1. Introduction
Deep salt mines serve as excellent geological structures for the underground storage of energy [
1]. Globally, hundreds of salt rock storage reservoirs have been constructed. In China, notable examples include the Jintan salt cavern gas storage, the Jintan salt cavern compressed air energy storage, and the Jianghan salt savern gas storage [
2]. While completed salt cavern gas storage reservoirs both domestically and internationally are typically constructed in high-grade salt mines, most salt mines in China are characterized by low-grade, high-impurity salt with numerous interlayers [
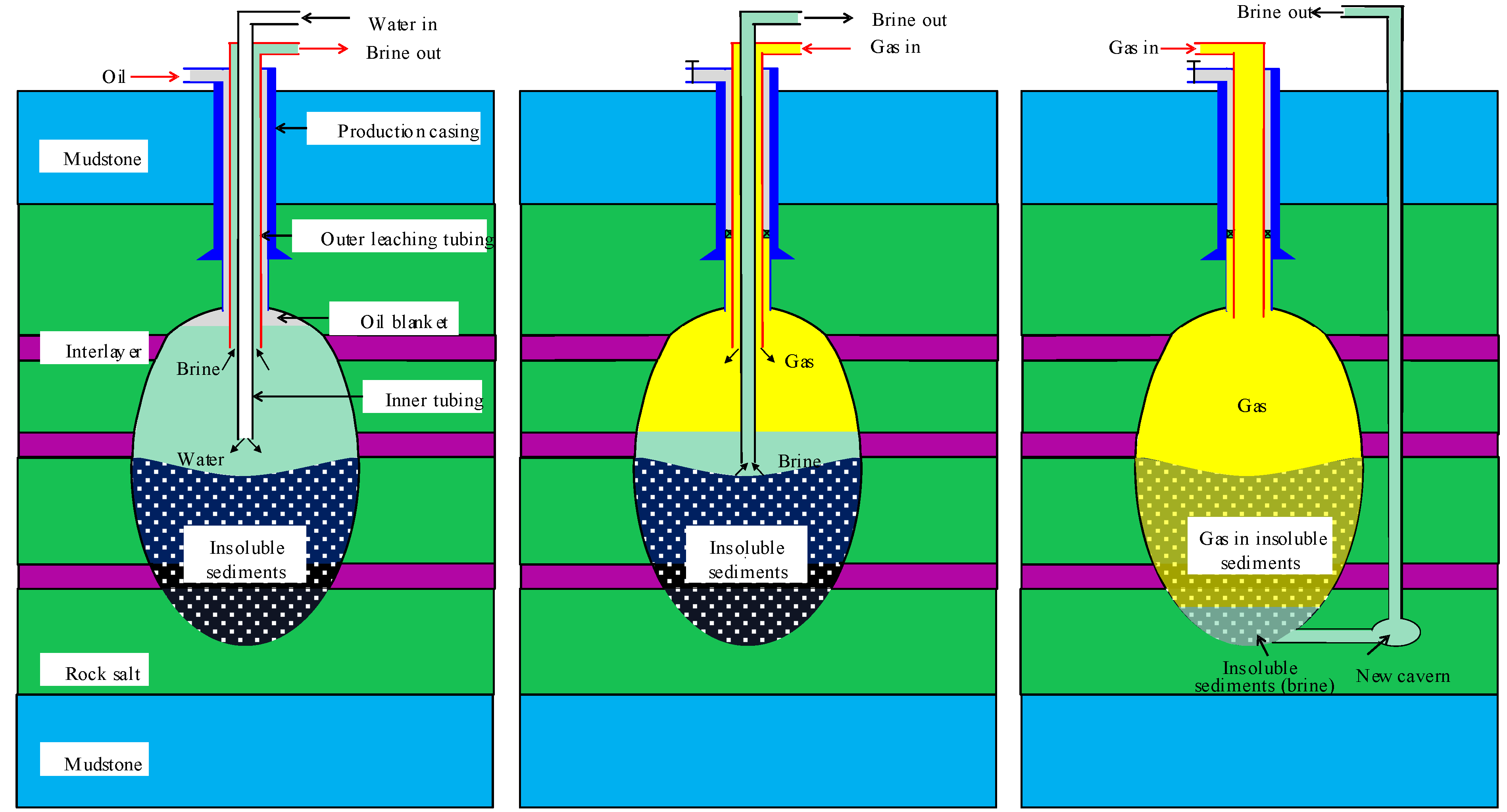
3]. In high-impurity salt mines, the traditional water-soluble cavern technology for salt cavern gas storage results in a significant accumulation of sediment at the cavern's bottom [
4]. This, in turn, limits the formation of a large-scale gas storage reservoir after the injection of gas brine, leading to a low rate of salt dissolution and poor economic feasibility for reservoir construction (
Figure 1). Advances in salt cavern gas storage technology suggest that sediment void gas storage may resolve this issue [
5]. The cavern formed by water-soluble mining in high-impurity layered salt rock contains numerous interlayers and insoluble particles. Fragmentation and expansion of these particles create voids larger than typical rock or soil pore spaces, allowing brine and fine particles to be transported within the sediment voids [
6]. During the long-term operation of salt cavern gas storage, the cavern experiences creep contraction. This leads to the extrusion and reduction of voids by the surrounding rock. The greater the deviatoric stress between the cavern and the surrounding rock, the more pronounced the contraction. However, as void compression decreases, support from the peripheral rock's sediment particles increases, eventually reaching equilibrium without the sediment pile compacting into a solid body [
7].
Salt cavern gas storage is a critical facility for natural gas storage, and the long-term stability of the salt cavern is essential for its safe operation. Recently, numerical simulation technology has been pivotal in stability analysis [
9], design optimization [
10], and risk assessment of salt cavern gas storage reservoirs [
11]. Chen et al. [
12] utilized ABAQUS software's numerical simulation results to investigate the feasibility of converting abandoned salt caverns into underground natural gas storage reservoirs. Liu et al. [
13] analyzed the impact of various cavern morphologies on the deformation characteristics of salt cavern gas storage reservoirs through numerical simulation, providing a foundation for the safety analysis of salt cavern storage reservoir groups. Zhao et al. [
14] evaluated the feasibility of constructing a salt cavern gas storage reservoir at a depth of over 2700 meters in Ningjin Salt Mine, providing key parameters such as optimal cavern morphology, dimensions, and operating pressure. Besides numerical simulation studies on salt cavern stability, related research also addresses the impact of sedimentation on the morphology of salt cavern gas storage reservoirs. Li et al. [
15] examined the influence of insoluble matter on cavern morphology during the water-soluble cavern creation in high-impurity salt rocks, derived the accumulation equation of insoluble matter, and integrated it into software to simulate the water-soluble cavern creation in high-impurity salt mines. Xue et al. [
16] analyzed the causes of twelve irregular salt cavities in China, identifying geological factors, construction technology, and pipeline damage as three key influencing factors. Currently, the impact of sedimentation on salt cavern stability is rarely considered during the long-term operation of salt cavern gas storage reservoirs, and detailed studies on the accumulation characteristics of sediment particles are lacking. Therefore, it is crucial to conduct research on the long-term mechanical behavior of sediment-type salt cavern gas storage reservoirs
To address this, a study on the coupling effect between sediment particles and the surrounding rocks of the cavern is conducted to analyze the influence of the sediment accumulator on the long-term operational stability of the salt cavern gas storage reservoir. The built-in PFC module in the software FLAC is utilized to establish a continuous-discontinuous medium coupling model to study the effects of sediment accumulation height, particle gradation, and operating pressure on the volumetric shrinkage rate of the cavern and the deformation of the surrounding rock. This aims to provide a reference for evaluating the long-term stability of high-impurity sediment-type salt cavern gas storage reservoirs.
2. Numerical Model
2.1. Continuous-Discontinuous Coupling Theory
FLAC is a numerical analysis method used to simulate the mechanical behavior of materials in continuous media, based on the explicit finite difference method. It is widely used in studying salt cavern stability [
17], tightness [
18], and intrinsic models of salt rock creep [
19]. PFC is a numerical analysis tool designed to study the fine-scale mechanical response of particles, providing data that is challenging to obtain through experimentation. It plays a significant role in studying the mechanical properties [
20] and fatigue creep [
21] of salt rock. Sediment accumulation consists of numerous insoluble particles that undergo significant deformation under compressive loading [
22]. Conventional continuous medium research methods struggle to characterize these deformation properties. Thus, the simulation and computation advantages of both FLAC and PFC can be utilized to analyze the long-term support effect of sediment on surrounding rock.
