1. Introduction
In the era of information explosion, users are confronted with an overwhelming number of choices. recommendation systems alleviate this issue by providing personalized recommendations [
1,
2,
3], helping users quickly find content or products of interest, thus reducing information overload and enhancing user satisfaction and experience. For e-commerce and content platforms, recommendation systems can efficiently guide users to content they are more likely to purchase or consume, significantly boosting conversion rates and sales, thereby directly increasing economic benefits for businesses. Collaborative filtering algorithms, widely employed in recommendation systems, leverage users’ historical behavior data to provide personalized recommendations for each user, improving the relevance of recommendations and user satisfaction [
4,
5,
6,
7]. However, real-world data often presents challenges such as data sparse and cold start, which greatly limit the performance of collaborative filtering-based recommendation algorithms [
8,
9,
10]. To address the issue of sparse data, an effective approach is to integrate auxiliary information into the collaborative filtering recommendation model, and Knowledge graph-based recommendation is a typical method in this regard [
11,
12,
13,
14,
15]. Knowledge graphs contain rich entity relationship information about items, enabling the construction of comprehensive item features and helping to uncover hidden relationships between items, thereby improving the accuracy of recommendations.
There already exists much research effort for sufficiently utilizing both collaborative filtering (CF) information and knowledge graph (KG) information. Earlier studies [
11,
16,
17] focus on independently learning from the two graphs, which mainly represent the triplet information from the item knowledge graph as embedding and use as contextual information for enhancing recommendations in the CF graph. These methods typically employ knowledge graph embedding (KGE) models (such as TransE [
18], TransH [
19]) to learn representations of entities in the KG. However, these approaches have limitations in extracting meaningful information from entities, and they can only extract information from a single graph structure, failing to integrate information from the CF graph. Therefore, subsequent works [
20,
21,
22] have increasingly focused on how to extract more relevant information for recommendations from the KG. One productive approach is to represent the interactions with multi-hop paths from users to items, which is hard to optimize because of the manually designed meta-paths. Recently, graph neural networks (GNNs) have demonstrated strong capabilities in representing structural knowledge in graphs [
12,
13,
23,
24]. They are widely used in recommendation methods based on knowledge graphs and have achieved excellent performance.
Although knowledge graph-based recommendation has achieved promising results, it still faces the following issues:
Insufficient Mining of the Two Graphs’ Own Information: Existing methods often use the interaction data between users and items as supervision signals to derive user and item representation vectors from the entities in KG for learning and training. However, these methods do not fully exploit the information inherent in the two graphs, especially the strong and effective features of user and item IDs in the recommendation domain. This oversight can lead to the loss of valuable information, adversely affecting the recommendation performance.
Unbalanced Information Between the Two Graphs: Unlike the sparse behavioral data between users and items, the connections in knowledge graphs are dense, containing a wealth of information. The difference in the amount of knowledge contained in the two graphs can cause issues in the subsequent utilization of the information. The supervision signals in CF are directly related to the predictions, whereas the abundant redundant information in the KG can weaken these CF supervision signals. If the dominance of CF information is not maintained, it can lead to a decline in recommendation accuracy.
Inspired by the success of contrastive learning (CL) methods in sparse data scenarios, this paper proposes a Dual-graph Contrastive learning recommendation model based on the Knowledge Graph (KGDC) to address the aforementioned issues. To fully exploit the effective information from each of the two graphs, KGDC utilizes information propagation and aggregation techniques from GNNs to learn the vector representations of IDs in the CF graph and the entities and relations in the KG, respectively. To integrate information from both graphs, the proposed method leverages the concept of contrastive learning to fuse information from two aspects. The first method treats the items interacted with by the same user in the CF graph as pseudo-positive item sets, using them as positive supervision signals in the KG, while using other non-similar, non-connected items as negative samples to further learn and train the representation vectors of entities in the KG. The second method considers the corresponding items and entities in the CF graph and KG as similar samples, with other non-corresponding samples as negative samples, to further enhance the information fusion and transfer between the two graphs. Finally, we employ a multi-objective training mode, where the vector representations of different components are used to calculate the loss according to different objectives, and the losses are summed with different weights to optimize and train the model parameters. We conducted extensive experiments on two public datasets, and the results show that our proposed method outperforms some state-of-the-art methods.
We summarize the contributions of this paper as follows:
We identify and analyze the shortcomings and challenges of existing graph-based recommendation methods, such as their inability to simultaneously mine each graph’s own information and effectively integrate information between two imbalanced graphs.
We propose a method named KGDC, which leverages contrastive learning and multi-objective learning to fully exploit the information within each graph while effectively integrating information between the graphs.
We conduct extensive experiments on public datasets, further validating the superior performance of the proposed method.
2. Related Work
The study in this paper is mainly relevant to two parts of works: knowledge graph-based recommendation and contrastive learning.
2.1. Knowledge Graph-Based Recommendation
Research into Knowledge graph-based recommendation systems has explored various methodologies, focusing on leveraging the structure and semantics of knowledge graphs to enhance recommendation performance. This part reviews notable contributions from two aspects: non-GNNs-based methods and GNNs-based methods.
2.1.1. Non-GNNs-Based Methods
Early work on integrating knowledge graphs with recommendation systems primarily focused on leveraging the rich semantic relationships inherent in knowledge graphs to improve recommendation accuracy [
11,
17,
31]. Zhang [
17] introduces the Collaborative Knowledge Base Embedding (CKE) framework, which combines collaborative filtering techniques with knowledge graph embeddings to enhance recommendation performance by incorporating additional contextual information. Similarly, KTUP [
31]considers both explicit user-item interactions and implicit knowledge graph relationships to improve the recommendation process with the TransH [
19] method. Wang [
11] proposes the RippleNet model, which propagates user preferences over a knowledge graph to uncover multi-hop relational paths, thereby enriching the user’s preference representation.
Another significant contribution in this area is the use of path-based methods. These approaches often employ random walk techniques or path ranking algorithms to identify relevant connections between entities. PER [
32] extracts meta-path or meta-graph latent features from the knowledge graph to exploit the connectivity between users and items along different types of relation paths or graphs. KPRN [
22]goes beyond predefined meta-paths by dynamically extracting paths that are relevant to user-item interactions, thereby improving the ability to capture complex relationships.
Embedding-based methods and path-based methods are both useful and effective. But embedding-based methods may not fully capture the nuances of user preferences in recommendation scenarios where user-item interactions are sparse or when personalized recommendation accuracy is critical. Path-based methods heavily rely on the quality of path extraction and the ability to capture relevant semantic relationships.
