1. Introduction
Visceral leishmaniasis (VL) is considered a potentially fatal tropical zoonotic disease, caused by protozoan of the Leishmania infantum species [
1]. The increasing expansion of transmitting vectors and reservoirs contribute to spread this disease [
2]. Dogs are considered the main reservoirs from the public health perspective [
3] due to the possibility of high parasitic load and absence of symptomatology or presence of nonspecific clinical signs [
4], thus making them a source of infection to phlebotomes and a link between animal/man transmission [
5]. The risk of vector infection become higher when dogs are positive and symptomatic [
6]. Thus, the surveillance and treatment of the dogs, in order to reduce the number of cases has a considerable relevance in LV control [
7].
Immunomodulatory drugs and even vaccines with well-defined protocols have been shown to be effective in restoring or stimulating the immune response leading to reduced parasitic load and consequently clinical improvement in animals [
8]. Miltefosine has been described as one of these drugs, because in addition to leishmanicide it has immunomodulatory action [
9]. The resistance or progression of the disease is determined by the host’s immune response to infection [
10] resulting in clinical signs that can be classified into four categories by the Canine Leishmaniasis Working Group in exposed, infected, sick and severely ill [
11]. Therefore, it is important to investigate the different phases of the disease, using prognostic tools, such as cellular blood biomarkers [
7].
Basophils are IL-4 producing blood cells responsible for differentiation of naive T cells into Th 2 cells, [
12] shaping the immune response Th2, inducing the immunoglobulins production [
13]. The increase in antibodies is responsible for the high parasitemia and progression of the disease with the presentation of symptomatic dogs, being the most involved classes: IgG, IgG2, IgM, IgA and IgE [
14]. While resistance to the disease is related to higher macrophage production and release of IL-12 [
15], in asymptomatic dogs it is associated with low parasitemia and IgG production [
14]. Thus, hematological alterations present as a strong biomarker, especially when associated with the characteristic VLC clinical signs [
7,
16].
The prediction with biomarkers during treatment can provide important data on the medical conduct and directing the permanence or modification of pre-established terapêuticas measures and the necessary care for animals, as well as in the diagnosis, monitoring and prognosis [
7]. Thus, the association of hematological alterations with clinical signs and reduction of the parasitic load are essential for establishing an appropriate clinical approach. In addition, animals treated with miltefosine and monitored decrease infection for vectors, controlling the infectious cycle of leishmaniasis. The treatment decreases the parasitic load of the dog, as stated in Nogueira et al. [
17], demonstrating that 74.2% of the animals treated with miltefosine became non-infectious.
Thus, this study aimed to identify possible new hematological biomarkers of high predictive value in dogs with visceral leishmaniasis treated with miltefosine, in different clinical phases, in order to contribute to new studies focusing in VL control.
2. Materials and Methods
Animals: an experimental study of a non-randomized clinical trial by convenience [
18], was performed with the purpose to evaluate hematological parameters and thus identifying predictive biomarkers of visceral leishmaniasis in dogs treated with miltefosine. For this, 15 dogs (Canis familiaris) of both sexes and several breeds were treated, at the Clinic School of Veterinary Medicine of the Cesmac University Center-Alagoas, Brazil.
Clinical examination: Initially, the physical-clinical examination of the animal was performed according to [
19], which were observed the parameters of heart and respiratory rates; capillary perfusion time; rectal temperature; palpation; verification of mucosal staining, presence of ectoparasites and skin lesions, as well as presence of ocular and/or genital secretion of animals and separated initially only in symptomatic and asymptomatic, before diagnosis for group formation.
Blood collection: 6mL of blood were collected from the dogs through cephalic venipuncture, with prior containment and antisepsis with 70% alcohol. The samples were stored and identified in sterile tubes without and with ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), then sent to the Clinical Analysis Laboratory and the Parasitic Diseases Laboratory of the Cesmac University Center School Clinic.