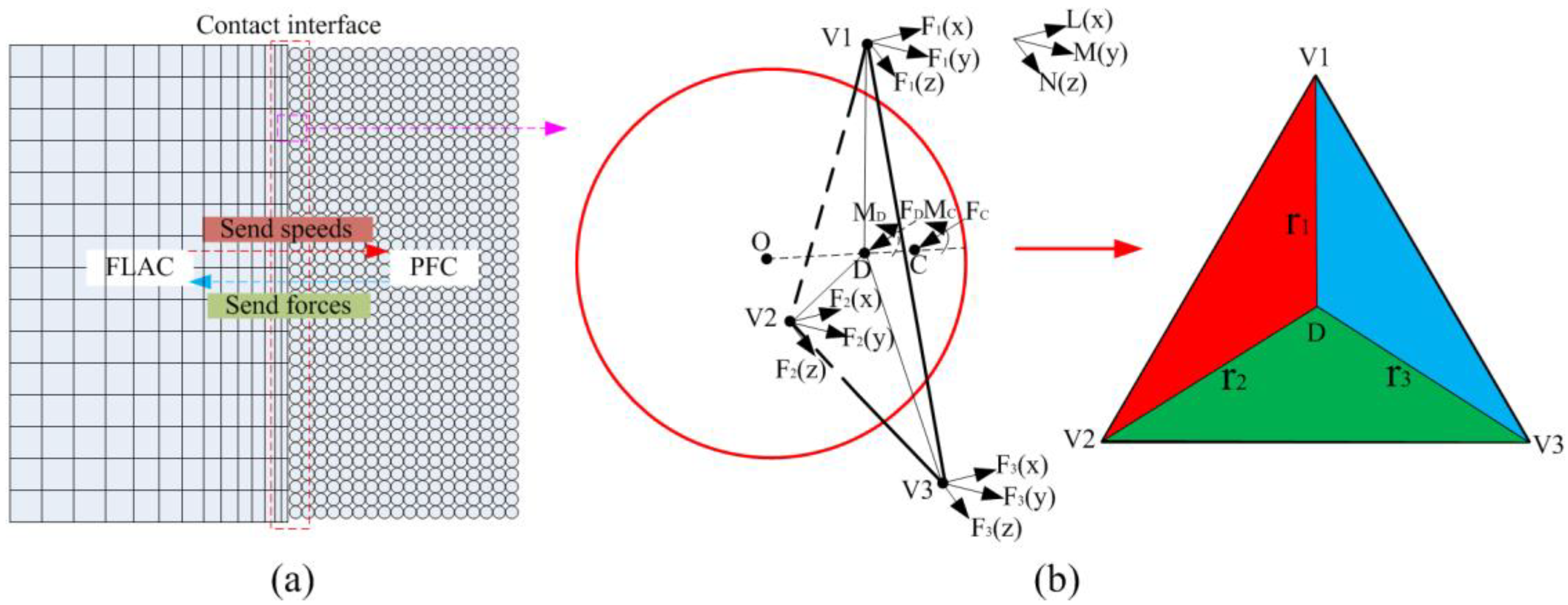
To enable interaction between PFC particles and FLAC, a coupled computing scheme must be established at the contact surface to transfer velocity and force information, facilitating information exchange between discrete particles and continuous elements. The coupled computing principle of PFC particles and FLAC (
Figure 2) involves transferring velocity information from the continuous media to the discontinuous medium through the contact surface, while the discontinuous medium transfers force information by altering displacement to the continuous medium. Force transfer on the contact surface is achieved by decomposing the force into triangular vertex on the contact surface using the coordinates of the contact particle centers. Velocity and displacement information is transferred through the triangular vertice as a function of computational time. Interaction occurs through the transfer of force and displacement information via contact forces and moments on the vertex of the triangular vertex. For coupling calculations, the contact surface is a PFC wall composed of triangles, with vertex velocities related to position and computation time. Contact forces and moments applied to the contact surfaces are converted to vertice velocities on the triangular surfaces using the equivalence method. On the continuous-discontinuous contact surface, the contact forces and moments are balanced using the following expression:
where
is the contact position,
is the closest point on the wall facet,
is the triangular vertice,
is the distance between the triangle vertice and the closest point,
and
are the moment and contact force at the contact point,
is the force applied at the vertex; and
is the cross product.
2.2. Numerical Simulation Model
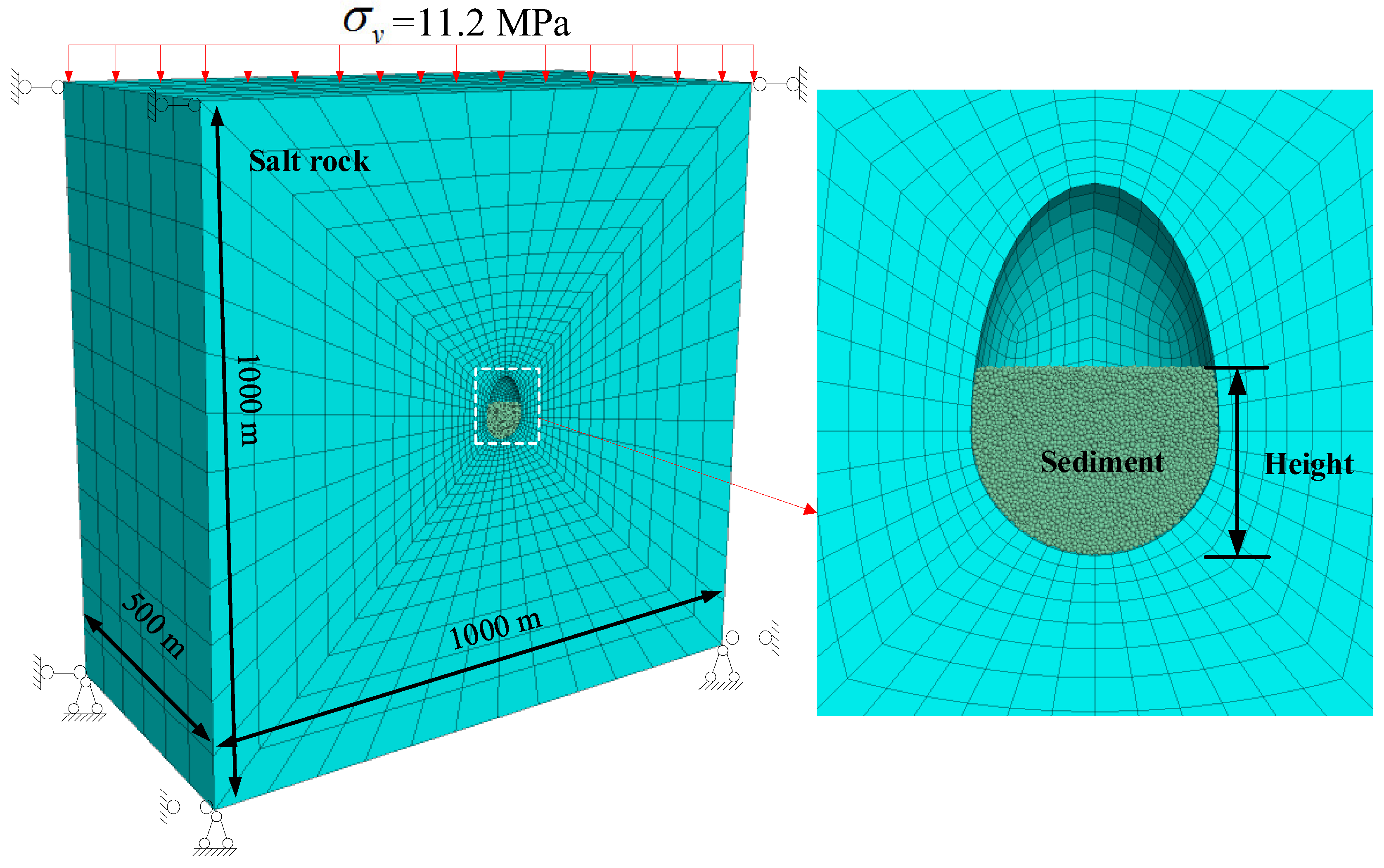
The numerical model was analyzed using an ideal salt cavern reservoir shape with a pear-shaped cavern and internal accumulation of sediment particles. The lower part of the cavern is a hemisphere with a radius of 40 m. The upper part is a semi-ellipsoid with a long axis of 80 m and a short axis of 40 m, and the center of the cavern is located at a depth of 1000 m. Assuming that the influence of interlayers is not considered, the cavern is situated in a pure salt rock layer. The overall model is a rectangular body with dimensions of 1200 m in length, 600 m in width, and 1200 m in height. Considering the symmetry of the cavern, half of the model is used as the research object (
Figure 3). Boundary conditions were set according to the average density and depth of the rock layer. The overlying rock layer was simplified to a top load with a pressure of 11.2 MPa. Normal simple constraints were applied at the bottom and four-face boundaries of the model. ANSYS was used to mesh the model as a whole [
23]. To improve solving accuracy and efficiency, all hexahedral elements were used, and a radioactive mesh was employed to refine the perimeter of the cavern.
