Submitted:
08 July 2024
Posted:
09 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Experimental Strategy
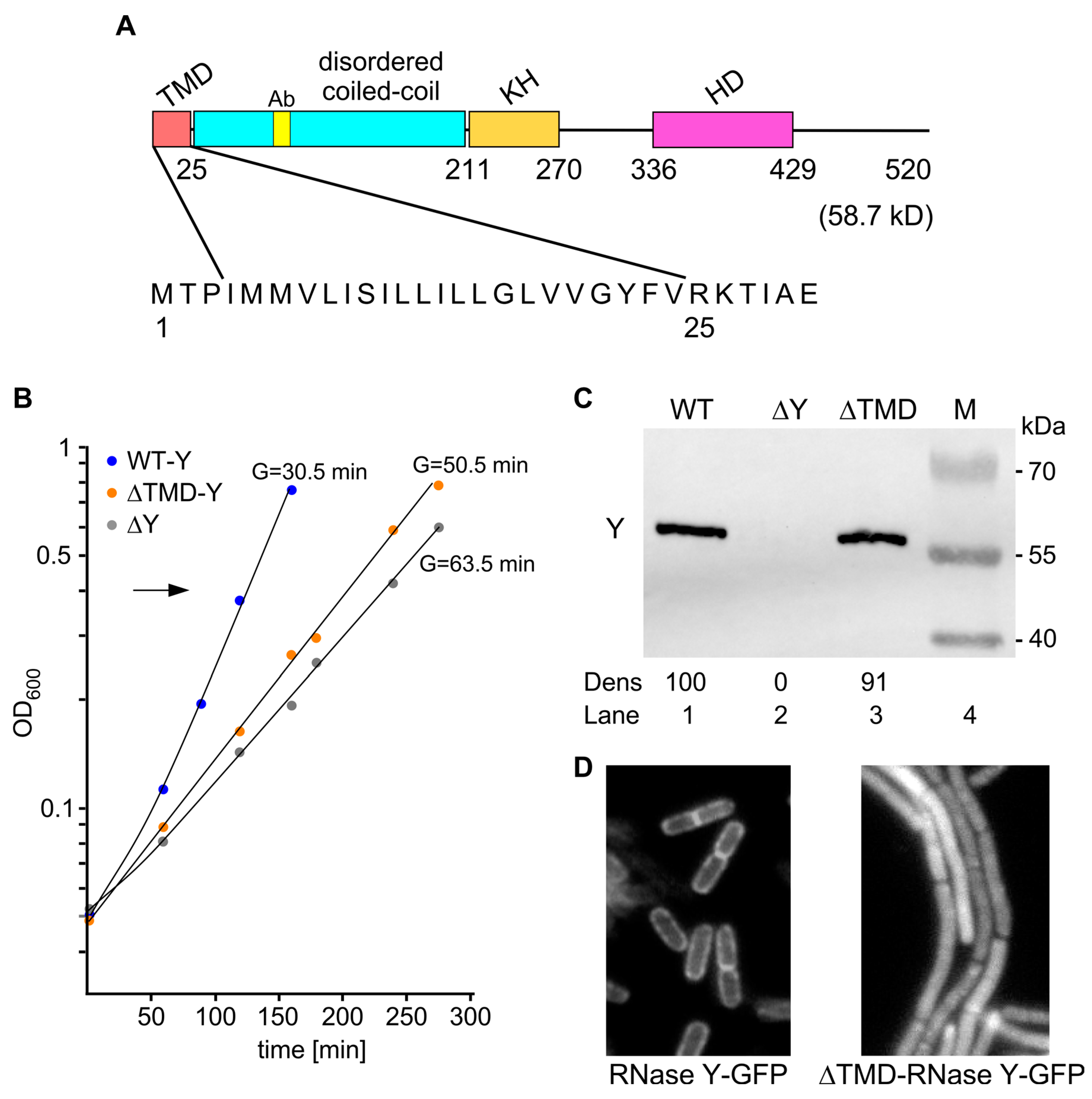
2.2. Cytoplasmic Localization of RNase Y Affects Gene Expression on a Genome-Wide Scale
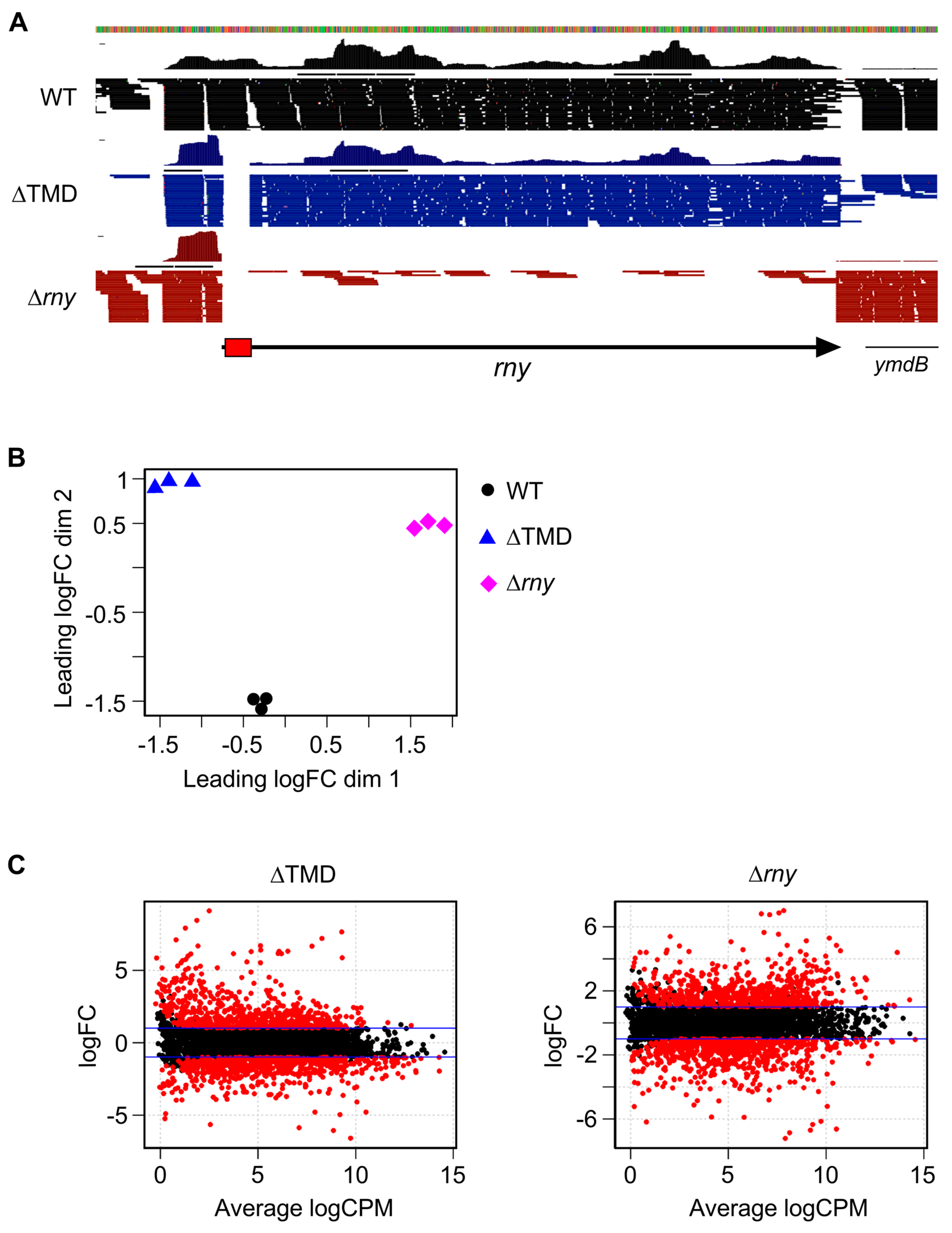
2.3. Modulation of Specific Transcript Levels by Cytoplasmic RNase Y
2.3.1. RNA Substrates that Require Membrane Localization of RNase Y
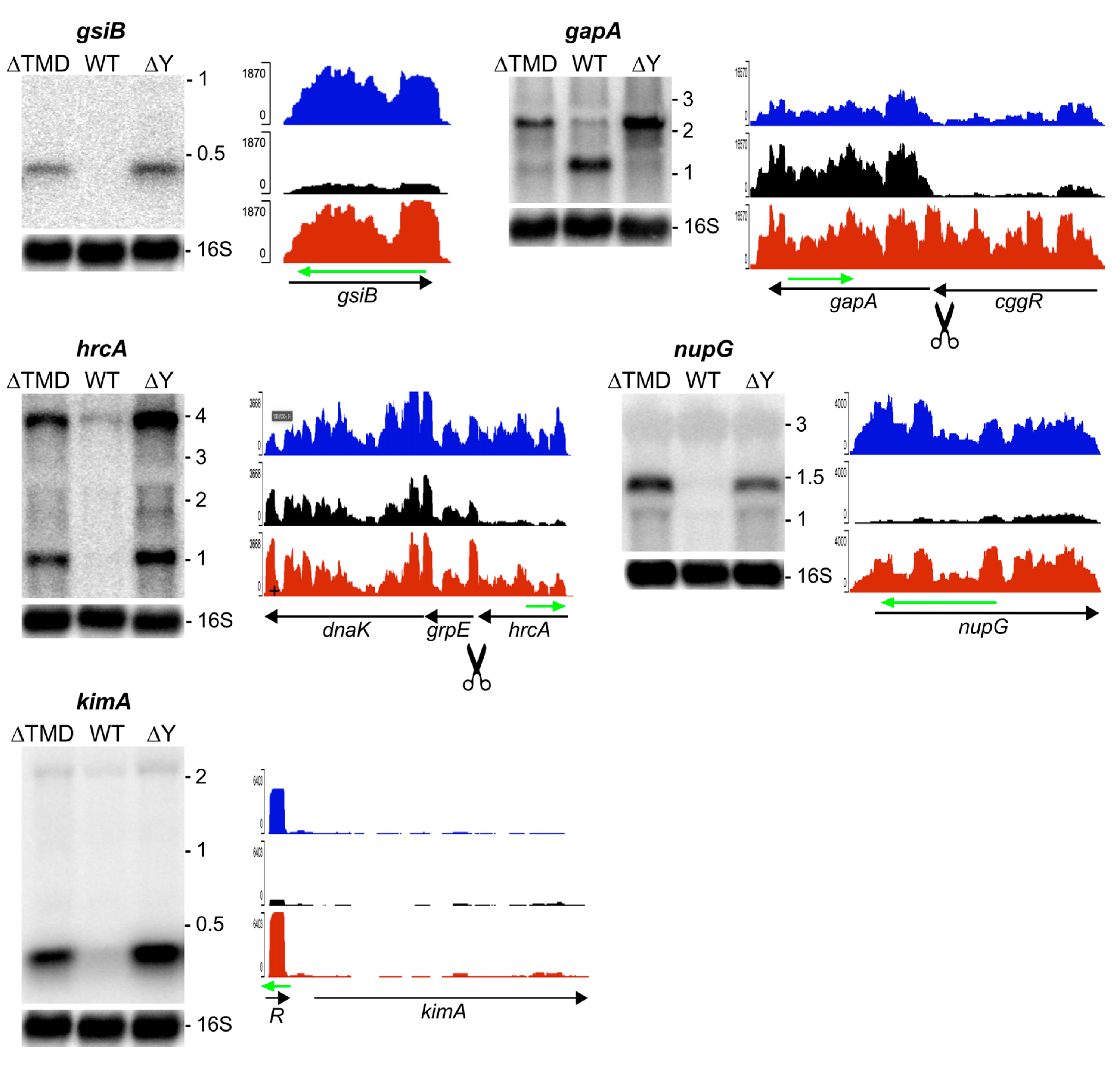
2.3.2. RNA Substrates Not Sensitive to RNase Y Localization
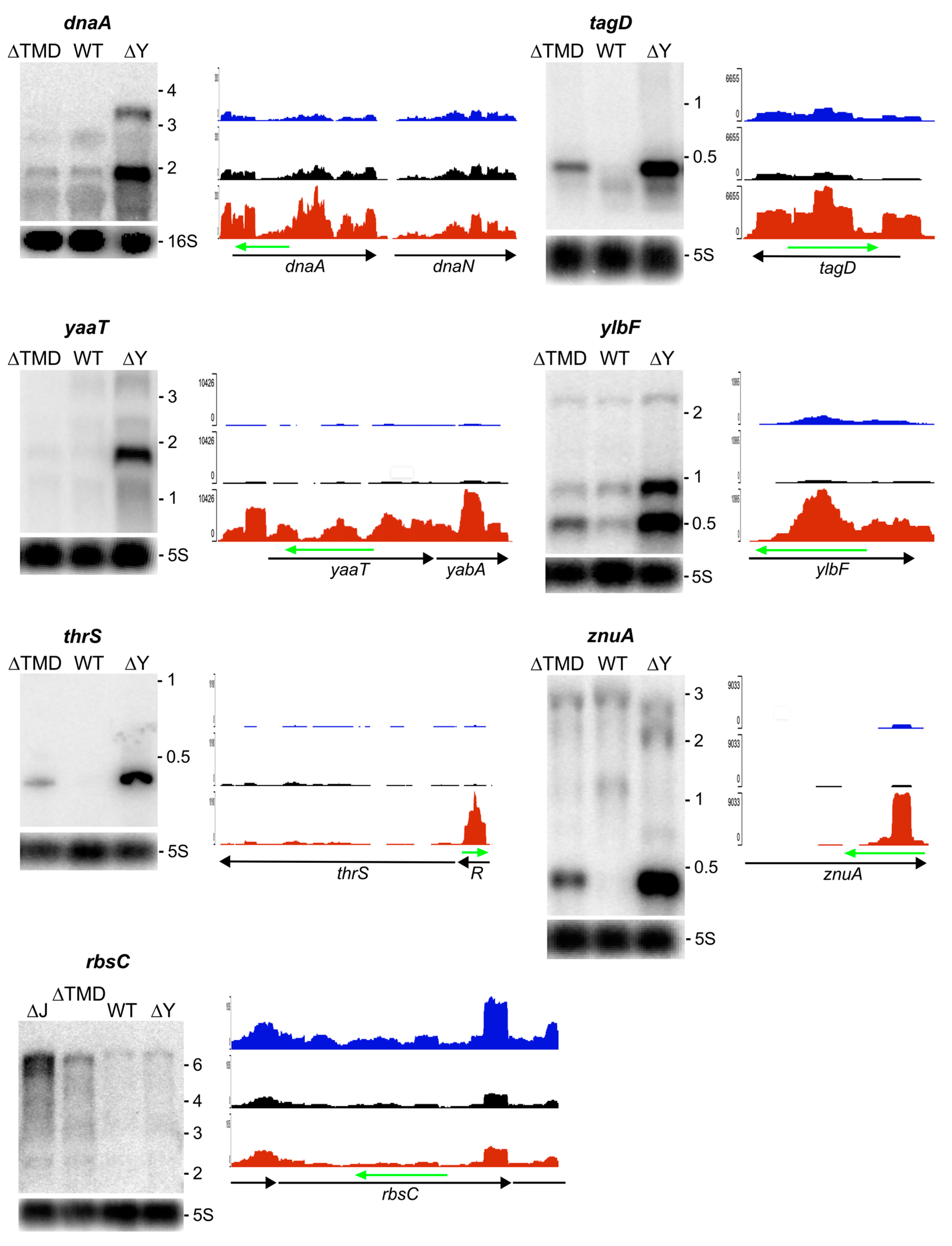
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Bacterial Strains and Growth Conditions
| B. subtilis Strain | Relevant Genotype | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| SSB1002 | Wild type strain | Lab stock |
| SSB507 | ∆amyE::pDR160T | This work |
| SSB508 | ∆rny::cat, ∆amyE::pDR160T | This work |
| SSB574 | ∆rny::cat, ∆amyE::pHMD40 | This work |
| Oligonucleotide | Sequence 5’-3’ |
|---|---|
| HP1696 | GACTCGAGCCGTAGAGTATGCAAAATAAAGGATCCTATC |
| HP1827 | AATGATTAATTAACAACAACCAAGTTCATAGCAAGAGGAGGTGAAAGTATGCGTAAAACCATTGCCGAAGCG |
4.2. Plasmid Constructs
4.3. Epi-Fluorescence Microscopy
4.4. Northern Blot
4.5. Western Blot