2.1.2. GNNs-Based Methods
GNNs-based methods in knowledge graph-based recommendation systems have evolved significantly, addressing challenges related to sparse interactions, unbalanced graph utilization, and knowledge extraction. KGCN [
12] focuses on leveraging user preferences to aggregate neighborhood information of items in KG. Similarly, KGAT [
13] uses GNNs to recursively aggregate information across the unified heterogeneous graph, emphasizing the importance of both collaborative filtering signals and knowledge signals. CKAN [
15] highlights the significance of collaborative filtering signals in addition to knowledge signals. In KGIN [
24], GNNs are applied on the user-intent-item-entity graph to capture nuanced user preferences. CG-KGR [
25] uses pre-trained collaborative signals to guide the aggregation process on the knowledge graph, focusing on extracting sufficient knowledge for recommendations. KGIC [
26] employs GNNs to capture hierarchical and structural dependencies within the KG.
Most of GNNs-based methods operate under supervised learning paradigms, which can be challenging when dealing with sparse user-item interactions. This limitation affects recommendation accuracy, particularly in scenarios with limited data. Moreover, the connections in knowledge graphs are dense, containing a wealth of information. These methods often overly emphasize the knowledge graph, potentially neglecting the crucial collaborative filtering signals inherent in user-item interactions.
2.2. Contrastive Learning
Contrastive learning, as an effective unsupervised learning method, has been widely studied and applied in recent years across domains such as image and natural language processing. Its core idea is to compare positive examples (similar samples) and negative examples (dissimilar samples), aiming to bring similar samples closer together in the representation space while pushing dissimilar samples further apart. This approach helps alleviate issues related to insufficient learning caused by sparse data. SimCLR [
33] utilizes data augmentation techniques to generate multiple views of the same instance and employs a contrastive loss function to maximize the similarity between different views of the same instance while minimizing the similarity between different instances.
In recent research, several approaches have applied contrastive learning to enhance knowledge graph (KG)-based recommendation systems. SGL introduces three operators to generate augmented views and employs a multi-task strategy, jointly optimizing contrastive loss and recommendation loss to improve the robustness of representation learning in KG-based recommendation systems. SEPT [
28] proposes a socially-aware contrastive learning framework, and mines additional social information of users to enrich the learning process, aiming to better capture user preferences and interactions in recommendation tasks. CKER [
29] integrates a contrastive learning module to enhance the sharing of user preferences, and derives additional supervision signals to improve the collaborative filtering aspect of KG-based recommendation systems. KGCL [
30] introduces a knowledge-guided contrastive learning paradigm to derive more robust node representations, enhancing the quality of recommendations. KGIC [
26] applies contrastive learning to learn embeddings or representations that distinguish relevant (positive) interactions from irrelevant (negative) ones based on the knowledge graph. KACL [
27] utilizes contrastive learning to discern meaningful patterns and relationships within the knowledge graph.
Despite these advancements, recent works in KG-based recommendation still face significant challenges such as interaction domination and knowledge overload. These refer to issues where the sheer volume of interactions or the complexity of knowledge representation within the KG can overwhelm the recommendation model, leading to suboptimal performance.
3. Problem Formulation
In this section, we first introduce the structural data: the collaborative filtering graph of user-item interactions and the knowledge graph, and then formulate the problem statement of knowledge graph-based recommendation.
Collaborative Filtering Graph: To maintain consistency with the settings in GNNs-based recommendation systems, we construct a bipartite graph based on the historical interactions between users and items, such as the consumption, viewing, clicking. In the construction of this graph, there are connections only between item and user nodes, with edges existing between nodes of users and items that have had historical interactions, where and denote the user and item involved in the interaction, and U and V are the sets of users and items respectively. is an indicator whether there is a connection between user u and item v based on the historical interactions. indicates an interaction, while indicates no interaction.
Knowledge Graph: In knowledge graph-based recommendation methods, in addition to the user-item interaction data, there is also a knowledge graph that provides relationships between items. In the knowledge graph, the connections are denoted as a set of triplets , and each triplet describes a connection from head entity to tail entity with the relationship . There, it usually denotes I and R as the sets of entities and relations in the knowledge graph, and I includes items V and non-item entities .
KG-based Recommendation: Based on the user-item interaction graph and item knowledge graph , the target of KG-based recommendation is to learn a function that predicts the probability how likely a user u would interact with an item v.
4. Methodology
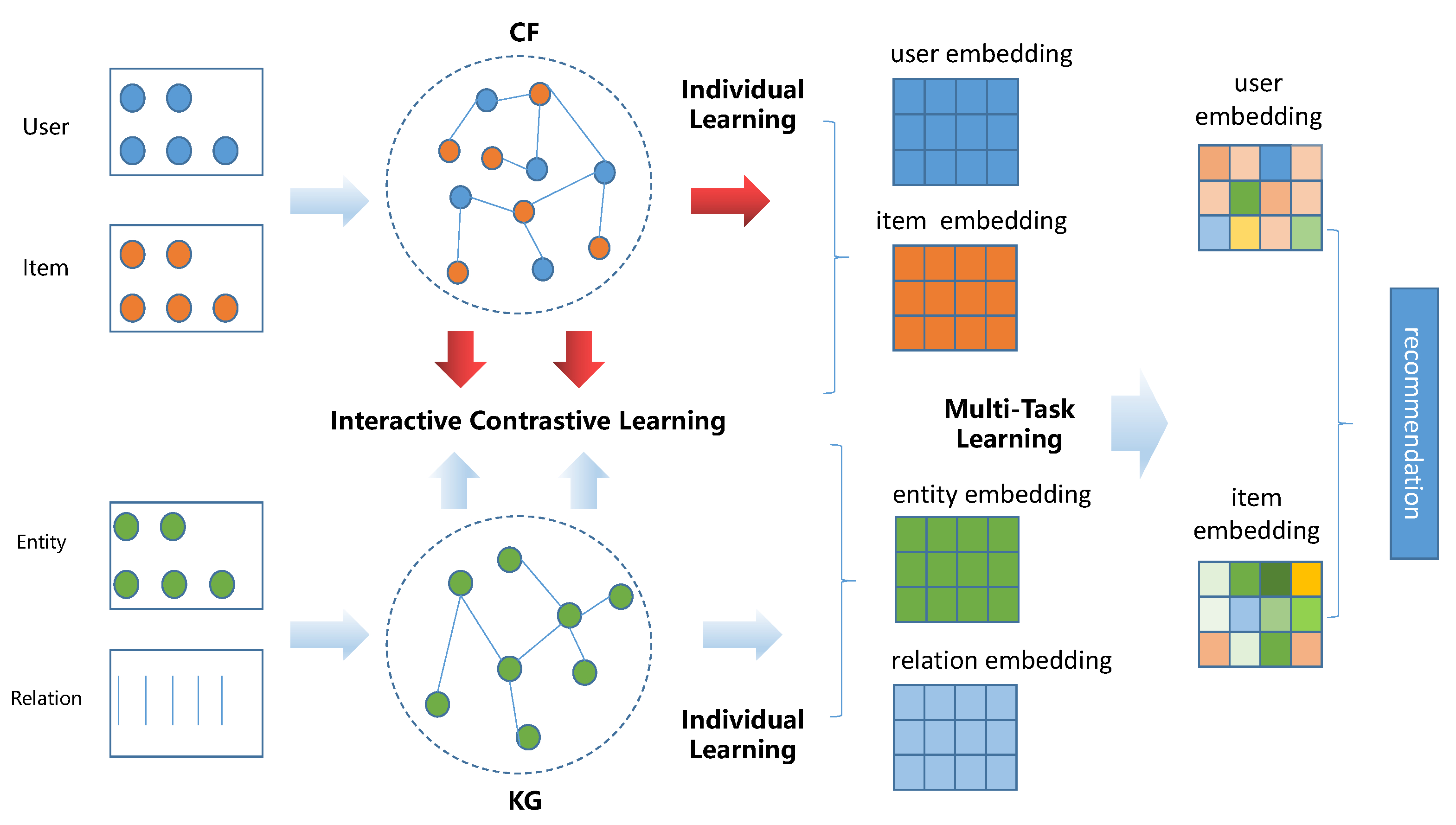
In this section, we present our proposed KGDC recommendation method. The purpose of the proposed KGDC is to fully exploit the individual information and interactive information from the CF graph and the KG graph.