According to the change in force situation in the cavern from the original stratum to the use of sediment voids for gas storage, the initial stress state of the model was first established. The initial stress state of three-way isobaric pressure was established as the horizontal ground stress of the rock layer increased until it equaled the vertical ground stress due to the long-term creep action of the salt rock, ultimately placing the rock layer below 433.2 m in a state of hydrostatic pressure [
24]. Then, the cavern was transiently excavated, and a brine gradient pressure was applied to the inner surface of the excavated cavern to simulate the brine-filled state of the salt cavern [
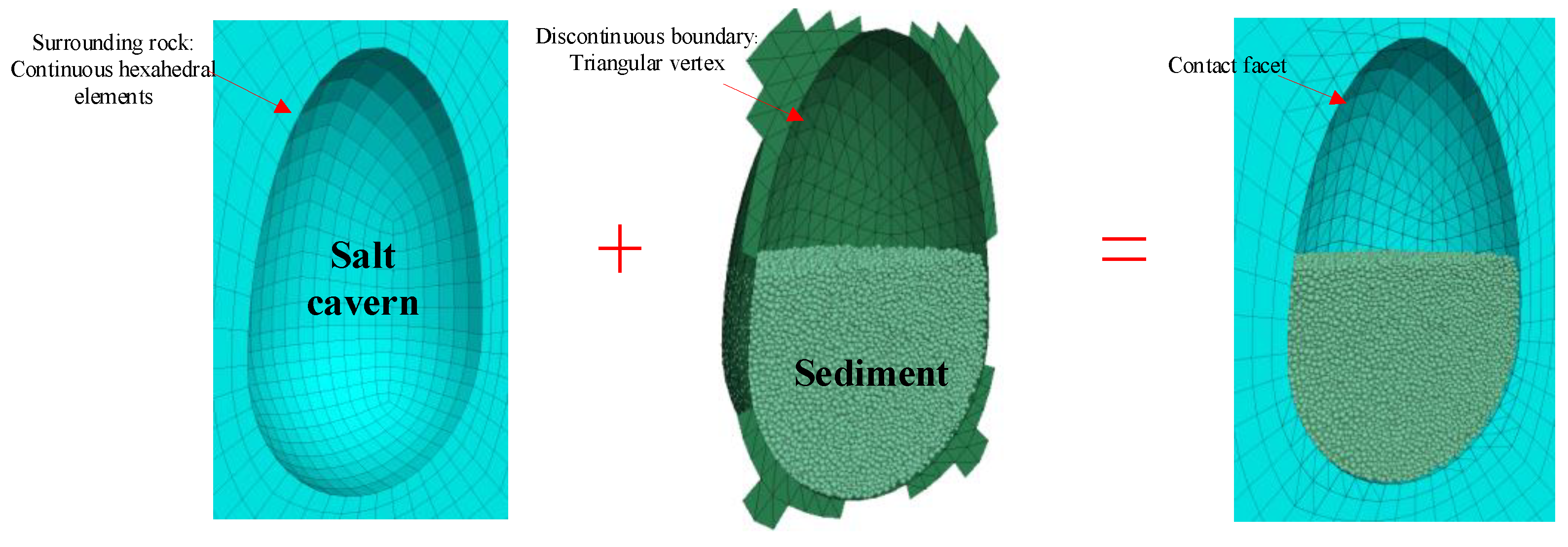
17]. The stress redistribution field after the excavation of the cavern was then calculated. Finally, the particle accumulator generated by PFC was embedded into the FLAC software. The detailed modeling process was as follows (
Figure 4):
(1) Establish the accumulation cavern of particles and generate a certain number of sediment particles. First, the PFC module is introduced into the software FLAC for coupling calculation. A certain gradation of sediment particles is generated in the particle calculation area, regarding the particle parameters and assigned to the sediment particles (
Table 1 and
Table 2). Taking the brine buoyancy into account, the density of the sediment particles is set to the density of the solids minus the density of brine, and the self-gravity is piled up in the cavern.
(2) Embed the excavated salt cavern model and the sediment particles accumulator in the same interface to achieve the coupled calculation of the continuous boundary of the surrounding rock and the discontinuous boundary of the particles. Then, delete the particles outside the boundary of the cavern and recalculate the stress redistribution after the excavation.
(3) Apply different pressures. Since the cavern is filled with natural gas during operation, the upper part of the cavern is subject to gas pressure, and the lower part is subject to the combined action of brine and sediment pressure. Brine pressure varying with depth is applied to the depth range where the cavern is located, and the sediment is modeled by the particle accumulator generated by PFC.
(4) Set the creep time to start the calculation. According to the creep parameters in the paper [
25] and assigned them to the salt rock (
Table 3), a combination of the viscoelastic Norton-Hoff model and Mohr-Coulomb elastoplastic model is used to calculate the coupled creep of the sediment particles in the cavity and the surrounding rock. To analyze the effects of the salt cavern sediment accumulation height, particle gradation, and operating pressure on the volume shrinkage of the cavern and the deformation of the surrounding rock, ten numerical simulation schemes were carried out (
Table 4).
3. Results and Analysis of Influencing Factors
3.1. Sediment Accumulation Height
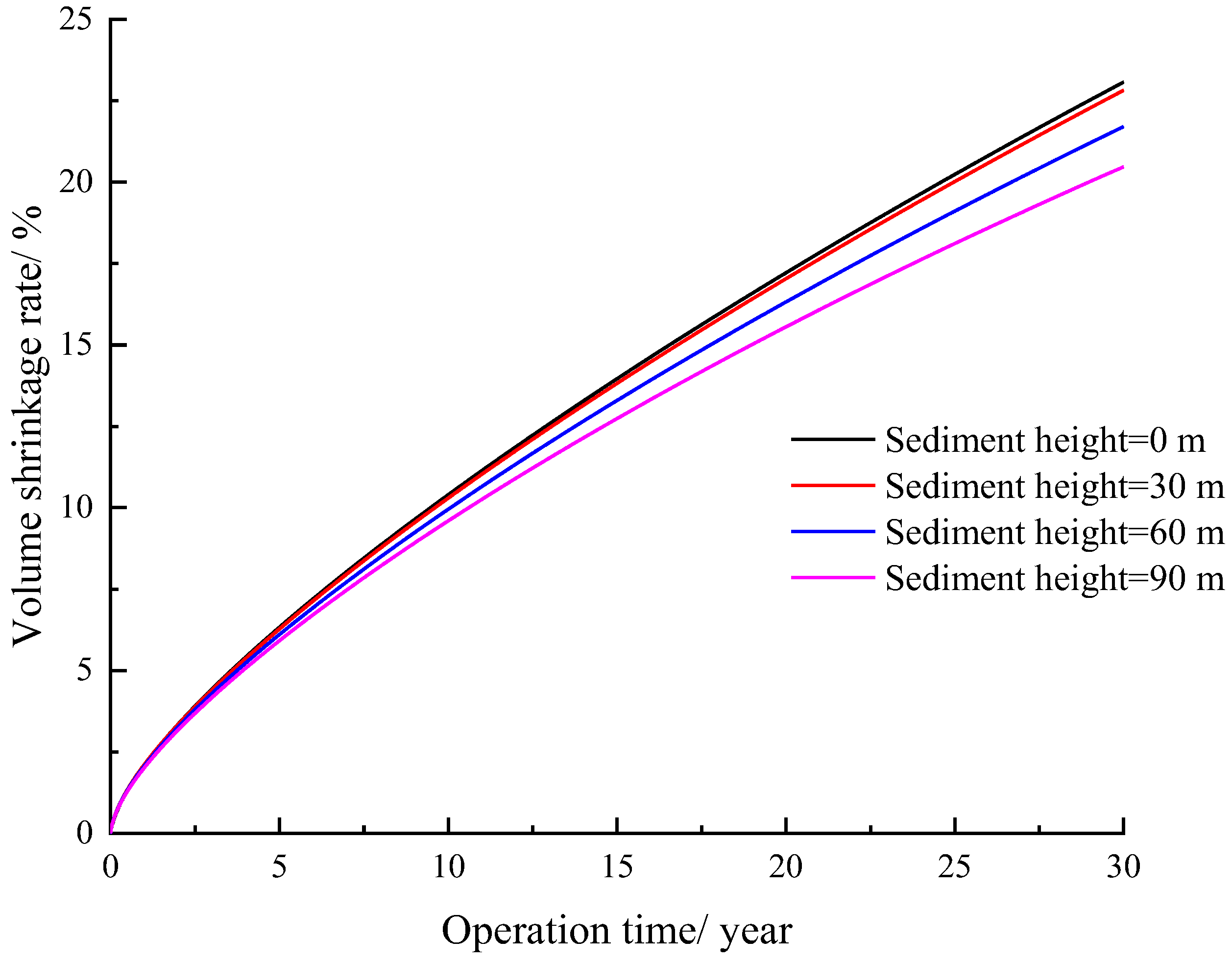
The salt grade is a key factor affecting the accumulation height of insoluble sediment, with more sediment accumulating at the bottom of the cavern in low-grade salt mines and less in high-grade salt mines [
26]. Therefore, different accumulation heights of 0, 30, 60, and 90 m were used to comparatively analyze the effect of sediment height on the stability of the salt cavern, and the volume shrinkage rate curves of the salt cavern at different sediment heights were obtained (
Figure 5). As creep time increases, cavern volume shrinkage gradually increases. As sediment height increases, cavern volume shrinkage gradually decreases. This indicates that sediment height has an inhibitory effect on the creep contraction of the salt cavern. To ensure the availability of the salt cavern gas storage reservoir [
27], the cavern volume shrinkage rate due to creep over 30 years should generally be no more than 30%. When the operating pressure is maintained at 10 MPa, the volume shrinkage due to cavern creep over 30 years is less than 30%.
