1. Introduction
With the continuous development of the economy and society and the accelerated pace of life, residents' eating habits and dietary structures are constantly evolving. Prepared dishes, as a kind of convenient and fast food, are increasingly gaining people’s attention. In 2023, the No. 1 Central Document explicitly proposed the need to "cultivate and develop the prepared dishes industry" for the first time, providing a strong impetus for the industry's growth. In March 2024, China's General Administration of Market Supervision, along with six other ministries and commissions, issued the "Notice on Strengthening Food Safety Supervision of Prepared Dishes and Promoting High-quality Development of the Industry".① This notice clearly defines the scope and definition of prepared dishes, mandates the advancement of regulatory and standard systems for prepared dishes, providing explicit guidelines for the high-quality development of the industry. Driven by both consumer demand and strong national policy support, the prepared dishes industry has entered a rapid growth phase. According to enterprise search data②, by the end of 2023, China had approximately 61,900 enterprises related to prepared dishes, with an output value exceeding 500 billion yuan, and it is expected to exceed one trillion yuan in 2026. However, urban residents in China currently have concerns about the safety and health of prepared dishes [
1]. Their continuous purchasing intention is relatively low, which will hinder the further development of the prepared dishes industry in the consumer market.
Cognition is how well residents know about a product and can directly or indirectly influence their continuous purchasing intention. The more information and knowledge consumers have about a product, the stronger their continuous purchasing intention.[
2]. For genetically modified foods [
3,
4], farmers' demand for pollution-free pesticides [
2], and commercial insurance [
5],they have all reached similar conclusions. Additionally, cognition can indirectly influence consumer purchasing intention through mediating variables. Empirical studies on the consumption intentions of genetically modified foods [
6] and fresh agricultural products [
7] have found that the more individuals understand the product, the lower their perceived risk and the stronger their purchase intention.
The current research on prepared dishes primarily focuses on the levels of industry development, technology research and industry standardization, etc. The research at the level of industry development focuses on the current status and trends of the entire prepared dishes industry [
8,
9],as well as regional or special cuisines[
10,
11].The technical aspects of the research mainly focuses on the processing of prepared dishes [
12], packaging [
13], storage and transportation [
14], safety control [
15], and other technologies exploration [
16,
17,
18]. Research at the level of industry regulation mainly focuses on the traceability system for prepared dishes [
19], food safety and legal regulation aspects [
20,
21], regulatory proposals for food additives [
22] and other studies. Some scholars have studied the factors influencing consumers' purchase intention of prepared dishes [
23] and the roles of perceived risk and trust on consumers' purchasing intention of prepared dishes [
24]. However, few studies have explored the relationship between residents' cognition and their continuous purchasing intentions of prepared dishes [
1], indicating a gap in empirical research on this topic.
Therefore, based on the distributed cognition theory, this paper introduces the concept of risk perception, and employs Structural Equation Modeling to deeply analyze the impact of cognition on continuous purchasing intention of prepared dishes, using data coming from urban residents in Beijing and Shanghai. Specifically, the study addresses the following questions:
(1)Does cognition of prepared dishes among Chinese urban residents influence their continuous purchasing intentions? How do different dimensions of cognition influence these intentions?
(2) Does risk perception plays a mediating role between dimensions of cognition and continuous purchasing intention?
This study extends the scope of application of distributed cognition theory, and analyzes the cognition of Chinese urban residents towards prepared dishes from the dimensions of "individual power", "geographical power", and "cultural power". It also examines the impact of each dimension of cognition on residents' continuous purchasing intention of prepared food, enriching the research on the consumption behavior related to prepared dishes and providing a reference for the applying distributed cognition theory to study the purchase intention and consumption behavior. Meanwhile, this paper aims to offer some theoretical support to enterprises in developing marketing programs related to prepared dishes and government departments in refining relevant policies.
The rest of the paper is organized as follows:
Section 2 presents the research hypotheses,
Section 3 presents the method and data,
Section 4 presents the research results analysis,
Section 5 presents the discussion of the findings and contributions,
Section 6 presents the conclusions, policy implications and limitations.
2. Research Hypothesis
Distributed Cognition Theory is derived from psychological research about individual cognition. It suggests that cognition is formed by the interaction of individual with the external environment, emphasizing that the individual maintains their independence while interacting with the environment. The concentric circles model proposed by Hatch and Gardner states that the model includes individual, geographical and cultural power from the center outward [
25]. Individual power mainly emphasizes the influence of personal subjective initiative and preference on cognition, while geographical and cultural power focus on external environmental factors affecting cognition. Based on this theory, this paper divides cognition into three dimensions, including individual power, geographical power and cultural power, and then explores their different effects on urban residents’ continuous purchasing intention of prepared dishes respectively.
Individual power cognition refers to the knowledge that acquires from personal experiences and eating preferences [
20]. For consumers, relevant food purchasing experiences have a significant impact on individual cognition [
26]. When residents seek product information, they utilize search engines, shopping websites, and personal experiences. These methods effectively generate individual cognition, providing comprehensive product knowledge [
27]. Moreover, the richer the personal purchasing experience, the more knowledge about the product is accumulated, the greater the role played by trust and knowledge, and the greater the impact on the future purchase intention and behavior of green food [
28]. By increasing the purchasing experience of prepared dishes, residents have a better understanding of the convenience, safety, and nutritional value of prepared dishes, which enhances their perceptions of improved quality of life and increased product utility, which in turn can increase consumers' continuous purchasing intention. Based on this, the following hypothesis is proposed:
H1: Individual power has a significant positive effect on urban residents’ continuous purchasing intention of prepared dishes.
