1. Introduction
Indoor environmental comfort represents a critical aspect of individual well-being and health [
1]. The term health, as defined by the World Health Organization, refers to “a state of complete physical, mental, and social well-being, and not merely the absence of disease or infirmity,” contrary to traditional beliefs [
2].
According to most literature sources, there are five primary factors influencing Indoor Environmental Quality (IEQ): building plan layout, indoor air quality, indoor thermal conditions, indoor lighting quality and acoustic environment comfort [
3,
4]. Indoor Air Quality (IAQ) is the only indicator among those that make up the environmental quality of indoor spaces that explicitly refers to healthiness rather than comfort and, for this reason, it should be considered the most important [
5,
6,
7].
The guidelines of American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers - ASHRAE emphasize the importance of indoor environmental quality, noting that individuals spend approximately 80-90% of their time indoors [
8]. ANSI/ASHRAE 62.1-2022 delineates the criteria for acceptable indoor air quality (IAQ) as follows: “air in which there are no known contaminants at harmful concentrations, as determined by cognizant authorities, and with which a substantial majority (80% or more) of the people exposed do not express dissatisfaction” [
9]. This factor assumes particular importance in the hospital context, where the quality of the indoor environment can have significant implications for patient health and recovery, as well as the well-being of healthcare personnel [
10,
11].
Hospitals, as facilities dedicated to medical care and treatment, must ensure environments that not only meet functional and technical requirements but also actively promote the health and well-being of their occupants. The quality of the air, the control of temperature and humidity, adequate lighting, and noise reduction are all critical factors in creating spaces that foster physical and psychological comfort.
Poor Indoor Environmental Quality (IEQ) has detrimental effects not only on the physical health of occupants but also on their psychological well-being [
12].
In this context, the ASHRAE guidelines provide a framework for the design and management of indoor spaces, offering detailed recommendations on how to optimize environmental parameters to ensure a high level of comfort and health. Given the significant amount of time individuals spend inside buildings, and particularly within hospital environments, it is essential to adopt a holistic and integrated approach to the design of indoor spaces to improve the quality of life and expedite the healing process for patients.
In the context of healthcare facilities, architectural quality plays a supporting role in therapeutic processes [
13]. This underscores the importance of a carefully calibrated design approach for hospitals.
Therefore, the quality of indoor spaces should not be considered a secondary aspect, but a fundamental element in the design and management of hospital buildings, with the aim of creating environments that meet the comfort and health needs of all occupants.
The emphasis on promoting the well-being and health of occupants, as well as the capacity of occupied environments to ensure optimal conditions of comfort and wellness for individuals, is evident in the 2018 version of the European Energy Performance of Building Directive (EPBD) [
14]. This directive highlights the necessity of calculating energy needs in a manner that optimizes indoor air quality to create a healthier indoor environment.
The objectives established in the 2030 Agenda have contributed to moving beyond the notion that sustainability is solely related to environmental concerns, fostering a holistic perspective focused on promoting human health (Sustainable Development Goal 3).
The design of a healthy and comfortable environment is further supported by environmental sustainability assessment and certification tools for buildings, such as the LEED (USA), BREEAM (UK), CASBEE (Japan) and the Itaca (Italy) Protocols [
15,
16,
17]. The most recent WELL Building Standard, established by the International WELL Building Institute, aims to measure and certify building characteristics based on their impact on human well-being [
18]. It focuses specifically on comfort and health enhancement for occupants and emphasizes the five primary factors that influence Indoor Environmental Quality (IEQ) among its various evaluation criteria [
19].
In this context, emerging methodologies and technologies such as Digital Twin (DT), Building Information Modeling (BIM), the Internet of Things (IoT), sensing technologies, and data analytics present new opportunities for ensuring healthier environments and more efficient building management [
20,
21].
A DT is defined as a virtual representation of physical assets, processes, or systems [
22]. In this scenario, the Digital Twin emerges as an enabling technology for the digitization of the AECO sector (Architecture, Engineering, Construction, and Operation) [
23,
24,
25,
26,
27,
28]. The technology of Digital Twins is increasingly gaining ground in the built environment sector [
29].
There are numerous studies on the various potentialities of emerging new technologies [
30,
31]. There are methods and approaches based on digital twin technology aimed at developing an intelligent system for the optimization and automation of building energy management [
32].
An example of a Digital Twin developed for the operational and maintenance phase of buildings is illustrated by the case study of the West Cambridge campus [
33].
Qian et al. have developed a DT for the assessment, prediction, and control of indoor air quality in a traditional residence located in Wufu City, Fujian, China [
34].
Nurumova et al. [
35] have developed a digital twin of a building at Roger Williams University to evaluate the potentialities and challenges of occupant-centered facility operations. Yu et al. [
36] have focused on hospital buildings, proposing innovations in both technical approaches and the management of these complex structures. Madubuike and Anumba [
37] have applied digital twin technology for a preventive maintenance approach in healthcare facilities.
Despite the growing interest in this technology [
38], clear guidelines for its large-scale adoption in the AECO sector are still lacking [
39]. Thus, there arises a need to create alignment on the methodologies [
40] to be followed for designing and implementing Digital Twin platforms for the management of the built environment [
41,
42], particularly for hospitals that must ensure high indoor environmental comfort in addition to energy efficiency.
In response to this need, the Agenzia del Demanio in Rome has entered into an agreement for technical and scientific collaboration with Sapienza University of Rome. This partnership aims to develop a Twin Strategy to guide the construction sector and various stakeholders, including contracting authorities, real estate managers, public and private organizations, and companies, in transitioning to digital approaches for managing complex processes in the building and infrastructure sectors. This strategy serves as an operational tool to support the various parties operating in the sector and involved in the definition and implementation of data-driven tools and methods oriented towards the Digital Twin. It encompasses the processes of planning, design, implementation, management, monitoring, and utilization of the built environment, providing a practical and methodological guide for the digital transition within the AECO sector [
43].
This paper provides an assessment of how digitalization can support decision-making processes related to maintaining high levels of indoor environmental comfort in hospital settings, crucial for the healing process, particularly by examining how real-time data processing and the application of machine learning can enable proactive interventions in these facilities.
2. Materials and Methods
This article serves as a practical guide for facilitating the design and deployment of platforms to develop Digital Twins in healthcare settings [
44]. Digital twin technology focuses on digitally managing the lifecycle of architectural and urban projects, utilizing advanced information management systems and artificial intelligence to support decision-making processes [
45]. Leveraging capabilities in simulation, control, monitoring, management, optimization, and automation, Digital Twins aim to improve energy efficiency, foster environmental sustainability, optimize spatial utilization, and enhance safety [
46].
