Submitted:
09 July 2024
Posted:
11 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Background
2. Nutritional Benefits and Side Effects of the Grass Pea
3. Conventional Improvement for β-ODAP Reduction and Influence of Environmental Factors
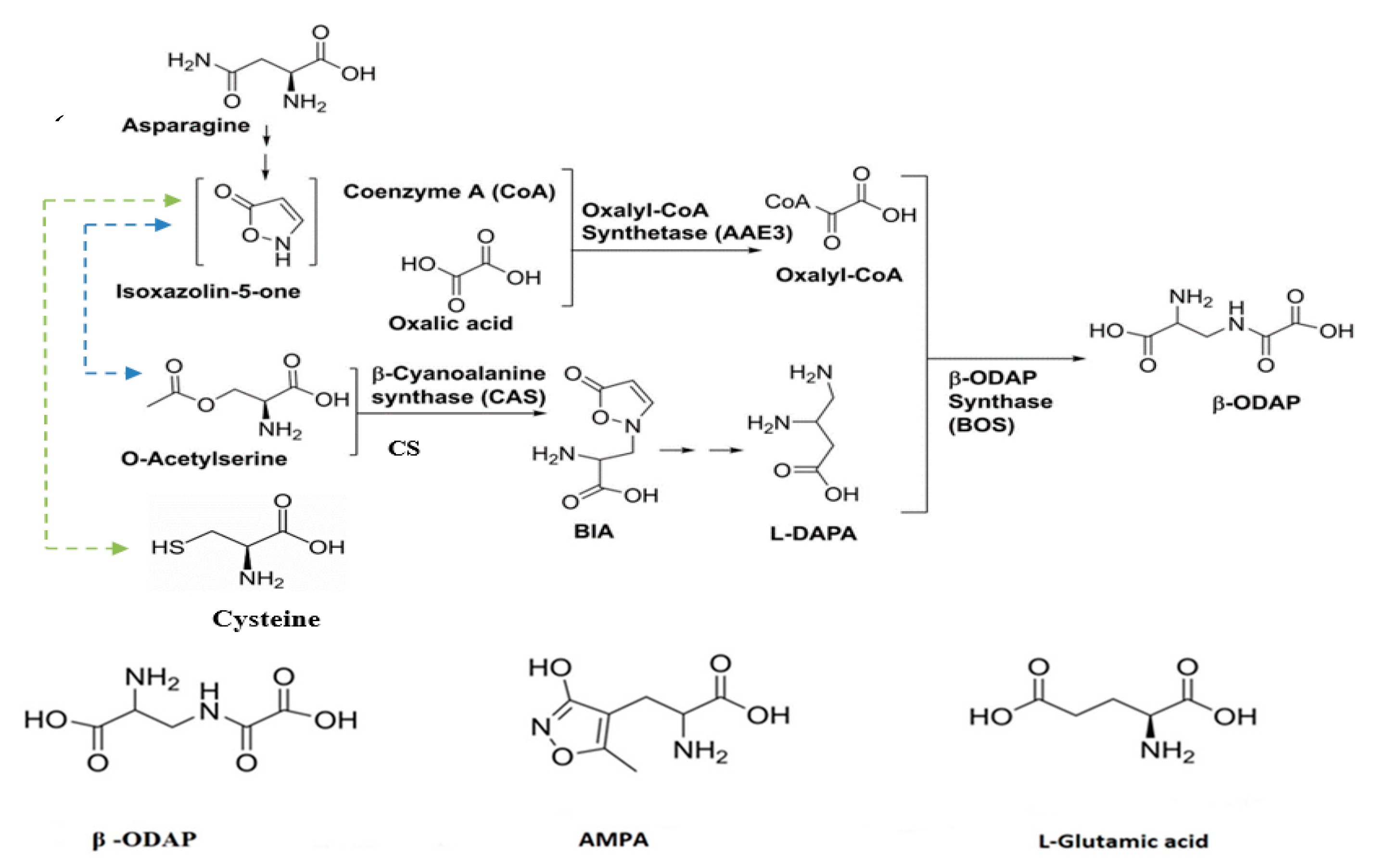
4. Biosynthesis of β-ODAP in Grass Pea
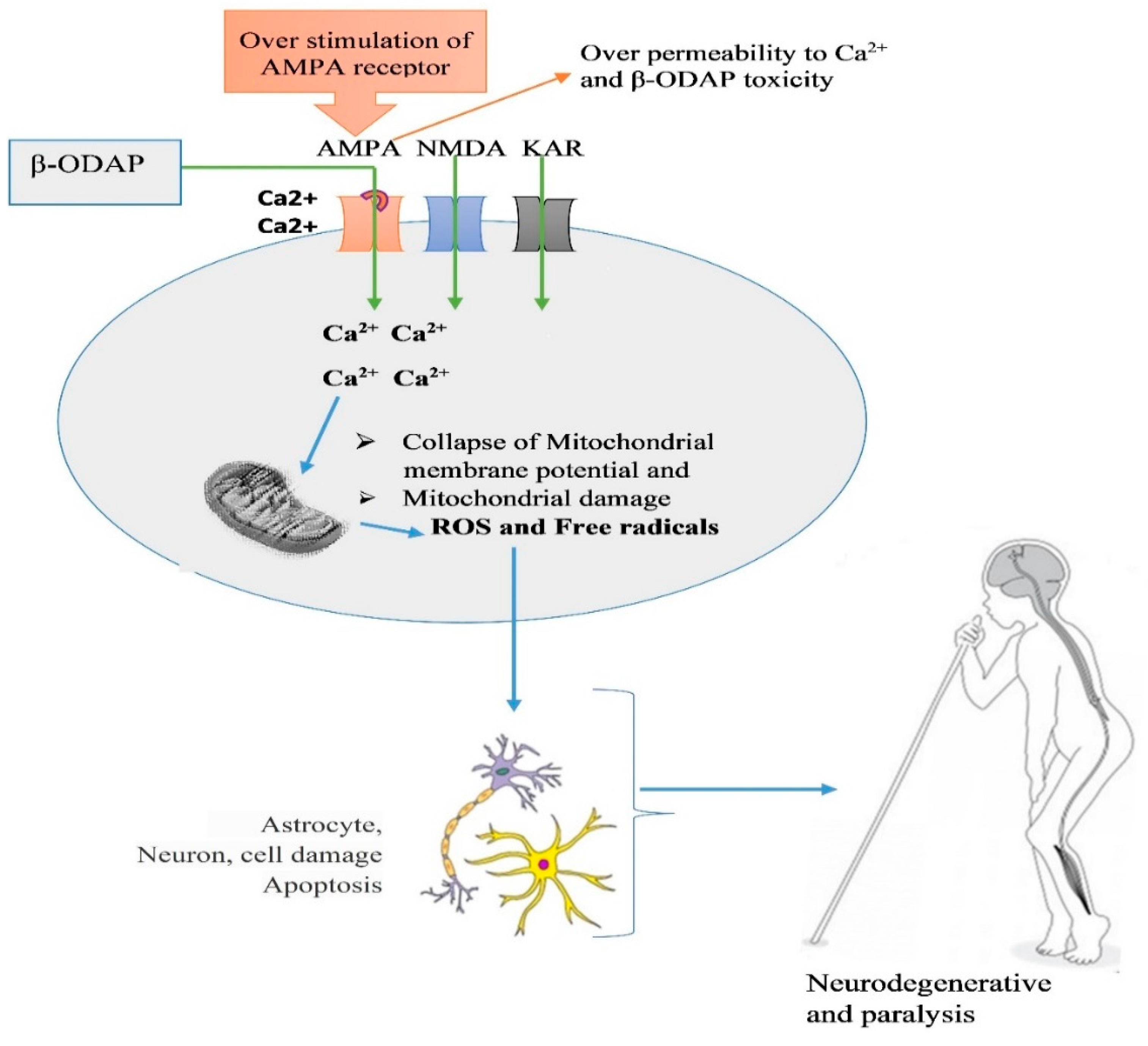
5. Mechanism of β-ODAP Action and Toxicity
6. Reducing β-ODAP Using Traditional Food Processing Strategies
7. Enhancing Sulfur-Containing Amino Acids (SCA) through Genetic Modification of Grass Pea
8. The Potential of Genome Editing Approach for Antinutritional Factors in Crops
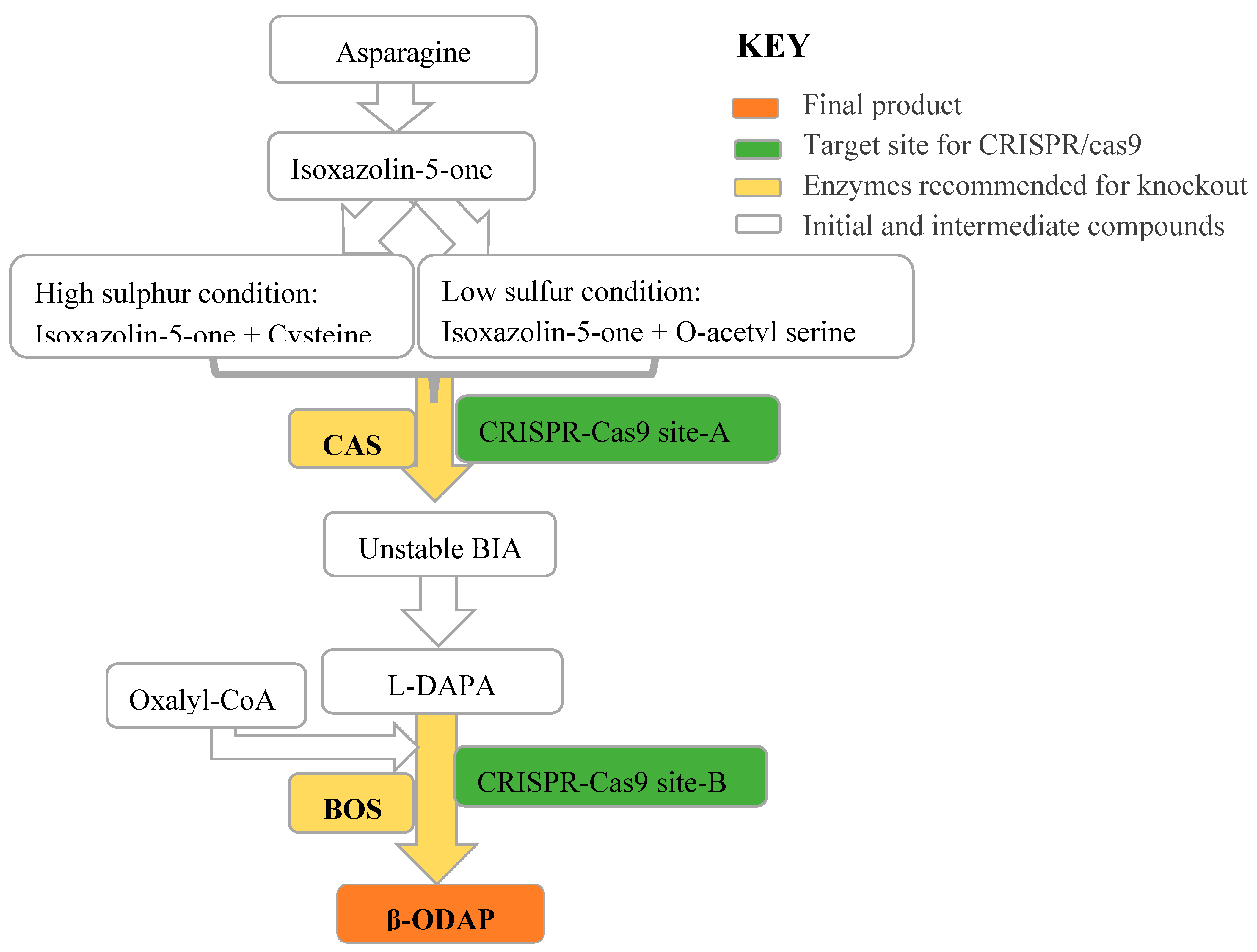
8.1. The Potential of CRISPR/Cas9 to Target β-ODAP Biosynthesis in Grass Pea
9. Conclusion and Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Ethics declarations
Consent of publication
Data availability
Competing interests
Acknowledgments
References
- Tan, R.-Y.; Xing, G.-Y.; Zhou, G.-M.; Li, F.-M.; Hu, W.-T.; Lambein, F.; Xiong, J.-L.; Zhang, S.-X.; Kong, H.-Y.; Zhu, H.; et al. Plant toxin β-ODAP activates integrin β1 and focal adhesion: A critical pathway to cause neurolathyrism. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambein, F.; Travella, S.; Kuo, Y.-H.; Van Montagu, M.; Heijde, M. Grass pea (Lathyrus sativus L.): orphan crop, nutraceutical or just plain food? Planta 2019, 250, 821–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, L.; Rubiales, D.; Bronze, M.R.; Patto, M.C.V. Grass Pea (Lathyrus sativus L.)—A Sustainable and Resilient Answer to Climate Challenges. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smartt, J. (1990). Pulses of the classical world. Grain legumes: evaluation and genetic resources. Cambridge Univ. Press, Cambridge, 190-200.