4.6. Transcriptome Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Laalami, S.; Zig, L.; Putzer, H. Initiation of mRNA decay in bacteria. Cellular and molecular life sciences: CMLS 2014, 71, 1799-1828. [CrossRef]
- Shahbabian, K.; Jamalli, A.; Zig, L.; Putzer, H. RNase Y, a novel endoribonuclease, initiates riboswitch turnover in Bacillus subtilis. EMBO J 2009, 28, 3523-3533. [CrossRef]
- Lehnik-Habrink, M.; Schaffer, M.; Mader, U.; Diethmaier, C.; Herzberg, C.; Stulke, J. RNA processing in Bacillus subtilis: identification of targets of the essential RNase Y. Mol Microbiol 2011, 81, 1459-1473. [CrossRef]
- Durand, S.; Gilet, L.; Bessieres, P.; Nicolas, P.; Condon, C. Three essential ribonucleases-RNase Y, J1, and III-control the abundance of a majority of Bacillus subtilis mRNAs. PLoS Genet 2012, 8, e1002520. [CrossRef]
- Laalami, S.; Bessieres, P.; Rocca, A.; Zig, L.; Nicolas, P.; Putzer, H. Bacillus subtilis RNase Y activity in vivo analysed by tiling microarrays. PLoS One 2013, 8, e54062. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Itzek, A.; Malke, H.; Ferretti, J.J.; Kreth, J. Multiple Roles of RNase Y in Streptococcus pyogenes mRNA Processing and Degradation. J Bacteriol 2013, 195, 2585-2594. [CrossRef]