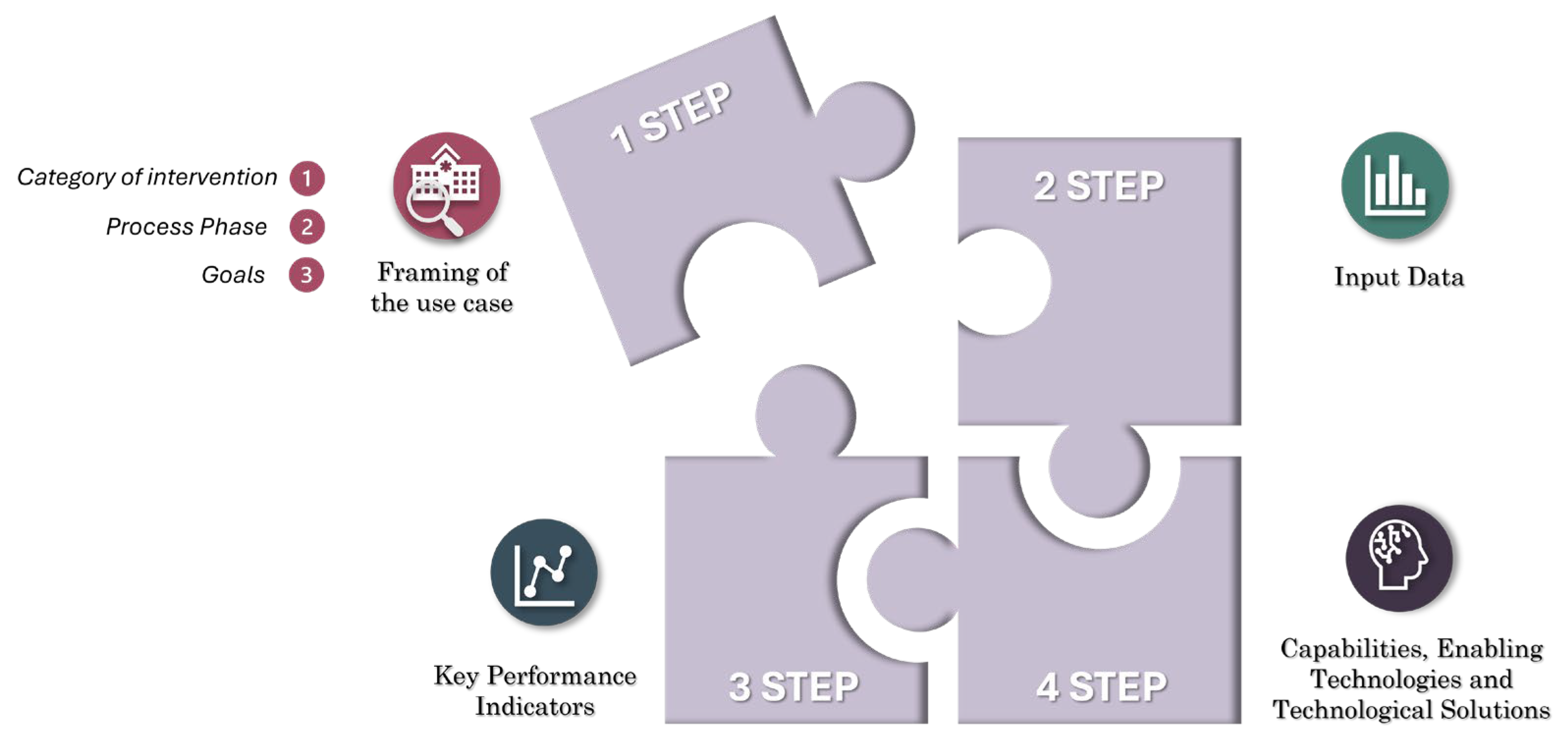
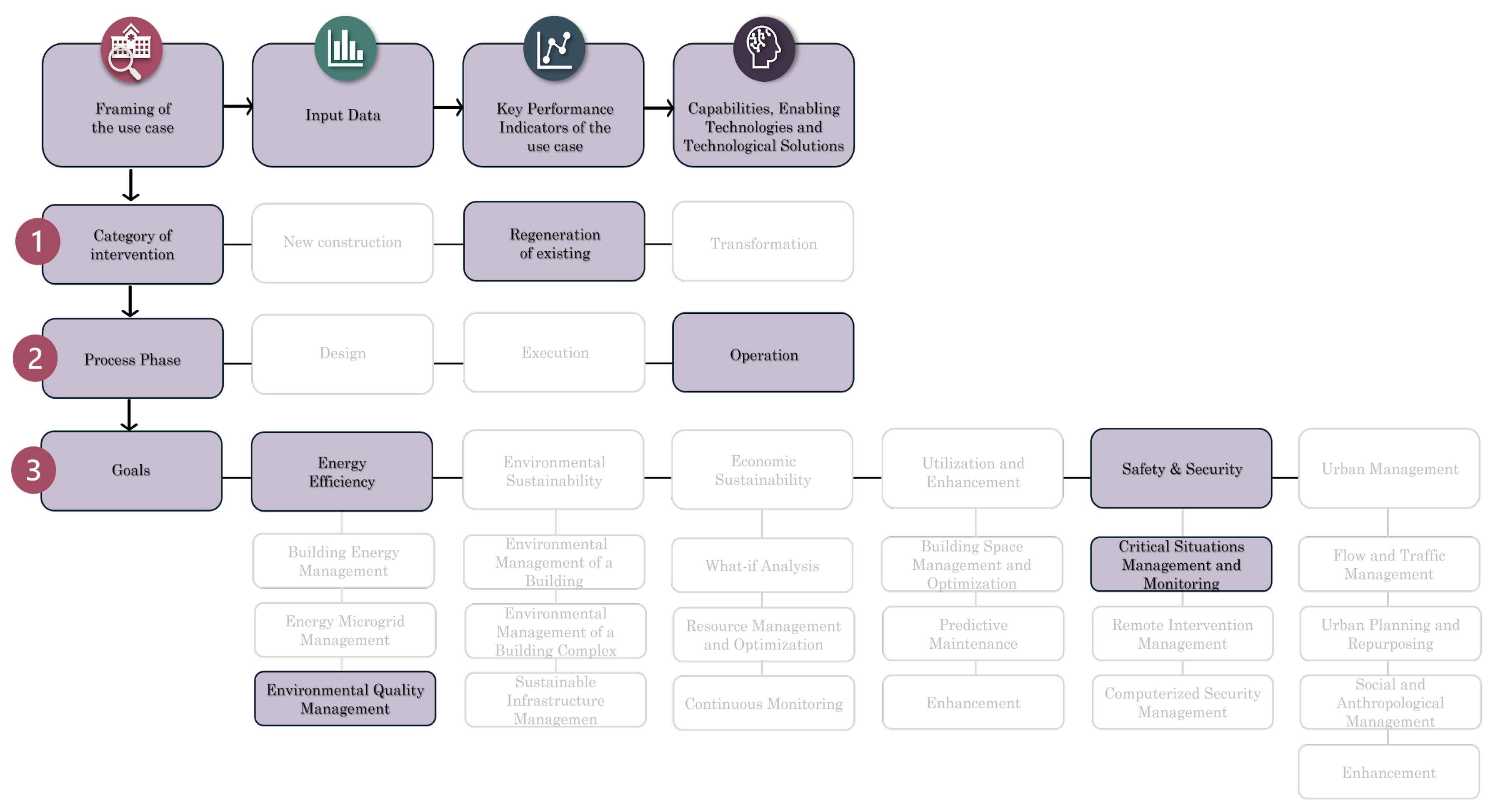
To define the requirements that a Digital Twin must meet based on specific use cases, and to identify the technological components that form the system architecture of the Digital Twin, a structured workflow consisting of four steps has been developed. This workflow is crucial for ensuring the efficient design and implementation of the Digital Twin, tailored to address the specific operational requirements of surgical suite environments.
The main steps of the methodological approach developed for implementing a Digital Twin framework have been graphically represented in
Figure 1.
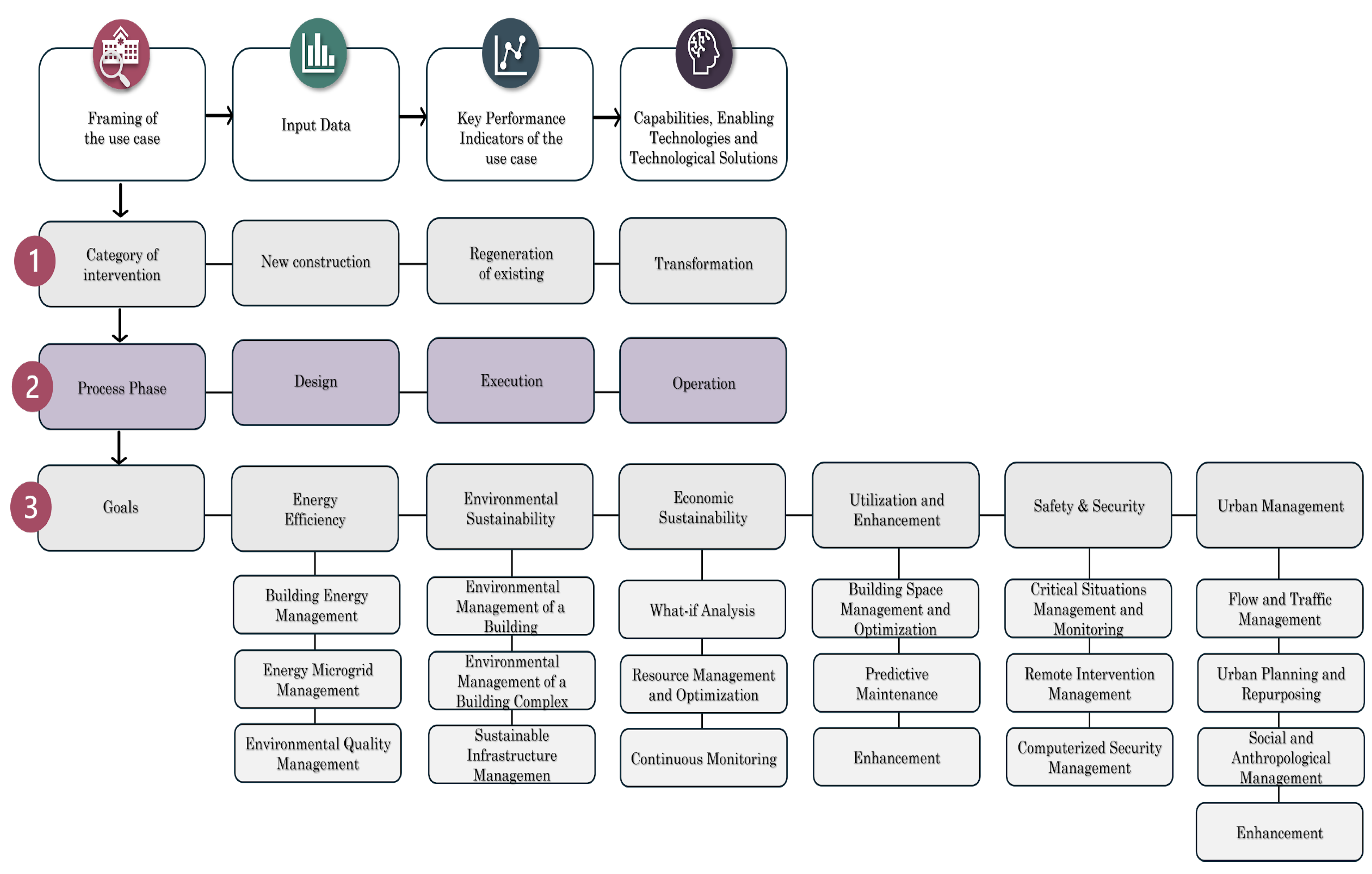
Framing the use case is the essential first step in understanding the context and specific needs of the project. This step is divided into three main sub-phases:
New Construction: includes new building and urban planning projects. In this case, the Digital Twin is integrated from the early stages of design and construction, allowing for process optimization from the beginning.
