Submitted:
06 July 2024
Posted:
08 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
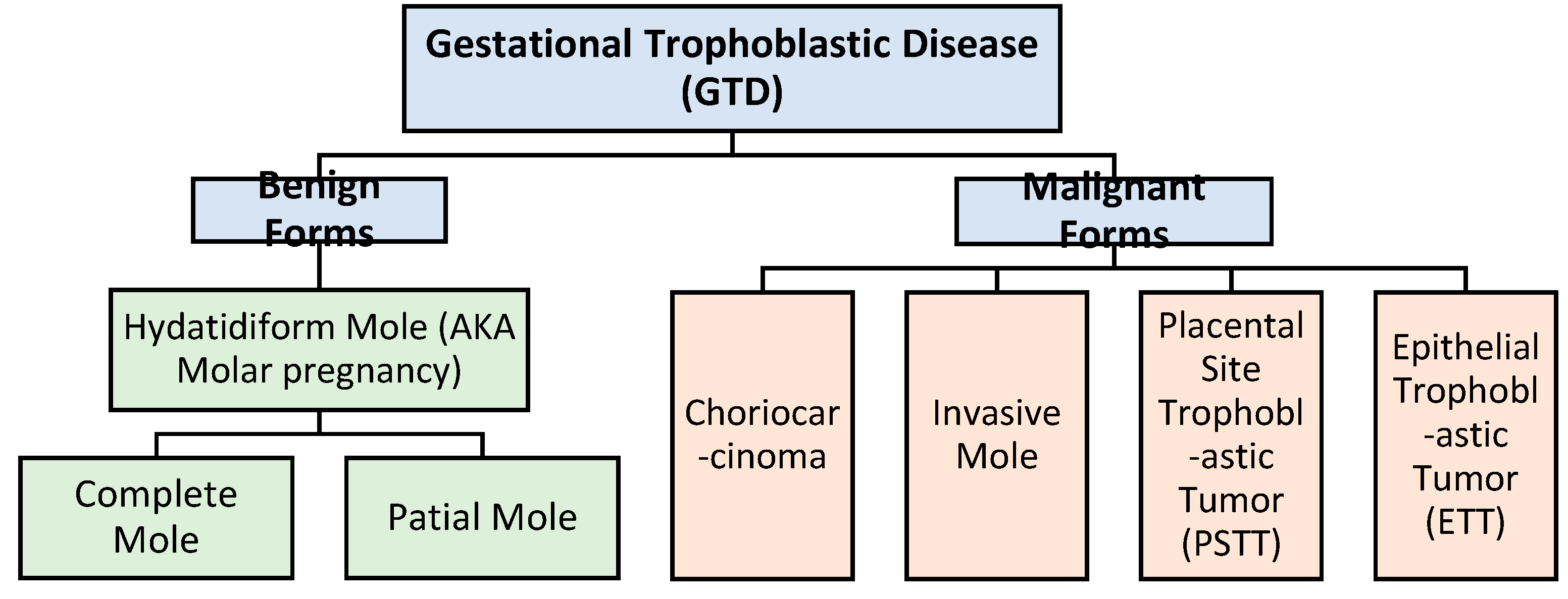
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Strategy
2.2. Eligibility Criteria:
2.2.1. Inclusion Criteria
2.2.2. Exclusion Criteria
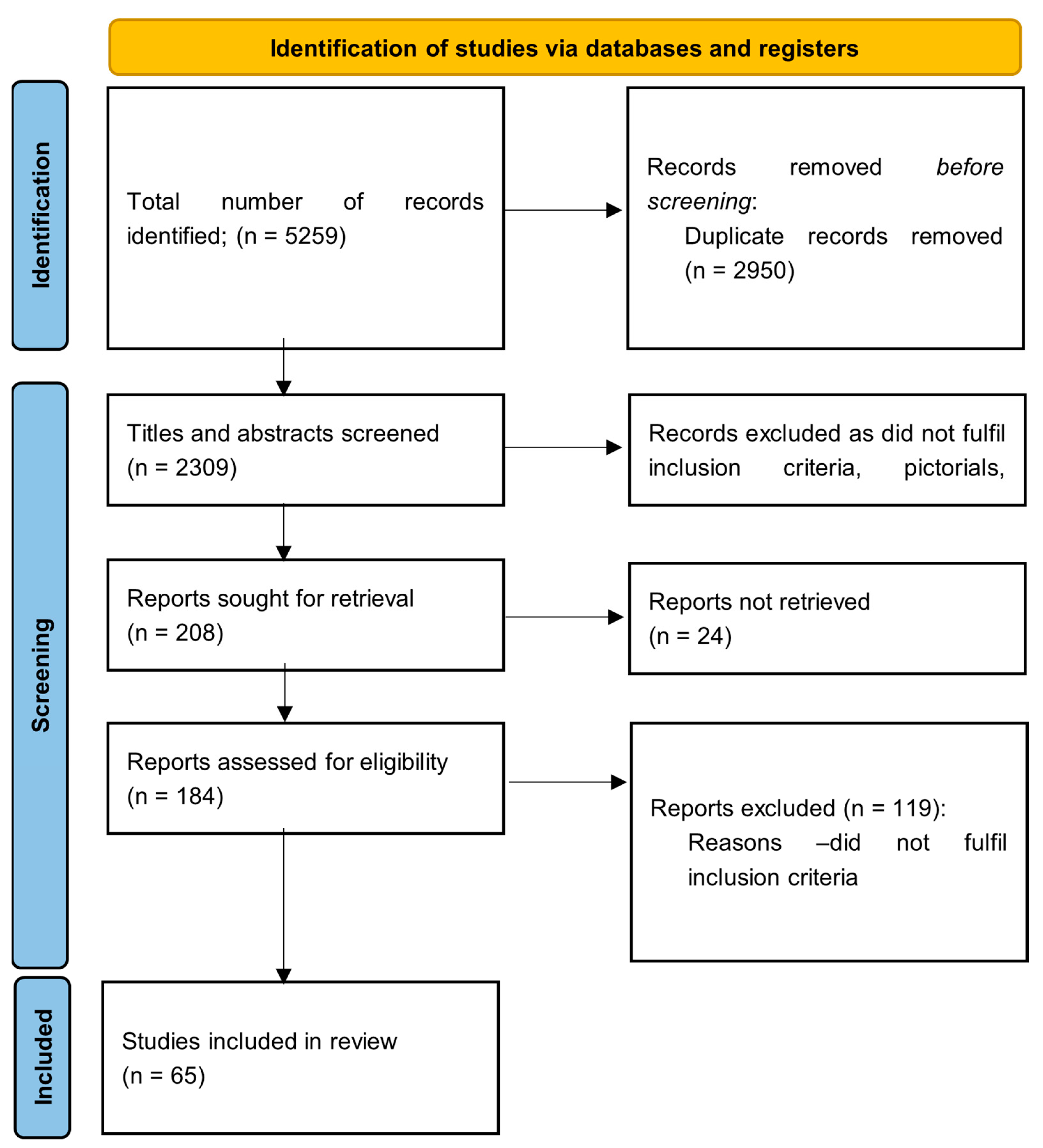
2.3. Study Selection
2.4. Data Collection
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Genomic Imprinting
3.2. Recurrent Hydatidiform Mole
3.3. Molecular Dysregulations in GTD
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lurain, J.R. Gestational trophoblastic disease I: epidemiology, pathology, clinical presentation and diagnosis of gestational trophoblastic disease, and management of hydatidiform mole. American journal of obstetrics and gynecology, 2010, 203(6), 531–539. [CrossRef]
- Bruce, S.; Sorosky, J. Gestational Trophoblastic Disease. StatPearls, Feb. 2024, Accessed: Jun. 26, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470267/.
