Submitted:
10 July 2024
Posted:
11 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- Provide a systematic review of RAG-based methodologies applied in the medical domain. Therefore contextualising the scope of RAG approaches in healthcare.
- Provide an overview of evaluation methods, including metrics used to evaluate the performance of RAG pipelines.
- Discuss ethical concerns associated with RAG pipelines in critical sectors such as healthcare.
- Provide insights for future research directions in RAG-based applications.
2. Materials and Methods
Exclusion Criteria
- Review articles, including surveys, comprehensive reviews or systematic reviews.
- Papers for which the full text is not available.
- Short conference papers.
2.1. Search Technique
2.2. Study Selection
2.3. Data Extraction
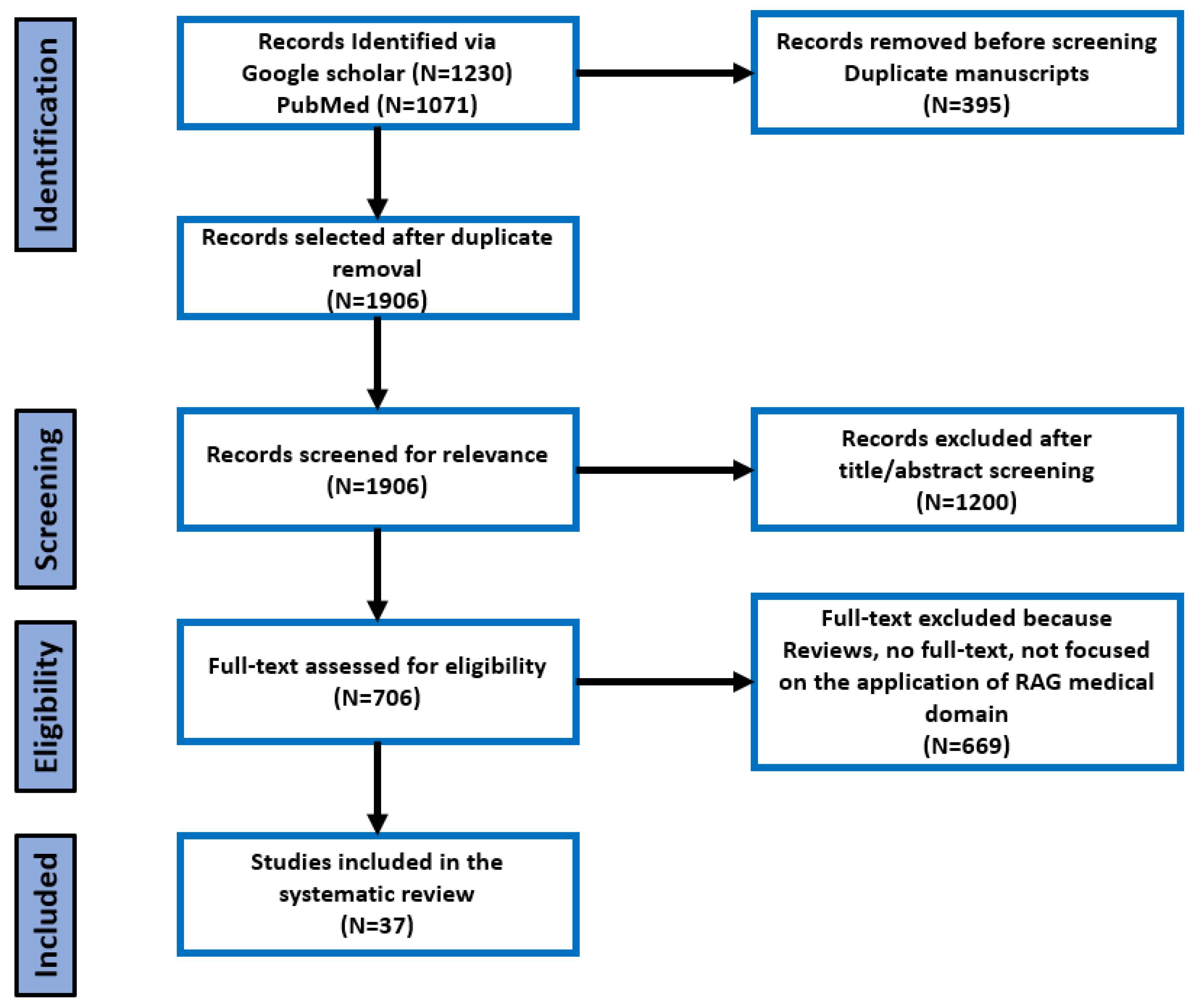
3. Results
3.1. Included Studies
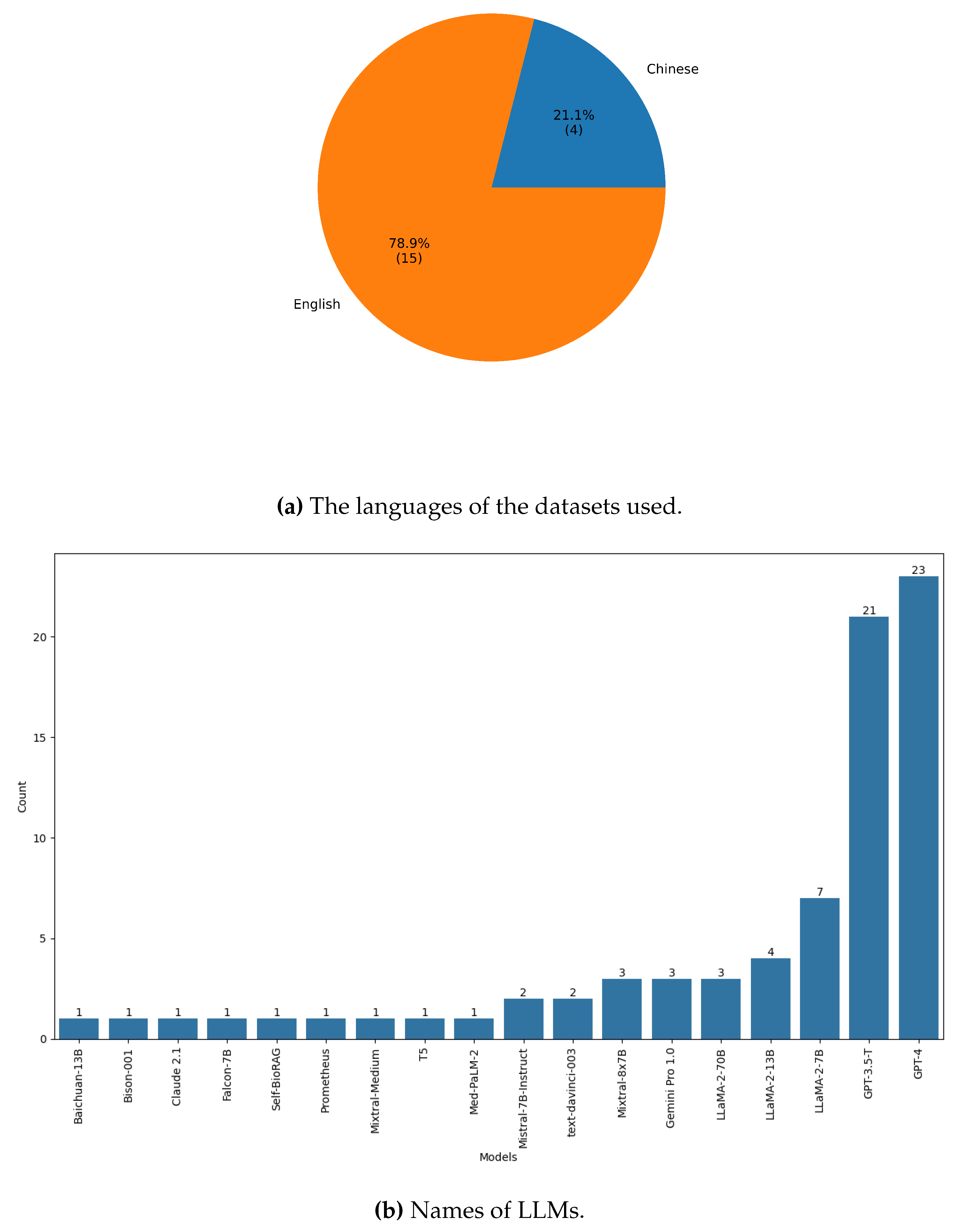
3.2. Datasets
| Category | Author | Domain | Dataset | #Q in Train | #label in train | #q in dev | #q in test | #instance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Question Answering |
Tsatsaronis et al. [30] | Biomedical | BioASQ | 3,743 | 35,285 | 497 | 15,559,157 | |
| Chen et al. [28] | Clinical | MedDialog | EN: 257,454 C: 1,145,231 |
|||||
| Liu et al. [29] | Gastointestinal | MedDG | 14,864 | - | 2,000 | 1,000 | ||
| Abacha et al. [31] | Biomedical | LiveQA | 634 | - | - | 104 | ||
| Zakka et al. [24] | Biomedical | ClinicalQA | 130 | |||||
| Lozano et al. [32] | Biomedical | PubMedRS-200 | 200 | |||||
| Jin et al. [33] | Biomedical | PubMedQA | 1,000 | 1,000 | ||||
| Jin et al. [34] | Biomedical | MedQA | USMLE 10,178 MCMLE 27,400 TWMLE 11,298 |
1272 3425 1412 |
1273 3426 1413 |
12,723 34,251 14,123 |
||
| Ma et al. [35] | Orthodontic | MD-QA | 59,642 | |||||
| Chen et al. [36] | 10 pediatric diseases | IMCS-21 | - | - | - | - | 4,116 | |
| Zeng[37] | Biomedical | MMCU-Medical | 2,819 | |||||
| Information Retrieval |
Boteva et al. [38] | Biomedical | NFCorpus | 5,922 | 110,575 | 24 | 323 | 3,633 |
| Roberts et al. [39] | COVID-19 | TREC- COVID-19 | - | - | - | - | ||
| Johnson et al. [40] | Radiology | MIMIC-CXR | - | - | - | - | Img: 377,110 Txt: 227,927 |
|
| Ramesh et al. [41] | Radiology | Adapted MIMIC-CXR | - | - | - | - | 226,759 |
3.3. RAG Overview
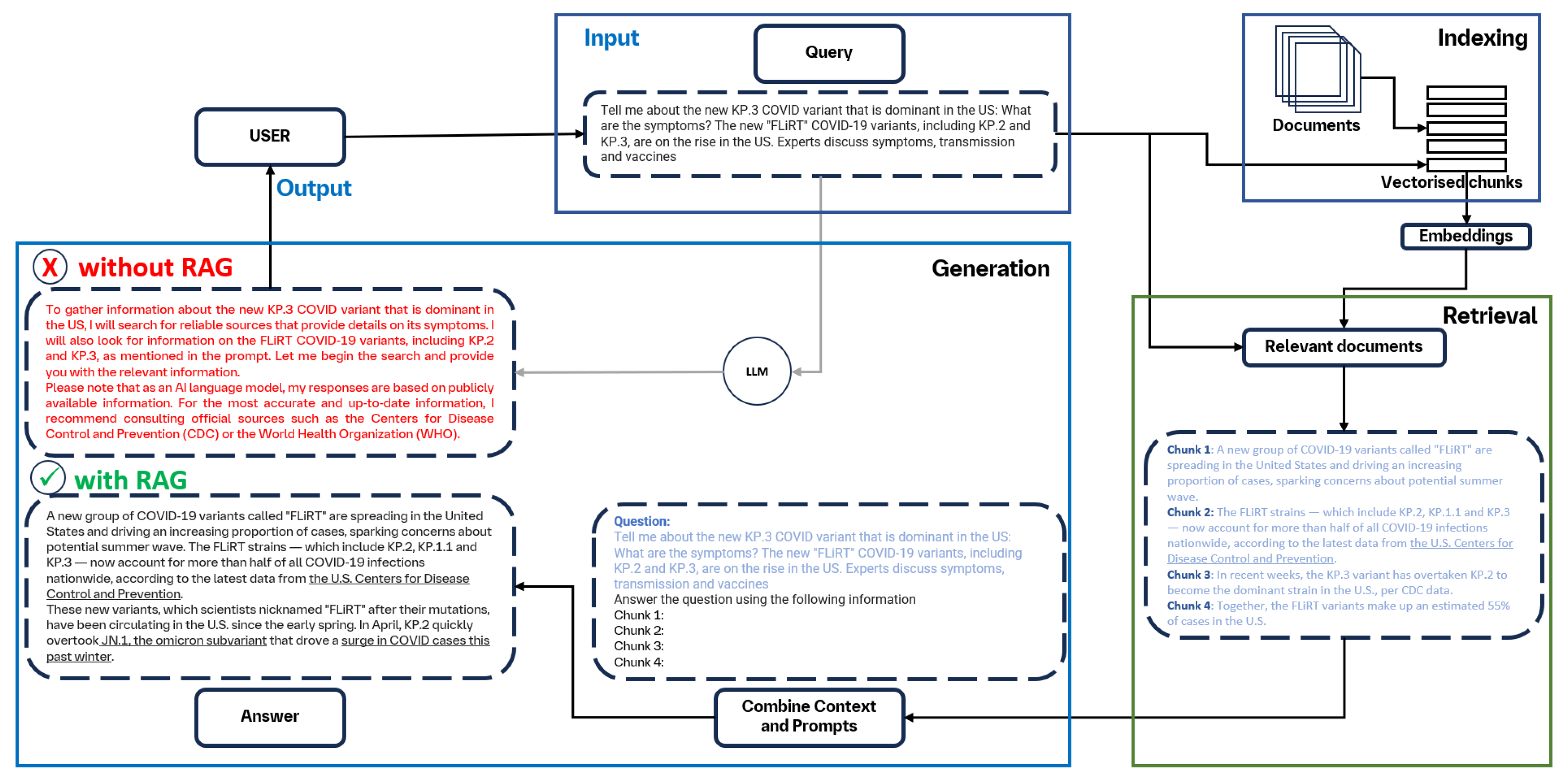
3.4. Naive RAG
| Authors | LLMs | Embedding | Pre-retrieval | Post-retrieval | Adv. Meth. | Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al Ghadban et al. [19] | GPT-4 | NA | Chunking | SS MMR |
One-shot learning. |
Acc: #141 (79%). Adeq: #49 (35%) Promising role RAG and LLMs in medical education. |
| Chen et al. [21] | GPT-4 | NA | OIS | SS | Zero-shot CoT |
Improved accuracy with RAG compared foundational models. |
| Chen et al. [22] | LLaMA-2-7B-chat | all-MiniLM -L6-v2 |
Chunking | SS | FT | FT+RAG provided best performance. |
| Gao et al. [51] | T5[52] GPT-3.5-T |
OIS KGs |
Path ranker. Aggregated |
Zero-shot with path prompts |
Improved diagnosis performance. | |
| Ge et al. [47] | GPT-3.5-T GPT-4 |
