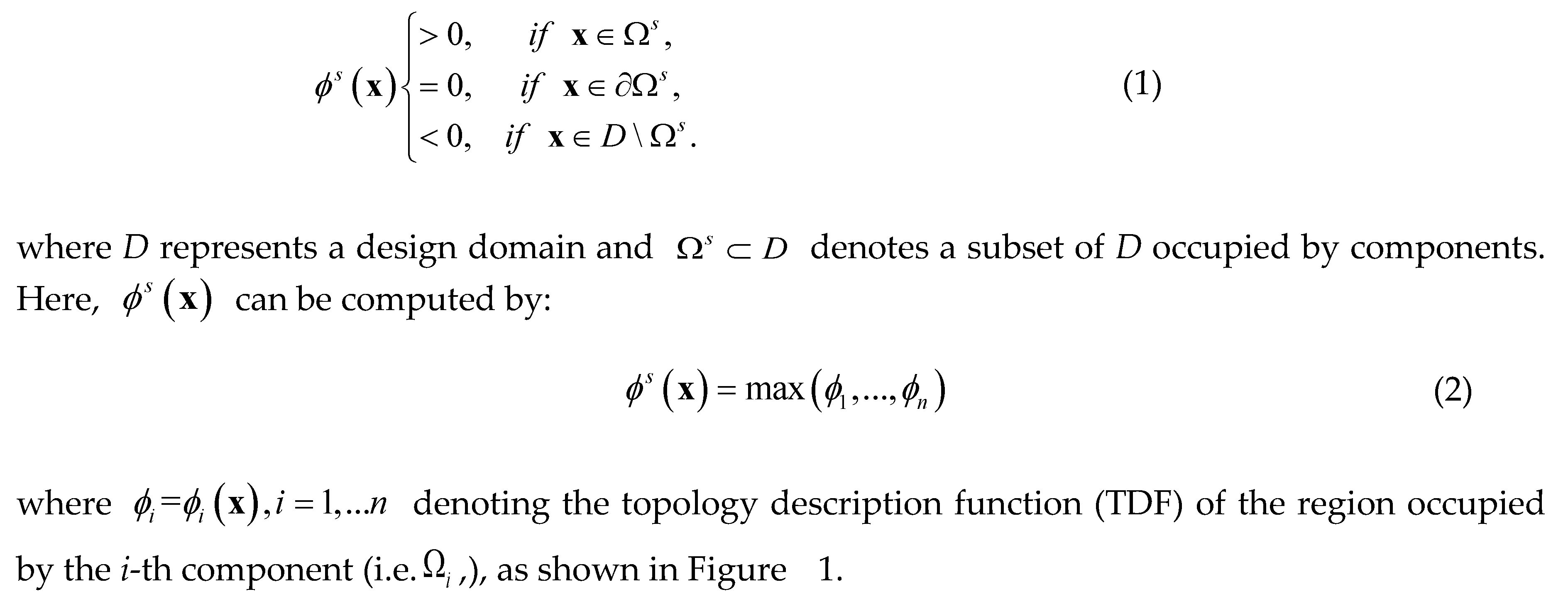
Submitted:
10 July 2024
Posted:
11 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Problem Formulation
2.1. Moving Morphable Component (MMC) Method
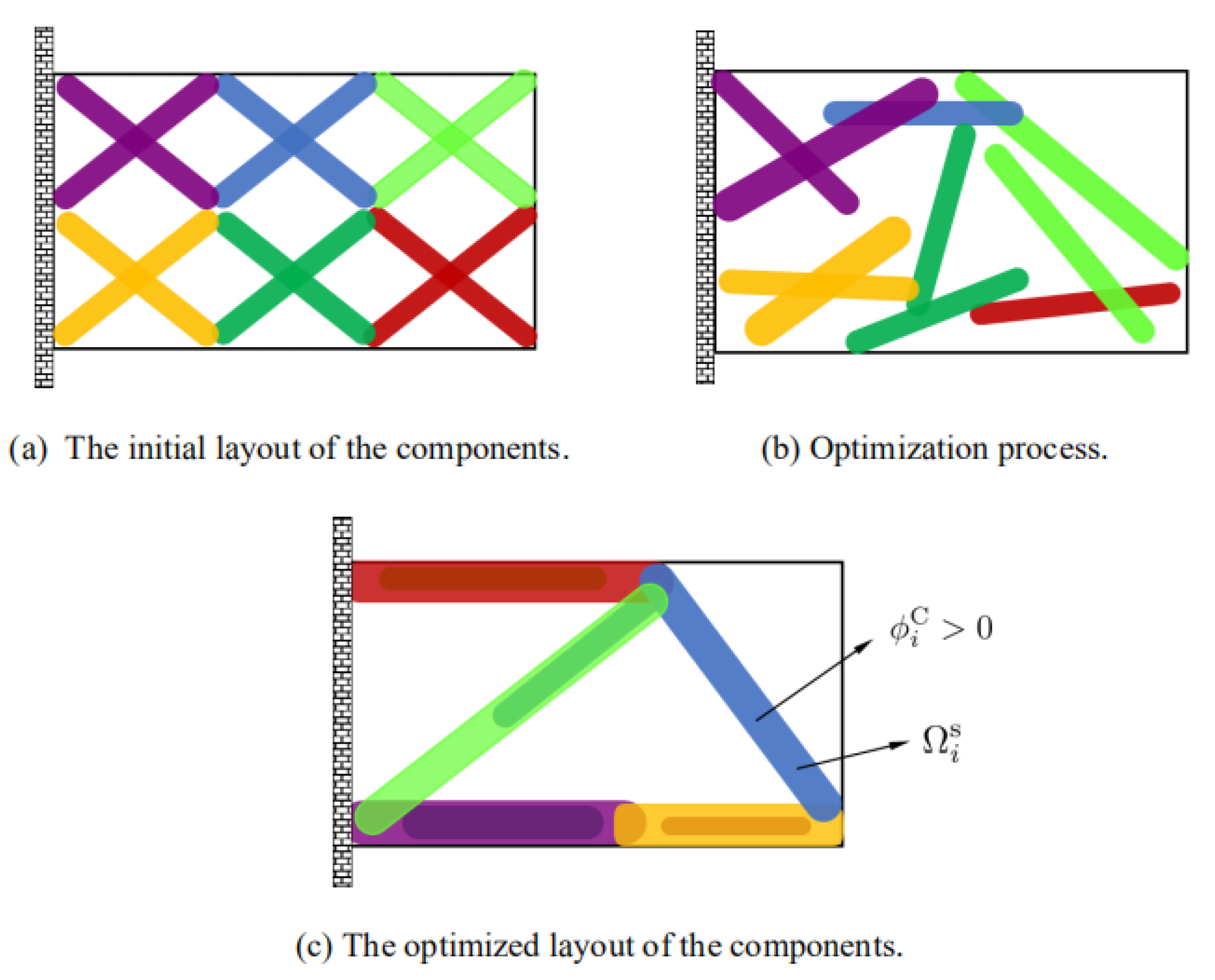
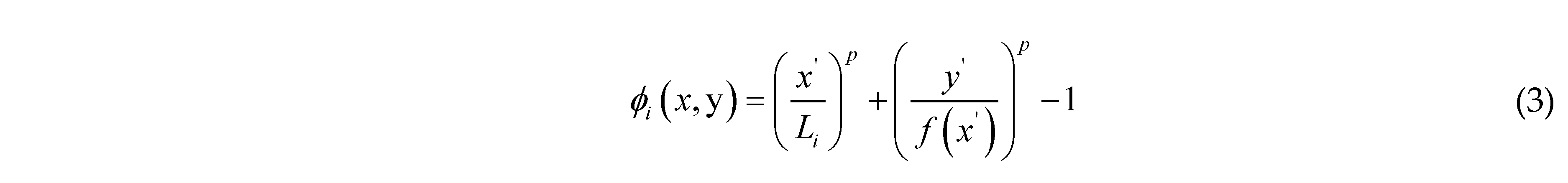
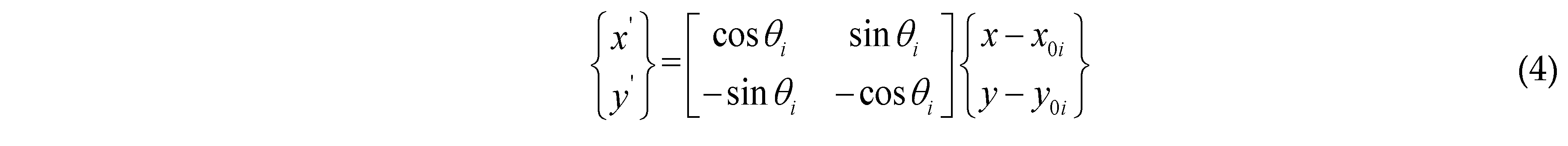
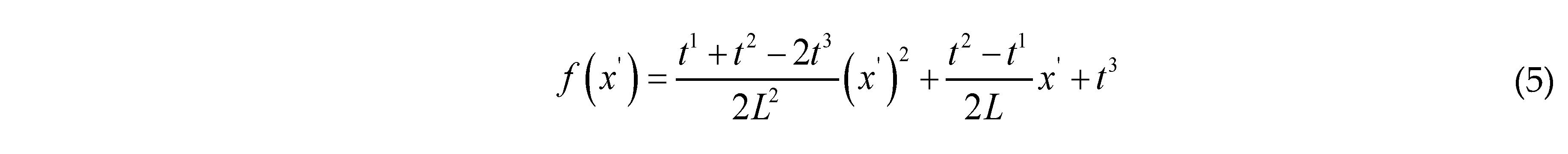
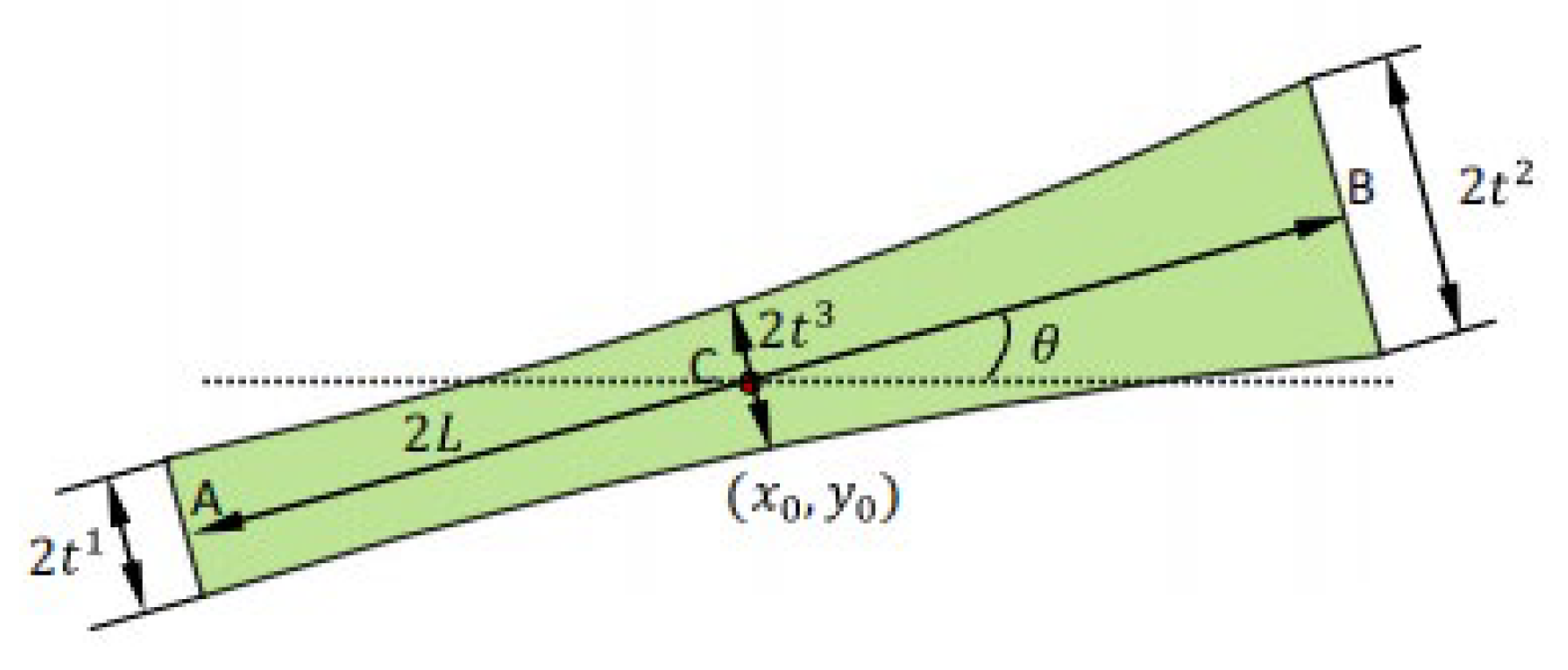
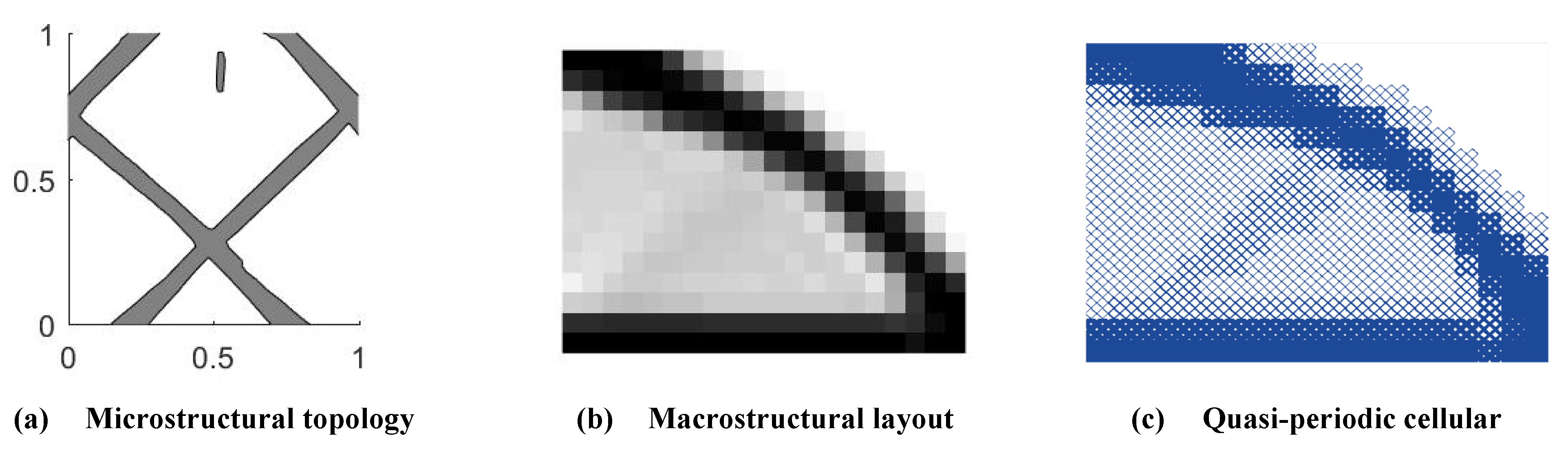
2.2. Topological Description of Quasi-Periodic Cellular Structures
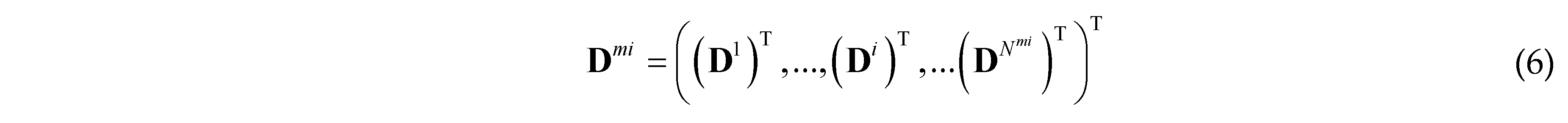
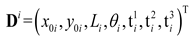 is the parameter vector of the i-th component, Nmi is the number of components. In order to get a series of quasi-periodic microstructures with a simple alterable parameter from the BUC, we define a parameter R which can scale the thickness of all components in the base unit cell, as shown in Figure 3, this means:
