Submitted:
11 July 2024
Posted:
15 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- Does the introduction of TSRs and the STS design method improve quality of the system design?
- Does the proposed methodology produce designs that are useful?
2. Related Work
3. TSR Definition
4. Proposed STS Design Method
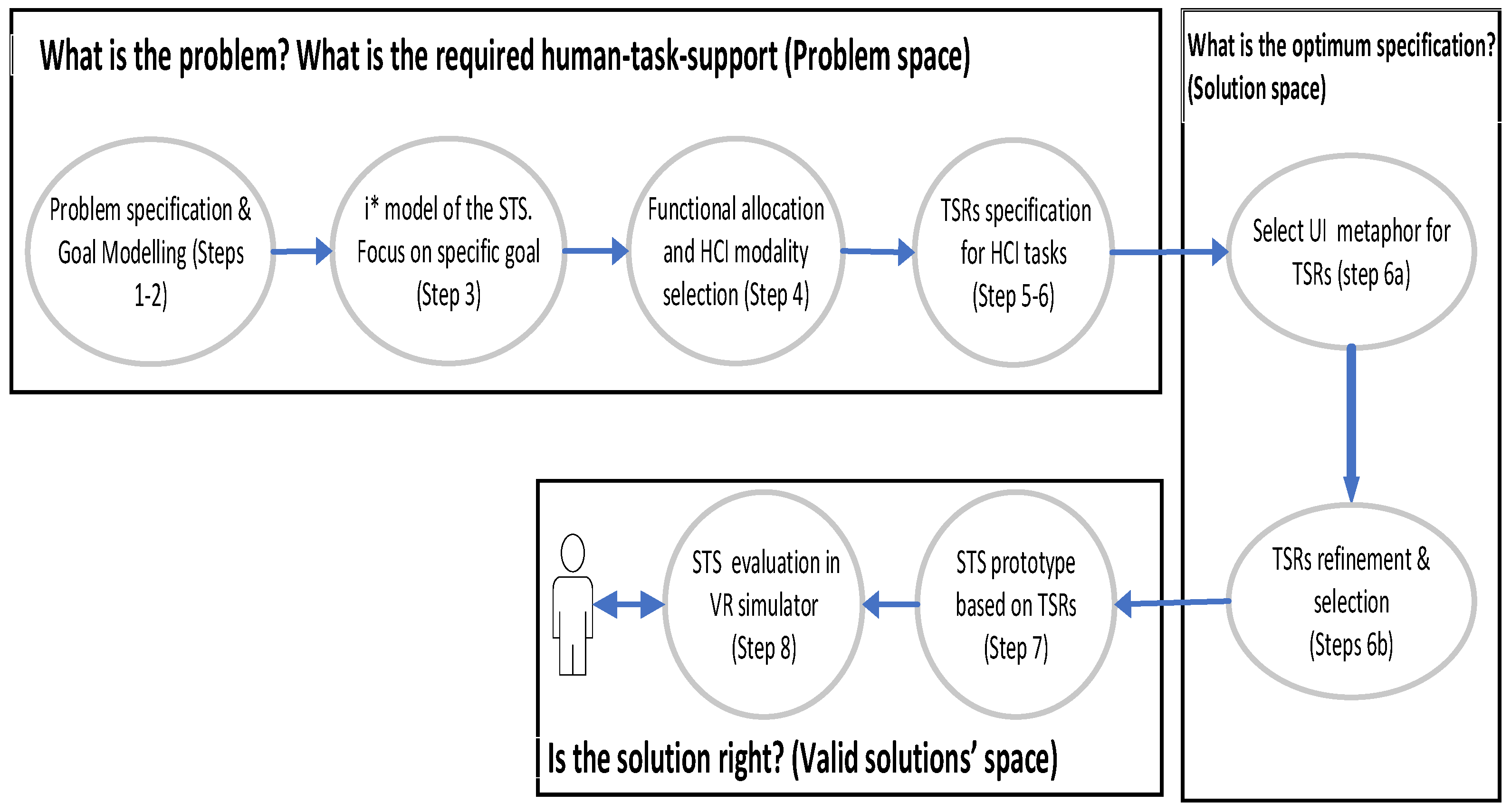
- Analysis of the problem domain and the main human factors issues that need to be considered during STS design.
