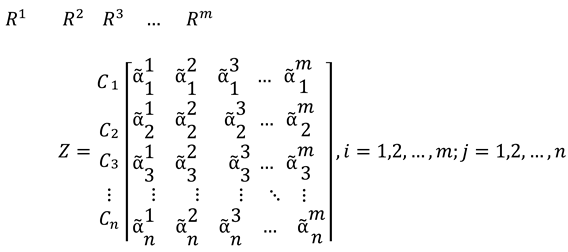1.0. Introduction
In the ever-evolving landscape of web services, optimization has become a paramount concern for enhancing efficiency, reliability, and user satisfaction. It is imperative to optimize web services based on some quantity metrics and quality metrics (experts’ inputs), precisely ranking optimization problems using objective weights(Entropy) and with not just the traditional fuzziness features (i.e. uncertainty, ambiguity, incomplete, bias) in mind, but also, the combined hesitation and intuition inherent in the data owing to the involvement of humans (experts’ inputs) is imminent. Brief review of the fuzzy linguistic terms and applications.
In 1965, [
1], laid the foundation for fuzzy linguistic terms. Zadeh proposed representing uncertainty and imprecision in natural language using fuzzy sets and linguistic variables. In 1986, [
2] started Intuitionistic Fuzzy Linguistic terms incorporate a degree of non-membership along with membership and non-membership functions. Intuitionistic fuzzy linguistic terms apply this idea to linguistic variables, allowing for a more comprehensive representation of uncertainty and hesitation in human reasoning. In 2010 for the first time, [
3] proposed Hesitant fuzzy linguistic terms to address situations where decision-makers are hesitant about the degree of membership of an element to a fuzzy set. Hesitant fuzzy linguistic terms extend this concept to linguistic variables, allowing for a more nuanced representation of uncertainty. Afterward, researchers deliberated on diverse Fuzzy Linguistic Terms, proposing varied methods for their resolution. For example, [
4,
5] conducted some recent reviews on Integrated Fuzzy Multi-Criteria Decision-Making methods. Fast-forward, in October 2022, [
6] proposed an Integrated Fuzzy DEMATEL-TOPSIS-VIKOR model applied to Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA). Additionally, [
7] presented an integrated fuzzy model utilizing new fuzzy-BWM and fuzzy-TOPSIS for the evaluation and selection of mobile banking (m-banking) applications, highlighting that all the above papers are grounded in Fuzzy Linguistic terms.
both studies leveraged on Fuzzy Theory based on Fuzzy Linguistic Terms to address security aspect of mobile-edge computing and brilliant but needy students selection. [
10,
11,
12,
13] each presented innovative applications of fuzzy Multi-Criteria Decision-Making (MCDM) methods utilizing fuzzy linguistic terms to solve complex problems in various domains. [
11] introduced a fuzzy TOPSIS-based approach for optimizing cell selection during handovers in LTE networks, improving decision-making under uncertain conditions to enhance network performance. [
12] proposed a Z-fuzzy TOPSIS method, integrating functional and dysfunctional judgments, to effectively select optimal transfer center locations, addressing the inherent fuzziness in spatial decision-making. [
13] evaluated various fuzzy MCDM techniques to determine the best web services based on quality of service metrics, showcasing the comparative strengths and the degree of association among the Fuzzy MCDM methods used in managing imprecise data. [
10] combined fuzzy DEMATEL and SAW methodologies to assess lecturers' performance across multiple criteria. The above papers demonstrated the effectiveness and adaptability of fuzzy MCDM approaches in handling fuzzy linguistic uncertainties across diverse application areas. However, the studies did not explore haste and intuition which has the potentials to better handle uncertainties.