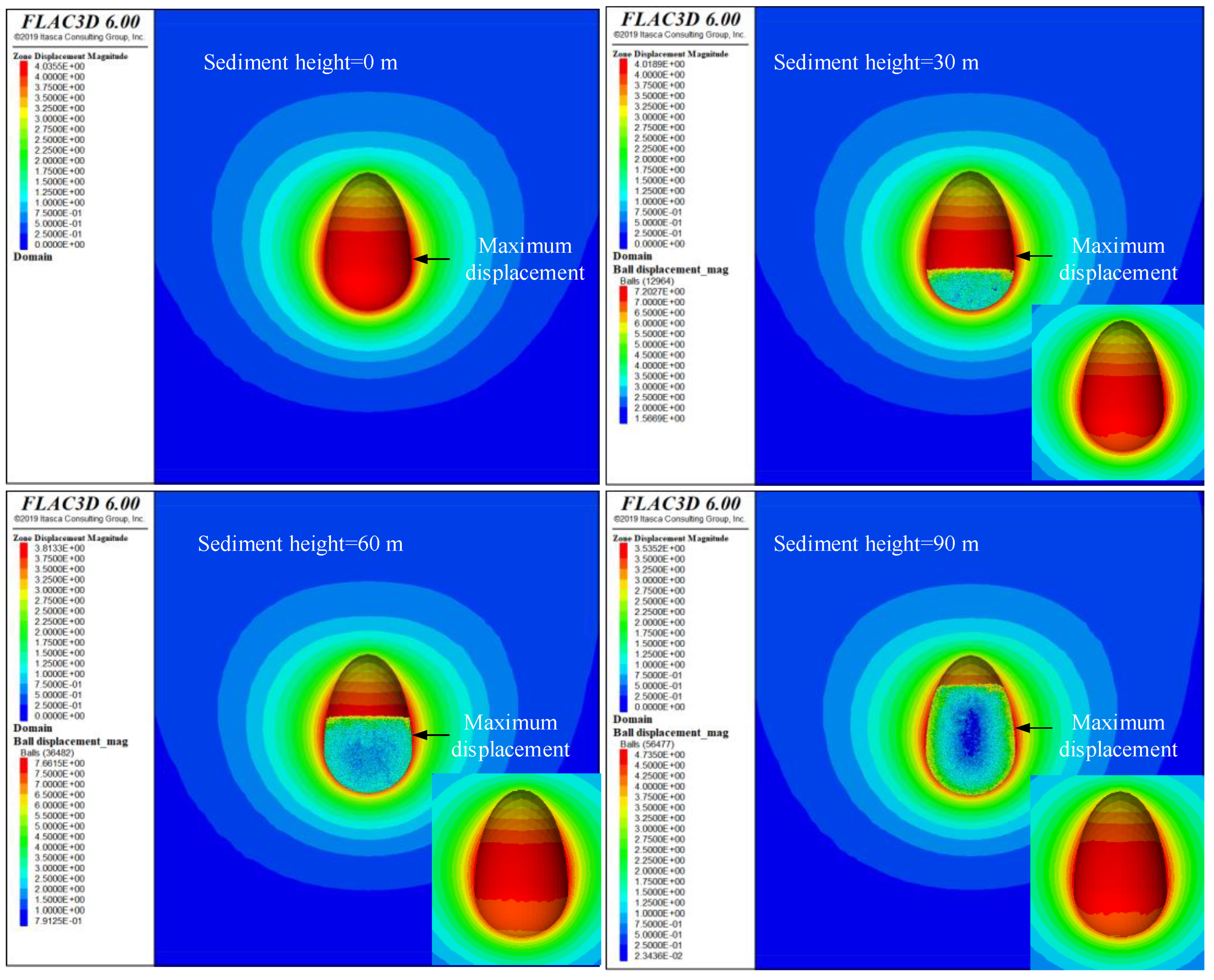
According to the displacement contours of the surrounding rock for 30 years of operation at different sediment heights (
Figure 6), it can be seen that under constant internal pressure, the maximum displacement of the surrounding rock gradually decreases as the sediment height increases. With sediment heights of 0, 30, 60, and 90 m, the maximum displacement around the cavern over 30 years of operation is 4.036, 4.019, 3.813, and 3.535 m, respectively. It is evident that the higher the sediment accumulation, the stronger the inhibition of sediment particles on the surrounding rock, particularly in the sediment-accumulated area where rock displacement is significantly reduced. The maximum displacement around the cavern occurs in the middle, but as the sediment height increases, the maximum displacement tends to move upward. This occurs because higher sediment accumulation enhances support at the bottom of the cavern due to the self-weight of the particles, causing the maximum displacement to shift upward. Generally, the maximum displacement around the cavern should not exceed 5%-10% of the maximum cavern diameter, which is an indicator of surrounding rock damage [
28]. When the sediment height exceeds 60 m, the maximum displacement around the cavern is less than 4 m. It is evident that a certain height of sediment in the salt cavern is beneficial for the stability of the surrounding rock. However, it reduces the net brine space in the upper part of the cavern. If the brine in the bottom sediment void can be partially discharged, the cavern mining space can be maximized.
3.2. Particle Gradation
The particle size distribution of sediment particles is influenced by the grade of the salt layer, stratigraphic distribution, and the process of water-soluble brine extraction [
29]. The size and distribution of sediment particles at the bottom of the cavern after water-soluble brine mining vary across regions, and the thickness of the salt layer and interlayer at different depths of the same salt mine also differ. This results in significant variations in the gradation of sediment particles accumulated at the bottom of the cavern, making it difficult to use a uniform particle gradation to describe the sediment. Intuitively, higher packing density of sediment particles enhances the gravity compaction effect on the cavern wall. Proper particle gradation ensures tight stacking, increases packing density, and consequently enhances the support and inhibition effect on the cavern wall [
30]. However, the sediment accumulation consists of larger intercalated blocks and smaller insoluble residues, with the water-soluble accumulation process being random and highly uncertain. For instance, the maximum particle size of water-soluble sediment particles prepared by indoor experimental dissolution in a salt mine in Dawenkou, Shandong Province, is 40 mm [
31]. A salt mine in Huai'an, Jiangsu Province, sediment particle sizes range from 0.075 to 40 mm, while in Jintan, Jiangsu Province, they range from 0.075 to 20 mm [
26]. This highlights the significant differences in particle gradation distributions of sediment across different regions. The size of sediment particles obtained from indoor experiments is 0.075 to 20 mm. However, these sizes may not accurately reflect actual sediment particle sizes, as insoluble particles around 20 mm can be carried out of the chamber by brine during discharge [
26]. Thus, this study selects larger sediment particles for numerical simulation, choosing a range of 1.0-2.0 m to reduce particle numbers and improve simulation efficiency.
