Submitted:
05 July 2024
Posted:
09 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
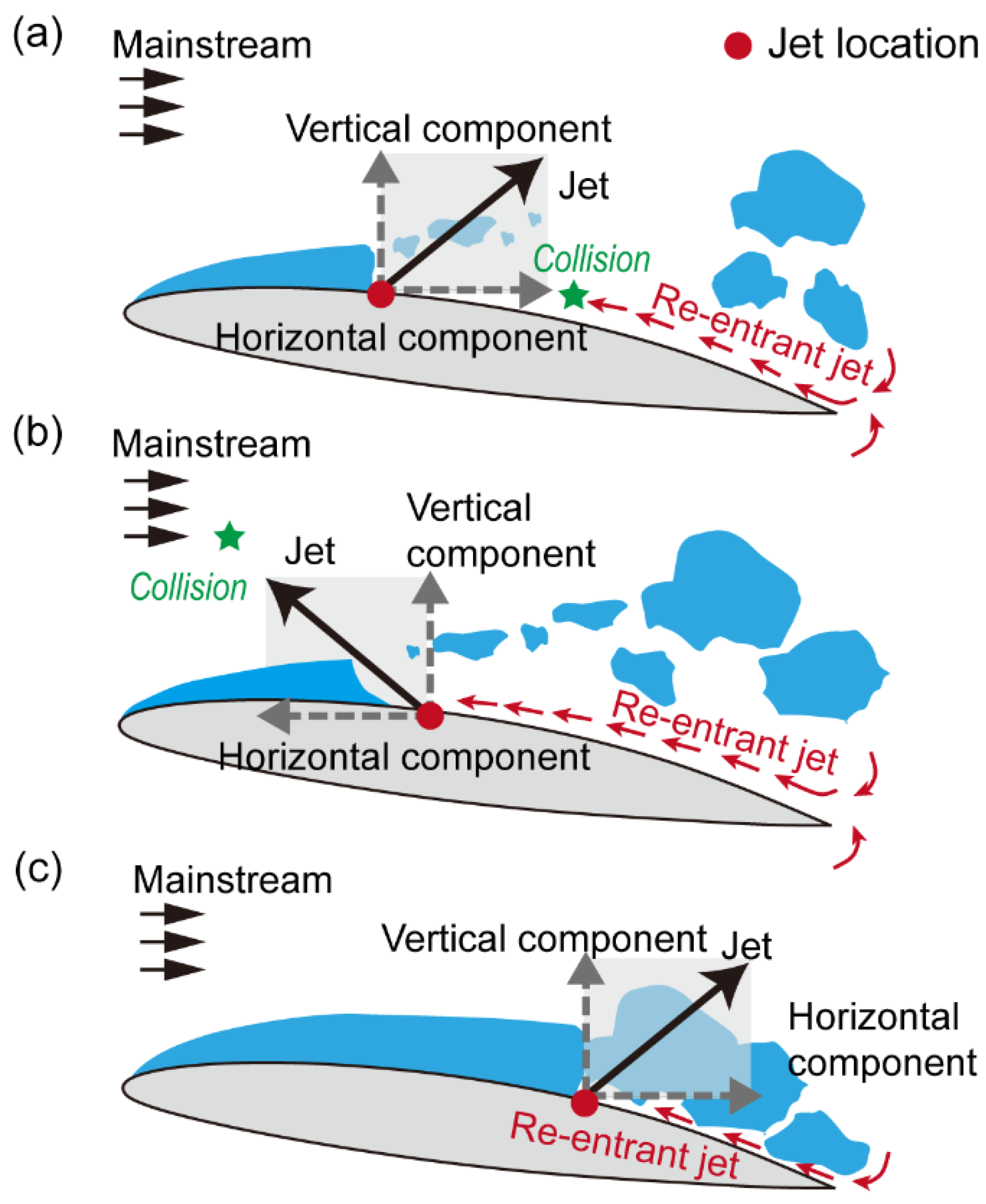
1. Introduction
2. Research Object
2.1. Hydrofoil and Jet Configuration
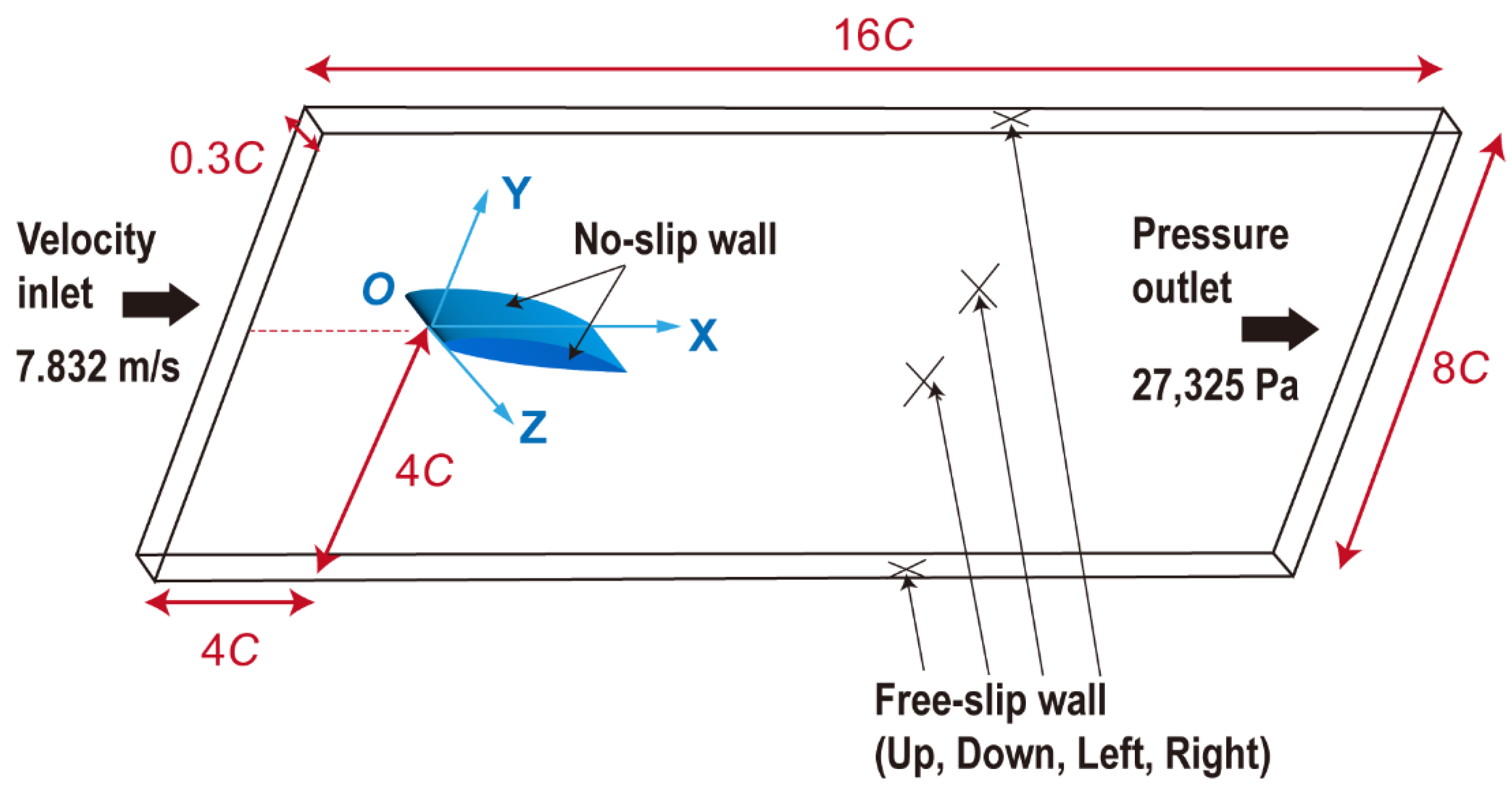
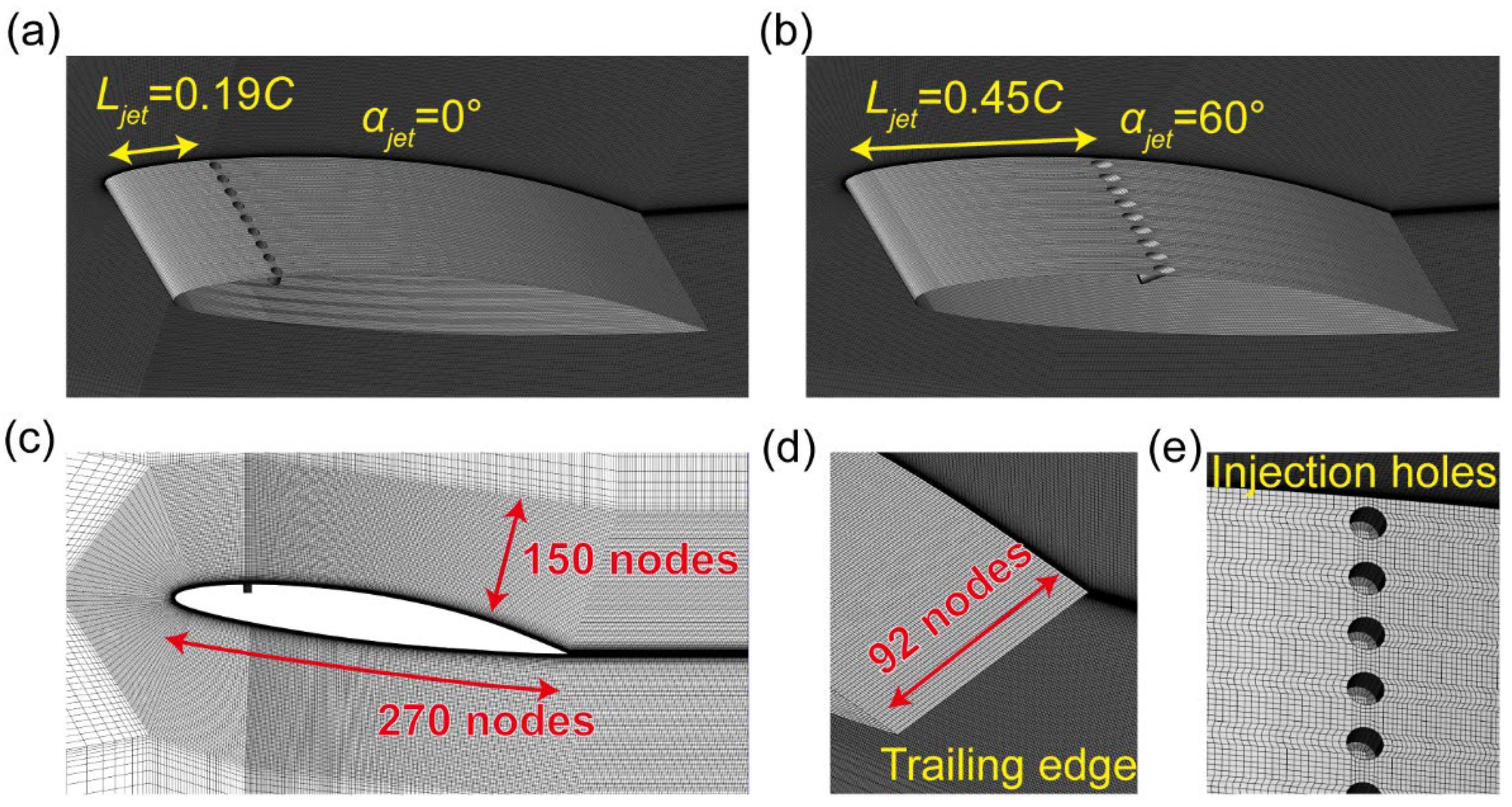
2.2. Computational Domain and Mesh Arrangement
3. Numerical Method and Validation
3.1. Governing Equation and Turbulence Model
3.2. Cavitation Model
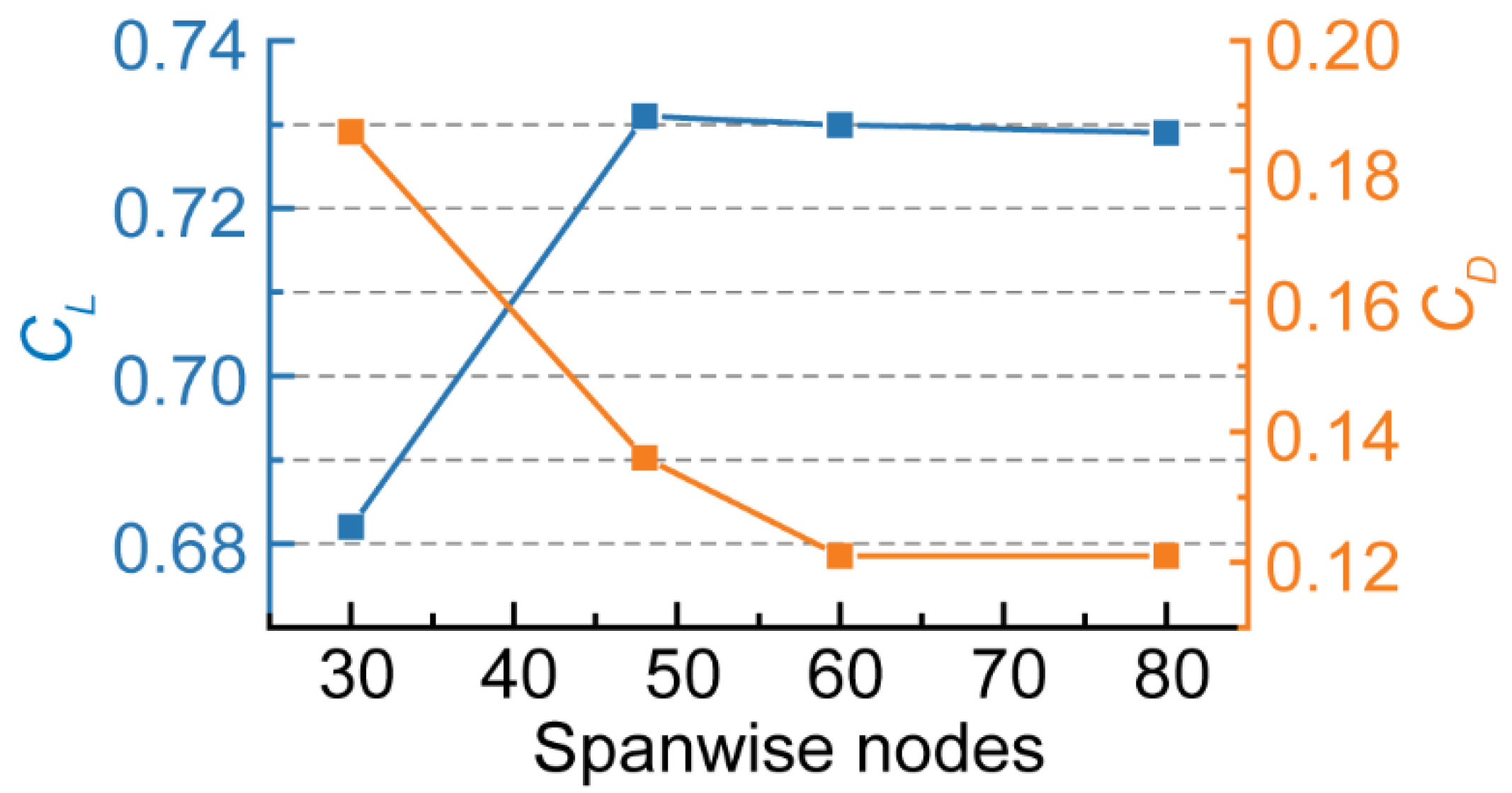
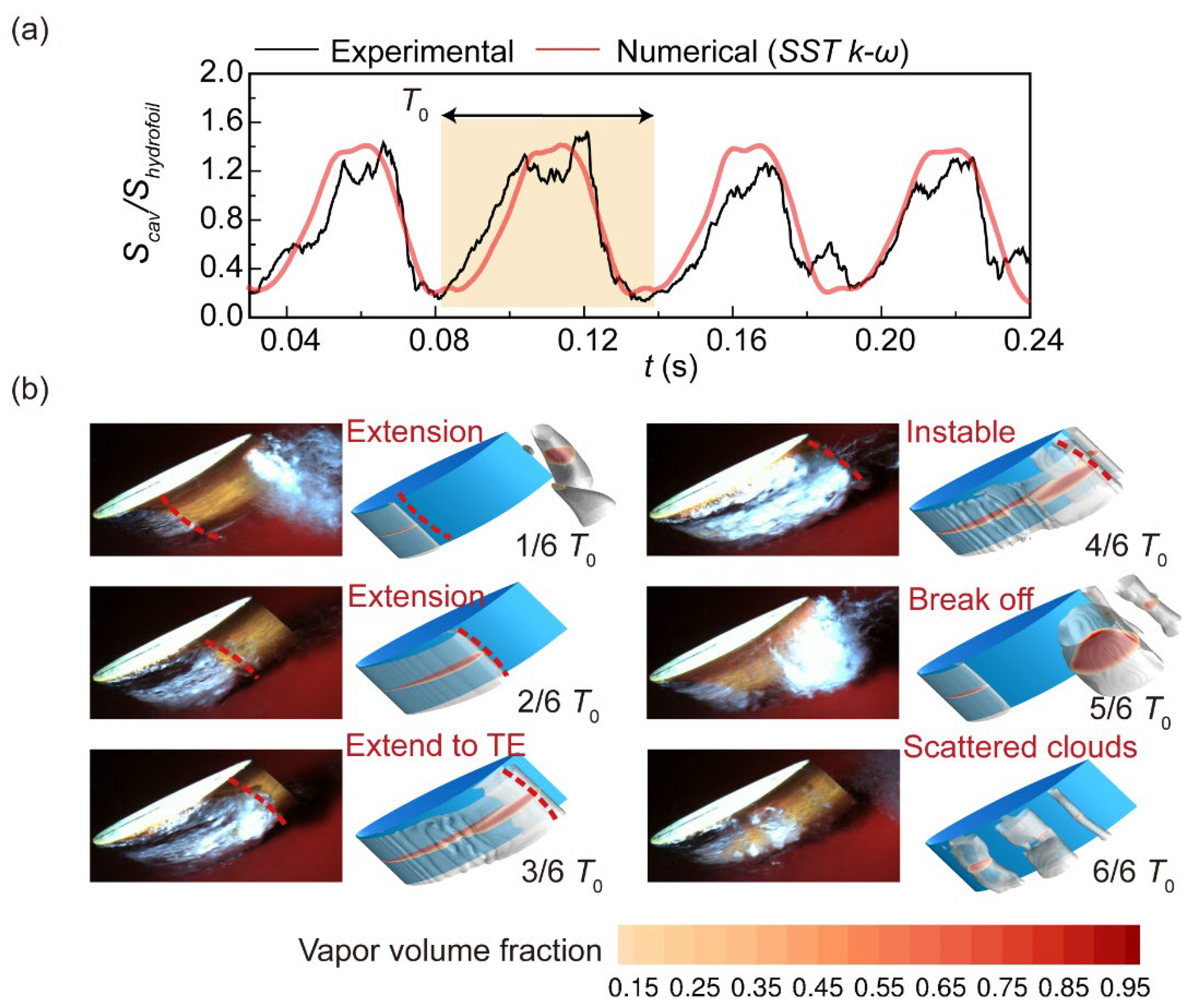
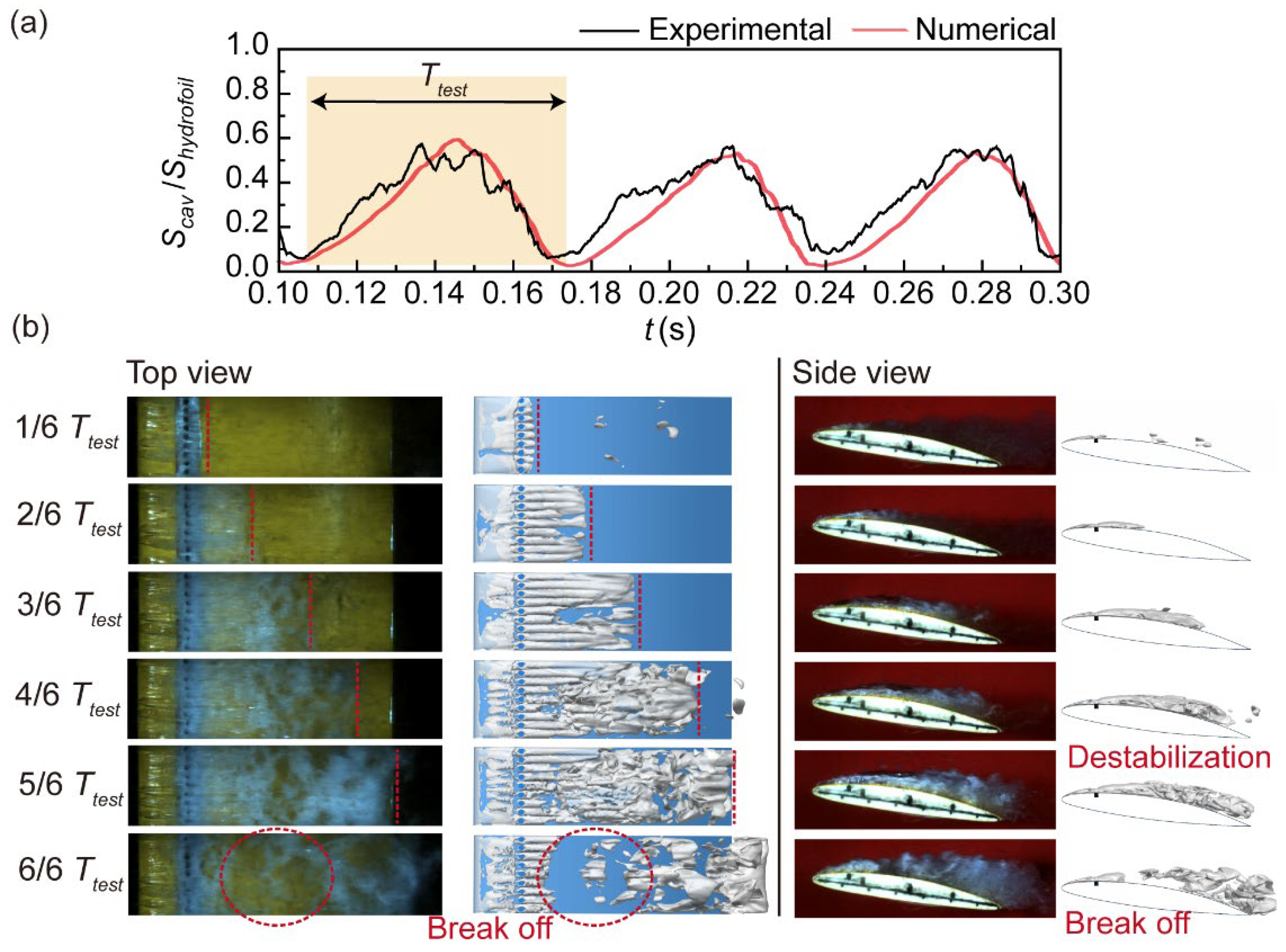
3.3. Calculation Setup, Uncertainty Analysis and Validation of Numerical Results
4. Setup of Orthogonal Test Method
5. Results and Discussion
5.1. Analysis of Orthogonal Results
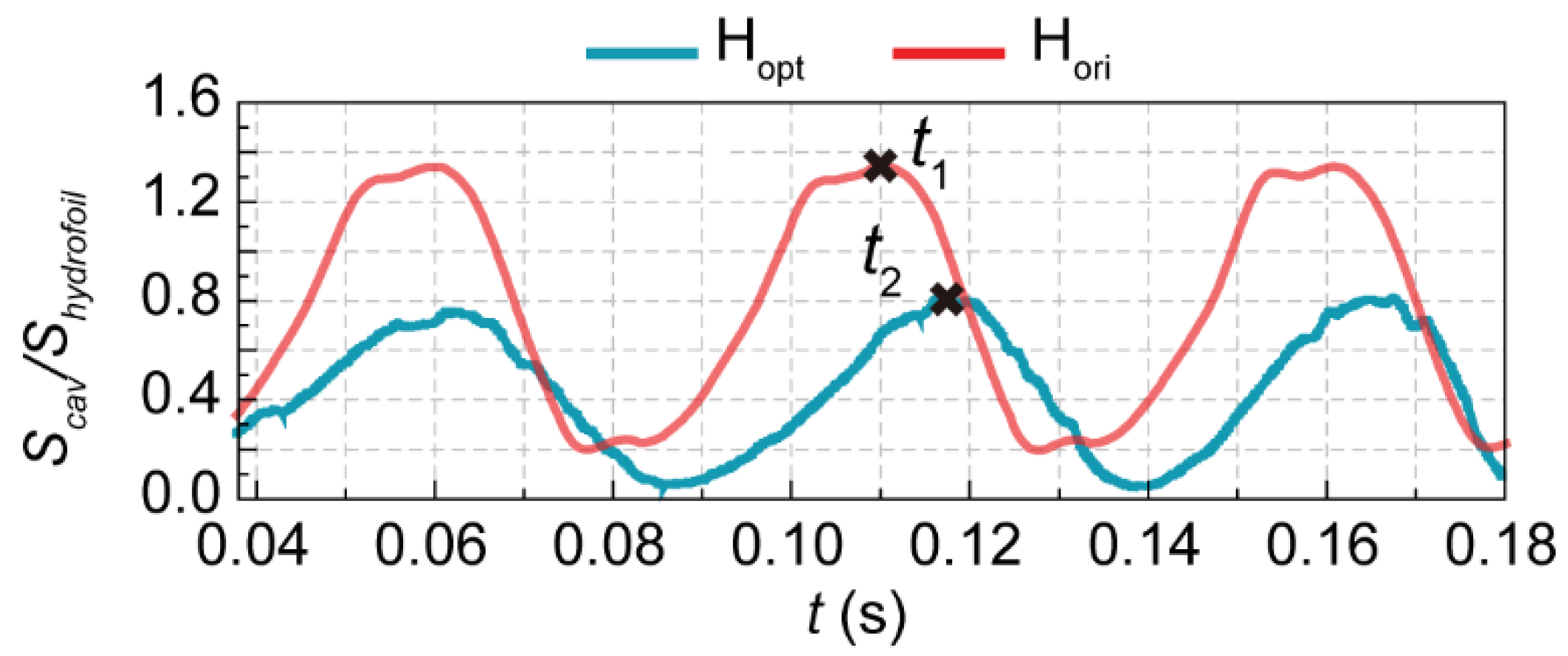
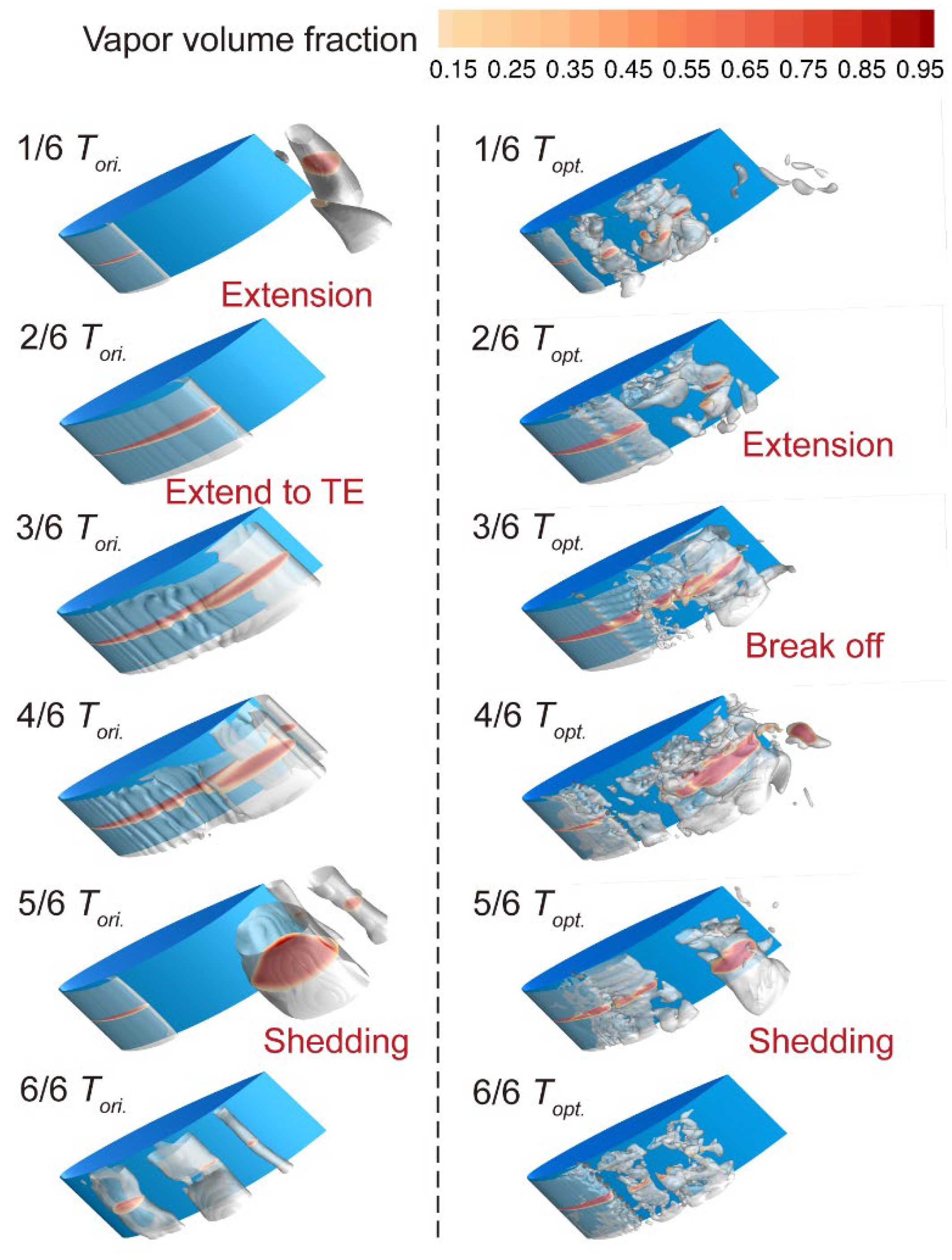
5.2. Cavitation Suppression Performance (σ = 0.83)
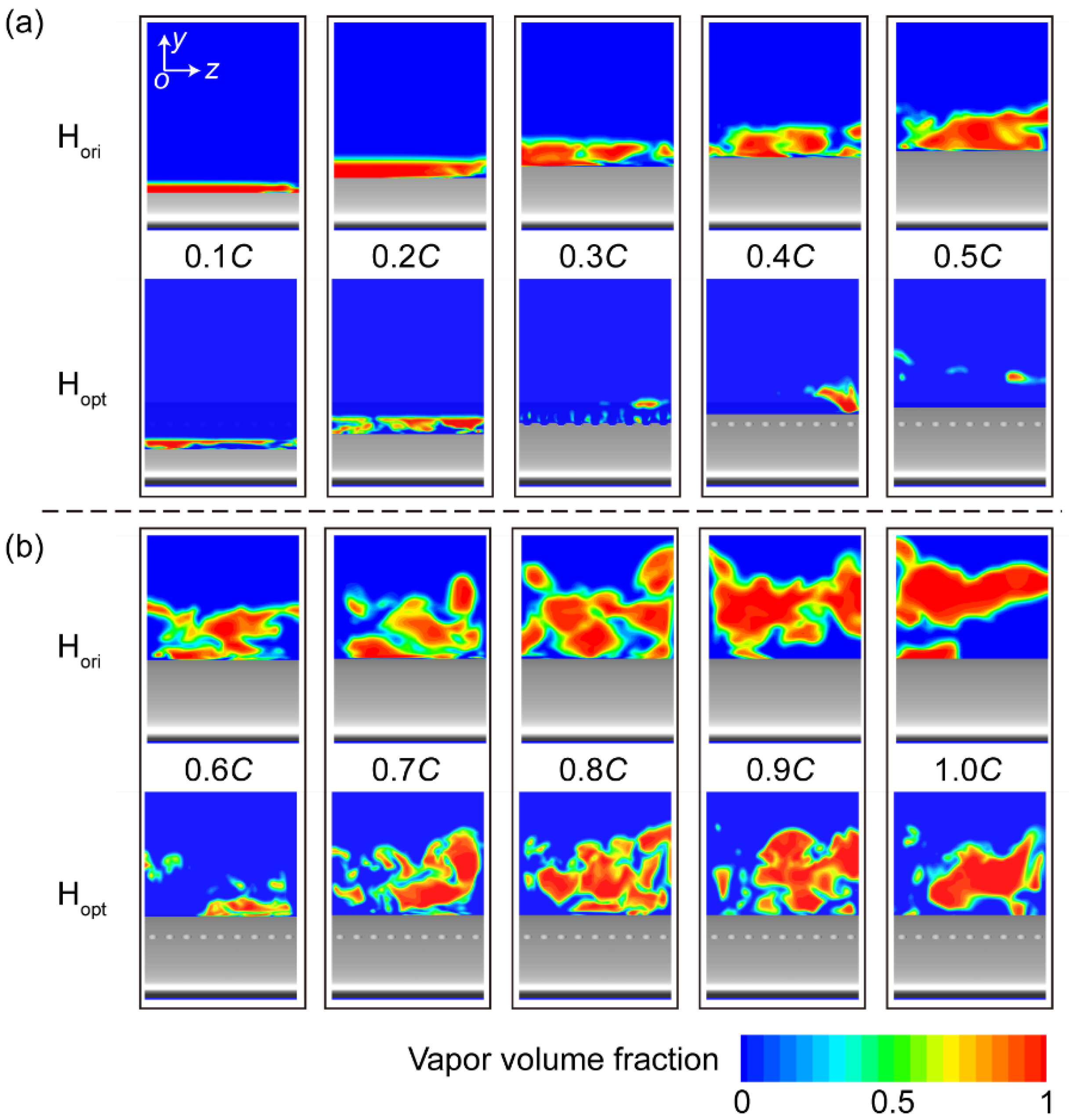
5.3. Energy Performance and Pressure Distribution
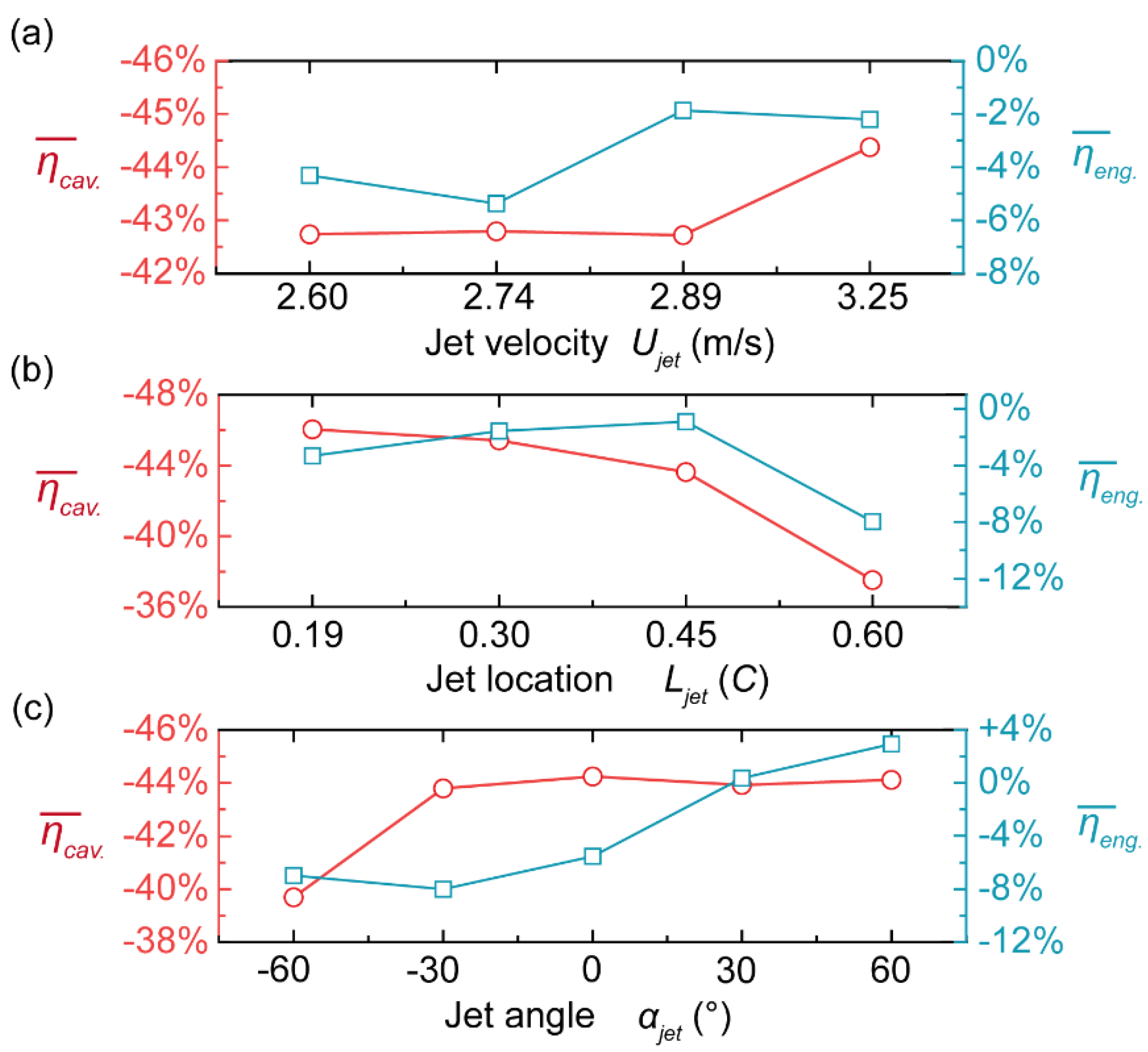
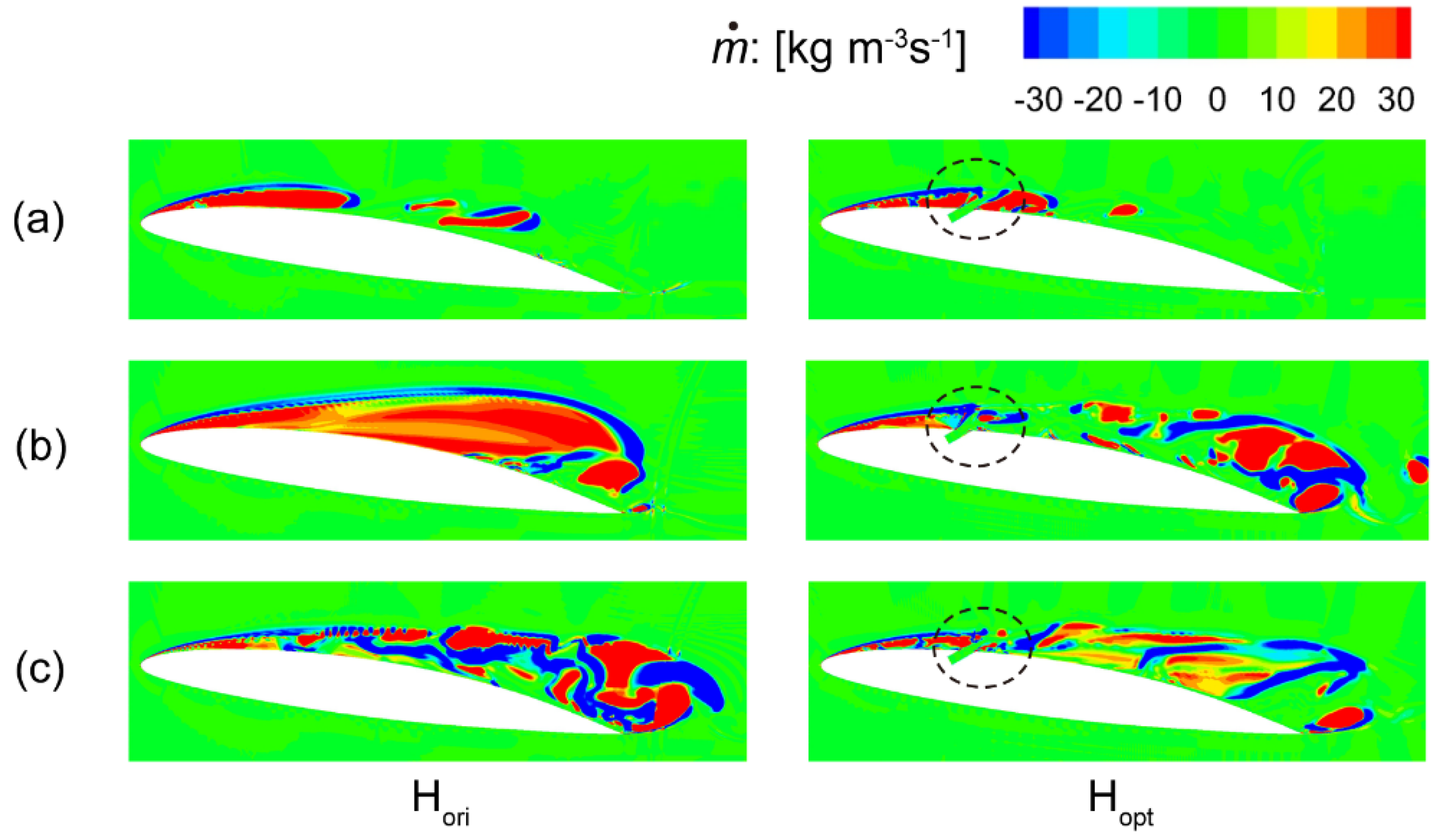
5.4. Influence Mechanism of Injection Parameters on Flow Performance
6. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, G.; Wu, Q.; Huang, B. Dynamics of Cavitation–Structure Interaction. Acta Mech. Sin. /Lixue Xuebao 2017, 33, 685–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Zhang, J.; Huang, Z. Numerical Study on Cavitation-Vortex-Noise Correlation Mechanism and Dynamic Mode Decomposition of a Hydrofoil. Phys. Fluids 2022, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.; Long, X.; Ji, B. LES Investigation of Cavitating Flows around a Sphere with Special Emphasis on the Cavitation–Vortex