Submitted:
30 June 2024
Posted:
10 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Materials and Methods
Results
Discussion
Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tarasewicz, D.; Conell, C.; Gilliam, L.K.; Melles, R.B. Quantification of risk factors for diabetic retinopathy progression. Acta Diabetol. 2023, 60, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kume, A.; Kashiwagi, K. Systemic and ocular diseases associated with the development of diabetic macular edema among Japanese patients with diabetes mellitus. BMC Ophthalmol. 2020, 20, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, X.; Cao, D.; Yang, D.; Zeng, Y.; Yu, H.; Wang, J.; Kuang, J.; Xie, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, L. Association of diabetic retinopathy and diabetic macular oedema with renal function in southern Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a single-centre observational study. BMJ Open. 2019, 9, e031194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liew, G.; Wong, V.W.; Saw, M.; Tsang, T.E.; Nolan, T.; Ong, S.; Ho, I.V. Profile of a population-based diabetic macular oedema study: the Liverpool Eye and Diabetes Study (Sydney). BMJ Open. 2019, 9, e021884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kung, E.W.T.; Chan, V.T.T.; Tang, Z.; Yang, D.; Sun, Z.; Wang, Y.M.; Chan, C.H.; Kwan, M.C.H.; Shi, J.; Cheung, C.Y. Alterations in the Choroidal Sublayers in Relationship to Severity and Progression of Diabetic Retinopathy: A Swept-Source OCT Study. Ophthalmol Sci. 2022, 2, 100130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, R.E.; Sasongko, M.B.; Sanmugasundram, S.; Nicolaou, T.; Jing, X.; Wang, J.J.; Wong, T.Y.; Lamoureux, E.L. Longer axial length is protective of diabetic retinopathy and macular edema. Ophthalmology 2012, 119, 1754–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acan, D.; Calan, M.; Er, D.; Arkan, T.; Kocak, N.; Bayraktar, F.; Kaynak, S. The prevalence and systemic risk factors of diabetic macular edema: a cross-sectional study from Turkey. BMC Ophthalmol. 2018, 18, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Bansal, P.; Shejao, H.; Hegde, R.; Roy, D.; Biswas, S. Correlation of morphological pattern of optical coherence tomography in diabetic macular edema with systemic risk factors in middle aged males. Int Ophthalmol. 2015, 35, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blodi, B.; Gardner, T.W.; Gao, X.; Sun, J.K.; Lorenzi, G.M.; de Koo, L.C.O.; Das, A.; White, N.H.; Gubitosi-Klug, R.A.; Aiello, L.P.; Bebu, I. DCCT/EDIC Research Group. Intensive Glycemic Management Is Associated With Reduced Retinal Structure Abnormalities on Ocular Coherence Tomography in the DCCT/EDIC Study. Diabetes Care, 2324. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, Y.H.; Boyer, D.S.; Maturi, R.K.; Bandello, F.; Belfort, R., Jr.; Augustin, A.J.; Li, X.Y.; Bai, Z.; Hashad, Y. Ozurdex MEAD Study Group. Natural history of diabetic macular edema and factors predicting outcomes in sham-treated patients (MEAD study). Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2019, 257, 2639–2653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acan, D.; Karahan, E.; Kocak, N.; Kaynak, S. Evaluation of systemic risk factors in different optical coherence tomographic patterns of diabetic macular edema. Int J Ophthalmol. 2018, 11, 1204–1209. [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson, C.P.; Ferris FL 3rd, Klein, R. E.; Lee, P.P.; Agardh, C.D.; Davis, M.; Dills, D.; Kampik, A.; Pararajasegaram, R.; Verdaguer, J.T. Global Diabetic Retinopathy Project Group. Proposed international clinical diabetic retinopathy and diabetic macular edema disease severity scales. Ophthalmology. 2003, 110, 1677–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yonekawa, Y.; Modi, Y.S.; Kim, L.A.; Skondra, D.; Kim, J.E.; Wykoff, C.C. American Society of Retina Specialists Clinical Practice Guidelines on the Management of Nonproliferative and Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy without Diabetic Macular Edema. J Vitreoretin Dis. 2020, 4, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koca, S.; Kılıç, D. Long-term longitudinal retinal changes after conventional and pattern scan laser panretinal photocoagulation in diabetic retinopathy. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 2023, 44, 103845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yazdani, S.; Samadi, P.; Pakravan, M.; Esfandiari, H.; Ghahari, E.; Nourinia, R. Peripapillary RNFL Thickness Changes after Panretinal Photocoagulation. Optom Vis Sci. 2016, 93, 1158–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, D.M.F.; Hassan, N.A.; Osman, A.A.; Osman, M.H. Subfoveal choroidal thickness in diabetic macular edema. Clin Ophthalmol. 2019, 13, 921–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, N.; Lee, I.G.; Kim, J.T. Changes in choroidal thickness in advanced diabetic retinopathy treated with pan-retinal photocoagulation using a pattern scanning laser versus a conventional laser. BMC Ophthalmol. 2020, 20, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Liu, L.; Rao, C.H.; Gao, J. Comparison of Chorioretinal Parameters in Diabetic Retinopathy with or without Pan-Retinal Photocoagulation Using Ultrawide-Field Swept-Source Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography. Ophthalmic Res. 2023, 66, 538–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, T.; Nishijima, K.; Sakamoto, A.; Ota, M.; Horii, T.; Yoshimura, N. Association of pathomorphology, photoreceptor status, and retinal thickness with visual acuity in diabetic retinopathy. Am J Ophthalmol. 2011, 151, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diabetic Retinopathy Clinical Research Network; Browning, D. J.; Glassman, A.R.; Aiello, L.P.; Beck, R.W.; Brown, D.M.; Fong, D.S.; Bressler, N.M.; Danis, R.P.; Kinyoun, J.L.; Nguyen, Q.D.; Bhavsar, A.R.; Gottlieb, J.; Pieramici, D.J.; Rauser, M.E.; Apte, R.S.; Lim, J.I.; Miskala, P.H. Relationship between optical coherence tomography-measured central retinal thickness and visual acuity in diabetic macular edema. Ophthalmology. 2007, 114, 525–536. [Google Scholar]