The versatile Atanassov Intuitionistic Fuzzy Linguistic Terms, in their diverse iterations, have seamlessly integrated into various Fuzzy Multi-Criteria Decision-Making frameworks, tackling an array of challenges with finesse. [
14] delved into the world of entropy measures for interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy sets, offering insights that shine in the realm of group decision-making. [
15] scrutinized trapezoidal intuitionistic fuzzy numbers within the framework of Intuitionistic Fuzzy Multi-Criteria Decision Making, comparing three pivotal ranking approaches—expected value-based, centroid-based, and score function-based—ultimately revealing their effective and precise alternative prioritization capabilities. [
16] introduced the concept of intuitionistic fuzzy weighted entropy and proposed a novel method for solving intuitionistic fuzzy multicriteria decision-making problems. As an extension of fuzzy set theory, intuitionistic fuzzy sets have garnered significant attention from researchers due to their ability to effectively model common real-world Multi-Criteria Decision-Making situations characterized by uncertainty. For instance, [
19,
20] provided significant contributions to the field of Integrated Fuzzy Intuitionistic Multi-Criteria Decision-Making (MCDM), applying these advanced methods to a variety of practical problems. presented a robust method for selecting smartphones by incorporating group decision-making and intuitionistic fuzzy TOPSIS, allowing for a more accurate reflection of individual preferences and uncertainties. [
17] developed an effective MCDM approach using intuitionistic fuzzy sets with TOPSIS to evaluate smartphone alternatives based on consumer preferences, uniquely addressed high uncertainty in decision-making, and presented a real case study for the first time. [
21] Evaluated of hospital web services using intuitionistic fuzzy AHP and intuitionistic fuzzy VIKOR. [
22] identified decision criteria for cloud computing technology (CCT) selection, develop a framework using Interval Valued Intuitionistic Fuzzy (IVIF) sets to evaluate and choose the most suitable CCT, and apply this methodology through an empirical study. It extended the MULTIMOORA technique to handle uncertainty and conflicting parameters, demonstrating its applicability with an illustrative case study. [
20] addressed the challenge of evaluating blockchain service providers by proposing an integrated multi-attribute group decision-making (MAGDM) method in an intuitionistic fuzzy environment. This method incorporated entropy and the best-worst method (BWM) to comprehensively weigh subjective and objective criteria, enhancing the reliability and reasonableness of decision outcomes. A numerical example and comparison were provided to demonstrate the method's practicality and usefulness, contributing to the advancement of blockchain technology and MAGDM analysis.
The concept of Hesitant Fuzzy Sets (HFS) arises in situations where decision makers grapple with uncertainty while assessing indicators, alternatives, variables, coefficients, and the like. This model becomes particularly relevant when experts hold differing opinions on parameter values due to incomplete information. Unlike traditional methods that assign a singular degree of membership to unknown parameters, Hesitant Fuzzy Sets accommodate the complexity by allowing for multiple degrees of membership for each parameter in these circumstances. After the introduction of Hesitant Fuzzy Linguistic terms by Torra, the technique has garnered significant attention from researchers in the field. [
23] advanced the proposition of a proficient Shapley function tailored for probabilistic hesitant fuzzy cooperative games. [
23] proposed approach is rooted in the utilization of the generalized Choquet integral, contributing to the enhancement of analytical frameworks in cooperative game theory within the context of probabilistic hesitant fuzzy sets. [
24] proposed a pioneering integrated approach within the realm of Multiple Criteria Decision Making (MCDM), amalgamating the constructs of Linguistic Hesitant Fuzzy Sets (LHFSs) and the TODIM method (acronym in Portuguese denoting interactive and multi-criteria decision making). [
24] primary objective was to undertake a comprehensive evaluation and selection process to identify the most suitable e-learning website for network teaching. Many more studies explored Hesitant Fuzzy Linguistic terms in varied categories such as Group Decision-Making Methodologies, Multi-Criteria-Making Techniques and Advanced Optimization Techniques.
Group decision-making methodologies, particularly those incorporating hesitant fuzzy linguistic frameworks, significantly enhance the precision and reliability of collective decisions in multi-attribute environments. For instance, [
25,
26] developed specific geometric operators and power geometric operators tailored for hesitant fuzzy contexts. Additionally, innovative approaches like the double hierarchy hesitant fuzzy linguistic preference information [
27] and the extended Heronian mean operator [
28] further refine the aggregation and structuring of group preferences.
Multi-criteria decision-making techniques are essential for optimizing decisions in environments with multiple conflicting criteria, and hesitant fuzzy linguistic frameworks are particularly effective in managing these complexities. [
29] introduced a possibility degree-based linear assignment method, enhancing decision-making processes involving multiple criteria. Additionally, [
30] applied hesitant fuzzy methods to address conflicting criteria in the optimization of electric vehicle charging station deployment, demonstrating the practical application of these frameworks in real-world problems.
Advanced optimization techniques that incorporate complex fuzzy information systems demonstrate the versatility and power of hesitant fuzzy methodologies in solving intricate decision-making problems. [
31] showcased an advanced approach by integrating complex Pythagorean fuzzy N-soft information, thereby effectively handling uncertainty and complexity in multi-criteria optimization scenarios. [
31]highlighted the significant improvements and applications of advanced optimization techniques facilitated by the incorporation of sophisticated fuzzy frameworks, underscoring their critical role in addressing complex decision-making challenges. However, a notable critique of the aforementioned studies is their omission of both haste and intuition in their models, elements which are essential for accurately representing uncertainties in decision-making processes. By not accounting for the urgency often inherent in real-world decision-making scenarios and the intuitive judgments that decision-makers frequently rely upon, these studies may fall short in fully capturing the complexities and nuances of uncertain environments.