Figure 1 presents the framework of KGDC, which consists of three parts: Individual Graph Constructing and Encoding, Interactive Graph Constructing and Encoding, Multi-task Learning. It performs contrastive learning in both individual graph and interactive graph learning to extract more effective information. Then we introduce the details of the three components.
4.1. Individual Graph Constructing and Encoding
Different from most existing methods, KGDC learns node and entity embedding from KG and CF respectively with GNNs methods. In the KG graph, KGDC uses contrastive learning to overcome the problem of missing explicit labels. In the CF graph, KGDC uses propagation and aggregation methods for learning ID embedding of users and items.
4.1.1. Graph Constructing and Encoding in KG
In the individual graph constructing and encoding in KG, only triplets are valid here. Considering that there are no explicit signals, KGDC utilizes contrastive learning to construct samples for information aggregation, loss calculation and parameters optimization.
In terms of sample construction, we first determine the set of entities, denoted as E, to be trained based on the specific scenario. For example, in the pre-training process, the entities to be trained are all the entities in the KG, , with the goal of fully training each entity in the graph. In the subsequent model fine-tuning process, the entities to be trained are those involved in user-item interactions , with the aim of performing better for the prediction target. For any entity , the positive samples of e are sampled from the connected tails and relations from , denoted as . Then the negative samples are sampled from all entities that are not connected in , denoted as . Combining the positive and negative samples, we can get the samples for KG, denoted as .
With the constructed samples, KGDC uses the attentive mechanism in GNNs to propagate and aggregate information in KG. Also for any entity
, we first compute the representations of positive samples by linear summation,
where
is the representation of entity
j, and
denotes the attention score between entity
and entity
. And
is calculated as follows:
Then the positive representation of entity
i is calculated as follows:
Similarly, the negative representation of entity
i is calculated as follows:
With these representations of entity
i, we calculate the similarity score between positive samples and sample
i through the inner product,
. Similarly, the similarity score between negative samples and sample
i is denoted as
. Then, we adopt a pairwise BPR loss to encourage the positive samples to be higher than the negative samples:
where
is the Sigmoid function.
4.1.2. Graph Constructing and Encoding in CF
In the individual graph constructing and encoding in CF, KGDC learns the embedding of users and items by user-item interactions. CF is a heterogeneous graph composed of users and items, and these nodes have no attribute features. Therefore, KGDC utilizes neighbor sampling and embedding aggregation, which are common in GNNs, to achieve information propagation.
During representation learning, the main idea is to update the vector representation of each vertex based on its own representation and that of its neighbors using some aggregation function. This process is repeated for all vertices for T iterations to obtain the representation of each node. Before representation learning, the neighbors of each vertex in CF are stored globally, denoted as , where the nodes s do not distinguish between users and items. Assuming it is the t-th iteration, for any node , KGDC directly retrieves its neighbor set from global storage, denoted as . Different from GCN, we randomly select a fixed number K of neighbors from , denoted as . If the number of neighbors is less than K, sampling with replacement is used to reach the desired number; if greater than K, sampling without replacement is used.
With the sampled neighbors of the node
in the
t-th iteration, we can obtain the embedding set of these nodes using the equation as follows:
where
means the aggregation method at the
-th iteration, such as mean pooling, sum pooling, max pooling, RNN, transformer, and other methods. Getting the presentation embedding of the neighbors, we perform a linear transformation and enhance the representation of the original node
by using a custom activation function. And the vector representation of vertex
at the
-th iteration is calculated as:
where
and
are the trainable weights and the trainable bis at the
-th iteration.
After
T iterations, the node representation
is L2-normalized to get the final representation vector:
With the nodes’ embedding in CF, we compute the Individual loss of CF as follows:
where
is the predicted score of node
and node
,
is namely the edges in CF and the value is the same as
.
4.2. Interactive Graph Constructing and Encoding
KGDC also leverages the concept of contrastive learning to learn the interactive information from the two graphs. To ensure the dominant position of the CF graph, KGDC takes the signals in CF to guide the learning of entities in the KG. To further enhance the information fusion between the two graphs, KGDC uses the entities corresponding to the items in both graphs as similar samples for alignment.
4.2.1. Graph Encoding in KG with signals of CF
In this section, KGDC extracts the signals of user/item from the user-item interactions in graph CF. And the signals are first-order relationships in CF. For any user
u in CF, all of the items that interacted with
u are collected. Therefore, the signals from graph CF are denoted as:
With the signals above, the initial entities learned in the KG are those that correspond to the items in the node set
, which are denoted as:
In the collaborative filtering recommendation, each user has interests and preferences, and there are commonalities in preferences among different users, which means that the items that interact with the same user tend to be more similar. Therefore, for any sample in CF
and
, the items in
are more similar with
than others. Furthermore, KGDC takes the items randomly selected from non-connected items across the entire dataset as negatives, denoted as
. Taking the positive samples
and negative samples
as the initial entity sets of KG, KGDC constructs the embedding through a natural propagation in the KG. The propagation is the same as in
Section 4.1.2 and aggregation is similar to
Section 4.1, which randomly selects a fixed number of connected
as neighbors and aggregates the information using attentive method as in Equation (
1). Supposing at the
th layer, the embedding of any entity
e (including the positive samples and negative samples) defined above is as follows:
where
is the embedding in KG.
Similarly, after
L iterations, we can get the entity presentation, denoted as
. Then we utilize the triplet function which is usually used in contrastive learning to compute the loss. The distance score between two entities is caculated through the inner product. Therefore, the loss function is as follows:
where
m is the margin.