- Rayess, N.; Rahimy, E.; Ying, G.S.; Bagheri, N.; Ho, A.C.; Regillo, C.D.; Vander, J.F.; Hsu, J. Baseline choroidal thickness as a predictor for response to anti-vascular endothelial growth factor therapy in diabetic macular edema. Am J Ophthalmol. 2015, 159, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Lin, S.; Zheng, Y.; Di, F.; Cao, X.; Liu, C.; Yang, J. [Association of choroidal thickness with diabetic retinopathy at different stages]. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2015, 95, 2584–2588. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kiciński, K.; Gawęcki, M. Choroidal and Retinal Thicknesses in Healthy Eyes Measured with Ultra-Wide-Field Optical Coherence Tomography. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornish, E.E.; Wickremasinghe, S.; Mehta, H.; Lim, L.; Sandhu, S.S.; Nguyen, V.; Gillies, M.C.; Fraser-Bell, S. Aflibercept monotherapy versus aflibercept with targeted retinal laser to peripheral retinal ischemia for diabetic macular oedema (LADAMO). Eye 2023, 37, 3417–3422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talks, S.J.; Bhatia, D.; Menon, G.; Cole, A.; Eleftheriadis, H.; Downey, L.; Chong, N.V.; Sivaprasad, S. RDP study group. Randomised trial of wide-field guided PRP for diabetic macular oedema treated with ranibizumab. Eye 2019, 33, 930–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanxia, C.; Xiongyi, Y.; Min, F.; Xiaoyun, K. Optical Coherence Tomography-Based Grading of Diabetic Macular Edema Is Associated with Systemic Inflammatory Indices and Imaging Biomarkers. Ophthalmic Res. 2024, 67, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueras-Roca, M.; Matas, J.; Llorens, V.; Sala-Puigdollers, A.; Navarro, M.; Zarranz-Ventura, J.; Adán, A.; Molins, B. Systemic contribution of inflammatory mediators to the severity of diabetic and uveitic macular edema. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2021, 259, 2695–2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pessoa, B.; Heitor, J.; Coelho, C.; Leander, M.; Menéres, P.; Figueira, J.; Meireles, A.; Beirão, M. Systemic and vitreous biomarkers - new insights in diabetic retinopathy. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2022, 260, 2449–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.H.; Lee, G.W.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, S.G. Association between the response of intravitreal antivascular endothelial growth factor injection and systemic factors of diabetic macular edema. BMC Ophthalmol. 2024, 24, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.E.; Jo, J.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, J. Factors Affecting Intensive Aflibercept Treatment Response in Diabetic Macular Edema: A Real-World Study. J Diabetes Res. 2023, 2023, 1485059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mititelu, M.; Uschner, D.; Doherty, L.; Bjornstad, P.; Domalpally, A.; Drews, K.L.; Gubitosi-Klug, R.; Levitsky, L.L.; Pak, J.W.; White, N.H.; Blodi, B.A. Retinal Thickness and Morphology Changes on OCT in Youth with Type 2 Diabetes: Findings from the TODAY Study. Ophthalmol Sci. 2022, 2, 100191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Qiu, W.; Liu, Q.; Jiang, Y. Relationship Between Risk Factors and Macular Thickness in Patients with Early Diabetic Retinopathy. Int J Gen Med. 2022, 15, 6021–6029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