- Ning, F.; Hou, H.; Morse, A.N.; Lash, G.E. Understanding and management of gestational trophoblastic disease. F1000Research, 2019, 8, F1000 Faculty Rev–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Moss, J.; Sebire, N.J.; Cui, Q.C.; Seckl, M.J.; et al. Analysis of the chromosomal region 19q13.4 in two Chinese families with recurrent hydatidiform mole. Human Reproduction, 2006, 21(2), 536–541. [CrossRef]
- Kalogiannidis, I.; Kalinderi, K.; Kalinderis, M.; Miliaras, D.; Tarlatzis, B.; et al. Recurrent complete hydatidiform mole: where we are, is there a safe gestational horizon? Opinion and mini-review. Journal of assisted reproduction and genetics, 2018, 35(6), 967–973. [CrossRef]
- Capozzi, V.A.; Butera, D.; Armano, G.; Monfardini, L.; Gaiano, M.; et al. Obstetrics outcomes after complete and partial molar pregnancy: Review of the literature and meta-analysis. European journal of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive biology, 2021, 259, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tantengco, O.A.G.; De Jesus, F.C. C. 2nd; Gampoy, E.F. S.; Ornos, E.D. B.; Vidal, M.S. Jr; et al. Molar pregnancy in the last 50 years: A bibliometric analysis of global research output. Placenta, 2021, 112, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngan, H.Y.S.; Seckl, M.J.; Berkowitz, R.S.; Xiang, Y.; Golfier, F.; et al. Diagnosis and management of gestational trophoblastic disease: 2021 update. International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics, 2021, 155 (S1), 86-93. [CrossRef]
- Albright, B.B.; Shorter, J.M.; Mastroyannis, S.A.; Ko, E.M.; Schreiber, C.A.; et al. Gestational Trophoblastic Neoplasia After Human Chorionic Gonadotropin Normalization Following Molar Pregnancy: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Obstetrics and gynecology, 2020, 135(1), 12–23. [CrossRef]
- Sebire, N.J.; Fisher, R.A.; Rees, H.C. Histopathological diagnosis of partial and complete hydatidiform mole in the first trimester of pregnancy. Pediatric and developmental pathology: the official journal of the Society for Pediatric Pathology and the Paediatric Pathology Society, 2003, 6(1), 69–77. [CrossRef]
- Ronnett, B.M. Hydatidiform Moles: Ancillary Techniques to Refine Diagnosis. Archives of pathology & laboratory medicine, 2018, 142(12), 1485–1502. [CrossRef]
- Khawajkie, Y.; Mechtouf, N.; Nguyen, N.M.P.; Rahimi, K.; Breguet, M.; et al. Comprehensive analysis of 204 sporadic hydatidiform moles: revisiting risk factors and their correlations with the molar genotypes. Modern pathology: an official journal of the United States and Canadian Academy of Pathology, Inc, 2020, 33(5), 880–892. [CrossRef]
- Joyce, C.M.; Fitzgerald, B.; McCarthy, T.V.; Coulter, J.; O’Donoghue, K. Advances in the diagnosis and early management of gestational trophoblastic disease. BMJ Medicine, 2022, 1, e000321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erol, O.; Süren, D.; Tutuş; B; Toptaş; T; Gökay, A.A.; et al. Immunohistochemical Analysis of E-Cadherin, p53 and Inhibin-α Expression in Hydatidiform Mole and Hydropic Abortion. Pathology oncology research: POR, 2016, 22(3), 515–521. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.R.; Cheng, W.W.; Wang, Y.X.; Cai, M.; Bin Wu, W.; et al. Identification of microRNA signature in the progression of gestational trophoblastic disease. Cell Death & Disease, 2018, 9 (2), 94. [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.Z.; Qin, X.Y.; Chen, S.W.; Wang, P.; Zhan, Y.; et al. Heterozygous/dispermic complete mole confers a significantly higher risk for post-molar gestational trophoblastic disease. Modern pathology: an official journal of the United States and Canadian Academy of Pathology, Inc, 2020, 33(10), 1979–1988. [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Jia, C.; Li, J.; Yin, L.; et al. The relationship between expression of c-ras, c-erbB-2, nm23, and p53 gene products and development of trophoblastic tumor and their predictive significance for the malignant transformation of complete hydatidiform mole. Gynecologic oncology, 2002, 85(3), 438–444. [CrossRef]
- Yazaki-Sun, S.; Daher, S.; De Souza Ishigai, M.M.; Alves, M.T.S.; Mantovani, T.M.; et al. Correlation of c-erbB-2 oncogene and p53 tumor suppressor gene with malignant transformation of hydatidiform mole. The Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Research, 2006, 32 (3). 265–272. [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, E.H.; Shibata, S.; Oike, A.; Kobayashi, N.; Hamada, H.; et al. Genomic imprinting in human placentation. Reproductive Medicine and Biology, 2022, 21(1). [CrossRef]
- Atabaki Pasdar, F.; Khooei, A.; Fazel, A.; Rastin, M.; Tabasi, N.; et al. DNA flow cytometric analysis in variable types of hydropic placentas. Iranian journal of reproductive medicine 2015, 13, 269–274. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ndukwe, C.O.; Ukah, C.O. Epidemiological Aspects and Diagnostic Accuracy of Morphological Diagnosis of Hydatidiform Mole Using p57kip2 Immunostain in Nnewi, South-East Nigeria – A Multicenter Study. Journal of Nature and Science of Medicine 2021, 4, 281–287. [Google Scholar]
