Submitted:
10 July 2024
Posted:
11 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
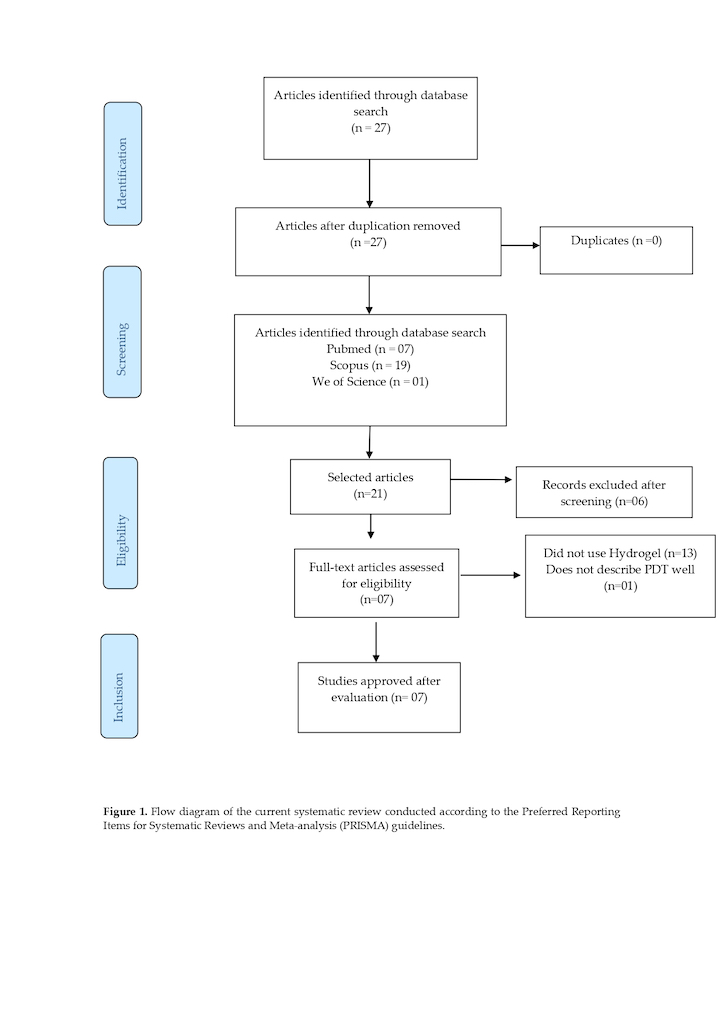
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Development
2.2. Data Extraction Process
2.4. Election Criteria
2.4.1. Design and Interventions
2.4.2. Methodological Design
3. Results
3.1. Study Description
3.2. Characteristics and Results of Individual Studies
3.2.1. Xylan-Porphyrin Hydrogels as Light-Triggered Gram-Positive Antibacterial Agents
3.2.2. Optimisation and Evaluation of a Chitosan/Hydroxypropylmethylcellulose Hydrogel Containing Toluidine Blue for Antimicrobial Photodynamic Inactivation
3.2.3. Hydrogen Peroxide (H2O2)-Supramolecular Material for the Treatment of Post-Irradiation Infected Wounds
- Photocatalytic Process and H2O2 Production: Riboflavin is used as a photocatalyst and has a strong absorption peak around 460 nm. After irradiation with blue light, riboflavin is excited and rapidly converted into a triple state with a high oxidation potential, generating H2O2. The amount of H2O2 was quantified by monitoring the changes in the absorbance at 652 nm [20].
- Choice of Guanosine: Among the nucleotides derived from guanine, guanosine generates the most substantial amount of H2O2 owing to hydrogen bonds and stacking interactions with riboflavin. Because of the differences in their oxidation potentials, guanosine produces more H2O2 than adenosine, uridine, or cytidine [21].
- G4 Supramolecular Materials: Guanosine was used to develop G4 supramolecular materials, which were formed into nanofibres and crosslinked using 4-formylphenylboronic acid and 1,8-diaminooctane. The properties of these materials were characterised using techniques such as electrospray mass spectrometry and FTIR spectroscopy [8].
- Controlled H2O2 Production: The amount of H2O2 generated can be controlled by varying the riboflavin concentration and irradiation time. This system maintains its robustness even after irradiation.
- Antibacterial Activity: The H2O2 generated was used to test the antibacterial activity. The post-irradiation riboflavin-loaded hydrogel effectively killed gram-positive, gram-negative, and multidrug-resistant bacteria with a sterilisation rate of over 99.999%. Incubation with catalase inhibited the antibacterial activity [22].