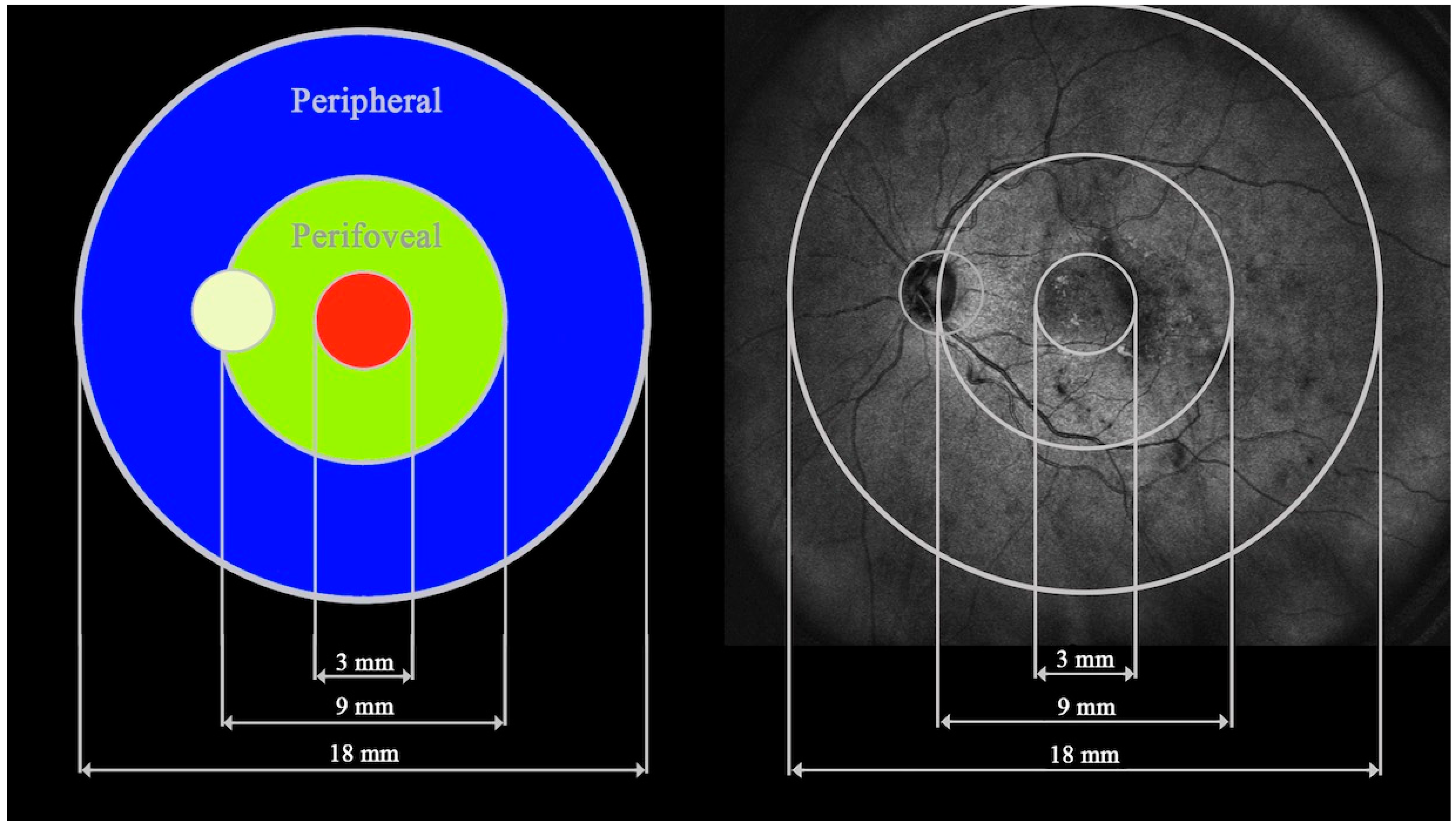

| Analyzed trait | Study group | P value | ||
| Control group | DME w/ laser |
DME w/o laser |
||
| No. of participants, n (%) | 75 (50.33) | 32 (21.48) | 42 (28.19) | |
| No. of eyes, n (%) | 125 (47.17) | 56 (21.13) | 84 (31.70) | |
| Gender, n (%) | ||||
|
44 (58.67) | 12 (37.50) | 18 (42.86) | = 0.0779 |
|
31 (41.33) | 20 (62.50) | 24 (57.14) | |
| Analyzed trait | DME/laser | Statistical parameter * | P value ** | |||
| M | SD | Me | Q1-Q3 | |||
| Age [years] | DME w/ laser | 60.22 | 13.03 | 66.00 | 51.00-69.00 | = 0.1448 |
| DME w/o laser | 63.67 | 9.17 | 64.00 | 57.50-71.50 | ||
| Control group | 59.03 | 15.92 | 63.00 | 48.00-71.00 | ||
| Axial length [mm] | DME w/ laser | 24.76 | 1.47 | 24.40 | 23.75-26.10 | = 0.3145 |
| DME w/o laser | 25.03 | 1.54 | 25.00 | 24.10-25.80 | ||
| Control group | 24.78 | 1.59 | 24.80 | 23.80-25.60 | ||
| BCVA (logMAR) | DME w/ laser | 0.56 | 0.36 | 0.55 | 0.30-0.70 | |
| DME w/o laser | 0.32 | 0.28 | 0.30 | 0.10-0.50 | ||
| Control group | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00-0.00 | ||
| Measured field | DME/laser | Statistical parameter | P value * | |||
| M | SD | Me | Q1-Q3 | |||
| Retinal thickness | ||||||
| Central | DME w/ laser | 369.79 | 66.84 | 363.00 | 313.00-394.00 | < 0.0001 a |
| DME w/o laser | 366.36 | 61.42 | 351.00 | 325.00-380.50 | ||
| Control group | 335.08 | 20.69 | 335.00 | 324.00-348.00 | ||
| Perifoveal |
DME w/ laser | 315.28 | 39.77 | 307.78 | 281.41-337.91 | < 0.0001 b |
| DME w/o laser | 302.20 | 30.00 | 296.47 | 283.72-313.72 | ||
| Control group | 287.50 | 14.98 | 289.81 | 277.37-297.75 | ||
| Peripheral |
DME w/ laser | 227.07 | 21.06 | 219.19 | 212.37-341.63 | = 0.0150 c |
| DME w/o laser | 225.60 | 17.32 | 220.94 | 214.62-234.94 | ||
| Control group | 220.29 | 12.43 | 221.37 | 211.50-228.63 | ||
| Choroidal thickness | ||||||
| Central | DME w/ laser | 288.18 | 76.63 | 293.00 | 220.50-353.50 | = 0.9227 |
| DME w/o laser | 285.82 | 85.33 | 288.00 | 230.50-352.00 | ||
| Control group | 293.87 | 87.10 | 300.00 | 223.00-357.00 | ||
| Perifoveal | DME w/ laser | 254.89 | 75.90 | 240.72 | 201.56-309.31 | = 0.7573 |
| DME w/o laser | 244.75 | 68.90 | 231.47 | 193.53-284.31 | ||
| Control group | 250.98 | 71.48 | 241.00 | 200.69-314.19 | ||
| Peripheral |
DME w/ laser | 196.54 | 56.46 | 183.56 | 159.00-227.19 | = 0.2139 |
| DME w/o laser | 185.10 | 45.71 | 176.06 | 153.06-206.63 | ||
| Control group | 186.57 | 46.02 | 174.12 | 152.62-221.00 | ||
| Patient characteristics | Axial length (mm) | BCVA (logMAR) | HbA1c (%) | BMI (kg*m–2) | Age (years) | |||||