is the parameter vector of the i-th component, Nmi is the number of components. In order to get a series of quasi-periodic microstructures with a simple alterable parameter from the BUC, we define a parameter R which can scale the thickness of all components in the base unit cell, as shown in Figure 3, this means: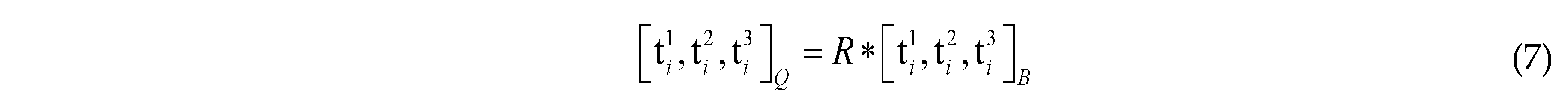
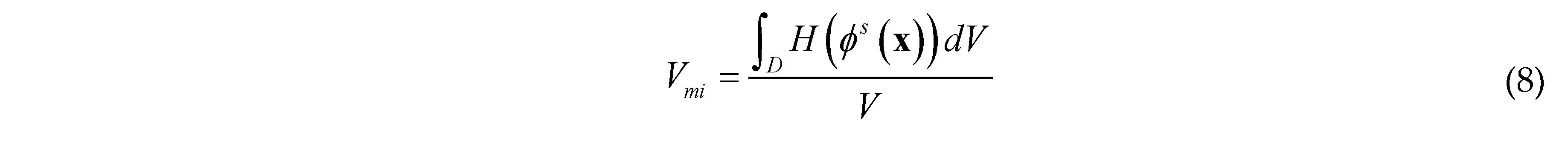
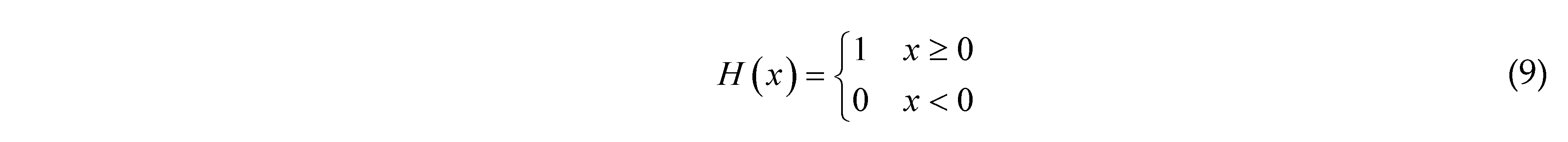
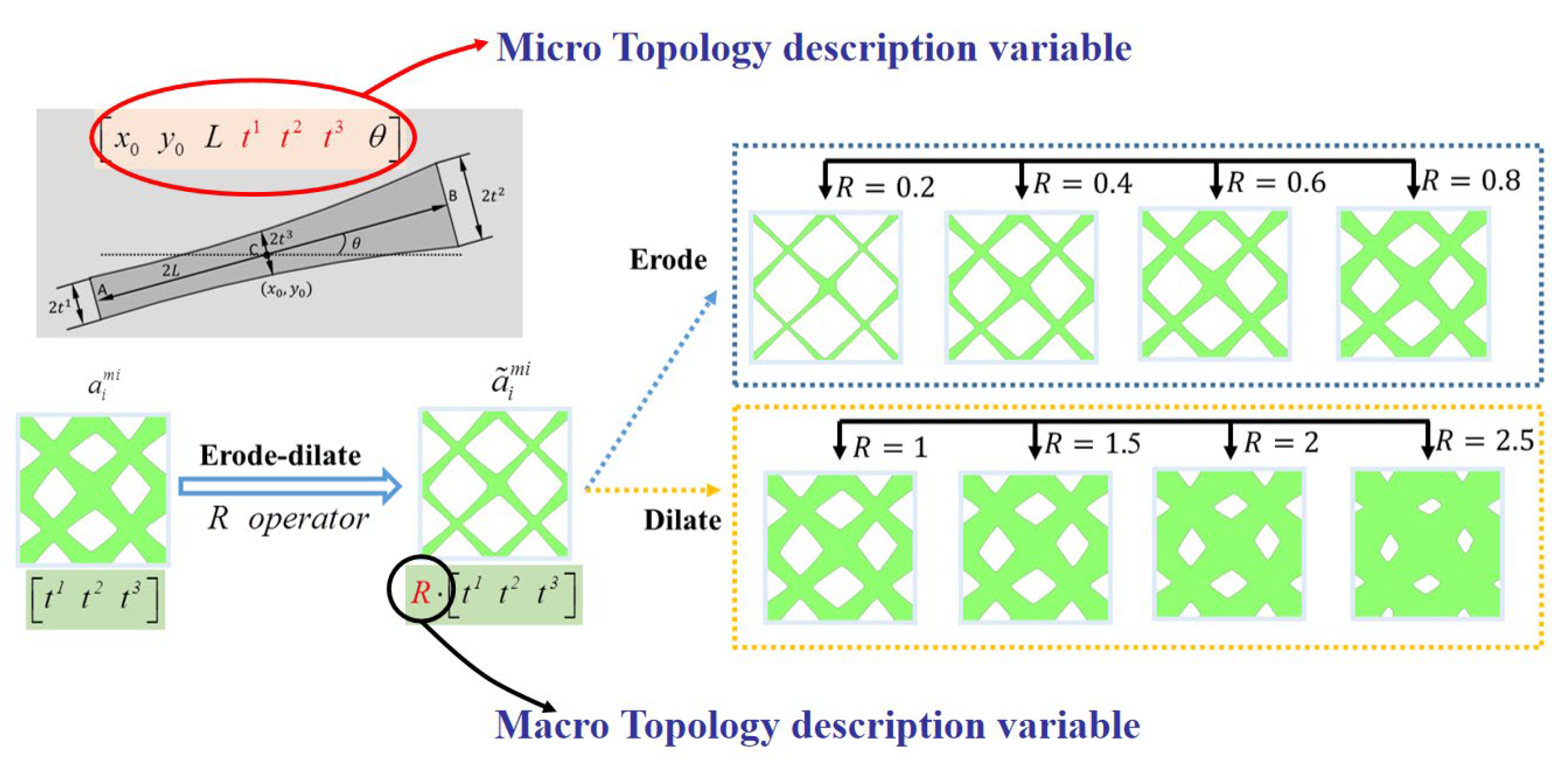
2.3. Optimization Formulation

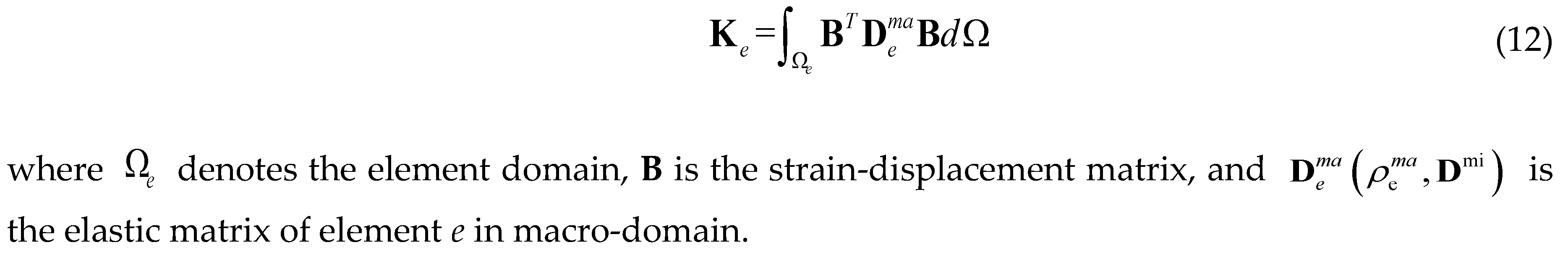
3. Numerical Implementations
3.1. Interpolation Scheme
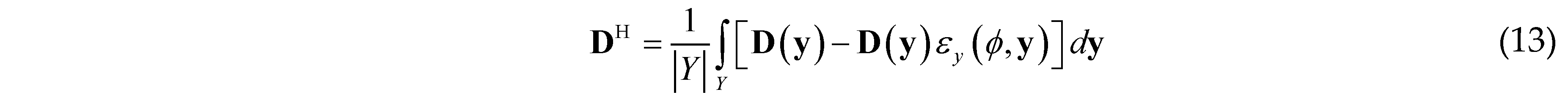
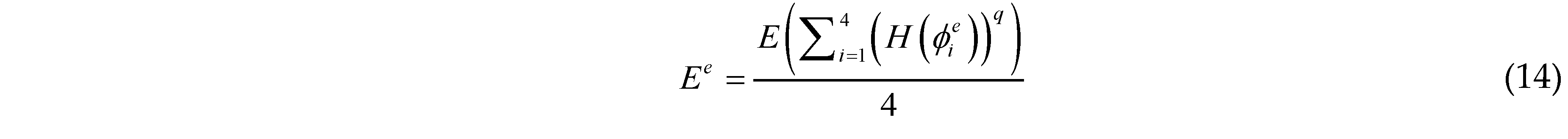
