1 sequences and selective pressure
Fixed effects likelihood (FEL) [
41] using the DataMonkey 2.0 server [
42] (
www.datamonkey.org) was used to better understand the presence of individual sites subject to pervasive positive (shown by a dN/dS ratio>1) or purifying selection.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: C.E.C., A.F.P., R.P., F.L; methodology, M.M., C.V., C.G., F.P., I.S., N.M. and R.N.; formal analysis, M.M., C.G.; investigation, C.E.C.; data curation, M.M, C.G, M.L.D.M., R.P., I.S and R.F; writing—original draft preparation, M.M. and C.G.; writing—review and editing, M.M., C.G., C.V., M.L.D.M., F.P., I.S., N.M.,A.F.P, R.P., R.N., R.F., F.L. and C.E.C.; supervision, C.E.C.; project administration, C.E.C and M.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Fondazione Cariplo, grant number 2019-1558”.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by Ethics Committee of University of Milano-Bicocca (protocol numbers 0037320/2017 and 0086409/2018) and by Ethical Committee of ATS Sardegna (Prot. 458/2022/CE).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Final study datasets generated by the study are stored locally and securely at the University of Milano-Bicocca. Anonymized data will be available by request to the corresponding author on a case-by-case basis pending approval by the University of Milano-Bicocca. All sequences were submitted to the NCBI database and their accession numbers in GenBank are from (to be defined).
Acknowledgments
The study group received free vaginal self-sample collection devices from Copan Italia Spa (Brescia, Italy), free Colli-pee® (20 mL) (Novosanis, Belgium), and a STARMag 96 × 4 Universal Cartridge Kit and Anyplex HPV28 kits from Seegene (Korea).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- de Villiers, E.M.; Fauquet, C.; Broker, T.R.; Bernard, H.U.; zur Hausen, H. Classification of papillomaviruses. Virology 2004, 324, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferlay, J.E.M.; Lam, F.; Laversanne, M.; Colombet, M.; Mery, L.; Piñeros, M.; Znaor, A.; Soerjomataram, I.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Observatory: Cancer Today. Lyon, France: International Agency for Research on Cancer. Available online: (accessed on 17/06/2024).
- Mühr, L.S.A.; Eklund, C.; Dillner, J. Towards quality and order in human papillomavirus research. Virology 2018, 519, 74–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Humans, I.W.G.o.t.E.o.C.R.t. Biological agents. Volume 100 B. A review of human carcinogens. IARC Monogr Eval Carcinog Risks Hum 2012, 100, 1–441. [Google Scholar]
- zur Hausen, H. Papillomaviruses in the causation of human cancers - a brief historical account. Virology 2009, 384, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernard, H.U.; Burk, R.D.; Chen, Z.; van Doorslaer, K.; zur Hausen, H.; de Villiers, E.M. Classification of papillomaviruses (PVs) based on 189 PV types and proposal of taxonomic amendments. Virology 2010, 401, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burk, R.D.; Harari, A.; Chen, Z. Human papillomavirus genome variants. Virology 2013, 445, 232–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiffman, M.; Rodriguez, A.C.; Chen, Z.; Wacholder, S.; Herrero, R.; Hildesheim, A.; Desalle, R.; Befano, B.; Yu, K.; Safaeian, M.; et al. A population-based prospective study of carcinogenic human papillomavirus variant lineages, viral persistence, and cervical neoplasia. Cancer Res 2010, 70, 3159–3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.C.; Schiffman, M.; Lin, C.Y.; Pan, M.H.; You, S.L.; Chuang, L.C.; Hsieh, C.Y.; Liaw, K.L.; Hsing, A.W.; Chen, C.J.; et al. Persistence of Type-Specific Human Papillomavirus Infection and Increased Long-term Risk of Cervical Cancer. Jnci-Journal of the National Cancer Institute 2011, 103, 1387–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernard, H.U.; Calleja-Macias, I.E.; Dunn, S.T. Genome variation of human papillomavirus types: Phylogenetic and medical implications. International Journal of Cancer 2006, 118, 1071–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Schiffman, M.; Herrero, R.; DeSalle, R.; Anastos, K.; Segondy, M.; Sahasrabuddhe, V.V.; Gravitt, P.E.; Hsing, A.W.; Burk, R.D. Evolution and taxonomic classification of