1. Introduction
Dams affect the environment, industry, residential areas, and agricultural lands by their very function. Efficient management of a dam can minimize its negative impacts and enhance its positive effects on all these elements. The environmental benefits of efficient management include reducing adverse effects like floods and droughts. For industry and residential areas, it improves energy efficiency and access to clean water. For agricultural lands, it provides more efficient irrigation opportunities. To achieve these benefits, Integrated Water Resource Management (IWRM) must be implemented. IWRM involves measuring and forecasting dam levels.
This study examines the optimal method for predicting dam occupancy levels in the context of IWRM precisely. In this study, it aims to combine physical calculations with data-driven models, which is essential for accurately and precisely predicting dam occupancy levels. This approach enables the implementation of intervention strategies to address scenarios such as droughts, characterized by declining water levels, and floods, marked by dangerously rising water levels.
The occupancy rates of seven different dams in Istanbul were estimated over the past five years. The reason for estimating occupancy is that it normalizes the varying water levels across different dams. The inputs for the prediction models consisted of weather data that has a high correlation with occupancy, Penman-Monteith equation parameters [
1], industrial and residential water consumption, and historical reservoir data. Thus, reservoir level, rainfall, and evapotranspiration were evaluated during the prediction process. The prediction performance of models with weather data and models without weather data are compared to understand the effect of weather data on the prediction.
We utilized AI algorithms with the proposed dataset to determine the most effective method through comparative analysis. The algorithms considered in this assessment include Orthogonal Matching Pursuit CV, Lasso Lars CV, Extra Trees, Random Forest, Ridge CV, Transformed Target Regressor, and LSTM. Our objective in choosing these algorithms is to assess their performance in water level prediction compared to alternative methods that we believe may offer superior results. To conduct this evaluation from multiple perspectives, we formulated four prediction scenarios: daily, weekly, bi-weekly (15-day periods), and monthly (30-day periods). We assessed the performance of these scenarios using statistical hypothesis tests.
The structure of this paper is as follows: first, the research background on dam level prediction studies and methods for predicting water levels is presented. Next, an in-depth introduction to selected dams in Istanbul is provided. This is followed by a detailed case study, results, and discussion. Finally, the paper concludes with a summary of key findings.
2. Literature Review
This section seeks to present a summary of the current research on the intersection of dam reservoir challenges and sea level prediction methods. It reviews the existing literature on the subject and highlights research gaps that form the foundation for this and future work.
Water is a highly valuable resource that significantly contributes to both the environment and the economy. Therefore, the levels of water resources, such as reservoir levels, directly impact total added value [
2] and the net present value of current and future incomes [
3]. Water resources serve multiple purposes, including agriculture, energy generation, fish farming, and drinking water [
4]. Consequently, both the reservoir levels and their intended uses influence how these resources are utilized. Scientific research on water resources thus focuses on areas such as safety, water level measurement technologies, integrated water resource management, and the effects on the environment and agriculture, with a particular emphasis on dams. From a safety perspective, environmental risks and structural health issues, such as dam floods, concrete displacement, and seepage, are investigated at the water level. [
5,
6,
7,
8] and water temperature [
9,
10]. Measuring the water level enables the IWRM in dams, as maintaining the water level is essential not only for ensuring the efficiency of dam operations but also for effective reservoir management and a reliable freshwater supply [
11]. The measurement of water levels relies on Internet of Things (IoT) technology, which involves placing sensors in the dam [
12,
13], or on remote sensing using artificial intelligence (AI) with satellite imagery [
11,
14,
15]. Whereas those technologies are essential in different aspects to improve dam management, one step ahead is to predict the water level and develop intervention strategies for enhancing the improvement [
16]. The prediction of water levels significantly contributes to IRWM [
17]. Especially prediction of climatic factors such as drought and excessive rainfalls is required to develop effective intervention strategies [
18,
19]. Overall, the strength of the contribution is related to the accuracy of the prediction methods used [
20]. The accuracy of predictions depends on the algorithms used, the input parameters, the climate, and the behavior of the reservoir as a system.
In the context of water level prediction, inflow, outflow, historical data of the reservoir, maximum temperature, visibility, humidity, wind speed, cloud cover, and rainfall are utilized as input parameters for models. [
20,
21,
22,
23,
24,
25]. Additionally, parameters such as evapotranspiration, solar radiation, and ambient temperature affect the water level of dams [
1]. These parameters are utilized by various ML algorithms, including artificial neural networks [
21,
22], long short-term memory [
16,
24], nonlinear autoregressive model [
24], multiple linear regression [
22] and, support vector machines [
23]. Overall, the level of water is predicted between 1% and 2% mean absolute percentage error (MAPE) [
9,
21,
23]. Models provide predictions on a daily or monthly basis which are one day to 13 days and one month [
17,
23,
24,
25]. At this level, three different input combinations are commonly used. The first combination includes only historical reservoir data [
22]. The second uses only weather data [
21]. The third combines both weather data and historical reservoir data [
21,
22]. The level of water in dams commonly having autocorrelation makes historical data of the reservoir an indispensable input parameter, however, prediction of future states of the dam requires weather events like rainfall variability or weather characteristics having environmental effects such as droughts [
26,
27].
When the previous studies were reviewed, it was seen that dam water levels were predicted using time series analysis. The literature shows that there is no available research providing dam water level prediction using a hybrid model combining a physical model of evapotranspiration and data-driven models like daily consumption and weather data. This research will be the first to fill this gap.
3. Dams of Istanbul
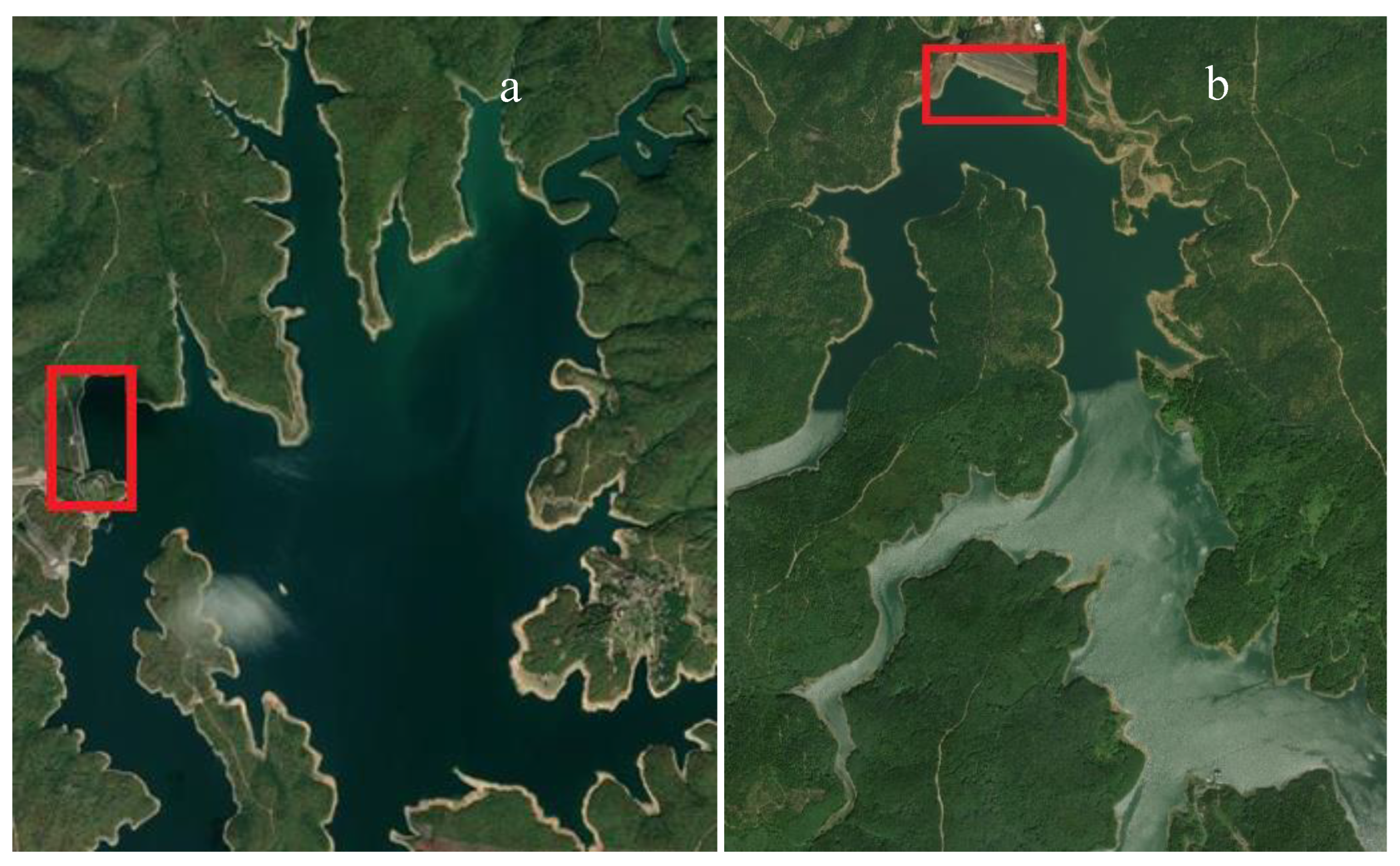
We considered seven dams in Istanbul: Ömerli, Darlık, Elmalı, Terkos, Alibey, Büyükçekmece, Sazlıdere. The Ömerli Dam (in Error! Reference source not found.a), the largest in Istanbul, was constructed primarily to supply the city's drinking water. The dam, which is of the earth-fill type, has a height of 52 meters from the riverbed. At the normal water level, the reservoir volume is 386.50 hm³, and the reservoir area is 23.10 km². It provides 180 hm³ of drinking and utility water annually. Darlık Dam (in Error! Reference source not found.b) is a dam built to supply drinking water, with a height of 73 meters from the riverbed. At the normal water level, the reservoir volume is 107 hm³, and the reservoir area is 5.56 km². The dam provides 108 hm³ of drinking and utility water annually. Elmalı Dam (in Error! Reference source not found.c) was built to supply drinking, utility, and industrial water. The dam, which is of the concrete type, has a body volume of 103,000 m³ and a height of 42.5 meters from the riverbed. At the normal water level, the reservoir volume is 10 hm³, and the reservoir area is 2.80 km². It ensures the supply of 10 hm³ of drinking water annually. Terkos Dam (in Error! Reference source not found.d) was constructed as a concrete fill-type dam to supply drinking water. The height of the dam from the riverbed is 8.80 meters. At the normal water level, the reservoir volume is 186.80 hm³, and the reservoir area is 30.40 km².