Geographical power cognition refers to the resources an individual possesses and the perceptions formed under the influence of people who have an impact on their behavior [
29]. Geographical power in the field of food consumption domain include personal capabilities (including time, money, experience and other factors [
30]), skills, accessible information, channel accessibility, other people's evaluation and other factors [
31,
32]. Peer effect points out that an individual's behavior will be influenced by the behavior of other people around them with the same status [
33] and influenced by changes in consumption trends of people around them, people pay more attention to the quality and safety of food, and are more inclined to choose green and healthy food[
34,
35]. Witek and Kuźniar [
28] have found that the opinions of people around them, such as family members, partners, friends, or peers, have a very important influence on an individual's own purchasing behavior. Based on this, the following hypothesis is proposed:
H2: Geographical power has a significant positive effect on urban residents continuous purchasing intention of prepared dishes.
Cultural power cognition refers to the understanding formed by individuals under the influence of intangible aspects of their environment, such as culture or institutions[
36]. In China, the majority of prepared dishes producers are small and medium-sized enterprises or individual businesses, which often have lower levels of product standardization, leading to potential food safety issues and product quality risks. To strengthen the food safety supervision and promote the healthy development of the prepared dishes industry, Chinese ministries and local governments have introduced multiple policies . These policies support the industry's healthy growth, increase consumer cognition of government regulatory systems and processes, and enhance consumer confidence in prepared dishes, thereby boosting their continuous purchasing intention. Han and Zhang [
37] found that the government regulation status and the level of information disclosure of traceable foods significantly affect consumer purchase intention. Zhuang and Yu [
38] found that ethically induced negative product performance-based exposure events have a significant negative effect on consumers' purchase intention for those with low cognitive demand. Based on these findings, the following hypothesis is proposed:
H3: Cultural power has a significant positive effect on urban residents continuous purchasing intention of prepared dishes.
Risk perception is the uncertainty and unfavorable consequences that consumers feel when purchasing a product or service [
39]. Consumers' risk perception of prepared dishes refers to consumers' judgment of the risk level of quality and safety of prepared dishes, and the possible adverse consequences to their health when eating prepared dishes. Consumers may have different types of risk perceptions of prepared dishes in the context of asymmetric market information, varying consumer information acquisition capabilities and risk preferences. Risk perception may play a mediating role between cognition and purchase intention. Wang and Gao [
40] found that risk perception plays a mediating role between information search and purchase intention for consumers buying fresh product online. Bi [
41] discovered that risk perception plays a mediating effect between consumers' relationship strength and purchase intention, with relationship strength representing the frequency and intensity of information search communication, and information exchange between parties. Xiang and Guo [
42] empirically found that risk perception plays a mediating effect between financial literacy and consumers' online loan purchase decisions. Liu and Yang [
43] empirically found that risk perception plays a mediating role between lenient return policies and purchase intention. Based on the above analyses, the following hypotheses are proposed:
H4: Risk perception plays a mediating role between the effects of individual power on urban residents continuous purchasing intention of prepared dishes.
H5: Risk perception plays a mediating role between the effects of geographical power on urban residents continuous purchasing intention of prepared dishes.
H6: Risk perception plays a mediating role between the effects of cultural power on urban residents continuous purchasing intention of prepared dishes.
3. Research Methods and Data
3.1 Questionnaire
The questionnaire is divided into three sections, the first section is to measure consumers' continuous purchasing intention. The measurement of continuous purchasing intention refers to Zhang et al [
24]. The second section is to measure consumers' individual power, geographical power, cultural power and risk perception. The scale measurement of individual power refers to Zou et al [
29], Han [
27], and Jin [
31] and Huang et al [
44]. For the geographic power scale, refers to Zou et al [
29] ,Wang et al [
45] , Sheng et al [
30] ,Duan [
34] and Huang et al [
44]. The scale of the cultural power measurement is modified from the scale of Zou et al [
29]. The risk perception measurement refers to Zhang et al [
24]. The third section is the demographic characteristics of consumers (including gender, age, income, education level, marital status, family structure, etc.). The questionnaire design drew on numerous related studies and involved evaluations by relevant experts, and finally formed the variable measurement table shown in
Table 1, with all variables measured using a five-point Likert scale.
3.2 Demographic Profile of Respondents
This paper utilized the internationally recognized research platform
Credamo to collect questionnaires and imposed respondent restrictions to enhance data quality. First, a historical response rate of over 80% was set to reduce the incidence of low-quality responses from less serious participants. Second, validation such as sliding and identity verification were implemented before respondents could answer, to prevent automated responses. Third, a distance restriction was imposed, preventing repeated responses within 1 km radius to avoid sample homogeneity due to respondent aggregation. Fourth, consumers from the first-tier cities of Shanghai and Beijing were selected as representatives to focus on questions related to prepared dishes. In the era of advanced internet information, with China’s internet users base reaching 1.092 billion, online questionnaires are both feasible and representative. After the modification and adjustment of the questionnaire in the pre-survey, 599 questionnaires were distributed in the formal survey, and 462 valid questionnaires were obtained by excluding invalid and poor quality questionnaires, with a questionnaire survey validity rate of 77.13%. This aligns with Bentler's recommendation that the sample size should be 10-15 times the number of observed variables [
46]and meets the suggested sample size of 400-500 for structural equation modeling [
47]. The sample distribution is consistent with the consumer portrait of prepared dishes, ensuring good representation. The demographic characteristics of the sample are presented in
Table 2.