- In Vivo Assays: Thestudy included in vivo assays using an MRSA-infected rat wound model. The post-irradiation hydrogel exhibited a significant therapeutic effect by eliminating wound infections and reducing the levels of typical inflammatory factors. This study demonstrated the effectiveness of controlled riboflavin-mediated H2O2 production for antibacterial purposes with promising results both in vitro and in vivo [23].
3.2.4. Photo-Inspired Antibacterial Activity and Acceleration of Wound Healing by Hydrogel Incorporated with Ag/Ag@Siver Chloride (AgCl)/Zinc Oxide (ZnO) Nanostructures
3.2.5. Carrageenan Embedded in Atomically Precise Au Nanocluster for Single Infrared Light-Driven Photothermal and Photodynamic Antibacterial Therapy
3.2.6. Optimisation of Hydrogel Containing Toluidine Blue for PDT in the Treatment of Acne
3.2.7. Optimisation of Hydrogel Containing Toluidine Blue for PDT Using RSM
4. Discussion
4.1. Main PSs
4.1.1. Methylene Blue (MB)
4.1.2. Rose Bengal (RB)
4.1.3. Porphyrins
4.1.4. Riboflavin (RF)
4.2. PDT in Clinical Isolates
4.3. Synergism with Antibiotics and Other Drugs
- Amoxicillin with Gold NPs (amoxi@AuNPs): The combination of gold NPs as a PS and amoxicillin proved to be a potent inhibitor of P. aeruginosa growth. When activated with white LED light at 490 nm for 3 h, the bacterial load was reduced by >70%. This synergistic approach has been suggested as a strategy to reduce the need for high doses of antibiotics and minimise their adverse effects. Furthermore, the amoxi@AuNP combination reduced the necessary light activation time, making the application of PDT more practical [54].
- MB with Gentamicin (Gen+MB): One study used a combination of MB and gentamicin for PDT against P. aeruginosa. Red LED light resulted in a notable inhibition of 6 log cm2 in planktonic cultures and 3 log cm2 in biofilms. The addition of gentamicin reduced the amount of methylene blue required for photoactivation, indicating potential advantages for the treatment of skin and mucosal infections [53].
- Polymyxin B with Cationic Porphyrin Derivative: The antibacterial activity was explored using a conjugate of polymyxin B with a cationic porphyrin derivative. This conjugate showed significant eradication of the bacterial load even after washing, with a small amount of light being sufficient to photoinactivate the concentrated bacterial inocula. The conjugate demonstrated selective affinity for bacteria, offering advantages in relation to the risk of bacterial resistance associated with the exclusive use of antibiotics. These synergistic combinations of PSs and antibiotics represent promising strategies for the fight against infections caused by P. aeruginosa, highlighting the versatility and potential of PDT as an effective and less resistance-prone approach [55].
4.4. PDT Associated with NPs
- Incorporation of PS into Polymeric NPs: PS can be incorporated into polymeric NPs, providing a stable and targeted platform for the efficient delivery of photosensitising agents. This approach helps overcome the limitations of solubility and bioavailability of PS.
- PS Attached to the Surface of NPs: PS can be attached to the surface of NPs, allowing for specific and targeted interactions with the target cells. This approach aimed to improve the selectivity and effectiveness of PDT. PS Close to NPs: Some strategies exploit the physical proximity of PS to NPs, enhancing their therapeutic effects. These strategies may involve physical proximity without direct connection but with beneficial interactions for the effectiveness of PDT [56].
- NPs such as PS: Certain NPs themselves can act as PSs, generating effective photodynamic reactions when exposed to adequate light. This feature of the NPs offers an integrated approach in which the NPs themselves play the role of phototherapeutic agents [57].
- Photothermal Therapy (PTT): In addition to PDT, NPs are used in PTT. In this context, near-infrared (NIR) laser irradiation is used to generate heat through the mediation of photoabsorbing agents, resulting in the denaturation of proteins, membrane rupture, and degradation of the genetic material of target cells.
- Microemulsions (MEs): MEs have been reported to improve the efficiency of PDT by overcoming the limitations associated with the use of aqueous media to disperse photosensitising agents. They consist of two phases (aqueous and organic), with the organic phase stabilised by surfactants. Eucalyptus oil was used to destabilise the cell wall, allowing for greater PS penetration and synergistic effects [58].
- Gold-Based NPs (AuNPs): AuNPs, including smaller gold nanoclusters, have received considerable attention owing to their photoactivatable properties, excellent biocompatibility, and ease of surface functionalisation. They can be used for both PDT and PTT, generating singlet oxygen under NIR light excitation and exhibiting photothermal properties when combined with organic dyes such as indocyanine green [53]. These approaches highlight the diversity of strategies that utilise NPs to improve the efficacy and specificity of PDT in diverse biomedical applications.