Alibey Dam (in Error! Reference source not found.a) was constructed as an earth-fill type dam to supply drinking, utility, and industrial water. The dam has a body volume of 1,930,000 m³ and a height of 30 meters from the riverbed. At the normal water level, the reservoir volume is 66.80 hm³, and the reservoir area is 4.66 km². It provides 39 hm³ of drinking water annually. Büyükçekmece Dam (in Error! Reference source not found.b) was constructed as an earth-fill type dam to supply drinking, utility, and industrial water. The dam has a body volume of 2,020,000 m³ and a height of 13 meters from the riverbed. At the normal water level, the reservoir volume is 161.61 hm³, and the reservoir area is 43 km². The dam provides 102 hm³ of drinking and utility water annually.
Sazlıdere Dam (in Error! Reference source not found.c) was constructed to obtain drinking water. The dam, which is of the rock-fill type, has a body volume of 1,880,000 m³. Its height from the riverbed is 48 meters. At the normal water level, the reservoir volume is 91.60 hm³, and the reservoir area is 11.81 km². The dam provides 50 hm³ of drinking water annually.
All dams contribute to supplying drinking water, but certain dams also provide water for industrial and other utility purposes. Notably, these dams lack hydroelectric plants, so they do not contribute to electricity production. Consequently, the water from these dams is used directly by consumers, making these dams irreplaceable. Therefore, accurately predicting their water occupancy levels is crucial for effective IWRM. This enables timely intervention strategies to be applied, ensuring better resource management and preventing shortages.
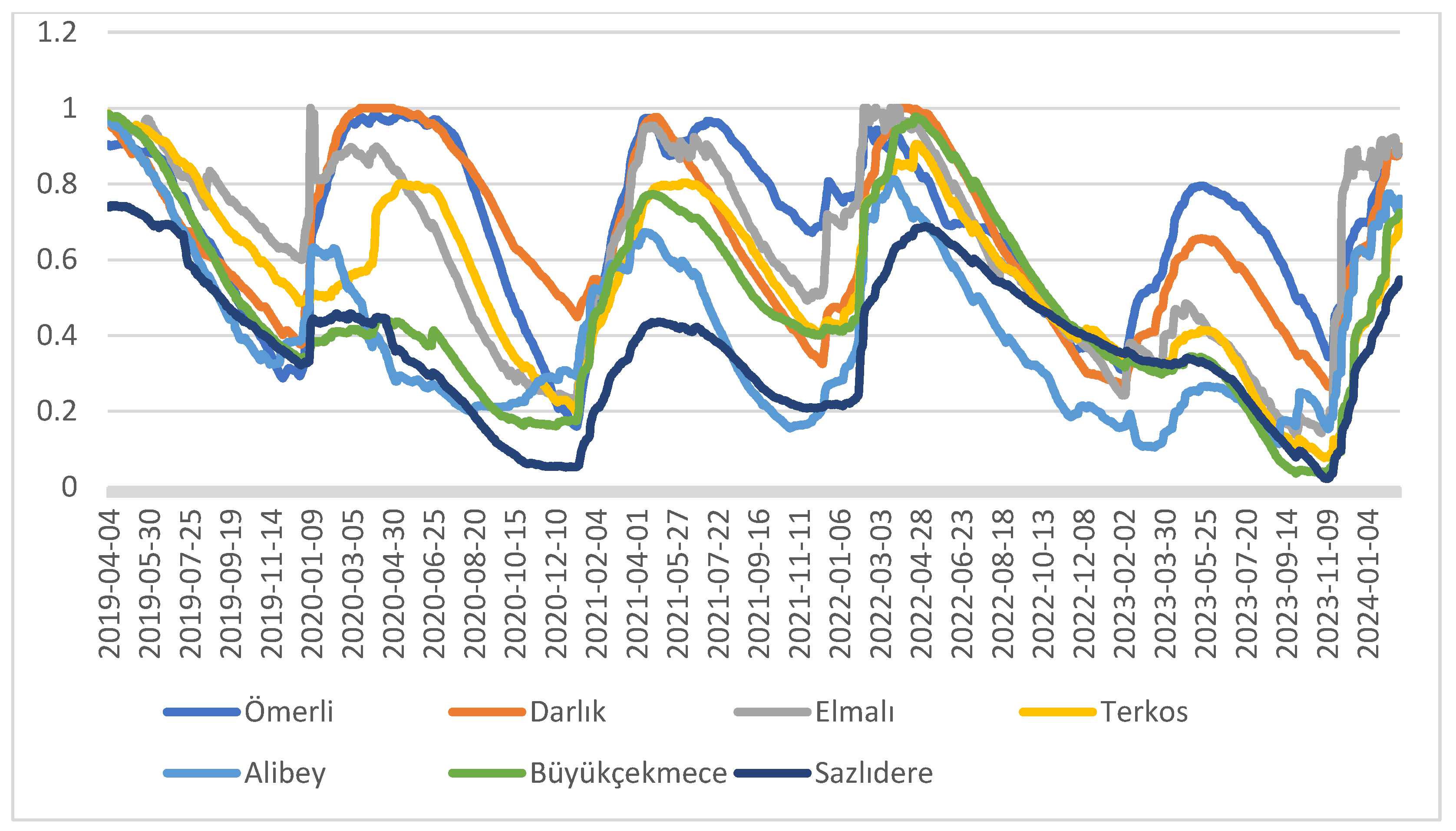
According to the occupancy data shown in
Figure 1, some dams are nearing zero occupancy levels, posing a significant risk of drought. Additionally, some dams are observed to be full for several months, which increases the risk of dam flooding in the event of extreme rainfall. Consequently, as indicated in Figure 3, predictive prevention strategies are necessary for these dams to mitigate the risks of both drought and flooding. The plots in
Figure 1 are exceptionally smooth, indicating that sharp fluctuations in the occupancy levels of the dams are rare. This inherent smoothness is beneficial for accurate predictions, as AI methods are particularly adept at fitting smooth curves. Consequently, our investigation focuses on identifying key indicators that shed light on water filling and water loss dynamics within the dam.
Figure 1.
Dam occupancy levels for 5 years period.
Figure 1.
Dam occupancy levels for 5 years period.
4. Design of the Dataset
The model's input data includes weather data, evapotranspiration data, daily water consumption data, and historical reservoir data. In this section, we provide a detailed explanation of each parameter within each dataset and present comprehensive calculations along with correlation values.
Firstly, The evapotranspiration (
) plays a significant role in predicting water levels in dams by providing critical information about water loss, the evapotranspiration data involve the evapotranspiration value calculated using the Penman-Monteith method (as described in Equation 1, as well as the method's input variables: solar radiation, wind speed, and pressure [
1]. The
, the combined process of water evaporation from the soil and transpiration from plants, influenced by several key factors including solar radiation, temperature, humidity, and wind speed. The
is calculated by the slope of the vapor pressure curve (Δ), the net radiation at the crop surface (
), the soil heat flux density (
), the mean daily air temperature at 2 m height (
), is the wind speed at 2 m height (
), the saturation vapor pressure (
), the actual vapor pressure (
), the saturation vapor pressure deficit (
), and the psychrometric constant (
) as given in Equation 1. Evapotranspiration has a noticeable correlation with occupancy levels than most weather parameters.
The saturation vapor pressure is calculated based on the daily temperature using Equation 2 below. Similarly, the actual vapor pressure is determined using the dew point as shown in Equation 3.
The slope of the vapor pressure curve is calculated from the saturation vapor pressure using Equation 4 shown below.
To calculate the psychrometric constant, we first determined the atmospheric pressure (
) using the latitude (
) of Istanbul, which is 41.0151. Equation 5 represents the atmospheric pressure. In Equation 6, we calculated the psychrometric constant using the specific heat at constant pressure (
) value of 0.001013.