According to demographic characteristics, the majority of respondents in Tier 1 cities are female (69.7%), reflecting that women are the primary purchasers in households, consistent with iMedia Consulting's 2022③ profile of prepared dishes consumers and the finding that over 60% of household consumption decisions in China are made by women [
48].The age distribution is concentrated between 18 and 40 years(86.2%), mainly young consumers, which may be due to the fact that young consumers are more curious about new things and have a higher demand for the convenience of prepared dishes, mirroring findings from related studies [
49]. Over 86% of respondents have a bachelor's degree or higher, and their monthly household income is evenly distributed above 5,000 RMB. The higher cost of prepared dishes compared to traditional cooking necessitates a certain purchasing power. High education level and high income level are the commonalities of these consumers. Marital status is evenly distributed, in line with the specifics of first-tier cities. In terms of family structure, 67.32% of the households have elderly people over 60 years old or children under 18 years old, probably due to the fact that family structure has less influence on the consumption of prepared dishes among urban residents .
4. Results
4.1. Reliability Analysis
4.1.1. Reliability and Convergent Validity Tests
Before evaluating the results of structural equation modeling, it is necessary to test the reliability and validity test of the measurement model. Based on research related to Smart PLS, this study uses three indexes of Cronbach's Alpha, CR(rh0_a), and CR(rh0_c) to assess reliability. The results, as shown in
Table 3, indicate that all three values exceed the critical thresholds of 0.6, 0.7, and 0.8 respectively. It indicates that the scale has good reliability. Convergent validity is tested using Average Variance Extracted (AVE), which evaluates the total amount of variance that can be explained by the latent variable relative to the measurement error. In this paper, some adjustments were made to the measurement items of individual and geographical power, and the measurement items with loading factors below 0.5 were deleted to improve the reliability and validity. As seen in
Table 3, that the AVE values all exceed the critical threshold of 0.5, indicating having a good convergent validity.
4.1.2. Tests of Discriminant Validity
Discriminant validity is the idea that there should be a clear distinction between different trait and connotation measurements [
50]. It is typically measured using the Fornell-Larcker criterion and the HTMT criterion. According to the Fornell-Larcker criterion, if the square root of the AVE is greater than the correlation coefficients between the latent variable and other variables, the scale exhibits good discriminant validity [
51]. The Fornell-Larcker Criterion discriminant validity test results, as shown in
Table 4, indicate good discriminant validity. According to the HTMT criterion, if the value between two latent variables is less than 0.9, the discriminant validity is considered good [
52]. The HTMT discriminant validity test results, as shown in
Table 5, demonstrate that the variables in this study exhibit good discriminant validity.
4.1.3. Hypothesis Testing
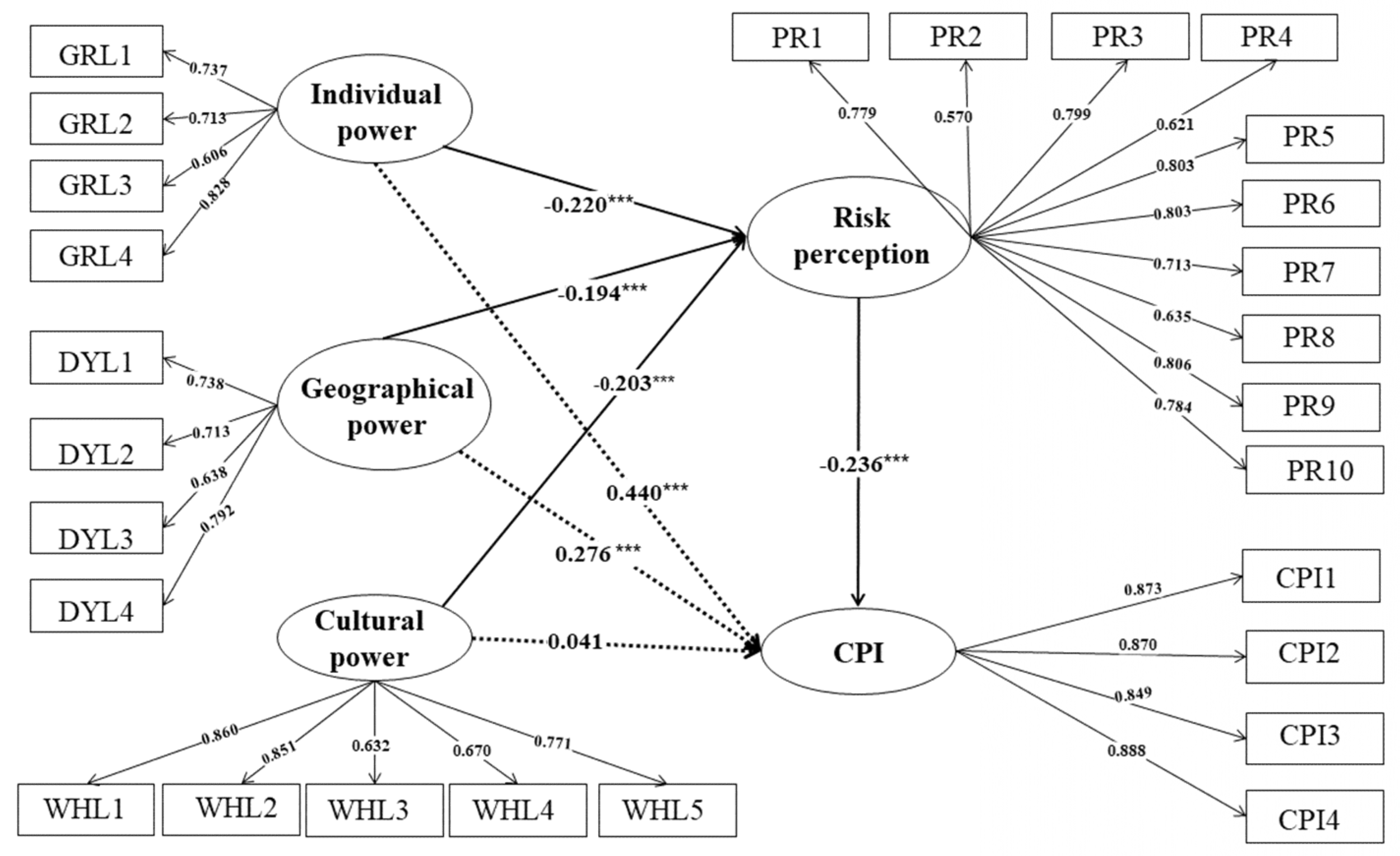
The structural equation modeling is path analyzed through SmartPLS4.0 and the standardized path coefficients are plotted as shown in
Figure 1. The hypotheses presented in the previous section are tested based on the path coefficient results and their significance. The results show that all hypotheses are valid except H3, and the standardized coefficients pass the test at 0.001 significance level.
4.2. Analysis of Results
4.2.1 Direct Effects Analysis