Regeneration of Existing: involves interventions on existing structures while maintaining their original use. This approach focuses on improving operational performance and energy efficiency.
Transformation: pertains to interventions that involve a change in the use of existing structures. This requires significant adaptation of the Digital Twin to support new functional and operational requirements.
- 2.
Definition of the process phase:
Design: in this phase, the Digital Twin facilitates decision-making through simulations and “what-if” analyses, allowing for the testing and evaluation of different design hypotheses.
Execution: during the construction or regeneration phase, the Digital Twin supports continuous monitoring of work progress, resource management, logistics, and safety.
Operation: in the operational phase, the Digital Twin enhances the management and monitoring of the built environment, optimizing energy efficiency, environmental sustainability, predictive maintenance, and safety.
- 3.
Definition of Objectives:
Energy Efficiency: improvement of energy performance throughout all project lifecycle phases.
Environmental Sustainability: promotion of more sustainable construction approaches and materials.
Economic Sustainability: optimization of operational and maintenance costs through energy-saving strategies and efficient resource management.
Utilization and Enhancement: Optimization of space use and improvement of user experience.
Safety & Security: enhancement of safety conditions and risk prevention.
Urban Management: integration and coordination with other urban infrastructures to improve mobility and accessibility.
The step 2 is the definition of input data: once the use case is framed, it is crucial to define the input data needed to feed the Digital Twin. This data covers various critical aspects for the operation of the digital model, ensuring that the system can provide accurate and useful information for operational management.
Step 3 involves defining key performance indicators (KPIs) to monitor and evaluate the effectiveness of the Digital Twin. KPIs offer measurable metrics essential for assessing the success of implemented strategies and identifying areas for improvement.
The final step involves defining capabilities according to the Digital Twin Capabilities Periodic Table (CPT) created by the Digital Twin Consortium [
47]. This framework is aimed at organizations wishing to design, develop, deploy, and manage digital twins, based on the specific capability requirements of use cases and the characteristics of technological solutions. In this phase, enabling technologies and specific technological solutions to be implemented are also identified, ensuring that the Digital Twin can fully meet the needs of the project.
The capabilities you’ve outlined are organized into six logical groupings in the Digital Twin Capabilities Periodic Table, each based on common features and applications [
48]:
Data Services: these capabilities enable the acquisition and management of data, establishing the connection between the physical and virtual realities. They ensure that data collected from various sources is processed and stored efficiently, making it accessible for real-time and analytical purposes.
Integration: these capabilities facilitate the communication of data between the digital twin and other systems and applications. This includes interoperability protocols and data exchange standards which ensure that the digital twin can seamlessly integrate with external systems, enhancing its functionality and the breadth of its applications.
Intelligence: this includes capabilities that set up an environment for the development and implementation of industrial solutions for the digital twin through data integration and analysis services, as well as the use of Artificial Intelligence. This allows for advanced analytics, predictive modeling, and decision support, enabling the digital twin to provide insights that go beyond simple data presentation.
User Experience (UX): these capabilities allow users to interact with the digital twin and visualize its data effectively. This could include interactive dashboards, virtual reality (VR) or augmented reality (AR) interfaces, and custom user interfaces designed to make the data understandable and actionable for different user profiles.
Management: capabilities that enable system and ecosystem management, ensuring efficient and continuous operation of the digital twin. This includes tools for system monitoring, updating, troubleshooting, and scaling, as well as managing the lifecycle of the digital twin and its components.
Trustworthiness: these capabilities ensure the security, privacy, protection, reliability, and resilience of the system. They are crucial for maintaining the integrity of the digital twin, protecting data and operations against cyber threats, and ensuring that the system remains robust and reliable under various conditions.
Each of these categories plays a critical role in ensuring the functionality and effectiveness of a digital twin, making it a versatile tool capable of transforming operations and decision-making processes within an organization.
Enabling technologies are those that must be integrated into the system to ensure its proper functioning, enable its features, and allow the achievement of set goals. The main enabling technologies for a Digital Twin include the Internet of Things (IoT), Cloud Computing and Edge Computing, 5G, Building Information Modeling (BIM), Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML), Big Data, and Advanced Analytics.
Technological solutions are defined as a combination of hardware, software, and services designed to implement a specific technology for a particular purpose. A single technology can be translated into multiple technological solutions. The choice of one solution over another can depend on several factors, including the type of deployment (proprietary or open-source), licensing options and associated costs, and the programming capabilities required for use.
Figure 2 depicts the Workflow for the definition of a Digital Twin system architecture developed by the authors and applied to a specific case study to validate its effectiveness.
3. Case Study of the Operating Room
This paper analyzes a case study focused on the development of an innovative framework for one of the most complex environments in a hospital: the operating room. The project’s goal is to create an advanced digital system for this setting, integrating and analyzing real-time data through cutting-edge technologies such as IoT, artificial intelligence, machine learning, and big data analysis. This system aims to provide an accurate and updated representation of the operating environment, enhancing the safety, comfort, and physical and psychological well-being of healthcare staff and patients. The integration of heterogeneous data and the definition of KPIs used to evaluate the effectiveness of activities in achieving set goals will be examined. The implementation of this framework is intended to improve various critical aspects in the healthcare context, optimizing the safety and comfort of the operating environment.
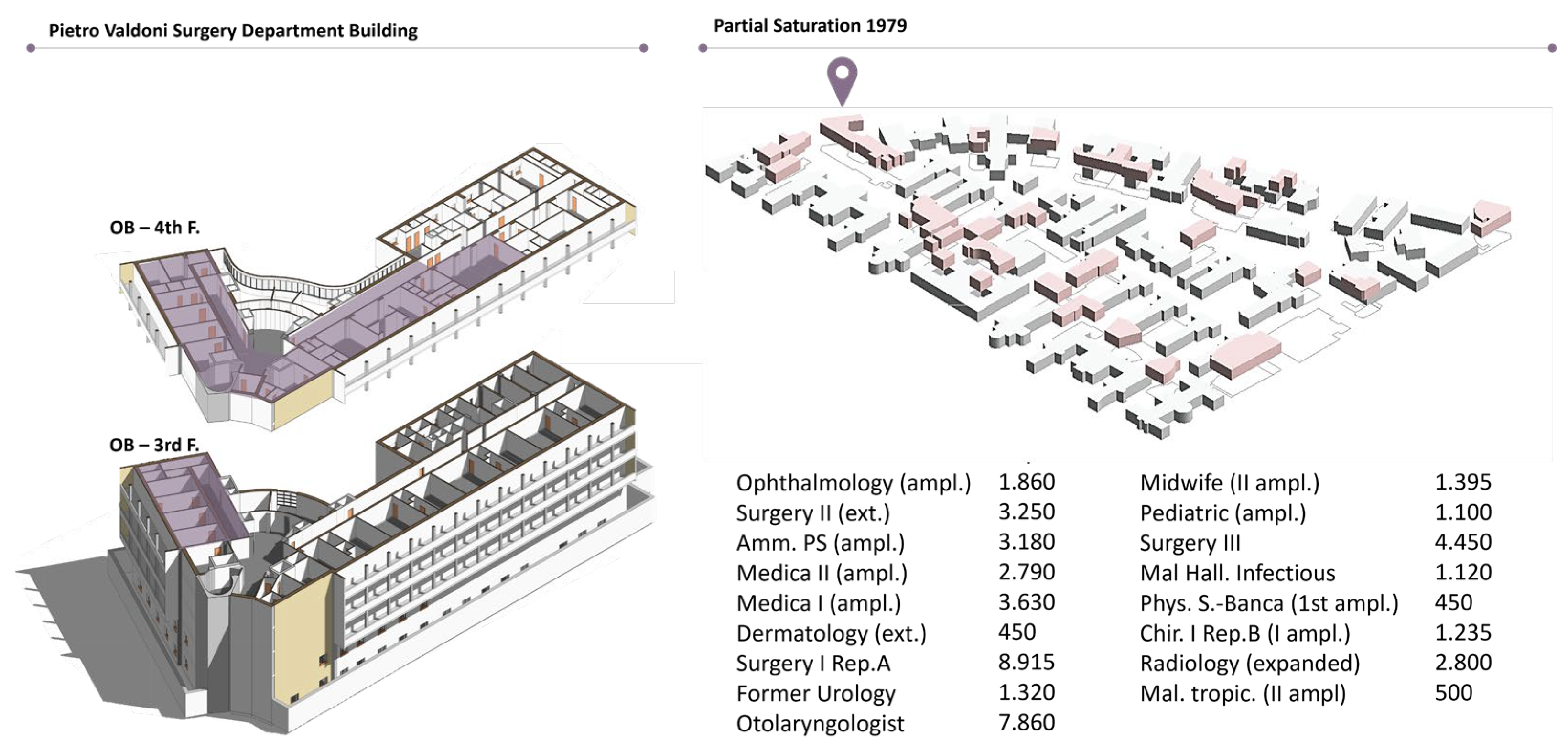
The surgical block under study is located within the Pietro Valdoni surgical building, part of the Umberto I Policlinic in Rome. This building replaced the former Surgical Clinic, dating back to 1888, which no longer met the demands of the high level of surgical activity promoted by P. Valdoni. Constructed between the 1950s and 1960s, the new building was considered one of the most advanced clinical facilities of its time, conceived as a “hospital within a hospital” [
49].