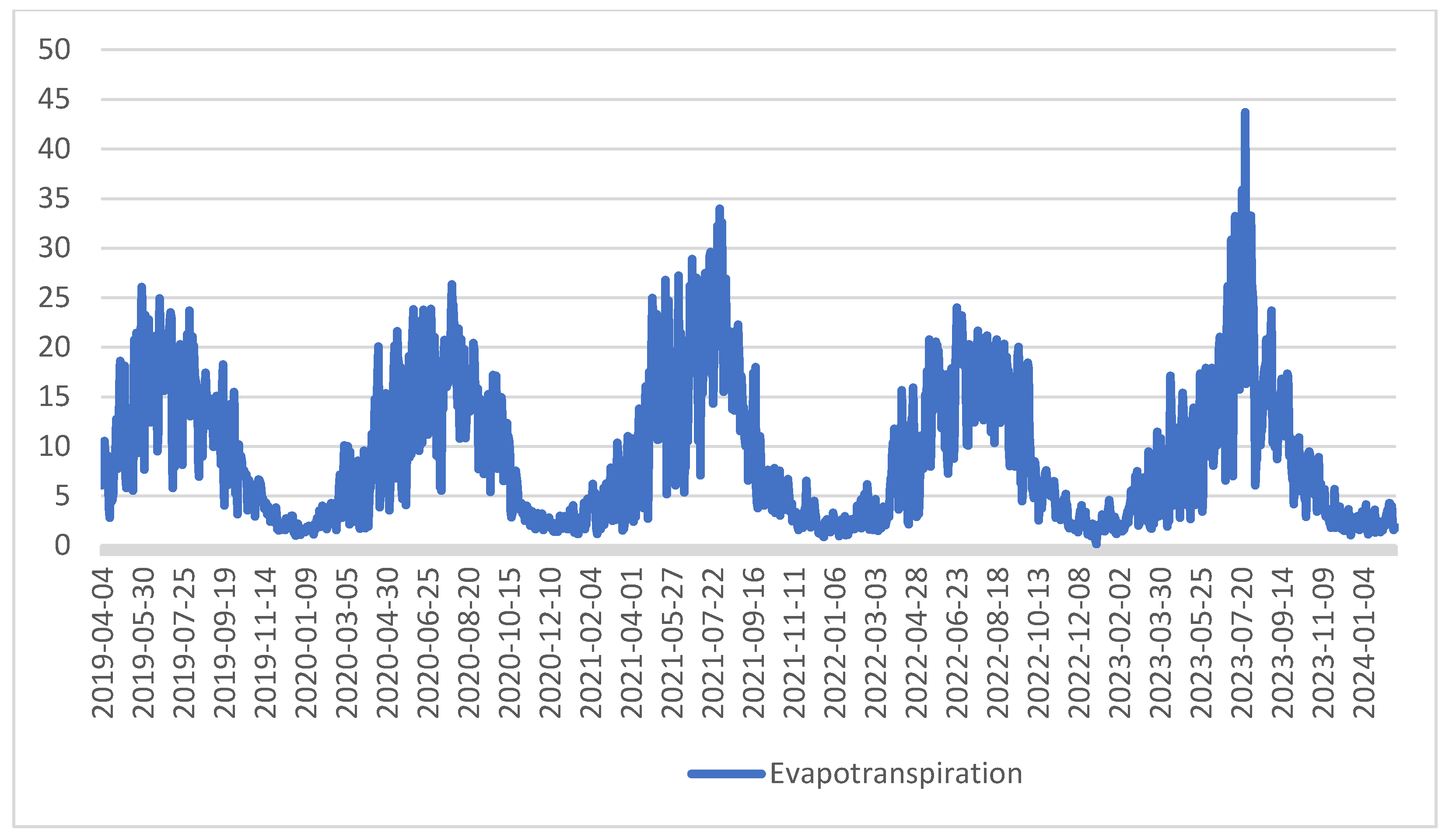
The wind speed, net radiation, and temperature were obtained from weather data, while the soil heat flux density was assumed to be zero for the calculation, as shown in Error! Reference source not found.. The figure indicates that occupancy levels generally start decreasing as increases.
Figure 4.
Evapotranspiration levels for 5 years period.
Figure 4.
Evapotranspiration levels for 5 years period.
Secondly, the weather data is noted as having a strong correlation with the water level of dams [
21]. We analyze the correlation between dam occupancy levels and various parameters of weather data, including temperature, felt temperature, humidity, dew point, cloud cover, rainfall, snow depth, and daylight duration. The cloud cover and daylight duration have a stronger correlation with dam occupancy levels than other factors as seen in
Error! Reference source not found..
Thirdly, we analyzed daily water consumption data and historical reservoir data to identify additional factors, beyond weather data, that influence occupancy rates. Daily water consumption does not have a strong correlation with occupancy rates. Daily and weekly historical reservoir data exhibits a strong correlation with dam water levels, demonstrating autocorrelation, as illustrated in
Table 1. This makes it feasible to predict the dam as a time series. To improve prediction accuracy, historical reservoir data is analyzed over periods ranging from 1 to 7 past intervals, with evaluations conducted on 1, 7, 15, and 30-day bases.
Lastly, based on the correlation values presented in
Table 1 and
Table 2, we generated the dataset by incorporating weather data, consumption data, evapotranspiration, and historical reservoir data. From the weather data, we selected only solar radiation, dew point, daylight duration, and rainfall. Despite rainfall showing a weak correlation with occupancy rates, it significantly enhanced prediction performance. After constructing the dataset, we split it into 80% for training and 20% for testing during the model development process.
5. Prediction Models
We implemented both correlation-based and entropy-based AI algorithms with the proposed dataset to identify the most effective method through comparative analysis. The algorithms considered for this evaluation include Orthogonal Matching Pursuit CV, Lasso Lars CV, Extra Trees, Random Forest, Ridge CV, Transformed Target Regressor, and LSTM. Our goal in selecting these algorithms is to compare the performance of commonly used methods in water level prediction studies with alternative approaches that we be-lieve may offer higher performance. To conduct this comparison from various perspec-tives, we designed four prediction scenarios which are daily, weekly, bi-weekly (15-day periods), and monthly (30-day periods). This approach allows us to analyze the perfor-mance of algorithms across different prediction horizons and identify which algorithms are more suitable for intervention strategies. In the correlation analysis tables, we abbreviated the following terms: weather data (WD), consumption data (CD), evapotranspiration (), and historical reservoir data (HRD).
5.1. Long Short-Term Memory
Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks are a type of Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) designed to capture long-term dependencies in sequential data. This capability makes them well-suited for tasks such as time series forecasting as presented in Error! Reference source not found..
Table 3.
Performance of the Long Short-Term Memory Model.
Table 3.
Performance of the Long Short-Term Memory Model.