- Khemici, V.; Prados, J.; Linder, P.; Redder, P. Decay-Initiating Endoribonucleolytic Cleavage by RNase Y Is Kept under Tight Control via Sequence Preference and Sub-cellular Localisation. PLoS Genet 2015, 11, e1005577. [CrossRef]
- Marincola, G.; Wolz, C. Downstream element determines RNase Y cleavage of the saePQRS operon in Staphylococcus aureus. Nucleic Acids Res 2017, 45, 5980-5994. [CrossRef]
- DeLoughery, A.; Lalanne, J.B.; Losick, R.; Li, G.W. Maturation of polycistronic mRNAs by the endoribonuclease RNase Y and its associated Y-complex in Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2018, 115, E5585-E5594. [CrossRef]
- Broglia, L.; Lecrivain, A.L.; Renault, T.T.; Hahnke, K.; Ahmed-Begrich, R.; Le Rhun, A.; Charpentier, E. An RNA-seq based comparative approach reveals the transcriptome-wide interplay between 3'-to-5' exoRNases and RNase Y. Nature communications 2020, 11, 1587. [CrossRef]
- Taggart, J.C.; Lalanne, J.-B.; Durand, S.; Braun, F.; Condon, C.; Li, G.-W. A high-resolution view of RNA endonuclease cleavage in <em>Bacillus subtilis</em>. bioRxiv 2023, 2023.2003.2012.532304. [CrossRef]
- Commichau, F.M.; Rothe, F.M.; Herzberg, C.; Wagner, E.; Hellwig, D.; Lehnik-Habrink, M.; Hammer, E.; Völker, U.; Stülke, J. Novel activities of glycolytic enzymes in Bacillus subtilis: interactions with essential proteins involved in mRNA processing. Mol Cell Proteomics 2009, 8, 1350-1360. [CrossRef]
