Submitted:
09 July 2024
Posted:
10 July 2024
Read the latest preprint version here
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Methods and Chemicals
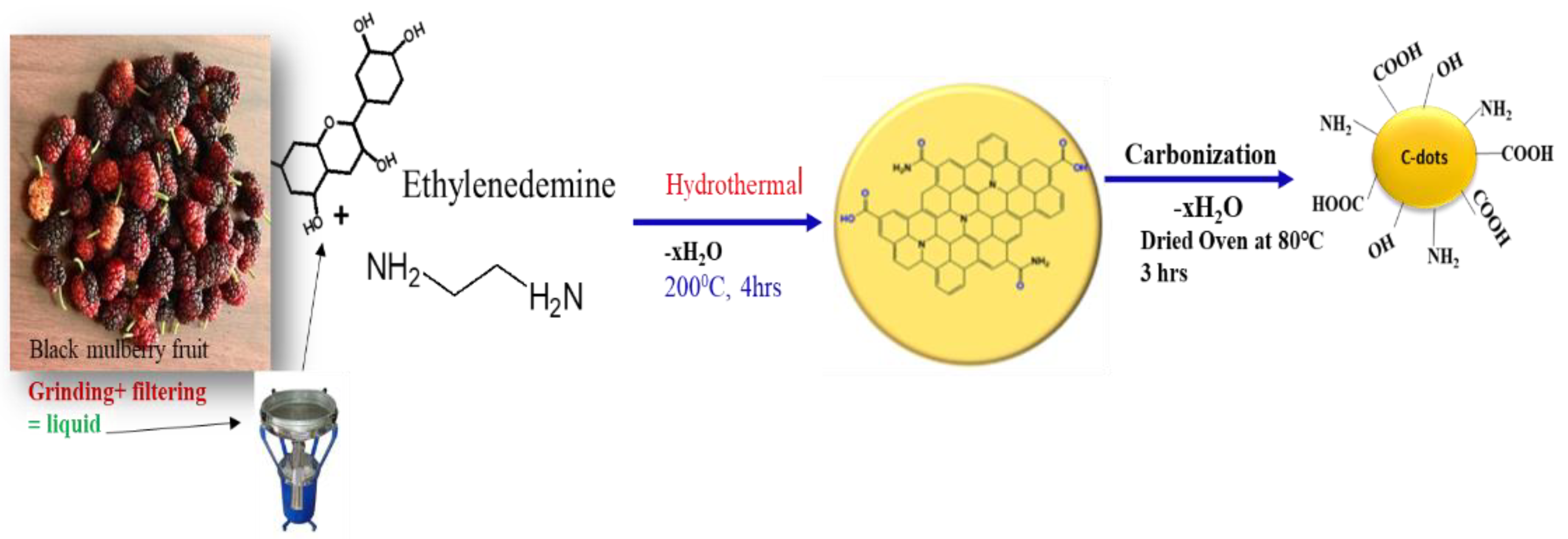
2.1. Extraction of Black Mulberry Fruits
2.2. Green Synthesis of C-Dots
2.3. Photocatalytic Degradation of Methylene Blue
3. Results and Discussion
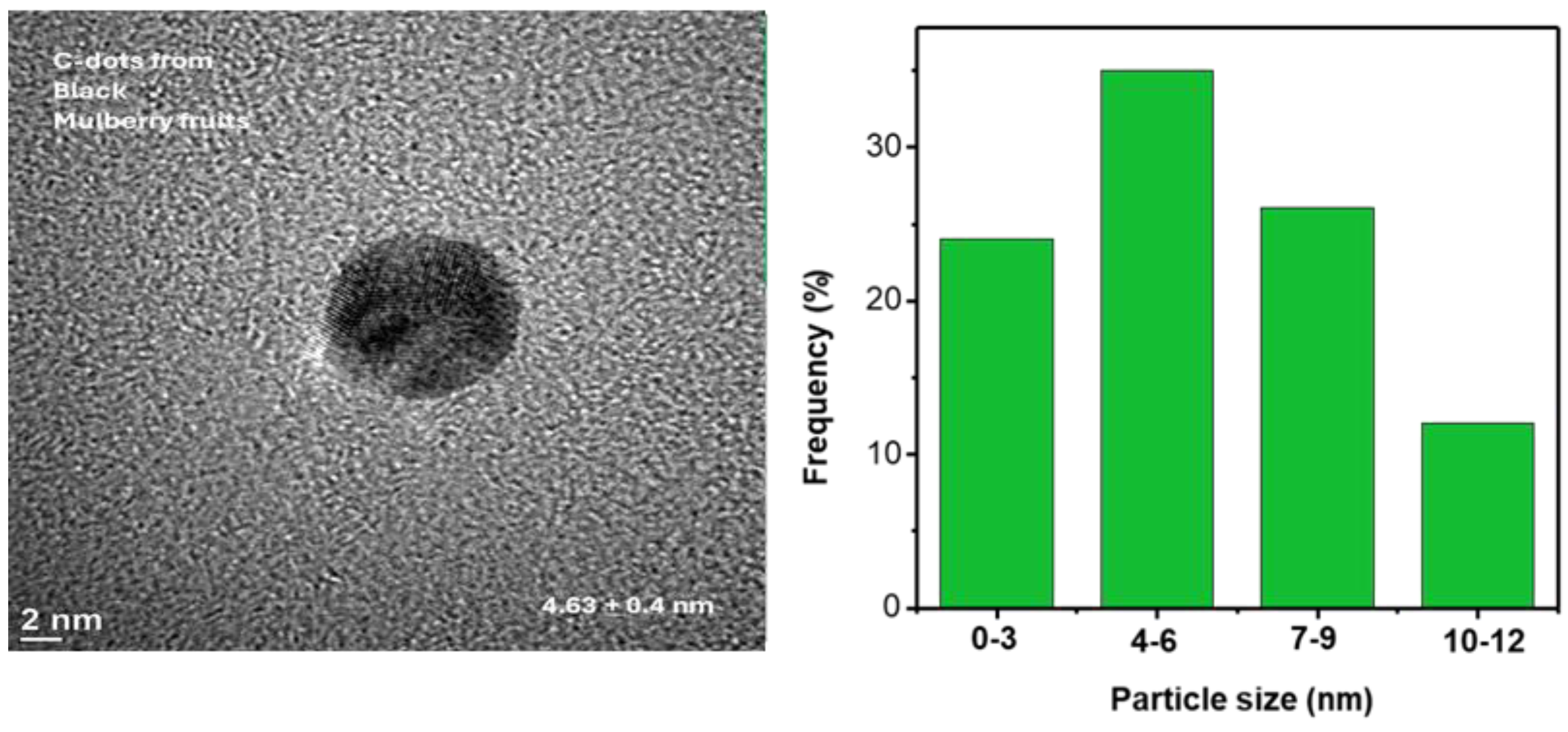
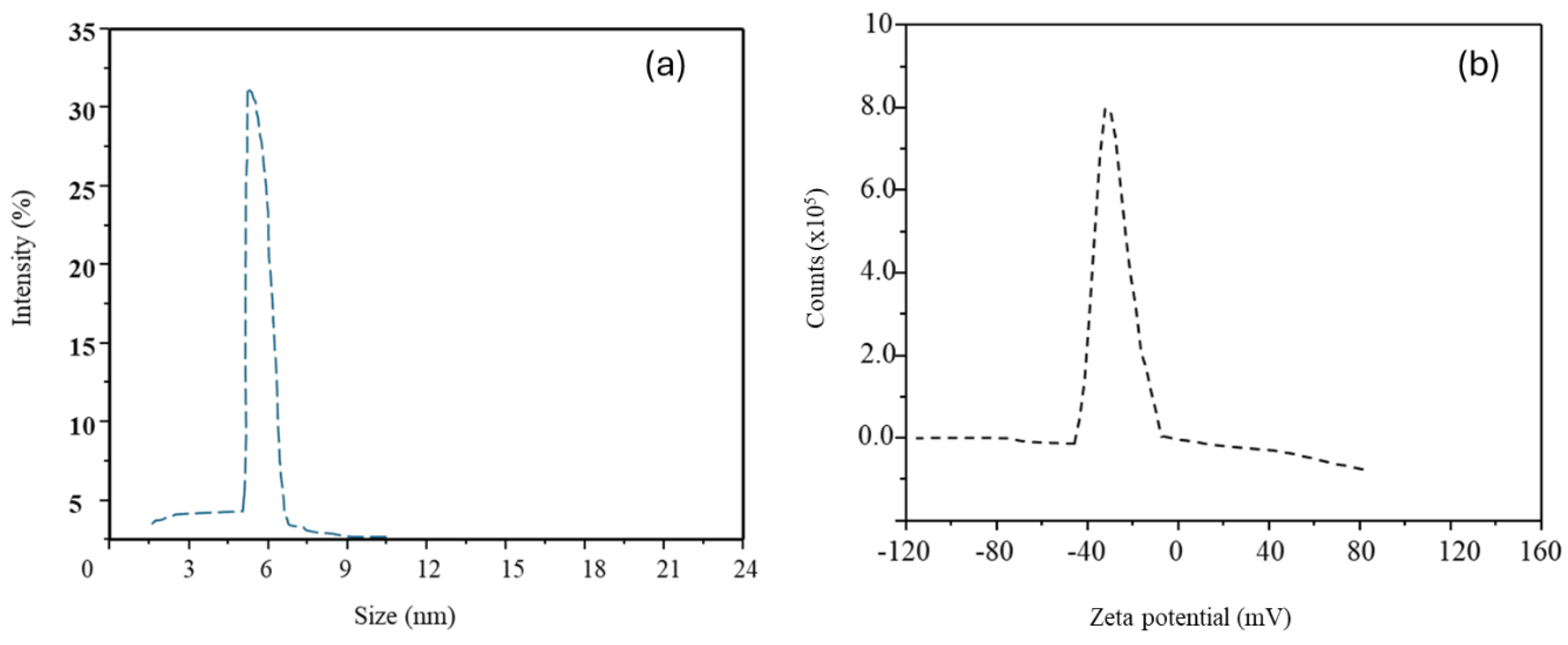
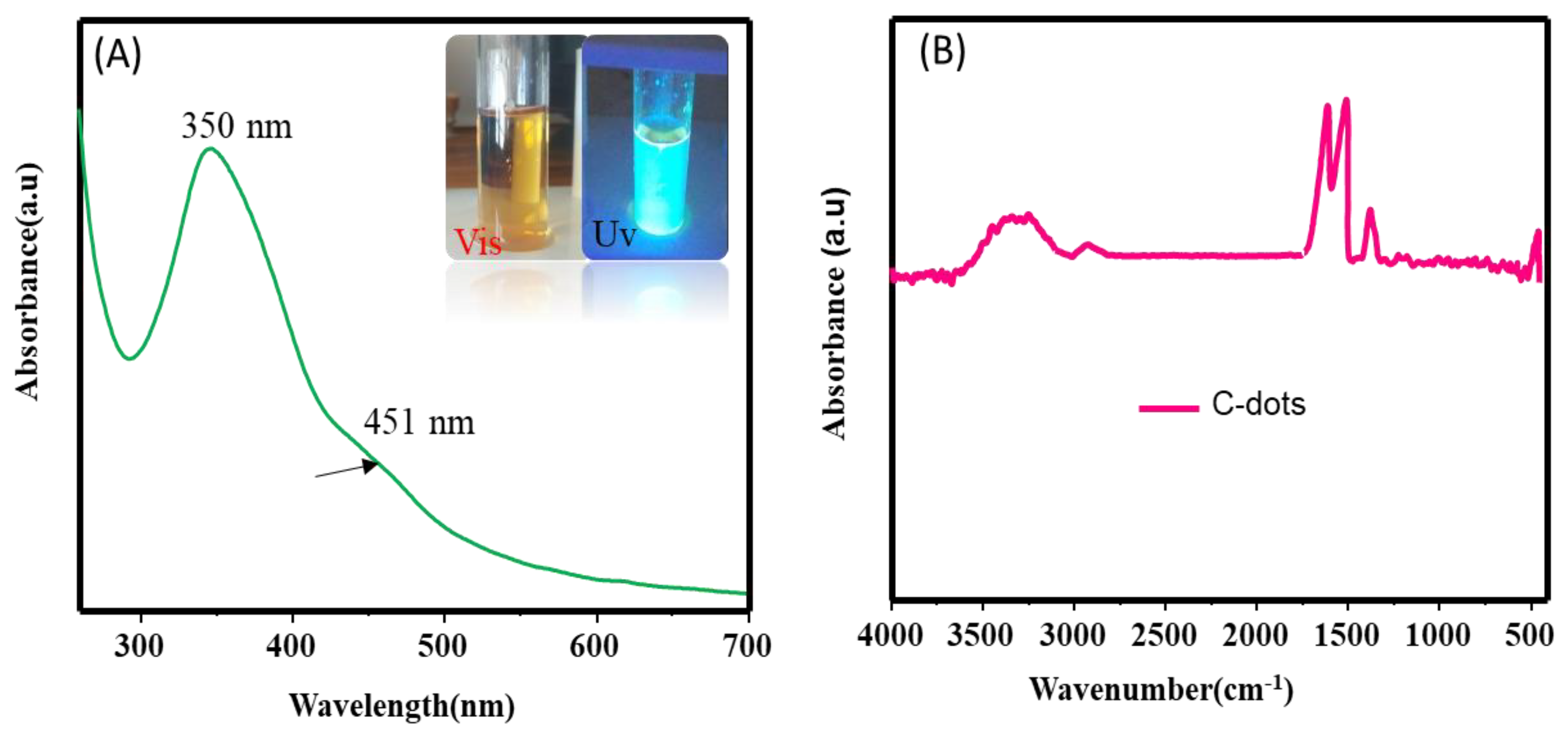
3.1. Characterization
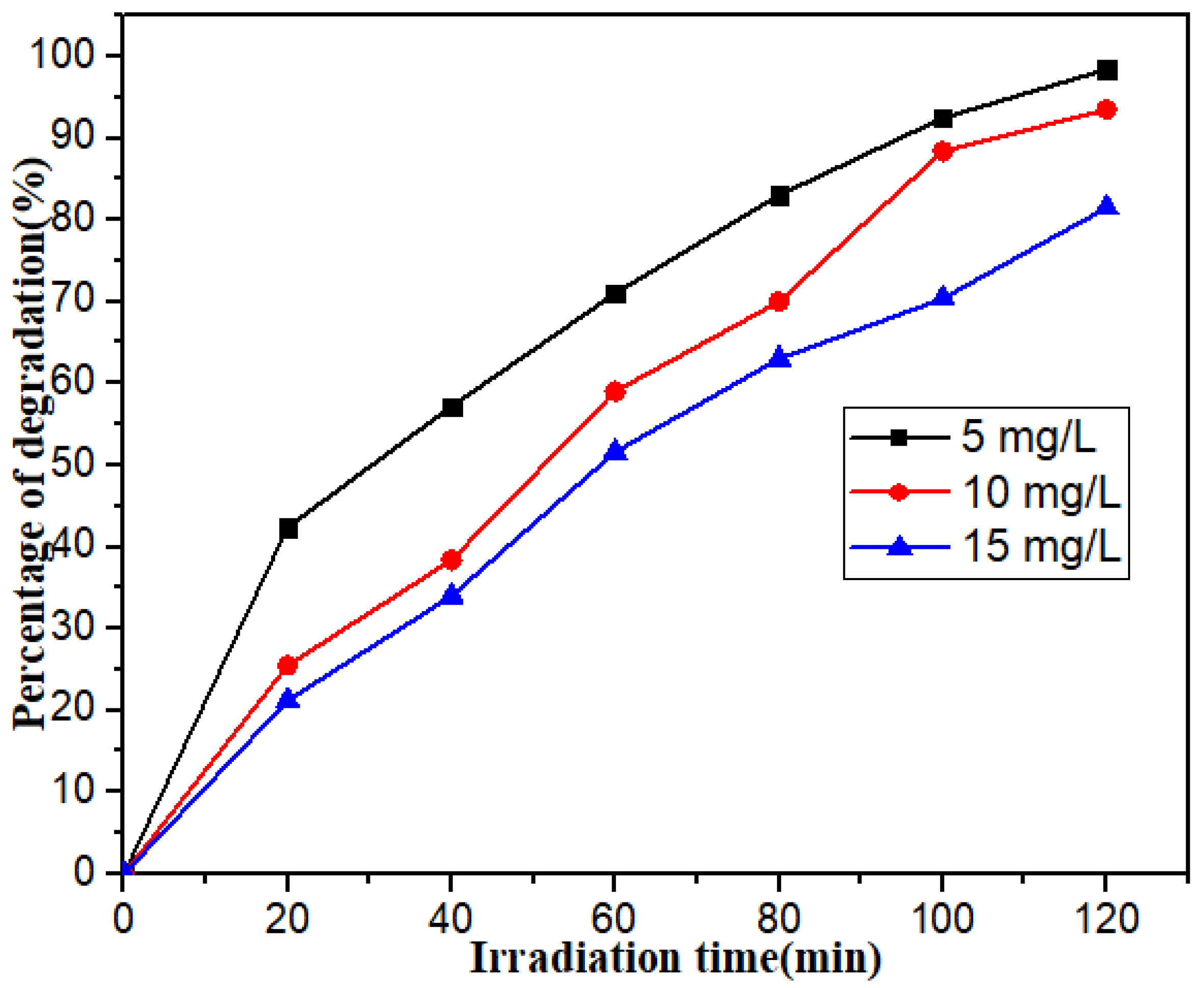
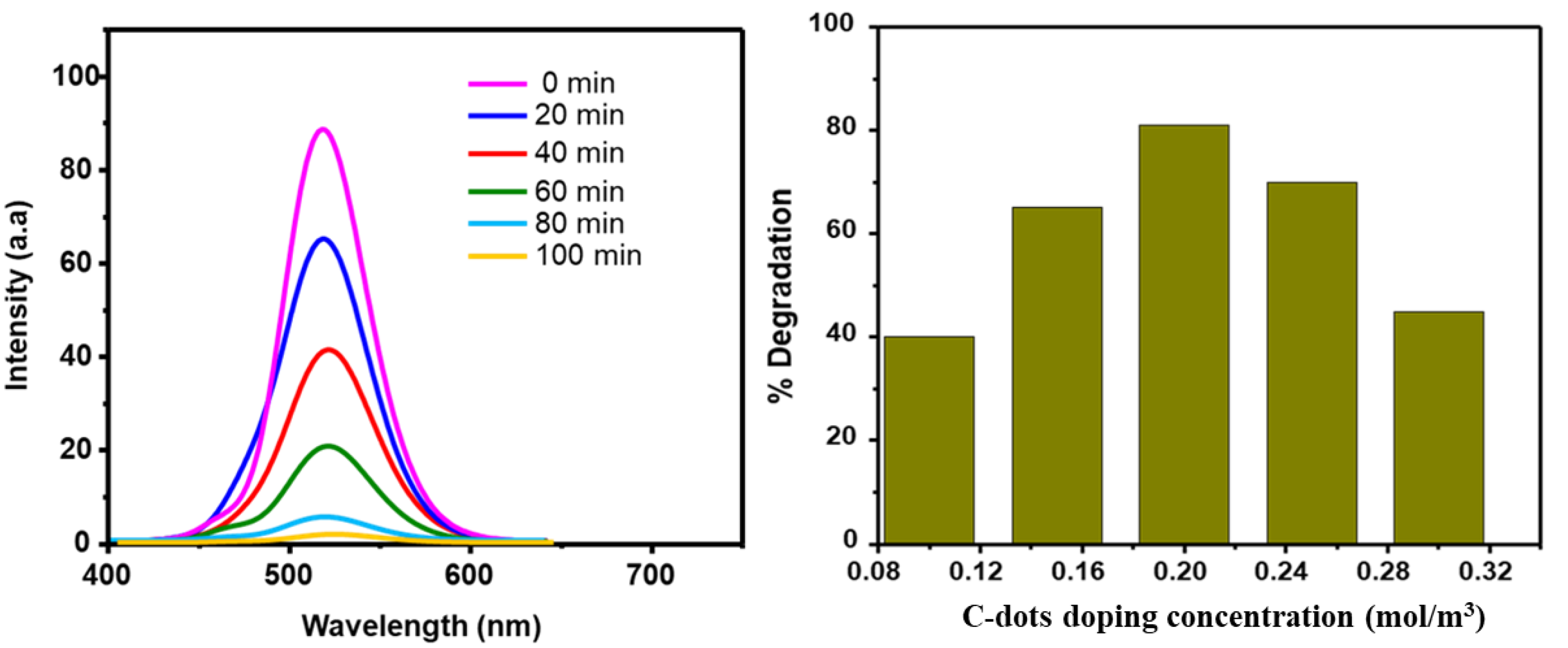
3.2. Photocatalytic Degradation Performance
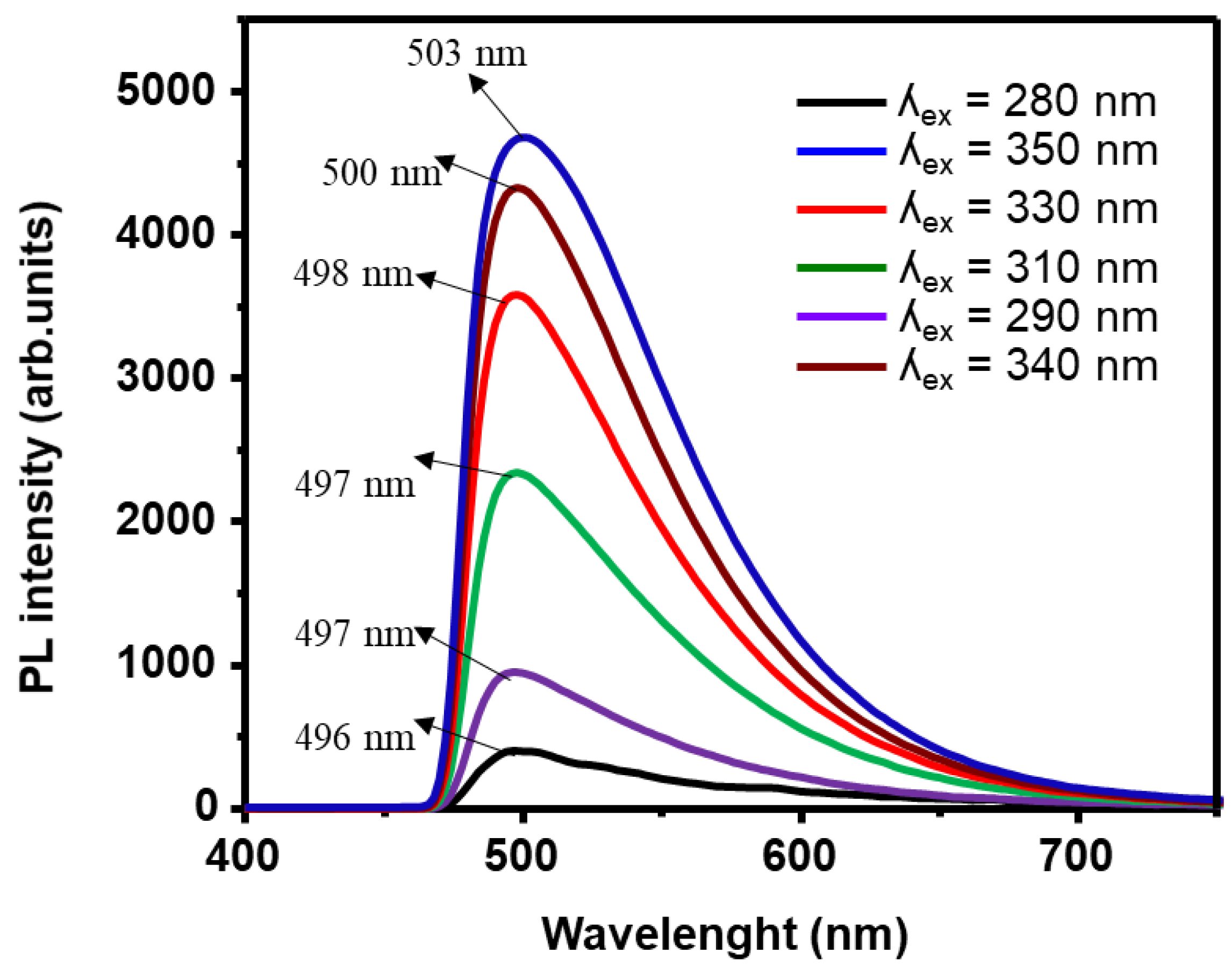
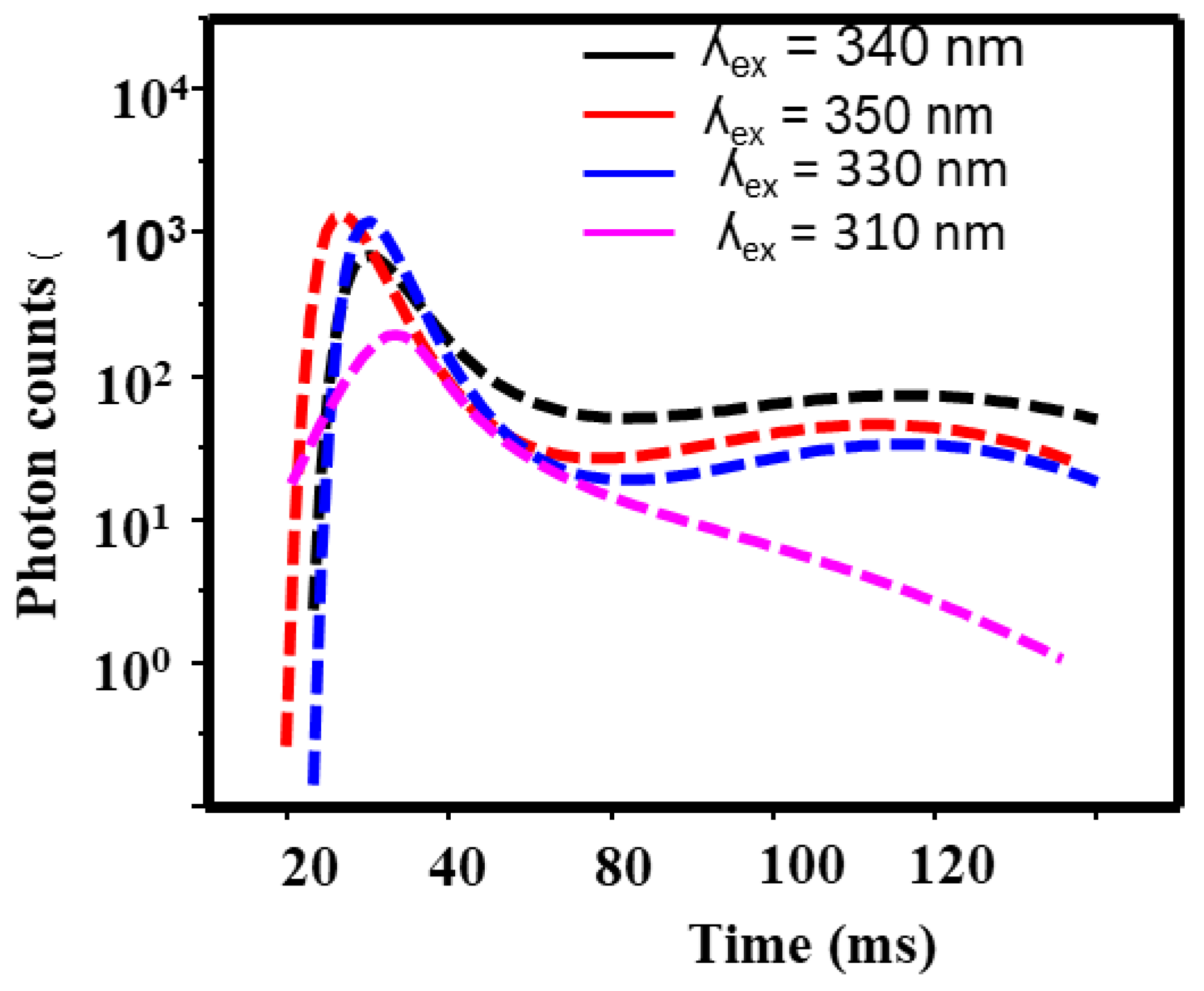
3.3. Photoluminsince Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, Z.; Shen, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, A.; Liu, S.; Zhang, Y. Chemical cleavage of layered carbon nitride with enhanced photoluminescent performances and photoconduction. ACS nano 2015, 9, 12480–12487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, L.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Wong, T.; Sun, H. Self-trapped exciton emission from carbon dots investigated by polarization anisotropy of photoluminescence and photoexcitation. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 12637–12646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Miao, P.; Zhou, W.; Gong, X.; Zhao, X. N-doped carbon-dots for luminescent solar concentrators. Journal of Materials Chemistry A 2017, 5, 21452–21459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hola, K.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Giannelis, E.P.; Zboril, R.; Rogach, A.L. Carbon dots—emerging light emitters for bioimaging, cancer therapy and optoelectronics. Nano Today 2014, 9, 590–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepanidenko, E.A.; Ushakova, E.V.; Fedorov, A.V.; Rogach, A.L. Applications of carbon dots in optoelectronics. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Lu, S. The light of carbon dots: From mechanism to applications. Matter 2022, 5, 110–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamiloglu, S.; Serali, O.; Unal, N.; Capanoglu, E. Antioxidant activity and polyphenol composition of black mulberry (morus nigra l.) products. Journal of Berry Research 2013, 3, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.-K.; Zhang, L.-L.; Yang, Z.-Y.; Guo, X.-H.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Luo, J.-K.; Tang, T.; Wang, Y. Herbal medicine derived carbon dots: Synthesis and applications in therapeutics, bioimaging and sensing. Journal of Nanobiotechnology 2021, 19, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanwal, A.; Bibi, N.; Hyder, S.; Muhammad, A.; Ren, H.; Liu, J.; Lei, Z. Recent advances in green carbon dots (2015–2022): Synthesis, metal ion sensing, and biological applications. Beilstein Journal of Nanotechnology 2022, 13, 1068–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umar, M.; Aziz, H.A. Photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants in water. Organic pollutants-monitoring, risk and treatment 2013, 8, 196–197. [Google Scholar]
- Ajith, M.; Aswathi, M.; Priyadarshini, E.; Rajamani, P. Recent innovations of nanotechnology in water treatment: A comprehensive review. Bioresource Technology 2021, 342, 126000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anju, A.; Ravi S, P.; Bechan, S. Water pollution with special reference to pesticide contamination in india. Journal of Water Resource and Protection 