Some few studies have also proposed Hesitant Intuitionistic Fuzzy Linguistics terms. For instance, [
32] proposed a recommender system devised to assess and rank alternative tourist attractions by scrutinizing online reviews. evaluation hinged upon aspect-level sentiment analysis, integrated with a multi-criteria decision-making (MCDM) framework. Notably, [
32] MCDM approach incorporated both intuitionistic and hesitant fuzzy information, enhancing the nuanced analysis of the complex and uncertain aspects inherent in the assessment process. [
31] methodology provided a versatile decision-making tool tailored for the ranking-based fuzzy modeling of two-dimensional parameterized data. The CPFNS-VIKOR method amalgamated the pioneering attributes of the VIKOR method with the exemplary parametric structure intrinsic to the complex Pythagorean fuzzy N-soft model. In 2023, [
33] proposed a theoretical foundation for Hesitant Intuitionistic Fuzzy linguistics terms and applied it to a hybrid Fuzzy DEMATEL-TOPSIS model for a cloud provider selection problem. The few studies above on Hesitant Intuitionistic Fuzzy Linguistics did not use datasets that balance subjective and objective aspects as well as offering a comprehensive evaluation. For instance, [
32] used only online review dataset which may not reflect actual user experiences, may not present standardized and professional knowledge on the subject matter. Hence depriving the study of comprehensive evaluation. Also, [
33] utilized only expert rating dataset which offered narrow perspectives due to limited representativeness affecting study’s generalizability and less practical insight because expert focused on theoretical or technical aspects of the Quality of Service(QoS) factors or criteria potentially overlooking practical, on the ground experiences on the subject matter. Hence, there is the need for studies that use Hesitant Intuitionistic Fuzzy Linguistics, balanced subjectivity with objectivity and ensure comprehensive evaluations.
Therefore, this study introduces a new Entropy-based Hesitant Intuitionistic Fuzzy TOPSIS method that is not only balanced but also offered a holistic evaluation for ranking web services. The main objective of this study is to develop an optimized ranking method for web services using a novel Entropy-based Hesitant Intuitionistic Fuzzy TOPSIS approach based on both qualitative and quantitative datasets.
Noteworthy Contributions of the present study are;
This pioneering study presents Hesitant Intuitionistic Fuzzy TOPSIS model by integrating entropy-based measures, improving its ability to manage uncertainty and variability, and increasing decision-making accuracy. The Entropy measure assigns weights based on QoS data from the WS-DREAM dataset, complementing expert QoS ratings.
This research enhances decision-making by introducing the Hesitant Intuitionistic Fuzzy TOPSIS model, which better handles hesitation and uncertainty, offering a more comprehensive evaluation method.
This research focuses on optimizing web services, providing tools for effective decision-making and demonstrating the model's effectiveness through a real-world example.
Section 2 details the theoretical foundations of entropy, Hesitant Intuitionistic(hesitationistic) Linguistic terms Fuzzy TOPSIS.
Section 3 Illustrative case and results, demonstrating the effectiveness of the proposed model. Finally,
Section 4 concludes the paper with a summary of findings and suggestions for future research directions.
3.0. Implementation
In the context of an e-commerce platform, the optimization of web services, namely; S1, S2, S3, and S4, becomes pivotal for ensuring seamless user interactions. These services cater to diverse aspects such as product search, order processing, user authentication, and content delivery. The selection of the optimal service hinges on key performance criteria, namely Availability, Response Time, Reliability, and Latency. Availability, representing the operational percentage, is critical for round-the-clock accessibility. Response Time and Reliability play key roles in providing a swift and trustworthy user experience, while Latency influences real-time interactions. Employing the proposed Entropy-based Hesitant Intuitionistic Fuzzy TOPSIS model involves assigning weights to these criteria and converting normalized data to fuzzy numbers, addressing uncertainties, hesitant and intuition. The calculation of entropy aids in measuring uncertainty levels, and subsequent weights derived from entropy values guide the decision-making process. The resulting optimal service selection enhances user experience, boosts reliability in transactions, and optimally utilizes resources, thus ensuring the e-commerce platform's sustained competitiveness and customer satisfaction. Since regular validation and updates to the model with real-world data are crucial for adapting to evolving conditions and maintaining the optimization of web services, this validate the model with real-world web service dataset downloaded from WS-DREAM dataset.