| |
DAM |
+ WD + CD + HRD |
HRD |
| MAPE |
R2 |
MSE |
RMSE |
MAPE |
R2 |
MSE |
RMSE |
| Daily Prediction |
Ömerli |
0.00496996 |
0.999754 |
1.80904e-05 |
0.00425328 |
0.00628446 |
0.999513 |
3.41411e-05 |
0.00584303 |
| Darlık |
0.00337642 |
0.999518 |
2.45226e-05 |
0.00495203 |
0.00587575 |
0.999081 |
5.18837e-05 |
0.00720303 |
| Elmalı |
0.0124002 |
0.997419 |
0.000192689 |
0.0138812 |
0.00957619 |
0.993972 |
0.000402123 |
0.020053 |
| Terkos |
0.00601339 |
0.999565 |
2.17048e-05 |
0.00465884 |
0.00655399 |
0.999733 |
1.46284e-05 |
0.00382471 |
| Alibey |
0.010467 |
0.997787 |
9.50388e-05 |
0.00974879 |
0.0098421 |
0.998924 |
4.93963e-05 |
0.00702825 |
| B.Çekmece |
0.0099909 |
0.999712 |
3.09754e-05 |
0.00556555 |
0.00967341 |
0.99953 |
3.67732e-05 |
0.00606409 |
| Sazlıdere |
0.00846746 |
0.999419 |
1.97302e-05 |
0.00444186 |
0.00656699 |
0.999691 |
9.44456e-06 |
0.0030732 |
| Weekly Prediction |
Ömerli |
0.014751 |
0.996468 |
0.000172075 |
0.0131177 |
0.0155757 |
0.997482 |
0.000155052 |
0.012452 |
| Darlık |
0.0152882 |
0.995803 |
0.000207155 |
0.0143929 |
0.0101446 |
0.998517 |
8.08303e-05 |
0.00899057 |
| Elmalı |
0.0280571 |
0.990919 |
0.000700975 |
0.0264759 |
0.0245444 |
0.990563 |
0.000644626 |
0.0253895 |
| Terkos |
0.0190461 |
0.996293 |
0.000197625 |
0.0140579 |
0.0183852 |
0.996289 |
0.000189051 |
0.0137496 |
| Alibey |
0.0301914 |
0.995427 |
0.000202811 |
0.0142412 |
0.0290158 |
0.996204 |
0.00017287 |
0.013148 |
| B.Çekmece |
0.0235451 |
0.997413 |
0.000150072 |
0.0122504 |
0.028585 |
0.997076 |
0.000203382 |
0.0142612 |
| Sazlıdere |
0.0216837 |
0.996221 |
0.000112867 |
0.0106239 |
0.0374822 |
0.996799 |
0.000116965 |
0.010815 |
| 15-Days Prediction |
Ömerli |
0.0171061 |
0.993161 |
0.000322059 |
0.017946 |
0.0256526 |
0.993155 |
0.000484254 |
0.0220058 |
| Darlık |
0.0188453 |
0.991981 |
0.000443239 |
0.0210532 |
0.0130614 |
0.998414 |
9.16712e-05 |
0.00957451 |
| Elmalı |
0.0296606 |
0.983374 |
0.00105234 |
0.0324398 |
0.0302839 |
0.991372 |
0.000620677 |
0.0249134 |
| Terkos |
0.019051 |
0.996649 |
0.000168989 |
0.0129996 |
0.0249967 |
0.997302 |
0.000177895 |
0.0133377 |
| Alibey |
0.0348007 |
0.937953 |
0.00277279 |
0.0526573 |
0.0269181 |
0.993971 |
0.00025642 |
0.0160131 |
| B.Çekmece |
0.0397847 |
0.99153 |
0.000542264 |
0.0232866 |
0.0333638 |
0.994774 |
0.000308434 |
0.0175623 |
| Sazlıdere |
0.0261945 |
0.995932 |
0.000122505 |
0.0110682 |
0.0337267 |
0.993445 |
0.000195627 |
0.0139867 |
| Monthly Prediction |
Ömerli |
0.012808 |
0.990179 |
0.000453095 |
0.021286 |
0.0224381 |
0.989099 |
0.000504953 |
0.0224712 |
| Darlık |
0.0180395 |
0.99514 |
0.000242745 |
0.0155803 |
0.0118325 |
0.998626 |
0.000110456 |
0.0105098 |
| Elmalı |
0.0361916 |
0.984145 |
0.00101564 |
0.0318691 |
0.0196329 |
0.992456 |
0.000483806 |
0.0219956 |
| Terkos |
0.0188625 |
0.997037 |
0.000145501 |
0.0120624 |
0.0142386 |
0.998762 |
7.7495e-05 |
0.00880313 |
| Alibey |
0.0207037 |
0.995571 |
0.000185797 |
0.0136307 |
0.017139 |
0.997741 |
9.65338e-05 |
0.00982516 |
| B.Çekmece |
0.0267443 |
0.997734 |
0.000190004 |
0.0137842 |
0.0302374 |
0.998214 |
0.000113374 |
0.0106477 |
| Sazlıdere |
0.0265639 |
0.994443 |
0.000177235 |
0.013313 |
0.0245632 |
0.991577 |
0.000254904 |
0.0159657 |
The performance of our LSTM network varies between 0.5% and 4% depending on the prediction horizon, typically remaining below 1% for daily predictions. Additionally, the positive impact of weather data becomes more evident as the term length increases. To achieve this performance, we implemented an LSTM network with two hidden layers: the first layer has 60 nodes with a ReLU activation function, and the second layer consists of 120 nodes, also with a ReLU activation function. We used the Adam optimizer with a learning rate of 0.015, a beta of 0.9, and an epsilon of 1e-7.
5.2. Orthogonal Matching Pursuit CV
Orthogonal Matching Pursuit CV (OMPCV) identifies the best features for a cross-validated estimation process using a sparse approximation algorithm. It employs an orthogonal projection basis to find the optimal matching projections of multidimensional data. We implemented OMPCV with 5 folds cross-validation parameter. The maximum number of iterations is limited to either 10% of the total number of features or 5, whichever is greater. Error! Reference source not found. presents the performance of the OMPCV model for each combination of features and prediction horizons. While short-term predictions perform exceptionally well, their accuracy significantly decreases as the forecast horizon lengthens. Furthermore, weather data does not significantly affect the prediction performance of OMPCV.
Table 4.
Performance of the Orthogonal Matching Pursuit CV model.
Table 4.
Performance of the Orthogonal Matching Pursuit CV model.
| |
DAM |
+ WD + CD + HRD |
HRD |
| MAPE |
R2 |
MSE |
RMSE |
MAPE |
R2 |
MSE |
RMSE |
| Daily Prediction |
Ömerli |
0.00312237 |
0.999746 |
1.16941e-05 |
0.00341967 |
0.00305702 |
0.999428 |
2.62668e-05 |
0.00512511 |
| Darlık |
0.00290634 |
0.999763 |
1.15753e-05 |
0.00340225 |
0.00292748 |
0.999498 |
2.45049e-05 |
0.00495024 |
| Elmalı |
0.00783492 |
0.997509 |
0.000157006 |
0.0125302 |
0.00773108 |
0.995666 |
0.000273552 |
0.0165394 |
| Terkos |
0.00585859 |
0.999649 |
1.71972e-05 |
0.00414695 |
0.0049944 |
0.999741 |
1.27535e-05 |
0.00357121 |
| Alibey |
0.00896704 |
0.999456 |
2.29451e-05 |
0.00479011 |
0.00705791 |
0.999152 |
3.57359e-05 |
0.00597795 |
| B.Çekmece |
0.00708775 |
0.999662 |
1.90968e-05 |
0.00436999 |
0.00692981 |
0.999618 |
2.15249e-05 |
0.00463949 |
| Sazlıdere |
0.00663554 |
0.999785 |
6.35257e-06 |
0.00252043 |
0.00611186 |
0.999673 |
9.82439e-06 |
0.00313439 |
| Weekly Prediction |
Ömerli |
0.0264899 |
0.987316 |
0.000589272 |
0.0242749 |
0.0249001 |
0.989311 |
0.000499273 |
0.0223444 |
| Darlık |
0.0234549 |
0.990203 |
0.000478221 |
0.0218683 |
0.0233937 |
0.99007 |
0.00048584 |
0.0220418 |
| Elmalı |
0.0361511 |
0.979043 |
0.00132487 |
0.0363988 |
0.0438259 |
0.978049 |
0.00140182 |
0.0374409 |
| Terkos |
0.0284242 |
0.991094 |
0.000436925 |
0.0209027 |
0.0304353 |
0.989684 |
0.000505364 |
0.0224803 |
| Alibey |
0.0454819 |
0.987379 |
0.000530643 |
0.0230357 |
0.0468775 |
0.985498 |
0.000608809 |
0.0246741 |
| B.Çekmece |
0.029464 |
0.993387 |
0.00037363 |
0.0193295 |
0.0357698 |
0.992313 |
0.00043693 |
0.0209029 |
| Sazlıdere |
0.0351539 |
0.993555 |
0.000191085 |
0.0138233 |
0.0353401 |
0.993112 |
0.000204982 |
0.0143172 |
| 15-Days Prediction |
Ömerli |
0.0597648 |
0.956384 |
0.00203142 |
0.0450713 |
0.0562393 |
0.959656 |
0.00188994 |
0.0434734 |
| Darlık |
0.0475681 |
0.970973 |
0.00143549 |
0.0378879 |
0.0488463 |
0.967032 |
0.00161382 |
0.0401724 |
| Elmalı |
0.0749328 |
0.930958 |
0.00436855 |
0.066095 |
0.0816497 |
0.920174 |
0.00506405 |
0.0711621 |
| Terkos |
0.0565462 |
0.976715 |
0.0011414 |
0.0337846 |
0.0627889 |
0.974832 |
0.00123485 |
0.0351404 |
| Alibey |
0.0958814 |
0.953379 |
0.00196719 |
0.044353 |
0.101744 |
0.951644 |
0.00206112 |
0.0453995 |
| B.Çekmece |
0.0649254 |
0.984549 |
0.000877351 |
0.0296201 |
0.0746038 |
0.982518 |
0.00100417 |
0.0316886 |
| Sazlıdere |
0.0863225 |
0.977034 |
0.000680156 |
0.0260798 |
0.0823396 |
0.978331 |
0.000645584 |
0.0254084 |
| Monthly Prediction |
Ömerli |
0.115295 |
0.840763 |
0.00730451 |
0.0854664 |
0.117424 |
0.832343 |
0.00769196 |
0.0877038 |
| Darlık |
0.096027 |
0.882832 |
0.00572044 |
0.0756336 |
0.101429 |
0.868235 |
0.00644469 |
0.0802788 |
| Elmalı |
0.139233 |
0.78605 |
0.0135715 |
0.116497 |
0.152306 |
0.762178 |
0.0151442 |
0.123062 |
| Terkos |
0.100622 |
0.927497 |
0.00355449 |
0.0596195 |
0.108371 |
0.921444 |
0.00386874 |
0.0621992 |
| Alibey |
0.170993 |
0.834706 |
0.00696293 |
0.0834442 |
0.170672 |
0.81118 |
0.00804831 |
0.0897124 |
| B.Çekmece |
0.152902 |
0.923799 |
0.00433834 |
0.0658661 |
0.140405 |
0.925902 |
0.0041832 |
0.0646777 |
| Sazlıdere |
0.15938 |
0.903594 |
0.00285824 |
0.0534625 |
0.162844 |
0.893396 |
0.00317065 |
0.0563085 |
5.3. Lasso Lars CV
Lasso Lars CV (LLCV) is a regression analysis method that simultaneously performs variable selection and regularization. This enhances the prediction accuracy and interpretability of the cross-validated estimation process on multidimensional data. We implemented LLCV with 5-fold cross-validation, similar to OMPCV. The maximum number of iterations is set to 500, and the maximum number of points for computing residuals in the cross-validation is 1000. The machine-precision regularization is 2.22044E-16. Error! Reference source not found. presents the performance of the LLCV model for each combination of features and prediction horizons. Similarly, with OMPCV, LLVC delivers outstanding short-term predictions. However, its accuracy significantly diminishes as the forecast horizon extends. Additionally, the positive impact of weather data becomes more evident as the term length increases.