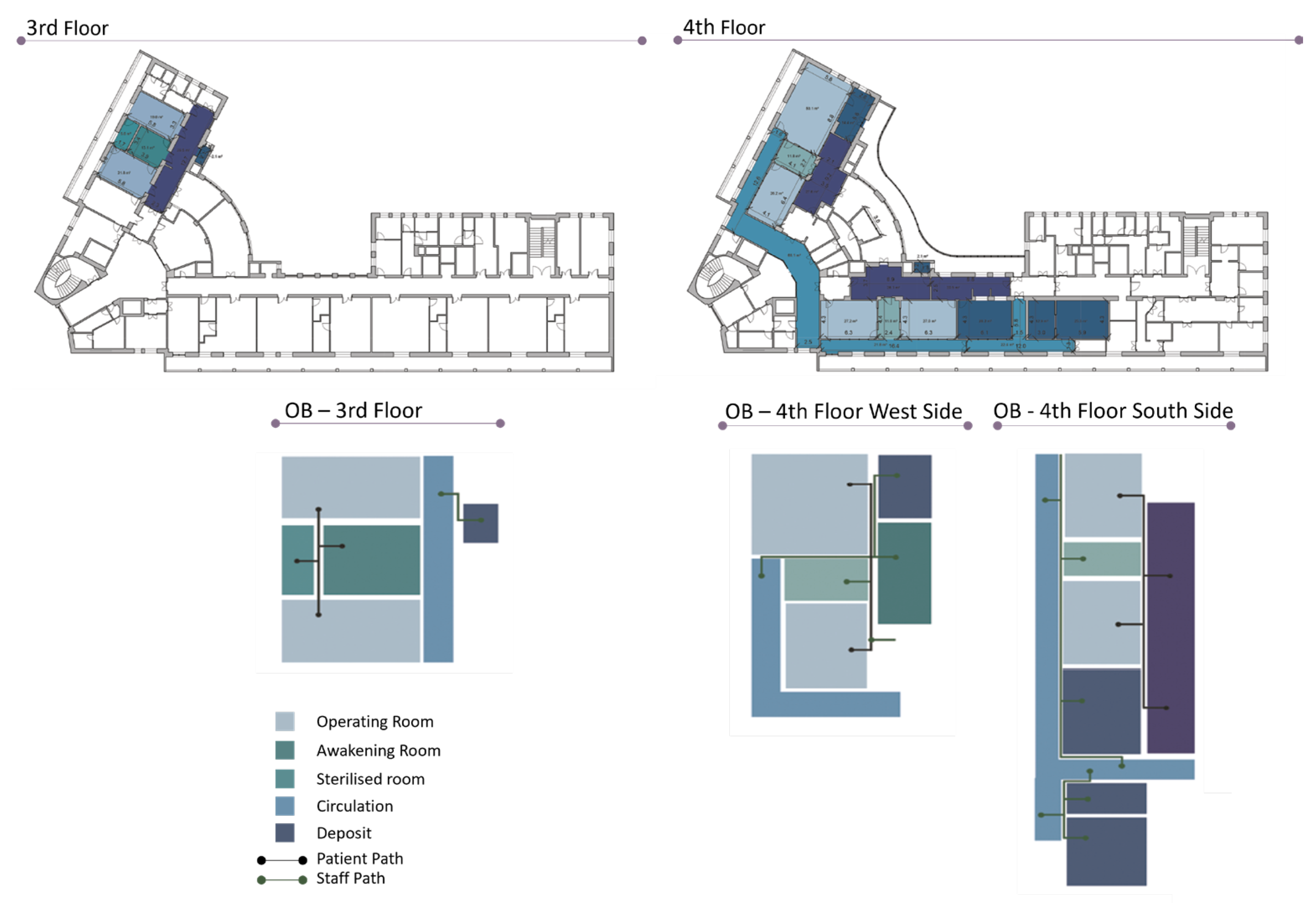
To fully appreciate the motivations that have guided the development of the Digital Twin aimed at transforming the operating block, it is essential to analyze the historical context of this environment. This perspective helps to understand how past evolutions have shaped current needs and directed research towards innovative solutions to optimize and revolutionize the surgical environment. The building, with a V-shape, has a central core that connects general services and two longitudinal wings dedicated to patient wards and outpatient services, distributed over six floors (
Figure 3).
The operating block is located on the third and fourth floors of the building (
Figure 4). On the third floor, accessible through a filter area, there are two ambulatory operating rooms, separated from the recovery room and the sterile room, with a small adjacent storage area. The fourth floor hosts a more complex surgical area, including a specialized operating room and an ambulatory one, separated by a handwashing area for medical staff. The specialized operating room, positioned on two external fronts, benefits from natural light, while the other room, although lacking direct light, receives illumination from large external windows. The floor is completed by a storage area and a clean-sterile corridor. On the opposite wing, two additional ambulatory operating rooms are separated by another handwashing area, with three large equipment storage areas and an adjacent dirty storage room [
50].
The detailed description of the surgical block’s layout underscores the intricate logistical and operational considerations inherent in hospital design, particularly in areas as critical as surgery. The placement and design of the rooms take into account both functionality and the well-being of medical staff and patients, incorporating elements such as natural light and strategically placed handwashing stations to maintain hygiene and operational efficiency.
Given the critical importance of Indoor Environmental Quality (IEQ) in hospital settings, as highlighted by the guidelines of the American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE), integrating Digital Twin technology could provide a robust framework for maintaining high levels of indoor environmental comfort. This integration supports the overarching goal of promoting patient health and well-being, which is crucial for the healing process.
Overall, the adoption of Digital Twin technology in the surgical block exemplifies how emerging technologies can transform hospital environments, ensuring optimal conditions for both patients and healthcare providers. This approach aligns with the broader objectives of enhancing indoor environmental quality and leveraging digital tools to create healthier and more efficient healthcare facilities.
Figure 5 depicts the Workflow diagram for defining the system architecture of a Digital Twin for the case study. Subsequently, the various phases are described in detail.
3.1. Framing of the Use Case
3.1.1. Category of Intervention
The “Regeneration of the Existing” intervention category for the Digital Twin of the operating block focuses on strategies for renovating and modernizing the healthcare setting. This process involves using advanced technologies to precisely map and monitor the current state of the environment. The data collected are then integrated into a centralized database and used for modeling that supports simulations and predictive analysis, leveraging tools of artificial intelligence and machine learning.
In the presented case study, the proposed interventions primarily focus on maintaining high levels of indoor environmental comfort. This is facilitated through continuous monitoring systems that allow for the identification of potential anomalies, thereby ensuring timely and informed interventions.
For the operating block, this not only implies adherence to current regulations but also effective management and monitoring, ensuring safety and comfort. This project, currently in execution, thus falls into the intervention category related to the regeneration of the existing.
3.1.2. Process Phase
In the development of a Digital Twin for the operating block of a hospital, the “Operation Phase” refers to the application of the Digital Twin to existing and operational healthcare infrastructures. This process begins with a comprehensive assessment of the current infrastructure of the operating block, including medical equipment, ventilation systems, and other critical infrastructures. Subsequently, historical and real-time data on various operational aspects are collected, including data on patient flow, energy consumption, and environmental conditions. These data are integrated into the digital model using advanced modeling technologies such as Building Information Modeling (BIM).
The Digital Twin is then used to monitor the existing infrastructure in real time, continuously updating the digital model to reflect the operational status of the operating block. This enables advanced analysis and simulations to predict future issues, optimize resource use, and improve overall operational management. The operation phase also requires particular attention to the security and privacy of the collected data, ensuring that all information is protected and compliant with current regulations regarding patient privacy and the security of health information. This aspect is crucial for maintaining trust and ensuring the integrity of the healthcare system as the Digital Twin provides critical insights and operational enhancements.
3.1.3. Objectives: Environmental Quality Management and Management and Monitoring of Critical Situations
The Digital Twin framework for the operating block is structured around two key objectives, essential for the project’s success. These objectives are:
Environmental Quality Management: managing environmental quality is a crucial element for the operating block, where precise control of internal conditions can directly influence the comfort, efficiency of medical staff, and the safety of surgical operations [
51]. This involves continuously monitoring and adjusting air quality, temperature, humidity, and lighting to ensure optimal conditions for both patients and healthcare professionals [
52]. The Digital Twin uses sensors and IoT technology to gather data in real-time, which is then analyzed to maintain or adjust the environment as needed.
Management and Monitoring of Critical Situations: managing and monitoring critical situations is vital to ensure safety and continuity of operations within the operating block. This process involves multiple stages and utilizes advanced technologies to identify, assess, and respond promptly to potential emergencies or abnormal conditions. The Digital Twin plays a critical role here, providing a dynamic and interactive platform that can simulate various scenarios and predict outcomes based on real-time data. This enables the healthcare team to implement preventive measures, prepare responses to potential critical events, and improve overall readiness and resilience.