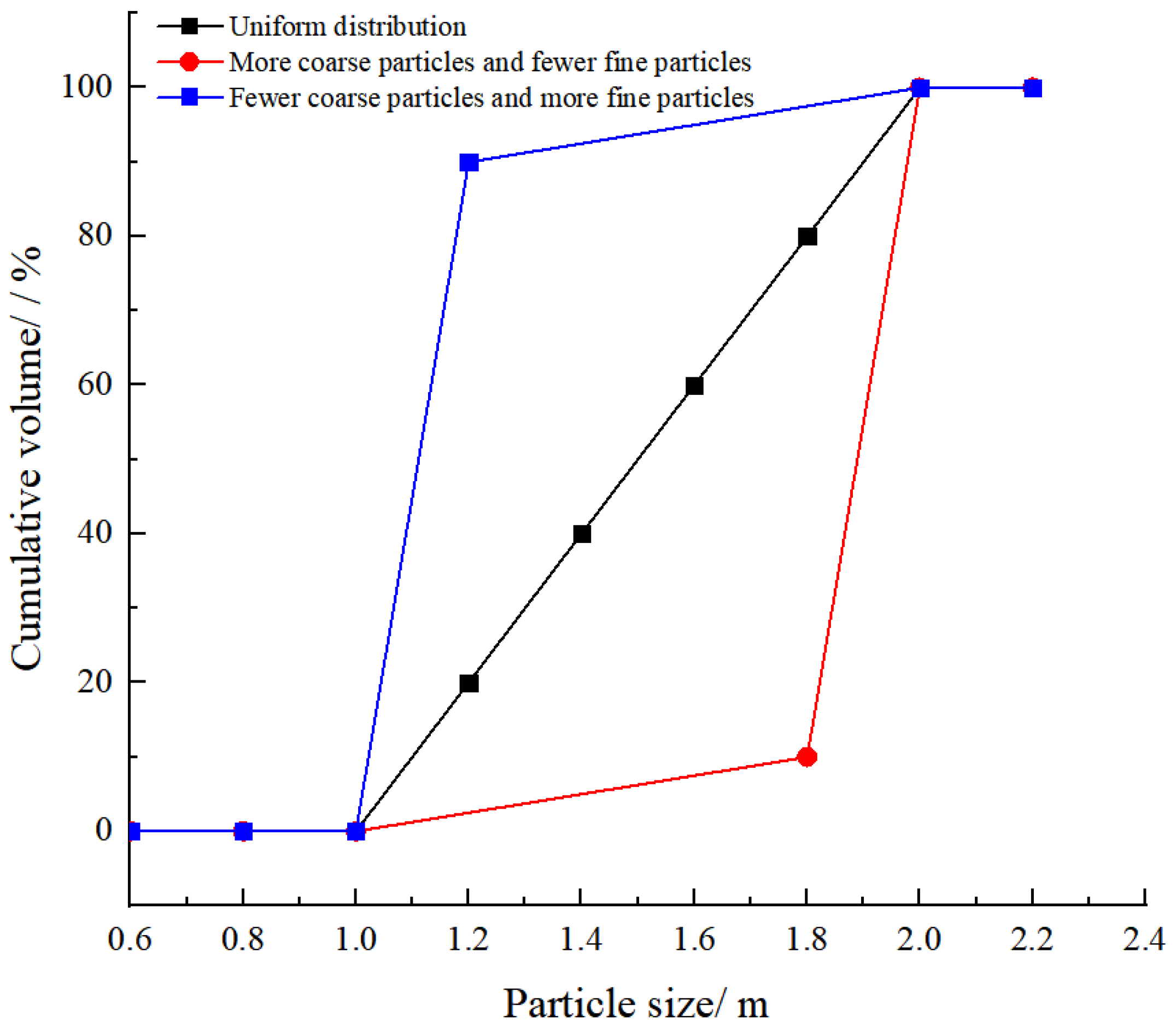
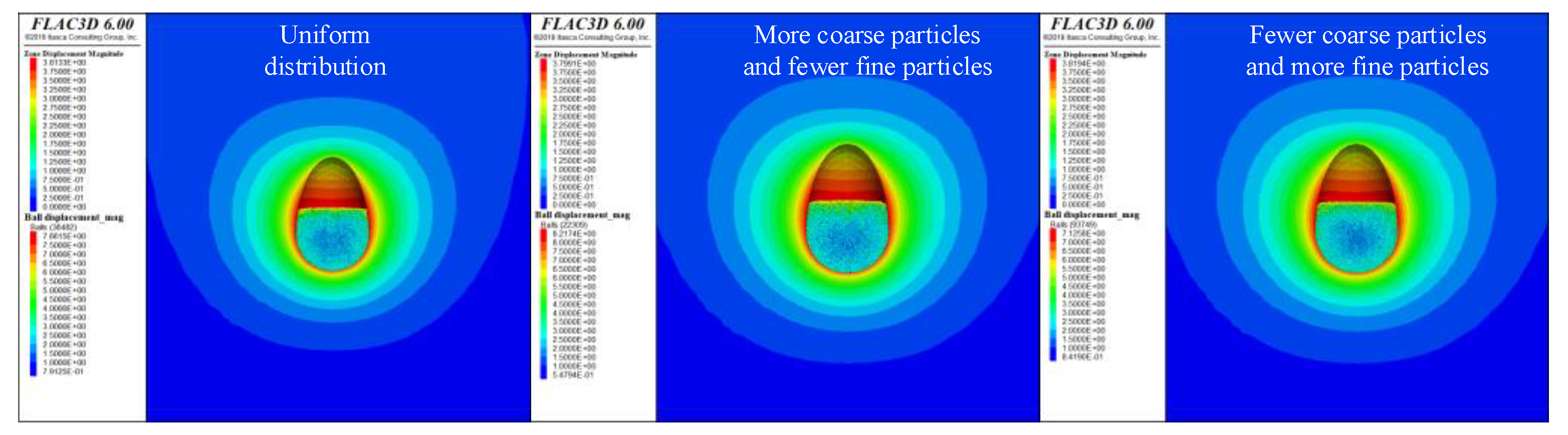
In this section, three types of salt sediment particle gradation curves—uniform distribution, more coarse particles and fewer fine particles, and fewer coarse particles and more fine particles (
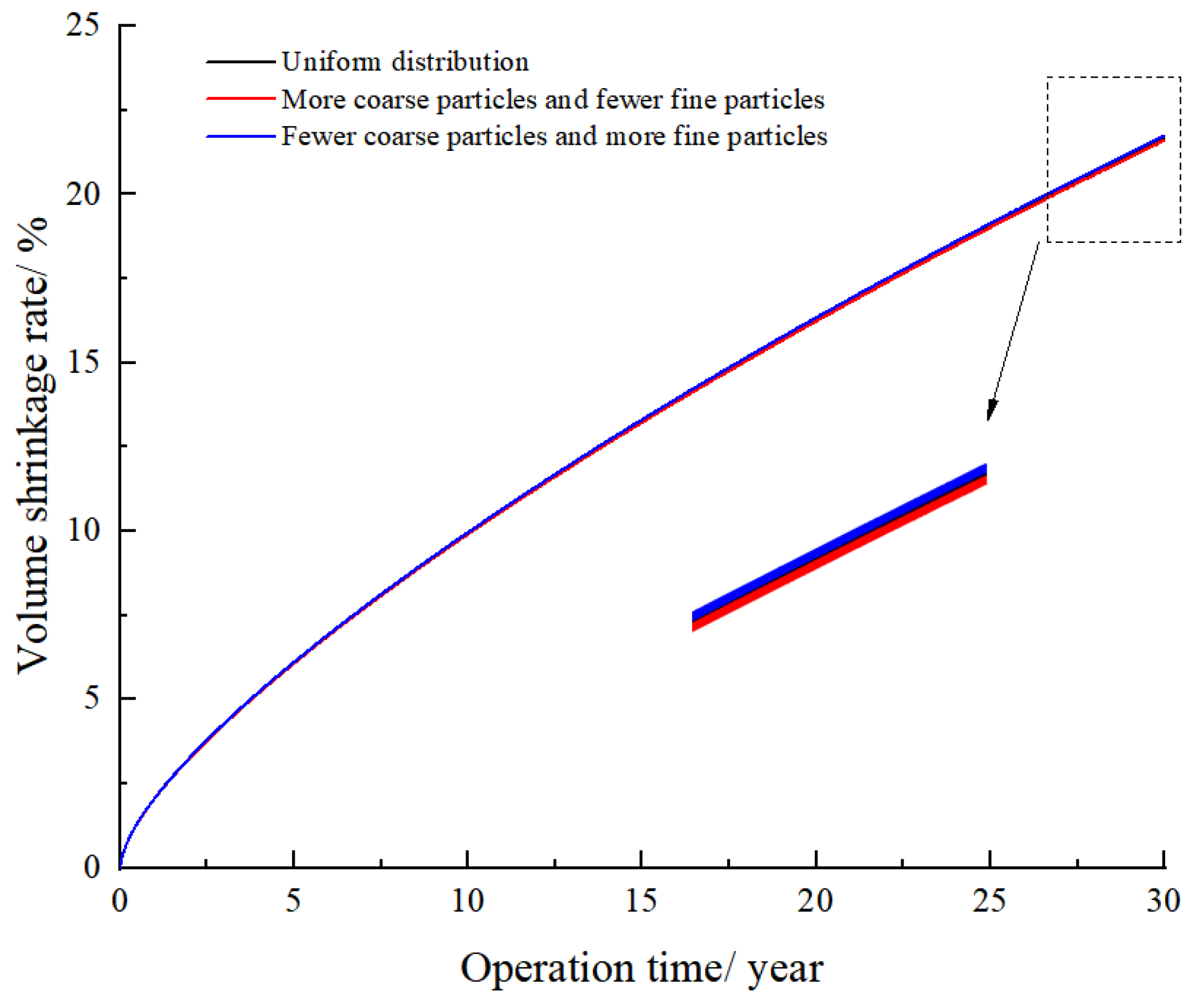
Figure 7), are used to simulate the effect of different sediment particle gradations on cavern stability. According to the simulation results, the volume shrinkage rate of the cavern operating for 30 years under different sediment particle gradations (
Figure 8), more coarse particles, uniform distribution, and fewer coarse particles are 21.61%, 21.70%, and 21.74%, respectively. Higher coarse particle content results in greater cavern volume shrinkage, but particle gradation has a smaller effect on volume shrinkage overall, indicating a minimal impact on packing density.
However, the numerical simulation primarily used spherical particles to characterize the shape of sediment particles, not considering the effect of irregularly shaped particles. Irregular particles lead to nested extrusion between packed particles, forming a more stable force chain structure. Thus, packing irregularly shaped particles provides stronger support to the surrounding rocks of the salt cavern. Displacement and cavern volume shrinkage follow the same trend: larger cavern volume shrinkage results in larger displacement. According to the displacement contours of surrounding rock after 30 years operation with different sediment particle gradations (
Figure 9), when the sediment contains more coarse particles and fewer fine particles, the maximum displacement is 3.805 m. When the sediment contains fewer coarse particles and more fine particles, the maximum displacement is 3.817 m, indicating a relatively small difference between the two gradations.