alphapapillomavirus 7 complete genomes: HPV18, HPV39, HPV45, HPV59, HPV68 and HPV70. PLoS One 2013, 8, e72565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zehender, G.; Frati, E.R.; Martinelli, M.; Bianchi, S.; Amendola, A.; Ebranati, E.; Ciccozzi, M.; Galli, M.; Lai, A.; Tanzi, E. Dating the origin and dispersal of Human Papillomavirus type 16 on the basis of ancestral human migrations. Infection Genetics and Evolution 2016, 39, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- zur Hausen, H. Papillomaviruses and cancer: from basic studies to clinical application. Nat Rev Cancer 2002, 2, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- zur Hausen, H. Papillomavirus infections--a major cause of human cancers. Biochim Biophys Acta 1996, 1288, F55–F78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanley, M.A. Epithelial cell responses to infection with human papillomavirus. Clin Microbiol Rev 2012, 25, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pattyn, J.; Van Keer, S.; Téblick, L.; Van Damme, P.; Vorsters, A. HPV DNA detection in urine samples of women: 'an efficacious and accurate alternative to cervical samples?'. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther 2019, 17, 755–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christensen, N.D.; Dillner, J.; Eklund, C.; Carter, J.J.; Wipf, G.C.; Reed, C.A.; Cladel, N.M.; Galloway, D.A. Surface conformational and linear epitopes on HPV-16 and HPV-18 L1 virus-like particles as defined by monoclonal antibodies. Virology 1996, 223, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsakogiannis, D.; Nikolaidis, M.; Zagouri, F.; Zografos, E.; Kottaridi, C.; Kyriakopoulou, Z.; Tzioga, L.; Markoulatos, P.; Amoutzias, G.D.; Bletsa, G. Mutation Profile of HPV16 L1 and L2 Genes in Different Geographic Areas. Viruses 2022, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsson, G.L.; Helenius, G.; Andersson, S.; Sorbe, B.; Karlsson, M.G. Prognostic impact of human papilloma virus (HPV) genotyping and HPV-16 subtyping in vaginal carcinoma. Gynecol Oncol 2013, 129, 406–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gauthier, B.; Cerigo, H.; Coutlée, F.; Franco, E.L.; Brassard, P. Persistence of human papillomavirus 16, 18 and 52 variants in Inuit women from Northern Quebec, Canada. Int J Circumpolar Health 2018, 77, 1556556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacevic, G.; Milosevic, V.; Knezevic, P.; Knezevic, A.; Knezevic, I.; Radovanov, J.; Nikolic, N.; Patic, A.; Petrovic, V.; Hrnjakovic Cvjetkovic, I.; et al. Prevalence of oncogenic Human papillomavirus and genetic diversity in the L1 gene of HPV16 HPV 18 HPV31 and HPV33 found in women from Vojvodina Province Serbia. Biologicals 2019, 58, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, Z.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Lu, H.; Liu, W.; Li, W.; Ren, P.; Geng, C.; Xiao, M.; Hu, G.; et al. Genetic signatures for lineage/sublineage classification of HPV16, 18, 52 and 58 variants. Virology 2021, 553, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Zhan, Q.; Guo, J.; Liu, M.; Ruan, Y.; Zhu, T.; Han, L.; Li, F. Phylogeny and polymorphism in the E6 and E7 of human papillomavirus: alpha-9 (HPV16, 31, 33, 52, 58), alpha-5 (HPV51), alpha-6 (HPV53, 66), alpha-7 (HPV18, 39, 59, 68) and alpha-10 (HPV6, 44) in women from Shanghai. Infect Agent Cancer 2019, 14, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz-Gutiérrez, F.; Sánchez-Minutti, L.; Martínez-Herrera, J.F.; Torres-Escobar, I.D.; Pezzat-Said, E.B.; Márquez-Domínguez, L.; Grandes-Blanco, A.I. Identification of Genetic Variants of Human Papillomavirus in a Group of Mexican HIV/AIDS Patients and Their Possible Association with Cervical Cancer. Pol J Microbiol 2021, 70, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, M.; Li, S.; Luo, P.; Tang, X.; Gong, Q.; Mei, B. Genetic variation of E6, E7, and L1 genes of human papillomavirus 51 from central China. J Med Virol 2022, 94, 2811–2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruni, L.; Albero, G.; Serrano, B.; Mena, M.; Collado, J.J.; Gómez, D.; Muñoz, J.; Bosch, F.X.; de Sanjosé, S. Human Papillomavirus and Related Diseases in the World. Summary Report 10 March 2023; ICO/IARC Information Centre on HPV and Cancer (HPV Information Centre). 2023.