- Khashaba, M.; Arafa, M.; Elsalkh, E.; Hemida, R.; Kandil, W. Morphological Features and Immunohistochemical Expression of p57Kip2 in Early Molar Pregnancies and Their Relations to the Progression to Persistent Trophoblastic Disease. Journal of pathology and translational medicine, 2017, 51(4), 381–387. [CrossRef]
- Lelic, M.; Fatusic, Z.; Iljazovic, E.; Ramic, S.; Markovic, S.; et al. Challenges in the Routine Praxis Diagnosis of Hydatidiform Mole: a Tertiary Health Center Experience. Medical archives (Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina), 2017, 71(4), 256–260. [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, S.; Sasaki, Y.; Kunimura, T.; Sekizawa, A.; Kojima, Y.; et al. Clinical Usefulness of Immunohistochemical Staining of p57 kip2 for the Differential Diagnosis of Complete Mole. BioMed research international, 2015, 905648. [CrossRef]
- Xing, D.; Adams, E.; Huang, J.; Ronnett, B.M. Refined diagnosis of hydatidiform moles with p57 immunohistochemistry and molecular genotyping: updated analysis of a prospective series of 2217 cases. Modern pathology: an official journal of the United States and Canadian Academy of Pathology, Inc, 2021, 34(5), 961–982. [CrossRef]
- Zainal, N.; Kampan, N.C.; Rose, I.M.; Ghazali, R.; Shafiee, M.N.; et al. Complementary role of p57kip2 immunostaining in diagnosing hydatidiform mole subtypes. Hormone Molecular Biology and Clinical Investigation, 2021, 42 (3), 311-316. [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, S.; Okae, H.; Kobayashi, N.; Kitamura, A.; Kumada, K.; et al. Loss of p57KIP2 expression confers resistance to contact inhibition in human androgenetic trophoblast stem cells. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2019, 116(52), 26606-26613. [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.Z.; Hui, P.; Chang, B.; Gao, Z.B.; Li, Y.; et al. STR DNA genotyping of hydatidiform moles in South China. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014, 7, 4704–4719. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Banet, N.; DeScipio, C.; Murphy, K.M.; Beierl, K.; Adams, E.; et al. Characteristics of hydatidiform moles: analysis of a prospective series with p57 immunohistochemistry and molecular genotyping. Modern Pathology, 2014, 27 (2), 238–254. [CrossRef]
- King, J.R.; Wilson, M.L.; Hetey, S.; Kiraly, P.; Matsuo, K.; et al. Dysregulation of Placental Functions and Immune Pathways in Complete Hydatidiform Moles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.F.; Chan, W.Y. The de novo DNA methyltransferase DNMT3A in development and cancer. Epigenetics, 2014, 9(5), 669–677. [CrossRef]
- Mahadevan, S; Wen, S.; Wan, Y.; Peng, H.; Otta, S.; et al. NLRP7 affects trophoblast lineage differentiation, binds to overexpressed YY1 and alters CpG methylation. Hum Mol Genet, 2014, 23 (3), 706–716. [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Delgado, M.; Martin-Trujillo, A.; Tayama, C.; Vidal, E.; Esteller, M.; et al. Absence of Maternal Methylation in Biparental Hydatidiform Moles from Women with NLRP7 Maternal-Effect Mutations Reveals Widespread Placenta-Specific Imprinting. PLoS Genetics, 2015, 11(11), e1005644. [CrossRef]
- Bolze, P.A.; Patrier, S.; Cheynet, V.; Oriol, G.; Massardier, J.; et al. Expression patterns of ERVWE1/Syncytin-1 and other placentally expressed human endogenous retroviruses along the malignant transformation process of hydatidiform moles. Placenta, 2016, 39, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langbein, M.; Strick, R.; Strissel, P.L.; Vogt, N.; Parsch, H.; et al. Impaired cytotrophoblast cell-cell fusion is associated with reduced Syncytin and increased apoptosis in patients with placental dysfunction. Molecular reproduction and development, 2008, 75(1), 175–183. [CrossRef]
- Lertkhachonsuk, R.; Paiwattananupant, K.; Tantbirojn, P.; Rattanatanyong, P.; Mutirangura, A. LINE-1 Methylation Patterns as a Predictor of Postmolar Gestational Trophoblastic Neoplasia, BioMed Research International, 2015, 421747 (7), 2015. [CrossRef]
- Rahat, B.; Thakur, S.; Bagga, R.; Kaur, J. Epigenetic regulation of STAT5A and its role as fetal DNA epigenetic marker during placental development and dysfunction. Placenta, 2016, 44, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Triratanachat, S.; Nakaporntham, P.; Tantbirojn, P.; Shuangshoti, S.; Lertkhachonsuk, R. Role of P57KIP2 Immunohistochemical Expression in Histological Diagnosis of Hydatidiform Moles. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev, 2016, 17 (4), 2061–2066, 2016. [CrossRef]
- Samadder, A.; Kar, R. Utility of p57 immunohistochemistry in differentiating between complete mole, partial mole & non-molar or hydropic abortus. Indian J Med Res, 2017, 145 (1), 133–137. [CrossRef]
- McConnell, T.G.; Murphy, K.M.; Hafez, M.; Vang, R.; Ronnett, B.M. Diagnosis and Subclassification of Hydatidiform Moles Using p57 Immunohistochemistry and Molecular Genotyping: Validation and Prospective Analysis in Routine and Consultation Practice Settings With Development of an Algorithmic Approach. The American Journal of Surgical Pathology, 2009, 33(6), 805-817. [CrossRef]