Interactions. Acta Mech. Sin. /Lixue Xuebao 2020, 36, 1238–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, A.; Sagar, H.; Lantermann, U.; el Moctar, O. Numerical Modelling and Prediction of Cavitation Erosion. Wear 2015, 338–339, 189–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, N.; Zhou, W.; Che, B.; Wu, D.; Wang, L.; Zhu, H. Effects of Microvortex Generators on Cavitation Erosion by Changing Periodic Shedding into New Structures. Phys. Fluids 2020, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, S.; Shimura, T.; Uchiumi, M.; Iga, Y. One-Dimensional Analysis Method for Cavitation Instabilities of a Rotating Machinery. J. Fluids Eng. Trans. ASME 2018, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Cheng, H.; Ji, B. LES Investigation of the Noise Characteristics of Sheet and Tip Leakage Vortex Cavitating Flow. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 2022, 146, 103880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gropper, D.; Wang, L.; Harvey, T.J. Hydrodynamic Lubrication of Textured Surfaces: A Review of Modeling Techniques and Key Findings. Tribol Int 2016, 94, 509–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, Z.; Liu, M.; Ji, X. Influence of Water Injection on Broadband Noise and Hydrodynamic Performance for a NACA66 (MOD) Hydrofoil under Cloud Cavitation Condition. Appl. Ocean Res. 2021, 115, 102858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, W.; Ji, X.; Wang, X. Investigation of Water Injection Influence on Cloud Cavitating Vortical Flow for a Naca66 (Mod) Hydrofoil. Energ. (Basel) 2021, 14, 5973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, B.; Wu, D. Study on