- Martinelli, M.; Villa, C.; Sotgiu, G.; Muresu, N.; Perdoni, F.; Musumeci, R.; Combi, R.; Cossu, A.; Piana, A.; Cocuzza, C. Analysis of Human Papillomavirus (HPV) 16 Variants Associated with Cervical Infection in Italian Women. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2020, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, V.N.; Le, V.N.B.; Hoang, X.S.; Le, V.D. Distribution of human papillomavirus among Vietnamese women with cervical cancer and unusual genetic variability of HPV16. Virology 2024, 594, 110058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bel Haj Rhouma, R.; Ardhaoui, M.; Othman, H.; Ben Jemia, Z.; Zine El Abidine, A.; Fehri, E.; Ouerheni, K.; Laassili, T.; Tounsi, H.; Guizani, I.; et al. The E6 gene polymorphism of Human papillomavirus 16 in relation to the risk of cervical cancer in Tunisian women. Infect Genet Evol 2023, 116, 105536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Wang, S.; Mei, B. Genetic variation of E6 and E7 genes of human papillomavirus type 16 from central China. Virol J 2023, 20, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frati, E.R.; Bianchi, S.; Amendola, A.; Colzani, D.; Petrelli, F.; Zehender, G.; Tanzi, E. Genetic characterization of variants of HPV-16, HPV-18 and HPV-52 circulating in Italy among general and high-risk populations. Mol Med Rep 2020, 21, 894–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Tan, L.; Wang, T.; Cui, F.; Ding, X.; Wan, Q.; Deng, D.; Chen, Z. Genetic variability of human papillomavirus type 51 E6, E7, L1 and L2 genes in Southwest China. Gene 2019, 690, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabet, F.; Mosavat, A.; Ahmadi Ghezeldasht, S.; Basharkhah, S.; Shamsian, S.A.A.; Abbasnia, S.; Shamsian, K.; Rezaee, S.A. Prevalence, genotypes and phylogenetic analysis of human papillomaviruses (HPV) in northeast Iran. Int J Infect Dis 2021, 103, 480–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piana, A.; Sotgiu, G.; Cocuzza, C.; Musumeci, R.; Marras, V.; Pischedda, S.; Deidda, S.; Muresu, E.; Castiglia, P. High HPV-51 prevalence in invasive cervical cancers: results of a pre-immunization survey in North Sardinia, Italy. PLoS One 2013, 8, e63395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godi, A.; Epifano, I.; Bissett, S.L.; Dell'Anna, T.; Piana, A.; Cocuzza, C.; Beddows, S. Amino acid motifs in both the major and minor capsid proteins of HPV51 impact antigenicity and infectivity. J Gen Virol 2015, 96, 1842–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.H. Bethesda 2001. Cytopathology 2002, 13, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Board, W.C.o.T.E. World Health Organization classification of tumours. Female Genital Tumours 5th ed.; IARC: 2020.
- Saitou, N.; Nei, M. The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 1987, 4, 406–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, M. A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J Mol Evol 1980, 16, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 7.0 for Bigger Datasets. Mol Biol Evol 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosakovsky Pond, S.L.; Frost, S.D. Not so different after all: a comparison of methods for detecting amino acid sites under selection. Mol Biol Evol 2005, 22, 1208–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, S.; Shank, S.D.; Spielman, S.J.; Li, M.; Muse, S.V.; Kosakovsky Pond, S.L. Datamonkey 2.0: A Modern Web Application for Characterizing Selective and Other Evolutionary Processes. Mol Biol Evol 2018, 35, 773–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).