- LeGallo, R.D.; Stelow, E.B.; Ramirez, N.C.; Atkins, K.A. Diagnosis of hydatidiform moles using p57 immunohistochemistry and HER2 fluorescent in situ hybridization. Am J Clin Pathol, 2008, 129 (5), 749–755. [CrossRef]
- Diwa, M.H.; Kim, M.A.; Avila, J.M.C.; Pedroza, D.G.; Encinas-Latoy, M.A.M. Utility of p57KIP2 and Her-2 Fluorescence in Situ Hybridization in Differentiating Partial from Complete Hydatidiform Mole. Acta Med Philipp, 2016, 50(4), 318–325. [CrossRef]
- Frost, J.M.; Moore, G.E. The importance of imprinting in the human placenta. PLoS Genet, 2010, 6 (7), 1–9. [CrossRef]
- Tycko, B.; Morison, I.M. Physiological functions of imprinted genes. Journal of Cellular Physiology, 2002, 192 (3), 245–258. [CrossRef]
- Reddy, R.; Akoury, E.; Nguyen, N.M.P.; Abdul-Rahman, O.A.; Dery, C.; et al. Report of four new patients with protein-truncating mutations in C6orf221/KHDC3L and colocalization with NLRP7. Eur J Hum Genet, 2013, 21(9), 957–964. [CrossRef]
- Ji, M.; Shi, X.; Xiang, Y.; Cui, Q.; Zhao, J. NLRP7 and KHDC3L variants in Chinese patients with recurrent hydatidiform moles. Japan Journal of Clinical Oncology, 2019, 49(7), 620–627. [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.M.P.; Slim, R. Genetics and Epigenetics of Recurrent Hydatidiform Moles: Basic Science and Genetic Counselling. Curr Obstet Gynecol Rep, 2014, 3(1), 55. [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.M.P.; Khawajkie, Y.; Mechtouf, N.; Rezaei, M.; Breguet, M.; et al. The genetics of recurrent hydatidiform moles: new insights and lessons from a comprehensive analysis of 113 patients. Mod Pathol, 2018, 31(7), 1116–1130. [CrossRef]
- Fallahi, J.; Anvar, Z.; Razban, V.; Momtahan, M.; Namavar-Jahromi, B.; et al. Founder Effect of KHDC3L, p.M1V Mutation, on Iranian Patients with Recurrent Hydatidiform Moles,” Iran J Med Sci, 2020, 45(2), 118. [CrossRef]
- Fallahi, J.; Alashti, S.K.; Aliabadi, B.E.; Mohammadi, S.; Fardaei, M. Recurrent pregnancy loss in the female with a heterozygous mutation in KHDC3L gene. Gene Rep, 2020, 20, 100721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, M.; Nguyen, N.M.P.; Foroughinia, L.; Dash, P.; Ahmadpour, F.; et al. Two novel mutations in the KHDC3L gene in Asian patients with recurrent hydatidiform mole. Human Genome Variation, 2016, 3(1), 1–5. [CrossRef]
- Shalabi, T.A.; Abdel-Hamid, M.S.; Shaker, M.M. Two Novel Variants in NLRP7 Gene in an Egyptian Female Patient with Consecutive Molar Pregnancies Complicated by Choriocarcinoma. International Journal of Infertility and Fetal Medicine, 2019, 10(3), 54-57. [CrossRef]
- Fallahi, J.; Razban, V.; Momtahan, M.; Akbarzadeh-Jahromi, M.; Namavar-Jahromi, B.; et al. A novel mutation in NLRP7 related to recurrent hydatidiform mole and reproductive failure. Int J Fertil Steril, 2019, 13(2), 135-138. [CrossRef]
- Messaed, C.; Akoury, E.; Djuric, U.; Zeng, J.; Saleh, M.; et al. NLRP7, a nucleotide oligomerization domain-like receptor protein, is required for normal cytokine secretion and co-localizes with Golgi and the microtubule-organizing center. J Biol Chem, 2011, 286(50), 43313–43323. [CrossRef]
- Sills, E.S.; Obregon-Tito, A.J.; Gao, H.; McWilliams, T.K.; Gordon, A.T.; et al. Pathogenic variant in NLRP7 (19q13.42) associated with recurrent gestational trophoblastic disease: Data from early embryo development observed during in vitro fertilization.Clinical and experimental reproductive medicine,2017,44(1),40–46. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Zhu, X.; Yu, X.; Huang, B.; Jiang, T.; et al. Abnormal processing of IL-1β in NLRP7-mutated monocytes in hydatidiform mole patients. Clinical and Experimental Immunology, 2020, 202(1), 72–79. [CrossRef]
- Reddy, R.; Nguyen, N.M.P.; Sarrabay, G.; Rezaei, M.; Rivas, M.C.G.; et al. The genomic architecture of NLRP7 is Alu rich and predisposes to disease-associated large deletions. European Journal of Human Genetics, 2016, 24(10), 1445–1452. [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, M.; Suresh, B.; Bereke, E.; Hadipour, Z.; Aguinaga, M.; et al. Novel pathogenic variants in NLRP7, NLRP5, and PADI6 in patients with recurrent hydatidiform moles and reproductive failure. Clin Genet, 2021, 99(6), 823–828. [CrossRef]
- Buza, N.; McGregor, S.M.; Barroilhet, L.; Zheng, X.; Hui, P. Paternal uniparental isodisomy of tyrosine hydroxylase locus at chromosome 11p15.4: spectrum of phenotypical presentations simulating hydatidiform moles. Modern pathology: an official journal of the United States and Canadian Academy of Pathology, Inc, 2019, 32(8), 1180–1188. [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Lu, B.; Lu, W.; Li, S.; Li, X.; et al. Whole-exome sequencing reveals genetic variants in ERC1 and KCNG4 associated with complete hydatidiform mole in Chinese Han women.Oncotarget. 2017; 8(3): 75264-75271. https://www.oncotarget.com/article/20769/text/.