Table 5.
Performance of the Lasso Lars CV model.
Table 5.
Performance of the Lasso Lars CV model.
| |
DAM |
+ WD + CD + HRD |
HRD |
| MAPE |
R2 |
MSE |
RMSE |
MAPE |
R2 |
MSE |
RMSE |
| Daily Prediction |
Ömerli |
0.00290696 |
0.999728 |
1.25172e-05 |
0.00353797 |
0.00305458 |
0.999455 |
2.50039e-05 |
0.00500039 |
| Darlık |
0.00293826 |
0.999738 |
1.27733e-05 |
0.00357398 |
0.00293714 |
0.999546 |
2.22023e-05 |
0.00471193 |
| Elmalı |
0.00770551 |
0.997462 |
0.00015997 |
0.0126479 |
0.00778144 |
0.995675 |
0.000272933 |
0.0165207 |
| Terkos |
0.00398731 |
0.999833 |
8.20228e-06 |
0.00286396 |
0.00496261 |
0.999749 |
1.23182e-05 |
0.00350973 |
| Alibey |
0.00682897 |
0.999635 |
1.54796e-05 |
0.00393441 |
0.00708108 |
0.999156 |
3.55807e-05 |
0.00596496 |
| B.Çekmece |
0.00596853 |
0.999819 |
1.02405e-05 |
0.00320008 |
0.00690164 |
0.999618 |
2.15236e-05 |
0.00463935 |
| Sazlıdere |
0.00519053 |
0.999801 |
5.93328e-06 |
0.00243583 |
0.00605372 |
0.999724 |
8.29238e-06 |
0.00287965 |
| Weekly Prediction |
Ömerli |
0.0232363 |
0.989629 |
0.000479234 |
0.0218914 |
0.0250712 |
0.989269 |
0.000501665 |
0.0223979 |
| Darlık |
0.0216811 |
0.992009 |
0.000389158 |
0.0197271 |
0.0233964 |
0.99009 |
0.000484886 |
0.0220201 |
| Elmalı |
0.0360924 |
0.979585 |
0.00129005 |
0.0359173 |
0.0442911 |
0.977976 |
0.00140899 |
0.0375365 |
| Terkos |
0.0280822 |
0.991154 |
0.00043457 |
0.0208463 |
0.030388 |
0.989652 |
0.000506874 |
0.0225139 |
| Alibey |
0.0421883 |
0.988026 |
0.000504023 |
0.0224505 |
0.0468775 |
0.985499 |
0.000608808 |
0.024674 |
| B.Çekmece |
0.0303865 |
0.993051 |
0.000393111 |
0.019827 |
0.03585 |
0.992356 |
0.000434515 |
0.020845 |
| Sazlıdere |
0.0315555 |
0.993665 |
0.000187303 |
0.0136859 |
0.0353786 |
0.993109 |
0.000205063 |
0.01432 |
| 15-Days Prediction |
Ömerli |
0.0533375 |
0.964082 |
0.00169918 |
0.0412211 |
0.0562392 |
0.959656 |
0.00188994 |
0.0434734 |
| Darlık |
0.0457542 |
0.972184 |
0.00137807 |
0.0371224 |
0.0494345 |
0.966858 |
0.00162141 |
0.0402667 |
| Elmalı |
0.0743163 |
0.933334 |
0.00423471 |
0.0650746 |
0.0815954 |
0.919795 |
0.00508274 |
0.0712933 |
| Terkos |
0.0540278 |
0.978052 |
0.00107749 |
0.0328252 |
0.0630082 |
0.974824 |
0.00123525 |
0.0351461 |
| Alibey |
0.0920288 |
0.959514 |
0.0017189 |
0.0414596 |
0.101746 |
0.951492 |
0.00206217 |
0.0454111 |
| B.Çekmece |
0.0617624 |
0.985375 |
0.000839167 |
0.0289684 |
0.0746552 |
0.982521 |
0.00100362 |
0.0316799 |
| Sazlıdere |
0.0781948 |
0.980241 |
0.000591595 |
0.0243227 |
0.082677 |
0.978315 |
0.000645751 |
0.0254116 |
| Monthly Prediction |
Ömerli |
0.104782 |
0.86507 |
0.00619161 |
0.0786868 |
0.117424 |
0.832343 |
0.00769196 |
0.0877038 |
| Darlık |
0.0906292 |
0.896114 |
0.00507109 |
0.0712116 |
0.101429 |
0.868235 |
0.00644469 |
0.0802788 |
| Elmalı |
0.132347 |
0.791852 |
0.0132286 |
0.115016 |
0.153111 |
0.761777 |
0.0151531 |
0.123098 |
| Terkos |
0.0940711 |
0.935074 |
0.0031903 |
0.0564828 |
0.108759 |
0.921323 |
0.0038717 |
0.062223 |
| Alibey |
0.15876 |
0.842755 |
0.00664744 |
0.0815318 |
0.170872 |
0.811342 |
0.00803104 |
0.0896161 |
| B.Çekmece |
0.115172 |
0.940945 |
0.00332585 |
0.0576702 |
0.140404 |
0.925902 |
0.0041832 |
0.0646777 |
| Sazlıdere |
0.148663 |
0.911828 |
0.00260789 |
0.0510675 |
0.162844 |
0.893396 |
0.00317065 |
0.0563085 |
5.4. Random Forest
The Random Forest (RF) algorithm combines ensemble learning methods with the decision tree algorithm to create multiple decision trees, each drawn randomly from the data. The results of these trees are averaged to produce a final result, often leading to more accurate predictions and classifications. RF is implemented with mean squared error as the criterion to minimize variance, utilizing a forest of 100 trees. The minimum number of samples required to split an internal node is set to 2, and at least 1 sample is required to form a leaf node. When searching for the best split, only 1 feature is considered. Error! Reference source not found. presents the performance of the RF model for each combination of features and prediction horizons. RF delivers outstanding short-term predictions and maintains relatively good performance as the forecast horizon extends. Also, weather data does not significantly affect the prediction performance of RF.
Table 6.
Performance of the Random Forest model.
Table 6.
Performance of the Random Forest model.