4.2.2. Align Encoding with CF and KG
To further enhance the interaction between the two graphs, we propose to map the item in CF and the corresponding entity in KG into the same space. For better understanding, we use to represent the item embedding in CF, and use to represent the entity embedding in KG, where are the same item. Based on the contrastive learning method, we take the corresponding items in CF and KG are similar pairs, and we randomly select other items in KG as the negative samples. Therefore, for any item v in CF, the positive sample is the corresponding item e in KG, and the negative sample is the randomly selected item j from batch-wise. With the batch-wise negative sampling strategy, we do not need to sample globally, addressing computational power constraints and reducing time consumption.
Before the alignment between the two graphs, KGDC utilizes two MLPs to map them into the same space
to achieve the information shared across interaction and knowledge views. Thus, the positive pair is denoted as
, and the negative pairs are denoted as
and
. With these samples, we adopt the InfoNCE function to calculate the loss, which is commonly used in contrastive learning. InfoNCE loss aims to encourage the consistency between the representations of its different views, while enforcing the divergence of negative pairs. The calculation formula is as follows:
where
measures the cosine similarity of two vectors, and
V (namely the items in CF) is the set of negative samples.
4.3. Multi-Task Learning
Considering that some of the losses obtained above are not directly related to the target, we take a portion of the representations to reconstruct the user and item embedding to ensure the update direct is more directly to the target. For any data
in the interaction dataset, the representations of individual CF in
Section 4.1.2 are
and
, and the representations of interactive learning in
Section 4.2.1 are
and
. Specifically, for the set of embedding
, we utilize the mean pooling method to aggregate them to obtain the user’s presentation, denoted as
. By concatenating these vectors, we can get the final presentations of the users and items, which are also the model’s predictions. The formulations of reconstruction and the matching score are as follows:
where
is the Sigmoid function. With the predicted scores
and the real labels
, we utilize the cross-entropy function to compute the loss as Equation (
9), denoted as
.
To combine the individual learning as well as the interactive learning proposed above with the recommendation task, we proposed a multi-task learning framework to jointly train the multiple losses as in Algorithm 1. In the proposed framework, the individual learning of KG is conducted in the pre-train process, which enables all of the entities and relations in KG can be fully trained compared with learning it in the training process. Besides, the equation of
consists of four parts, where
and
are directly related to the final objective and the other two are indirectly related. This ensures that the user-item interaction signal maintains a dominant position.
|
Algorithm 1:KGDC Algorithm |
- 1:
Input: user-item interaction graph ; knowledge graph ; trainable parameters: , , , ; hyper-parameters and functions: - 2:
Output: Prediction vectors - 3:
fordo - 4:
for do - 5:
- 6:
Calculate loss - 7:
Update parameters by gradient descent - 8:
end for - 9:
end for - 10:
fordo - 11:
for in do - 12:
- 13:
Calculate loss , , - 14:
Reconstruct , - 15:
Calculate target loss - 16:
- 17:
Update parameters by gradient descent - 18:
end for - 19:
end for - 20:
return
|
5. Experiments
In this section, we conduct extensive experiments on two real-world datasets to evaluate the proposed KGDC. Next, we will sequentially provide detailed introductions to the experimental datasets, comparison baselines, experiment settings, and experimental results.
5.1. Datasets
We evaluate the proposed KGDC through experiments across two distinct scenarios: books and music. These datasets are publicly available and vary significantly in size and sparsity, and they are often used in the field of knowledge graph-based recommendation. Below are the details of each dataset:
Amazon-book.
1: This dataset includes user ratings and extensive metadata for books, such as descriptions, category information, price, and brand, sourced from Amazon.
LFM.FM
2: Collected from the Last.FM online platform, this music dataset consists of user-generated music listening events.
The basic statistics of the two datasets are presented in
Table 1.
We adopt the method in [
11] to convert explicit feedback across three datasets into implicit feedback, where a label of 1 denotes positive samples. In the Book-Crossing dataset, the ratings greater than or equal to 4 are labeled as 1, while the threshold is 0 in the Last.FM dataset. For every dataset, the ratio of training, evaluation, and test set is 6 : 2 : 2. Each experiment is repeated 3 times, and the average performance is reported. For constructing sub-KGs, we utilize Microsoft Satori4, which are similar to RippleNet [
11] and KGCN [
12]. Each sub-KG adheres to the triple format and constitutes a subset of the entire KG with confidence levels exceeding 0.9. From the sub-KG, we extract Satori IDs of all valid movies, books, or musicians by matching their names with the tail of triples. Subsequently, we match item IDs with the head of all triples and select well-matched triples from the sub-KG.
5.2. Baselines
To demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed KGDC, we compare it with the recent state-of-the-art methods, including BPRMF, CKE, KGCN, KGNN-LS, KGAT, CKAN, KGIN, and KGIC. The description of these methods are as follows:
BPRMF [
34]: It aims to rank user-item interactions in a way that places higher preference scores on items that users have interacted with, which is a traditional CF-based method;
CKE [
17]: It leverages structured information from knowledge graphs to enhance the quality of recommendations by embedding both user-item interactions and the rich semantic relationships present in the knowledge graph;
KGCN [
12]: It captures both the structural and semantic information from the knowledge graph, enabling it to learn more comprehensive and rich representations of items;
KGNN-LS [
14]: It integrates knowledge graph information with neural networks, incorporating the technique of label smoothing to improve model performance;
KGAT [
13]: It integrates knowledge graph information using attention mechanisms;
CKAN [
15]: It employs attention mechanisms to dynamically focus on the most relevant entities and relationships within the knowledge graph, enhancing the collaborative filtering process;
KGIN [
24]: It applies GNN to the user-intent-item-entity graph, allowing for a more granular and nuanced understanding of these interactions;
KGIC [
26]: It enhances traditional collaborative filtering by leveraging rich semantic relationships from knowledge graphs with the contrastive learning method;
CG-KGR [
25]: It employs a collaborative guidance mechanism, which encodes historical interactions as guidance for personalized knowledge extraction, making it particularly effective for tasks like Top-K recommendation.
5.3. Experiment Settings
The settings of hyper-parameters for baselines and the proposed KGDC are as follows. To ensure the fairness of the experimental results, some parameters are set to fixed values. The dimensions of nodes in CF and nodes(and relations) in KG are set as 64, and the batch size is set as 1024. Model parameters are initialized using Xavier, and optimization is performed using Adam.
For some parameters, we search for the optimal values within a certain range. We explore learning rates in the range {0.0001, 0.0005, 0.001, 0.0015}, and vary the number of neighbors between 2 to 50. And the depth exploration of GNNs ranges from 1 to 4. Baselines retain their default hyper-parameter settings except for the aforementioned parameters. To mitigate over-fitting, we ensure training convergence by limiting the number of steps to 50.
To evaluate the effectiveness of our proposed KGDC in the knowledge graph-based recommendations, we employ four widely used metrics: AUC, F1, Recall@K and NDCG@K, where the K values of Recall@K and NDCG@K are set to [10, 20, 50]. AUC and F1 are two widely used metrics in click-through rate (CTR) prediction, while Recall@K and NDCG@K are two methods usually used in the Top-k recommendation.