Together, these objectives contribute to a robust operational strategy for the operating block, enhancing not only the surgical environment but also ensuring that the healthcare facility can adapt and respond effectively to any challenges that arise.
3.2. Input Data for the Operating Room Digital Twin
To optimize indoor environmental comfort and, specifically, indoor air quality, it is crucial to clearly define input data and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs).
As shown in the
Table 1, these elements allow for monitoring critical aspects of operation, ensuring that all procedures are conducted in the best possible conditions.
Monitoring the operational hours of medical equipment is vital for understanding their usage and efficiency. Measuring the type and quantity of medical fluids used daily ensures the availability of necessary resources, reducing waste. The levels of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and carbon dioxide (CO2) are key indicators of air quality, essential for maintaining a healthy environment and minimizing health risks for patients and staff. The intensity of lighting is critical for the success of surgical operations and the safety of the operators, while monitoring the energy consumption of equipment helps identify opportunities to reduce usage without compromising functionality. Tracking the number of contracted infections is essential for assessing the effectiveness of infection control practices.
3.3. KPIs for the Operating Room Digital Twin
The KPIs that ensure quality and efficiency in this specific case are listed in
Table 2. Monitoring pollutants protects health and maintains sterile conditions. Controlling temperature, humidity, and CO2 levels reduces the risk of microbial proliferation. Optimizing the efficiency of HVAC systems is crucial for maintaining ideal environmental conditions and reducing operating costs. Keeping an adequate air exchange rate ensures effective ventilation, diluting and removing pollutants and pathogens from the air. The number of contracted infections is a direct indicator of environmental quality and the effectiveness of infection control procedures. A low number of infections indicates a well-managed and safe environment for performing surgeries. The occupancy rate measures how effectively operating room spaces are utilized, affecting logistics, accessibility, and the safety of operations. High occupancy efficiency indicates good space management, avoiding overcrowding and ensuring a smooth workflow.
3.4. Capabilities, Enabling Technologies and Technological Solutions
Identifying the capabilities that the Digital Twin must possess to achieve the set objectives is a crucial step in selecting the necessary technological components for building the system architecture. These requirements include the ability to accurately capture and analyze real-time data, integrate various sources of information, and provide actionable insights for ongoing operations. This approach exemplifies the intervention category related to the regeneration of existing structures, demonstrating a commitment to maintaining high levels of indoor environmental comfort, sustainability, and efficiency in healthcare facility management. By leveraging the capabilities of the Digital Twin, the project sets a new standard for modernizing healthcare infrastructures, ensuring they are equipped to meet the demands of the future. The following tables (
Table 3,
Table 4,
Table 5,
Table 6,
Table 7 and
Table 8) present, for each logical grouping of Digital Twin capabilities as defined by the Digital Twin Consortium, the specific enabling technologies and the corresponding solutions that can be adopted to achieve the objectives defined in the project.
3. Results
The case study delves into the utilization of digitalization to enhance decision-making processes within hospital environments, focusing on maintaining optimal conditions for comfort and safety [
51]. The study particularly investigates how the application of real-time data processing and machine learning facilitates proactive management to sustain high levels of environmental comfort.
Sensors are strategically placed in the environments to monitor various parameters, while historical data is analyzed to detect anomalies and schedule preventive maintenance. This proactive approach not only reduces system downtime but also cuts associated costs. At the heart of the study is the utilization of Digital Twin technology, serving as an advanced decision-support tool. This system utilizes predictive models and algorithms to offer data-driven recommendations focused on enhancing resource utilization and decision-making quality across the hospital’s lifecycle.