Individual power and geographical power have a significant positive effect on the intention to continue purchasing, which verifies H1 and H2, However, cultural power has no significant direct effect on the intention to continuous purchasing intention and rejects H3. According to the path coefficients and
p-values in
Table 6, both individual power and geographical power have a significant positive effect on the intention to continue purchasing at
p<0.001, with individual power having the greatest effect on the intention to continue purchasing, followed by geographical power, which has the greatest effect on the intention to continue purchasing. At the same time, this conclusion also confirms the hypotheses drawn earlier: the higher the level of consumer cognition of prepared dishes, the stronger continuous purchasing intention. It indicates that when consumers have more knowledge of prepared dishes, they will form personal opinions about prepared dishes, which in turn will have an impact on their continuous purchasing intention of prepared dishes.
4.2.2. Mediating Effects Analysis
To further explore the influence mechanism between residents' cognition (individual power, geographical power, cultural power) and continuous purchasing intention of prepared dishes. This paper selects risk perception as a mediating variable to examine its effect in cognition and continuous purchasing intention through Bootstrapping setup with repetitive sampling for 5000 times. According to the mediation effect testing and analysis procedures by Zhao et al [
53], if the 95% confidence interval does not contain zero, the mediating effect is significant.
The indirect path coefficient of individual power on consumers' continuous purchasing intention is 0.052, which is smaller than its direct path coefficient of 0.440, and H4 is verified. Similarly, the indirect path coefficient of geographical power is 0.046, which is smaller than its direct path coefficient of 0.203, and H5 is verified. It indicates that it exists mediating effect. Since the direct effect of cultural power on continuous purchasing intention is not significant, but the indirect effect is significant, the path coefficient is 0.048, indicating that risk perception plays a fully mediating role in the effect of cultural power on continuous purchasing intention, and H6 is verified. According to the procedure diagram by Zhao et al [
53], it can be seen that the product of the indirect path coefficient and the direct path coefficient is greater than zero, indicating the presence of other mediating variables in the same direction as the hypothesized mediating effect. The product of the indirect path coefficients and the direct path coefficients of personal and geographic power is greater than zero, indicating that risk perception plays a partial mediating role in the influence of individual and geographic power on the continuous purchasing intention respectively.
The mediating effect indicates that risk perception plays a negative mediating role in the influence of individual power on consumers' continuous purchasing intention of prepared dishes. Residents' experiences and preference in purchasing prepared dishes form their judgment of the risk level of prepared dishes. Higher perceived risk among residents correlates with lower intentions to continue purchasing prepared dishes. Risk perception plays a negative mediating role in the influence of geographical power on consumers' continuous purchasing intention for prepared dishes, indicating that the evaluation of prepared dishes by the people around the consumers influences their risk perception and own resources, which then reduces the continuous purchasing intention of prepared dishes. Risk perception plays a negative mediating role in cultural power and continuous purchasing intention. It indicates that consumers learn more negative news about prepared dishes in the market and then they will have a strong risk perception about them, which reduces consumers' continuous purchasing intention.
Table 7.
Model indirect effects testing results.
Table 7.