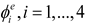 are the values of the TDF function of the whole structure (i.e., ϕs(x)) at four nodes of element e. For numerical implementation purpose, as a common practice in the literature, H(x) is often replaced by its regularized version Hϵ(x). In the present work, the form of Hϵ(x) is taken as
are the values of the TDF function of the whole structure (i.e., ϕs(x)) at four nodes of element e. For numerical implementation purpose, as a common practice in the literature, H(x) is often replaced by its regularized version Hϵ(x). In the present work, the form of Hϵ(x) is taken as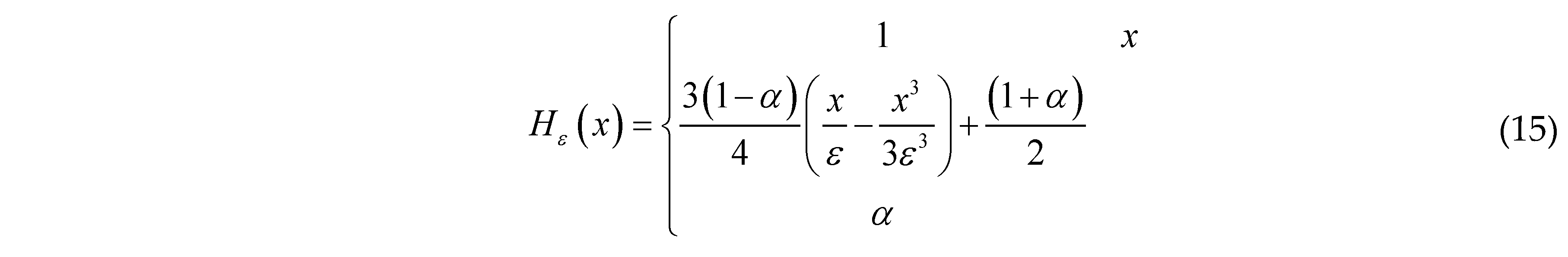
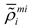 :
: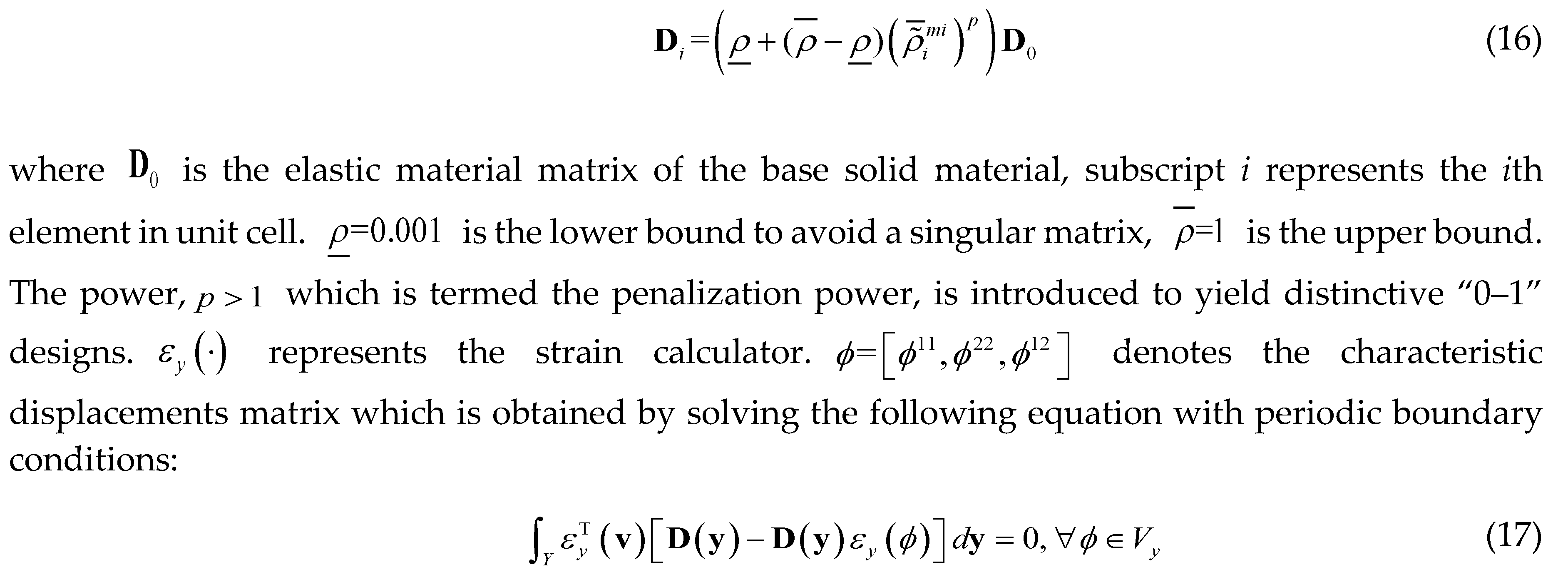
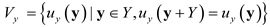 denotes the function space of periodic functions defined in unit cell Y and v represents the virtual displacement field.