3.3. Operating Pressure
The design of operational parameters for salt cavern gas storage reservoirs is influenced by the burial depth of the salt cavern, cavern morphology, and stratigraphic properties [
32]. Numerical simulations are typically used to determine the upper and lower pressure limits for reservoir operation [
33]. The “Safety rules of salt cavern underground gas storage” (SY/T 6806-2019) states that "the upper limit pressure of a salt cavern gas storage reservoir shall not exceed 80% of the rupture pressure of the formation at the shoe of the production casing, and shall not be higher than 80% of the pressure of the overlying strata." Given the simulation depth of the center of the salt cavern is 1000 m, the upper pressure is set to be no more than 18 MPa [
34]. The simulation uses constant operating pressures of 4, 6, 8, and 10 MPa to calculate the shrinkage of the cavern over 30 years of operation. Comparing the volume shrinkage curves of the cavern over 30 years at different operating pressures (
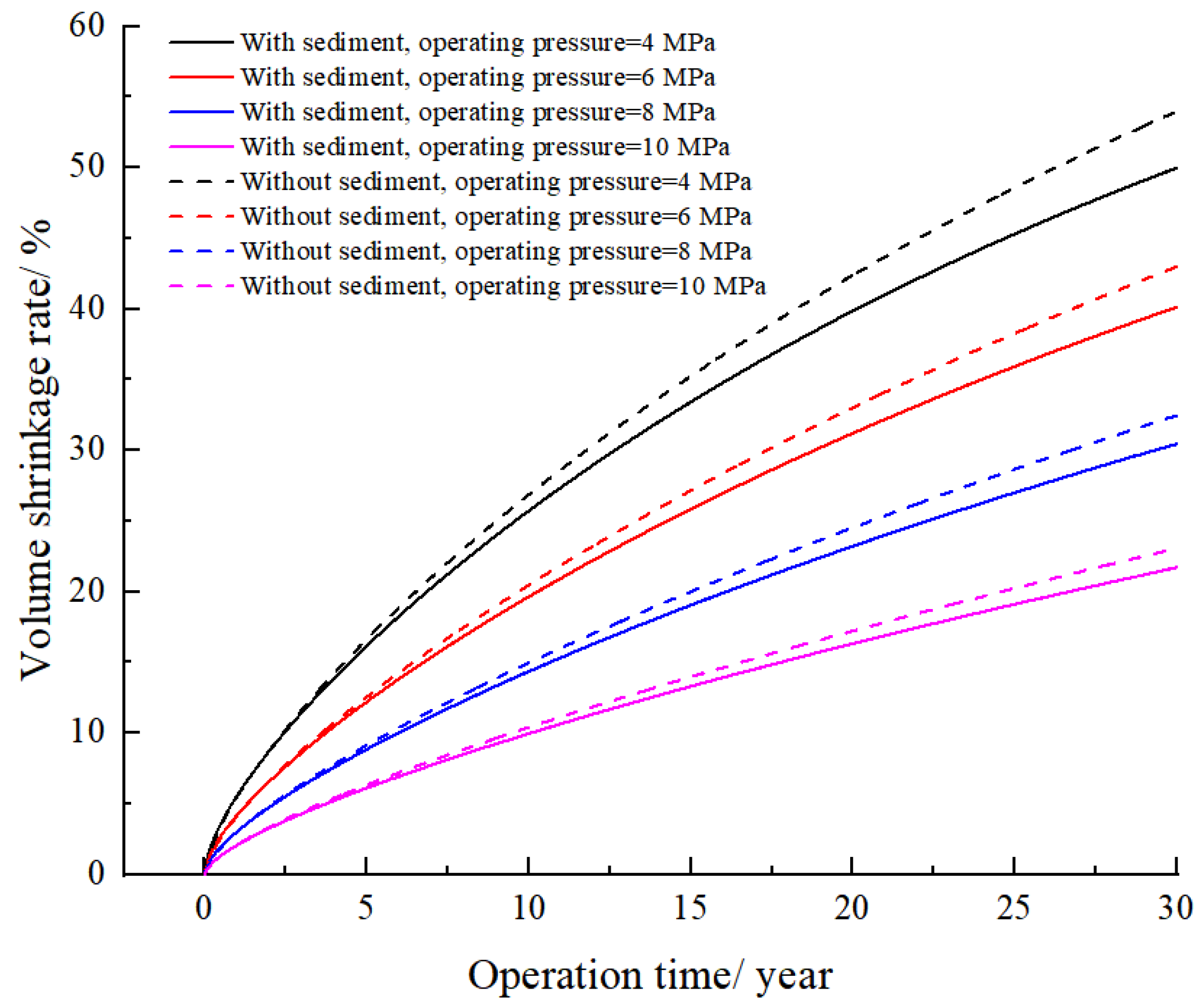
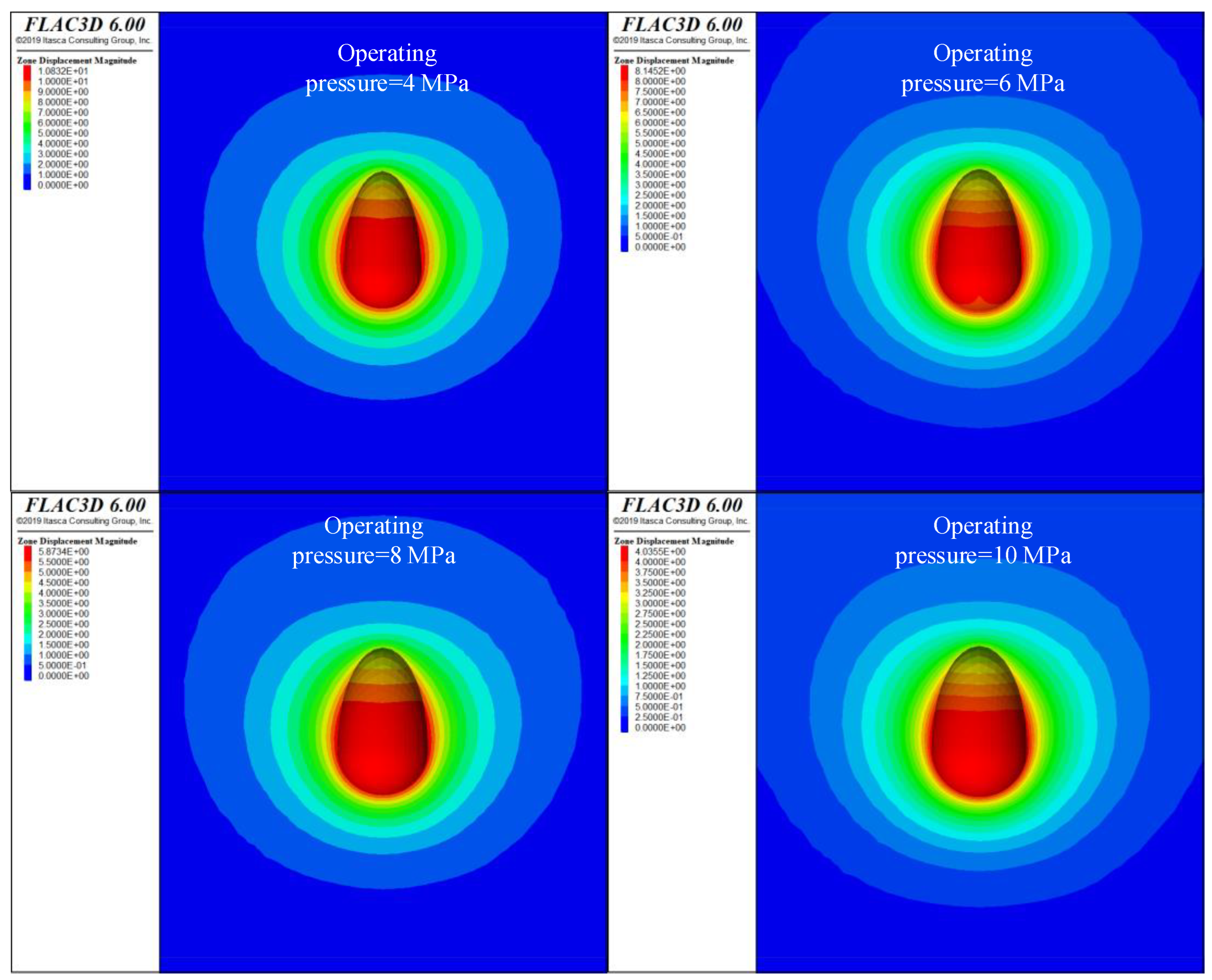
Figure 10) reveals that higher operating pressure results in smaller volume shrinkage and reduces the maximum displacement.