4.5. PDT Delivered via Hydrogels
4.6. Application of PDT in Biofilm and Its Usefulness in Vivo
- EP Matrix: The EPS matrix forms a three-dimensional structure surrounding the bacterial cells. In some cases, the matrix is composed of polysaccharides, proteins, and metal ions. The presence of metal ions can confer a neutral or polyanionic charge on the matrix, depending on the predominant type of EP [63].
- Resistance to External Aggression: The biofilm acts as a protective barrier, providing resistance to bacteria against external aggression, such as the host immune response, medications, and other antimicrobial agents. The matrix can trap antimicrobials, preventing them from reaching bacterial cells [63].
- Greater Resistance Compared to Planktonic Cells: Biofilm formation confers significantly greater resistance, estimated to be between 10 and 1,000 times greater than that of planktonic bacterial cells. This feature makes biofilms challenging to eradicate [64].
- Chemical Signalling and Bacterial Cooperation: Biofilm formation involves chemical signalling between bacteria, allowing the coordination of surface adherence and cell differentiation. This bacterial cooperation results in the creation of a complex and organised microbial community [62].
- Protection from Environmental Fluctuations: The matrix protects against environmental fluctuations, such as changes in humidity, temperature, and pH. Furthermore, the concentration of nutrients is favoured and waste can be efficiently eliminated.
- Challenges for PDT: In PDT, the presence of a biofilm represents a challenge, as the matrix limits the diffusion of PSs into the bacterial plasma membrane, leading to a reduction in the production of singlet oxygen. Specific strategies must be developed to overcome these barriers and make PDT effective against bacteria in biofilms [64].
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nathan, C. Resisting antimicrobial resistance. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2020;18;5:259-260. [CrossRef]
- Navarro, DB.; Llanos, R.; Miravet, JF.; Galindo, F. Photodynamic inactivation of Staphylococcus aureus in the presence of aggregation-prone photosensitizers based on BODIPY used at submicromolar concentrations. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2022;235:112543. [CrossRef]
- Beyer, P., Paulin, S. The antibacterial research and development pipeline needs urgent solutions. ACS Infectious Diseases. 2020;6;6:1289-1291. [CrossRef]
- Youf, R.; Müller, M.; Balasini, A.; Thétiot, F.; Müller, M.; Hascoët, A.; et al. Antimicrobial Photodynamic Therapy: Latest Developments with a Focus on Combinatory Strategies. Pharmaceutics. 2021;24;13;12:1995. [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Yu, E.; Weng, Q.; Zhou, L.; Li, Q. Optimization of hydrogel containing toluidine blue O for photodynamic therapy in treating acne. Lasers in Medical Science. 2019;34:1535-1545.
- Oliveira, LVF.; Apostólico, N.; Uriarte, JJ.; da Palma, RK.; Prates, RA.; Deana, AM.; Martins, RABL. Photodynamic Therapy in the Extracellular Matrix of Mouse Lungs: Preliminary Results of an Alternative Tissue Sterilization Process. International Journal of Photoenergy. 2021;1-9.
- Yanten, N.; Vilches, S.; Palavecino, CE. Photodynamic therapy for the treatment of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections: A scoping review. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 2023;13;44:103803.
- Du, P.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, B.; Li, S.; Gao, M.; Wang, T.; et al. A H2 O2 -Supplied Supramolecular Material for Post-irradiated Infected Wound Treatment. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023;10;9:e2206851.
- Choi, JR.; Yong, KW.; Choi, JY.; Cowie, AC. Recent advances in photo-crosslinkable hydrogels for biomedical applications. Biotechniques. 2019;66;1:40-53.
- Goding, J.; Vallejo, CG.; Syed, O.; Green, R. Considerations for hydrogel applications to neural bioelectronics. J Mater Chem B. 2019;14;7;10:1625-1636.
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, DG. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Annals of internal medicine. 2009;151;4:264-269.
- Chen, CP.; Hsieh, CM.; Tsai, T.; Yang, JC.; Chen, CT. Optimization and evaluation of a chitosan/hydroxypropyl methylcellulose hydrogel containing toluidine blue O for antimicrobial photodynamic inactivation. International journal of molecular sciences. 2015;16;9:20859-20872.
- Liang, H.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Peng, W.; Yan, J.; et al. Optimization of hydrogel containing toluidine blue O for photodynamic therapy by response surface methodology. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2017;173:389-396.
- Mao, C., Xiang, Y., Liu, X., Cui, Z., Yang, X., Yeung, K.; et al. Wound Healing Acceleration by Hydrogel Embedded with Ag/Ag@ AgCl/ZnO Nanostructures. ACS Nano. 2017;11;9:9010-9021.