| Measured field | r | p * | r | p * | r | p * | r | p * | r | p * |
| Retinal thickness | ||||||||||
| Central | –0.11 | 0.3385 | 0.33 | 0.0025 | 0.001 | 0.9904 | –0.20 | 0.2320 | 0.11 | 0.3086 |
| Perifoveal | 0.06 | 0.5659 | 0.23 | 0.0384 | 0.08 | 0.5240 | –0.15 | 0.3818 | –0.07 | 0.5473 |
| Peripheral | 0.30 | 0.0052 | 0.16 | 0.1411 | –0.03 | 0.7980 | –0.10 | 0.5468 | –0.14 | 0.1916 |
| Choroidal thickness | ||||||||||
| Central | 0.20 | 0.0656 | –0.25 | 0.0223 | –0.04 | 0.7082 | –0.12 | 0.4593 | –0.44 | < 0.0001 |
| Perifoveal | 0.21 | 0.0518 | –0.26 | 0.0187 | –0.07 | 0.5467 | –0.11 | 0.5322 | –0.48 | < 0.0001 |
| Peripheral | 0.18 | 0.1084 | –0.15 | 0.1796 | –0.14 | 0.2306 | 0.02 | 0.8998 | –0.38 | 0.0004 |
| Patient characteristics | DM duration (years) | Insulin therapy (years) | IVI count | DRSS | ||||
| Measured field | r | p * | r | p * | r | p * | r | p * |
| Retinal thickness | ||||||||
| Central | –0.11 | 0.3707 | –0.22 | 0.1256 | –0.15 | 0.3103 | –0.13 | 0.3009 |
| Perifoveal | –0.19 | 0.1220 | –0.15 | 0.3078 | –0.17 | 0.2580 | 0.19 | 0.1213 |
| Peripheral | 0.01 | 0.9322 | 0.20 | 0.1700 | 0.10 | 0.5131 | 0.07 | 0.5730 |
| Choroidal thickness | ||||||||
| Central | –0.14 | 0.2557 | 0.28 | 0.0531 | 0.13 | 0.4047 | –0.06 | 0.6371 |
| Perifoveal | –0.15 | 0.2313 | 0.25 | 0.0910 | 0.06 | 0.6952 | –0.08 | 0.5064 |
| Peripheral | –0.16 | 0.1828 | 0.15 | 0.2982 | 0.07 | 0.6251 | –0.10 | 0.4545 |
| Patient characteristics | Axial length (mm) | BCVA (logMAR) | HbA1c (%) | BMI (kg*m–2) | Age (years) | |||||
| Measured field | r | p * | r | p * | r | p * | r | p * | r | p * |
| Retinal thickness | ||||||||||
| Central | –0.02 | 0.9030 | 0.01 | 0.9362 | 0.06 | 0.6852 | –0.08 | 0.7058 | 0.13 | 0.3548 |
| Perifoveal | 0.10 | 0.4693 | 0.13 | 0.3667 | 0.08 | 0.5709 | –0.15 | 0.5069 | 0.04 | 0.7504 |
| Peripheral | 0.36 | 0.0066 | 0.24 | 0.0870 | –0.11 | 0.4549 | –0.06 | 0.7869 | –0.13 | 0.3627 |
| Choroidal thickness | ||||||||||
| Central | –0.16 | 0.2495 | –0.05 | 0.7246 | 0.08 | 0.5955 | 0.27 | 0.2213 | –0.31 | 0.0213 |
| Perifoveal | –0.14 | 0.3171 | –0.07 | 0.6144 | 0.15 | 0.3035 | 0.14 | 0.5195 | –0.25 | 0.0693 |
| Peripheral | –0.08 | 0.5485 | –0.01 | 0.9365 | –0.01 | 0.9667 | –0.03 | 0.9001 | –0.18 | 0.1859 |
| Patient characteristics | DM duration (years) | Insulin therapy (years) | IVI count | DRSS | ||||
| Measured field | r | p * | r | p * | r | p * | r | p * |
| Retinal thickness | ||||||||
| Central | –0.27 | 0.0837 | –0.30 | 0.0606 | –0.38 | 0.0504 | 0.02 | 0.8886 |
| Perifoveal | –0.28 | 0.0656 | –0.38 | 0.0171 | –0.61 | 0.0006 | 0.17 | 0.3036 |
| Peripheral | –0.09 | 0.5611 | –0.10 | 0.5364 | –0.49 | 0.0088 | 0.31 | 0.0519 |
| Choroidal thickness | ||||||||
| Central | –0.24 | 0.1279 | 0.16 | 0.3326 | –0.001 | 0.9963 | 0.05 | 0.7673 |
| Perifoveal | –0.16 | 0.3008 | 0.26 | 0.1144 | 0.04 | 0.8574 | 0.04 | 0.8128 |
| Peripheral | –0.02 | 0.8748 | 0.29 | 0.0761 | –0.10 | 0.6279 | –0.002 | 0.9883 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