Diagnosis of L. infantum: The Rapid Immunochromatographic Test Dual Path Platform (DPP®) was performed for the diagnosis of canine visceral leishmaniasis. To confirm the result, the enzyme immunosprayed or immunoenzymatic immunoabsorption immunosorption assay (ELISA®), the indirect immunofluorescence reaction (IIF) was performed in house using sensitized slides from L. infantum promastigote culture samples, from the Laboratory of Leishmaniasis and Mutagenesis. The was used a second antibody marked with fluorescein (IgG anti-dog®) produced in rabbit and applied in the same laboratory of the Department of Parasitology of Aggeu Magalhães Institute-Fiocruz-PE. The quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) was performed using the LINF 1B system, which detects a fragment of 132 base pairs from kDNA of the L. donovani Complex. The standard genomic DNA curve of L. infantum from 1 ng to 1 fg with dilution factor of 10, and as a negative control sample without DNA were used. The final volume used was 50 μL, 25 of (SYBR® Green Master Mix), 1.0 μL of linf 1B Forward primer (5’-TCCCAAACTTTTTCTGGTCCT-3’) and 1.0 μL of Linf 1B Reverse primer (5’-TTACACCAACCACCACCCAGTTTC-3’), 21 μL of water type 1 and 2 μL of Genomic DNA of L. infantum. Animals that presented color reaction to DPP in the test window, and/or cut-off above 0.371 to ELISA, and/or positive to IIF in the cut-off of 1:40, or positive to qPCR with detection of L. infantum DNA confirmed by the amplification logarithmic curve, with melt temperature close to 80°C, were considered positive.
Groups of study: Group 1 (G1): Sick dogs - With typical clinical changes, positive serology with high titration and positive qPCR; Group 2 (G2): infected dogs - With or without clinical signs, with low positive qPCR antibodies; Group 3 (G3): exposed dogs- animals with no clinical signs or nonspecific signs, serology with low antibodies and negative qPCR. The layout of the group formation was adapted from the Canine’s suggestion Leishmaniasis Working Group (CLWG) [
11].
Treatment: In order to eliminate gastrointestinal parasites, Ivermectin + Pirantel + Praziquantel + Febantel was administered orally in a single dose. For fleas, ticks, lice and bites of female phlebotomes control, a 4% Deltamethrin-based collar was used. Animals with change in blood count suggestive of hemoparasitosis and/or presence of hemoparasites on the slide for Babesia, Ehrlichia and/or Anaplasma were treated with with imidocarb dipropionate at a dose of 3.5mg/kg, the equivalent of 1mL of the product for every 20kg intramuscularly and repeated with 15 days and Doxycycline at the dose of 50mg/10kg every 12 hours for 21 days according to each specific case, before starting the treatment with miltephosphosin Miltefosine, that was administered at 2% orally at a dose of 1mL/10kg/day for 28days after parasitic treatment in all animals of the study groups.
Hematological examination: The hemocytometer methodology was applied to determine the total number of leukocytes using turk diluent. The differential count of leukocytes, as well as the evaluation of the cell’s morphology was carried out through blood stretching stained by fast dye for hematology [
20].
Monitoring: The animals of all groups were clinically evaluated and submitted to hematological examination before treatment (T0), with 20 days of treatment (T20) and 30 days (T30) after the beginning of treatment with miltefosine.
Statistical analysis: The data were tabulated and classified according to the groups studied (sick, exposed and infected), as well as the moment at which each parameter was evaluated (0, 20 and 30 days). To assess data normality, the Shapiro-Wilk test was used. The means were compared using variance analysis (One-Way ANOVA), followed by the Student Newman-Keuls test (SNK) for hematological data and Tukey test for the other parameters (ELISA and qPCR). All data were analyzed using the Software RStudio v1.4 and the differences were considered significant when p<0.05.