2010, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Akhtar, N.; Syakir Ishak, M.I.; Bhawani, S.A.; Umar, K. Various natural and anthropogenic factors responsible for water quality degradation: A review. Water 2021, 13, 2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhosale, T.; Kuldeep, A.; Pawar, S.; Shirke, B.; Garadkar, K. Photocatalytic degradation of methyl orange by eu doped sno 2 nanoparticles. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics 2019, 30, 18927–18935. [Google Scholar]
- Georgakilas, V.; Perman, J.A.; Tucek, J.; Zboril, R. Broad family of carbon nanoallotropes: Classification, chemistry, and applications of fullerenes, carbon dots, nanotubes, graphene, nanodiamonds, and combined superstructures. Chemical reviews 2015, 115, 4744–4822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barman, M.K.; Patra, A. Current status and prospects on chemical structure driven photoluminescence behaviour of carbon dots. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology C: Photochemistry Reviews 2018, 37, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Das, J. Small molecules derived carbon dots: Synthesis and applications in sensing, catalysis, imaging, and biomedicine. Journal of nanobiotechnology 2019, 17, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özkara, A.; Akyıl, D.; Konuk, M. Pesticides, environmental pollution, and health. In Environmental health risk-hazardous factors to living species; IntechOpen, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Chauhan, D.S.; Quraishi, M.; Verma, C. Carbon nanodots: Recent advances in synthesis and applications. Carbon Letters 2022, 32, 1603–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansuriya, B.D.; Altintas, Z. Carbon dots: Classification, properties, synthesis, characterization, and applications in health care—an updated review (2018–2021). Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cailotto, S.; Massari, D.; Gigli, M.; Campalani, C.; Bonini, M.; You, S.; Vomiero, A.; Selva, M.; Perosa, A.; Crestini, C. N-doped carbon dot hydrogels from brewing waste for photocatalytic wastewater treatment. ACS omega 2022, 7, 4052–4061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patial, S.; Sudhaik, A.; Chandel, N.; Ahamad, T.; Raizada, P.; Singh, P.; Chaukura, N.; Selvasembian, R. A review on carbon quantum dots modified g-c3n4-based photocatalysts