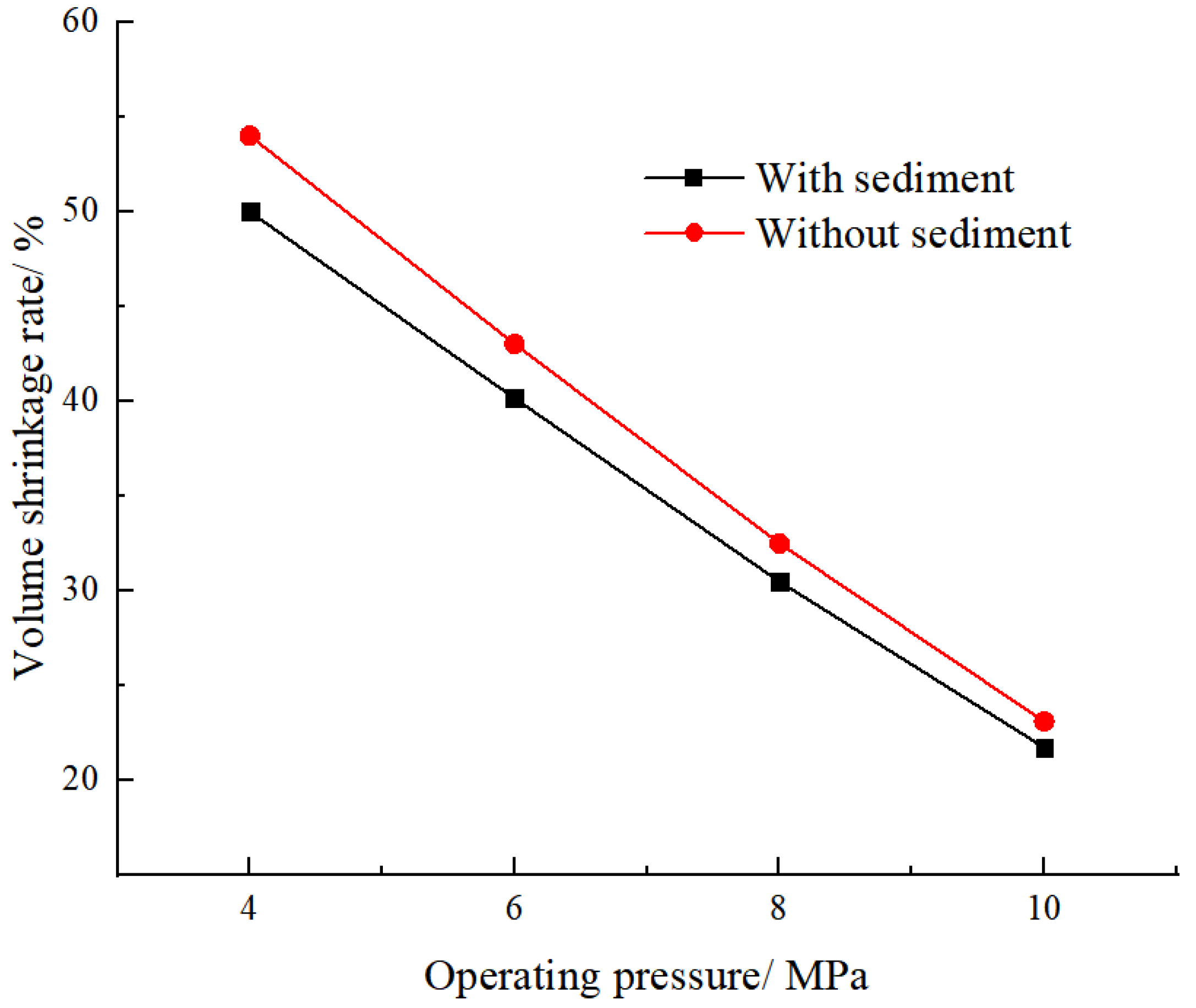
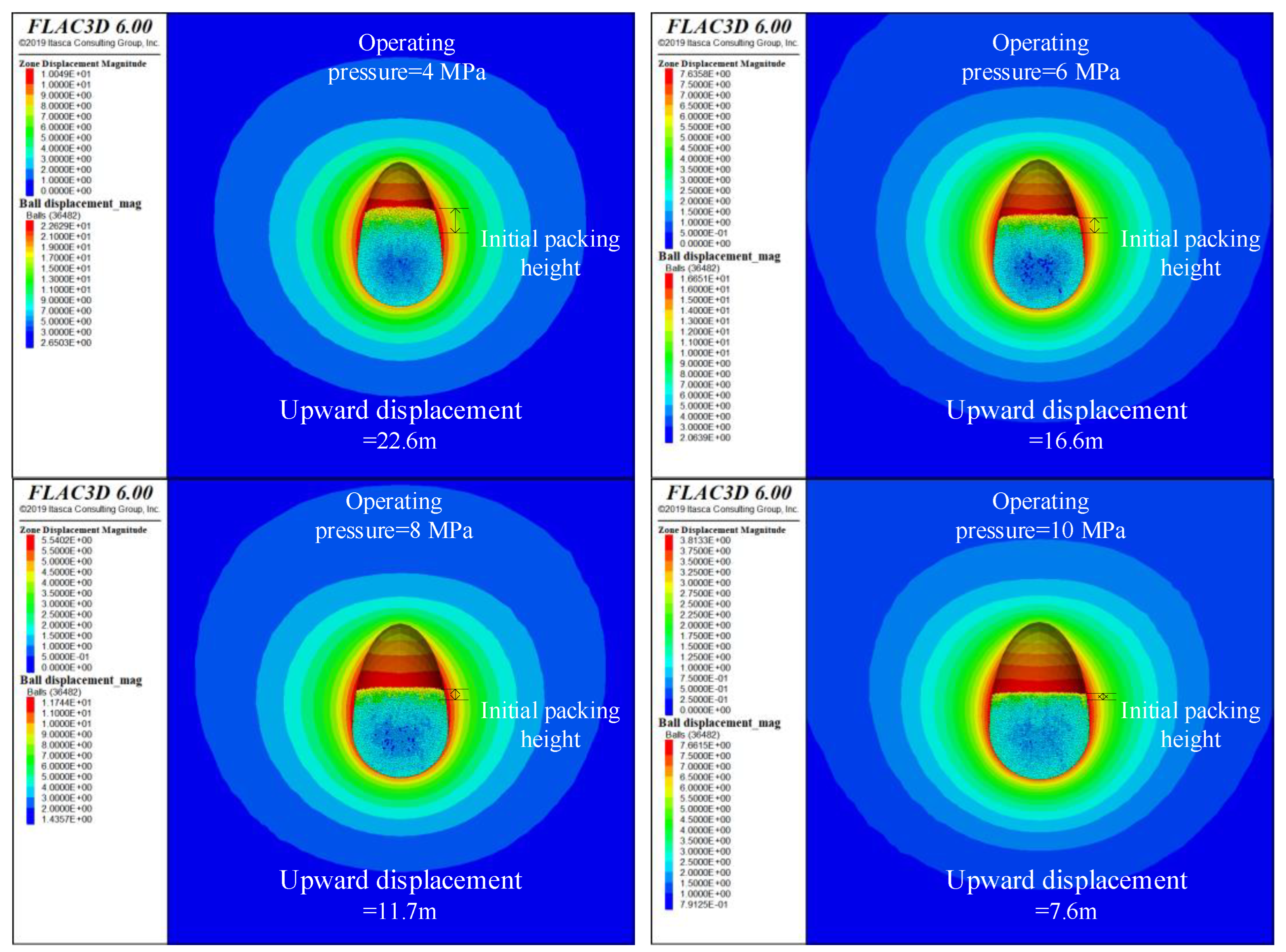
For a salt cavern sediment height of 60 m and operating pressures of 4, 6, 8, and 10 MPa after 30 years of operation, the maximum displacements of the cavern were 10.0, 7.6, 5.5, and 3.8 m, respectively. The volume shrinkage rates were 49.9%, 40.1%, 30.4%, and 21.7% (
Figure 11), respectively. Correspondingly, the upward displacements of the salt cavern sediment body due to extrusion were 22.6, 16.6, 11.7, and 7.6 m, respectively (
Figure 12). Without sediment in the salt cavern, the maximum displacements of the cavern after 30 years of operation at operating pressures of 4, 6, 8, and 10 MPa are 10.8, 8.1, 5.8, and 4.0 m, respectively (
Figure 13), with volume shrinkage rates of 53.9%, 42.9%, 32.4%, and 23.0%. Comparing the differences in the maximum displacement of the cavern after 30 years of operation with and without sediment at operating pressures of 4, 6, 8, and 10 MPa reveals differences of 0.8, 0.5, 0.3, and 0.2 m, respectively. The differences in volume shrinkage were 4.0%, 2.8%, 2.0%, and 1.3%, respectively, indicating that the inclusion of sediment is more favorable for cavern stability. As operating pressure increases, the upward displacement of the sediment body slows down, the upper air storage space of the cavern increases, and the trends of maximum displacement of the cavern perimeter and volume shrinkage of the sediment-containing salt cavern both gradually reduce.