- Lehnik-Habrink, M.; Pfortner, H.; Rempeters, L.; Pietack, N.; Herzberg, C.; Stülke, J. The RNA degradosome in Bacillus subtilis: identification of CshA as the major RNA helicase in the multiprotein complex. Mol Microbiol 2010, 77, 958-971. [CrossRef]
- Haq, I.U.; Muller, P.; Brantl, S. A comprehensive study of the interactions in the B. subtilis degradosome with special emphasis on the role of the small proteins SR1P and SR7P. Mol Microbiol 2024, 121, 40-52. [CrossRef]
- Newman, J.A.; Hewitt, L.; Rodrigues, C.; Solovyova, A.S.; Harwood, C.R.; Lewis, R.J. Dissection of the network of interactions that links RNA processing with glycolysis in the Bacillus subtilis degradosome. J Mol Biol 2012, 416, 121-136. [CrossRef]
- Cascante-Estepa, N.; Gunka, K.; Stulke, J. Localization of Components of the RNA-Degrading Machine in Bacillus subtilis. Frontiers in microbiology 2016, 7, 1492. [CrossRef]
- Redder, P. Molecular and genetic interactions of the RNA degradation machineries in Firmicute bacteria. Wiley interdisciplinary reviews. RNA 2018, 9. [CrossRef]