ada-002 | EDG | SS | Prompting strategy |
7/10 completely correct with RAG. |
| Guo et al. [42] | LLaMA-2 GPT-4 |
BERT | Alignment optimisation |
RR Summary |
RALL | Improved generation performance and interpretability. |
| Jeong et al. [23] | Self-BioRAG | Chunking | RR | Critic & LLMS Generator |
7.2% absolute improvement over SOTA with 7B or less. |
|
| Jiang et al. [53] | GPT-3.5 Baichuan13B-chat |
BGE[54] | OIS KGs |
RR | Query expansion CoK Noise filtering |
Superior performance with RAG. F1: 4.62% better than baseline. |
| Jin et al. [55] | GPT-3.5-T GPT-4 |
ada-002 | Chunking | SS | Integration with XGBoost |
F1: 0.762. Acc: 83.3%. RAG surpasses the performance traditional methods. |
| Kang et al. [56] | GPT-3.5-T GPT-4 |
None | Create TOC | Truncation Summary |
Use LLM for retrieval & generation |
Improved retrieval capabilities. Score: 5.5. |
| Ke et al. [57] | GPT-4 GPT-3.5-T LLaMA-2 7B LLaMA-2 13B |
ada-002 | EDG Chunking |
SS | Acc: 91.4%. RAG the performance comparable to human evaluators. Faster decision-making. |
|
| Li et al. [58] | LLaMA-7B | NA | EDG Chunking |
RR | FT + wikipedia retrieval |
RAG improved acc & efficiency F1 score: 0.84. Reduced workload. |
| Long et al. [48] | GPT-4 | ada-002 | Chunking | SS | Knowledge specific database |
Improved performance with RAG over base models. |
| Lozano et al. [32] | GPT-3.5-T GPT-4 |
NA | Relevance Classifier |
Synthesis Summary |
Online search |
Improvement with RAG over base models. |
| Manathunga & Illangasekara[59] |
GPT-3.5-T | ada-002 | Chunking | SS Summary |
Embedding visualisation |
Benefits of RAG in retrieving information quickly from large knowledge bases. |
| Markey et al. [60] | GPT-4 | NA | Chunking | SS | Online search. |
Potential for GenAI-powered clinical writing. |
| Miao et al. [61] | GPT-4 | FT + CoT | RAG provides specialised & accurate medical advice for nephrology practices |
|||
| Murugan et al. [62] | GPT-4 | ada-002 | MR | SS MMR |
Prompt engineering Guardrails |
Improvements with RAG. |
| Neupane et al. [63] | GPT-3.5-T Mistral-7B -Instruct |
ada-002 | Structured context. Chunking |
Contextual compression |
Online search |
Efficacy in generating relevant responses. GPT-3.5-T: 0.93 & Mistral-7B: 0.92. |
| Ong et al. [64] | GPT-4 Gemini Pro 1.0 Med-PaLM-2 |
ada-002 bgeSENv1.5[65] |
Manual indexing. Auto-merging retrieval. |
SS | LLM vs "copilot" |
RAG-LLM outperformed LLM alone. |
| Parmanto et al. [66] | LLaMA-2-7B Falcon-7B GPT 3.5-T |
BGE[54] | Chunking | SS | FT | RAG + FT best results. |
| Quidwai & | ||||||
| Lagana[67] | Mistral-7B -Instruct |
bgeSENv1.5 | Indexing Chunking |
SS | Pubmed dataset curation |
Improved accuracy over base models. |
| Ranjit et al. [68] | davinci-003 GPT-3.5-T GPT-4 |
ALBEF[69] | Compression | Coupling to vision model |
RAG achieved better outcomes BERTScore: 0.2865. Semb: 0.4026. |
|
| Rau et al. [70] | GPT-3.5-T GPT-4 |
ada-002 | Chunking | SS | Visual interface |
Superior performance with RAG. Time & cost savings. |
| Russe et al. [71] | GPT 3.5-T GPT-4 |