Vortex Generators for Control of Attached Cavitation. Am. Soc. Mech. Eng. Fluids Eng. Div. (Publ. ) FEDSM 2017, 1A-2017, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, B.; Chu, N.; Cao, L.; Schmidt, S.J.; Likhachev, D.; Wu, D. Control Effect of Micro Vortex Generators on Attached Cavitation Instability. Phys. Fluids 2019, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, B.; Cao, L.; Chu, N.; Likhachev, D.; Wu, D. Effect of Obstacle Position on Attached Cavitation Control through Response Surface Methodology. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2019, 33, 4265–4279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, M.; Shao, X. Inhibition of Cloud Cavitation on a Flat Hydrofoil through the Placement of an Obstacle. Ocean Eng. 2018, 155, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadivar, E.; Moctar, O. el; Javadi, K. Stabilization of Cloud Cavitation Instabilities Using Cylindrical Cavitating-Bubble Generators (CCGs). Int. J. Multiph. Flow 2019, 115, 108–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadivar, E.; Timoshevskiy, M. V.; Pervunin, K.S.; Moctar, O. el Cavitation Control Using Cylindrical Cavitating-Bubble Generators (CCGs): Experiments on a Benchmark CAV2003 Hydrofoil. Int. J. Multiph. Flow 2020, 125, 103186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Tan, L. Influence of C Groove on Suppressing Vortex and Cavitation for a NACA0009 Hydrofoil with Tip Clearance in Tidal Energy. Renew Energy 2020, 148, 907–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Tan, L. Method of C Groove on Vortex Suppression and Energy Performance Improvement for a NACA0009 Hydrofoil with Tip