The framework developed for this study aids in pinpointing crucial capabilities needed for the construction of our Digital Twin, aligned with predefined objectives, necessary data analyses, and key performance indicators (KPIs) monitoring.
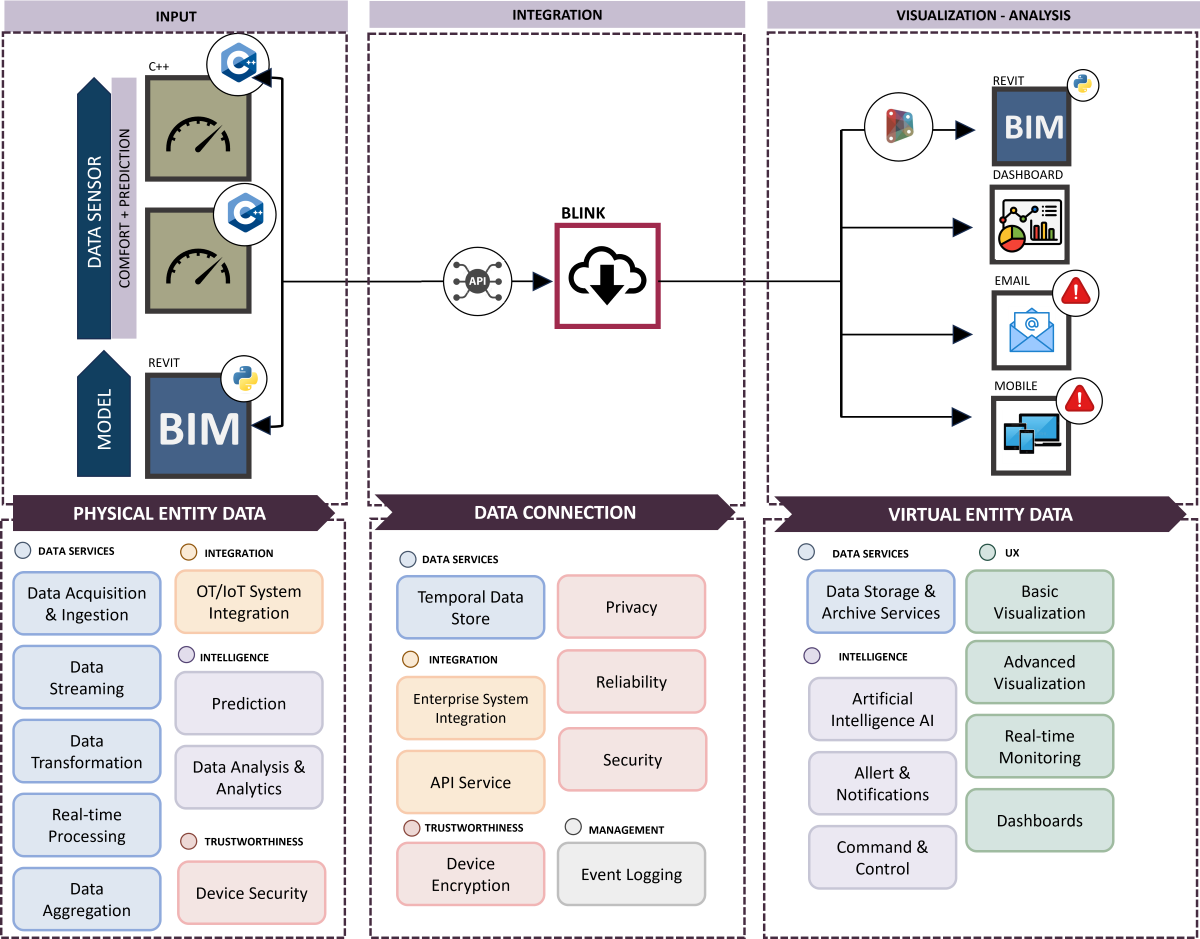
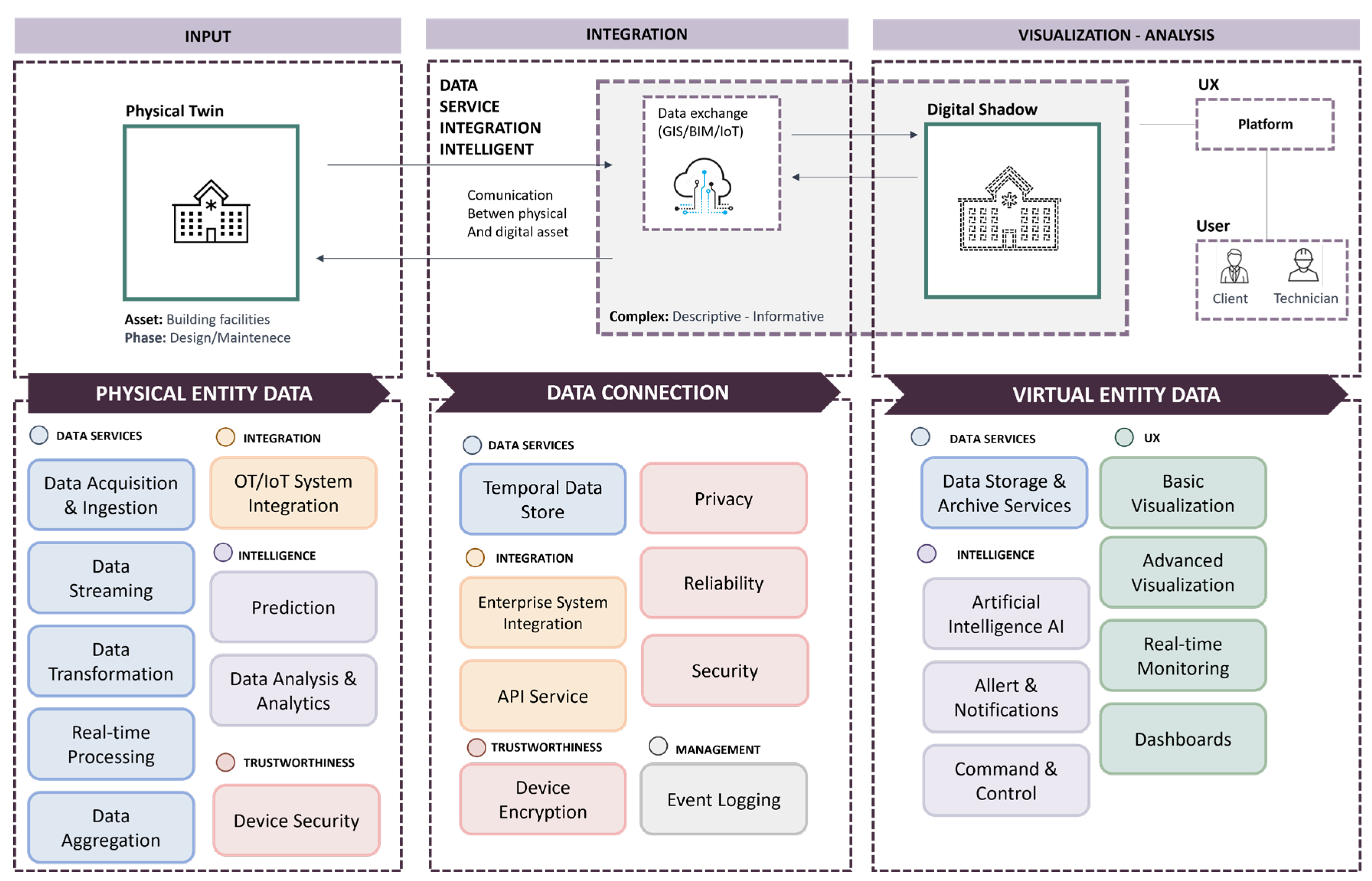
The
Figure 6 illustrates a comprehensive framework for managing data pertaining to a physical entity, tracing the flow from data input to visualization and analysis. The process is segmented into three principal phases:
Input Phase (Physical entity data): The collection of data from physical entities, such as building structures during daily operations, constitutes the foundational layer for subsequent digital processing and integration. This initial phase includes data acquisition and ingestion, data streaming, transformation, real-time processing, and aggregation. Operational Technology (OT) and Internet of Things (IoT) systems are utilized for data collection, followed by predictive and analytical analyses, while simultaneously ensuring security and safety measures.
Integration Phase (Data connection): Data undergo enrichment and processing using sophisticated technologies like GIS, BIM, and IoT. This stage is pivotal for constructing a comprehensive and detailed representation that faithfully captures the qualitative and quantitative aspects of the monitored structures. Security and privacy are paramount, focusing specifically on device encryption and event logging. Data are archived temporally and integrated with enterprise systems through API services, thereby guaranteeing the dependability and security of processed information.
Visualization - Analysis Phase (Virtual entity data): The culmination of the process occurs in the “Visualization - Analysis” phase, where the “Digital Shadow” is created—a highly detailed digital model enabling in-depth analysis and supporting decisions regarding technical and managerial aspects. This model is accessible to clients and technicians, fostering effective and informed interactions among stakeholders. Additionally, data storage and visualization services, both basic and advanced, enrich the model. Artificial intelligence enhances this stage with real-time monitoring capabilities, alerts, and notifications, while also offering management and control tools through dashboards. This facilitates decision-making based on current and precise data.
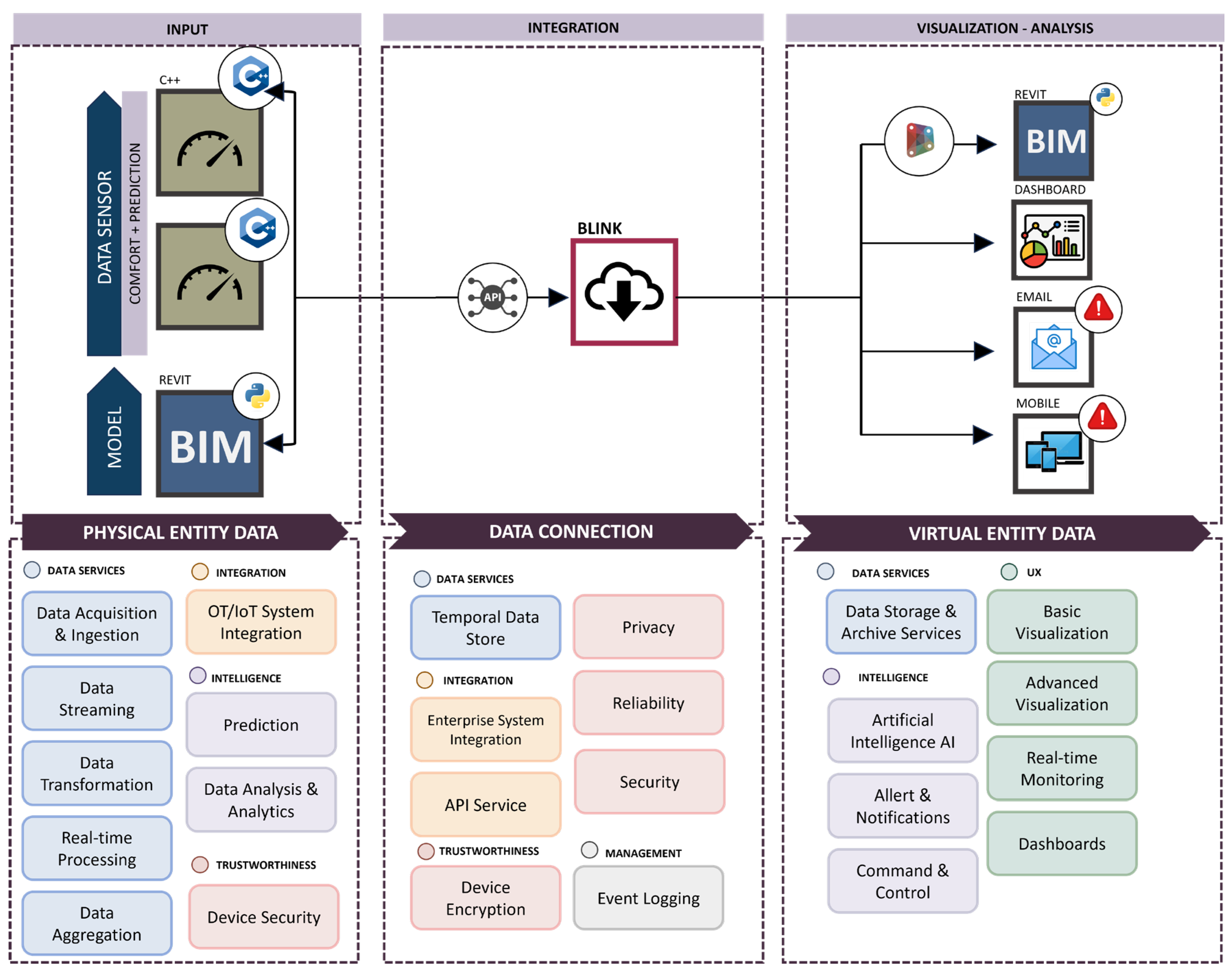
Figure 7 schematically represents the process for real-time data management and analysis, designed for indoor air quality in the operating block under study, developed according to the methodology described above. The sequence of components illustrates the interoperability and synergistic integration of data acquisition technologies, cloud processing, and advanced analytics, with significant implications for the field of indoor environmental comfort.
In the input phase, real-time data (such as operating time, type and quantity of medical fluids used, VOC levels, CO2 levels, illumination intensity, energy absorption data, and number of infections) within the BIM model are obtained through specific sensors installed within the operating block. These data are processed to provide accurate and real-time inputs.
In the integration phase, the ‘BLYNK’ platform plays a crucial role as a gateway for data management through APIs and as an intermediary for visualization on the BIM model or directly through dashboards.
In the final phase of visualization and analysis, it is possible to obtain graphical representations for real-time monitoring (
Figure 8), alert systems, and notifications that serve as early warning mechanisms, along with applications for data processing and review.
The architecture of the Digital Twin as conceived aims to ensure a real-time data flow and advanced analytics, establishing itself as an essential tool to support anomaly detection and immediate intervention.
The DT developed according to the proposed methodology is a Predictive Digital Twin, born from the integration of Information Technology (IT) and Operational Technology (OT), providing detailed real-time data. This tool utilizes sophisticated algorithms to identify issues and suggest corrective solutions, elevating the Digital Twin to a fundamental level for planning and implementing effective strategies to achieve predefined goals.