ada-002 | Chunking | SS | Prompting strategy |
Acc: GPT 3.5-T: 57% GPT-4: 83%. |
| Shi et al. [72] | GPT-3.5-T | MP-Net | Chunking MR |
SS | ReAct architecture | Improved performance with RAG over baseline models. |
| Soman et al. [73] | LLaMA-2-13B GPT-3.5-T GPT-4 |
PubMedBert MiniLM |
KGs | Similarity Context pruning. |
KG-RAG enhanced performance. | |
| Soong et al. [49] | Prometheus GPT-3.5-T GPT-4 |
ada-002 | Chunking | Summary | Improved performance with RAG over baseline models. |
|
| Thompson et al. [50] | Bison-001 | NA | Token splitter. Regex |
Map Reduce | Regex + LLM aggregation |
RAG-LLM outperformed rule-based method. F1: 0.75. |
| Unlu et al. [74] | GPT-4 | ada-002 | Adding metadata Chunking |
SS | Iterative prompting |
Potential to improve efficiency and reduce costs. Acc: 92.7%. |
| Vaid et al. [75] | GPT-3.5 GPT-4 Gemini Pro LLaMA-2-70B Mixtral-8x7B |
CoT prompting. Agents |
RAG with GPT-4 best performance. | |||
| Wang et al. [76] | LLaMA-2-13B GPT-3.5-T GPT-4 |
QO HR |
Knowledge self-refiner |
LLM-aided pre- and post-retrieval |
RAG outperform baseline models. | |
| Wang et al. [77] | LLaMA-2-7B LLaMA-2-13B |
ColBERT | QO | RR | JMLR | Demonstrate potential of joint IR & LLM training. |
| Wornow et al. [78] | GPT 3.5-T GPT-4 LLaMA-2-70B Mixtral-8x7B |
MiniLM BGE |
Chunking | SS | Compared zero-shot and retrieval. |
RAG with GPT-4 beats SOTA in zero-shot. |
| Yu, Guo and Sano[79] | LLaMA-2-7B LLaMA-2-7B GPT-3.5 |
ada-002 | Chunking | SS | Feature extraction from ECG |
RAG outperform few-shot approach. |
| Zakka et al. [24] | text-davinci-003 | ada-002 | Chunking | Similarity threshold |
Adversarial prompting |
RAG-LLM outperform ChatGPT. |
| Ziletti and D’Ambrosi[80] |
GPT-3.5-T GPT-4-T Gemini Pro 1.0 Claude 2.1 Mixtral-8x7B Mixtral-Medium |
bgeSENv1.5 | Entity masking |
SS EN |
Text-to-SQL | GPT-4-T best accuracy and executability. |
3.5. Advanced RAG
3.6. Modular RAG
3.7. Evaluation Metrics and Frameworks
3.8. Ethical Considerations
3.9. Data Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BERT | Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers |
| GPT | Generative Pre-trained Transformers |
| HyKGE | Hypothesis Knowledge Graph Enhanced |
| KGs | Knowledge Graphs |
| LLM | Large Language Models |
| RAG | Retrieval Augmented Generation |
| QA | Question answering |
| SOTA | State-of-the-art (SOTA) |
References
- Brown, T.B.; Mann, B.; Ryder, N.; Subbiah, M.; Kaplan, J.; Dhariwal, P.; Neelakantan, A.; Shyam, P.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; Agarwal, S.; Herbert-Voss, A.; Krueger, G.; Henighan, T.; Child, R.; Ramesh, A.; Ziegler, D.M.; Wu, J.; Winter, C.; Hesse, C.; Chen, M.; Sigler, E.; Litwin, M.; Gray, S.; Chess, B.; Clark, J.; Berner, C.; McCandlish, S.; Radford, A.; Sutskever, I.; Amodei, D. Language models are few-shot learners. Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems; Curran Associates Inc.: Red Hook, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- OpenAI. GPT-4 Technical Report, 2023, [arXiv:cs.CL/2303.08774]. arXiv:cs.CL/2303.08774].