3. Results
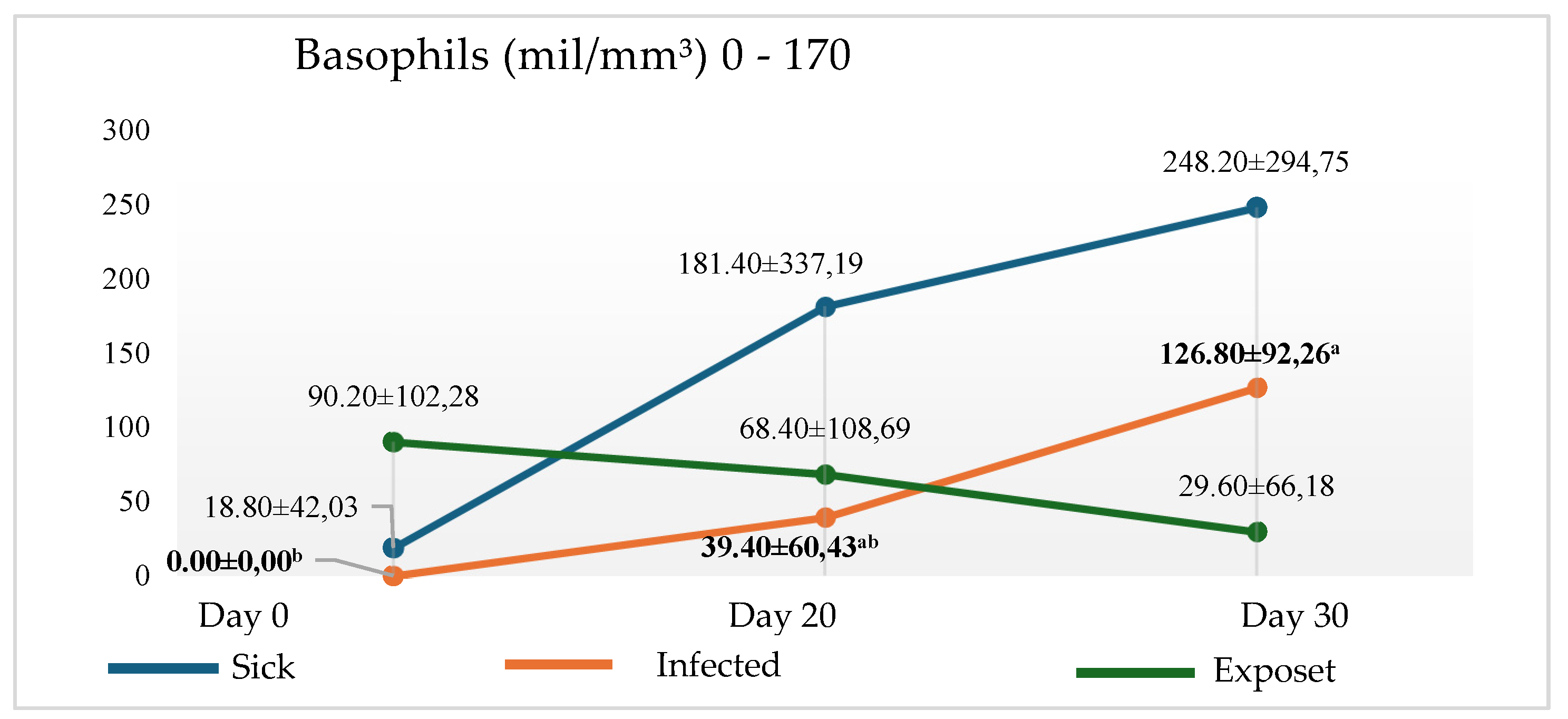
The increase in the number of basophils was verified in the patient group (clinical symptom + high amount of antibodies + high parasitic load), as well as and in the infected group (nonspecific clinical signs + low antibody titration + low parasitic load), with statistical significance (p< 0.05) in T20 and T30 of the infected group (
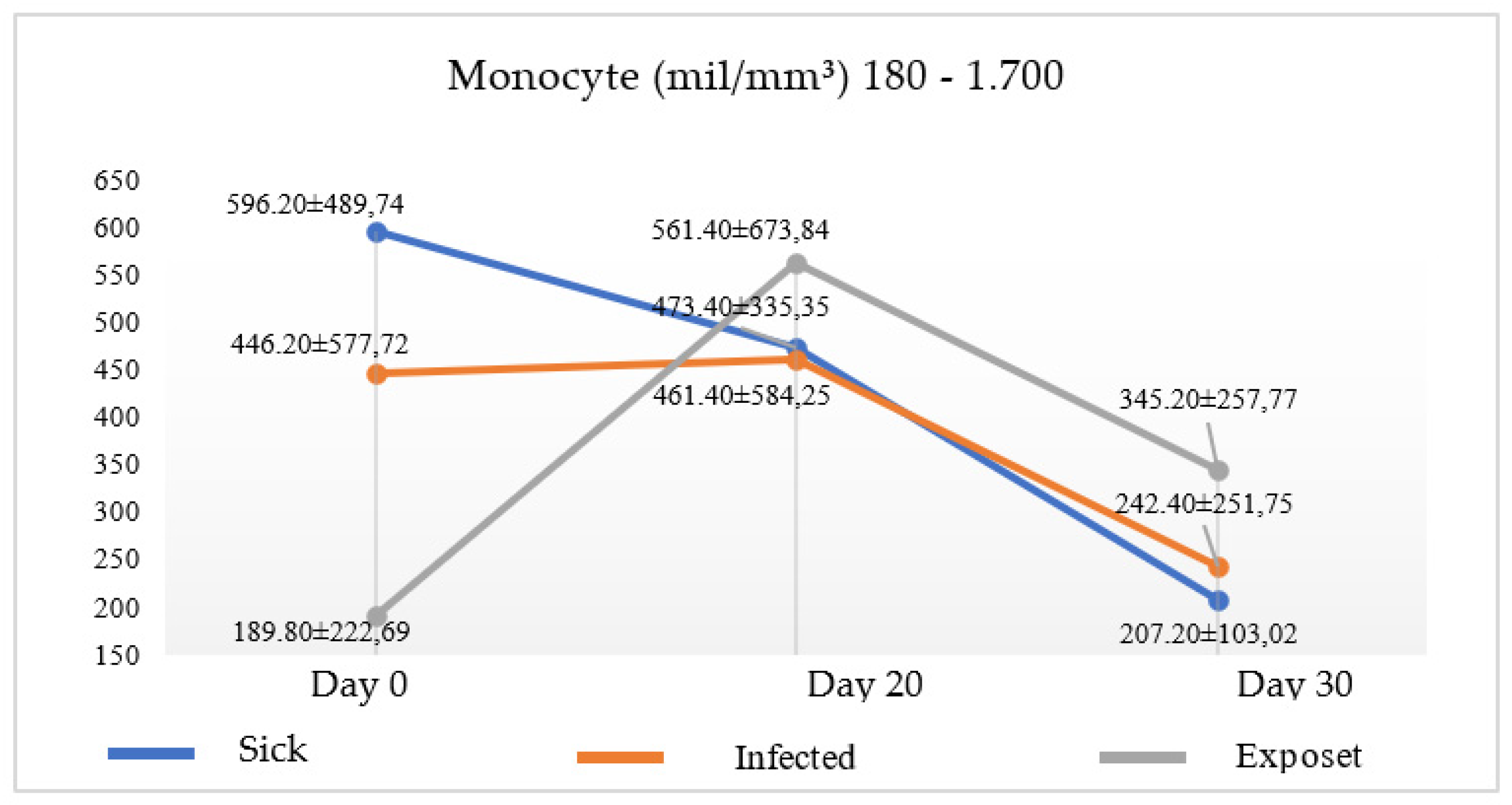
Figure 1). Parallel to the increase of basophils, a decrease in monocytes was observed in both groups in the two times analyzed (
Figure 2), suggesting the progression of the disease, since there was no cellular signs indicating miltefosine immunomodulation.