- Chan, K.K.; Wong, E.S.Y.; Wong, O.G. W.; Ngan, H.Y. S.; Cheung, A.N. Y. Identification of nonsynonymous TP53 mutations in hydatidiform moles. Mutation Research/Fundamental and Molecular Mechanisms of Mutagenesis, 2018, 809, 20–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemida, R.; van Doorn, H.; Fisher, R. A Novel Genetic Mutation in a Patient With Recurrent Biparental Complete Hydatidiform Mole: A Brief Report. International journal of gynecological cancer: official journal of the International Gynecological Cancer Society, 2016, 26(7), 1351–1353. [CrossRef]
- Ito, Y.; Maehara, K.; Kaneki, E.; Matsuoka, K.; Sugahara, N.; et al. Novel Nonsense Mutation in the NLRP7 Gene Associated with Recurrent Hydatidiform Mole. Gynecol Obstet Invest, 2016, 81(4), 353–358. [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.M.P.; Ge, Z.J.; Reddy, R.; Fahiminiya, S.; Sauthier, P.; et al. Causative Mutations and Mechanism of Androgenetic Hydatidiform Moles. Am J Hum Genet, 2018, 103(5), 740–751. [CrossRef]
- Dube, R.; Kar, S.S.; Jhancy, M.; George, B.T. Molecular Basis of Müllerian Agenesis Causing Congenital Uterine Factor Infertility—A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Jabri, M.; Al-Badi, S.; Al-Kindi, H.; Arafa, M. Immunohistochemical expression of BCL-2 in hydatidiform moles: a tissue microarray study. Pathologica - Journal of the Italian Society of Anatomic Pathology and Diagnostic Cytopathology, 2023, 115(3), 148–154. [CrossRef]
- Wargasetia, T.L.; Shahib, M.N.; Martaadisoebrata, D.; Dhianawaty, D.; Hernowo, B. Characterization of apoptosis and autophagy through Bcl-2 and Beclin-1 immunoexpression in gestational trophoblastic disease. Iran J Reprod Med 2015, 13, 413. [Google Scholar]
- Khooei, A.; Pasdar, F.A.; Fazel, A.; Mahmoudi, M.; Reza, N.M.; et al. View of Expression of Pro-Apoptotic Bax and Anti-Apoptotic Bcl-2 Proteins in Hydatidiform Moles and Placentas With Hydropic Changes. Acta Medica Iranica, 2019,57(1), 27-32. [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.H.; Maestá, I.; St Laurent, J.D.; Hasselblatt, K.T.; Horowitz, N.S.; et al. Distinct microRNA profiles for complete hydatidiform moles at risk of malignant progression. American journal of obstetrics and gynecology, 2021, 224(4), 372.e1–372.e30. [CrossRef]
- Missaoui, N.; Landolsi, H.; Mestiri, S.; Essakly, A.; Abdessayed, N.; et al. Immunohistochemical analysis of c-erbB-2, Bcl-2, p53, p21WAF1/Cip1, p63 and Ki-67 expression in hydatidiform moles. Pathology, research and practice, 2019, 215(3), 446–452. [CrossRef]
- Erol, O.; Suren, D.; Tutus, B.; Yararbas, K.; Sayiner, A.; et al. Comparison of p57, c-erbB-2, CD117, and Bcl-2 expression in the differential diagnosis of hydatidiform mole and hydropic abortion. European journal of gynaecological oncology 2016, 37, 522–529. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Braga, A.; Maestá, I.; Rocha Soares, R.; Elias, K.M.; Custódio Domingues, M.A.; et al. Apoptotic index for prediction of postmolar gestational trophoblastic neoplasia. American journal of obstetrics and gynecology, 2016, 215(3), 336.e1–336.e12. [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, M.; Xiao, J.; Wu, M.; Song, Y.; et al. E-Cadherin, CD44v6, and Insulin-Like Growth Factor-II mRNA-Binding Protein 3 Expressions in Different Stages of Hydatidiform Moles. Journal of biochemical and molecular toxicology, 2016, 30(9), 455–461. [CrossRef]
- Hasanzadeh, M.; Sharifi, N.; Farazestanian, M.; Nazemian, S.S.; Sani, F.M. Immunohistochemistry Study of P53 and C-erbB-2 Expression in Trophoblastic Tissue and Their Predictive Values in Diagnosing Malignant Progression of Simple Molar Pregnancy. Iran J Cancer Prev, 2016, 9(3), 1–7. [CrossRef]
- Moussa, R.A.; Eesa, A.N.; Abdallah, Z.F.; Abdelmeged, A.; Mahran, A.; et al. Diagnostic Utility of Twist1, Ki-67, and E-Cadherin in Diagnosing Molar Gestations and Hydropic Abortions. Am J Clin Pathol, 2018, 149(5), 442–455. [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.K.; Wong, E.S.; Wong, I.T.; Cheung, C.L.; Gee-Wan, O.; et al. Overexpression of iASPP is required for autophagy in response to oxidative stress in choriocarcinoma. BMC Cancer, 2019, 19(1), 1–13. [CrossRef]
- Yucel Cicek, O.S.; Hekimoglu, E.R.; Turgal, M.; Atilla, P.; Cakar, A.N.; et al. Differential expression of leukemia inhibitory factor and insulin like growth factor-1 between normal pregnancies, partial hydatidiform moles and complete hydatidiform moles. Placenta, 2018, 69, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deka FF, H.A.; ZH, A.A. A. S.; Z, K.A. Role of the Immunohistochemical Marker (Ki67) in Diagnosis and Classification of Hydatidiform Mole. IIUM Medical Journal Malaysia, 2019, 18 (3). [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Sui, L.; Qi, J.; Sun, Q.; Xu, Y.; et al. miR-196b inhibits cell migration and invasion through targeting MAP3K1 in hydatidiform mole. Biomedicine & pharmacotherapy, 2019, 113, 108760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Wu, Q.; Ruan, G.; Zheng, X.; Song, Y.; et al. Expression patterns of maspin and mutant p53 are associated with the development of gestational trophoblastic neoplasia. Oncology Letters, 2016, 12(5), 3135-3142. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.X.; Zhao, J.R.; Xu, Y.Y.; Wu, W.B.; Zhang, H.J. miR-21 Is Overexpressed in Hydatidiform Mole Tissues and Promotes Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion in Choriocarcinoma Cells. Int J Gynecol Cancer, 2017, 27(2), 364–374. [CrossRef]