- Decomposition of the problem into sub problems until goals become apparent and can be realised through technology. This goal hierarchy analysis is performed using the GORE method [68]. Goals are statements of the intentions and desired outcomes of a system that have different levels of abstraction. During this step goals are refined into sub-goals up until the human factors issues become apparent.
- Next is i* modelling focusing on a sub-problem from the goal-hierarchy of step 2. The key human factors that need to be satisfied are specified as NFR (soft-goals) realised through functional requirements. The i* framework is a goal-oriented requirement engineering technique that models relationships between different actors in the STS and is used in the early phase of system modelling [32]. Soft-goals in i* are satisfied when their subgoals are satisfied. Tasks refer to activities performed by human or machine agents in the STS. The i*diagram elaborates on the tasks, goals, soft-goals and resources required for the selected sub-problem.
- Functional allocation (FA) analysis of the selected goal from the i* diagram, to identify the best automation scheme. The selected FA scheme is refined into different human-machine interaction options. Different human factors evaluation criteria are used (i.e., situation awareness, reliability) to analyse the effect of each HCI modality on human performance. To visualise the influence of each evaluation criterion we chose the Questions, Options, and Criteria (QOC) notation [91], since it is expressive and deals directly with evaluation of system features [92]. Questions in QOC represent key issues (goals in i*), “Options” are alternative functional allocation solutions/modality responding to a question, while “Criteria” represent the desirable properties of the system that it must satisfy, for instance, cost of development, safety, or HF criteria. The output from this step is the best functional allocation scheme for the task.
- The next step focuses on its decomposition into low level tasks (sub-tasks) that need to be performed either by IT or human to satisfy the goal associated with it in i*.
- Identify the best level of automation for each of the tasks from previous step. For tasks that are either not fully manual or can not be fully automated (HCI tasks) specify the required functionality that the technology should have to support the human agent to perform his/her task without failing (TSRs).
- 6a.
- This step uses design space exploration to identify candidate user interface (UI) metaphors (representing familiar analogies e.g., radar analogy). Design rationale is used to explain the reasons behind the decisions made. Options are alternative design solutions. Criteria represent the desirable properties (NFR /Softgoals) of the technology and the requirements that it must satisfy. The links between options and criteria make trade-offs explicit and turn the focus on to the purpose of the design.
- 6b.
- The selected UI metaphors from step 6a are used to refine the TSRs identified at step 6. TSRs are then evaluated against a set of non-functional requirements (criteria) and the best TSRs are selected to form the specification of the candidate designs that will be prototyped.
- 7.
- Implement VR prototypes of each candidate design and specify VR scenarios and NFR metrics.
- 8.
- Evaluate STS prototypes experimentally with users in VR settings. Evaluation criteria (defined as human NFR) are assessed explicitly during the experiments using different metrics (e.g., electroencephalography-EEG, Eye tracking’s Eye fixations, Heart Rate, Respiration etc). If the performance of the design is not satisfactory (evaluation metrics not satisfactory) the TSRs are refined, and the process is repeated.