- Touvron, H.; Martin, L.; Stone, K.; Albert, P.; Almahairi, A.; Babaei, Y.; Bashlykov, N.; Batra, S.; Bhargava, P.; Bhosale, S.; Bikel, D.; Blecher, L.; Ferrer, C.C.; Chen, M.; Cucurull, G.; Esiobu, D.; Fernandes, J.; Fu, J.; Fu, W.; Fuller, B.; Gao, C.; Goswami, V.; Goyal, N.; Hartshorn, A.; Hosseini, S.; Hou, R.; Inan, H.; Kardas, M.; Kerkez, V.; Khabsa, M.; Kloumann, I.; Korenev, A.; Koura, P.S.; Lachaux, M.A.; Lavril, T.; Lee, J.; Liskovich, D.; Lu, Y.; Mao, Y.; Martinet, X.; Mihaylov, T.; Mishra, P.; Molybog, I.; Nie, Y.; Poulton, A.; Reizenstein, J.; Rungta, R.; Saladi, K.; Schelten, A.; Silva, R.; Smith, E.M.; Subramanian, R.; Tan, X.E.; Tang, B.; Taylor, R.; Williams, A.; Kuan, J.X.; Xu, P.; Yan, Z.; Zarov, I.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, A.; Kambadur, M.; Narang, S.; Rodriguez, A.; Stojnic, R.; Edunov, S.; Scialom, T. Llama 2: Open Foundation and Fine-Tuned Chat Models, 2023, [arXiv:cs.CL/2307.09288]. O: 2, 2023; arXiv:cs.CL/2307.09288]. [Google Scholar]
- Gemini Team. Gemini: A Family of Highly Capable Multimodal Models, 2023, [arXiv:cs.CL/2312.11805].
- Pal, A.; Umapathi, L.K.; Sankarasubbu, M. Med-HALT: Medical Domain Hallucination Test for Large Language Models, 2023, [arXiv:cs.CL/2307.15343]. arXiv:cs.CL/2307.15343].
- Ji, Z.; Lee, N.; Frieske, R.; Yu, T.; Su, D.; Xu, Y.; Ishii, E.; Bang, Y.J.; Madotto, A.; Fung, P. Survey of Hallucination in Natural Language Generation. ACM Comput. Surv. 2023, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bubeck, S.; Chandrasekaran, V.; Eldan, R.; Gehrke, J.; Horvitz, E.; Kamar, E.; Lee, P.; Lee, Y.T.; Li, Y.; Lundberg, S.; Nori, H.; Palangi, H.; Ribeiro, M.T.; Zhang, Y. Sparks of Artificial General Intelligence: Early experiments with GPT-4, 2023, [arXiv:cs.CL/2303.12712]. E: of Artificial General Intelligence, 2023; -4, arXiv:cs.CL/2303.12712]. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Yoon, W.; Kim, S.; Kim, D.; Kim, S.; So, C.H.; Kang, J. BioBERT: a pre-trained biomedical language representation model for biomedical text mining. Bioinformatics 2019, 36, 1234–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsentzer, E.; Murphy, J.R.; Boag, W.; Weng, W.H.; Jin, D.; Naumann, T.; McDermott, M.B.A. Publicly Available Clinical BERT Embeddings, 2019, [arXiv:cs.CL/1904.03323]. arXiv:cs.CL/1904.03323].
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.W.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. BERT: Pre-training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding, 2019, [arXiv:cs.CL/1810.04805]. arXiv:cs.CL/1810.04805].
- Singhal, K.; Azizi, S.; Tu, T.; Mahdavi, S.S.; Wei, J.; Chung, H.W.; Scales, N.; Tanwani, A.; Cole-Lewis, H.; Pfohl, S.; Payne, P.; Seneviratne, M.; Gamble, P.; Kelly, C.; Babiker, A.; Schärli, N.; Chowdhery, A.; Mansfield, P.; Demner-Fushman, D.; Agüera y Arcas, B.; Webster, D.; Corrado, G.S.; Matias, Y.; Chou, K.; Gottweis, J.; Tomasev, N.; Liu, Y.; Rajkomar, A.; Barral, J.; Semturs, C.; Karthikesalingam, A.; Natarajan, V. Large language models encode clinical knowledge. Nature 2023, 620, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, P.; Perez, E.; Piktus, A.; Petroni, F.; Karpukhin, V.; Goyal, N.; Küttler, H.; Lewis, M.; tau Yih, W.; Rocktäschel, T.; Riedel, S.; Kiela, D. Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Knowledge-Intensive NLP Tasks, 2021. arXiv:cs.CL/2005.11401.
- Dong, Q.; Li, L.; Dai, D.; Zheng, C.; Wu, Z.; Chang, B.; Sun, X.; Xu, J.; Li, L.; Sui, Z. A Survey on In-context Learning, 2023, [arXiv:cs.CL/2301.00234]. arXiv:cs.CL/2301.00234].
- Das, S.; Saha, S.; Srihari, R.K. Diving Deep into Modes of Fact Hallucinations in Dialogue Systems, 2023, [arXiv:cs.CL/2301.04449]. arXiv:cs.CL/2301.04449].
- Wang, C.; Ong, J.; Wang, C.; Ong, H.; Cheng, R.; Ong, D. Potential for GPT Technology to Optimize Future Clinical Decision-Making Using Retrieval-Augmented Generation. Annals of Biomedical Engineering 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Gao, X.; Jia, K.; Pan, J.; Bi, Y.; Dai, Y.; Sun, J.; Guo, Q.; Wang, M.; Wang, H. Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Large Language Models: A Survey, 2024, [arXiv:cs.CL/2312.10997].
- Zhao, P.; Zhang, H.; Yu, Q.; Wang, Z.; Geng, Y.; Fu, F.; Yang, L.; Zhang, W.; Cui, B. Retrieval-Augmented Generation for AI-Generated Content: A Survey, 2024, [arXiv:cs.CV/2402.19473].
- Gao, L.; Ma, X.; Lin, J.; Callan, J. Precise Zero-Shot Dense Retrieval without Relevance Labels, 2022, [arXiv:cs.IR/2212.10496].
- Al Ghadban, Y.; Lu, H.Y.; Adavi, U.; Sharma, A.; Gara, S.; Das, N.; Kumar, B.; John, R.; Devarsetty, P.; Hirst, J. Transforming Healthcare Education: Harnessing Large Language Models for Frontline Health Worker Capacity Building using Retrieval-Augmented Generation, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Belyaeva, A.; Cosentino, J.; Hormozdiari, F.; Eswaran, K.; Shetty, S.; Corrado, G.; Carroll, A.; McLean, C.Y.; Furlotte, N.A. Multimodal LLMs for Health Grounded in Individual-Specific Data. Machine Learning for Multimodal Healthcare Data; Maier, A.K., Schnabel, J.A., Tiwari, P., Stegle, O., Eds.; Springer Nature Switzerland: Cham, 2024; pp. 86–102. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; You, M.; Wang, L.; Liu, W.; Fu, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhang, S.; Chen, G.; Li, K.; Li, J. Evaluating and Enhancing Large Language Models Performance in Domain-specific Medicine: Osteoarthritis Management with DocOA, 2024, [arXiv:cs.CL/2401.12998]. arXiv:cs.CL/2401.12998].