- Abdipour, M.; Vaezi, B.; Khademi, K.; Ghasemi, S. An optimized artificial intelligence approach and sensitivity analysis for predicting the biological yield of grass pea (Lathyrus sativus L.). Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2019, 66, 1909–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sammour RH. (2014) Genetic diversity in Lathyrus sativus L. germplasm. Res Rev BioSci 8:325–336.
- Gupta, P.; Udupa, S.M.; Gupta, D.S.; Kumar, J.; Kumar, S. Population structure analysis and determination of neurotoxin content in a set of grass pea (Lathyrus sativus L.) accessions of Bangladesh origin. Crop. J. 2018, 6, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.C.; Ohri, D. Chromosome and nuclear phenotype in the legume Lathyrus sativus L. CYTOLOGIA 1979, 44, 77–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanbury, C.; White, C.; Mullan, B.; Siddique, K. A review of the potential of Lathyrus sativus L. and L. cicera L. grain for use as animal feed. Anim. Feed. Sci. Technol. 2000, 87, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patto, M.C.V.; Skiba, B.; Pang, E.C.K.; Ochatt, S.J.; Lambein, F.; Rubiales, D. Lathyrus improvement for resistance against biotic and abiotic stresses: From classical breeding to marker assisted selection. Euphytica 2006, 147, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, N. , Rubiales, D., Vaz Patto, M. (2015). Grass Pea. In: De Ron, A. (eds) Grain Legumes. Handbook of Plant Breeding, vol 10. Springer, New York, NY. [CrossRef]
- Shiferaw, E.; Pè, M.E.; Porceddu, E.; Ponnaiah, M. Exploring the genetic diversity of Ethiopian grass pea (Lathyrus sativus L.) using EST-SSR markers. Mol. Breed. 2011, 30, 789–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadi, L. , Teklewold, H., Aw-Hassan, A., Moneim, A.A., Bejiga, G., 2003. The Socioeconomic Factors Affecting Grass Pea Consumption and Influence of Lathyrism in Ethiopia. Integr. National Resources Management Res. Report Series, No. 4. ICARDA, Aleppo, Syria, pp. 7–11.
- Gabrekiristos E, Wondimu M (2022) Emerging and Reemerging Diseases of Common Bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) in major production areas: In the case of Ethiopia. J Plant Pathol Microbiol. 13:619.
- Sarkar, A.; Emmrich, P.M.F.; Sarker, A.; Zong, X.; Martin, C.; Wang, T.L. (2019). Grass pea: Remodelling an ancient insurance crop for climate resilience. In Genomic Designing of Climate-Smart Pulse Crops; Kole, C., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, pp.
- Fikre, A.; Van Moorhem, M.; Ahmed, S.; Lambein, F.; Gheysen, G. Studies on neurolathyrism in Ethiopia: Dietary habits, perception of risks and prevention. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 678–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arslan, M.; Basak, M.; Aksu, E.; Uzun, B.; Yol, E. Genotyping of Low β-ODAP Grass Pea (Lathyrus sativus L.) Germplasm with EST-SSR Markers. Braz. Arch. Biol. Technol. 2020, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Parihar, A.K.; Barpete, S.; Kumar, S.; Gupta, S. Current Perspectives on Reducing the β-ODAP Content and Improving Potential Agronomic Traits in Grass Pea (Lathyrus sativus L.). Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, J. , Das, A., Parihar, A.K., Sharma, R., Pramanik, K., Barpete, S. (2022). Genomic Designing Towards Development of Abiotic Stress Tolerant Grass Pea for Food and Nutritional Security. In: Kole, C. (eds) Genomic Designing for Abiotic Stress Resistant Pulse Crops. Springer, Cham. [CrossRef]
- Rizvi, A.H.; Sarker, A.; Dogra, A. Enhancing grasspea (Lathyrus sativus L.) production in problematic soils of South Asia for nutritional security. Indian J. Genet. Plant Breed. (The) 2016, 76, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, S. L. , Adiga, P. R. & Sarma, P. S. (1964). The Isolation and Characterization of Beta-N-Oxalyl-L-Alpha,Beta-Diaminopropionic Acid: A Neurotoxin from the Seeds of Lathyrus Sativus. Biochemistry 3, 432–436.
- Goldsmith, M.; Barad, S.; Knafo, M.; Savidor, A.; Ben-Dor, S.; Brandis, A.; Mehlman, T.; Peleg, Y.; Albeck, S.; Dym, O.; et al. Identification and characterization of the key enzyme in the biosynthesis of the neurotoxin β-ODAP in grass pea. J. Biol. Chem. 2022, 298, 101806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, A.; Njaci, I.; Sarkar, A.; Jiang, Z.; Kaithakottil, G.G.; Moore, C.; Cheema, J.; Stevenson, C.E.M.; Rejzek, M.; Novák, P.; et al. Genomics and biochemical analyses reveal a metabolon key to β-L-ODAP biosynthesis in Lathyrus sativus. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathi, D.; Chakraborty, S.; Chakraborty, N. Grasspea, a critical recruit among neglected and underutilized legumes, for tapping genomic resources. Curr. Plant Biol. 2021, 26, 100200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urga k, Fufa H, Biratu E, Husain A (2005). Evaluation of Lathyrus sativus cultivated in Ethiopia for proximate composition, mineral and b-ODAP and antinutritional components. African Journal of Food Agriculture and Nutritional Development, 5: 1-15.
- Arslan M (2017) Diversity for vitamin and amino acid content in grass pea (Lathyrus sativus L.). Legume Research 40:803–810.
- Rao, S.L.N.; Ramachandran, L.K.; Adiga, P.R. The Isolation and Characterization of L-Homoarginine from Seeds of Lathyrus sativus*. Biochemistry 1963, 2, 298–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, S. A look at the brighter facets of β-N-oxalyl-l-α,β-diaminopropionic acid, homoarginine and the grass pea. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 620–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodionov, R.N.; Begmatov, H.; Jarzebska, N.; Patel, K.; Mills, M.T.; Ghani, Z.; Khakshour, D.; Tamboli, P.; Patel, M.N.; Abdalla, M.; et al. Homoarginine Supplementation Prevents Left Ventricular Dilatation and Preserves Systolic Function in a Model of Coronary Artery Disease. J. Am. Hear. Assoc. 2019, 8, e012486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsikas D, Wu G. (2015). Homoarginine, arginine, and relatives: analysis, metabolism, transport, physiology, and pathology. Amino Acids. 47:1697–1702.