4. Discussion
The research focuses on developing a Twin Strategy to guide the construction sector and various stakeholders in transitioning to digital approaches for managing complex processes in the building and infrastructure sectors. The methodological approach developed has been employed to create an architecture specifically designed to ensure high levels of indoor environmental comfort, a particularly crucial aspect in environments such as hospitals. In the proposed digital system architecture, the selected capabilities are those listed according to the Digital Twin Capabilities Periodic Table (CPT), created by the Digital Twin Consortium, since the technologies available on the market are continuously evolving.
A crucial point to emphasize is that the quality of collected data is essential to support informed decisions and gain insights. To ensure an accurate and faithful representation of the physical reality, the Digital Twin must be capable of acquiring data from a variety of sources [
53]. Having diverse data sources is necessary to obtain useful and reliable information, which then needs to be interpreted, processed, and compared with other sources to extract meaningful insights [
54]. The high number and variety of data sources present technical challenges, particularly regarding the management of the large volume of data produced by sensors and BIM systems. The research highlights that the complexity is not only related to the vast amount of data but also to the reconstruction and management of historical data of a building within a BIM interface. For instance, for a building from the 1990s modeled in BIM, reconstructing its entire history involves managing such a vast volume of information that it becomes extremely challenging for current computing technologies and data processing programs. Therefore, it is crucial to anticipate improvements in data management systems within BIM models to make the processing and analysis of these extensive digital databases more efficient and secure. This is essential as the collection and analysis of historical data can provide valuable insights for every phase of the building’s lifecycle, enhancing both strategic and operational decision-making.
Another critical issue concerns the use of the Internet of Things (IoT) in the healthcare sector, which poses a significant increase in the risk of cybersecurity threats. Consequently, IoT systems can represent a vulnerability within the cybersecurity infrastructure of hospitals, clinics, and other healthcare facilities. Security incidents in the healthcare sector highlight the paramount need to ensure robust cybersecurity protection in IoT environments.
The adoption of the Digital Twin methodology underscores the growing demand for new specialized professional roles. This research highlights, for instance, the importance of providing IT support to construction industry professionals, offering consultancy on the most appropriate and effective technological solutions for specific purposes.
Within this evolving landscape, there emerges a need for an innovative professional role that collaborates synergistically with the BIM Manager and/or Project Manager.
The implementation of a Digital Twin in the Operating Block can lead to several significant improvements, including the optimization of space and available resources, as well as the management of workflows using data from sensors to prevent errors and enhance patient safety. The Digital Twin can also support decision-making processes, facilitate management of medical records, and monitor medical equipment. Furthermore, it should be considered as a tool for training and educating Operating Block staff through virtual simulations based on digital models, enabling the team to gain practical experience in a secure virtual environment and improve their skills.
The use of technologies, combined with the adoption of data-driven strategies, is driving a profound transformation in the methodologies for managing and maintaining infrastructures. The proposed approach can be integrated with additional emerging technologies to achieve various objectives, such as energy efficiency, economic and environmental sustainability, the utilization and enhancement of the built environment, and even urban management for improving mobility and accessibility, for example.
Artificial intelligence undoubtedly constitutes a fundamental enabling technology for achieving the most advanced level of Digital Twin: the Autonomous DT [
55]. It integrates real-time data from various sources and applies sophisticated algorithms to model and simulate entire structures or facilities. Predictive and prescriptive analytics, combined with artificial intelligence and machine learning, enable 3D visualization, integration of high-speed calculations, and interaction with augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) [
56]. This allows the Digital Twin to make autonomous decisions to solve problems, radically transforming operations and asset management [
57].
5. Conclusions
The construction industry has begun to recognize Digital Twins as a key element for digital transformation, capable of improving the historically poor outcomes of the sector in the field of digitalization [
58]. However, research and application of this technology in the built environment are still in their early stages compared to other sectors [
59]. Despite the growing interest in Digital Twins, there are currently no specific guidelines or standards for the construction sector. Therefore, there is a need to establish consistent methodologies for the design and implementation of Digital Twin platforms dedicated to managing the built environment. Artificial intelligence will be crucial in addressing the challenges arising from managing vast amounts of data. Interdisciplinary collaboration, investments in training new professional figures, and the promotion of developing AI systems oriented towards human well-being will be essential to foster further advancements in artificial intelligence.
In this context, it is evident that research, regulation, and institutions must closely collaborate to foster innovative and sustainable progress. Such synergy is essential to guide the development and adoption of new technologies and methodologies, while also ensuring that regulations remain up-to-date and relevant. In this cooperative framework, institutions are responsible for creating an environment conducive to innovation, while research must continue to explore new horizons of knowledge and technology, paving the way toward a future characterized by greater efficiency, reliability, and adaptability.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, F.C. and A.M.G.; methodology, E.P. and V.A.T.; validation, F.C., E.P. and V.A.T.; formal analysis, E.P. and V.A.T.; investigation, E.P. and V.A.T.; resources, E.P. and V.A.T.; data curation, E.P. and V.A.T.; writing—original draft preparation, F.C., A.M.G., E.P. and V.A.T.; writing—review and editing, E.P. and V.A.T.; visualization, F.C., A.M.G., E.P. and V.A.T.; supervision, F.C. and A.M.G.; project administration, F.C.; funding acquisition, F.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by AGENZIA DEL DEMANIO, grant number 0002716”.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data sharing is not applicable to this article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Sun, Y.; Kojima, S.; Nakaohkubo, K.; Zhao, J.; Ni, S. Analysis and Evaluation of Indoor Environment, Occupant Satisfaction, and Energy Consumption in General Hospital in China. Buildings 2023, 13, 1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization (1948). Constitution of the World Health Organization. Available online: https://www.globalhealthrights.org/wp-content/uploads/2013/10/Constitution-of-the-WorldHealth-Organization-WHO.pdf (accessed on 25 June 2024).
- Mewomo, M.C.; Olaonipekun, T.J.; Iyiola Olubukola, C.; Aluko, O.R. The Impact of Indoor Environmental Quality on Building Occupants Productivity and Human Health: A Literature Review. In Proceedings of the Bbuilding smart, resilient and sustainable infrastructure in developing countries, Livingstone, Zambia, 6-7 October 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Mujan, I.; Anđelković, A.S.; Munćan, V.; Kljajić, M.; Ružić, D. Influence of Indoor Environmental Quality on Human Health and Productivity-A Review. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 217, 646–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, J.G.; MacNaughton, P.; Laurent, J.G.; Flanigan, S.S.; Eitland, E.S.; Spengler, J.D. Green Buildings and Health. Curr Environ Health Rep. 2015, 2, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitroulopoulou, S.; Dudzińska, M. R.; Gunnarsen, L.; Hägerhed, L.; Maula, H.; Singh, R.; Toyinbo, O.; Haverinen-Shaughnessy, U. Indoor air quality guidelines from across the world: An appraisal considering energy saving, health, productivity, and comfort. Environment International 2023, 178, 108127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joo Son, Y. .; Pope, Z. C.; Pantelic, J. Perceived air quality and satisfaction during implementation of an automated indoor air quality monitoring and control system. Building and Environment 2023, 243, 110713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al horr, Y.; Arif, M.; Katafygiotou, M.; Mazroei, A.; Kaushik, A.; Elsarrag, E. Impact of indoor environmental quality on occupant well-being and comfort: A review of the literature. International Journal of Sustainable Built Environment 2016, 5, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ANSI American National Standards Institute. ANSI/ASHRAE 62.1-2022: Ventilation for Indoor Air Quality. Available online: https://blog.ansi.org/ansi-ashrae-62-1-2022-ventilation-indoor-air/ (accessed on 25 June 2024).
- Ackley, A.; Olanrewaju, O. I.; Oyefusi, O. N.; Enegbuma, W. I.; Olaoye, T. S.; Ehimatie, A. E.; Ukpong, E.; Akpan-Idiok, P. Indoor environmental quality (IEQ) in healthcare facilities: A systematic literature review and gap analysis. Journal of Building Engineering 2024, 86, 108787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willems, S.; Saelens, D.; & Heylighen, A. Comfort requirements versus lived experience: combining different research approaches to indoor environmental quality. Architectural Science Review 2020, 63, 316–324. [Google Scholar]
- Nimlyat, P.S.; Kandar, M.Z. Appraisal of indoor environmental quality (IEQ) in healthcare facilities: A literature review, Sustainable Cities and Society 2015, 17, 61–68. 17.
- Anåker, A.; Heylighen, A.; Nordin, S.; Elf, M. Design Quality in the Context of Healthcare Environments: A Scoping Review. Health Environments Research & Design Journal 2017, 10, 136–150. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. Promoting healthy and highly energy performing buildings in the European Union. Available online: https://www.rehva.eu/fileadmin/content/documents/Promoting_healthy_and_highly_energy_performing_buildings_in_European_Union.pdf (accessed on 25 June 2024).
- Asdrubali, F.; Baldinelli, G.; Bianchi, F.; Sambuco, S. A comparison between environmental sustainability rating systems LEED and ITACA for residential buildings. Building and Environment 2015, 86, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Wargocki, P.; Zirngibl, J.; Bendžalová, J.; Mandin, C. Review of parameters used to assess the quality of the indoor environment in Green Building certification schemes for offices and hotels. Energy and Buildings 2020, 209, 109683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, M.; gang Hwang, B. Green building rating systems: Global reviews of practices and research efforts. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 39, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WELL certified. Available online: https://v2.wellcertified.com/en/wellv2/overview (accessed on 25 June 2024).