- Hoeijmakers, Y.M.; Gorris, M.A.J.; Sweep, F.C. G. J.; Bulten, J.; Eysbouts, Y.K.; et al. Immune cell composition in the endometrium of patients with a complete molar pregnancy: Effects on outcome. Gynecologic oncology, 2021, 160(2), 450–456. [CrossRef]
- Kheradmand, P.; Goudarzi, M.; Tavakoli, M. Analysis of p53 expression in partial hydatidiform mole and hydropic abortion. Front Biol (Beijing), 12(5), 357–360. [CrossRef]
- Khooei, A.; Pasdar, F.A.; Fazel, A.; Mahmoudi, M.; Nikravesh, M.R.; et al. P53 expression in various types of hydropic placentas (through ploidy analysis as a complementary tool in diagnosis of samples). Caspian J Intern Med, 2019, 10(2), 205. [CrossRef]
- Hadi, F.; Kazemi, N.; Hosseini, M.S.; Ebrahimi, A. Evaluation of TP53 and HER-2/neu Genes Expression Levels in Gestational Trophoblastic Diseases Cases and Determining Their Predictive Value in Diagnosis of Malignancy and Disease Progression. International Journal of Cancer Management, 2022, 15(8), 119264. [CrossRef]
- Kubelka-Sabit, K.; Prodanova, I.; Jasar, D.; Bozinovski, G.; Filipovski, V.; et al. Molecular and immunohistochemical characteristics of complete hydatidiform moles. Balkan Journal of Medical Genetics, 2017, 20(1) 27-34. [CrossRef]
- Masood, S.; Kehar, S.I.; Shawana, S.; Aamir, I. Differential expression of p63 in hydropic and molar gestations. Journal of the College of Physicians and Surgeons Pakistan 2015, 25, 198–202. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jahanbin, B.; Sarmadi, S.; Ghasemi, D.; Nili, F.; Moradi, J.A.; et al. Pathogenic role of Twist-1 protein in hydatidiform molar pregnancies and investigation of its potential diagnostic utility in complete moles. Diagn Pathol, 2023, 18(1), 1–8. [CrossRef]
- Luchini, C.; Parcesepe, P.; Mafficini, A.; Nottegar, A.; Parolini, C.; et al. Specific expression patterns of epithelial to mesenchymal transition factors in gestational molar disease. Placenta, 2015, 36(11), 1318–1324. [CrossRef]
- Chen, J. The Cell-Cycle Arrest and Apoptotic Functions of p53 in Tumor Initiation and Progression. Cold Spring Harbor perspectives in medicine, 2016, 6(3), a026104. [CrossRef]
- Mak, V.C.Y.; Lee, L.; Siu, M.K.Y.; Wong, O.G.W.; Lu, X.; et al. Downregulation of ASPP2 in choriocarcinoma contributes to increased migratory potential through Src signaling pathway activation. Carcinogenesis, 2013, 34(9), 2170–2177. [CrossRef]
- Mak, V.C.Y.; Lee, L.; Siu, M.K.Y.; Wong, O.G.W.; Lu, X.; et al. Downregulation of ASPP1 in gestational trophoblastic disease: correlation with hypermethylation, apoptotic activity and clinical outcome. Mod Pathol, 2011, 24(4), 522–532. [CrossRef]
- Kar, A.; Mishra, C.; Biswal, P.; Kar, T.; Panda, S.; et al. Differential expression of cyclin E, p63, and Ki-67 in gestational trophoblastic disease and its role in diagnosis and management: A prospective case-control study. Indian J Pathol Microbiol, 2019, 62(1), 54–60. [CrossRef]
- Toki, T.; Horiuchi, A.; Ichikawa, N.; Mori, A.; Nikaido, T.; et al. Inverse relationship between apoptosis and Bcl-2 expression in syncytiotrophoblast and fibrin-type fibrinoid in early gestation. Mol Hum Reprod, 1999, 5(3), 246–251. [CrossRef]
- Ronnett, B.M.; Descipio, C.; Murphy, K.M. Hydatidiform moles: Ancillary techniques to refine diagnosis. International Journal of Gynecological Pathology, 2011, 30(2), 101–116. [CrossRef]
- Fulop, V.; Mok, S.C.; Genest, D.R.; Szigetvari, I.; Cseh, I.; et al. c-myc, c-erbB-2, c-fms and bcl-2 oncoproteins. Expression in normal placenta, partial and complete mole, and choriocarcinoma. J Reprod Med. 1998, 43, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Al-Bozom, I.A. P53 and Bcl-2 oncoprotein expression in placentas with hydropic changes and partial and complete moles. APMIS, 2000, 108(11), 756-760. [CrossRef]
- Pinkas-Kramarski, R.; Alroy, I.; Yarden, Y. ErbB receptors and EGF-like ligands: Cell lineage determination and oncogenesis through combinatorial signaling. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia, 1997, 2(2), 97–107. [CrossRef]
- Fock, V.; Plessl, K.; Fuchs, R.; Dekan, S.; Milla, S.K.; et al. , Trophoblast subtype-specific EGFR/ERBB4 expression correlates with cell cycle progression and hyperplasia in complete hydatidiform moles. Human Reproduction, 2015, 30(4), 789–799. [CrossRef]
- Miettinen, M.; Lasota, J. KIT (CD117): a review on expression in normal and neoplastic tissues, and mutations and their clinicopathologic correlation. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol, 2005, 13(3), 205–220. [CrossRef]