- Jammulamadaka, N.; Burgula, S.; Medisetty, R.; Ilavazhagan, G.; Rao, S.L.N.; Singh, S.S. β-N-Oxalyl-l-α,β-diaminopropionic acid regulates mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling by down-regulation of phosphatidylethanolamine-binding protein 1. J. Neurochem. 2011, 118, 176–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, M.; Kayacelebi, A.A.; Batkai, S.; Jordan, J.; Tsikas, D.; Engeli, S. Plasma and tissue homoarginine concentrations in healthy and obese humans. Amino Acids 2015, 47, 1847–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsikas, D.; Bollenbach, A.; Hanff, E.; Kayacelebi, A.A. Asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA), symmetric dimethylarginine (SDMA) and homoarginine (hArg): the ADMA, SDMA and hArg paradoxes. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2018, 17, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llorent-Martínez, E.J.; Zengin, G.; Fernández-de Córdova, M.L.; Bender, O.; Atalay, A.; Ceylan, R.; Mollica, A.; Mocan, A.; Uysal, S.; Guler, G.O.; et al. Traditionally Used Lathyrus Species: Phytochemical Composition, Antioxidant Activity, Enzyme Inhibitory Properties, Cytotoxic Effects, and in silico Studies of L. czeczottianus and L. nissolia. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Striefler M, Cohn D, Hirano A, Schujman E. (1977). The central nervous system in a case of neurolathyrism Neurology, 27 (12) (1977), pp. 1176-1178.
- Haimanot H, Kidane Y, Wuhib E, Kalissa A, Alemu T, Zein Z, Spencer P. (1990). Lathyrism in rural northwestern Ethiopia: a highly prevalent neurotoxic disorder Int. J. Epidemiol., 19 (3) (1990), pp.
- Van Moorhem, M.; Lambein, F.; Leybaert, L. Unraveling the mechanism of β-N-oxalyl-α,β-diaminopropionic acid (β-ODAP) induced excitotoxicity and oxidative stress, relevance for neurolathyrism prevention. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 550–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getahun, H.; Mekonnen, A.; TekleHaimanot, R.; Lambein, F. Epidemic of neurolathyrism in Ethiopia. Lancet 1999, 354, 306–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woldeamanuel, Y.W.; Hassan, A.; Zenebe, G. Neurolathyrism: two Ethiopian case reports and review of the literature. J. Neurol. 2011, 259, 1263–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girma, A.; Tefera, B.; Dadi, L. Grass Pea and Neurolathyrism: Farmers’ perception on its consumption and protective measure in North Shewa, Ethiopia. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 668–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoque, H., Jamali, S., Akther, J., & Prodhan, S. H. (2012). Computational analysis of milk sources from different domestic animals as supplementary food source to protect Lathyrism. International Journal of Biosciences, 2(7), 74-82.
- Girma, D.; Korbu, L. Genetic improvement of grass pea (Lathyrus sativus) in Ethiopia: an unfulfilled promise. Plant Breed. 2012, 131, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, E.; O'Donovan, J.P. The isolation of α- and γ-oxalyl derivatives of α,γ-diaminobutyric acid from seeds of Lathyrus latifolius, and the detection of the α-oxalyl isomer of the neurotoxin α-amino-β-oxalylaminopropionic acid which occurs together with the neurotoxin in this and other species. Phytochemistry 1966, 5, 1211–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patto, M.C.V.; Rubiales, D. Lathyrus diversity: available resources with relevance to crop improvement – L. sativus and L. cicera as case studies. Ann. Bot. 2014, 113, 895–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girish Prasad Dixit, Ashok Kumar Parihar, Abhishek Bohra, Narendra Pratap Singh (2016) Achievements and prospects of grass pea (Lathyrus sativus L.) provement for sustainable food production., ICAR-Indian Institute of Pulses Research (IIPR), Kanpur 208024, India.
- Song, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, F.; Jiao, C.; Nan, H.; Shen, X.; Chen, H.; Li, Y.; Lei, B.; Jiang, J.; et al. β-Cyanoalanine Synthase Regulates the Accumulation of β-ODAP via Interaction with Serine Acetyltransferase in Lathyrus sativus. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 1953–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusama-Eguchi, K.; Yoshino, N.; Minoura, A.; Watanabe, K.; Kusama, T.; Lambein, F.; Ikegami, F. Sulfur amino acids deficiency caused by grass pea diet plays an important role in the toxicity of l-β-ODAP by increasing the oxidative stress: Studies on a motor neuron cell line. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 636–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, L.; Rubiales, D.; Bronze, M.R.; Patto, M.C.V. Grass Pea (Lathyrus sativus L.)—A Sustainable and Resilient Answer to Climate Challenges. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Bejiga, G.; Ahmed, S.; Nakkoul, H.; Sarker, A. Genetic improvement of grass pea for low neurotoxin (β-ODAP) content. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010, 49, 589–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCutchan, J. S. (2003). A brief history of grasspea and its use in crop improvement. Lath. Newsl. 3, 18–23.
- Rahman, M.; Ali, M.; Alam, F.; Banu, M.; Faruk, M.; Bhuiyan, M. Biocontrol of Foot and Root Rot Disease of Grasspea (Lathyrus sativus) by Dual Inoculation with Rhizobium and Arbuscular Mycorrhiza. Bangladesh J. Microbiol. 2019, 34, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, C.G.; Briggs, C.J. Registration of Low Neurotoxin Content Lathyrus Germplasm LS 8246. Crop. Sci. 1987, 27, 821–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H. M., & Zhang, X. Y. (2005). Considerations on the reintroduction of grass pea in China. Lathyrus Lathyrism Newsletter, 4, 22-26.
- Tadesse, W.; Bekele, E. Variation and association of morphological and biochemical characters in grass pea (Lathyrus sativus L.). Euphytica 2003, 130, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santha, I. M. , and Mehta, S. L. (2001). Development of low ODAP somaclones of Lathyrus sativus. Lath. Lath. Newsl. 2:42.
- Yadav, C. R. (1996). “Genetic evaluation and varietal improvement of grasspea in Nepal,” in: Lathyrus Genetic Resources in Asia: Proceedings of a Regional Workshop (Raipur:.
- Grela, E.R.; Rybiński, W.; Klebaniuk, R.; Matras, J. Morphological characteristics of some accessions of grass pea (Lathyrus sativus L.) grown in Europe and nutritional traits of their seeds. Genet. Resour. Crop. Evol. 2010, 57, 693–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granati, E.; Bisignano, V.; Chiaretti, D.; Crinò, P.; Polignano, G.B. Characterization of Italian and exotic Lathyrus germplasm for quality traits. Genet. Resour. Crop. Evol. 2003, 50, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, D., and Krause, I. (2003). New green manuring Lathyrus sativus variety AC Greenfix available in USA. Lath. Lath. Newsl. 3, 13–14.
- Mera, M. , Tay, J., France, A., Montenegro, A., Espinoza, N., and Gaete, N. (2003). Luanco-INIA, a large-seeded cultivar of Lathyrus sativus released in Chile. Lath. Lath. Newsl. 3:26.