Model indirect effects testing results.
| Hypothesis |
Path |
Original sample(O) |
Sample mean(M) |
STDEV |
T |
p |
Results |
| H4 |
GRL -> PR -> CPI |
0.052 |
0.052 |
0.012 |
4.365 |
0.000 |
Support |
| H5 |
DYL -> PR -> CPI |
0.046 |
0.046 |
0.013 |
3.643 |
0.000 |
Support |
| H6 |
WHL -> PR -> CPI |
0.048 |
0.048 |
0.012 |
3.924 |
0.000 |
Support |
5. Discussion
In this paper, by introducing the distributed cognition theory and using risk perception as a mediating variable, we explore the mechanisms influencing consumers continuous purchasing intention of prepared dishes from different dimensions of cognition. Specifically:
Firstly, this study confirms that distributed cognition theory provides a critical theoretical foundation for explaining consumers' continuous purchasing intention in prepared dishes markets. Previous studies often relied on theories such as the Theory of Planned Behavior to study food purchase intention. This study broadens the application of distributed cognition theory and deepens the research on the field of prepared dishes consumption.
Secondly, cognition directly or indirectly impacts residents' continuous purchasing intention. This finding is consistent with Zheng et al. [
54], who also found that cognition plays a key role in influencing consumers' continuous purchasing intention. In terms of individual power, residents form their personal perceptions of prepared dishes through their own experiences and preference choices, which, to some extent, influence their purchasing decisions after collecting and integrating information. In contrast to individual power, geographical power is the purchasing decision made by consumers with reference to the feelings of people around them, such as family members, relatives, friends, and so on. To a certain extent, it indicates that for residents with low individual cognition, they will consider whether to purchase prepared dishes by referring to the feelings and suggestions of people around them [
55]. This finding is consistent with the study of GM food [
56] and Organic Milk [
57] knowledge and purchase intention. It is also consistent with the results of peer effect and herd behavior: the higher the level of personal experience and understanding, the more rationally one will consume based on the evaluations of the people around them. Whereas, when individuals do not have any knowledge of the product, their purchase intention or behavior will be more significantly influenced by the people around them. In addition, this study's findings have a contrast with those of Zou et al [
29], on food safety consumption among rural residents, which concluded that the individual power and geographical power do not have a direct impact on continuous purchasing intention, and cultural power has a direct impact on purchase intention, probably due to the differences in factors such as the economic level of urban and rural residents, consumer awareness, information channels, purchasing channels, and the difference in governmental attention [
58] , which brought about the different results of the study.
Thirdly, risk perception plays a mediating role in the effect of perception on continuous purchasing intention. Risk perception is playing a partial mediating role between individual power and geographical power on continuous purchasing intention, which is consistent with the finding of Cheng and Yin [
59]. The main components of cultural power include laws, regulations and regulatory events related to prepared dishes. Residents tend to focus on negative news occurring in the prepared dishes market, such as food safety and quality issues caused by manufacturers’ ethical problems, as well as legal regulation and complaint feedback process of prepared dishes. When it comes to the government's handling of related events, the clearer and more informed consumers are about the event, the lower their risk perception is, and the stronger their continuous purchasing intention will be. In line with the finding of Liu and Yang [
43], risk perception plays a mediating role between policy leniency and purchase intention. It aligns broadly with the finding of Zou et al [
29], the only difference is that risk perception plays a partially mediating role in the effect of cultural power on purchase intention. This may be due to the difference between food safety consumption and the continuous purchasing intention of prepared dishes, where relevant governmental norms and authoritative information have a direct impact on the former, but not on the latter, because the enhancement of relevant governmental norms and authority reduces consumers' risk perception of prepared dishes, which in turn enhances their purchasing intention to continue to buy.
6. Conclusions
6.1. Conclusions
This paper takes urban residents in Shanghai and Beijing as the object, combines distributed cognition theory, and analyzes the influence paths of cognition in the three dimensions of individual power, geographical and cultural power on urban residents' continuous purchasing intention of prepared dishes. The conclusions are as follows:
Individual power has the greatest impact on residents' continuous purchasing intention of prepared dishes. Therefore, firstly, to cultivate and enhance consumer cognition, enterprises need to objectively and truthfully disclose product information regarding the production process, nutritional labels and test results. These will help consumers comprehensively understand the product during the purchasing process. Secondly, enterprises should make more efforts to publicize the functions and knowledge of prepared dishes, enhancing consumers' cognition and catering to the different consumption needs of different residents. Thirdly, in response to the asymmetry of market information, enterprises need to improve the information flow channels, with the help of the Internet platform to actively and objectively publicize the information of prepared dishes, reduce consumer doubts in the purchasing of prepared dishes.
The influence of geographic power on the residents' continuous purchasing intention of prepared dishes cannot be ignored. Therefore, firstly, from the perspective of consumers' cognition of geographical power, enterprises should pay attention to the peer effect and information transmission among consumers. By enhancing product and service quality, enterprises can build a positive reputation and value through word-of-mouth, facilitating consumer recognition and acceptance of prepared dishes. Secondly residents' food choice are influenced by conformity effects. Under the prevalent trend of pursuing popular dining experiences, residents seek dietary concepts that align with contemporary trends. To improve the consumers' recognition of this new type of prepared dishes, enterprises can engage celebrities and internet influencers to endorse their product, leveraging the demonstration effect of celebrity public figures to enhance consumers’ continuous purchasing intention of prepared dishes.