Clearance in Tidal Energy. Energy 2018, 155, 448–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhao, X.; Cheng, H.; Ji, B. LES Investigation of the Wavy Leading Edge Effect on Cavitation Noise. Ultrason Sonochem 2024, 103, 106780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, N.; Zhu, H.; Che, B.; Zhou, W.; Bai, Y.; Wang, C. Interaction Mechanism between Cloud Cavitation and Micro Vortex Flows. Ocean Eng. 2024, 297, 117004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, A.; Reclari, M.; Sano, T.; Iino, M.; Farhat, M. Suppressing Tip Vortex Cavitation by Winglets. Exp Fluids 2019, 60, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H. yu; Ji, B.; Long, X. ping; Huai, W. xin; Farhat, M. A Review of Cavitation in Tip-Leakage Flow and Its Control. Journal of Hydrodynamics 2021 33:2 2021, 33, 226–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Long, X.; Ji, B.; Peng, X.; Farhat, M. Suppressing Tip-Leakage Vortex Cavitation by Overhanging Grooves. Exp Fluids 2020, 61, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timoshevskiy, M. V.; Zapryagaev, I.I. Generation of a Wall Jet to Control Unsteady Cavitation over a 2D Hydrofoil: Visualization and Hydroacoustic Signal Analysis. J Phys Conf Ser 2017, 899, 032021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timoshevskiy, M. V.; Zapryagaev, I.I.; Pervunin, K.S.; Markovich, D.M. Cavitation Control on a 2D Hydrofoil through a Continuous Tangential Injection of Liquid: Experimental Study. AIP Conf Proc 2016, 1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timoshevskiy, M. V.; Zapryagaev, I.I.; Pervunin, K.S.; Markovich, D.M. Cavitating Flow Control through