denotes the function space of periodic functions defined in unit cell Y and v represents the virtual displacement field.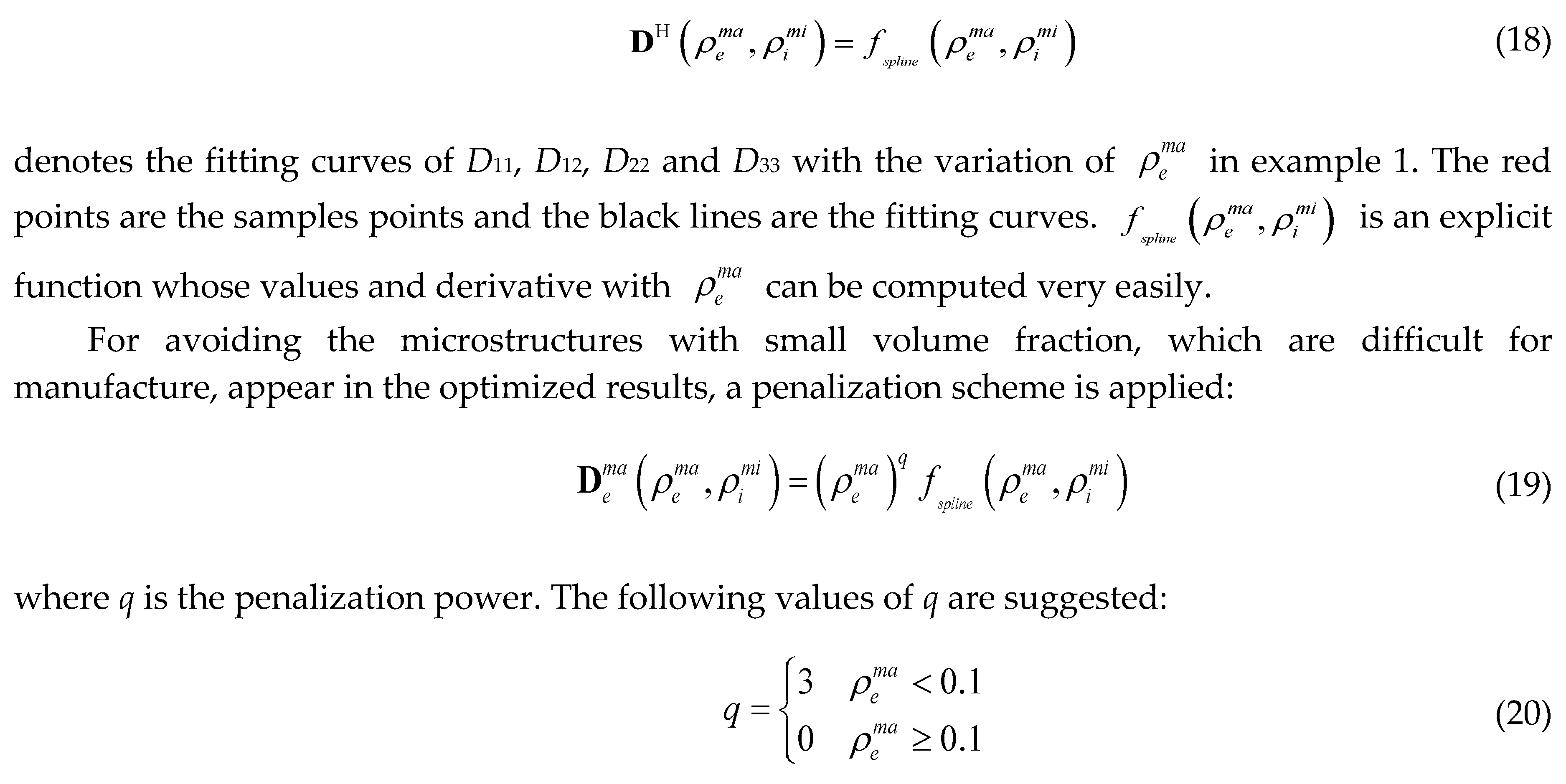
3.2. Sensitivity Analysis
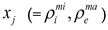 can be obtained based on adjoint method:
can be obtained based on adjoint method: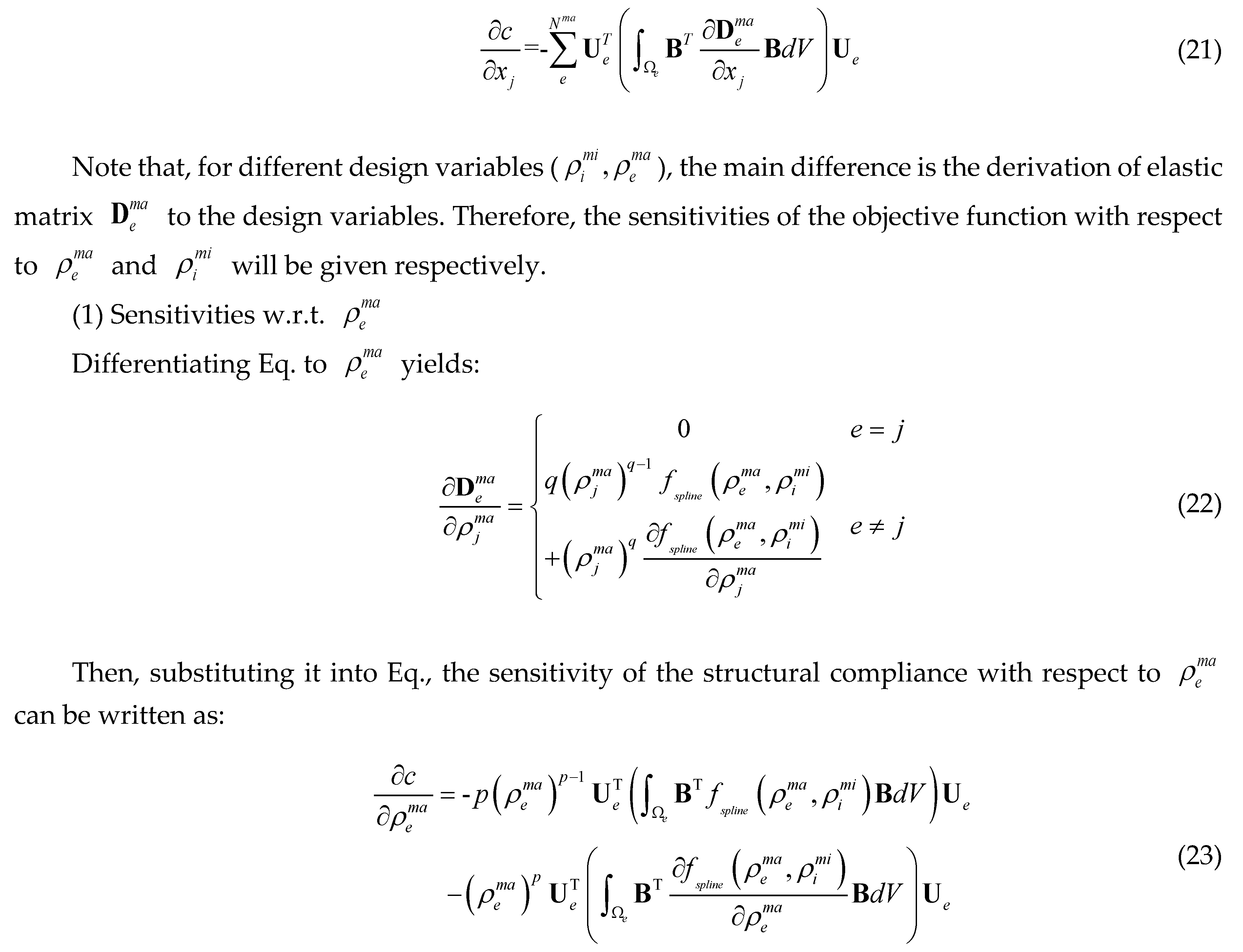
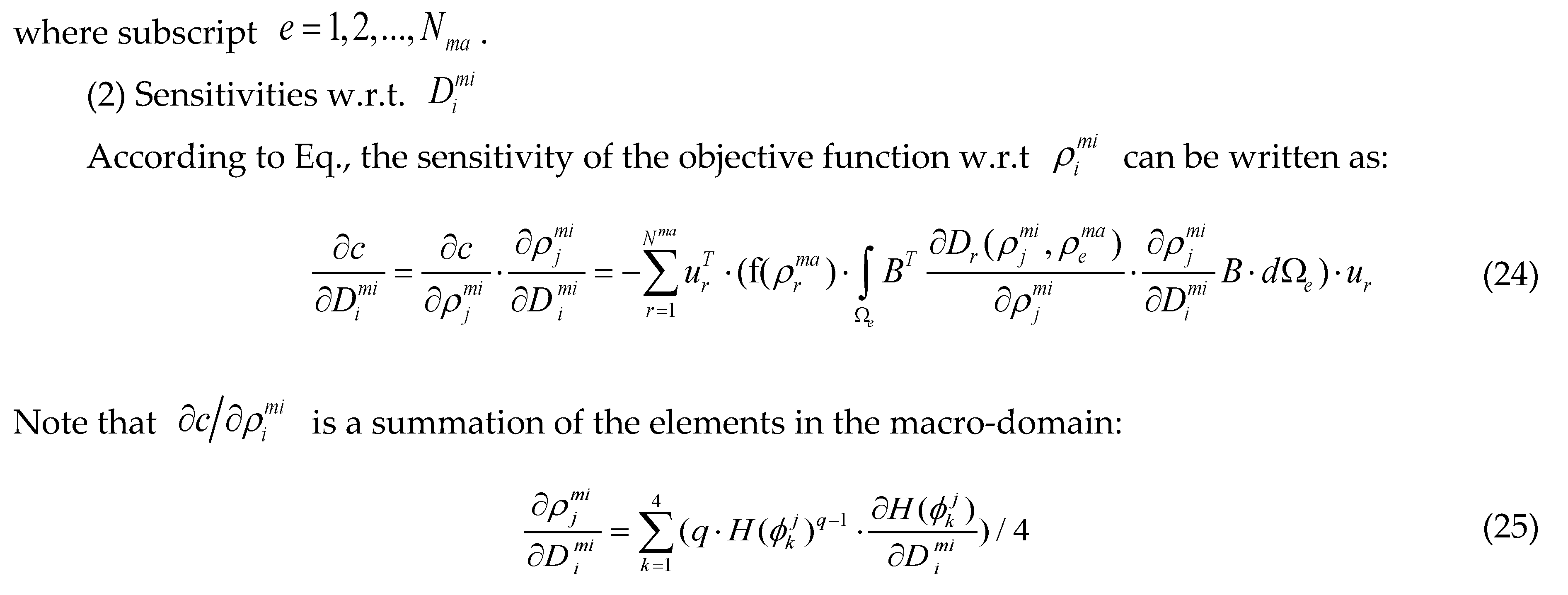
4. Numerical Examples
 and
and 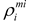 are set to be equal to the volume fractions
are set to be equal to the volume fractions 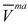 and
and 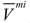 , respectively. It should be noted that, the volume fraction of the base unit cell
, respectively. It should be noted that, the volume fraction of the base unit cell 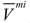 is chosen as 0.2 in this paper. For the design variables
is chosen as 0.2 in this paper. For the design variables  defined in macro-domain, the density filtering technique with filtering radius rma = 1.5 is applied to avoid the check-board phenomena. All the optimization problems are solved using the gradient driven MMA algorithm. The convergence criterion is chosen as:
defined in macro-domain, the density filtering technique with filtering radius rma = 1.5 is applied to avoid the check-board phenomena. All the optimization problems are solved using the gradient driven MMA algorithm. The convergence criterion is chosen as: 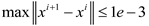 and the maximum iteration number is 300.