- Elkihel, A.; Vernisse, C.; Ouk, TS.; Roper, RL.; Chaleix, V.; Sol, V. Xylan-Porphyrin Hydrogels as Light-Triggered Gram-Positive Antibacterial Agents. Gels. 2023;2;9;2:124.
- Zheng Y, Zhu Y, Dai J, Lei J, You J, Chen N, Wang L, Luo M, Wu J. Atomically precise Au nanocluster-embedded carrageenan for single near-infrared light-triggered photothermal and photodynamic antibacterial therapy. Int J Biol Macromol. 2023 Mar 1;230:123452.
- Vidro, S.; Kuhnert, M.; Lippmann, N.; Zimmer, J.; Werderhausen, R.; Abel, B.; Eulenburg, V.; Schulze, A. Hidrogéis carregados com fotossensibilizador para inativação fotodinâmica de bactérias multirresistentes em feridas. RCS Av. 2021;11;7600–7609.
- Brown, MR; Gilbert, P. Sensibilidade de biofilmes a agentes antimicrobianos. J. Appl. Bacteriol. 1993;74;87S–97S.
- Jori, G.; Fabris, C.; Soncin, M.; Ferro, S.; Coppellotti, O.; Dei, D.; et al. Terapia fotodinâmica no tratamento de infecções microbianas: princípios básicos e aplicações em perspectiva. Cirurgia de Lasers. Med. 2006;38;468-481.
- He, YQ.; Fudickar, W.; Tang, JH.; Wang, H.; Li, X.; Han, J.; et al. Capture and Release of Singlet Oxygen in Coordination-Driven Self-Assembled Organoplatinum(II) Metallacycles. J Am Chem Soc. 2020;5;142;5:2601-2608.
- Turan, IS.; Yildiz, D.; Turksoy, A.; Gunaydin, G.; Akkaya, EU. A Bifunctional Photosensitizer for Enhanced Fractional Photodynamic Therapy: Singlet Oxygen Generation in the Presence and Absence of Light. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2016;18;55;8:2875-8.
- Wang, Y.; Shen, X.; Ma, S.; Guo, Q.; Zhang, W.; Cheng, L.; et al. Oral biofilm elimination by combining iron-based nanozymes and hydrogen peroxide-producing bacteria. Biomater Sci. 2020;7;8;9:2447-2458.
- Li, Y.; Su, L.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Huang, F.; Ren, Y.; et al. A Guanosine-Quadruplex Hydrogel as Cascade Reaction Container Consuming Endogenous Glucose for Infected Wound Treatment-A Study in Diabetic Mice. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022;9;7:e2103485.
- Scherer, S.; Wagner, C.; Leuner, C.; Fleischer, W. Hydrogel. US patent US9415133, August 16, 2016.
- Liu M, Ishida Y, Ebina Y, Sasaki T, Aida T. Photolatently modulable hydrogels using unilamellar titania nanosheets as photocatalytic crosslinkers. Nat Commun. 2013;4:2029.
- Zhou, YF.; Yang, W.; Zhang, S.; Liu, AB.; Shaikh, L.; Yang, Y.; et al. Hidrogel bioinspirado, injetável, adesivo de tecido e antibacteriano para regeneração de tecidos múltiplos por terapia minimamente invasiva. Appl. Matéria. 2022;101290.
- Gan, D.; Xu, T.; Xing, W.; Ge, X.; Fang, L.; Wang, K.; et al. Hidrogel antibacteriano ativo de contato inspirado em mexilhões com alta afinidade celular, resistência e recuperabilidade. Av. Função. Matéria. 2019;29:1805964.
- Mo, S.; Song, Y.; Lin, M.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, J.; et al. Nanofolhas de CuS ricas em vagas de enxofre responsivas ao infravermelho próximo para atividade antibacteriana eficiente via fototérmica sinérgica e vias fotodinâmicas. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2022;608:2896–2906.
- Yang, Y.; Liang, Y.; Chen, J.; Duan, X.; Guo, B. Curativo de hidrogel composto hemostático antioxidante adesivo inspirado em mexilhão via fotopolimerização para cicatrização de feridas em pele infectada. Bioact.Mater. 2022;8:341–354.
- Liang, JY.; He, B. Hidrogéis funcionais como curativo para melhorar a cicatrização de feridas. ACS Nano. 2021;8:12687–12722.
- Park, H.; Park, H.; Na, K. Terapia Dual Propionibacterium acnes usando lipossomas com penetração na pele carregados com um fotossensibilizador e um antibiótico. J Porphyr Phthalocya. 2015;19;8:956–966.
- Lee, CJ.; et al. Correlações dos componentes do óleo da árvore do chá com seus efeitos antibacterianos e irritação da pele. J Food Drug Anal. 2013;21;2:169–176.