Continuous Tangential Mass Injection on a 2D Hydrofoil at a Small Attack Angle. MATEC Web Conf. 2016, 84, 00039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, N.; Ganesh, H.; Yakushiji, R.; Ceccio, S.L. Tip Vortex Cavitation Suppression by Active Mass Injection. J. Fluids Eng. Trans. ASME 2011, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.S.; Ahn, B.K.; Han, J.M.; Kim, J.H. Propeller Tip Vortex Cavitation Control and Induced Noise Suppression by Water Injection. J. Mar. Sci. Technol. (Jpn. ) 2018, 23, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Giorgi, M.G.; Ficarella, A.; Fontanarosa, D. Active Control of Unsteady Cavitating Flows in Turbomachinery. Proc. ASME Turbo Expo 2019, 2A-2019, 2A–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maltsev, L.I.; Dimitrov, V.D.; Milanov, E.M.; Zapryagaev, I.I.; Timoshevskiy, M. V.; Pervunin, K.S. Jet Control of Flow Separation on Hydrofoils: Performance Evaluation Based on Force and Torque Measurements. J. Eng. Thermophys. 2020, 29, 424–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Yi, Q.; Lu, S.; Wang, X. Exploration and Research of the Impact of Hydrofoil Surface Water Injection on Cavitation Suppression. In Proceedings of the Volume 2D: Turbomachinery; American Society of Mechanical Engineers, June 26 2017; Vol. 2D-2017; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, S.P.; Wang, W.; Hou, T.; Zhang, M.; Jiao, J.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, X.F. Experiment Research on Cavitation Control by Active Injection. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 10th International Symposium on Cavitation (CAV2018); pp. 2019363–368.