- Sheikh, E.; Tran, T.; Vranic, S.; Levy, A.; Bonfil, R.D. Role and significance of c-KIT receptor tyrosine kinase in cancer: A review. Bosn J Basic Med Sci, 2022, 22(5), 683. [CrossRef]
| Chromosome Number | Mutation [Reference] |
Gene Involved |
| 1 | c.[1796T > A]; [1796T > A] [58] |
PADI6 |
| 6 | 6p21.33 Mutation p.M1V, c.1A>G [50] |
KHDC3L |
| 6 | c.322_325delGACT [6,15,16,17] |
KHDC3L |
| 6 | c.602 C>G [46] |
KHDC3L |
| 6 | c.299_302delTCAA, p.Ile100Argfs*2 c.322_325delGACT, p.Asp108Ilefs*30 [45] |
KHDC3L |
| 6 | c.17_20delGGTT, p.Arg6Leufs*7 c.349+1G4A [51] |
KHDC3L |
| 6 | c.334 1G>A [59] |
REC114 |
| 11 | pUPD 11p15.4 [60] |
TH01 |
| 11 | c.783dup (p.Glu262*) missense variant c.1501T>C (p.Ser501Pro) [59] |
TOP6BL/C11orf80 |
| 13 | G48C(p.Q16H) [61] |
ERC1c |
| 16 | c.G1114A(p.G372S) [61] |
KCNG4 |
| 17 | Exon6-213(nonsense) p.Arg213X Exon6-220(missense) p.Tyr220Cys Exon7-245(missense) p.Gly245Ser Exon7-248(missense) p.Arg248Gln Exon7-249(missense) p.Arg249Ser Exon8-295(missense) p.Pro295Leu [62] |
TP53 |
| 19 | c.1441 G>A [46] |
NLRP7 |
| 19 | Exon 4 (missense) c.1358T>G, p.Ile453Ser Exon 7 (Frameshift) c.2655dupC, p.Ile886HisfsTer11 [52] |
NLRP7 |
| 19 | c.555_557delCAC, p.Thr185del [53] |
NLRP7 |
| 19 | c.2810+2T>G [55] |
NLRP7 |
| 19 | Exon 2, c.197G>A [63] |
NLRP7 |
| 19 | c.584G>A; p.W195X [64] |
NLRP7 |
| 19 | Exon 6/intron 9 (c.[2248C4G]; [2810+2T4G]) Exon 4 (c.[1374_1375delAG]; [1374_1375delAG]) Exon 4/6 (c.[1908dup]; [2161C4T]) Exon4/intron 10 (c.[939_952dup14]; [2982-2A4G]) Exon 9 (c.[2759G4A]; [2759G4A]) Exon 9 (c.[2777T4G]; [2777T4G]) Intron 5 (c.[2130-6_2132del]; [ = ]) Intron 5 & 6 (c.[2130-266_2300+782del]; [2130-266_2300+782del]) Before exon 1 & intron 5 (c.[ −39-231_2130-510del]; [-39-231_2130-510del]) Intron 1 & intron 5/exon 8 (c.[-40+251_2130-681del];[2571dup]) Intron 1 & intron 5 (c.[-3998_2130-668del]; [-3998_2130-668del]) Before exon 1/exon 6 (c.[-13413_2982-344del];[2248C4G]) [57] |
NLRP7 |
| 19 | c.[1812_1837dup]; [1812_1837dup] c.[2162G > A]; [2162G > A] c.[2204A > C]; [2204A > C] c.[−40 + 3G > C]; [−40 + 3G > C] c.[−6831_-39–1586]; [2248C > G] [58] |
NLRP7 |
| 19 |
c.1093G > A, p.(Asp365Asn) c.[1093G > A]; [1093G > A] [58] |
NLRP5 |
| 22 | c.3452G>A c.1196þ1G>A, affecting the splice donor of exon 10, and a 1-bp deletion, c.2206del (p.Val736Serfs*31), in exon 19 [59] |
MEI1 |
| Gene | Reference | Detection method | GTD Diagnosis method | Number of cases | Result |
| BCL-2 | [66] | TMA | Morphological appearance and p57 IHC | Control 202 PHM 95 CHM 142 |
Decreased expression in CHM compared to PHM and control |
| BCL-2 | [67] | IHC | Not specified | Control 6 PHM 11 CHM 11 IM 11 CC 9 |
Decreasing expression from PHM, to CHM, to invasive mole, to choriocarcinoma compared to normal placenta |
| BCL-2 | [68] | IHC | Morphological appearance and ploidy analysis by flow cytometry | HA 10 PHM 8 CHM 11 |
Decreased expression in CHM compared to PHM and HA |
| BCL-2 | [69] | IHC | Morphological appearance | Regressed HM 30 Post-molar GTN 9 |
Decreased expression is associated with progression from CHM to GTN |
| BCL-2 | [70] |
IHC | Morphological appearance and p57 IHC nuclear DNA micro- satellite polymorphism for discordant cases |
HA 39 PHM 41 CHM 140 |
Increased expression in CHM and PHM compared to HA |
| BCL-2 | [71] | IHC | Morphological appearance and STR genotyping | HA 17 PHM 23 CHM 20 |
Increased expression in HA compared to CHM and PHM |
| Beclin-1 | [67] | IHC | Not specified | Control 6 PHM 11 CHM 11 IM 11 CC 9 |
Increased expression in choriocarcinoma |
| Capase-3 | [72] | IHC | Morphological appearance and p57 IHC | Regressed CHM 590 Post-CHM GTN 190 |
The NPV for GTN of apoptotic index ≥ 4.0% was 97% |
| CD117 | [71] | IHC | Morphological appearance and STR genotyoing | HA 17 PHM 23 CHM 20 |
Decreased staining percentage in HA compared to CHM and PHM |
| CD44v6 | [73] | IHC | Not specified | Control 36 PHM 25 CHM 48 IM 12 |
No significant difference in CD44v6 expression |
| c-erB-2 | [71] | IHC | Morphological appearance and STR genotyoing | HA 17 PHM 23 CHM 20 |
Increased expression in CHM compared to PHM and HA |
| c-erB-2 | [74] |
IHC | Morphological appearance and immunohistochemistry and serial beta HCG | PHM 10 CHM 18 GTN 30 |
Increased expression in GTN compared to simple molar pregnancy. |
| E-cadherin | [14] | IHC | Morphological appearance and molecular genotyping | HA 23 PHM 24 CHM 23 |
Decreasing expression from HA to PHM to CHM |
| E-cadherin | [75] | IHC | Morphological appearance, ploidy analysis by flow cytometry, and p57 IHC | HA 16 PHM 17 CHM 16 |
Decreased expression in HM compared to HA |
| E-cadherin | [73] | IHC | Not specified | Control 36 PHM 25 CHM 48 IM 12 |
No significant difference in E-cadherin expression |
| iASPP | [76] | IHC siRNA transfection |
Not specified | First trimester placenta 10 Term placenta 11 HM 63 CC 7 |