- Liu, K.; Luo, Y.; Hao, L.; Chen, J. Antimicrobial effect of methylene blue in microbiologic culture to diagnose periprosthetic joint infection: an in vitro study. J Orthop Surg Res. 2022;28;17;1::571.
- Perez-Laguna, I.; Garcia-Luque, S.; Ballesta, L.; Perez-Artiaga, V.; Lampaya-Perez, A.; Rezusta, Y. Gilaberte, Photodynamic therapy using methylene blue, combined or not with gentamicin, against Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Photodiagnosis and photodynamic therapy. 2020;31:101810.
- Tardivo, JP.; Del, AG.; Oliveira, CS.; Gabrielli, DS.; Junqueira, HC.; Tada, DB.; et al. Methylene blue in photodynamic therapy: From basic mechanisms to clinical applications. Photodiagnosis. Photodyn Ther. 2005;2;2:175-91.
- Prochnow, EP.; Martins, MR.; Campagnolo, CB.; Santos, RC.; Villetti, MA.; Kantorski, KZ. Antimicrobial photodynamic effect of phenothiazinic photosensitizers in formulations with ethanol on Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 2016;13:291-296.
- Vanerio, N.; Stijnen, M.; Mol, BAJM.; Kock, LM. Biomedical Applications of Photo- and Sono-Activated Rose Bengal. A Review. Photobiomodul Photomed Laser Surg. 2019;37;7:383-394.
- Rauf, MA.; Graha, JP.; Bukallah, SB.; Al-Saedi, MA. Solvatochromic behavior on the absorption and fluorescence spectra of Rose Bengal dye in various solvents. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2009;72;1:133-7.
- Spagnul, C.; Turner, LC.; Boyle, RW. Immobilized photosensitizers for antimicrobial applications. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2015;150:11-30.
- López, AMF.; Muñoz, IR.; Llanos, R.; Galindo, F. Photodynamic Inactivation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by PHEMA Films Loaded with Rose Bengal: Potentiation Effect of Potassium Iodide. Polymers (Basel). 2021;6;13;14:2227.
- Shrestha, A.; Cordova, M.; Kishen, A. Photoactivated polycationic bioactive chitosan nanoparticles inactivate bacterial endotoxins. J Endod. 2015;41;5:686-91.
- Refsnes, M.; Hetland, RB.; Øvrevik, J.; Sundfør, I.; Schwarze, PE.; Låg, M. Different particle determinants induce apoptosis and cytokine release in primary alveolar macrophage cultures. Part Fibre Toxicol. 2006;14;3:10.
- Yuan, J.; Li, ([2.2.2]Cryptand)potassium (4-methyl-benzene-thiol-ato)[5,10,15,20-tetra-kis-(4-chloro-phenyl)porphyr-inato]manganate(II) tetra-hydro-furan disolvate, IUCrData. 2022;7:3x220241.
- Meerovich, EV.; Akhlyustina, IG.; Tiganova, EA.; Lukyanets, EA.; Makarova, ER.; Tolordava, OA. Novel Polycationic Photosensitizers for Antibacterial Photodynamic Therapy, Advances in experimental medicine and biology. 2020;1282;1-19.
- Zagami, R.; Franco, D.; Pipkin, JD.; Antle, V.; Plano, L.; Patanè, S.; et al. Sulfobutylether-β-cyclodextrin/5,10,15,20-tetrakis(1-methylpyridinium-4-yl)porphine nanoassemblies with sustained antimicrobial phototherapeutic action. Int J Pharm. 2020;30;585:119487.
- Goto, R.; Nishida, E.; , Kobayashi, S.; Aino, M.; Ohno, T.; Iwamura, Y.; et al. Gelatin Methacryloyl-Riboflavin (GelMA-RF) Hydrogels for Bone Regeneration. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;6;22;4:1635.
- Kingsley, DH.; Perez, RE.; Boyd, G.; Sites, J.; Niemira, BA. Evaluation of 405-nm monochromatic light for inactivation of Tulane virus on blueberry surfaces. J Appl Microbiol. 2018;124;4:1017-1022.
- Kang, Y.; Kim, JH.; Kim, SY.; Koh, WG.; Lee, HJ. Blue Light-Activated Riboflavin Phosphate Promotes Collagen Crosslinking to Modify the Properties of Connective Tissues. Materials (Basel). 2021;3;14;19:5788.
- Piluso, S.; Flores, DG.; Dokter, I.; Moreira, LT.; Li, Y.; Leijten, J.; et al. Rapid and cytocompatible cell-laden silk hydrogel formation via riboflavin-mediated crosslinking. J Mater Chem B. 2020;28;8;41:9566-9575.