- DeLoughery, A.; Dengler, V.; Chai, Y.; Losick, R. Biofilm formation by Bacillus subtilis requires an endoribonuclease-containing multisubunit complex that controls mRNA levels for the matrix gene repressor SinR. Mol Microbiol 2016, 99, 425-437. [CrossRef]
- Adusei-Danso, F.; Khaja, F.T.; DeSantis, M.; Jeffrey, P.D.; Dubnau, E.; Demeler, B.; Neiditch, M.B.; Dubnau, D. Structure-Function Studies of the Bacillus subtilis Ric Proteins Identify the Fe-S Cluster-Ligating Residues and Their Roles in Development and RNA Processing. mBio 2019, 10. [CrossRef]
- Carabetta, V.J.; Tanner, A.W.; Greco, T.M.; Defrancesco, M.; Cristea, I.M.; Dubnau, D. A complex of YlbF, YmcA and YaaT regulates sporulation, competence and biofilm formation by accelerating the phosphorylation of Spo0A. Mol Microbiol 2013, 88, 283-300. [CrossRef]
- Hamouche, L.; Billaudeau, C.; Rocca, A.; Chastanet, A.; Ngo, S.; Laalami, S.; Putzer, H. Dynamic Membrane Localization of RNase Y in Bacillus subtilis. mBio 2020, 11. [CrossRef]
- Hunt, A.; Rawlins, J.P.; Thomaides, H.B.; Errington, J. Functional analysis of 11 putative essential genes in Bacillus subtilis. Microbiology 2006, 152, 2895-2907.
- Khemici, V.; Poljak, L.; Luisi, B.F.; Carpousis, A.J. The RNase E of Escherichia coli is a membrane-binding protein. Mol Microbiol 2008, 70, 799-813, doi:MMI6454 [pii] 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2008.06454.x.