4. Conclusions
The influence of sediment accumulation on the long-term operational stability of high-impurity salt cavern gas storage reservoirs was investigated. A discrete-continuous coupling calculation model was constructed to analyze the interaction between sediment particles and the surrounding rock. The effects of sediment accumulation height, particle gradation, and operating pressure on cavern stability were examined, offering new insights into the long-term mechanical behavior of these reservoirs. The following conclusions were obtained:
(1) For the same particle gradation and operating pressure, a larger height of sediment accumulation results in smaller maximum displacement of the cavern wall and reduced volume shrinkage of the cavern, indicating a stronger inhibitory effect of the sediment particles on the surrounding rock. The self-weight effect of the accumulated particles enhances the support force on the cavern bottom, slows down the creep shrinkage at the cavern base, and shifts the maximum displacement location of the surrounding rock to the upper part of the cavern.
(2) At the same accumulation height and operating pressure, a higher coarse particle content leads to smaller cavern volume shrinkage. However, the effect of particle gradation on volume shrinkage is minimal, primarily due to its limited impact on packing density. The simulation did not account for the stable force chain structure formed by irregularly shaped particles, indicating a need for further study on the influence of particle morphology on long-term operation stability.
(3) For the same particle gradation and accumulation height, higher operating pressure results in smaller maximum displacement around the cavern and reduced volume shrinkage rate, as well as smaller maximum upward displacement of the sediment particles after extrusion, increasing gas storage space in the upper part of the cavern. Compared to scenarios without sediment in the salt cavern the accumulation of sediment particles helps maintain cavern stability. Utilizing the sediment voids for gas storage does not compromise cavern stability and maximizes the use of the cavern mining space for gas storage.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to express their gratitude to the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 52304069), and the Excellent Youth Scientists Fund Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 52122403). The authors would gratefully like to acknowledge the financial support from the PipeChina Energy Storage Technology Corporation Limited (No. GWHT20230041899BG1, GWHT20230039074BG1).
References
- Liu, W.; Li, Q.; Yang, C.; Shi, X.; Wan, J.; Jurado, M.J.; et al. The role of underground salt caverns for large-scale energy storage: A review and prospects. Energy Storage Materials 2023, 63, 103045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Li, Y.; Shi, X.; Wei, X.; Yang, K.; Ma, H.; et al. Pressure monitoring and deformation analysis of a brine-filled salt cavern - A case study of Jianghan, China. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences 2024, 177, 105737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Li, L.; Jiang, D.; Fan, J.; et al. Optimization of operating pressure of hydrogen storage salt cavern in bedded salt rock with multi-interlayers. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy 2024, 58, 974–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.L.; Tang, Y.; Shi, X.L.; Xu, W.J.; Yang, C.H. Modeling the construction of energy storage salt caverns in bedded salt. Applied Energy 2019, 255, 113866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Li, Y.; Shi, X.; Xie, D.; Ma, H.; Yang, C.; et al. Experimental and theoretical research on the debrining process in sediments for a gas storage salt cavern. Geoenergy Science and Engineering 2023, 225, 211667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Li, Y.; Shi, X.; Ma, H.; Zhao, K.; Liang, X.; et al. Pore Structure and Brine Flow Simulation of Salt Cavern Sediments Based on X-ray Computed Tomography. Rock Mechanics and Rock Engineering 2023. [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Chen, Q.; Ma, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, T.; Zhang, C. Geomechanical investigation for abandoned salt caverns used for solid waste disposal. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment 2020, 80, 1205–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Li, Y.; Shi, X.; Zhao, K.; Liu, X.; Ma, H.; et al. Prediction method for calculating the porosity of insoluble sediments for salt cavern gas storage applications. Energy 2021, 221, 119815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.T.; La, B.; Bw, C.; Sd, C.; Kw, B.; Fy, B.; et al. Tightness of an underground energy storage salt cavern with adverse geological conditions. Energy. 2022. [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.T.; Yan, X.Z.; Yang, H.L.; Yang, X.J.; Jiang, T.T.; Zhao, S. A new shape design method of salt cavern used as underground gas storage. Applied Energy 2013, 104, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, T.; Yang, C.; Li, Y.; Shi, X.; Ma, H.; Wei, X.; et al. Disposal of drilling waste in salt mines in China. Science of The Total Environment. 2023, 168746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Wu, G.; Dai, Y.; Yang, C. Stability analysis of abandoned salt caverns used for underground gas storage. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering 2006, 25, 848–854. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Zhang, Z.X.; Fan, J.Y.; Jiang, D.Y.; Daemen, J.J.K. Research on the Stability and Treatments of Natural Gas Storage Caverns With Different Shapes in Bedded Salt Rocks. Ieee Access 2020, 8, 18995–19007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Liu, Y.X.; Li, Y.P.; Ma, H.L.; Hou, W.; Yu, C.F.; et al. Feasibility analysis of salt cavern gas storage in extremely deep formation: A case study in China. Journal of Energy Storage 2022, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.L.; Shi, X.; Yang, C.; Li, Y.; Wang, T.; Ma, H. Mathematical model of salt cavern leaching for gas storage in high-insoluble salt formations. Scientific Reports 2018, 8, 372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, T.; Yang, C.; Shi, X.; Hongling, M.; Liu, X. The formation mechanism of irregular salt caverns during solution mining for natural gas storage. Energy Sources Part A Recovery Utilization and Environmental Effects. 2020, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Li, Y.; Shi, X.; Zhao, A.; Liu, Y. Stability analysis of U-shaped horizontal salt cavern for underground natural gas storage. Journal of Energy Storage 2021, 38, 102541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.T.; Ma, H.L.; Yang, C.H.; Shi, X.L.; Daemen, J.J.K. Gas seepage around bedded salt cavern gas storage. Journal of Natural Gas Science and Engineering 2015, 26, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yang, C.; Ma, H.; Shi, X.; Zhang, H.; Dong, Z. A 3D grain-based creep model (3D-GBCM) for simulating long-term mechanical characteristic of rock salt. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering. 2019, 106672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Yang, J.; Han, Y.; Yang, C.H.; Daemen, J.J.K.; Li, P. Weibull grain-based model (W-GBM) for simulating heterogeneous mechanical characteristics of salt rock. Engineering Analysis with Boundary Elements 2019, 108, 227–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Shi, X.; Ma, H.; Zhao, K.; et al. Influence of loading history on creep behavior of rock salt. Journal of Energy Storage 2022, 55, 105434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Li, Y.; Shi, X.; Zhao, K.; Liu, X.; Ma, H.; et al. Compaction and restraining effects of insoluble sediments in underground energy storage salt caverns. Energy 2022, 249, 123752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ANSYS Inc, 2012. ANSYS 14.5 Mechanical APDL Verification Manual. Canonsburg, Pennsylvania, USA. http://www.ansys.com.
- Zhang, N.; Shi, X.L.; Wang, T.T.; Yang, C.H.; Liu, W.; Ma, H.L.; et al. Stability and availability evaluation of underground strategic petroleum reserve (SPR) caverns in bedded rock salt of Jintan, China. Energy 2017, 134, 504–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.T.; Yang, C.H.; Chen, J.S.; Daemen, J.J.K. Geomechanical investigation of roof failure of China's first gas storage salt cavern. Engineering Geology 2018, 243, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Chai, G.; Cen, X.; Yang, J.; Daemen, J.J.K. Safe distance between debrining tubing inlet and sediment in a gas storage salt cavern. Journal of Petroleum Science and Engineering 2021, 196, 107707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.H.; Wang, T.T.; Li, Y.P.; Yang, H.J.; Li, J.J.; Qu, D.A.; et al. Feasibility analysis of using abandoned salt caverns for large-scale underground energy storage in China. Applied Energy 2015, 137, 467–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Yang, C.; Ma, H.; Shi, X.; Zhang, N.; Ge, X.; et al. Stability evaluation of underground gas storage salt caverns with micro-leakage interlayer in bedded rock salt of Jintan, China. Acta Geotechnica 2020, 15, 549–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, W.; Shi, X.; Yang, C.; Zhu, S.; Wei, X.; Li, Y.; et al. Assessment of the potential of salt mines for renewable energy peaking in China. Energy 2024, 300, 131577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liu, Y.; He, C.; Chen, L.; du Toit, C.G.; Liu, S. Investigation into the packing structure of binary pebble beds using X-ray tomography. Powder Technology 2022, 406, 117589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Ma, H.; Cai, R.; Zhao, K.; Zeng, Z.; Li, H.; et al. Feasibility analysis of natural gas storage in the voids of sediment within salt cavern——A case study in China. Energy 2023, 129340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.T.; Li, J.J.; Jing, G.; Zhang, Q.Q.; Yang, C.H.; Daemen, J.J.K. Determination of the maximum allowable gas pressure for an underground gas storage salt cavern - A case study of Jintan, China. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering 2019, 11, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.L.; Yang, C.H.; Li, Y.P.; Shi, X.L.; Liu, J.F.; Wang, T.T. Stability evaluation of the underground gas storage in rock salts based on new partitions of the surrounding rock. Environmental Earth Sciences 2015, 73, 6911–6925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, J.; Shang, H.; Ji, W.; Wan, J.; Xing, T.; Ma, H.; et al. Feasibility Analysis of Compressed Air Energy Storage in Salt Caverns in the Yunying Area. Energies 2023. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).