- Glass, S.; Kühnert, M.; Lippmann, N.; Zimmer, J.; Werdehausen, R.; Abel, B.; et al. Photosensitizer-loaded hydrogels for photodynamic inactivation of multirestistant bacteria in wounds. RSC Adv. 2021;17;11;13:7600-7609.
- Lebreton, F.; Snesrud, E.; Hall, L.; Mills, E.; Galac, M.; Stam, J.; et al. A panel of diverse Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinical isolates for research and development. JAC Antimicrob Resist. 2021;10;3;4:dlab179.
- Bayat, F.; Karimi, AR. Projeto de hidrogéis fotodinâmicos de quitosana contendo conjugado de ftalocianina-colistina como agente antibacteriano, Jornal internacional de macromoléculas biológicas. 2019;129:927-935.
- Rocca, DM.; Silvero, CM.; Aiassa, V.; Becerra, MC. Tratamento fotodinâmico rápido e eficaz de infecções por biofilme usando baixas doses de nanopartículas de ouro revestidas com amoxicilina, Fotodiagnóstico e terapia fotodinâmica. 2020;31:101811.
- Perez, ILV.; Garcia, SL.; Ballesta, L.; Perez, VA.; Lampaya, AP.; Rezusta, Y. Terapia fotodinâmica com azul de metileno, combinada ou não com gentamicina, contra Staphylococcus aureus e Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Fotodiagnóstico e terapia fotodinâmica. 2020;31:101810.
- Guern, FL.; Sol, V.; Ouk, C.; Arnoux, P.; Frochot, C.; Ouk, TS. Enhanced Photobactericidal and Targeting Properties of a Cationic Porphyrin following the Attachment of Polymyxin B. Bioconjug Chem. 2017;20;28;9:2493-2506.
- Perni, PS.; Prokopovich, J.; Pratten, IP.; Parkin, M.; Nanopartículas: seu uso potencial em terapia fotodinâmica antibacteriana, Ciências fotoquímicas e fotobiológicas: Jornal oficial da Associação Europeia de Fotoquímica e da Sociedade Europeia de Fotobiologia. 2011;5;10:712-20.
- Tondro, N.; Behzadpour, Z.; Keykhaee, N.; Akbari, N. Sattarahmady, Carbon@polypyrrole nanotubos como fotossensibilizador em fototerapia a laser de Pseudomonas aeruginosa, colóides e superfícies. B, Biointerfaces. 2019;180:481-486.
- Parasuraman, YTR.; Shaji, AC.; Sharan, AH.; Bahkali, HF.; Al-Harthi, A.; Syed, VT.; et al. Nanopartículas de prata biogênicas decoradas com azul de metileno potencializaram o Inativação fotodinâmica de Pseudomonas aeruginosa e Staphylococcus aureus, Pharmaceutics. 2020;12:8.
- Choi, JR.; Yong, KW.; Choi, JY.; Cowie, AC. Recent advances in photo-crosslinkable hydrogels for biomedical applications. Biotechniques. 2019;66;1:40-53.
- Goding, J.; Vallejo, CG.; Syed, O.; Green, R. Considerations for hydrogel applications to neural bioelectronics. J Mater Chem B. 2019;14;7;10:1625-1636.
- Xiang, Y.; Mao, C.; Liu, X.; Cui, Z.; Jing, D.; Yang, X.; Wu, S. Rapid and superior bacteria killing of carbon quantum dots/ZnO decorated injectable folic acid--conjugated PDA hydrogel through dual--light triggered ROS and membrane permeability. Small. 2019;15;22:1900322.
- Meerovich, EV.; Akhlyustina, IG.; Tiganova, EA.; Lukyanets, EA.; Makarova, ER.; Tolordava, OA. Novel Polycationic Photosensitizers for Antibacterial Photodynamic Therapy, Advances in experimental medicine and biology. 2020;1282;1-19.
- Martinez, SR.; Ibarra, LE.; Ponzio, RA.; Forcone, MV.; Wendel, AB.; Chesta, CA.; et al. Inativação fotodinâmica de patógenos bacterianos do grupo ESKAPE em culturas planctônicas e de biofilme usando nanopartículas de polímero conjugado dopado com porfirina metalizada. ACS infeccioso doenças. 2020;6;8:2202-2213.