5.4. Results
In this section, we present a comprehensive performance analysis between the CG-KGR model and all representative baselines in the tasks of CTR prediction and Top-K recommendation.
5.4.1. Results of CTR Prediction
We present the experimental results of CTR prediction task across all datasets in the
Table 2. From these results, we draw the following observations and analyses. Our proposed method KGDC demonstrates significant improvements in performance for the CTR prediction task, particularly on the Book-Crossing dataset. KGDC enhances the baselines on the Book-Crossing datasets with AUC and F1 improvements of 2.45% and 1.15% respectively. While on the Last.FM dataset, KGDC only improves AUC by 0.7% and F1 by 0.23%.
This is likely due to the relatively limited impact of knowledge supplementation on the Music dataset. We use the ratio of the number of KG triplets to the number of items to measure the average knowledge contribution to enrich item embeddings. A higher ratio typically indicates richer semantics in the KG, enhancing item backgrounds. For the Music dataset, this ratio is 4.03, while the ratio of the Book dataset is 10.12. Thus KGDC can perform significantly better on the Book dataset by effectively utilizing the rich semantics in these KGs for accurate predictions.
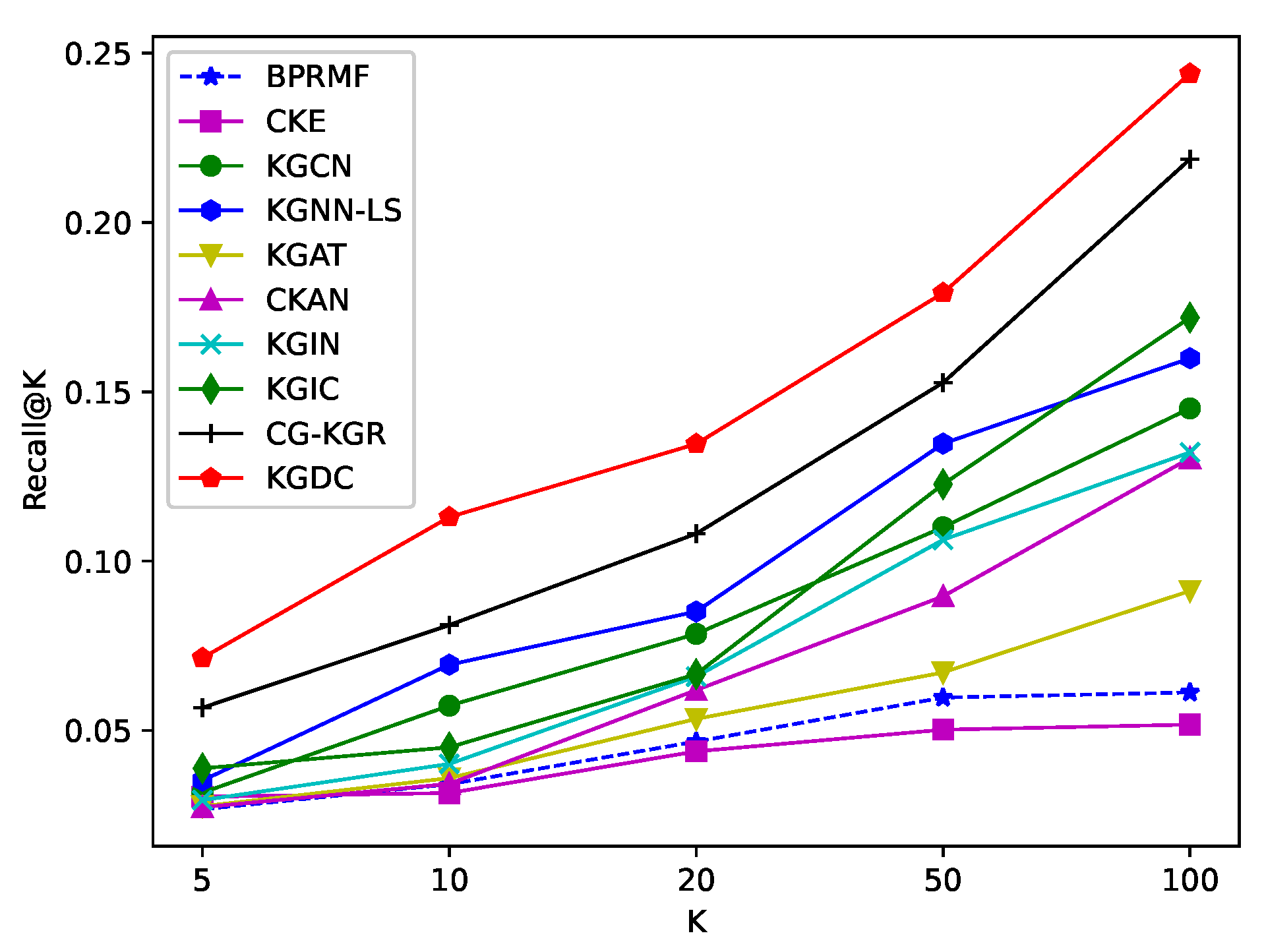
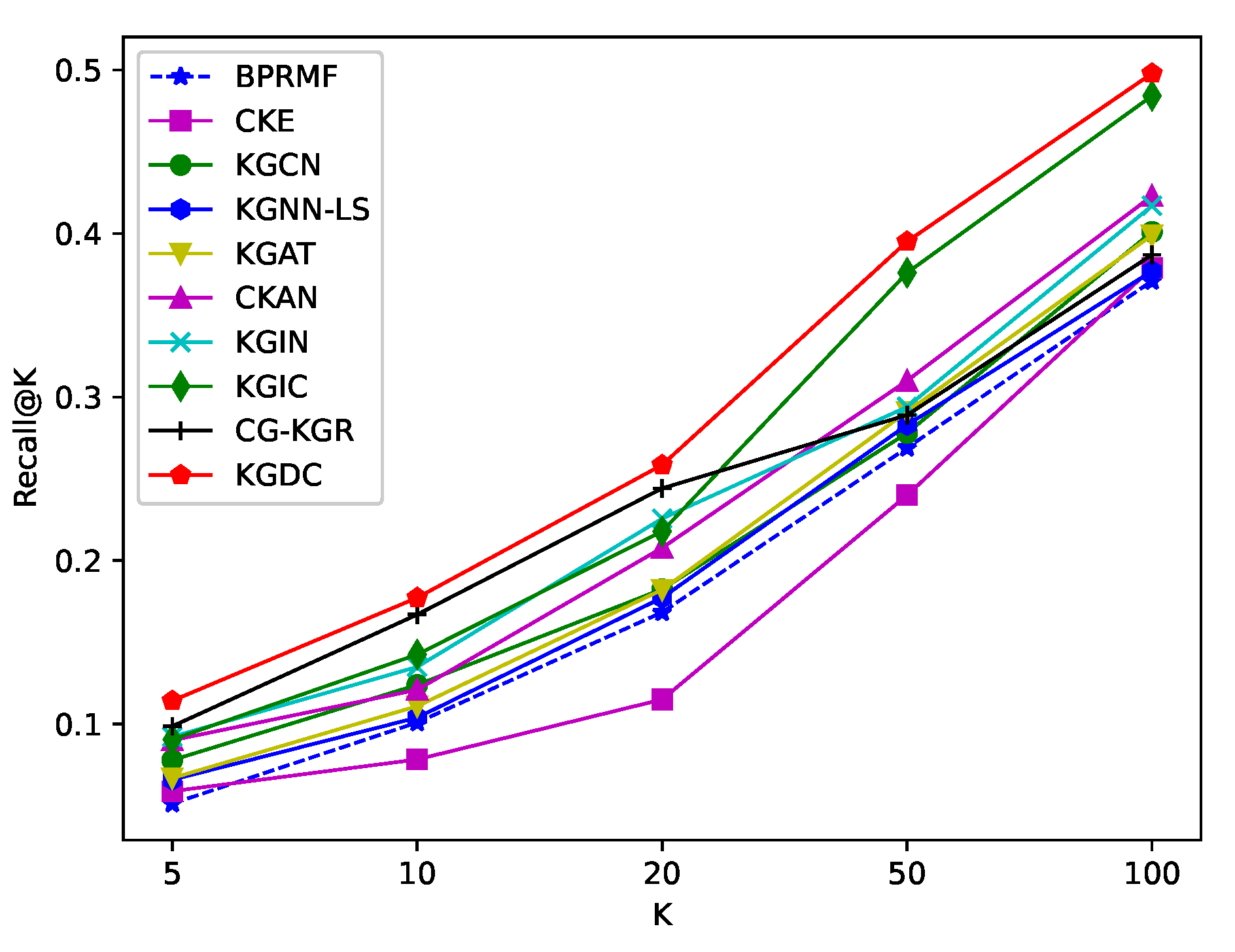
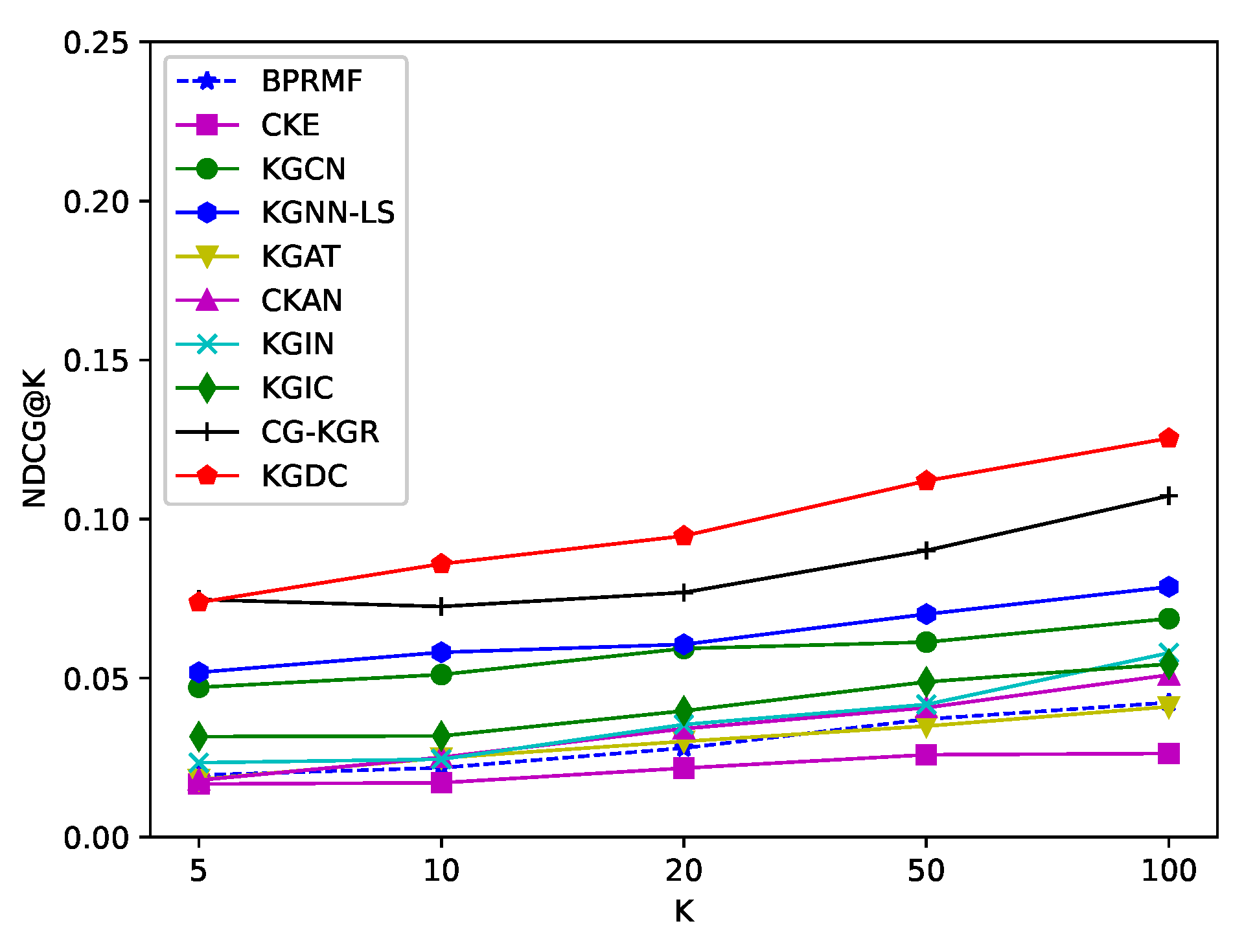
5.4.2. Results of the Top-K Recommendation
Similarly, we conduct experiments of Top-K recommendations across all datasets, and vary K in { 5, 10, 20, 50, 100}. For a better comparison between KGDC and these baselines, we firstly show the average results of the Top20 in
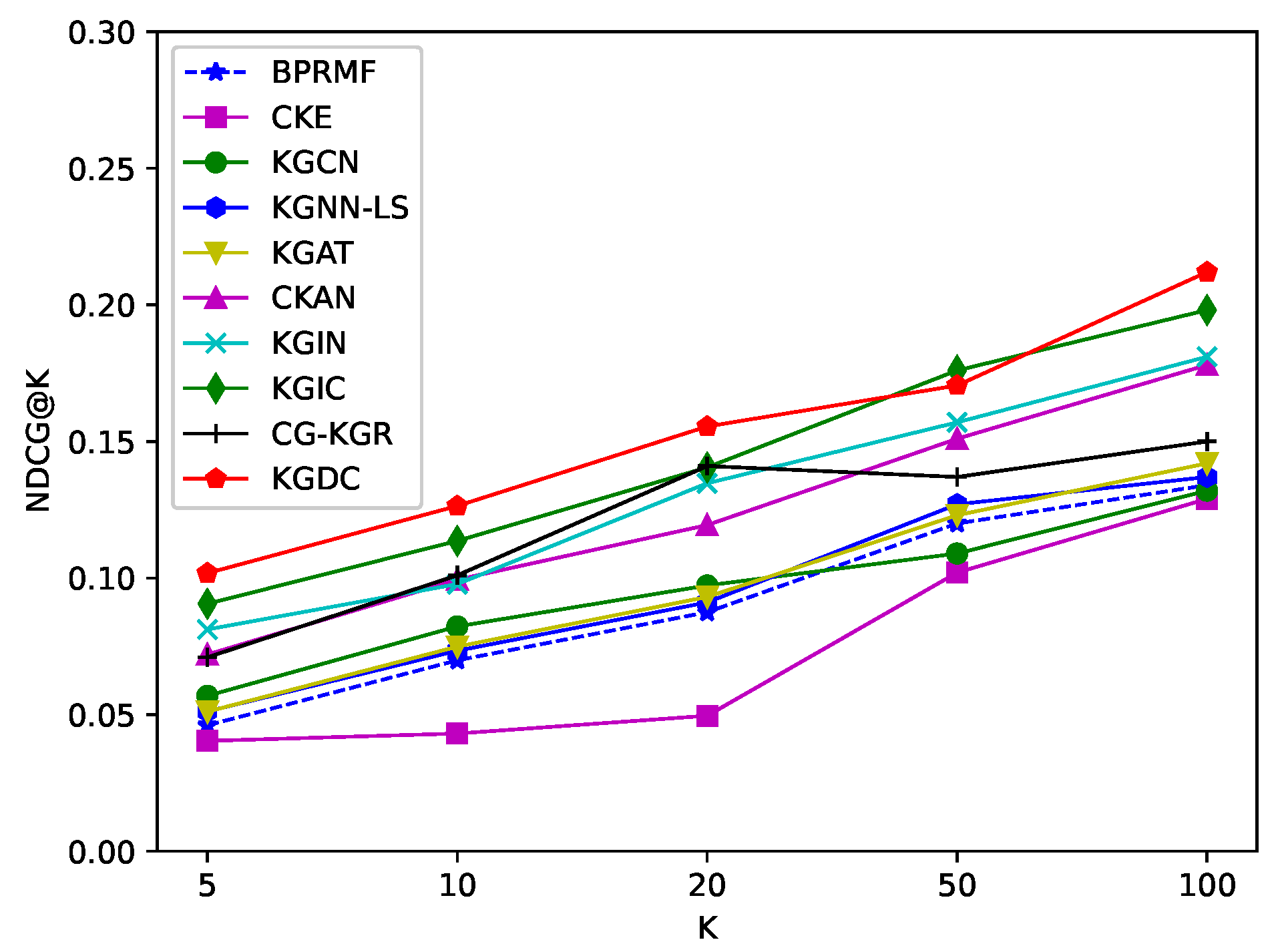
Table 3. And then we take use of four figures (
Figure 2,
Figure 3,
Figure 4 and
Figure 5) to further illustrate the complete results for the Recall@K and NDCG@K metrics. From these results, we have the following observations:
The proposed method shows more significant improvement in the Top-K recommendation task. As shown in
Table 3, KGDC improves Recall@20 and NDCG@20 by 8.418% and 6.762% compared to the state-of-the-art method on the Book-Crossing dataset. On the Last.FM dataset, it improves Recall@20 and NDCG@20 by 5.856% and 6.525%, separately. Compared with the CTR task, the improvements in the Top-K task are significantly larger. We believe that the significant improvements are attributed to the extensive integration of contrastive learning techniques and pair-wise loss formulations in the algorithm.