- Strahl, H.; Turlan, C.; Khalid, S.; Bond, P.J.; Kebalo, J.M.; Peyron, P.; Poljak, L.; Bouvier, M.; Hamoen, L.; Luisi, B.F.; et al. Membrane recognition and dynamics of the RNA degradosome. PLoS Genet 2015, 11, e1004961. [CrossRef]
- Lewis, P.J.; Thaker, S.D.; Errington, J. Compartmentalization of transcription and translation in Bacillus subtilis. EMBO J 2000, 19, 710-718. [CrossRef]
- Mascarenhas, J.; Weber, M.H.; Graumann, P.L. Specific polar localization of ribosomes in Bacillus subtilis depends on active transcription. EMBO Rep 2001, 2, 685-689. [CrossRef]
- Hadjeras, L.; Poljak, L.; Bouvier, M.; Morin-Ogier, Q.; Canal, I.; Cocaign-Bousquet, M.; Girbal, L.; Carpousis, A.J. Detachment of the RNA degradosome from the inner membrane of Escherichia coli results in a global slowdown of mRNA degradation, proteolysis of RNase E and increased turnover of ribosome-free transcripts. Mol Microbiol 2019, 111, 1715-1731. [CrossRef]
- Hosoya, S.; Asai, K.; Ogasawara, N.; Takeuchi, M.; Sato, T. Mutation in yaaT leads to significant inhibition of phosphorelay during sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol 2002, 184, 5545-5553.