- Dixit, G.P.; Parihar, A.K.; Bohra, A.; Singh, N.P. Achievements and prospects of grass pea ( Lathyrus sativus L.) improvement for sustainable food production. Crop. J. 2016, 4, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen Gupta, D. , Barpete, S., Kumar, J., and Kumar, S. (2021). “Breeding for better grain quality in lathyrus,” in Breeding for Enhanced Nutrition and Bio-Active Compounds in Food Legumes, eds D. S. Gupta, S. Gupa, and J. Kumar (Switzerland: Springer), 131–156. [CrossRef]
- Malek, M. A. , Sarwar, C. D. M., Sarker, A., and Hassan, M. S. (1996). “Status of grass pea research and future strategy in Bangladesh”, in Lathyrus Genetic Resources in Asia, ed. R. K., Arora, P. N., Mathur, K. W., Riley, Y., Adham (Rome: International Plant Genetic Resources Institute), 7–12.
- Kumar, S. , Gupta P., Barpete S., Sarker A., Amri, A., Mathur, P. N., et al. (2013). “Grass pea,” in Improvement, Genetic and Genomic Resources for Grain Legume eds M. Singh, H. D. Upadhyaya, I. S. Bisht (London: Elsevier), 269-293. [CrossRef]
- ICARDA (2007). ICARDA Annual report. International Center for Agricultural Research in the Dry Areas.
- Mehta, S. L. , and I. M. Santha, 2008: Somaclonal variation and genetic transformation in Lathyrus sativus. In: P. B. Kirti (eds), Handbook of New Technologies for Genetic Improvement of Legumes, 177— 184. CRS Press, New York.
- Campbell, C.G.; Mehra, R.B.; Agrawal, S.K.; Chen, Y.Z.; El Moneim, A.M.A.; Khawaja, H.I.T.; Yadov, C.R.; Tay, J.U.; Araya, W.A. Current status and future strategy in breeding grasspea (Lathyrus sativus). Euphytica 1993, 73, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MoARD, 2008: Animal and plant health regulatory directorate. Crop Variety Register, 11. Addis Ababa, Ethiopia.
- Hussain, M. , Chowdhury, B., Hoque, R., Lambein, F., 1997. Effect of water stress, salinity, interaction of cations, stage of maturity of seeds and storage devices on the ODAP content of Lathyrus sativus. In: Tekle Haimanot, R., Lambein, F. (Eds.), Lathyrus and Lathyrism a Decade of Progress. University of Ghent, Belgium, pp.
- Xing, G.; Cui, K.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z. (2001). Water stress and accumulation of beta- N-oxalyl-L-alpha,beta-diaminopropionic acid in grass pea (Lathyrus sativus). J. Agric. Food Chem. 49, 216–220.
- Jiao, C.J. , Xu, Q.L., Wang, C.Y., Li, Z.X., Wang, Y.F., 2006. Accumulation pattern of toxin beta-ODAP during lifespan and effect of nutrient elements on beta-ODAP content in Lathyrus sativus seedlings. J. Agric. Sci. 144, 369–375.
- Haque, R.M.; Kuo, Y.-H.; Lambein, F.; Hussain, M. Effect of environmental factors on the biosynthesis of the neuro-excitatory amino acid β-ODAP (β-N-oxalyl-l-α,β-diaminopropionic acid) in callus tissue of Lathyrus sativus. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2010, 49, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokarz, B.; Wójtowicz, T.; Makowski, W.; Jędrzejczyk, R.J.; Tokarz, K.M. What is the Difference between the Response of Grass Pea (Lathyrus sativus L.) to Salinity and Drought Stress?—A Physiological Study. Agronomy 2020, 10, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malathi, K. , Padmanaban, G., Rao, S. L., and Sarma, P. S. (1967) Studies on the biosynthesis of beta-N-oxalyl-L-alpha, beta-diaminopropionic acid, the Lathyrus sativus neurotoxin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 141, 71–78.
- Malathi, K., Padmanaban, G., and Sarma, P. S. (1970) Biosynthesis of beta-N-Oxalyl-L-Alpha,Beta-Diaminopropionic acid, Lathyrus-sativus neurotoxin. Phytochemistry 9, 1603±.
- Ikegami, F.; Ongena, G.; Sakai, R.; Itagaki, S.; Kobori, M.; Ishikawa, T.; Kuo, Y.-H.; Lambein, F.; Murakoshi, I. Biosynthesis of β-(isoxazolin-5-on-2-yl)-l-alanine by cysteine synthase in Lathyrus sativus. Phytochemistry 1993, 33, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, J. M. , & Raushel, F. M. (1994) Biochemistry 33, 4265—4272.
- Song, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, F.; Jiao, C.; Nan, H.; Shen, X.; Chen, H.; Li, Y.; Lei, B.; Jiang, J.; et al. β-Cyanoalanine Synthase Regulates the Accumulation of β-ODAP via Interaction with Serine Acetyltransferase in Lathyrus sativus. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 1953–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Liu, F.; Chen, P.; Jez, J.M.; Krishnan, H.B. β-N-Oxalyl-l-α,β-diaminopropionic Acid (β-ODAP) Content in Lathyrus sativus: The Integration of Nitrogen and Sulfur Metabolism through β-Cyanoalanine Synthase. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.-Y.; Spencer, P.S.; Li, Z.-X.; Liang, Y.-M.; Wang, Y.-F.; Wang, C.-Y.; Li, F.-M. Lathyrus sativus (grass pea) and its neurotoxin ODAP. Phytochemistry 2006, 67, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feinberg, A.; Stenke, A.; Peter, T.; Hinckley, E.-L.S.; Driscoll, C.T.; Winkel, L.H.E. Reductions in the deposition of sulfur and selenium to agricultural soils pose risk of future nutrient deficiencies. Commun. Earth Environ. 2021, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krogsgaard-Larsen, P.; Hansen, J.J. Naturally-occurring excitatory amino acids as neurotoxins and leads in drug design. Toxicol. Lett. 1992, 64-65, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grosskreutz J, Van Den Bosch L, Keller B. (2010). Calcium dysregulation in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis Cell Calcium, 47 (2010), pp. 165-174.
- Kusama-Eguchi, K.; Miyano, T.; Yamamoto, M.; Suda, A.; Ito, Y.; Ishige, K.; Ishii, M.; Ogawa, Y.; Watanabe, K.; Ikegami, F.; et al. New insights into the mechanism of neurolathyrism: L-β-ODAP triggers [Ca2+]i accumulation and cell death in primary motor neurons through transient receptor potential channels and metabotropic glutamate receptors. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 67, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khandare, A.L.; B, K.; Validandi, V.; Ssyh, Q.; Harishankar, N.; Singh, S.S.; Kodali, V. Neurolathyrism in goat (Capra hircus) kid: Model development. Res. Veter- Sci. 2020, 132, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doble A. (1999).The role of excitotoxicity in neurodegenerative disease: implications for therapy. Pharmacol. Ther., 81 (3) (1999), pp. 163-221.