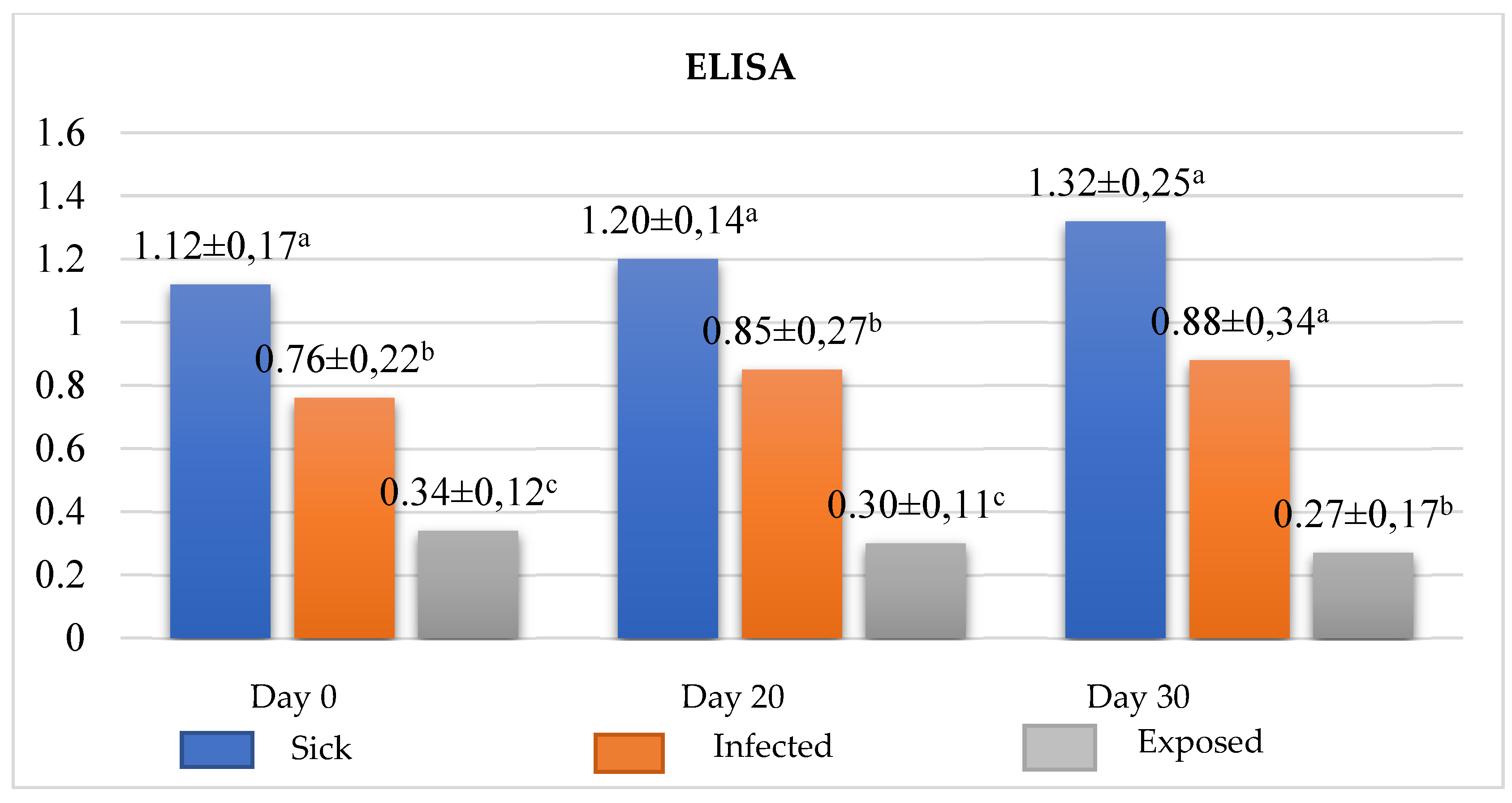
Emphasizing that this result is possibly involved with increased of IL-4, produced in basophils stimulated by the presence of the parasite, and thus differentiating naive T cells in Th2 cells with consequent increase in immunoglobulin, as ratified by the result of ELISA (
Figure 3). On the other hand, the exposed group (with no clinical signs or nonspecific signs + low titration + negative qPCR) had its number of basophils reduced after beginning the treatment and an increase in the number of monocytes up to T20. IgG concentration reached undetectable levels in one or more serological tests, there was a reduction in the clinical signs reaching the clinical cure, demonstrating the immunomodulatory action of miltefosine in exposed dogs with good prognosis. Highlighting that, these results suggest the increase of macrophage with consequent release of IL-12 and differentiation of naive T cells in Th1 cells with consequent reduction immunoglobulins as seen in ELISA (
Figure 3).
The parasitic load analysis was performed only in the groups of sick and infected animals, in which was possible to observe a reduction in the continuous parasitic load, after treatment with miltefosine (
Table 1). Associated with decreased parasitic load, at the time of analysis, T20, there was a reduction of monocytes and an increase in basophils and immunoglobulins.