- Mujan, I.; Anđelković, A.S.; Munćan, V.; Kljajić, M.; Ružić, D. Influence of indoor environmental quality on human health and productivity - A review. Journal of Cleaner Production 2019, 217, 646–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Chen, J.; Hu, y.; Li, S.; He, Q. Digital twin for healthy indoor environment: A vision for the post-pandemic era. Front. Eng. Manag. 2023, 10, 300–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghalzadeh Shishehgarkhaneh, M.; Keivani, A.; Moehler, R.C.; Jelodari, N.; Roshdi Laleh, S. Internet of Things (IoT), Building Information Modeling (BIM), and Digital Twin (DT) in Construction Industry: A Review, Bibliometric, and Network Analysis. Buildings 2022, 12, 1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laplante, P. Trusting Digital Twins. Computer 2022, 55, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal, M.; Li, R.Y.M.; Shoaib, M.; Ayyub, M.F.; Tagliabue, L.C.; Bilal, M.; Ghafoor, H.; Manta, O. Delving into the Digital Twin Developments and Applications in the Construction Industry: A PRISMA Approach. Sustainability 2023, 15, 16436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Ma, L.; Broyd, T.; Chen, K. Digital twin and its implementations in the civil engineering sector. Automation in Construction 2021, 130, 103838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, A.; Fan, Z.; Day, C.; Barlow, C. Digital twin: enabling technologies, challenges and open research. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 108952–108971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khajavi, S.H.; Motlagh, N.H.; Jaribion, A.; Werner, L.C.; Holmstrom, J. Digital twin: vision, benefits, boundaries, and creation for buildings. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 147406–147419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuhaise, V.V.; Tah, J. H. M.; Abanda, F.H. Technologies for digital twin applications in construction. Automation in Construction 2023, 152, 104931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piras, G.; Agostinelli, S.; Muzi, F. Digital Twin Framework for Built Environment: A Review of Key Enablers. Energies 2024, 17, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Pu, Y.; Shelden, D.R. A Graph Database and Query Approach to IFC Data Management. Future Inf. Exch. Interoperability 2019, 28–36. [Google Scholar]
- Tuhaise, V.V.; Handibry Mbatu Tah, J.; Abanda, F.H. Technologies for digital twin applications in construction. Automation in Construction 2023, 152, 104931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khajavi, S. H.; Motlagh, N. H.; Jaribion, A.; Werner, L. C.; Holmström, J. Digital Twin: Vision, Benefits, Boundaries, and Creation for Buildings, IEEE Access 2019, 7, 147406–147419.
- Agostinelli, S.; Cumo, F.; Guidi, G.; Tomazzoli, C. Cyber-Physical Systems Improving Building Energy Management: Digital Twin and Artificial Intelligence. Energies 2021, 14, 2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Parlikad, A.K.; Woodall, P.; Xie, X.; Liang, Z.; Konstantinou, E.; Heaton, J.; Schooling, J. M. Developing a dynamic digital twin at building and city levels: A case study of the West Cambridge campus. Journal of Management in Engineering 2019, 36, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Yuchong, Q.; Jiawei, L.; Kai, Z.; Yuxuan, L. How to measure and control indoor air quality based on intelligent digital twin platforms: A case study in China. Building and Environment 2024, 253, 111349. [Google Scholar]
- Nurumova, K.; Ramaji, I.; Kermanshachi, S. Leveraging Digital Twin for enhancing occupants’ comfort: A Case Study. In Computing in Civil Engineering 2021; Raymond, R., Issa, A., Eds.; American Society of Civil Engineers: Reston, Virginia, volume 1, pp. 417-424; 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, P.; Wen, W.; Ji, D.; Zhai, C.; Xie, L. A framework to assess the seismic resilience of urban hospitals. Advances in Civil Engineering 2019, 11, 7654683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madubuike, O. C.; Anumba, C. J. Digital Twin Application in Healthcare Facilities Management. In Computing in Civil Engineering 2021; Raymond, R., Issa, A., Eds.; American Society of Civil Engineers: Reston, Virginia, 2022; volume 1, pp. 366-373. [Google Scholar]
- Deren, L.; Wenbo, Y.; Zhenfeng, S. Smart city based on digital twins. Computational Urban Science 2021, 1, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marmo, R.; Polverino, F.; Nicolella, M.; Tibaut, A. Building performance and maintenance information model based on IFC schema. Autom. Constr. 2020, 118, 103275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.; Snider, C.; Nassehi, A.; Yon, J.; Hicks, B. Characterising the Digital Twin: A systematic literature review. CIRP journal of manufacturing science and technology 2020, 29, 36–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casini, M. Construction 4.0: Advanced Technology, Tools and Materials for the Digital Transformation of the Construction Industry, 1st ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, United Kingdom, 2021; pp. 1–694. [Google Scholar]
- Tagliabue, L.C.; Cecconi, F.R.; Rinaldi, S.; Ciribini, A.L.C. Data driven indoor air quality pre-diction in educational facilities based on IoT network. Energy and Buildings 2021, 236, 110782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CDBB. Monthly Paper: On the Governance of City Digital Twins; Centre for Digital Built Britain: Cambridge, UK, 2019; Available online: https://www.cdbb.cam.ac.uk/news/monthly-paper-governance-city-digital-twins (accessed on 29 June 2024).
- Borissova, D.I.; Danev, V.K.; Rashevski, M.B.; Garvanov, I.G.; Yoshinov, R.D.; Garvanova, M.Z. Using IoT for automated heating of a smart home by means of OpenHAB software platform. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2022, 55, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messi, L.; Naticchia, B.; Carbonari, A.; Ridolfi, L.; Di Giuda, G.M. Development of a digital twin model for real-time assessment of collision hazards. In Proceedings of the Creative Construction e-Conference 2020. Budapest University of Technology and Economics, Budapest, Hungary, 29 June–2 July 2020; pp. 14–19. [Google Scholar]
- Moretti, N.; Xie, X.; Garcia, J.; Chang, J.; Parlikad, A. K. Digital Twin based built environment asset management services development. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science 2022, 1101, 092023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Digital Twins Consortium. Capabilities Periodic Table. Available online: https://www.digitaltwinconsortium.org/initiatives/capabilities-periodic-table/ (accessed on 29 June 2024).
- Digital Twins Consortium. Digital Twin Capabilities Periodic Table. Available online: https://www.digitaltwinconsortium.org/wp-content/uploads/sites/3/2022/06/Digital-Twin-Capabilities-Periodic-Table-User-Guide.pdf (accessed on 29 June 2024).
- Messinetti, S. , Bartolucci, P. Il policlinico Umberto 1. di Roma nella storia dello stato unitario italiano, Rpoligrafico e Zecca dello Stato: Rome, Italy, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Tiburcio, V.A. Il Digital Twin in fase di Post-Costruzione con applicazione ad un edificio del Policlinico Umberto I, PhD Thesis, in Engineering-based Architecture and Urban Planning, University of Rome La Sapienza, 2024; pp. 233–238.
- Melino, C.; Messineo, A.; Rubino, S.; Allocca, A. L’Ospedale: Igiene, Prevenzione e Sicurezza; Società Editrice Universo, Roma, 2001; pp. 339–353.
- Dall’Acqua, G. Igiene ambientale, Edizioni Minerva Medica: Torino, Italy, 1990; pp. 52–56.
- Bevilacqua, M.; Bottani, E.; Ciarapica, F.E.; Costantino, F.; Di Donato, L.; Ferraro, A.; Mazzuto, G.; Monteriù, A.; Nardini, G.; Ortenzi, M.; et al. Digital Twin Reference Model Development to Prevent Operators’ Risk in Process Plants. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldoseri, A.; Al-Khalifa, K.N.; Hamouda, A.M. Re-Thinking Data Strategy and Integration for Artificial Intelligence: Concepts, Opportunities, and Challenges. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 7082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldt, J.; Kourouklis, T.; Kontny, H.; Wagenitz, A. Digital twin: revealing potentials of real-time autonomous decisions at a manufacturing company. Procedia CIRP 2020, 88, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, J.M.D.; Oyedele, L.; Demian, P.; Beach, T. A research agenda for augmented and virtual reality in architecture, engineering and construction. Advanced Engineering Informatics 2020, 45, 101122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.; Farnsworth, M.; McWilliam, R.; Erkoyuncu, J. On the requirements of digital twin-driven autonomous maintenance. Annual Reviews in Control. 2020, 50, 13–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brilakis, I.; Pan, Y.; Borrmann, A.; Mayer, H.G.; Rhein, F.; Vos, C.; Pettinato, E.; Wagner, S. Built Environment Digital Twining. International Workshop on Built Environment Digital Twinning presented by TUM Institute for Advanced Study and Siemens AG, 2019, pp. 1–40.
- AlBalkhy, W.; Karmaoui, D.; Ducoulombier, L.; Lafhaj, Z.; Linner, T. Digital twins in the built environment: Definition, applications, and challenges. Automation in Construction 2024, 162, 105368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).