- Hertz L. (2006). Glutamate, a neurotransmitter–and so much more A synopsis of Wierzba III. Neurochem. Int., 48 (6–7) (2006), pp. 416-425.
- Saeed, U.; Durgadoss, L.; Valli, R.K.; Joshi, D.C.; Joshi, P.G.; Ravindranath, V. Knockdown of Cytosolic Glutaredoxin 1 Leads to Loss of Mitochondrial Membrane Potential: Implication in Neurodegenerative Diseases. PLOS ONE 2008, 3, e2459–e2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravindranath, V. (2002). Neurolathyrism: mitochondrial dysfunction in excitotoxicity mediated by L-β-oxalyl aminoalanine. Neurochemistry international, 40(6), 505-509.
- López-Martín, M.C.; Becana, M.; Romero, L.C.; Gotor, C. Knocking Out Cytosolic Cysteine Synthesis Compromises the Antioxidant Capacity of the Cytosol to Maintain Discrete Concentrations of Hydrogen Peroxide in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2008, 147, 562–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hailu D, Abera S, Abera T. (2015), Effects of Processing on Nutritional Composition and Anti-Nutritional Factors of Grass pea (Lathyrus Sativus L) journal of Food Science and Quality Management www.iiste.org ISSN 2224-6088 (Paper) ISSN 2225-0557, Vol.36.
- Haileyesus Getahun, Fernand Lambein, Michel Vanhoorne and Patrick Van der Stuyft, (2005). Neurolathyrism risk depends on type of grass pea preparation and on mixing with cereals and antioxidants volume 10no 2 pp 169–178.
- Tadele, D. , Alemu, Y., Nigusie, D. and Peters, K. J. (2003). Evaluation of Processing Methods on the Feeding Value of Grass Pea to Broilers. Inter. J. Poult. Sci., 2(2): 120- 127.
- Akalu, G. , Johansson, G., & Nair, B. M. (1998). Effect of processing on the content of β-N-oxalyl-α, β-diaminopropionic acid (gb-ODAP) in grass pea (Lathyrus sativus) seeds and flour as determined by flow injection analysis. Food Chemistry, 62(2), 233-237.
- Barik, D.P.; Mohapatra, U.; Chand, P.K. Transgenic grasspea (Lathyrus sativus L.): Factors influencing Agrobacterium-mediated transformation and regeneration. Plant Cell Rep. 2005, 24, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barna, K.S.; Mehta, S.L. Genetic Transformation and Somatic Embryogenesis in Lathyrus sativus. J. Plant Biochem. Biotechnol. 1995, 4, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girma, D. (2010). Ethiopian grass pea (Lathyrus sativus L.) started the genomics era: transient genetic transformation of grass pea. LAP Lambert Academic Publishing, Köln.
- Krishnan, H.B. Engineering Soybean for Enhanced Sulfur Amino Acid Content. Crop. Sci. 2005, 45, 454–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kortt, A.A.; Caldwell, J.B.; Lilley, G.G.; Higgins, T.J.V. Amino acid and cDNA sequences of a methionine-rich 2S protein from sunflower seed (Helianthus annuus L.). Eur. J. Biochem. 1991, 195, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirihara, J.A.; Petri, J.B.; Messing, J. Isolation and sequence of a gene encoding a methionine-rich 10-kDa zein protein from maize. Gene 1988, 71, 359–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chui, C.F.; Falco, S.C. A New Methionine-Rich Seed Storage Protein from Maize. Plant Physiol. 1995, 107, 291–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Planta, J.; Xiang, X.; Leustek, T.; Messing, J. Engineering sulfur storage in maize seed proteins without apparent yield loss. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2017, 114, 11386–11391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinkins, R.D.; Reddy, M.S.S.; Meurer, C.A.; Yan, B.; Trick, H.; Thibaud-Nissen, F.; Finer, J.J.; Parrott, W.A.; Collins, G.B. Increased sulfur amino acids in soybean plants overexpressing the maize 15 kDa zein protein. Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol. - Plant 2001, 37, 742–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.S.; Krishnan, H.B. Allelic variation and differential expression of methionine-rich δ-zeins in maize inbred lines B73 and W23a1. Planta 2003, 217, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, C.; Liu, X.; Chen, L.; Cai, Y.; Yao, W.; Yuan, S.; Wu, C.; Han, T.; Sun, S.; Hou, W. Elevated methionine content in soybean seed by overexpressing maize β-zein protein. Oil Crop. Sci. 2020, 5, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.-S.; Sun-Hyung, J.; Oehrle, N.W.; Jez, J.M.; Krishnan, H.B. Overexpression of ATP sulfurylase improves the sulfur amino acid content, enhances the accumulation of Bowman–Birk protease inhibitor and suppresses the accumulation of the β-subunit of β-conglycinin in soybean seeds. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, W.-S.; Chronis, D.; Juergens, M.; Schroeder, A.C.; Hyun, S.W.; Jez, J.M.; Krishnan, H.B. Transgenic soybean plants overexpressing O-acetylserine sulfhydrylase accumulate enhanced levels of cysteine and Bowman–Birk protease inhibitor in seeds. Planta 2011, 235, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avraham, T. , Badani, H., Galili, S., & Amir, R. (2005). Enhanced levels of methionine and cysteine in transgenic alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) plants over-expressing the Arabidopsis cystathionine γ-synthase gene. Plant Biotechnology Journal, 3(1), 71-79.
- Endo, M.; Mikami, M.; Toki, S. Biallelic Gene Targeting in Rice. Plant Physiol. 2015, 170, 667–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilscher, J.; Bürstmayr, H.; Stoger, E. Targeted modification of plant genomes for precision crop breeding. Biotechnol. J. 2016, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrichs, S.; Takasu, Y.; Kearns, P.; Dagallier, B.; Oshima, R.; Schofield, J.; Moreddu, C. An overview of regulatory approaches to genome editing in agriculture. Biotechnol. Res. Innov. 2019, 3, 208–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zannoni, L. Evolving Regulatory Landscape for Genome-Edited Plants. CRISPR J. 2019, 2, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Hussain, A.; Manghwar, H.; Xie, K.; Xie, S.; Zhao, S.; Larkin, R.M.; Qing, P.; Jin, S.; Ding, F. Genome editing with the CRISPR-Cas system: an art, ethics and global regulatory perspective. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2020, 18, 1651–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emmrich, P. M. , Sarkar, A., Njaci, I., Kaithakottil, G. G., Ellis, N., Moore, C.,... & Wang, T. L. (2020). A draft genome of grass pea (Lathyrus sativus), a resilient diploid legume. BioRxiv, 2020-04.