Table 1.
Decision Matrix of extracted dataset.
Table 1.
Decision Matrix of extracted dataset.
| Availability |
Response Time |
Reliability |
Latency |
|
| 96 |
93.37 |
67 |
41.66 |
S1 |
| 84 |
134.07 |
60 |
8.21 |
S2 |
| 83 |
132 |
73 |
16 |
S3 |
| 97 |
151.3 |
73 |
8.66 |
S4 |
Calculate the Sum of Each Column
Normalize
Table 2.
Normalized Decision Matrix based on Equation (1).
Table 2.
Normalized Decision Matrix based on Equation (1).
| Availability |
Response Time |
Reliability |
Latency |
|
| 0.2667 |
0.183 |
0.2458 |
0.5593 |
S1 |
| 0.2333 |
0.183 |
0.2198 |
0.1103 |
S2 |
| 0.2306 |
0.2586 |
0.2674 |
0.2145 |
S3 |
| 0.2694 |
0.2956 |
0.2674 |
0.116 |
S4 |
Entropy for Each Criterion
Calculating Redundancy for Criteria
Weight Computation
Table 3.
Proposed Hesitant Intuitionistic Fuzzy Linguistic Scale.
Table 3.
Proposed Hesitant Intuitionistic Fuzzy Linguistic Scale.
| Code |
Linguistic terms |
L |
M |
U |
| 1 |
Very low |
1 |
1 |
3 |
| 2 |
Low |
1 |
3 |
5 |
| 3 |
Medium |
3 |
5 |
7 |
| 4 |
High |
5 |
7 |
9 |
| 5 |
Very high |
7 |
9 |
9 |
Table 4.
Fuzzy TOPSIS Decision Matrix.
Table 4.
Fuzzy TOPSIS Decision Matrix.
| |
Availability |
Response Time |
Reliability |
Latency |
| S1 |
(6.600,8.600,9.000) |
(4.600,6.600,8.200) |
(4.200,6.200,7.800) |
(4.600,6.200,7.400) |
| S2 |
(3.800,5.400,7.400) |
(5.000,7.000,8.200) |
(3.400,5.000,6.600) |
(4.600,6.600,8.200) |
| S3 |
(3.000,4.200,5.800) |
(3.000,5.000,7.000) |
(4.600,6.600,7.800) |
(4.600,6.600,8.600) |
| S4 |
(3.800,5.800,7.800) |
(3.000,4.200,5.800) |
(5.800,7.800,8.200) |
(5.400,7.400,8.600) |
Table 5.
Fuzzy Normalized Decision Matrix.
Table 5.
Fuzzy Normalized Decision Matrix.
| |
Availability |
Response Time |
Reliability |
Latency |
| S1 |
(0.733,0.956,1.000) |
(0.366,0.455,0.652) |
(0.512,0.756,0.951) |
(0.622,0.742,1.000) |
| S2 |
(0.422,0.600,0.822) |
(0.366,0.429,0.600) |
(0.415,0.610,0.805) |
(0.561,0.697,1.000) |
| S3 |
(0.333,0.467,0.644) |
(0.429,0.600,1.000) |
(0.561,0.805,0.951) |
(0.535,0.697,1.000) |
| S4 |
(0.422,0.644,0.867) |
(0.517,0.714,1.000) |
(0.707,0.951,1.000) |
(0.535,0.622,0.852) |
Table 6.
The Fuzzy Weighted Normalized Decision Matrix.
Table 6.
The Fuzzy Weighted Normalized Decision Matrix.
|
Availability |
Response Time |
Reliability |
Latency |
| S1 |
(0.215,0.280,0.293)
|
(0.122,0.151,0.217)
|
(0.161,0.238,0.300)
|
(0.036,0.043,0.058)
|
| S2 |
(0.124,0.176,0.241)
|
(0.122,0.143,0.200)
|
(0.131,0.192,0.254)
|
(0.033,0.040,0.058)
|
| S3 |
(0.098,0.137,0.189)
|
(0.143,0.200,0.333)
|
(0.177,0.254,0.300)
|
(0.031,0.040,0.058)
|
| S4 |
(0.124,0.189,0.254)
|
(0.172,0.238,0.333)
|
(0.223,0.300,0.315)
|
(0.031,0.036,0.049)
|
= [\left(\max\below{j} {0.215, 0.124, 0.098, 0.124} \right) = 0.215 \]
= [\left(\max\below{j} {0.280, 0.176, 0.137, 0.189} \right) = 0.280 \]
= [\left(\max\below{j} {0.293, 0.241, 0.189, 0.254} \right) = 0.293 \]
= [\left(\max\below{j} {0.293, 0.217, 0.189, 0.254} \right) = 0.293 \]
Negative Ideal Solution (NIS)
= [\left(\min\below{j} {0.215, 0.124, 0.098, 0.124} \right) = 0.098 \]
= [\left(\min\below{j} {0.280, 0.176, 0.137, 0.189} \right) = 0.137 \]
= [\left(\min\below{j} {0.293, 0.241, 0.189, 0.254} \right) = 0.189 \]
= [\left(\min\below{j} {0.293, 0.217, 0.189, 0.254} \right) = 0.189 \] Hence, for Availability, the PIS is (0.215, 0.280, 0.293, 0.293), and the NIS is (0.098, 0.137, 0.189, 0.189).