Over-expression might be related to development of GTN Overexpression is associated with increased autophagy related protein expression Silencing is associated with cellular senescence |
| IGF-1 | [77] | IHC | Morphological appearance and p57 IHC | Control 8 PHM 8 CHM 8 |
Downregulation in CHM decidua and chorionic villi |
| IMP3 | [73] | IHC | Not specified | Control 36 PHM 25 CHM 48 IM 12 |
Decreasing expression from normal placental tissues, to PHM, to CHM, to IM |
| Inhibin-alpha | [14] | IHC | Morphological appearance and molecular genotyping | HA 23 PHM 24 CHM 23 |
Increased expression in molar pregnancy compared with HA |
| Ki-67 | [70] |
IHC | Morphological appearance and p57 IHC | HA 39 PHM 41 CHM 140 |
Increased expression in CHM compared to PHM and HA |
| Ki-67 | [78] | IHC | Morphological appearance | HA 30 PHM 30 CHM 30 |
Expression in cytotrophoblasts is significantly higher in CHM than PHM than HA Expression in stromal cells is significantly higher in molar pregnancy than HA |
| Ki-67 | [75] | IHC | Morphological appearance, ploidy analysis by flow cytometry, and p57 IHC | HA 16 PHM 17 CHM 16 |
Significantly increased expression in PHM compared to HA |
| LIF | [77] | IHC | Morphological appearance and p57 immunostaining | Control 8 PHM 8 CHM 8 |
Downregulated in CHM decidua but upregulated in CHM trophoblasts. |
| MAP3K1 | [79] | IHC | Not specified | Controls 15 CHM 20 |
Significantly higher expression in CHM compared to control |
| Maspin m-p53 |
[80] | IHC | Not specified | Control 48 Regressed HM 49 Progressed HM 39 |
Maspin was inversely correlated with FIGO prognostic score whereas expression of m-p53 was positively correlated with FIGO stage. |
| miR-181 | [69] |
miRNA-sequencing and qRT-PCR and western blot | Morphological appearance | Regressed HM 30 Post-molar GTN 9 |
Increased miR-181 expression in post-molar GTN. |
| miR-371a-5p and miR-518a-3p | [15] | miRNA array and qRT-PCR | Morphological appearance | Control 6 Regressed CHM 35 Post-CHM GTN 21 |
miR-371a-5p and miR-518a-3p were upregulated in progressed CHMs (GTN) |
| miRNA-21 | [81] | qRT-PCR | Morphological appearance | Control 20 HM 16 |
miRNA-21 is upregulated in HM |
| miR-196b | [79] | qRT-PCR | Not specified | Control 15 CHM 20 |
Significantly lower expression in CHM compared to control. |
| NKT-like cells | [82] | mIHC | The FIGO 2000 guideline | 16 CHM with spontaneous regression 16 CHM with progress to post-molar GTN |
The density of NKT-like cells was significantly higher in patients with spontaneous regression compared to those who progressed to GTN |
| P53 | [70] |
IHC | Morphological appearance and p57 immunostaining | HA 39 PHM 41 CHM 140 |
Increased expression in CHM compared to PHM and HA |
| P53 | [83] | IHC | Morphological appearance | HA 20 PHM 20 |
Significantly higher positive rate and grade of staining in PHM compared to HA. |
| P53 | [14] | IHC | Morphological appearance and molecular genotyping | HA 23 PHM 24 CHM 23 |
Increased expression of p53 in CHM compared to PHM and HA |
| P53 | [74] |
IHC | Morphological appearance and immunohistochemistry and serial beta HCG | PHM 10 CHM 18 GTN 30 |
Increased expression of p53 in GTN compared to simple HM. |
| P53 | [84] |
IHC | Morphological appearance and ploidy analysis by flow cytometry | HA 10 PHM 8 CHM 11 |
Increased expression in HM compared to HA |
| P53 | [85] | IHC | Not specified | PHM 32 CHM 24 4 IM 2 CC |
Expression was significantly associated with tendency to invasion and metastatic behaviours |
| P57 | [86] | IHC | Not specified | CHM 8 | Absent expression in all CHM (both androgenetic diploidy and biparental diploidy) |
| P57 | [71] | IHC | Morphological appearance and STR genotyoing | HA 17 PHM 23 CHM 20 |
Absent expression in CHM No significant difference between PHM and HA |
| P63 | [70] | IHC | Morphological appearance, p57 immunostaining, and nuclear DNA micro- satellite polymorphism for discordant cases |
HA 39 PHM 41 CHM 140 |
Increased expression in CHM and PHM compared to HA |
| P63 | [87] | IHC | Morphological appearance | HA 30 PHM 30 CHM 30 |
Increased intensity of staining in HM compared to HA |
| Syncyntin-1 |
[34] | IHC | Not specified | Control 8 PHM 6 CHM 12 IM 1 CC 1 PSTT 1 |
the staining intensity of the surface subunit C-terminus was significantly higher in HM, especially those with malignant transformation on follow up |
| Twist-1 | [88] | IHC | Morphological appearance and p57 immunostaining | CHM 47 PHM 40 |
Expression is significantly higher villous stromal cells of CHM compared to PHM |
| Twist-1 | [89] | IHC | Morphological appearance and p57 immunostaining and ploidy analysis | Abortion 23 PHM 10 CHM 12 Term placenta 7 |
Expression is significantly higher in CHM compared to PHM and HA |
| Twist-1 | [75] | IHC | Morphological appearance, ploidy analysis by flow cytometry, and p57 immunostaining | CHM 16 PHM 17 HA 16 |
Expression is significantly higher in CHM compared to PHM and HA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