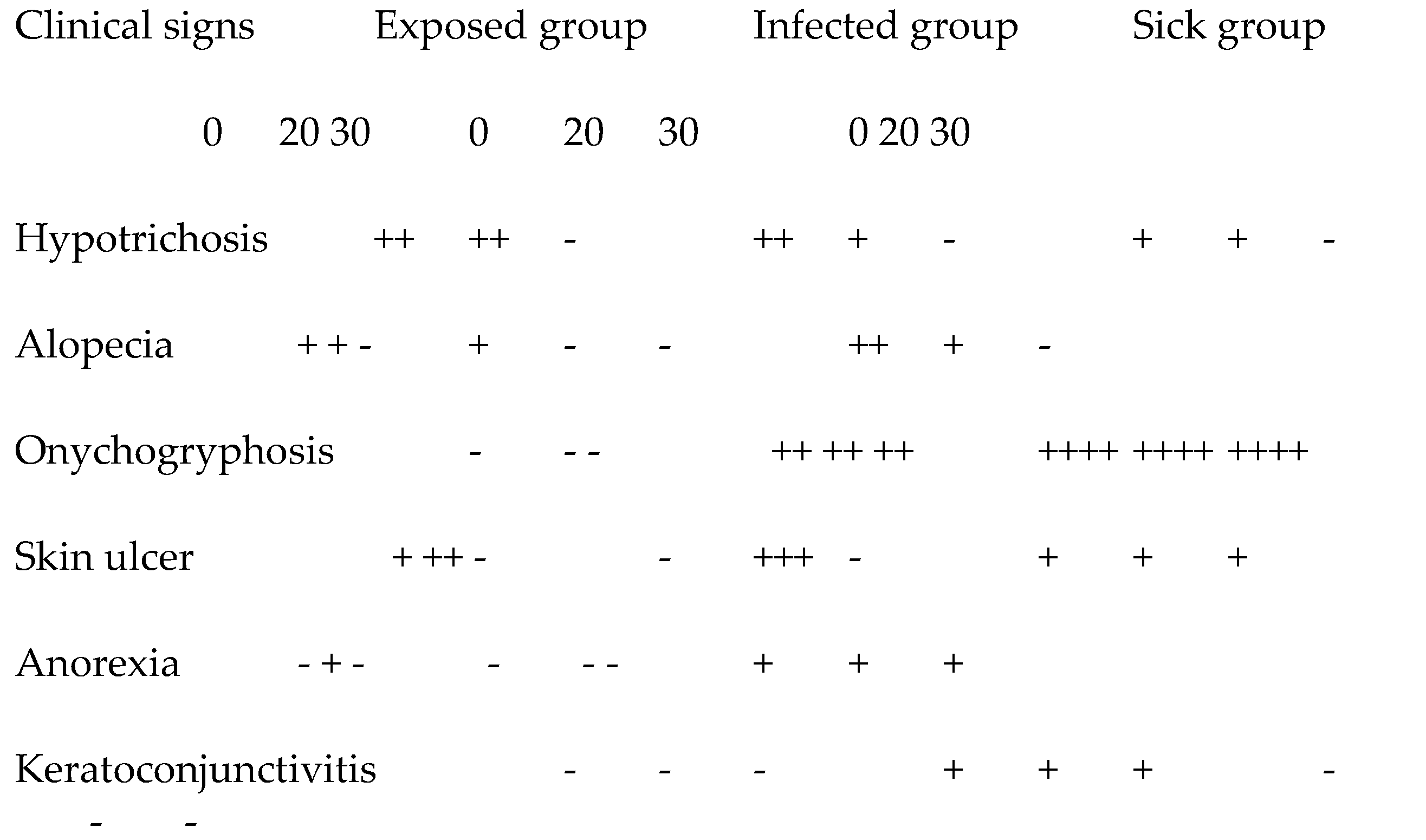
The analysis of clinical aspects, it was observed that there was variation between the study groups (
Table 2). The animals demonstrated clinical improvement in all groups at the end of the treatment. At 20 days, T20, there was clinical worsening in all groups after the beginning of the treatment. The most present clinical signs were onychogryphosis and followed by hypotrichosis and ulcerative skin lesions frequently in the carpic, tartaric and humerus-radioulnar joints, which can be confused with decubitus calluses.
4. Discussion
Our results indicated basophils as an efficient predictive cellular marker of CanL in dogs undergoing miltefosine treatment. However, despite its important role, the basophil is a neglected cell over the years, reducing its action to mere adjuvant of mast cells. Some of the authors include these cells among the granulocytic [
21] others do not mention in their articles as Dias et al. [
22] and Smalbroek [
23]. There are also those who expose the results in the blood count in relative values rather than absolute values [
24], which hinders a careful analysis of these cells. Nevertheless, only in the recent years basophil has been identified as an IL-4-producing cell responsible for the differentiation of naive T cells in Th2 cells, as an antigen-presenting cell (APCs), class II MHC expression (MHC-II), and considered costimulator of CD80, CD86 and CD40 [
12].
ELISA can verify the animal’s immune response through anti-Leishmania IgG levels. Therefore, it has been widely used both in the diagnosis and monitoring of dogs under treatment, especially when associated with clinical signs and with cells involved in the immune response such as basophils and monocytes, which can help significantly in prognosis, besides directing the therapeutic interventions necessary for animal welfare. In our study, the major-like Leishmania ELISA used in the diagnosis and monitoring proved to be efficient regarding the cellular evaluation proposed in this study, corroborating the hypothesis that the increase in basophils is related to the increase in the concentration of immunoglobulins after the beginning of treatment in the infected and sick groups, Despite studies show 75% and 72% of sensitivity and specificity, respectively, of this test when using in asymptomatic dogs, 93.2% of sensitivity, and 100.0% of specificity in symptomatic dogs, according to Fujimori et al. study [
3].