- Laalami, S.; Cavaiuolo, M.; Roque, S.; Chagneau, C.; Putzer, H. Escherichia coli RNase E can efficiently replace RNase Y in Bacillus subtilis. Nucleic Acids Res 2021, 49, 4643-4654. [CrossRef]
- Aravind, L.; Koonin, E.V. The HD domain defines a new superfamily of metal-dependent phosphohydrolases. Trends Biochem Sci 1998, 23, 469-472.
- Lehnik-Habrink, M.; Newman, J.; Rothe, F.M.; Solovyova, A.S.; Rodrigues, C.; Herzberg, C.; Commichau, F.M.; Lewis, R.J.; Stulke, J. RNase Y in Bacillus subtilis: a Natively disordered protein that is the functional equivalent of RNase E from Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 2011, 193, 5431-5441. [CrossRef]
- Hardouin, P.; Velours, C.; Bou-Nader, C.; Assrir, N.; Laalami, S.; Putzer, H.; Durand, D.; Golinelli-Pimpaneau, B. Dissociation of the Dimer of the Intrinsically Disordered Domain of RNase Y upon Antibody Binding. Biophys J 2018, 115, 2102-2113. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Stulke, J. SubtiWiki in 2018: from genes and proteins to functional network annotation of the model organism Bacillus subtilis. Nucleic Acids Res 2018, 46, D743-D748. [CrossRef]
- Maul, B.; Volker, U.; Riethdorf, S.; Engelmann, S.; Hecker, M. sigma B-dependent regulation of gsiB in response to multiple stimuli in Bacillus subtilis. Molecular & general genetics: MGG 1995, 248, 114-120. [CrossRef]
- Homuth, G.; Mogk, A.; Schumann, W. Post-transcriptional regulation of the Bacillus subtilis dnaK operon. Mol Microbiol 1999, 32, 1183-1197.
- Mulhbacher, J.; Lafontaine, D.A. Ligand recognition determinants of guanine riboswitches. Nucleic Acids Res 2007, 35, 5568-5580. [CrossRef]
- Nelson, J.W.; Sudarsan, N.; Furukawa, K.; Weinberg, Z.; Wang, J.X.; Breaker, R.R. Riboswitches in eubacteria sense the second messenger c-di-AMP. Nature chemical biology 2013, 9, 834-839. [CrossRef]
- Gundlach, J.; Herzberg, C.; Kaever, V.; Gunka, K.; Hoffmann, T.; Weiss, M.; Gibhardt, J.; Thurmer, A.; Hertel, D.; Daniel, R.; et al. Control of potassium homeostasis is an essential function of the second messenger cyclic di-AMP in Bacillus subtilis. Sci Signal 2017, 10. [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.H.; Helmann, J.D. Molecular logic of the Zur-regulated zinc deprivation response in Bacillus subtilis. Nature communications 2016, 7, 12612. [CrossRef]
- Even, S.; Pellegrini, O.; Zig, L.; Labas, V.; Vinh, J.; Brechemmier-Baey, D.; Putzer, H. Ribonucleases J1 and J2: two novel endoribonucleases in B. subtilis with functional homology to E. coli RNase E. Nucleic Acids Res 2005, 33, 2141-2152.