- Chen, X.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, W.; Xu, P.; Gao, L.; Xu, M.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y.; Shi, D.; He, M. EyeGPT: Ophthalmic Assistant with Large Language Models, 2024, [arXiv:cs.CL/2403.00840].
- Jeong, M.; Sohn, J.; Sung, M.; Kang, J. Improving Medical Reasoning through Retrieval and Self-Reflection with Retrieval-Augmented Large Language Models, 2024, [arXiv:cs.CL/2401.15269].
- Zakka, C.; Shad, R.; Chaurasia, A.; Dalal, A.R.; Kim, J.L.; Moor, M.; Fong, R.; Phillips, C.; Alexander, K.; Ashley, E.; Boyd, J.; Boyd, K.; Hirsch, K.; Langlotz, C.; Lee, R.; Melia, J.; Nelson, J.; Sallam, K.; Tullis, S.; Vogelsong, M.A.; Cunningham, J.P.; Hiesinger, W. Almanac — Retrieval-Augmented Language Models for Clinical Medicine. NEJM AI 2024, 1, AIoa2300068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liberati, A.; Altman, D.G.; Tetzlaff, J.; Mulrow, C.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Ioannidis, J.P.A.; Clarke, M.; Devereaux, P.J.; Kleijnen, J.; Moher, D. The PRISMA Statement for Reporting Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses of Studies That Evaluate Health Care Interventions: Explanation and Elaboration. PLOS Medicine 2009, 6, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefana, E.; Marciano, F.; Cocca, P.; Alberti, M. Predictive models to assess Oxygen Deficiency Hazard (ODH): A systematic review. Safety Science 2015, 75, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hambarde, K.A.; Proença, H. Information Retrieval: Recent Advances and Beyond. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 76581–76604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Ju, Z.; Dong, X.; Fang, H.; Wang, S.; Yang, Y.; Zeng, J.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, R.; Zhou, M.; Zhu, P.; Xie, P. MedDialog: a large-scale medical dialogue dataset. arXiv preprint arXiv:2004.03329, 2020; arXiv:2004.03329 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Tang, J.; Cheng, Y.; Li, W.; Zheng, Y.; Liang, X. MedDG: An Entity-Centric Medical Consultation Dataset for Entity-Aware Medical Dialogue Generation, 2022, [arXiv:cs.CL/2010.07497]. arXiv:cs.CL/2010.07497].
- Tsatsaronis, G.; Balikas, G.; Malakasiotis, P.; Partalas, I.; Zschunke, M.; Alvers, M.R.; Weissenborn, D.; Krithara, A.; Petridis, S.; Polychronopoulos, D.; Almirantis, Y.; Pavlopoulos, J.; Baskiotis, N.; Gallinari, P.; Artiéres, T.; Ngomo, A.C.N.; Heino, N.; Gaussier, E.; Barrio-Alvers, L.; Schroeder, M.; Androutsopoulos, I.; Paliouras, G. An overview of the BIOASQ large-scale biomedical semantic indexing and question answering competition. BMC Bioinformatics 2015, 16, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abacha, A.B.; Agichtein, E.; Pinter, Y.; Demner-Fushman, D. Overview of the Medical Question Answering Task at TREC 2017 LiveQA. Text Retrieval Conference, 2017.
- Lozano, A.; Fleming, S.L.; Chiang, C.C.; Shah, N. Clinfo.ai: An Open-Source Retrieval-Augmented Large Language Model System for Answering Medical Questions using Scientific Literature, 2023. arXiv:cs.IR/2310.16146].
- Jin, Q.; Dhingra, B.; Liu, Z.; Cohen, W.W.; Lu, X. PubMedQA: A Dataset for Biomedical Research Question Answering, 2019, [arXiv:cs.CL/1909.06146].
- Jin, D.; Pan, E.; Oufattole, N.; Weng, W.H.; Fang, H.; Szolovits, P. What Disease Does This Patient Have? A Large-Scale Open Domain Question Answering Dataset from Medical Exams. Applied Sciences 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Han, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, D. CephGPT-4: An Interactive Multimodal Cephalometric Measurement and Diagnostic System with Visual Large Language Model, 2023, [arXiv:cs.AI/2307.07518]. arXiv:cs.AI/2307.07518].
- Chen, W.; Li, Z.; Fang, H.; Yao, Q.; Zhong, C.; Hao, J.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, X.; Peng, J.; Wei, Z. A Benchmark for Automatic Medical Consultation System: Frameworks, Tasks and Datasets. Bioinformatics, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, H. Measuring Massive Multitask Chinese Understanding, 2023, [arXiv:cs.CL/2304.12986].
- Boteva, V.; Gholipour, D.; Sokolov, A.; Riezler, S. A Full-Text Learning to Rank Dataset for Medical Information Retrieval. Advances in Information Retrieval; Ferro, N., Crestani, F., Moens, M.F., Mothe, J., Silvestri, F., Di Nunzio, G.M., Hauff, C., Silvello, G., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2016; pp. 716–722. [Google Scholar]
- Roberts, K.; Alam, T.; Bedrick, S.; Demner-Fushman, D.; Lo, K.; Soboroff, I.; Voorhees, E.; Wang, L.L.; Hersh, W.R. TREC-COVID: rationale and structure of an information retrieval shared task for COVID-19. Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association 2020, 27, 1431–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, A.E.W.; Pollard, T.J.; Berkowitz, S.J.; Greenbaum, N.R.; Lungren, M.P.; Deng, C.y.; Mark, R.G.; Horng, S. MIMIC-CXR, a de-identified publicly available database of chest radiographs with free-text reports. Scientific Data 2019, 6, 317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramesh, V.; Chi, N.A.; Rajpurkar, P. Improving Radiology Report Generation Systems by Removing Hallucinated References to Non-existent Priors, 2022, [arXiv:cs.CL/2210.06340]. arXiv:cs.CL/2210.06340].
- Guo, Y.; Qiu, W.; Leroy, G.; Wang, S.; Cohen, T. Retrieval augmentation of large language models for lay language generation. Journal of Biomedical Informatics 2024, 149, 104580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, A.; Umapathi, L.K.; Sankarasubbu, M. MedMCQA: A Large-scale Multi-Subject Multi-Choice Dataset for Medical domain Question Answering. Proceedings of the Conference on Health, Inference, and Learning; Flores, G.; Chen, G.H.; Pollard, T.; Ho, J.C.; Naumann, T., Eds. PMLR, 2022, Vol. 174, Proceedings of Machine Learning Research, pp. 248–260.
- Ben Abacha, A.; Mrabet, Y.; Sharp, M.; Goodwin, T.; Shooshan, S.E.; Demner-Fushman, D. Bridging the Gap between Consumers’ Medication Questions and Trusted Answers. MEDINFO 2019, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Hendrycks, D.; Burns, C.; Basart, S.; Zou, A.; Mazeika, M.; Song, D.; Steinhardt, J. Measuring Massive Multitask Language Understanding, 2021, [arXiv:cs.CY/2009.03300].
- Xiong, G.; Jin, Q.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, A. Benchmarking Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Medicine, 2024, [arXiv:cs.CL/2402.13178].