Cultural power, as an intangible aspect of the social environment encompassing culture and institutions, indirectly influences purchase intention, indicating that residents are very concerned about food safety. Although cultural power does not have a significant direct effect on continuous purchasing intention, it influences residents' continuous purchasing intention through the mediating role of risk perception. Health and quality risks actually exist in the current prepared dish industry, which is a problem that must be standardized and solved in the development of the industry. Therefore, firstly, prepared dishes enterprises need to strictly abide by the industry norms, comply with the industry ethics, uphold the concept of consumer-centered, and firmly guard the insurmountable bottom line of food safety to guarantee the safety and quality of prepared dishes. Secondly, the government needs to strengthen the formulation and dissemination of relevant regulations, intensify law enforcement against illegal prepared dishes enterprises, improve and publicize the relevant laws, regulations and complaint channels in a timely and transparent manner, so as to create a favorable environment for residents to consume prepared dishes.
6.2. Limitations and Future Research
This study makes several contributions but also has some limitations. Firstly, due to the research purpose and background, the model only considers the mediating role of risk perception. How to incorporate trust and perceived value into the analytical framework as mediating variables remains to be further discussed. Secondly, this paper focuses on consumers' continuous purchasing intention rather than purchasing behavior. Although some studies have shown a strong positive relationship between purchasing intention and purchasing behavior, further investigation into specific purchasing behaviors is needed. Thirdly, prepared dishes encompass a wide variety of food types, and consumer cognition may vary across different types. Future research could explore the differences in consumer cognition and behavior for different types of prepared dishes to understand their influencing factors more precisely..
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at:
①Food Production Safety Supervision and Management Department. Notice of the General Administration of Market Supervision, Ministry of Education, Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs, Ministry of Commerce, Ministry of Commerce, National Health and Health Commission on Strengthening Food Safety Supervision of Prepared Dishes and Promoting High-Quality Development of the Industry: State Municipal Supervision of Food and Health Issues [2024] No. 27 [A/OL]. (2024-03-18)[2024-03-21].
https://www.samr.gov.cn/zw/zfxxgk/fdzdgknr/spscs/art/2024/art_e1ba9385be204186adc0f2cfef717693.html
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, W.Z. and Y.F.; methodology, W.Z., Y.F. and J.Z; software, Y.F. and J.Z.; validation, Y.F., W.Z. and J.Z.; formal analysis, Y.F.; investigation, Y.F.; resources, Y.F.; data curation, Y.F.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.F.; writing—review and editing, Y.F., W.Z. , R.W and J.Z.; visualization, Y.F.; supervision, W.Z., R.W and J.Z.; project administration, Y.F.; funding acquisition, Y.F. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the normal project of National college Student Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program fund in 2023: Prepared dishes market and Enterprise competitiveness analysis, grant number 202310264026.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This study was approved by IRB of Shanghai Ocean University.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding authors upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- LIU, J.; LI, H.; MENG, T.; WU, X. A Consumer Survey on Cognition and Purchase Intention of Pre-prepared Food. Food and Nutrition in China 1-9.
- ZHAO, J.; ZHANG, X. Awareness, Acceptance and Willingness to Buy Biopesticide -Analysis on Survey Samples of 120 dish Farmers in Hebei Province. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research 2007, 70–73. [Google Scholar]
- GE, L.; LV, J. Consumers' Cognitive Attitude and Purchase Intention towards Genetically Modified Foods. COMMERCIAL RESEARCH 2009, 189 -192.
- HUANG, J.; QIU, H.; BAI, J.; Pray, C. Awareness, Acceptance and Willingness to Buy Genetically Modified Foods in Urban China. China Soft Science Magazine 2006, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, G.; Wang, N.; Ren, C. Cognitive Ability, Financial Knowledge and Demand for Family Business Insurance. Financial Tribune 2020, 25, 48–58. [Google Scholar]
- Xiang, G.; Zeng, Z.; Shen, Y.; Shen SXiang, G.; Zeng, Z.; Shen, Y.; Shen, S. Study on Consumers Purchase Intention of Genetically Modified Food Based on Risk Perception - -An Analysis Based on Nanjing Consumers. -An Analysis Based on Nanjing Consumers. the Food Industry 2016, 37, 256–261. [Google Scholar]
- ZHANG, Y.; ZHANG, M.; WANG, Q.; REN, Y.; MA, Y.; MA, S.; SHAO, W.; YIN, S.; SHI, Z. The Research on Purchasing Intention of Fresh Agricultural Products under O2O Mode Based on the Framework of Perceived Benefits-Perceived Risk. China soft science magazine 2015, 128–138. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, L. Study on the Current Situation and Problems of the Prefabricated dish Industry. Modern Marketing (Business Edition) 2021, 146 Modern Marketing (Business Edition) 2021, 146 -147.