- Friedrichs S, Takasu Y, Kearns P et al (2019) Meeting report of the OECD conference on “genome editing: applications in agriculture—implications for health, environment and regulation.” Transgenic Res 28:419–463.
- Chilcoat D, Liu ZB, Sander J (2017) Use of CRISPR/Cas9 for crop improvement in maize and soybean. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci 149:27–46.
- Fiaz, S.; Ahmad, S.; Noor, M.A.; Wang, X.; Younas, A.; Riaz, A.; Riaz, A.; Ali, F. Applications of the CRISPR/Cas9 System for Rice Grain Quality Improvement: Perspectives and Opportunities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, J.; Fan, W.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, S.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, P. CRISPR/Cas9-Based Mutagenesis of Starch Biosynthetic Genes in Sweet Potato (Ipomoea Batatas) for the Improvement of Starch Quality. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuncel, A.; Corbin, K.R.; Ahn-Jarvis, J.; Harris, S.; Hawkins, E.; Smedley, M.A.; Harwood, W.; Warren, F.J.; Patron, N.J.; Smith, A.M. Cas9-mediated mutagenesis of potato starch-branching enzymes generates a range of tuber starch phenotypes. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2019, 17, 2259–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Jiao, G.; Sun, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhong, Y.; Yan, L.; Jiang, D.; Ma, Y.; Xia, L. Modification of starch composition, structure and properties through editing of TaSBEIIa in both winter and spring wheat varieties by CRISPR/Cas9. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2020, 19, 937–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieves-Cordones, M.; Mohamed, S.; Tanoi, K.; Kobayashi, N.I.; Takagi, K.; Vernet, A.; Guiderdoni, E.; Périn, C.; Sentenac, H.; Véry, A. Production of low-Cs+ rice plants by inactivation of the K+ transporter OsHAK1 with the CRISPR-Cas system. Plant J. 2017, 92, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez, M.A.; Berkoff, K.C.; Gill, B.K.; Iavarone, A.T.; Lieberman, S.E.; Ma, J.M.; Schultink, A.; Karavolias, N.G.; Wyman, S.K.; Chauhan, R.D.; et al. CRISPR-Cas9-mediated knockout of CYP79D1 and CYP79D2 in cassava attenuates toxic cyanogen production. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 13, 1079254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.H.; Shin, G.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, S.B.; Moon, J.Y.; Jeong, J.C.; Choi, H.-K.; Kim, I.A.; Song, H.J.; Kim, C.Y.; et al. Mutation of GmIPK1 Gene Using CRISPR/Cas9 Reduced Phytic Acid Content in Soybean Seeds. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sashidhar, N.; Harloff, H.J.; Potgieter, L.; Jung, C. Gene editing of three BnITPK genes in tetraploid oilseed rape leads to significant reduction of phytic acid in seeds. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2020, 18, 2241–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffan, S.; Sparks, C.; Huttly, A.; Hyde, L.; Martignago, D.; Mead, A.; Hanley, S.J.; Wilkinson, P.A.; Barker, G.; Edwards, K.J.; et al. Wheat with greatly reduced accumulation of free asparagine in the grain, produced by CRISPR/Cas9 editing of asparagine synthetase gene TaASN2. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2021, 19, 1602–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenar, J.A. Reaction chemistry of gossypol and its derivatives. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2006, 83, 269–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.-L.; Fang, X.; Li, J.-X.; Chen, Z.-W.; Wu, W.-K.; Guo, X.-X.; Liu, N.-J.; Huang, J.-F.; Chen, F.-Y.; Wang, L.-J.; et al. Dirigent gene editing of gossypol enantiomers for toxicity-depleted cotton seeds. Nat. Plants 2023, 9, 605–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schachtsiek, J.; Stehle, F. Dataset on nicotine-free, nontransgenic tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum l.) edited by CRISPR-Cas9. Data Brief 2019, 26, 104395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakaria, M.; Schemmerling, B.; Ober, D. CRISPR/Cas9-Mediated Genome Editing in Comfrey (Symphytum officinale) Hairy Roots Results in the Complete Eradication of Pyrrolizidine Alkaloids. Molecules 2021, 26, 1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Sun, S.; Whelan, J.; Shou, H. CRISPR/Cas9-Mediated Knockout of GmFATB1 Significantly Reduced the Amount of Saturated Fatty Acids in Soybean Seeds. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Shea, Z.; Rosso, L.; Shang, C.; Li, J.; Bewick, P.; Li, Q.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, B. Development of new mutant alleles and markers for KTI1 and KTI3 via CRISPR/Cas9-mediated mutagenesis to reduce trypsin inhibitor content and activity in soybean seeds. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajarammohan, S.; Kaur, L.; Verma, A.; Singh, D.; Mantri, S.; Roy, J.K.; Sharma, T.R.; Pareek, A.; Kandoth, P.K. Genome sequencing and assembly of Lathyrus sativus - a nutrient-rich hardy legume crop. Sci. Data 2023, 10, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riepe, M.; Spencer, P.S.; Lambein, F.; Ludolph, A.C.; Allen, C.N. In vitro toxicological investigations of isoxazolinone amino acids of Lathyrus sativus. Nat. Toxins 1995, 3, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, T. , Shee, R., Sahid, S., Shee, D., Roy, C., Sharma, R.,... & Datta, R. (2023). Designer grass pea for transgene-free minimal neurotoxin-containing seeds with CRISPR-Cas9. bioRxiv, 2023-03.