The introduction of contrastive learning and pair-wise loss have significantly improved the effectiveness of Top-K recommendation. Compared to traditional methods, introducing contrastive learning and pair-wise loss can achieve better results. It also demonstrates that contrastive learning can help the model to fully and effectively mine information when the supervision signals are insufficient. Meanwhile, the pair-wise loss function enhances the model’s learning of local ranking, which is particularly beneficial for Top-K recommendation scenarios.
BPRMF performs better than CKE: As a traditional CF-based method, BPRMF performs better than the knowledge graph-based CKE on both Book-Crossing and Last.FM datasets. It also demonstrates that simply integrating KGs into recommendation systems does not always guarantee improved performance. Both CF and KG graphs contain rich information, while not all information within KGs may contribute effectively to recommendations. Therefore, optimizing recommendation effectiveness requires making comprehensive and coherent use of CF and KG. This also indicates that the proposed KGDC can fully leverage the individual information and the interactive information.
As the value of K ranges, KGDC shows consistently better performance compared to baselines. As illustrated in
Figure 2,
Figure 3,
Figure 4 and
Figure 5, KGDC consistently outperforms best across different values of K in the evaluations of Recall@K, and it demonstrates competitive performance in the evaluation of NDCG@K. By explicitly propagating interaction information between users, items and entities, KGDC effectively learns latent representations of user preferences and item attraction patterns from CF and KG graphs. Besides, instead of directly integrating the individual graph information, KGDC also employs a collaborative guidance mechanism and an alignment mechanism to enhance the interaction between CF and KG. Moreover, KGDC adopts a multi-task framework to ensure the dominance of the supervision signals in CF. These results prove that KGDC has a significant advantage in Top-K recommendation.