- Ge, J.; Sun, S.; Owens, J.; Galvez, V.; Gologorskaya, O.; Lai, J.C.; Pletcher, M.J.; Lai, K. Development of a Liver Disease-Specific Large Language Model Chat Interface using Retrieval Augmented Generation. medRxiv, 2023; [https://www.medrxiv.org/content/early/2023/11/11/2023.11.10.23298364.full.pdf]. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, C.; Subburam, D.; Lowe, K.; dos Santos, A.; Zhang, J.; Saduka, N.; Horev, Y.; Su, T.; Cote, D.; Wright, E. ChatENT: Augmented Large Language Models for Expert Knowledge Retrieval in Otolaryngology - Head and Neck Surgery. medRxiv, 2023; [https://www.medrxiv.org/content/early/2023/08/21/2023.08.18.23294283.full.pdf]. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soong, D.; Sridhar, S.; Si, H.; Wagner, J.S.; Sá, A.C.C.; Yu, C.Y.; Karagoz, K.; Guan, M.; Hamadeh, H.; Higgs, B.W. Improving accuracy of GPT-3/4 results on biomedical data using a retrieval-augmented language model, 2023, [arXiv:cs.CL/2305.17116].
- Thompson, W.E.; Vidmar, D.M.; Freitas, J.K.D.; Pfeifer, J.M.; Fornwalt, B.K.; Chen, R.; Altay, G.; Manghnani, K.; Nelsen, A.C.; Morland, K.; Stumpe, M.C.; Miotto, R. Large Language Models with Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Zero-Shot Disease Phenotyping, 2023, [arXiv:cs.AI/2312.06457].
- Gao, Y.; Li, R.; Caskey, J.; Dligach, D.; Miller, T.; Churpek, M.M.; Afshar, M. Leveraging A Medical Knowledge Graph into Large Language Models for Diagnosis Prediction, 2023, [arXiv:cs.CL/2308.14321].
- Raffel, C.; Shazeer, N.; Roberts, A.; Lee, K.; Narang, S.; Matena, M.; Zhou, Y.; Li, W.; Liu, P.J. Exploring the Limits of Transfer Learning with a Unified Text-to-Text Transformer, 2023, [arXiv:cs.LG/1910.10683].
- Jiang, X.; Zhang, R.; Xu, Y.; Qiu, R.; Fang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Tang, J.; Ding, H.; Chu, X.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Y. Think and Retrieval: A Hypothesis Knowledge Graph Enhanced Medical Large Language Models, 2023, [arXiv:cs.CL/2312.15883].
- Xiao, S.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, P.; Muennighoff, N. C-Pack: Packaged Resources To Advance General Chinese Embedding, 2023, [arXiv:cs.CL/2309.07597].
- Jin, M.; Yu, Q.; Zhang, C.; Shu, D.; Zhu, S.; Du, M.; Zhang, Y.; Meng, Y. Health-LLM: Personalized Retrieval-Augmented Disease Prediction Model, 2024, [arXiv:cs.CL/2402.00746].
- Kang, B.; Kim, J.; Yun, T.R.; Kim, C.E. Prompt-RAG: Pioneering Vector Embedding-Free Retrieval-Augmented Generation in Niche Domains, Exemplified by Korean Medicine, 2024, [arXiv:cs.CL/2401.11246].
- Ke, Y.; Jin, L.; Elangovan, K.; Abdullah, H.R.; Liu, N.; Sia, A.T.H.; Soh, C.R.; Tung, J.Y.M.; Ong, J.C.L.; Ting, D.S.W. Development and Testing of Retrieval Augmented Generation in Large Language Models – A Case Study Report, 2024, [arXiv:cs.CL/2402.01733].
- Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, K.; Dan, R.; Jiang, S.; Zhang, Y. ChatDoctor: A Medical Chat Model Fine-Tuned on a Large Language Model Meta-AI (LLaMA) Using Medical Domain Knowledge, 2023, [arXiv:cs.CL/2303.14070].
- Manathunga, S.S.; Illangasekara, Y.A. Retrieval Augmented Generation and Representative Vector Summarization for large unstructured textual data in Medical Education, 2023, [arXiv:cs.CL/2308.00479].
- Markey, N.; El-Mansouri, I.; Rensonnet, G.; van Langen, C.; Meier, C. From RAGs to riches: Using large language models to write documents for clinical trials, 2024, [arXiv:cs.CL/2402.16406].
- Miao, J.; Thongprayoon, C.; Suppadungsuk, S.; Garcia Valencia, O.A.; Cheungpasitporn, W. Integrating Retrieval-Augmented Generation with Large Language Models in Nephrology: Advancing Practical Applications. Medicina 2024, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugan, M.; Yuan, B.; Venner, E.; Ballantyne, C.M.; Robinson, K.M.; Coons, J.C.; Wang, L.; Empey, P.E.; Gibbs, R.A. Empowering personalized pharmacogenomics with generative AI solutions. Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association, /, 2024; ocae039[https://academic.oup.com/jamia/advance-article-pdf/doi/10.1093/jamia/ocae039/56880048/ocae039.pdf]. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neupane, S.; Mitra, S.; Mittal, S.; Golilarz, N.A.; Rahimi, S.; Amirlatifi, A. MedInsight: A Multi-Source Context Augmentation Framework for Generating Patient-Centric Medical Responses using Large Language Models, 2024, [arXiv:cs.CL/2403.08607].
- Ong, J.C.L.; Jin, L.; Elangovan, K.; Lim, G.Y.S.; Lim, D.Y.Z.; Sng, G.G.R.; Ke, Y.; Tung, J.Y.M.; Zhong, R.J.; Koh, C.M.Y.; Lee, K.Z.H.; Chen, X.; Chng, J.K.; Than, A.; Goh, K.J.; Ting, D.S.W. Development and Testing of a Novel Large Language Model-Based Clinical Decision Support Systems for Medication Safety in 12 Clinical Specialties, 2024, [arXiv:cs.CL/2402.01741].
- Chen, J.; Xiao, S.; Zhang, P.; Luo, K.; Lian, D.; Liu, Z. BGE M3-Embedding: Multi-Lingual, Multi-Functionality, Multi-Granularity Text Embeddings Through Self-Knowledge Distillation, 2024, [arXiv:cs.CL/2402.03216]. arXiv:cs.CL/2402.03216].
- Parmanto, B.; Aryoyudanta, B.; Soekinto, W.; Setiawan, I.M.A.; Wang, Y.; Hu, H.; Saptono, A.; Choi, Y.K. Development of a Reliable and Accessible Caregiving Language Model (CaLM), 2024, [arXiv:cs.CL/2403.06857].
- Quidwai, M.A.; Lagana, A. A RAG Chatbot for Precision Medicine of Multiple Myeloma. medRxiv, 2024; [https://www.medrxiv.org/content/early/2024/03/18/2024.03.14.24304293.full.pdf]. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjit, M.; Ganapathy, G.; Manuel, R.; Ganu, T. Retrieval Augmented Chest X-Ray Report Generation using OpenAI GPT models, 2023, [arXiv:cs.CL/2305.03660].
- Li, J.; Selvaraju, R.R.; Gotmare, A.D.; Joty, S.; Xiong, C.; Hoi, S. V: before Fuse, 2021; arXiv:cs.CV/2107.07651].