Another tool that can be used to understand the cellular results is qPCR, since the death of the parasite causes the death of the host cell, in this case the monocyte, leading to a direct relationship of the parasitic load with the monocyte. Although the reduction of the parasitic load is something expected in animals treated with miltefosine [
17], studies that focused on this relationship were not found. However, this association is important, since the monocyte, although uncommon, is also considered a biomarker [
7].
In contrast with the results, there are clinical findings. The parasitic load does not initially indicate clinical improvement, but at the end of treatment a low parasitic load shows a significant clinical improvement as shown in the studies by Nogueira et al. [
17], demonstrating that 94.2% of the dogs treated with miltefosine 2% for four weeks (28 days) achieved a progressive clinical improvement. At the beginning of the week 0 (W0) whose the percentage of improvement was 16.29 ± 7.57, in two weeks (W2) this percentage was 15.26 ± 7.45, and post-treatment with four weeks (W4) this number was 12.14 ± 5.31) [
15]. While an expressive humoral response with high IgG titers does not mean an effective defense, even with absence of clinical signs, but on the contrary, it reflects a progression [
14]. Hematological biomarkers are strong in the clinical prognosis [
7], but a cellular biomarker is needed to predict the immune response related to disease progression or resistance to the disease for early intervention for CanL.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, basophils are possible markers related to the Th2 response responsible for progression or resistance to CanL, but to confirm the hypothesis of it as an effective immunological marker would be necessary the flow cytometry to identify the release of cytokine types by stimulating Leishmania infantum in PBMC.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Gilsan, Marcos and Luiz ; methodology, Gilsan, Claudia, Natália and Rachel; software, Márcio Calixto; validation, Luiz and Gilsan; formal analysis, Gilsan e Marcio e Ana Paula; investigation, Gilsan, Natália and Rachel; resources, CESMAC and Fiocruz; data curation, Gilsan, Luiz, Ana Paula, Fábio.; writing—original draft preparation, Gilsan and Ana Paula.; writing—review and editing, Luiz, Ana Paula, Fábio, Marcos and Gilsan; visualization, Luiz; supervision, Luiz; project administration, Luiz, Fábio, Ana Paula and Gilsan. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The animal study protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee on Animal Experimentation of the Cesmac University Center with approval protocol number: 13A-2018. The treated animals were monitored and the tutors instructed about the necessary care. Ethical statement: This study was carried out in strict accordance with the Brazilian Law of Animal Experimentation No. 11,794 / 08.
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Fiocruz, Lika and Cesmac for providing equipment and material necessary for the development of the research.
Conflicts of Interest
The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Lopes, J.V.; Michalsky, É.M.; Pereira, N.C.L.; Paula, A.J.V.; Souza, A.G.M.; Pinheiro, L.C.; et al. Visceral canine leishmaniasis in area with recent Leishmaniatransmission: prevalence, diagnosis, and molecular identification of the infecting species. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop. 2020, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferroglio, E.; Battisti, E.; Zanet, S.; Bolla, C.; Concialdi, E.; Trisciuoglio, A.; et al. Epidemiological evaluation of Leishmania infantum zoonotic transmission risk in the recently established endemic area of Northwestern Italy. Public Health Zoonoses 2018, 65, 675–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujimori, M.; de Almeida, A.B.P.F.; Barrouin-Melo, S.M.; Cortez, L.R.P.B.; Duthie, M.S.; Hiramoto, R.M.; et al. Validation of ELISA with recombinant antigens in serological diagnosis of canine Leishmania infantum infection. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 2021, 116, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacintho, A.P.P.; Melo, G.D.; Machado, G.F.; Bertolo, P.H.L.; Moreira, P.R.R.; Momo, C.; Souza, T.A.; Vasconcelos, R.O. Expression of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and metalloproteinase-9 in the skin of dog with visceral Leishmaniasis. Parasitol Res 2018, 117, 1819–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, E.M.; Silva, J.C.F.; Costa, R.T.; Costa, D.C.; Barata, R.A.; Paula, E.V.; et al. Visceral leishmaniasis: study of sandbum and canine infection in Montes Claros, Minas Gerais. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop 2005, 38, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaves, M.M.; Teixeira, M.J.; Pompeu, M.M.L.; Sousa, R.N.; Lima, J.W.O. Evaluation of the potential reservoir of the dog in Visceral Leishmaniasis in two municipalities of the State of Ceará. PUBVET 2013, 7, 1568. [Google Scholar]