- Sun, L.; Jiang, W.; Zhang, H.; Guo, Y.; Chen, W.; Jin, Y.; et al. Carregado com fotossensibilizador Nanopartículas multifuncionais de quitosana para imagens simultâneas in situ, erradicação de biofilme bacteriano altamente eficiente e ablação de tumores, materiais aplicados ACS e interfaces. 2019;11;2:2302-2316.
| Authors | Country | Methods | What was analysed? | Conclusion |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chen, C. P., et al., 2015 [12] | Taiwan | Toluidine blue O (TBO) and chitosan were mixed with various amounts of hydroxypropylmethylcellulose (HPMC) to form chitosan/HPMC hydrogel (HCT). Irradiation with 100 J•cm−2 of 630 nm laser light. Irradiated with a set of light-emitting diodes (LEDs), with a wavelength of 635 nm and total bandwidth at half the maximum of 20 nm. | The photodynamic (PDT) efficacy of the hydrogel was examined in vitro against Staphylococcus aureus biofilms. Confocal laser scanning microscopy was performed to investigate the penetration level of TBO into viable solutions. The incorporation of HMPC could increase the physicochemical properties of chitosan hydrogel, including hardness, viscosity and also bioadhesion; however, higher concentrations of HMPC also resulted in a reduced antimicrobial effect. | The optimal choice of bioadhesive formulation for use in topical antimicrobial PDT will involve a compromise between achieving the required drug release rate and mechanical characteristics of the formulation, as these factors will affect clinical efficacy and ease of topical application. The penetration of the TBO biofilm is related to the physicochemical properties of the HTC hydrogel. Strategies for enhancing TBO diffusion in biofilm, along with formulation strategies, should be considered in detail for future clinical applications. |
| Liang, H., et al., 2017 [13] | China | TBO was used as a photosensitiser. Treatment with TBO hydrogel alone or with light alone (630 nm) could not show antibacterial activity against S. aureus. | A new TBO hydrogel was prepared for the treatment of periodontitis, with carbomer and NaOH used as the base and neutraliser, respectively. TBO hydrogel formulations have been used as demand-based drug delivery platforms for clinical treatments. The antibacterial activity of PDT treated with TBO hydrogel was performed on S. aureus. TBO hydrogel formulations were optimised using response surface methodology. | A TBO hydrogel was developed for photodynamic therapy against S. aureus. The results obtained were better than those for PDT with aqueous TBO solution. TBO (50% and 68.26%) were released from the TBO hydrogel in approximately 4 and 24 h, respectively. The TBO hydrogel showed no significant difference in colour, transparency, pH, and viscosity within 6 weeks at 4, 25 and 40 °C. The hydrogel alone or light alone had no antimicrobial effect on S. aureus; only light with TBO hydrogel showed antibacterial activity. Therefore, photodynamic therapy with new optimised TBO hydrogel formulations is a promising treatment strategy for periodontitis. |
| Mao, C., et al., 2017 [14] | China | Hybrid Ag/Ag@AgCl/ZnO nanostructures incorporated into a hydrogel, with chemical reduction using ultraviolet light followed by incorporation of ZnO nanostructures through NaOH precipitation. Visible light irradiation, using a 300 W xenon lamp | A hydrogel composite incorporated with carboxymethyl cellulose and Ag/Ag@AgCl/ZnO hybrid nanostructures has been described. It exhibits excellent photocatalytic activity and broad antibacterial efficiency against gram-positive bacteria under visible light irradiation. | Taking advantage of reactive oxygen species photogeneration, the system showed significantly enhanced photocatalytic activity, broad antibacterial activity against S. aureus (gram-positive), as well as accelerated wound healing. The hydrogel system showed controllable and sustained release of Ag+ and Zn2+ originating from the reversible swelling-shrinkage transition triggered by pH change and has great potential in tissue repair and antibacterial applications. |
| Zheng, Y., et al., 2019 [5] | China | The light source (CMC Dental, Rosiev, Denmark) applied in the study was a type of diode laser with an effective wavelength of 630 nm, equipped with a 23 mm periotip. Its output power and maximum output intensity were 5 and 4 mW/cm2, respectively. The photosensitiser used was toluidine blue. | In vitro antibacterial experiments (against S. aureus), wherein response surface methodology was used to optimise the TBO hydrogel formulation. The stability, pH, and antibacterial activity of TBO hydrogel did not change significantly under 4, 25, and 40 °C during 6-week storage. Furthermore, TBO combined with carbomer hydrogel showed release rates of 51.28% (4 h) and 69.80% (24 h). | The ideal TBO hydrogel was 0.5% (w/v) carbomer 934, TBO concentration of 0.01 mg/mL, ethanol concentration of 0.5% (v/v), Tween 80 ratio of 0.5% (v/v), and the mass ratio of NaOH to carbomer of 0.4 (w/c). The properties of the TBO hydrogel, such as appearance, clarity, viscosity, antibacterial activity, and pH, were generally stable at 4, 25 and 40 °C till 6 months. It also showed effective antibacterial activity against Propionibacterium acnes, S. aureus, and Escherichia coli. All of the above results supported the new TBO hydrogels that were viable for the treatment of acne, and additional studies on cellular toxicity and animal studies would be performed. In summary, TBO hydrogel could be a vital therapeutic strategy to promote PDT applied in topical acne therapy. |