- Rau, A.; Rau, S.; Zöller, D.; Fink, A.; Tran, H.; Wilpert, C.; Nattenmüller, J.; Neubauer, J.; Bamberg, F.; Reisert, M.; Russe, M.F. A Context-based Chatbot Surpasses Radiologists and Generic ChatGPT in Following the ACR Appropriateness Guidelines. Radiology 2023, 308, e230970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russe, M.F.; Fink, A.; Ngo, H.; Tran, H.; Bamberg, F.; Reisert, M.; Rau, A. Performance of ChatGPT, human radiologists, and context-aware ChatGPT in identifying AO codes from radiology reports. Scientific Reports 2023, 13, 14215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, W.; Zhuang, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Iwinski, H.; Wattenbarger, M.; Wang, M.D. Retrieval-Augmented Large Language Models for Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis Patients in Shared Decision-Making. Proceedings of the 14th ACM International Conference on Bioinformatics, Computational Biology, and Health Informatics; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soman, K.; Rose, P.W.; Morris, J.H.; Akbas, R.E.; Smith, B.; Peetoom, B.; Villouta-Reyes, C.; Cerono, G.; Shi, Y.; Rizk-Jackson, A.; Israni, S.; Nelson, C.A.; Huang, S.; Baranzini, S.E. Biomedical knowledge graph-enhanced prompt generation for large language models, 2023, [arXiv:cs.CL/2311.17330].
- Unlu, O.; Shin, J.; Mailly, C.J.; Oates, M.F.; Tucci, M.R.; Varugheese, M.; Wagholikar, K.; Wang, F.; Scirica, B.M.; Blood, A.J.; Aronson, S.J. Retrieval Augmented Generation Enabled Generative Pre-Trained Transformer 4 (GPT-4) Performance for Clinical Trial Screening. medRxiv, 2024; [https://www.medrxiv.org/content/early/2024/02/08/2024.02.08.24302376.full.pdf]. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaid, A.; Lampert, J.; Lee, J.; Sawant, A.; Apakama, D.; Sakhuja, A.; Soroush, A.; Lee, D.; Landi, I.; Bussola, N.; Nabeel, I.; Freeman, R.; Kovatch, P.; Carr, B.; Glicksberg, B.; Argulian, E.; Lerakis, S.; Kraft, M.; Charney, A.; Nadkarni, G. Generative Large Language Models are autonomous practitioners of evidence-based medicine, 2024, [arXiv:cs.AI/2401.02851].
- Wang, Y.; Ma, X.; Chen, W. Augmenting Black-box LLMs with Medical Textbooks for Clinical Question Answering, 2023, [arXiv:cs.CL/2309.02233].
- Wang, J.; Yang, Z.; Yao, Z.; Yu, H. JMLR: Joint Medical LLM and Retrieval Training for Enhancing Reasoning and Professional Question Answering Capability, 2024, [arXiv:cs.CL/2402.17887].
- Wornow, M.; Lozano, A.; Dash, D.; Jindal, J.; Mahaffey, K.W.; Shah, N.H. Zero-Shot Clinical Trial Patient Matching with LLMs, 2024, [arXiv:cs.CL/2402.05125].
- Yu, H.; Guo, P.; Sano, A. Zero-Shot ECG Diagnosis with Large Language Models and Retrieval-Augmented Generation. Proceedings of the 3rd Machine Learning for Health Symposium; Hegselmann, S.; Parziale, A.; Shanmugam, D.; Tang, S.; Asiedu, M.N.; Chang, S.; Hartvigsen, T.; Singh, H., Eds. PMLR, 2023, Vol. 225, Proceedings of Machine Learning Research, pp. 650–663.
- Ziletti, A.; D’Ambrosi, L. Retrieval augmented text-to-SQL generation for epidemiological question answering using electronic health records, 2024, [arXiv:cs.CL/2403.09226].
- Team, L.D. LlamaIndex: A Framework for Context-Augmented LLM Applications, 2024.
- Team, L.D. Langchain: A framework for developing applications powered by large language models, 2024.
- Cuconasu, F.; Trappolini, G.; Siciliano, F.; Filice, S.; Campagnano, C.; Maarek, Y.; Tonellotto, N.; Silvestri, F. The Power of Noise: Redefining Retrieval for RAG Systems, 2024, [arXiv:cs.IR/2401.14887]. R.
- Yang, R.; Marrese-Taylor, E.; Ke, Y.; Cheng, L.; Chen, Q.; Li, I. Integrating UMLS Knowledge into Large Language Models for Medical Question Answering, 2023, [arXiv:cs.CL/2310.02778].
- Varshney, D.; Zafar, A.; Behera, N.K.; Ekbal, A. Knowledge graph assisted end-to-end medical dialog generation. Artificial Intelligence in Medicine 2023, 139, 102535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varshney, D.; Zafar, A.; Behera, N.K.; Ekbal, A. Knowledge grounded medical dialogue generation using augmented graphs. Scientific Reports 2023, 13, 3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, J.H.; Soman, K.; Akbas, R.E.; Zhou, X.; Smith, B.; Meng, E.C.; Huang, C.C.; Cerono, G.; Schenk, G.; Rizk-Jackson, A.; Harroud, A.; Sanders, L.; Costes, S.V.; Bharat, K.; Chakraborty, A.; Pico, A.R.; Mardirossian, T.; Keiser, M.; Tang, A.; Hardi, J.; Shi, Y.; Musen, M.; Israni, S.; Huang, S.; Rose, P.W.; Nelson, C.A.; Baranzini, S.E. The scalable precision medicine open knowledge engine (SPOKE): a massive knowledge graph of biomedical information. Bioinformatics 2023, 39, btad080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Q.; Wang, Z.; Floudas, C.S.; Sun, J.; Lu, Z. Matching Patients to Clinical Trials with Large Language Models, 2023, [arXiv:cs.CL/2307.15051].
- Douze, M.; Guzhva, A.; Deng, C.; Johnson, J.; Szilvasy, G.; Mazaré, P.E.; Lomeli, M.; Hosseini, L.; Jégou, H. The Faiss library, 2024, [arXiv:cs.LG/2401.08281].
- Lin, X.V.; Chen, X.; Chen, M.; Shi, W.; Lomeli, M.; James, R.; Rodriguez, P.; Kahn, J.; Szilvasy, G.; Lewis, M.; Zettlemoyer, L.; Yih, S. RA-DIT: Retrieval-Augmented Dual Instruction Tuning, 2023, [arXiv:cs.CL/2310.01352].
- Chen, T.; Guestrin, C. Xgboost: A scalable tree boosting system. Proceedings of the 22nd acm sigkdd international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining, 2016, pp. 785–794.
- Luo, L.; Li, Y.F.; Haffari, G.; Pan, S. Reasoning on Graphs: Faithful and Interpretable Large Language Model Reasoning, 2024, [arXiv:cs.CL/2310.01061]. arXiv:cs.CL/2310.01061].
- Hong, S.; Zhuge, M.; Chen, J.; Zheng, X.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Yau, S.K.S.; Lin, Z.; Zhou, L.; Ran, C.; Xiao, L.; Wu, C.; Schmidhuber, J. 2023; arXiv:cs.AI/2308.00352].
- Weng, L. LLM-powered Autonomous Agents. lilianweng.github.io 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Es, S.; James, J.; Espinosa-Anke, L.; Schockaert, S. RAGAS: Automated Evaluation of Retrieval Augmented Generation, 2023, [arXiv:cs.CL/2309.15217].
- Team, C.E.D. Continuous Eval: an open-source package created for granular and holistic evaluation of GenAI application pipelines, 2024.
- Team, T.D. TruLens: Evaluate and Track LLM Applications, 2024.