- Maia, C.; Campino, L. Biomarkers associated with Leishmania infantum exposure, infection and disease in dog. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2018, 8, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, A.A.M.; Leite, J.C.; Resende, L.A.; Mariano, R.M.D.S.; Silveira, P.; Melo-Júnior, O.A.O. ; An overview of immunotherapeutic approaches against canine visceral Leishmaniasis: What has been tested on dog and new perspective on improving treatment efficacy. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2019, 18, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palić, S.; Bhairosing, P.; Beijnen, J.h.; Dorlo, T.P.C. Systematic review of host-mediated activity of miltefosine in leishmaniasis through immunomodulation. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2019, 63, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gradoni, L. Canine Leishmania vaccine: still a long way to go. Parasitol Vet 2015, 28, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paltrinieri, S.; Solano-Gallego, L.; Fondati, A.; Lubas, G.; Gradoni, L.; Castagnaro, M.; et al. Canine Leishmaniasis Working Group, Italian Society of Veterinarians of Companion Animals. Guidelines for diagnosis and clinical classification of leishmaniasis in dogs. J Am Vet Med Assoc 2010, 236, 1184–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karasuyama, H.; Shibata, S.; Yoshikawa, S.; Miyake, K. ; Basophils, a neglected minority in the immune system, have come into the limelight at last. Int Immunol 2021, 33, 809–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokol, C.L.; Medzhitov, R. Role of basophils in the initiation of Th2 responses. Curr Opin Immunol 2010, 22, 73–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reis, A.B.; Martins-Filho, O.A.; Teixeira-Carvalho, A.; Giunchetti, R.C.; Cordeiro, C.M.; Mayrink, W.; et al. Systemic and compartmentalized immune response in canine visceral leishmaniasis. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 2009, 128, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva, A.V.A.; Figueiredo, F.B.; Menezes, R.C.; Mendes-Junior, A.A.; Miranda, L.H.M.; Cupolillo, E.; et al. Morphophysiological changes in the splenic extracellular matrix of Leishmania infantum-naturally infected dogs is associated with alterations in lymphoid niches and the CD4+ T cell frequency in spleens. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 2018, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Sousa Gonçalves, R.; Alves de Pinho, F.; Dinis-Oliveira, R.J.; Azevedo, R.; Gaifem, J.; Larangeira, G.F.; et al. Mathematical Modelling Using Predictive Biomarkers for the Outcome of Canine Leishmaniasis upon Chemotherapy. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueira, C.T.; Cistia, M.L.D.; Urbaczek, A.C.; Mg Jusi, M.; Velásquez, A.M.A.; Machado, R.Z.; et al. Potential application of rLc36 protein for diagnosis of canine visceral leishmaniasis. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz 2018, 113, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedel, W.L.; Silveira, F.D. Different research designs and their characteristics in intensive care. Rev Bras Ter Intensiva 2016, 28, 256–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bichard, S.J.; Sherding, R.G., B. Manual Saunders: small animal clinic.; Roca: São Paulo, Brazil, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Thrall, M.A. Hematology and veterinary clinical biochemistry, 2nd ed., Roca: Rio de Janeiro, 2015, pp. 678.
- Reis, A.B.; Martins-Filho, O.A.; Teixeira-Carvalho, A.; Carvalho, M.G.; Mayrink, W.; França-Silva, J.C.; et al. Parasite density and impaired biochemical/hematological status are associated with severe clinical aspects of canine visceral leishmaniasis. Res Vet Sci 2006, 81, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, Á.F.L.R.; Ayres, E.D.C.B.S.; de Oliveira Martins, D.T.; Maruyama, F.H.; de Oliveira, R.G.; de Carvalho, M.R.; et al. Comparative study of the use of miltefosine, miltefosine plus allopurinol, and allopurinol in dogs with visceral leishmaniasis. Exp Parasitol 2020, 217, 107947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utrecht University. Available online: https://studenttheses.uu.nl/handle/20.500.12932/39089 (accessed on 21 June 2024).
- Braz, P.H.; Sartoretto, M.C.; Souza, A.S. de; Melo, F.M.G. Perfil hematológico de cães naturalmente infectados por Leishmania spp / Hematological abnormalities in dogs naturally infected by Leishmania spp. Acta Vet. Brasilica 2015, 9, 87–90. [Google Scholar]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).