| |
DAM |
+ WD + CD + HRD |
HRD |
| MAPE |
R2 |
MSE |
RMSE |
MAPE |
R2 |
MSE |
RMSE |
| Daily Prediction |
Ömerli |
0.00478378 |
0.999315 |
3.14498e-05 |
0.00560801 |
0.00463194 |
0.999336 |
3.05549e-05 |
0.00552765 |
| Darlık |
0.00451081 |
0.999451 |
2.67768e-05 |
0.00517463 |
0.00483447 |
0.999142 |
4.17943e-05 |
0.00646485 |
| Elmalı |
0.00784472 |
0.995614 |
0.00027652 |
0.0166289 |
0.00866333 |
0.995561 |
0.000279763 |
0.0167261 |
| Terkos |
0.00702186 |
0.999559 |
2.1677e-05 |
0.00465586 |
0.00765764 |
0.999522 |
2.3537e-05 |
0.0048515 |
| Alibey |
0.00972596 |
0.998967 |
4.3398e-05 |
0.00658772 |
0.0102261 |
0.998795 |
5.05776e-05 |
0.00711179 |
| B.Çekmece |
0.00893934 |
0.999442 |
3.1638e-05 |
0.00562477 |
0.00946453 |
0.999326 |
3.81665e-05 |
0.00617791 |
| Sazlıdere |
0.00773455 |
0.999674 |
9.58492e-06 |
0.00309595 |
0.00895021 |
0.999584 |
1.22647e-05 |
0.0035021 |
| Weekly Prediction |
Ömerli |
0.0116603 |
0.997192 |
0.000129324 |
0.0113721 |
0.012716 |
0.996169 |
0.000176682 |
0.0132922 |
| Darlık |
0.00935386 |
0.99813 |
9.12824e-05 |
0.00955418 |
0.0107126 |
0.997725 |
0.000112508 |
0.010607 |
| Elmalı |
0.016616 |
0.994286 |
0.000362236 |
0.0190325 |
0.0184659 |
0.993695 |
0.00039896 |
0.019974 |
| Terkos |
0.0136593 |
0.997804 |
0.000107734 |
0.0103795 |
0.0117802 |
0.998326 |
8.20781e-05 |
0.0090597 |
| Alibey |
0.0209691 |
0.99649 |
0.000147373 |
0.0121397 |
0.0219477 |
0.996266 |
0.000157022 |
0.0125308 |
| B.Çekmece |
0.0180959 |
0.996682 |
0.000187673 |
0.0136994 |
0.0165157 |
0.997882 |
0.000119767 |
0.0109438 |
| Sazlıdere |
0.0140014 |
0.99839 |
4.75184e-05 |
0.00689336 |
0.0143782 |
0.998286 |
5.06218e-05 |
0.0071149 |
| 15-Days Prediction |
Ömerli |
0.0163452 |
0.99262 |
0.000338375 |
0.018395 |
0.0154685 |
0.992315 |
0.000352475 |
0.0187743 |
| Darlık |
0.0139163 |
0.995521 |
0.000219014 |
0.0147991 |
0.0153309 |
0.994914 |
0.000248236 |
0.0157555 |
| Elmalı |
0.0141098 |
0.997065 |
0.000186092 |
0.0136416 |
0.0178281 |
0.995037 |
0.000313711 |
0.0177119 |
| Terkos |
0.0128188 |
0.997946 |
0.000100647 |
0.0100323 |
0.011547 |
0.998247 |
8.60822e-05 |
0.00927805 |
| Alibey |
0.0256763 |
0.992852 |
0.000301602 |
0.0173667 |
0.0276765 |
0.993673 |
0.000265811 |
0.0163037 |
| B.Çekmece |
0.0175794 |
0.995509 |
0.000256572 |
0.0160179 |
0.0183209 |
0.99189 |
0.000465323 |
0.0215714 |
| Sazlıdere |
0.0168793 |
0.99781 |
6.45727e-05 |
0.00803571 |
0.0183391 |
0.99753 |
7.27287e-05 |
0.00852811 |
| Monthly Prediction |
Ömerli |
0.0170516 |
0.988768 |
0.000523402 |
0.022878 |
0.0144575 |
0.991073 |
0.000413032 |
0.0203232 |
| Darlık |
0.0195599 |
0.991975 |
0.000397903 |
0.0199475 |
0.0204259 |
0.987695 |
0.000599909 |
0.024493 |
| Elmalı |
0.0155737 |
0.995631 |
0.000276242 |
0.0166205 |
0.0200283 |
0.989257 |
0.000678663 |
0.0260512 |
| Terkos |
0.0163963 |
0.996502 |
0.000171737 |
0.0131048 |
0.0103605 |
0.99769 |
0.00011409 |
0.0106813 |
| Alibey |
0.020811 |
0.994479 |
0.000233697 |
0.0152871 |
0.0198052 |
0.993651 |
0.000268836 |
0.0163962 |
| B.Çekmece |
0.019981 |
0.997114 |
0.000168074 |
0.0129643 |
0.0139536 |
0.998958 |
6.0931e-05 |
0.00780583 |
| Sazlıdere |
0.0222951 |
0.990182 |
0.000292531 |
0.0171036 |
0.0202211 |
0.988411 |
0.000347147 |
0.0186319 |
5.5. Extra Trees
The Extra Trees (ET) algorithm, similar to the Random Forests algorithm, generates multiple decision trees. However, unlike Random Forests, Extra Trees uses random sampling without replacement, resulting in a unique dataset for each tree. Additionally, a specific number of features from the total set are randomly selected for each tree. The most distinctive characteristic of Extra Trees is its random selection of splitting values for features. Instead of computing a locally optimal value using criteria like Gini impurity or entropy, the algorithm randomly selects a split value. This approach enhances the diversity and reduces the correlation among the trees. ET is implemented with the same parameters as RF.
Table 2 presents the performance of the ET model for each combination of features and prediction horizons. ET is the most accurate method for predicting occupancy levels across all horizons. The impact of weather data on ET's prediction accuracy is noticeable only for daily occupancy predictions.
Table 2.
Performance of the Extra Trees model.
Table 2.
Performance of the Extra Trees model.
| |
DAM |
+ WD + CD + HRD
|
HRD |
| MAPE |
R2 |
MSE |
RMSE |
MAPE |
R2 |
MSE |
RMSE |
| Daily Prediction |
Ömerli |
0.00388508 |
0.999396 |
2.77199e-05 |
0.00526497 |
0.00409498 |
0.999321 |
3.11635e-05 |
0.00558243 |
| Darlık |
0.00316241 |
0.999506 |
2.41255e-05 |
0.00491177 |
0.00419955 |
0.99908 |
4.47778e-05 |
0.00669163 |
| Elmalı |
0.00787504 |
0.995719 |
0.00026978 |
0.016425 |
0.00817141 |
0.995634 |
0.000275109 |
0.0165864 |
| Terkos |
0.00539017 |
0.99952 |
2.35185e-05 |
0.00484958 |
0.00689247 |
0.999458 |
2.66004e-05 |
0.00515756 |
| Alibey |
0.00898673 |
0.99892 |
4.5326e-05 |
0.00673246 |
0.00940576 |
0.99884 |
4.86806e-05 |
0.00697715 |
| B.Çekmece |
0.00792777 |
0.99922 |
4.40525e-05 |
0.00663721 |
0.00901684 |
0.999183 |
4.62988e-05 |
0.00680433 |
| Sazlıdere |
0.00585024 |
0.999691 |
9.11219e-06 |
0.00301864 |
0.00813567 |
0.999521 |
1.41438e-05 |
0.00376083 |
| Weekly Prediction |
Ömerli |
0.00847044 |
0.998648 |
6.28527e-05 |
0.00792797 |
0.00840095 |
0.998775 |
5.71785e-05 |
0.00756165 |
| Darlık |
0.00837819 |
0.998271 |
8.51257e-05 |
0.00922636 |
0.0085435 |
0.998717 |
6.50426e-05 |
0.0080649 |
| Elmalı |
0.011828 |
0.997304 |
0.000170395 |
0.0130535 |
0.0145746 |
0.995954 |
0.000256698 |
0.0160218 |
| Terkos |
0.00810674 |
0.99879 |
5.91995e-05 |
0.00769412 |
0.00790464 |
0.998976 |
5.0213e-05 |
0.00708611 |
| Alibey |
0.0137394 |
0.998191 |
7.60133e-05 |
0.00871856 |
0.0147247 |
0.998268 |
7.28824e-05 |
0.00853712 |
| B.Çekmece |
0.0114554 |
0.998938 |
6.02968e-05 |
0.0077651 |
0.0103776 |
0.99894 |
6.06342e-05 |
0.00778679 |
| Sazlıdere |
0.0100015 |
0.999083 |
2.71342e-05 |
0.00520905 |
0.00966369 |
0.999046 |
2.81089e-05 |
0.00530178 |
| 15-Days Prediction |
Ömerli |
0.009211 |
0.997901 |
9.69083e-05 |
0.0098442 |
0.00885978 |
0.996761 |
0.000148606 |
0.0121904 |
| Darlık |
0.0105688 |
0.997329 |
0.000134036 |
0.0115774 |
0.00965656 |
0.998596 |
7.19347e-05 |
0.00848143 |
| Elmalı |
0.0118076 |
0.996929 |
0.000195466 |
0.0139809 |
0.0121011 |
0.996713 |
0.000207453 |
0.0144032 |
| Terkos |
0.00792414 |
0.999192 |
3.98185e-05 |
0.00631019 |
0.00846756 |
0.998901 |
5.38046e-05 |
0.00733517 |
| Alibey |
0.0167746 |
0.99691 |
0.000129863 |
0.0113957 |
0.0156182 |
0.997685 |
9.71879e-05 |
0.00985839 |
| B.Çekmece |
0.00992255 |
0.999053 |
5.40958e-05 |
0.00735499 |
0.0110676 |
0.997837 |
0.00012336 |
0.0111068 |
| Sazlıdere |
0.0105529 |
0.998642 |
4.02893e-05 |
0.00634738 |
0.0110314 |
0.998534 |
4.32387e-05 |
0.00657561 |
| Monthly Prediction |
Ömerli |
0.0119018 |
0.995007 |
0.000232166 |
0.015237 |
0.0065634 |
0.997882 |
9.80702e-05 |
0.00990304 |
| Darlık |
0.0131245 |
0.995145 |
0.000240917 |
0.0155215 |
0.0112884 |
0.994835 |
0.000251898 |
0.0158713 |
| Elmalı |
0.0115828 |
0.997537 |
0.000156458 |
0.0125083 |
0.0111112 |
0.997498 |
0.000158287 |
0.0125812 |
| Terkos |
0.00872503 |
0.998963 |
5.12378e-05 |
0.00715806 |
0.00647818 |
0.999267 |
3.62939e-05 |
0.00602444 |
| Alibey |
0.015773 |
0.997818 |
9.30908e-05 |
0.00964836 |
0.0133573 |
0.997926 |
8.80544e-05 |
0.00938373 |
| B.Çekmece |
0.0100021 |
0.999439 |
3.2496e-05 |
0.00570052 |
0.00723422 |
0.999597 |
2.27595e-05 |
0.00477069 |
| Sazlıdere |
0.0145424 |
0.996183 |
0.00011351 |
0.0106541 |
0.0137383 |
0.993712 |
0.00018706 |
0.013677 |
6. Results and Discussion
The importance of water for the environment and its economic value makes it a resource that must be managed carefully. In this context, we evaluated how to implement the most effective IWRM in dams, which are one of the most crucial water resources in the world. Our review of studies presented in the scientific literature revealed that efficient water management requires measuring water levels and predicting these levels for more advanced planning. Accordingly, we investigated the most suitable prediction model necessary for the most effective IWRM. We considered the correlation between weather data, water consumption, evapotranspiration historical reservoir data, and dam occupancy levels for the seven dams in Istanbul, as given in
Error! Reference source not found. and
Table 1. The correlation analysis shows that historical reservoir data and dam occupancy levels have a very strong correlation, which points to the occupancy levels being considered as time series. Water consumption and rainfall do not show a strong correlation with dam occupancy levels. However, since all dams supply drinking water and rainfall contributes to their water supply, daily water consumption and rainfall are included as features in the proposed models. We concluded that the prediction model should be developed using parameters that help understand the water level in the dam as well as the inflow and outflow of water [
1]. Additionally, solar radiation, humidity, cloud cover, daylight duration, and evapotranspiration have a meaningful correlation with dam occupancy levels.