- Team, D.D. DeepEval: the open-source LLM evaluation framework, 2024.
- Liu, Y.; Ott, M.; Goyal, N.; Du, J.; Joshi, M.; Chen, D.; Levy, O.; Lewis, M.; Zettlemoyer, L.; Stoyanov, V. RoBERTa: A Robustly Optimized BERT Pretraining Approach, 2019, [arXiv:cs.CL/1907.11692].
- Steinbock, B. The Oxford Handbook of Bioethics; Oxford University Press, 2009. [CrossRef]
- Carlini, N.; Ippolito, D.; Jagielski, M.; Lee, K.; Tramer, F.; Zhang, C. Quantifying Memorization Across Neural Language Models, 2023, [arXiv:cs.LG/2202.07646].
- Zhang, C.; Ippolito, D.; Lee, K.; Jagielski, M.; Tramèr, F.; Carlini, N. Counterfactual Memorization in Neural Language Models. 2023; arXiv:cs.CL/2112.12938. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Le, T.; Chen, J.; Lee, D. Do Language Models Plagiarize? Proceedings of the ACM Web Conference 2023; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, S.; Zhang, J.; He, P.; Xing, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xu, H.; Ren, J.; Wang, S.; Yin, D.; Chang, Y.; Tang, J. The Good and The Bad: Exploring Privacy Issues in Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG). 2024; arXiv:cs.CR/2402.16893. [Google Scholar]
- Vassilev, A.; Oprea, A.; Fordyce, A.; Anderson, H. Adversarial machine learning: A taxonomy and terminology of attacks and mitigations. Technical report, National Institute of Standards and Technology, 2024.
- Wu, S.; Koo, M.; Blum, L.; Black, A.; Kao, L.; Fei, Z.; Scalzo, F.; Kurtz, I. Benchmarking Open-Source Large Language Models, GPT-4 and Claude 2 on Multiple-Choice Questions in Nephrology. NEJM AI 2024, 1, AIdbp2300092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, R.; Sanders, T.; Weng, L.; Neelakantan, A. New and improved embedding model, Dec. 15, 2022.
- Amugongo, L.M.; Bidwell, N.J.; Corrigan, C.C. Invigorating Ubuntu Ethics in AI for healthcare: Enabling equitable care. Proceedings of the 2023 ACM Conference on Fairness, Accountability, and Transparency; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergman, A.S.; Hendricks, L.A.; Rauh, M.; Wu, B.; Agnew, W.; Kunesch, M.; Duan, I.; Gabriel, I.; Isaac, W. Representation in AI Evaluations. Proceedings of the 2023 ACM Conference on Fairness, Accountability, and Transparency; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Yang, Y. MultiHop-RAG: Benchmarking Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Multi-Hop Queries. 2024; arXiv:cs.CL/2401.15391. [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin, T.R.; Demner-Fushman, D. Clinical Language Understanding Evaluation (CLUE). 2022; arXiv:cs.CL/2209.14377. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, M.A.; Yaramis, I.; Roy, T.D. Creating Trustworthy LLMs: Dealing with Hallucinations in Healthcare AI. 2023; arXiv:cs.CL/2311.01463. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Xu, S.; Shum, K.; Niu, C.; Zhong, R.; Song, J.; Zhang, T. RAGTruth: A Hallucination Corpus for Developing Trustworthy Retrieval-Augmented Language Models. 2023; arXiv:cs.CL/2401.00396. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, A.; Dao, T. Mamba: Linear-Time Sequence Modeling with Selective State Spaces. 2023; arXiv:cs.LG/2312.00752. [Google Scholar]
- Gemini Team, G. Gemini 1.5: Unlocking multimodal understanding across millions of tokens of context. https://storage.googleapis.com/deepmind-media/gemini/gemini_v1_5_report.pdf, 2024. [Accessed 26-02-2024].
- Wu, K.; Wu, E.; Cassasola, A.; Zhang, A.; Wei, K.; Nguyen, T.; Riantawan, S.; Riantawan, P.S.; Ho, D.E.; Zou, J. How well do LLMs cite relevant medical references? An evaluation framework and analyses. 2024; arXiv:cs.CL/2402.02008. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Li, J.; Ma, W.; Liu, Y. Citation-Enhanced Generation for LLM-based Chatbots. 2024; arXiv:cs.CL/2402.16063. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Hu, T.; Zhang, Y.; Gai, X.; Feng, Y.; Liu, Z. A ChatGPT Aided Explainable Framework for Zero-Shot Medical Image Diagnosis. 2023; arXiv:eess.IV/2307.01981. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Ren, C.; Xie, S.; Liu, S.; Ji, H.; Wang, Z.; Sun, T.; He, L.; Li, Z.; Zhu, X.; Pan, C. 2024; arXiv:cs.AI/2402.07016].
- Amugongo, L.M.; Kriebitz, A.; Boch, A.; Lütge, C. Operationalising AI ethics through the agile software development lifecycle: a case study of AI-enabled mobile health applications. AI and Ethics 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucci, V.; Saary, J.; Doyle, T.E. Factors influencing trust in medical artificial intelligence for healthcare professionals: a narrative review. Journal of Medical Artificial Intelligence 2021, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amugongo, L.M.; Kriebitz, A.; Boch, A.; Lütge, C. Mobile Computer Vision-Based Applications for Food Recognition and Volume and Calorific Estimation: A Systematic Review. Healthcare 2023, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Criteria | Definition |
|---|---|
| Languages of articles | English |
| Years of publication | 2020 - 2024 |
| Solutions considered | • Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) |
| • Large Language Models (LLMs) |
| Database | Search keywords |
|---|---|
| PubMed | (large language models OR LLMs OR "transformer models" OR "Generative AI") AND (healthcare OR medicine OR medical) AND (retrieval OR augmented OR generation OR grounded) |
| Google Scholar | ("Large Language Models" OR LLMs OR Transformer Models" OR "Generative Models") AND (Retrieval-Augmented Generation OR grounding) AND (healthcare OR medical OR medicine) |
| Ethical Issues | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Author |
Accuracy (Correctness) |
Complete |
Faithfulness (Consistency) |
Fluency | Relevance |
Verify Source |
Privacy | Safety | Robust | Bias | Trust | Eval |
| Al Ghadban et al. [19] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | Auto |
| Chen et al. [21] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | Man |
| Chen et al. [22] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | Man |
| Ge et al. [47] | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | Man |
| Guo et al. [42] | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | Both |
| Jin et al. [88] | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | Man |
| Jin et al. [55] | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | Auto |
| Kang et al. [56] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | Man |
| Ke et al. [57] | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | Man |
| Li et al. [58] | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | Auto |
| Long et al. [48] | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | Man |
| Lozano et al. [32] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | Auto |
| Muragan et al. [62] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | Man |
| Neupane et al. [63] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | Auto |
| Parmanto et al. [66] | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | Both |
| Ranjit et al. [68] | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | Auto |
| Rau et al. [70] | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | Auto |
| Russe et al. [71] | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | Auto |
| Shi et al. [72] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | Man |
| Soong et al. [49] | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | Man |
| Thompson et al. [50] | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | Auto |
| Unlu et al. [74] | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | Auto |
| Vaid et al. [75] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | Man |
| Wang et al. [76] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | Auto |
| Wornow et al. [78] | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | Auto |
| Yu, Guo and Sana[79] | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | Auto |
| Zekka et al. [24] | ✓ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✓ | ✗ | ✗ | ✗ | Man |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