Table 7.
Fuzzy Positive and Negative Ideal solutions.
Table 7.
Fuzzy Positive and Negative Ideal solutions.
| |
Positive ideal |
Negative ideal |
| Availability |
(0.215,0.280,0.293) |
(0.098,0.137,0.189) |
| Response Time |
(0.122,0.143,0.200) |
(0.172,0.238,0.333) |
| Reliability |
(0.223,0.300,0.315) |
(0.131,0.192,0.254) |
| Latency |
(0.031,0.036,0.049) |
(0.036,0.043,0.058) |
Table 8.
Fuzzy Distance Positive and Negative.
Table 8.
Fuzzy Distance Positive and Negative.
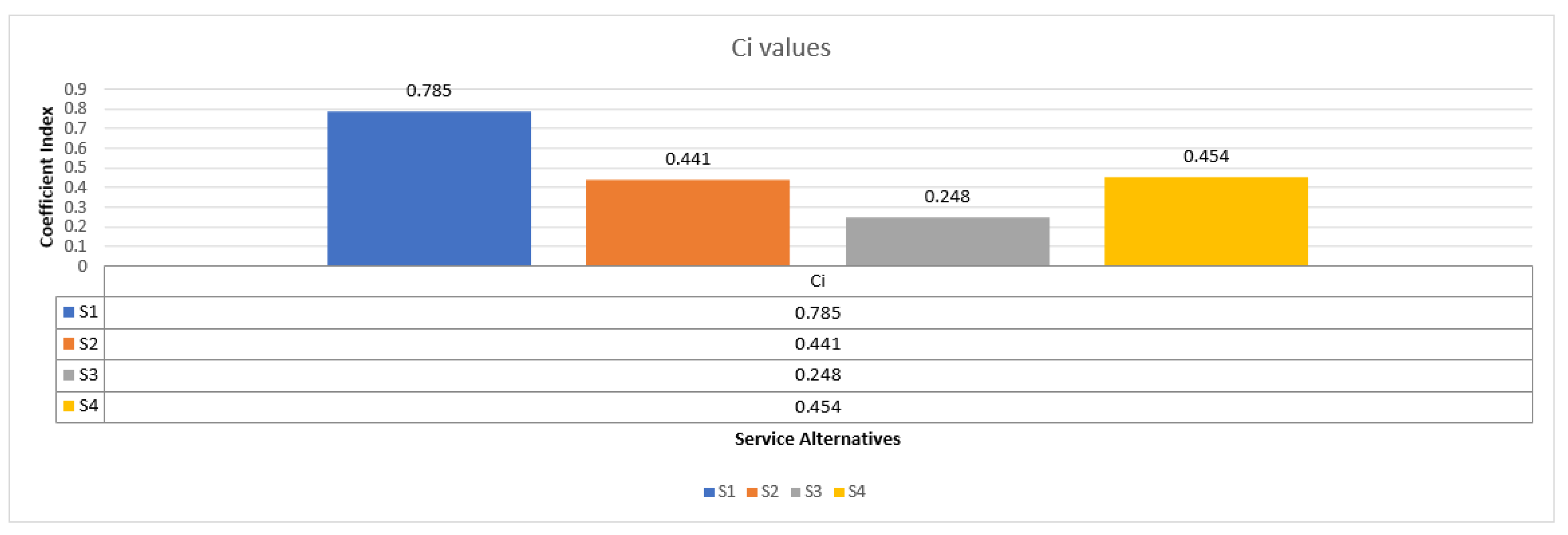
| |
Distance from positive ideal |
Distance from negative ideal |
| S1 |
0.069 |
0.253 |
| S2 |
0.18 |
0.142 |
| S3 |
0.251 |
0.083 |
| S4 |
0.177 |
0.147 |
| |
|
|