Based on this analysis, we propose that the most effective model for predicting dam occupancy levels should incorporate weather data, water consumption data, evapotranspiration calculations, and historical reservoir data. To validate this approach, we used RF and LSTM, which have shown successful results in the scientific literature, as well as ET, OMPCV, and LLCV to make predictions for daily, weekly, bi-weekly, and monthly intervals. To understand the impact of weather data, water consumption data, and evapotranspiration on prediction performance, we compared the prediction performance of identical models created with a dataset consisting of weather data and historical reservoir data against models created using only historical reservoir data.
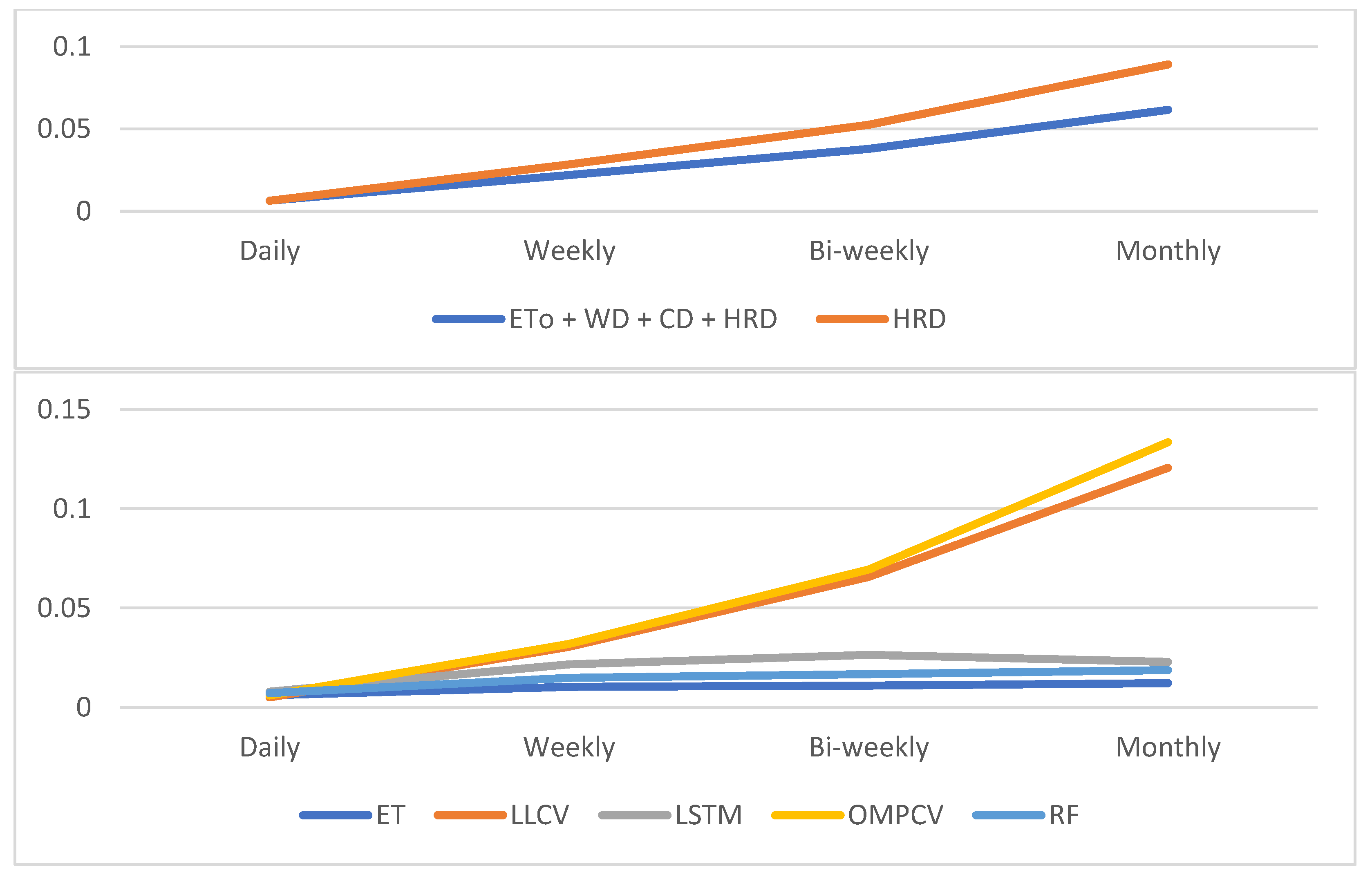
As shown in Error! Reference source not found.a, the ET method, which utilizes , whether data, consumption data and historical reservoir data, provides the best predictions. Daily, RF and ET produce similar results. However, when considering weekly, bi-weekly, and monthly intervals, the average MAPE across all models for each dam ranges from 1% to 2%. This accuracy is consistent with levels reported in similar scientific studies. Based on this result, Error! Reference source not found.a demonstrates that , whether data and consumption data, have a positive effect on prediction accuracy as the prediction horizon increases. As illustrated in Error! Reference source not found.b, models incorporating both historical reservoir levels and additional data achieve lower MAPE compared to those using only historical reservoir data, particularly for daily intervals. Consequently, our research contributes to the scientific literature by proposing AI models such as ET, OMPCV, and LLCV for predicting dam reservoir levels. We demonstrate that ET provides more precise predictions of dam occupancy levels compared to other methods in the literature, such as RF and LSTM.
Figure 5.
a. MAPE in dataset basis b. MAPE of AI methods.
Figure 5.
a. MAPE in dataset basis b. MAPE of AI methods.
To reinforce our proposed model with more robust evidence, we conducted a statistical test on the MAPE values. This analysis aimed to identify the conditions that result in the smallest prediction errors. First, we performed the Kolmogorov-Smirnov (KS) test on the MAPE values for two different input sets. The first input set, which includes , weather data, consumption data, and historical reservoir data, fit the normal distribution with a p-value of 4.74E-33. The second input set, which includes only historical reservoir data, also fits the normal distribution with a p-value of 4.73E-33. Based on these results, we then performed a two-sided Z-Test to determine whether the samples were identical. The Z-Test resulted in a p-value of 0.0155. This indicates that the two samples are not identical at the 1% significance level, leading us to accept the null hypothesis. To compare the means of the samples, we performed both the Z-Test and paired T-Test with a less-than-alternative hypothesis. The Z-test produced a p-value of 0.0078, while the T-test resulted in a p-value of 2.59E-6 with 139 degrees of freedom (DF). Consequently, the null hypothesis was rejected in both tests. Therefore, it can be concluded that , weather data, and consumption data is turned out to reduce the prediction error rate. After validating our hypothesis with statistical tests, we tried to figure out the best model utilizing the dataset “+ WD + CD + HRD”. Firstly, we performed an ANOVA test on the performance data of all models. The test resulted in a p-value of 7.579E-11, which led us to accept the alternative hypothesis. Since the alternative hypothesis of the ANOVA test posits that the samples are not identical, we compared their performances using a paired t-test with a less-than-alternative hypothesis. First, we compared LLCV and OMPCV. The performance of LLCV is superior to OMPCV, as indicated by a p-value of 0.0008 with 27 degrees of freedom. Next, we compared LSTM and LLCV. The performance of LSTM is superior to that of LLCV, with a p-value of 5.535E-5 and 27 degrees of freedom. Third, we compared RF and LSTM. The performance of RF is superior to that of LSTM, with a p-value of 6.54E-5 and 27 degrees of freedom. Finally, ET and RF. The performance of ET is superior to that of RF, with a p-value of 2.085E-9 and 27 degrees of freedom. As a result of this comparison, the best AI method for predicting dam occupancy levels is ET, using the dataset consisting of “, weather data, consumption data and historical reservoir data”. The results of all statistical tests leading to this conclusion are summarized in Error! Reference source not found. below.
Table 8.
Summary of statistical tests analysis.
Table 8.