- Woodson, K.; Devine, K.M. Analysis of a ribose transport operon from Bacillus subtilis. Microbiology (Reading) 1994, 140 (Pt 8), 1829-1838. [CrossRef]
- Mora, L.; Ngo, S.; Laalami, S.; Putzer, H. In Vitro Study of the Major Bacillus subtilis Ribonucleases Y and J. Methods Enzymol 2018, 612, 343-359. [CrossRef]
- Mogk, A.; Homuth, G.; Scholz, C.; Kim, L.; Schmid, F.X.; Schumann, W. The GroE chaperonin machine is a major modulator of the CIRCE heat shock regulon of Bacillus subtilis. Embo J 1997, 16, 4579-4590.
- Ogura, Y.; Imai, Y.; Ogasawara, N.; Moriya, S. Autoregulation of the dnaA-dnaN operon and effects of DnaA protein levels on replication initiation in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol 2001, 183, 3833-3841. [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.; Santa Maria, J.P., Jr.; Walker, S. Wall teichoic acids of gram-positive bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol 2013, 67, 313-336. [CrossRef]
- Sattler, L.; Graumann, P.L. Real-Time Messenger RNA Dynamics in Bacillus subtilis. Frontiers in microbiology 2021, 12, 760857. [CrossRef]
- Gorke, B.; Rak, B. Efficient transcriptional antitermination from the Escherichia coli cytoplasmic membrane. J Mol Biol 2001, 308, 131-145. [CrossRef]
- Al-Husini, N.; Tomares, D.T.; Bitar, O.; Childers, W.S.; Schrader, J.M. alpha-Proteobacterial RNA Degradosomes Assemble Liquid-Liquid Phase-Separated RNP Bodies. Mol Cell 2018, 71, 1027-1039 e1014. [CrossRef]
- Laalami, S.; Putzer, H. mRNA degradation and maturation in prokaryotes: the global players. Biomolecular Concepts 2011, 2, 491-506. [CrossRef]
- Mäder, U.; Zig, L.; Kretschmer, J.; Homuth, G.; Putzer, H. mRNA processing by RNases J1 and J2 affects Bacillus subtilis gene expression on a global scale. Mol Microbiol 2008, 70, 183-196. [CrossRef]
- Yanisch-Perron, C.; Vieira, J.; Messing, J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene 1985, 33, 103-119.
- Horinouchi, S.; Weisblum, B. Nucleotide sequence and functional map of pC194, a plasmid that specifies inducible chloramphenicol resistance. J Bacteriol 1982, 150, 815-825.
- Arnaud, M.; Chastanet, A.; Debarbouille, M. New vector for efficient allelic replacement in naturally nontransformable, low-GC-content, gram-positive bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 2004, 70, 6887-6891. [CrossRef]
- Rudner, D.Z.; Breger, K.S.; Rio, D.C. Molecular genetic analysis of the heterodimeric splicing factor U2AF: the RS domain on either the large or small Drosophila subunit is dispensable in vivo. Genes Dev 1998, 12, 1010-1021.
- Korobeinikova, A.; Laalami, S.; Berthy, C.; Putzer, H. RNase Y Autoregulates Its Synthesis in Bacillus subtilis. Microorganisms 2023, 11. [CrossRef]
- Cavaiuolo, M.; Chagneau, C.; Laalami, S.; Putzer, H. Impact of RNase E and RNase J on Global mRNA Metabolism in the Cyanobacterium Synechocystis PCC6803. Frontiers in microbiology 2020, 11, 1055. [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Durbin, R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1754-1760. [CrossRef]
- Quinlan, A.R.; Hall, I.M. BEDTools: a flexible suite of utilities for comparing genomic features. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 841-842. [CrossRef]
- Robinson, J.T.; Thorvaldsdottir, H.; Winckler, W.; Guttman, M.; Lander, E.S.; Getz, G.; Mesirov, J.P. Integrative genomics viewer. Nat Biotechnol 2011, 29, 24-26. [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.D.; McCarthy, D.J.; Smyth, G.K. edgeR: a Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 139-140. [CrossRef]
| Strain, Relevant Genotype | No. Upregulated Transcripts |
No. Downregulated Transcripts |
|---|---|---|
| SSB574, ∆TMD-RNase Y | 665 | 652 |
| SSB508, ∆rny | 712 | 751 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