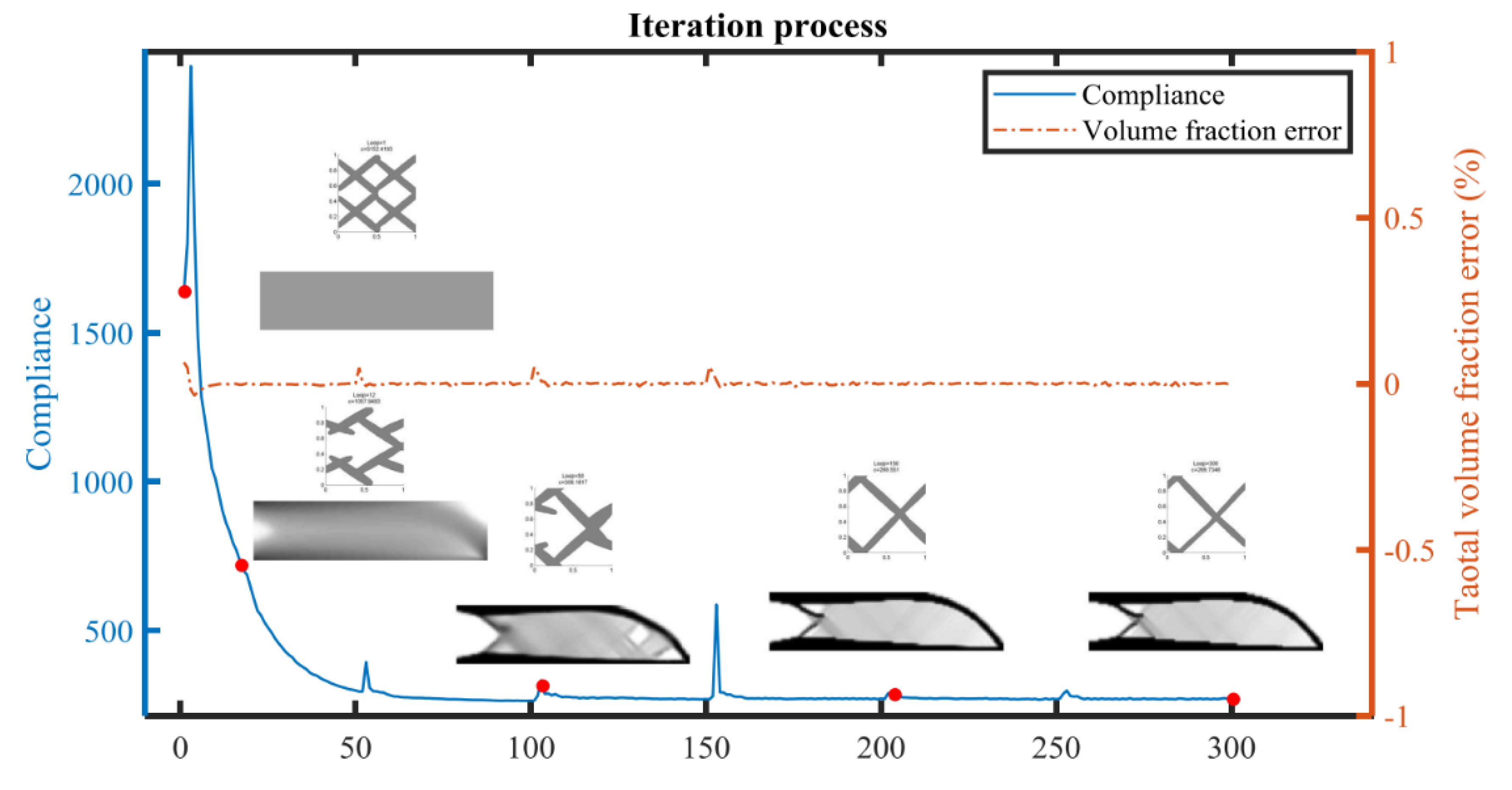
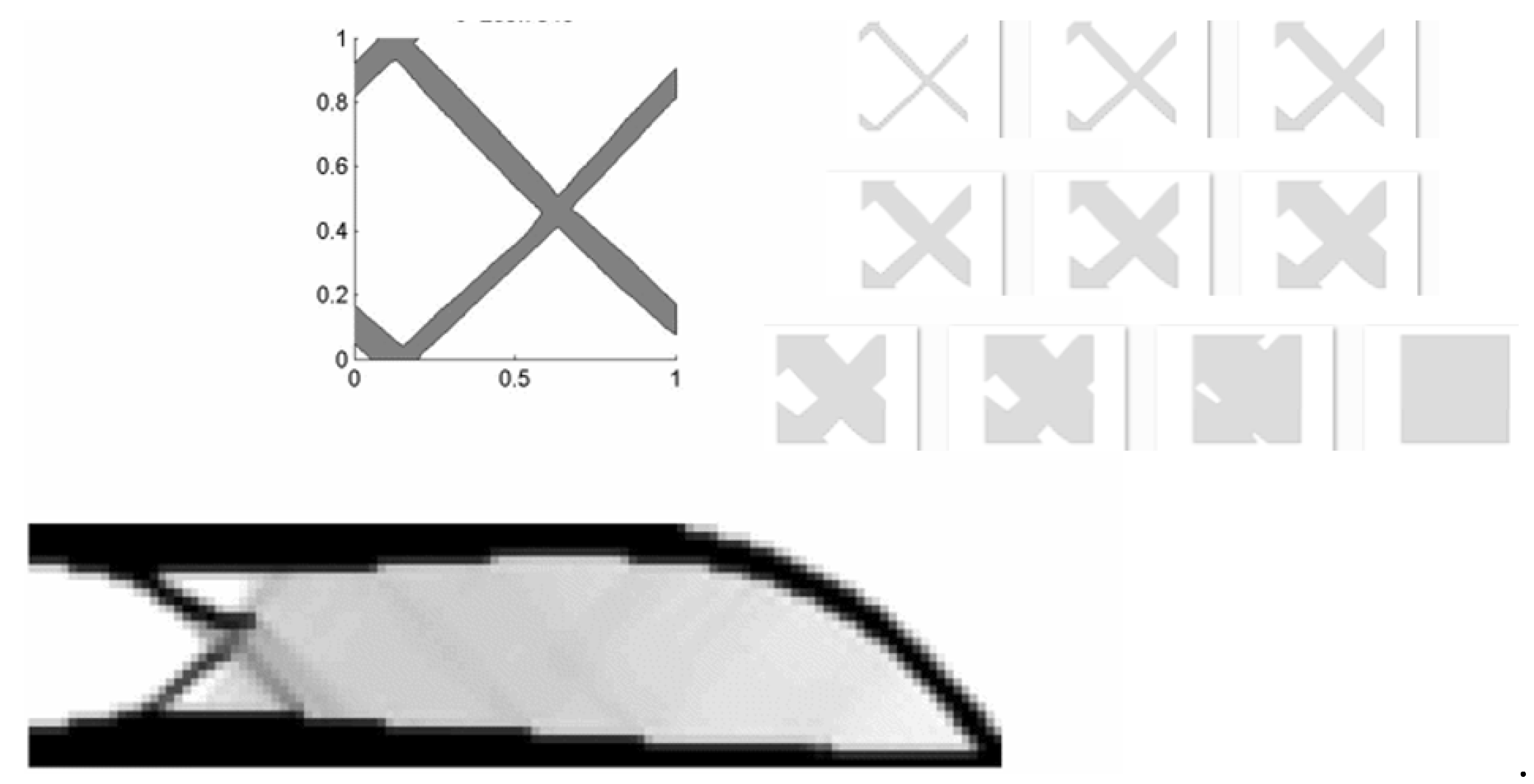
and the maximum iteration number is 300.4.1. Short Cantilever Beam Problem
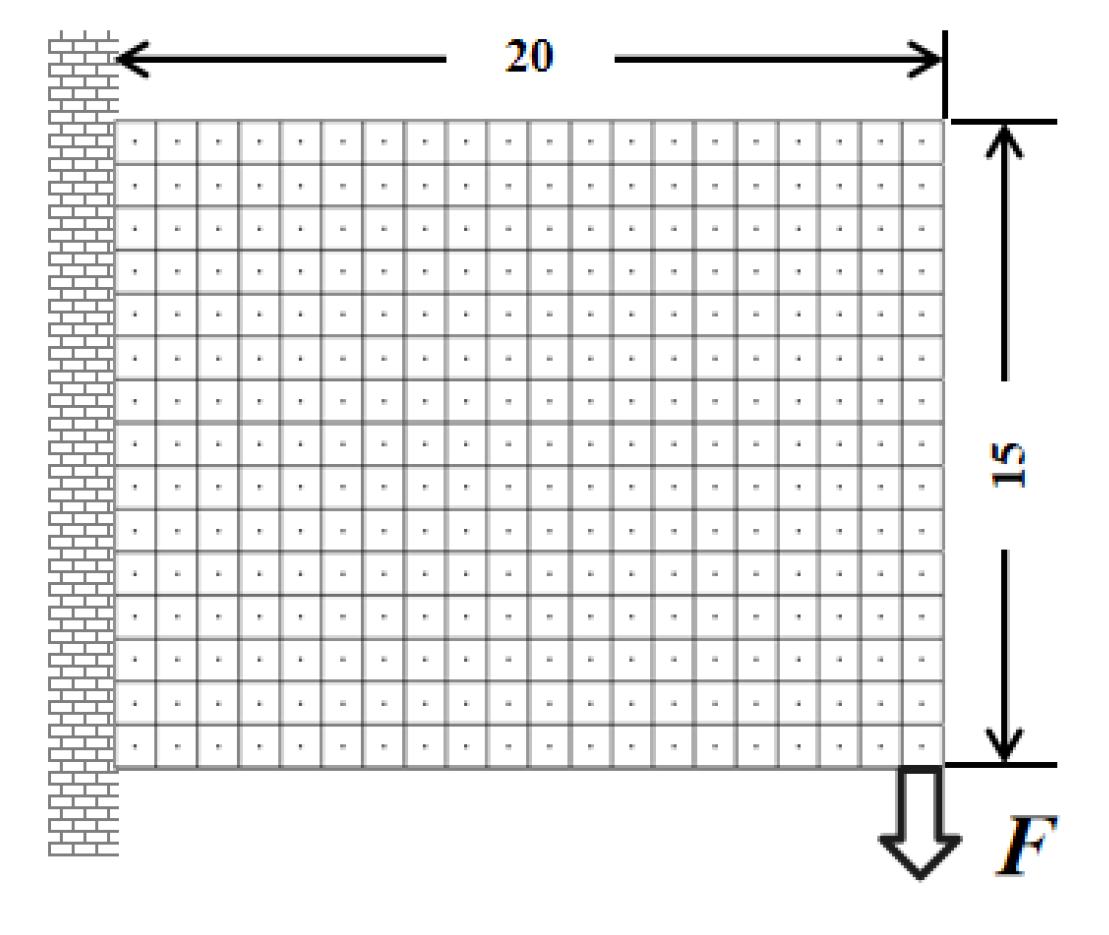

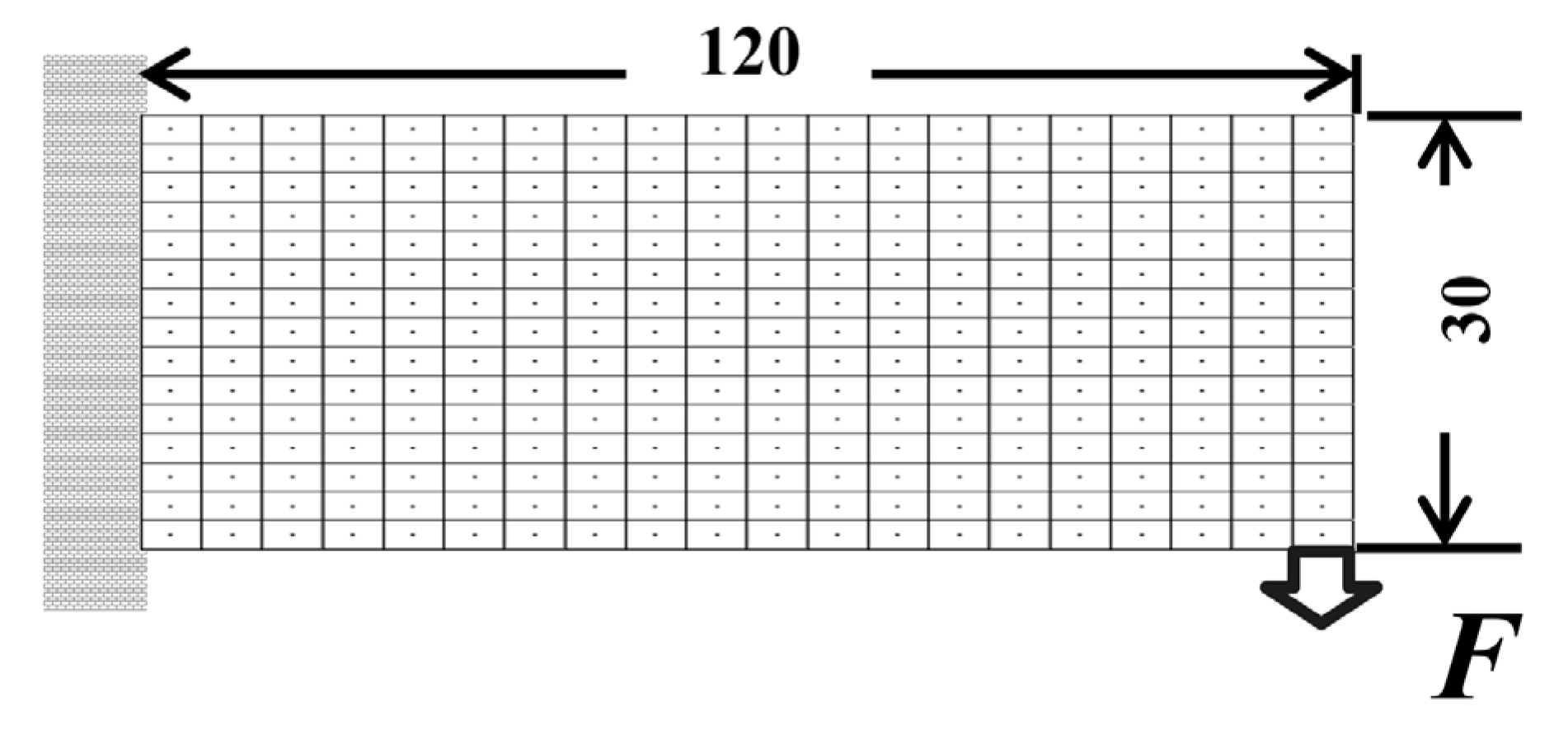
4.2. Long Cantilever Beam Problem
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Duncan, O.; Shepherd, T.; Moroney, C.; Foster, L.; Venkatraman, D. P.; Winwood, K.; Allen, T.; Alderson, A. Review of Auxetic Materials for Sports Applications: Expanding Options in Comfort and Protection. Applied Sciences 2018, 8. [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Yang, Y.; Xiao, R.; Bai, Y.; Song, C.; Wang, D. Evaluation of topology-optimized lattice structures manufactured via selective laser melting. Materials & Design 2018, 143, 27-37. [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Dong, G.; Zhou, Q.; Zhao, Y. F. Lattice Structure Design and Optimization With Additive Manufacturing Constraints. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering 2018, 15, 1546-1562. [CrossRef]
- Panesar, A.; Abdi, M.; Hickman, D.; Ashcroft, I. Strategies for functionally graded lattice structures derived using topology optimisation for Additive Manufacturing. Additive Manufacturing 2018, 19, 81-94. [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.-H.; Zhang, W.-H.; Xia, L. Topology optimization in aircraft and aerospace structures design. Archives of Computational Methods in Engineering 2015, 1-28. [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Hu, R.; Li, Q.; Zhou, P.; Dong, Z.; Kang, R. Topology optimization-based lightweight primary mirror design of a large-aperture space telescope. Applied Optics 2014, 53, 8318-8325. [CrossRef]
- Clausen, A.; Wang, F.; Jensen, J. S.; Sigmund, O.; Lewis, J. A. Topology Optimized Architectures with Programmable Poisson's Ratio over Large Deformations. Advanced Materials 2015, 27, 5523-5527.