- Wang, J.; Gao, Q.; Lou, W. Development Status and Trends of the Pre-prepared Food Industry in China. Modern Food Science and Technology 2023, 39, 99–103. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Liu, M.; Chen, Y.; Deng, N.; Zhang, B.; Li, C.; Xiao, Z.; Fang, F.; Liu, D.; Yang, D. Analysis of Current Situation and Development Path of Prepared Dishes Industry in Hunan. Industry in Hunan. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology 2022, 22, 20–26. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, F.; Chen SXu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, F.; Chen, S. Analysis on the Development Mode and Current Situation of Prepared Dishes in Guangdong. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology 2022, 22, 27–38. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Rao, L.; Zhang, H.; Hu, X.; Liao XWu, X.; Rao, L.; Zhang, H.; Hu, X.; Liao, X. Quality and safety improvement of premade cuisine by novel food processing technologies. journal of Food Science and Journal of Food Science and Technology 2022, 40, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, E.; Zhang, C.; Li, D.; Liang, D. Research and Prospect of Packaging Technology for Prepared Dishes. PACKAGING ENGINEERING 2023, 44, 142–147. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, X.; Cao, S.; Ma, J.; Cheng, J.; Wang, L. Recent Advances on Quality Monitoring and Block-Chain Traceability Technology of Prefabricated Food Supply Chain. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology 2022, 22, 48–57. [Google Scholar]
- Osaili, T.M.; Giatrakou, V.; Ntzimani, A.; Tsiraki, M.; Savvaidis, I.N. Application of Quantitative Microbiology and Challenge Tests to Reach a Suggested Food Safety Objective in a Middle Eastern-Style Ready-to-Cook Chicken Product. foods 2022, 11, 1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Liu, H.; Sun, X.; Wei, X.; Yang, X.; Shi, H. Analysis of Current Situation and Trends of Industrial Processing Technology for Prepared Dishes. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology 2022, 22, 39–47. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, C.; Xia, Y.; Che, Z.; Ren, M. Progress on application of ultrasound treatment technology in meat industry. food and Machinery 2016, 32, 232–236. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, T.; Zhang, M.; Lim Law, C.; Mujumdar, A.S. Novel Strategies for Controlling Nitrite Content in Prepared Dishes: Current Status, Limitations and Future Challenges. Food Research International 2023, 170, 112984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, Z. Review of Safety Traceability System for Prepared Dishes. Storage and Process 2024, 24, 71–75. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, X. Food Safety and Security and Legal Response of Prepared Dishes in China. Storage and Process 2024, 24, 65–70. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, C. The Risk of Food Safety in Prefabricated Dishes Industry and Its Countermeasures. science and technology of cereals, oils and foods 2024, 32, 201–208. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, N. Regulated Use of Food Additives in Prepared Dishes. Storage and Process 2024, 24, 118–123. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X. A Study on Consumers' Willingness to Purchase Prepared dishes and Its Influencing Factors. CHINA COLLECTIVE ECONOMY 2023, 73 -76.
- Zhang, W.; Zheng, J.; Li, Y. Explaining Chinese Consumers' Continuous Consumption Intention toward Prepared Dishes: The Role of Perceived Risk and Trust. Foods 2024, 13, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HATCH, T.; GARDNER, H. Finding Cognition in the Classroom an Expanded View of Human Intelligence. m, Cambridge University: Cambridge, 1993.
- MA, J.; QIN, F. Consumers' Perceived Ability of Safe Agricultural Products and Its Influencing Factors: An Empirical Analysis Based on Consumers' Consumption Behavior of Organic Agricultural Products in Beijing's Urban Areas. Review 2009, 26–34. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Z. The Driving Factors for the Evolution of Users' Mental Model of Academic Database Based on Distributed Cognition. journal of the China Society for Scientific and Technical Information 2017, 36, 79–88. [Google Scholar]
- Witek, L.; Kuźniar, W. Green Purchase Behavior Gap: The Effect of Past Behavior on Green Food Product Purchase Intentions among Individual Consumers. Foods 2024, 13, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ZOU, X.; CHEN, J.; WANG, H. Impact of Cognitive Characteristics on Rural Residents' Safe Consumption Behavior of Food Based on Distributed Cognitive Theory. Journal of Agro-Forestry Economics and Management 2023, 22, 233–242. [Google Scholar]
- SHENG, G.; XIA, Q.; FENG, Z. The Effect of Green Product Experience on Consumers' Green Purchasing Intention. Journal of Northeastern University (Social Science) 2022, 24, 26–34. [Google Scholar]
- JIN, Z. Research on the Effects of Micro-blog Marketing on Consumers' Willingness to Buy. CHINA BUSINESS AND MARKET 2015, 29, 37–45. [Google Scholar]
- ZHOU, H.; WANG, D. Study on Purchase Intention of Green dish Consumers Based on Structural Equation Model. northern Horticulture.