KGDC performs better on the datasets that KG owns richer semantics to boost items’ backgrounds. Similar to CTR-based recommendations, KGDC shows greater improvement on the Book-Crossing dataset compared to the Last.FM dataset. This further demonstrates that the proposed method can extract more valuable information from semantically rich knowledge graphs while maintaining the dominant role of CF information and preventing interference from irrelevant redundancies of KG.
6. Conclusions
In this paper, we propose a new method KGDC to tackle the aforementioned challenges. KGDC leverages GNNs-based information propagation and aggregation techniques to effectively utilize the individual information from CF and KG, and also enhance the interaction of the two graphs by leveraging contrastive learning and multi-task learning. The extensive experiments show that KGDC significantly improves the recommendation performance over state-of-the-art methods on both tasks of CTR recommendation and Top-K prediction.
In this paper, we do not distinguish the different ratings that users give to items. For future work, we will explore the effective information related to different ratings to further improve the recommendation performance.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Jinchao Huang and Han Zhang; methodology, Jinchao Huang and Zhipu Xie; software, Jinchao Huang and Zhipu Xie; validation, Jinchao Huang and Bin Yang; formal analysis, Jinchao Huang and Bin Yang; investigation, Jinchao Huang and Chong Di; resources, Zhipu Xie; data curation, Jinchao Huang; writing—original draft preparation, Jinchao Huang; writing—review and editing, Han Zhang, Zhipu Xie, Bin Yang and Chong Di; visualization, Jinchao Huang and Han Zhang; supervision, Runhe Huang; project administration, Runhe Huang. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
References
- Covington P, Adams J, Sargin E. Deep neural networks for youtube recommendations. Proceedings of the 10th ACM conference on recommendation systems 2016, 191–198. [Google Scholar]
- Wang J, Huang P, Zhao H, et al. Billion-scale commodity embedding for e-commerce recommendation in alibaba. In Proceedings of the 24th ACM SIGKDD international conference on knowledge discovery & data mining; 2018; pp. 839–848.