and potential application in wastewater treatment. Applied Sciences 2022, 12, 11286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, S.; Agrawal, H.; Thakur, M.; Akbari, A.; Sharda, H.; Kaur, R.; Amini, M. Metal oxides and metal organic frameworks for the photocatalytic degradation: A review. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering 2020, 8, 103726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Kamali, M.; Zhang, S.; Yu, X.; Appels, L.; Cabooter, D.; Dewil, R. Photo-assisted (waste) water treatment technologies—a scientometric-based critical review. Desalination 2022, 538, 115905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudimella, K.K.; Appidi, T.; Wu, H.-F.; Battula, V.; Jogdand, A.; Rengan, A.K.; Gedda, G. Sand bath assisted green synthesis of carbon dots from citrus fruit peels for free radical scavenging and cell imaging. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces 2021, 197, 111362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutiérrez-Cruz, A.; Ruiz-Hernández, A.R.; Vega-Clemente, J.F.; Luna-Gazcón, D.G.; Campos-Delgado, J. A review of top-down and bottom-up synthesis methods for the production of graphene, graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide. Journal of Materials Science 2022, 57, 14543–14578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shafey, A.M. Carbon dots: Discovery, structure, fluorescent properties, and applications. Green Processing and Synthesis 2021, 10, 134–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemera, D.J.; Etefa, H.F.; Kumar, V.; Dejene, F.B. Hybridization of nickel oxide nanoparticles with carbon dots and its application for antibacterial activities. Luminescence 2022, 37, 965–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzoor, S.; Dar, A.H.; Dash, K.K.; Pandey, V.K.; Srivastava, S.; Bashir, I.; Khan, S.A. Carbon dots applications for development of sustainable technologies for food safety: A comprehensive review. Applied Food Research 2023, 100263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanker, U.; Hussain, C.M.; Rani, M. Green functionalized nanomaterials for environmental applications; Elsevier, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Etefa, H.F.; Nemera, D.J.; Dejene, F.B. Green synthesis of nickel oxide nps incorporating carbon dots for antimicrobial activities. ACS Omega 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etefa, H.F.; Kumar, V.; Dejene, F.B.; Efa, M.T.; Jule, L.T. Modification of flexible electrodes for p-type (nickel oxide) dye-sensitized solar cell performance based on the cellulose nanofiber film. ACS omega 2023, 8, 15249–15258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzahrani, E.A.; Nabi, A.; Kamli, M.R.; Albukhari, S.M.; Althabaiti, S.A.; Al-Harbi, S.A.; Khan, I.; Malik, M.A. Facile green synthesis of zno nps and plasmonic ag-supported zno nanocomposite for photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue. Water 2023, 15, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, G.; Chou, N.-N.; Lin, Y.-S.; Yang, C.-F.; Meen, T.-H. Comparison of the degradation effect of methylene blue for zno nanorods synthesized on silicon and indium tin oxide substrates. Materials 2023, 16, 4275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etefa, H.F.; Imae, T.; Yanagida, M. Enhanced photosensitization by carbon dots co-adsorbing with dye on p-type semiconductor (nickel oxide) solar cells. ACS applied materials & interfaces 2020, 12, 18596–18608. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