- Liu, R.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Liang, F.; Ma, H. A REVIEW OF AGRICULTURAL GREEN TECHNOLOGY ADOPTION BY FARMERS: FROM THE PERSPECTIVE OF SOCIAL NETWORKS AND PEER EFFECTS. Chinese Journal of Agricultural Resources and Regional Planning 2023, 44, 119–130. [Google Scholar]
- DUAN, L. Analysis on change tendency of food consumption in China. Journal of Food Safety and Quality 2018, 9, 4138–4142. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, E.S.-T.; Lin, H.-C.; Tsai, M.-C. Effect of Institutional Trust on Consumers' Health and Safety Perceptions and Repurchase Intention for Traceable Fresh Food. foods 2021, 10, 2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- REN, L.; WU, M.; GAN, C.; CHEN, Y. Influencing Factors of Farmers' Risk Perception on Land Investment in the Suburbs: an Empirical Research Based on DCT. China Land Science 2019, 33, 66–73. [Google Scholar]
- HAN, W.; ZHANG, W. Based on the Effects of Three Factors, the Empirical Analysis of Consumers Purchasing Intention for Traceable Food: Taking Tianjin as an Example. ECOLOGICAL ECONOMY 2013, 119–124. [Google Scholar]
- ZHUANG, A.; YU, W. An Empirical Study of the Spillover Effect of Immorality Brand Publicity: The Interaction of Event Type and Need for Cognition. JOURNAL OF BUSINESS ECONOMICS 2011, 60–67. [Google Scholar]
- Dowling, G.R.; Staelin, R. A Model of Perceived Risk and Intended Risk-Handling Activity. j CONSUM RES 1994, 21, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WANG, J.; GAO, Z. Research on online fresh food purchase intention based on individual behavior characteristics of consumers - the mediating role of perceived risk and the moderating role of individual innovation. Guizhou Social Sciences 2020, 119–127. [Google Scholar]
- BI, J. An Empirical Study on Internet Word of Mouth Affecting Consumer Purchase Intention. JOURNAL OF INTELLIGENCE 2009, 28, 46–51. [Google Scholar]
- XIANG, H.; GUO, Z. An Empirical Study of Financial Literacy's Impact on Online Lending Consumption Behavior: Based on the Mediating Role of Perceived Risk. CONSUMER ECONOMICS 2019, 35, 62–70. [Google Scholar]
- LIU, H.; YANG, L. The impact of the Leniency of Return Policy on Consumers' Purchasing Intentions in Online Shopping: An Analysis of Moderated Dual-mediator or Effects Based on the SOR Model. WEST FORUM 2024, 34, 111–124. [Google Scholar]
- HUANG, Y.; ZHANG, X.; ZHAO, M. Healthy Driving Mechanism of Grain Consumption Behavior-A Micro Survey from Buckwheat Top Eight Provinces. World Agriculture 2022, 57–69. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Weng, N.; Liu, W. Research on the Willingness to Buy Camellia Oil of Consumer --Based on Survey Data of Consumer in Fujian Province. forestry ECONOMICS 2015, 37, 68–72. [Google Scholar]
- Bentler, P.M.; Chou, C.-P. Practical Issues in Structural Modeling. Sociological Methods & Research 1987, 16, 78–117. [Google Scholar]
- GAO, J.; MA, Y.; WU, B.; KANG, X. A RESEARCH ON TOURISM MOTIVATION AND THE DIFFERENCES OF DOMESTIC AND FOREIGN TOURISTS--A Case Study of Xi' an. HUMAN GEOGRAPHY 2011, 26, 132–139. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y. Female consumer market expansion based on experiential marketing. marketing Management 2019, 63–66. [Google Scholar]
- LUO, F.; SHANG, W. Pre-Made Meal Products Information Defects Lead to Product Crisis and Consumer Mental Injury. ECONOMY AND MANAGEMENT 2023, 37, 67–75. [Google Scholar]
- JIANG, X.; SHEN, Z.; ZHANG, N.; LIAO, H.; XU, H. Reliability and validity analysis of the questionnaire. Modern Preventive Medicine 2010, 37, 429. [Google Scholar]
- Fornell, C.; Larcker, D.F. Evaluating Structural Equation Models with Unobservable Variables and Measurement Error. JOURNAL OF MARKETING RESEARCH 1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henseler, J.; Ringle, C.M.; Sarstedt, M. A New Criterion for Assessing Discriminant Validity in Variance-Based Structural Equation Modeling. j. of the Acad. Mark. Sci. 2015, 43, 115–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Lynch, J.; Chen, Q. Reconsidering Baron and Kenny: Myths and Truths about Mediation Analysis. Journal of Consumer Research 2010, 37, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M.; Tang, D.; Xu, A. Zheng, M.; Tang, D.; Xu, A. Attribute-Driven or Green-Driven: The Impact of Subjective and Objective Knowledge on continuous Tea Consumption. Foods 2023, 12, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, M.H.; Nguyen, P.M. Integrating the Theory of Planned Behavior and the Norm Activation Model to Investigate Organic Food Purchase Intention. Evidence from Vietnam. Sustainability 2022, 14, 816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GUO, J.; WU, X.; YE, W. The Empirical Research on Chinese Consumer Purchase Intent of Genetically Modified Food --Based on the Perspectives of Product Knowledge, Perceived Benefits, Risk Reduction Strategies and Perceived Risk. techno economics & Management Research.
- Yuan, X.; Xiao, Y. Yuan, X.; Xiao, Y. Cognition, Value Perception and Purchase Intention of Organic Food-Evidence from China's Organic Milk Market. Market. Sustainability 2021, 13, 910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhou, Y.; He, G.; Chen, Z. Li M.; Zhou Y.; He G.; Chen Z. Analyzing the differences in awareness of food safety between urban and rural residents in Foshan. Management 2011, 28, 544–547. [Google Scholar]
- CHENG, Y.; YIN, J. Has COVID-19 Increased the Intention to Undertake Health Tourism? Examination Using a Conditional Process Model. tourism Tribune 2022, . 37, 119–132. [Google Scholar]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).