- Liu, M.; Tan, L.; Cao, S. Cavitation-Vortex-Turbulence Interaction and One-Dimensional Model Prediction of Pressure for Hydrofoil ALE15 by Large Eddy Simulation. J. Fluids Eng. Trans. ASME 2018, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, Z.; Li, X.; Zhu, Z. Multiscale Modeling of Tip-Leakage Cavitating Flows by a Combined Volume of Fluid and Discrete Bubble Model. Phys. Fluids 2021, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Jiang, B.; Wei, G.; Li, X.; Zhu, Z. Multiscale Multiphase Flow Simulations Using Interface Capturing and Lagrangian Particle Tracking. Phys. Fluids 2022, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Huang, Q.; Pan, G.; Shi, Y. Effect of Hydrofoil Leading Edge Waviness on Hydrodynamic Performance and Flow Noise. Ocean Eng. 2021, 231, 108883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Huang, Q.; Pan, G.; Shi, Y. Numerical Study on Hydrodynamic Performance and Flow Noise of a Hydrofoil with Wavy Leading-Edge. AIP Adv 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, A.; Ji, B.; Huang, R.F.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.N.; Luo, X.W. Cavitation Shedding Dynamics around a Hydrofoil Simulated Using a Filter-Based Density Corrected Model. Sci China Technol Sci 2015, 58, 864–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.Y.; Long, X.P.; Ji, B.; Liu, Q.; Bai, X.R. 3-D Lagrangian-Based Investigations of the Time-Dependent Cloud Cavitating Flows around a Clark-Y Hydrofoil with Special Emphasis on Shedding Process Analysis. J. Hydrodyn. 2018, 30, 122–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, X.; Cheng, H.; Ji, B.; Arndt, R.E.A. Numerical Investigation of Attached Cavitation Shedding Dynamics around the Clark-Y Hydrofoil with the FBDCM and an Integral Method. Ocean Eng. 2017, 137, 247–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Liu, Y.; Tan, L. Method of Variable-Depth Groove on Vortex and Cavitation Suppression for a NACA0009 Hydrofoil with Tip Clearance in Tidal Energy. Renew Energy 2022, 199, 546–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Tang, T.; Zhang, Q.D.; Wang, X.F.; An, Z.Y.; Tong, T.H.; Li, Z.J. Effect of Water Injection on the Cavitation Control:Experiments on a NACA66 (MOD) Hydrofoil. Acta Mech. Sin. /Lixue Xuebao 2020, 36, 999–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroux, J.B.; Astolfi, J.A.; Billard, J.Y. An Experimental Study of Unsteady Partial Cavitation. J. Fluids Eng. Trans. ASME 2004, 126, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroux, J.B.; Coutier-Delgosha, O.; Astolfi, J.A. A Joint Experimental and Numerical Study of Mechanisms Associated to Instability of Partial Cavitation on Two-Dimensional Hydrofoil. Phys. Fluids 2005, 17, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Tan, L.; Liu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Cao, S. Large Eddy Simulation of Cavitation Vortex Interaction and Pressure Fluctuation around Hydrofoil ALE 15. Ocean Eng. 2018, 163, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, W.; Ji, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y. Loading Noise Induced by Cavitating Flow and Its Simplified Model Prediction. Ocean Eng. 2023, 280, 114584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M. sheng; Zhao, W. wen; Wan, D. cheng Numerical Simulations of Propeller Cavitation Flows Based on OpenFOAM. J. Hydrodyn. 