- Huang, X.; Zhou, S.; Sun, G.; Li, G.; Xie, Y. M. Topology optimization for microstructures of viscoelastic composite materials. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering 2015, 283, 503-516. [CrossRef]
- Osanov, M.; Guest, J. K. Topology Optimization for Architected Materials Design. Annual Review of Materials Research 2016, 46, 211-233. [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Liu, S. Topology optimization of microstructures of viscoelastic damping materials for a prescribed shear modulus. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization 2014, 50, 287-296. [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Cheng, G.-D. Recent development in structural design and optimization. Acta Mechanica Sinica 2010, 26, 807-823. [CrossRef]
- Sigmund, O.; Maute, K. Topology optimization approaches. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization 2013, 48, 1031-1055.
- van Dijk, N. P.; Maute, K.; Langelaar, M.; van Keulen, F. Level-set methods for structural topology optimization: a review. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization 2013, 48, 437-472. [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Xia, Q.; Huang, X.; Xie, Y. M. Bi-directional Evolutionary Structural Optimization on Advanced Structures and Materials: A Comprehensive Review. Archives of Computational Methods in Engineering 2016. [CrossRef]
- Aage, N.; Andreassen, E.; Lazarov, B. S.; Sigmund, O. Giga-voxel computational morphogenesis for structural design. Nature 2017, 550, 84-86. [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Zong, H.; Wang, M. Y. Efficient structure topology optimization by using the multiscale finite element method. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization 2018, 58, 1411-1430. [CrossRef]
- Sigmund, O. Materials with prescribed constitutive parameters: An inverse homogenization problem. International Journal of Solids and Structures 1994, 31, 2313-2329. [CrossRef]
- Groen, J. P.; Sigmund, O. Homogenization-based topology optimization for high-resolution manufacturable microstructures. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering 2018, 113, 1148-1163. [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, H.; Guedes, J. M.; Bendsoe, M. P. Hierarchical optimization of material and structure. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization 2002, 24, 1-10. [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Breitkopf, P. Concurrent topology optimization design of material and structure within FE2 nonlinear multiscale analysis framework. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering 2014, 278, 524-542.
- Xia, L.; Breitkopf, P. Multiscale structural topology optimization with an approximate constitutive model for local material microstructure. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering 2015, 286, 147-167. [CrossRef]
- Coelho, P. G.; Rodrigues, H. C. Hierarchical topology optimization addressing material design constraints and application to sandwich-type structures. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization 2015, 52, 91-104. [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Yan, J.; Cheng, G. Optimum structure with homogeneous optimum truss-like material. Computers & Structures 2008, 86, 1417-1425. [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Cheng, G.-d.; Liu, L. A uniform optimum material based model for concurrent optimization of thermoelastic structures and materials. International Journal for Simulation and Multidisciplinary Design Optimization 2008, 2, 259-266. [CrossRef]
- Long, K.; Han, D.; Gu, X. Concurrent topology optimization of composite macrostructure and microstructure constructed by constituent phases of distinct Poisson's ratios for maximum frequency. Computational Materials Science 2017, 129, 194-201.
- Yan, J.; Guo, X.; Cheng, G. Multi-scale concurrent material and structural design under mechanical and thermal loads. Computational Mechanics 2016, 57, 437-446. [CrossRef]
- Long, K.; Wang, X.; Gu, X. Concurrent topology optimization for minimization of total mass considering load-carrying capabilities and thermal insulation simultaneously. Acta Mechanica Sinica 2017. [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Huang, X.; Xie, Y. M. Two-scale dynamic optimal design of composite structures in the time domain using equivalent static loads. Composite Structures 2016, 142, 335-345. [CrossRef]
- Andreassen, E.; Jensen, J. S. Topology optimization of periodic microstructures for enhanced dynamic properties of viscoelastic composite materials. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization 2014, 49, 695-705. [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Yang, R. Vibro-acoustic design of plate using bi-material microstructural topology optimization. Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology 2015, 29, 1413-1419. [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Luo, Z.; Li, H.; Jiang, C. Robust topology optimization for cellular composites with hybrid uncertainties. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering 2018, 115, 695-713. [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Luo, Z.; Jiang, C.; Gao, J. Robust topology optimization for concurrent design of dynamic structures under hybrid uncertainties. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing 2019, 120, 540-559. [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Yan, J.; Cheng, G. Multi-objective concurrent topology optimization of thermoelastic structures composed of homogeneous porous material. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization 2013, 47, 583-597. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Toman, J.; Yu, Y.; Biyikli, E.; Kirca, M.; Chmielus, M.; To, A. C. Efficient Design-Optimization of Variable-Density Hexagonal Cellular Structure by Additive Manufacturing: Theory and Validation. Journal of Manufacturing Science & Engineering 2015, 137. [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, P.; Ludwick, S.; Belski, E.; To, A. C. Natural frequency optimization of 3D printed variable-density honeycomb structure via a homogenization-based approach. Additive Manufacturing 2017. [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Bai, J.; To, A. C. Functionally graded lattice structure topology optimization for the design of additive manufactured components with stress constraints. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering 2019, 344, 334-359. [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Xia, L.; Wang, S.; Shi, T. Topology optimization of hierarchical lattice structures with substructuring. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering 2019, 345, 602-617. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, F.; Wang, M. Y. Concurrent design with connectable graded microstructures. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering 2017, 317, 84-101.
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Daynes, S.; Zhang, H.; Feih, S.; Wang, M. Y. Design of graded lattice structure with optimized mesostructures for additive manufacturing. Materials & Design 2018, 142, 114-123. [CrossRef]
- Zong, H.; Liu, H.; Ma, Q.; Tian, Y.; Zhou, M.; Wang, M. Y. VCUT level set method for topology optimization of functionally graded cellular structures. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering 2019, 354, 487-505. [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhong, W. Doing Topology Optimization Explicitly and Geometrically—A New Moving Morphable Components Based Framework. Journal of Applied Mechanics 2014, 81, 081009-081009-081012. [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, J.; Yuan, J. Explicit structural topology optimization based on moving morphable components (MMC) with curved skeletons. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering 2016, 310, 711-748. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Chen, J.; Zhu, X.; Zhou, J.; Xue, D.; Lei, X.; Guo, X. Explicit three dimensional topology optimization via Moving Morphable Void (MMV) approach. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering 2017, 322, 590-614. [CrossRef]
- Svanberg, K. The method of moving asymptotes—a new method for structural optimization. International journal for numerical methods in engineering 1987, 24, 359-373. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhao, L.; Gao, T.; Cai, S. Topology optimization with closed B-splines and Boolean operations. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering 2017, 315, 652-670. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, J. A comprehensive study of feature definitions with solids and voids for topology optimization. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering 2017, 325, 289-313. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Yuan, J.; Zhang, J.; Guo, X. A new topology optimization approach based on Moving Morphable Components (MMC) and the ersatz material model. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization 2016, 53, 1243-1260. [CrossRef]
- Papanicolau, G.; Bensoussan, A.; Lions, J.-L.: Asymptotic analysis for periodic structures; Elsevier, 1978.
- Bendsøe, M. P.; Sigmund, O. Material interpolation schemes in topology optimization. Archive of applied mechanics 1999, 69, 635-654. [CrossRef]
- Bendsøe, M. P.; Sigmund, O. Material interpolation schemes in topology optimization. Archive of Applied Mechanics 1999, 69, 635-654. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).