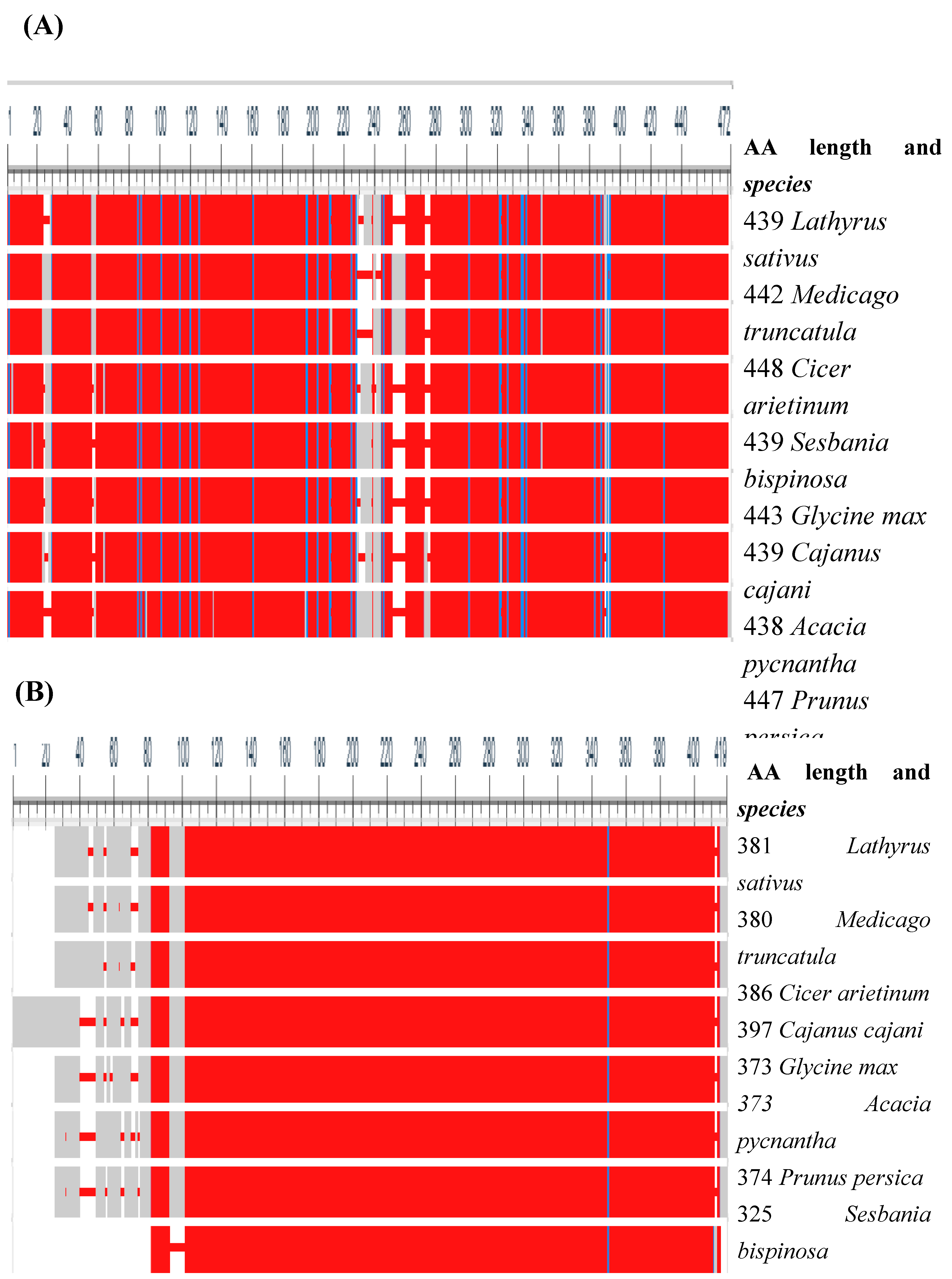
- Papadopoulos, J.S.; Agarwala, R. COBALT: constraint-based alignment tool for multiple protein sequences. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, 1073–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
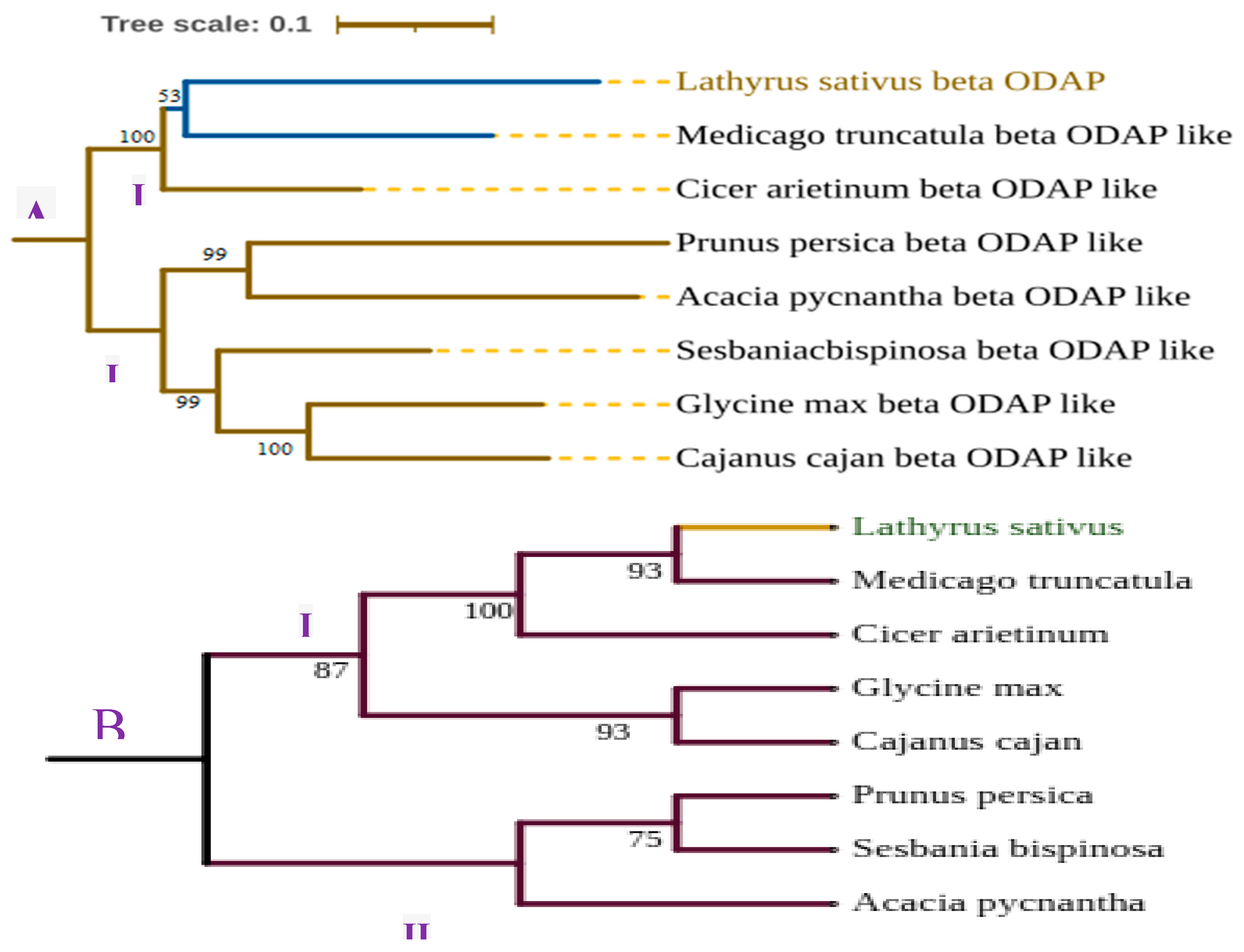
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree Of Life (iTOL) v5: an online tool for phylogenetic tree display and annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W293–W296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).