2020, 32, 1071–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, B.; Yu, B.; Ren, Y.; Chen, B. Calculation of Cavitation Evolution and Associated Turbulent Kinetic Energy Transport around a NACA66 Hydrofoil. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2019, 33, 1231–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.Q.; Grekula, M.; Lindell, P. Towards Numerical Prediction of Unsteady Sheet Cavitation on Hydrofoils. J. Hydrodyn. 2010, 22, 741–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutier-Delgosha, O.; Fortes-Patella, R.; Reboud, J.L. Evaluation of the Turbulence Model Influence on the Numerical Simulations of Unsteady Cavitation. J. Fluids Eng. Trans. ASME 2003, 125, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwart, P.J.; Gerber, A.G.; Belamri, T. A Two-Phase Flow Model for Predicting Cavitation Dynamics. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Multiphase Flow; 2004; Vol. 152; p. 152. [Google Scholar]
- Xing, T.; Stern, F. Factors of Safety for Richardson Extrapolation. J. Fluids Eng. Trans. ASME 2010, 132, 0614031–0640313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, R.; Shao, J.; Stern, F. Discussion: Criticisms of the “Correction Factor” Verification Method. J Fluids Eng 2004, 126, 704–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, F.; Wilson, R. V.; Coleman, H.W.; Paterson, E.G. Comprehensive Approach to Verification and Validation of CFD Simulations—Part 1: Methodology and Procedures. J Fluids Eng 2001, 123, 793–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roache, P. 1998.
- Wang, B.; Lin, R.; Liu, D.; Xu, J.; Feng, B. Investigation of the Effect of Humidity at Both Electrode on the Performance of PEMFC Using Orthogonal Test Method. Int J Hydrog. Energy 2019, 44, 13737–13743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.; Li, H.; Liu, X.; Liu, Z.; Wang, B. Transport Performance Improvement of a Multiphase Pump for Gas–Liquid Mixture Based on the Orthogonal Test Method. Processes 2021, Vol. 9, Page 1402 2021, 9, 1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, L.; Liu, Z.; Zeng, Y. Optimization Design of the Unsmooth Bionic Structure of a Hydrofoil Leading Edge Based on the Grey–Taguchi Method. 2022. [CrossRef]