| Du, P., et al., 2023 [8] | China | Photoactive supramolecular material based on G-quartet, self-assembled from guanosine (G) and 4-formylphenylboronic acid/1,8-diaminooctane, with incorporation of riboflavin as photocatalyst to the G4 nanowire, for post-irradiation photodynamic antibacterial therapy. G4 materials, which exhibit hydrogel-like properties, provide a scaffold to load riboflavin, and the guanosine reductant for riboflavin for phototriggered production of therapeutic H2O2. The excitation wavelength was set to 450 nm, and emission spectra from 500 to 600 nm were collected. | A photoactive supramolecular material based on G-quartet has been reported. It is self-assembled from guanosine (G) and 4-formylphenylboronic acid/1,8-diaminooctane, with the incorporation of riboflavin as photocatalyst to the G4 nanowire, for post-irradiation photodynamic antibacterial therapy. G4 materials, which exhibit hydrogel-like properties, provide a scaffold to load riboflavin, and the guanosine reductant for riboflavin for phototriggered production of therapeutic H2O2. | Supramolecular riboflavin-loaded G4 materials, which exhibited gel-like properties, were presented as a proof-of-concept for post-irradiation antibacterial therapy of the infected wound. The G4 hydrogels served as dressing materials to structure riboflavin through covalent bonding and aromatic stacking, and provided the reductant guanosine for the reduction of photoexcited riboflavin, followed by O2 reduction to generate H2O2. The post-irradiated hydrogels exhibited strong antibacterial activity, sufficient to kill gram-positive bacteria, gram-negative bacteria and multidrug-resistant bacteria in vitro and in vivo, and showed biosafety and no obvious cytotoxicity. Riboflavin-loaded G4 hydrogels, after photoirradiation, are capable of killing gram-positive bacteria (S. aureus), gram-negative bacteria (E. coli) and multi-resistant bacteria (methicillin-resistant S. aureus) with a sterilisation rate greater than 99.999%. The post-irradiated hydrogels also showed great antibacterial activity in the infected wound of rats. |
| Elkihel, A., et al., 2023 [15] | France | Hydrogels conjugated with xylan. Xylan-tetra(4-carboxyphenyl) porphyrin (TCPP) hydrogels with different PS/xylan ratios were obtained, characterised, and studied for their swelling behaviour. White LED light irradiated for 5 h at the same temperature (total fluence of 25/cm2). The photosensitiser used was meso-TCPP. The hydrogels were conjugated with xylan. | The antimicrobial activity of the hydrogels was tested under visible light irradiation against two strains of gram-positive bacteria, S. aureus and Bacillus cereus. Preliminary results showed interesting activity on these bacteria, indicating that these hydrogels could have great potential in the treatment of bacterial skin infections with this species using photodynamic antimicrobial chemotherapy. | Xylan-based hydrogels containing PS were developed using TCPP as a cross-linker. The swelling tests of the obtained hydrogels showed that the xyl-TCPP-3 hydrogel functionalised with the smallest amount of TCPP has a good swelling property. Preliminary antibacterial tests against two strains of gram positive bacteria showed photobacterial activity of this hydrogel only under light, and the covalent grafting of TCPP onto the xylan portion appears to reduce the toxicity of the photosensitiser in the absence of light. However, the required concentration appears to be significant for an effective photosensitiser compared to what is reported in the literature. |
| Zheng, Y., et al., 2023 [16] | China | Atomically precise captopril-capped Au nanoclusters (Au25Capt18) prepared using alkaline NaBH and then embedded them into biosafe carrageenan to achieve superior photothermal (PTT) and PDT dual-mode antibacterial effect. Irradiated by a near infrared light source (NIR, 808 nm). | Natural polysaccharide carrageenan embedded in atomically precise gold nanoparticles has been reported as a novel hydrogel platform for PTT and PDT antibacterial therapy triggered using single infrared light. | Atomically precise gold nanocluster-embedded hydrogels were developed via cross-linking Au25Capt18 and carrageenan as an efficient photothermal and photodynamic agent for practical antibacterial applications under single NIR laser irradiation. The contribution of PTT to antibacterial elimination was more significant than that of PDT in Au25Capt18 hydrogels. In vivo investigation demonstrated that Au25Capt18 hydrogels could eliminate pathogenic bacteria and accelerate the healing of bacteria-infected wounds. This investigation provides a simple, efficient, and alternative strategy for the design and fabrication of composite hydrogels that activate PTT and PDT functions under a single laser source and expand the antibacterial capacity of hydrogel-based platforms. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