Summary of statistical tests analysis.
| Test |
Dataset |
P-Value |
Statistic |
Description |
| Kolmogorov-Smirnov |
, WD, CD |
4.74E-33 |
0.5012 |
Evaluation of the fit to the normal distribution |
| Kolmogorov-Smirnov |
|
4.73E-33 |
0.5012 |
| Z-Test (Two-sided) |
MAPE of (, WD, CD HRD) model, MAPE of (HRD) model |
0.0155 |
-2.4197 |
Assessment of performance equivalence |
| Z-Test (Less Than) |
MAPE of (, WD, CD HRD) model, MAPE of (HRD) model |
0.0078 |
-2.4197 |
To validate that the additional data reduced the error rate. |
| Paired T-Test (Less Than) |
MAPE of (, WD, CD HRD) model, MAPE of (HRD) model |
2.59E-6 |
-4.742 (DF: 139) |
To validate that the additional data reduced the error rate. |
| Paired T-Test (Less Than) |
MAPE of LLCV model and MAPE of OMPCV model |
0.0008 |
-3.464 (DF:27) |
To compare the performance of LLCV and OMPCV |
| Paired T-Test (Less Than) |
MAPE of the LSTM model and MAPE of the LLCV model |
5.535E-5 |
-4.52 (DF:27) |
To compare the performance of LSTM and LLCV |
| Paired T-Test (Less Than) |
MAPE of RF model and MAPE of LSTM model |
6.54E-5 |
-4.457 (DF:27) |
To compare the performance of RF and LSTM |
| Paired T-Test (Less Than) |
MAPE of ET model and MAPE of RF model |
2.085E-9 |
-8.493 (DF:27) |
To compare the performance of ET and RF |
6. Conclusions
IWRM is a key function to utilize water resources serving multiple purposes, including agriculture, energy generation, fish farming, and drinking water [
4]. One of the significant contributions to the IRWM [
17] field is the prediction of water levels. Predicting water levels enables the implementation of intervention strategies to enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of IWRM. However, precise water level predictions are essential to achieve truly efficient and effective IWRM. In this context, we proposed that combining physical model-based calculations and measured data related to inflow and outflow water can significantly improve the accuracy of AI-based water level predictions. We utilized two distinct datasets derived from data collected from seven dams in Istanbul. The first dataset includes “
, WD, CD, and HRD” while the second dataset contains only HRD. We applied LSTM, RF, LLCV, OMPCV, and ET algorithms to these datasets, aiming to validate our hypothesis and evaluate alternative AI algorithms compared to those commonly used for IWRM in scientific literature. Finally, we developed occupancy level prediction models to standardize data from dams with varying depths.
After the model development phase, we conclude by validating our proposed model. We contributed to the scientific literature with both our hybrid model and explored significant input parameters for water level prediction: solar radiation, dew point, daylight duration and rainfall, daily water consumption, evapotranspiration, and historical reservoir data. Additionally, we consider AI algorithms that are not frequently used in the IWRM field against the algorithms used. Finally, we discovered that ET has a superior performance against commonly used algorithms such as LSTM and RF. We predicted the occupancy level one month ahead with only a 1% error margin using ET.
In future studies, we plan to investigate how integrating weather forecasts and hyperparameter optimization can further enhance the performance of AI models. Additionally, we aim to explore novel approaches for incorporating real-time data streams and improving the robustness of predictive models in dynamic environments.
References
- Allen RG, Pereira LS, Raes D, Smith M, W a B (1998) Crop evapotranspiration - Guidelines for computing crop water requirements - FAO Irrigation and drainage paper 56. Irrigation and Drainage. [CrossRef]
- Foudi S, McCartney M, Markandya A, Pascual U (2023) The impact of multipurpose dams on the values of nature’s contributions to people under a water-energy-food nexus framing. Ecological Economics. [CrossRef]
- Bieber N, Ker JH, Wang X, Triantafyllidis C, van Dam KH, Koppelaar RHEM, Shah N (2018) Sustainable planning of the energy-water-food nexus using decision making tools. Energy Policy 113:584–607.
- Jalilov SM, Keskinen M, Varis O, Amer S, Ward FA (2016) Managing the water-energy-food nexus: Gains and losses from new water development in Amu Darya River Basin. J Hydrol (Amst) 539:648–661.
- Lee EH (2024) Proactive dam operation based on inflow prediction by modified long short-term memory for improving resilience. Eng Appl Artif Intell 133:108525.
- Li M, Ren Q, Li M, Fang X, Xiao L, Li H (2024) A separate modeling approach to noisy displacement prediction of concrete dams via improved deep learning with frequency division. Advanced Engineering Informatics 60:102367.
- Zin MFM, Kamal FZ, Ismail SI, Noh KSSKM, Kassim AH (2023) Development of dam controller technology water level and alert system using Arduino UNO. Indonesian Journal of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science. [CrossRef]
- Ziggah YY, Issaka Y, Laari PB (2022) Evaluation of different artificial intelligent methods for predicting dam piezometric water level. Model Earth Syst Environ. [CrossRef]
- Tshireletso T, Moyo P, Kabani M (2021) Predicting the effects of climate change on water temperatures of roode elsberg dam using nonparametric machine learning models. Infrastructures (Basel). [CrossRef]
- Vishwakarma DK, Ali R, Bhat SA, Elbeltagi A, Kushwaha NL, Kumar R, Rajput J, Heddam S, Kuriqi A (2022) Pre- and post-dam river water temperature alteration prediction using advanced machine learning models. Environmental Science and Pollution Research. [CrossRef]
- Ouma YO, Moalafhi DB, Anderson G, Nkwae B, Odirile P, Parida BP, Qi J (2022) Dam Water Level Prediction Using Vector AutoRegression, Random Forest Regression and MLP-ANN Models Based on Land-Use and Climate Factors. Sustainability 14:14934.
- Ganesh RS, Sasipriya S, Gowtham Balaji M, Ashok Karthi G, Gokul Dharan S (2022) An IoT-based Dam Water Level Monitoring and Alerting System. Proceedings - International Conference on Applied Artificial Intelligence and Computing, ICAAIC 2022. [CrossRef]
- R K, C J, K SK (2018) Dam Water Level Monitoring and Alerting System using IOT. International Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering. [CrossRef]
- Ngebe S, Malunda KB, du Plessis A (2022) Utility of geospatial techniques in estimating dam water levels: insights from the Katrivier Dam. Water SA. [CrossRef]
- Li W, Qin Y, Sun Y, Huang H, Ling F, Tian L, Ding Y (2016) Estimating the relationship between dam water level and surface water area for the Danjiangkou Reservoir using Landsat remote sensing images. Remote Sensing Letters. [CrossRef]
- Ibañez SC, Dajac CVG, Liponhay MP, Legara EFT, Esteban JMH, Monterola CP (2022) Forecasting reservoir water levels using deep neural networks: A case study of angat dam in the philippines. Water (Switzerland). [CrossRef]
- Ahmed E-SN, Amr E-S (2019) DAILY FORECASTING OF DAM WATER LEVELS USING MACHINE LEARNING.
- Yu W, Nakakita E, Kim S, Yamaguchi K (2016) Improving the accuracy of flood forecasting with transpositions of ensemble NWP rainfall fields considering orographic effects. J Hydrol (Amst) 539:345–357.
- Zhang R, Chen ZY, Xu LJ, Ou CQ (2019) Meteorological drought forecasting based on a statistical model with machine learning techniques in Shaanxi province, China. Science of the Total Environment 665:338–346.
- Ryu YM, Lee EH (2022) Application of Neural Networks to Predict Daecheong Dam Water Levels. Journal of the Korean Society of Hazard Mitigation. [CrossRef]
- Dayal A, Bonthu S, T VN, Saripalle P, Mohan R (2024) Deep learning for Multi-horizon Water levelForecasting in KRS reservoir, India. Results in Engineering 21:101828.
- Üneş F, Demirci M, Kişi Ö (2015) Prediction of Millers Ferry Dam Reservoir Level in USA Using Artificial Neural Network. Periodica Polytechnica Civil Engineering 59:309–318.
- Hipni A, El-shafie A, Najah A, Karim OA, Hussain A, Mukhlisin M (2013) Daily Forecasting of Dam Water Levels: Comparing a Support Vector Machine (SVM) Model With Adaptive Neuro Fuzzy Inference System (ANFIS). Water Resources Management. [CrossRef]
- Huang S, Xia J, Zeng S, Wang Y, She D (2021) Effect of Three Gorges Dam on Poyang Lake water level at daily scale based on machine learning. Journal of Geographical Sciences. [CrossRef]
- Larrea PP, Ríos XZ, Parra LC (2021) Application of neural network models and anfis for water level forecasting of the salve faccha dam in the andean zone in Northern Ecuador. Water (Switzerland). [CrossRef]
- Ayanlade A, Radeny M, Morton JF, Muchaba T (2018) Rainfall variability and drought characteristics in two agro-climatic zones: An assessment of climate change challenges in Africa. Science of the Total Environment 630:728–737.
- Fowler HJ, Kilsby CG (2002) A weather-type approach to analysing water resource drought in the Yorkshire region from 1881 to 1998. J Hydrol (Amst) 262:177–192.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).