- Mohanta, D.K.; Sahoo, B.; Mohanty, A.M. Optimization of Process Parameter in AI7075 Turning Using Grey Relational, Desirability Function and Metaheuristics. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Li, J.; Wu, M.; Xie, C.; Liu, C.; Qi, F. Study on the Influence of Active Jet Parameters on the Cavitation Performance of Clark-Y Hydrofoil. Ocean Eng. 2022, 261, 111900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correction Ji, B.; Luo, X.; Arndt, R.E.A.; Wu, Y. Numerical Simulation of Three Dimensional Cavitation Shedding Dynamics with Special Emphasis on Cavitation–Vortex Interaction. Ocean Eng. 2014, 87, 64–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
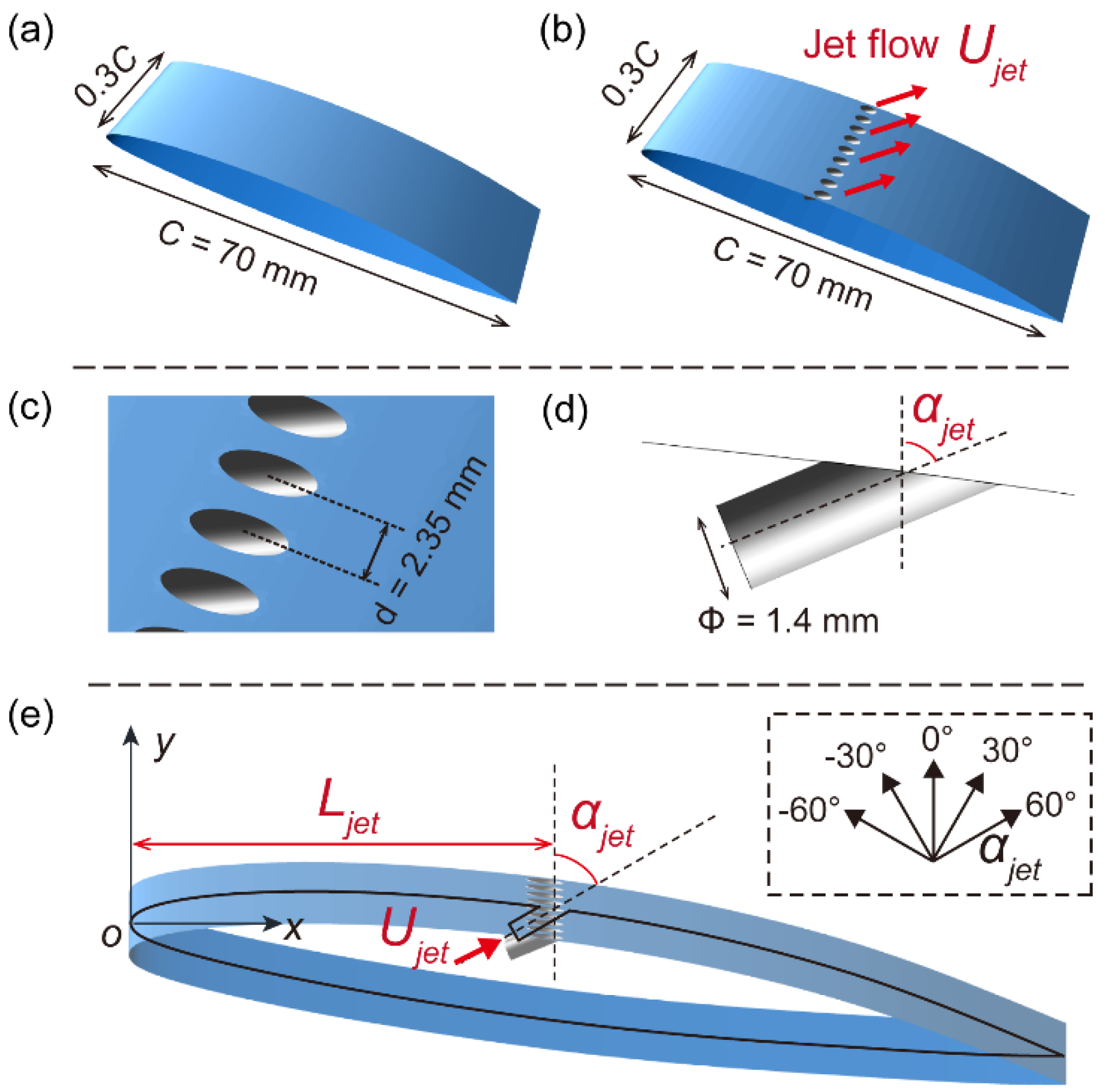
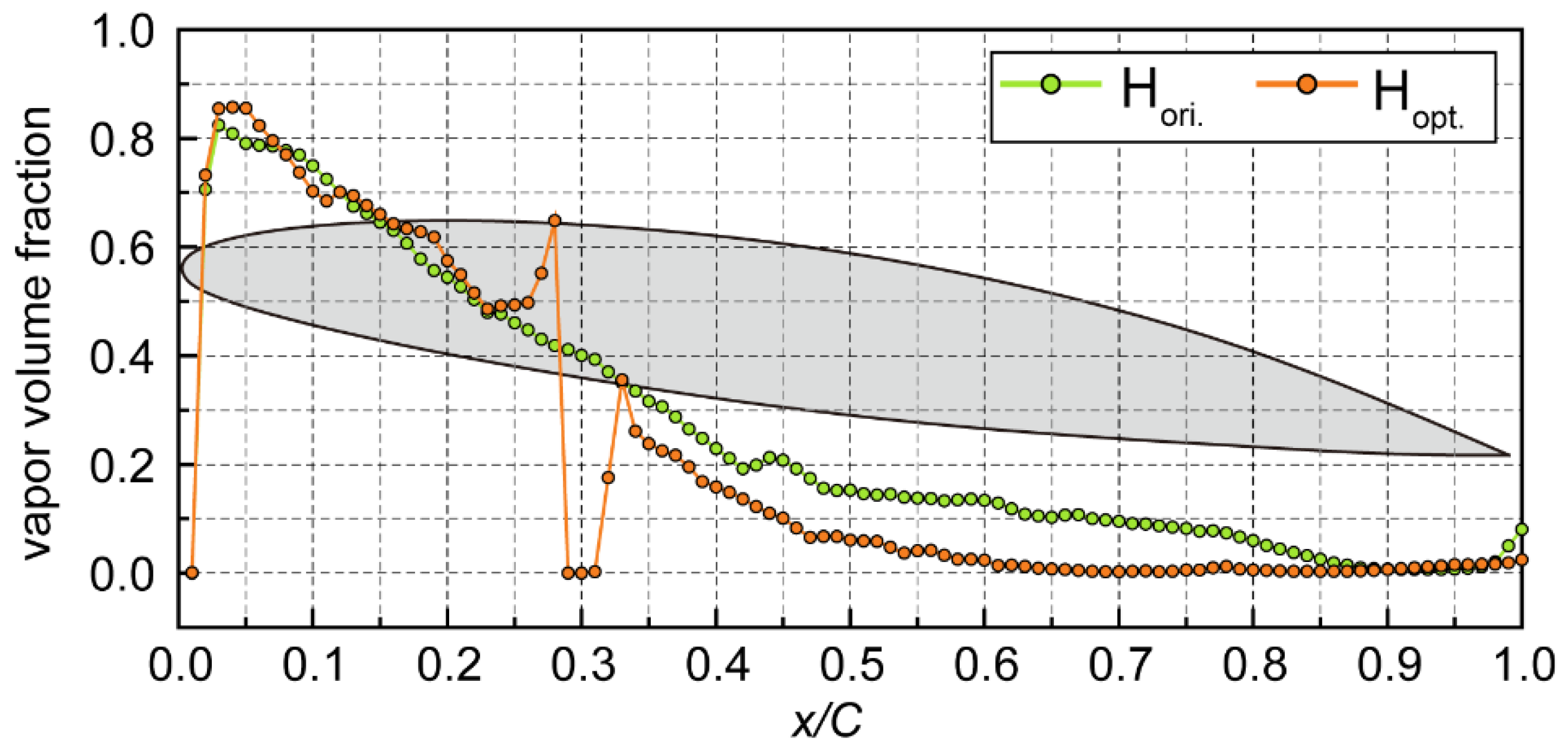
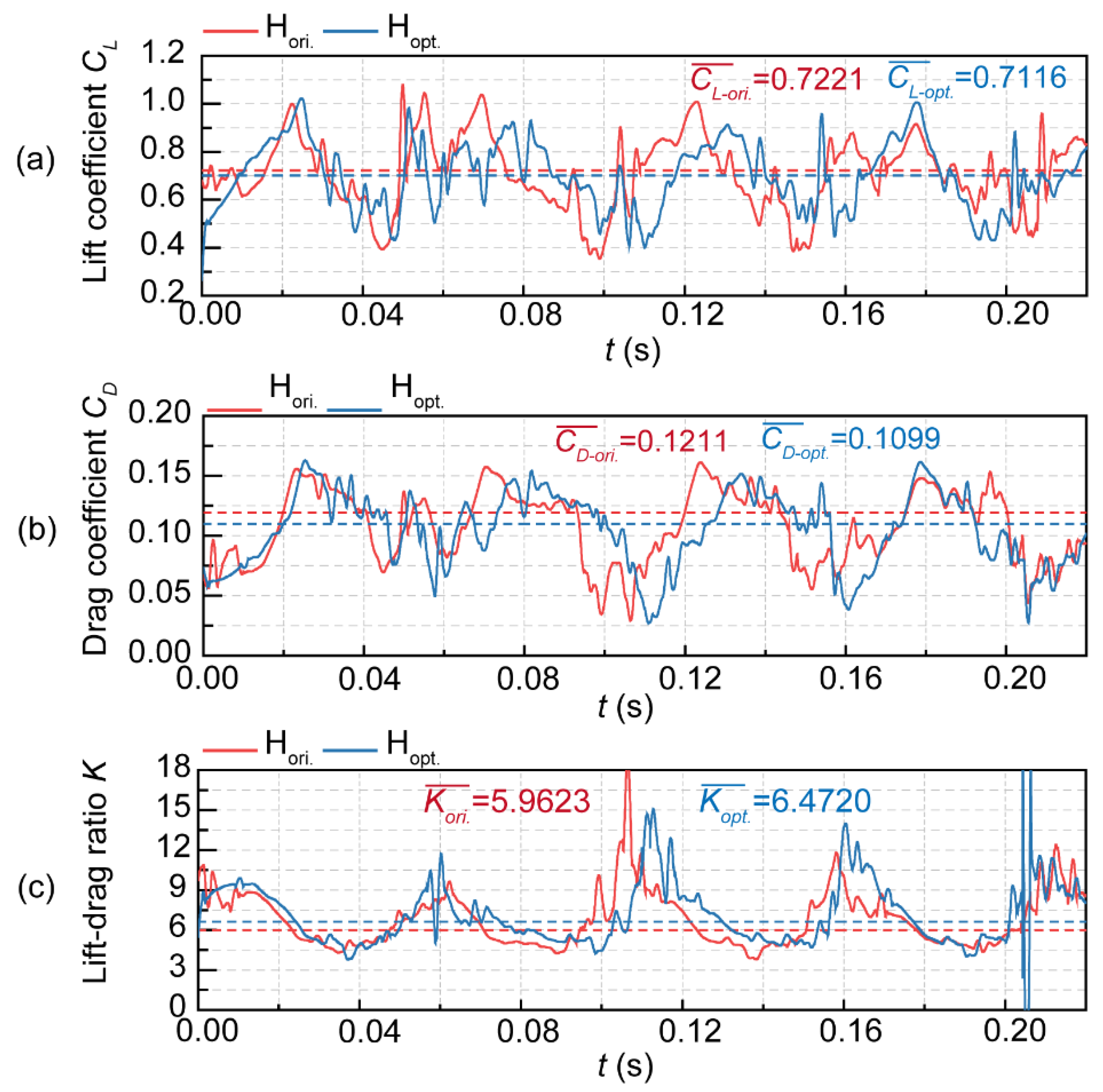
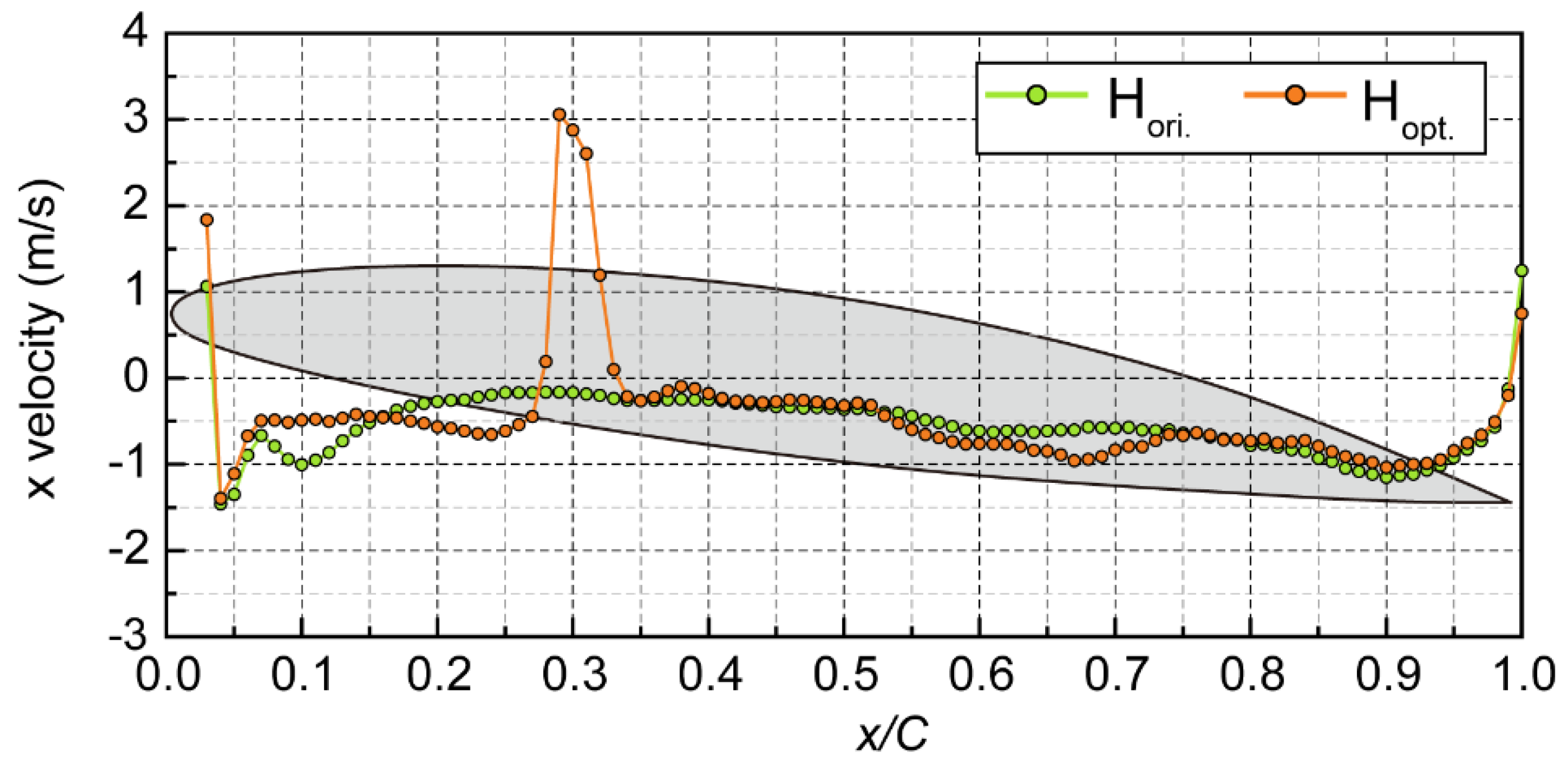

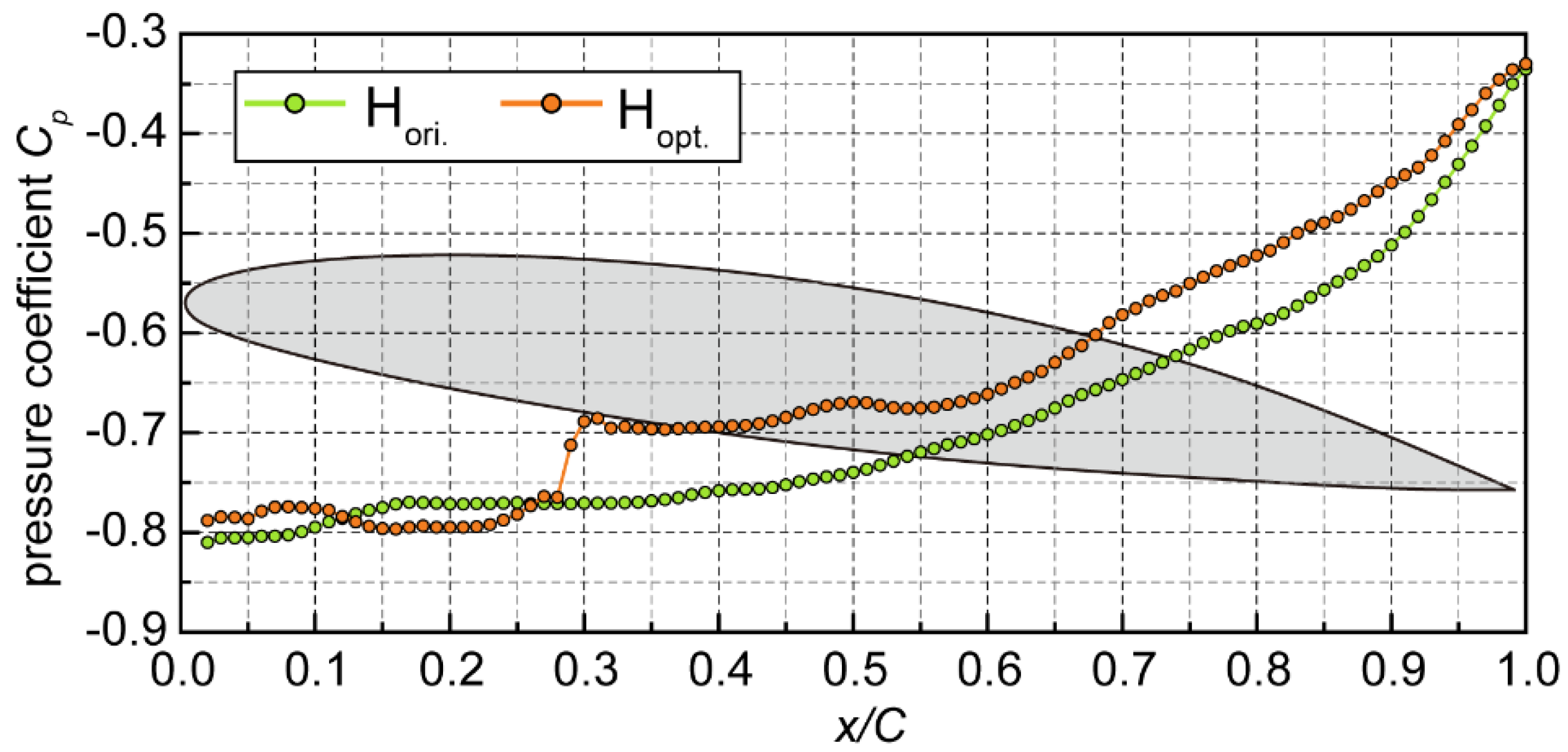
| Levels | Jet angle αjet (°) Factor A |
Jet location Ljet (C) Factor B |
Jet velocity Ujet (m/s) Factor C |
| Level 1 | -60 | 0.19 | 2.60 |
| Level 2 | -30 | 0.30 | 2.74 |
| Level 3 | 0 | 0.45 | 2.89 |
| Level 4 | +30 | 0.60 | 3.25 |
| Level 5 | +60 | / | / |
| Item | Total number of cells | Spanwise × Chordwise nodes | Cells of each jet hole |
| Original hydrofoil | 6,566,400 | 60 × 220 | / |
| Jet hydrofoils | 13,828,200 | 92 × 270 | 3,875 |
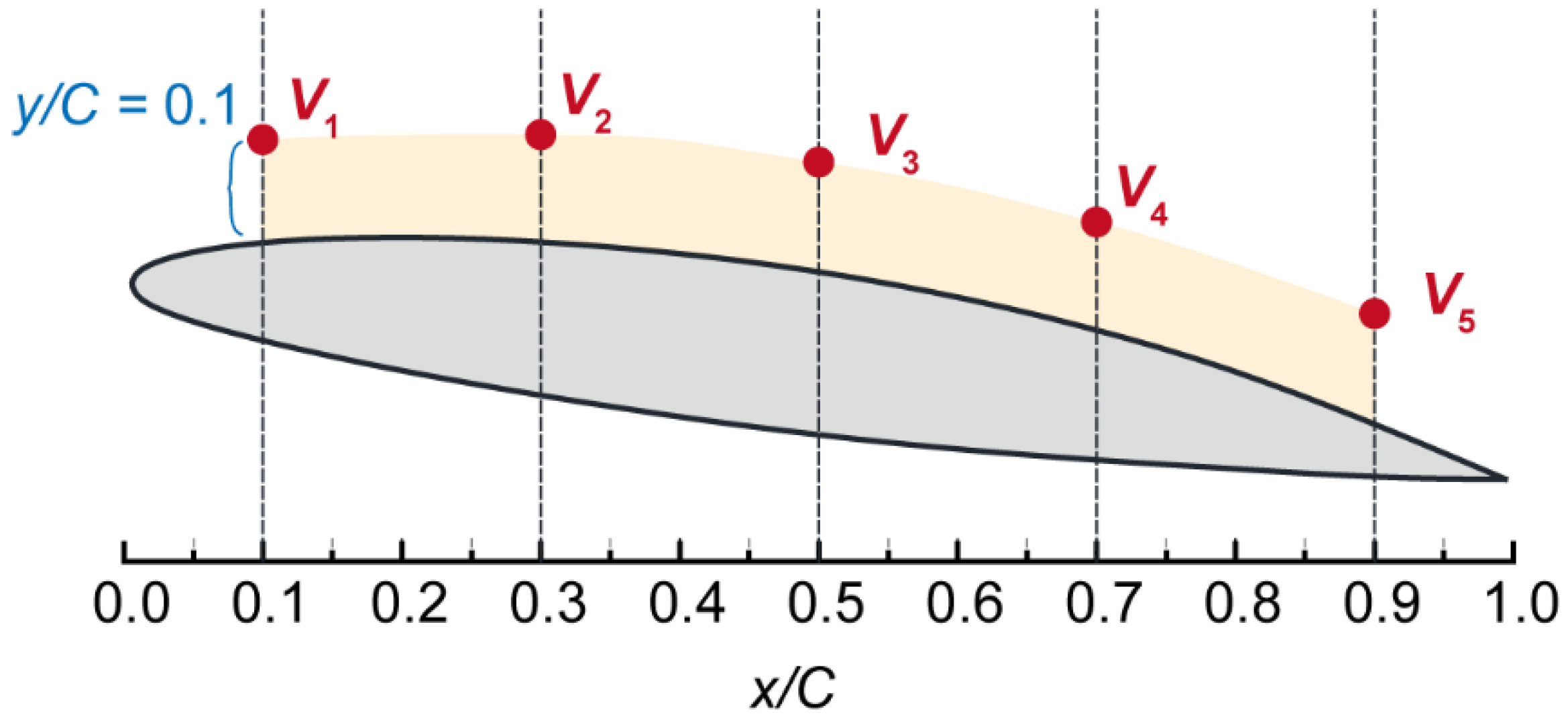
| V1 | V2 | V3 | V4 | V5 | |
| UCF | 0.022 | 0.031 | 0.047 | 0.114 | 0.135 |
| UFS | 0.017 | 0.035 | 0.048 | 0.092 | 0.103 |
| UGCI | 0.035 | 0.042 | 0.056 | 0.089 | 0.122 |
| Series | Jet angle (°) | Jet location (C) | Jet velocity (m/s) | ηcav | ηeng |
| H01 | -60 | 0.19 | 2.60 | -37.71% | -4.62% |
| H02 | -60 | 0.30 | 2.74 | -38.23% | -4.85% |
| H03 | -60 | 0.45 | 2.89 | -38.34% | -8.94% |
| H04 | -60 | 0.60 | 3.25 | -44.46% | -9.47% |
| H05 | -30 | 0.19 | 3.25 | -47.18% | -4.77% |
| H06 | -30 | 0.30 | 2.89 | -45.86% | -4.27% |
| H07 | -30 | 0.45 | 2.74 | -42.94% | -4.78% |
| H08 | -30 | 0.60 | 2.60 | -39.21% | -18.23% |
| H09 | 0 | 0.19 | 2.89 | -49.09% | -3.69% |
| H10 | 0 | 0.30 | 3.25 | -48.82% | -2.31% |
| H11 | 0 | 0.45 | 2.60 | -42.34% | +1.33% |
| H12 | 0 | 0.60 | 2.74 | -36.74% | -17.41% |
| H13 | +30 | 0.19 | 2.74 | -47.51% | -3.12% |
| H14 | +30 | 0.30 | 2.60 | -45.64% | +0.35% |
| H15 | +30 | 0.45 | 3.25 | -48.38% | +2.28% |
| H16 | +30 | 0.60 | 2.89 | -34.18% | +1.95% |
| H17 | +60 | 0.19 | 2.60 | -48.78% | -0.41% |
| H18 | +60 | 0.30 | 2.74 | -48.54% | +3.27% |
| H19 | +60 | 0.45 | 2.89 | -46.12% | +5.59% |
| H20 | +60 | 0.60 | 3.25 | -33.02% | +3.28% |
| Levels | Jet angle αjet Factor A |
Jet location Ljet Factor B |
Jet velocity Ujet Factor C |
| ?1j | -39.69% | -46.05% | -42.74% |
| ?2j | -43.80% | -45.42% | -42.79% |
| ?3j | -44.25% | -43.62% | -42.72% |
| ?4j | -43.93% | -37.52% | -44.37% |
| ?5j | -44.12% | / | / |
| Rj | 4.56% | 8.53% | 1.65% |
| Levels | Jet angle αjet Factor A |
Jet location Ljet Factor B |
Jet velocity Ujet Factor C |
| ?1j | -6.97% | -3.32% | -4.32% |
| ?2j | -8.01% | -1.56% | -5.38% |
| ?3j | -5.52% | -0.90% | -1.87% |
| ?4j | 0.37% | -7.98% | -2.20% |
| ?5j | 2.93% | / | / |
| Rj | 10.95% | 7.07% | 3.51% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