- Zheng G, Zhang F, Zheng Z, et al. DRN: A deep reinforcement learning framework for news recommendation. In Proceedings of the 2018 world wide web conference; 2018; pp. 167–176.
- Lee D, Kang S K, Ju H, et al. Bootstrapping user and item representations for one-class collaborative filtering. In Proceedings of the 44th international ACM SIGIR conference on Research and Development in information retrieval; 2018; pp. 167–176.
- Wang C, Yu Y, Ma W, et al. Towards representation alignment and uniformity in collaborative filtering. In Proceedings of the 28th ACM SIGKDD conference on knowledge discovery and data mining; 2022; pp. 1816–1825. [Google Scholar]
- Wu J, Wang X, Feng F, et al. Proceedings of the 44th international ACM SIGIR conference on research and development in information retrieval. Proceedings of the 28th ACM SIGKDD conference on knowledge discovery and data mining 2021, 726–735. [Google Scholar]
- Yu J, Yin H, Xia X, et al. Are graph augmentations necessary? simple graph contrastive learning for recommendation. Proceedings of the 45th international ACM SIGIR conference on research and development in information retrieval 2022, 1294–1303. [Google Scholar]
- Ma H, King I, Lyu M R. Effective missing data prediction for collaborative filtering. Proceedings of the 30th annual international ACM SIGIR conference on Research and development in information retrieval 2007, 39–46. [Google Scholar]
- Volkovs M, Yu G, Poutanen T. Dropoutnet: Addressing cold start in recommendation systems. Advances in neural information processing systems 2017, 30.
- Khawar F, Zhang N L. Modeling multidimensional user preferences for collaborative filtering. 2019 IEEE 35th International Conference on Data Engineering (ICDE), IEEE, 2019; 1618–1621.
- Wang H, Zhang F, Wang J, et al. Ripplenet: Propagating user preferences on the knowledge graph for recommendation systems. Proceedings of the 27th ACM international conference on information and knowledge management, 2018; 417–426.
- Wang H, Zhao M, Xie X, et al. Knowledge graph convolutional networks for recommendation systems. The world wide web conference 2019, 3307–3313. [Google Scholar]
- Wang X, He X, Cao Y, et al. Kgat: Knowledge graph attention network for recommendation. Proceedings of the 25th ACM SIGKDD international conference on knowledge discovery & data mining, 2019; 950–958.
- Wang H, Zhang F, Zhang M, et al. Knowledge-aware graph neural networks with label smoothness regularization for recommendation systems. Proceedings of the 25th ACM SIGKDD international conference on knowledge discovery & data mining, 2019; 968–977.
- Wang Z, Lin G, Tan H, et al. CKAN: Collaborative knowledge-aware attentive network for recommendation systems. Proceedings of the 43rd International ACM SIGIR conference on research and development in Information Retrieval, 2020; 219–228.
- Huang J, Zhao W X, Dou H, et al. Improving sequential recommendation with knowledge-enhanced memory networks. The 41st international ACM SIGIR conference on research & development in information retrieval, 2018; 505–514.
- Zhang F, Yuan N J, Lian D, et al. Collaborative knowledge base embedding for recommendation systems. Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining 2016, 353–362. [Google Scholar]
- Bordes A, Usunier N, Garcia-Duran A, et al. Translating embeddings for modeling multi-relational data[J]. Advances in neural information processing systems, 2013, 26.
- Wang Z, Zhang J, Feng J, et al. Knowledge graph embedding by translating on hyperplanes. Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence, 2014; 28.
- Hu B, Shi C, Zhao W X, et al. Leveraging meta-path based context for top-n recommendation with a neural co-attention model. Proceedings of the 24th ACM SIGKDD international conference on knowledge discovery & data mining, 2018; 1531–1540.
- Shi C, Hu B, Zhao W X, et al. Heterogeneous information network embedding for recommendation. IEEE transactions on knowledge and data engineering 2018, 357–370. [Google Scholar]
- Wang X, Wang D, Xu C, et al. Explainable reasoning over knowledge graphs for recommendation. Proceedings of the AAAI conference on artificial intelligence 2019, 5329–5336. [Google Scholar]
- Sha X, Sun Z, Zhang J. Hierarchical attentive knowledge graph embedding for personalized recommendation. Electronic Commerce Research and Applications 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wang X, Huang T, Wang D, et al. Learning intents behind interactions with knowledge graph for recommendation. Proceedings of the web conference 2021 2021, 878–887. [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y, Yang Y, Wang Y, et al. Attentive knowledge-aware graph convolutional networks with collaborative guidance for personalized recommendation. 2022 IEEE 38th International Conference on Data Engineering (ICDE). IEEE, 2022; 299–231.
- Zou D, Wei W, Wang Z, et al. Improving knowledge-aware recommendation with multi-level interactive contrastive learning. Proceedings of the 31st ACM international conference on information & knowledge management, 2022; 2817–2826.
- Wang H, Xu Y, Yang C, et al. Knowledge-adaptive contrastive learning for recommendation. Proceedings of the sixteenth ACM international conference on web search and data mining, 2023; 535–543.
- Yu J, Yin H, Gao M, et al. Socially-aware self-supervised tri-training for recommendation. Proceedings of the 27th ACM SIGKDD conference on knowledge discovery & data mining, 2021; 2084–2092.
- Pan Z, Chen H. Collaborative knowledge-enhanced recommendation with self-supervisions. Mathematics, 2021.
- Yang Y, Huang C, Xia L, et al. Knowledge graph contrastive learning for recommendation. Proceedings of the 45th international ACM SIGIR conference on research and development in information retrieval 2021, 1434–1443. [Google Scholar]
- Cao Y, Wang X, He X, et al. Unifying knowledge graph learning and recommendation: Towards a better understanding of user preferences. The world wide web conference, 2019; 151–161.
- Yu X, Ren X, Sun Y, et al. Personalized entity recommendation: A heterogeneous information network approach. Proceedings of the 7th ACM international conference on Web search and data mining, 2014; 283–292.
- Chen T, Kornblith S, Norouzi M, et al. A simple framework for contrastive learning of visual representations. International conference on machine learning 2020, 1597–1607. [Google Scholar]
- Rendle S, Freudenthaler C, Gantner Z, et al. BPR: Bayesian personalized ranking from implicit feedback. [J]. arXiv:1205.2618, 2012.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).