5. Detailed Application of the Proposed Method
6. Empirical Evaluation of the Proposed Method
7. Threats to Validity
8. Lessons Learned
9. Discussion
10. Conclusions
Appendix A. Evaluation Criteria during Empirical Evaluation
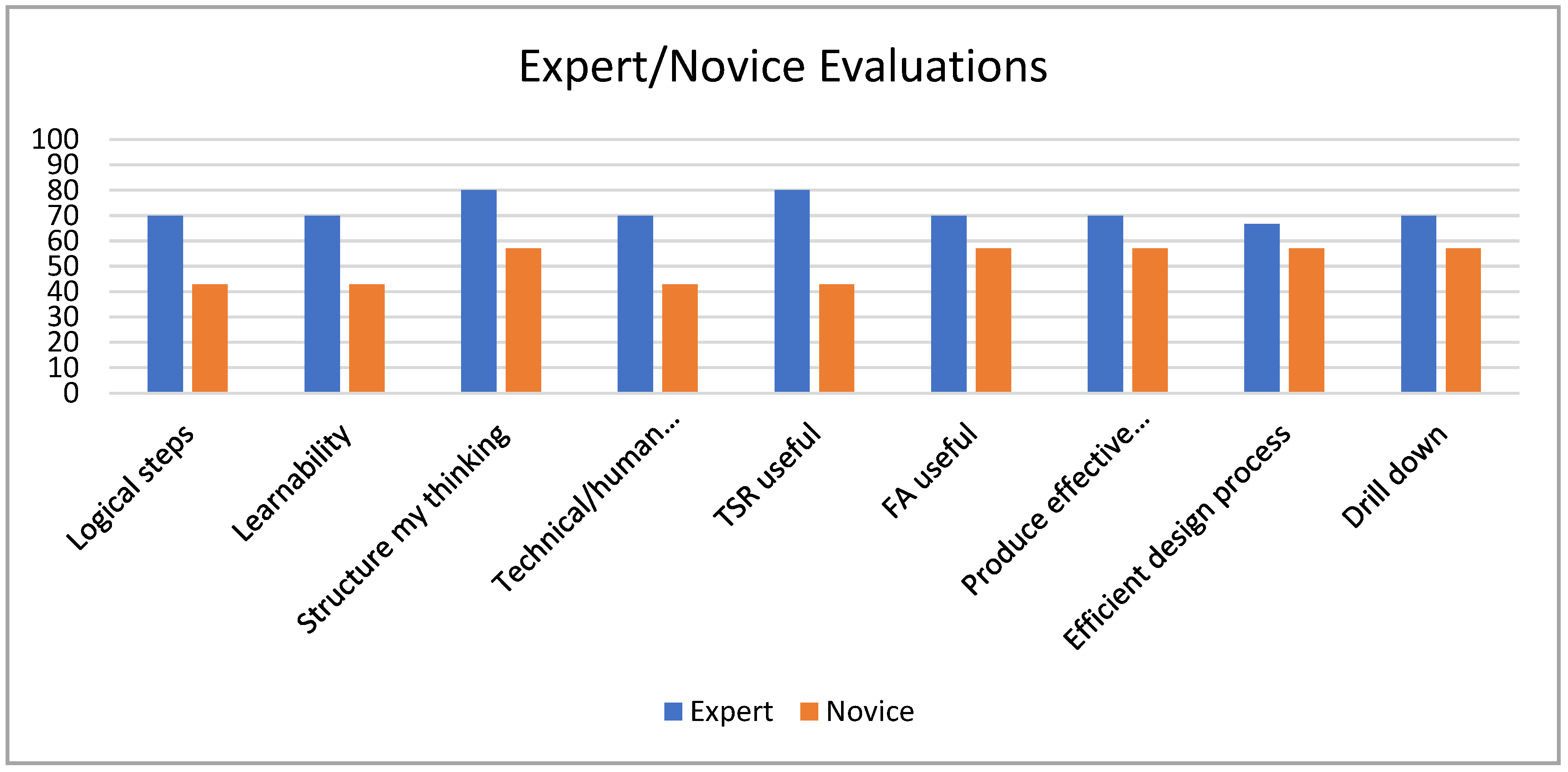
| Evaluation criteria | COVID19 -Method’s Evaluation Questions | Scale |
|---|---|---|
| Logical steps | How easy was the method to follow (logic and structure)? | [1 very hard – 5 very easy] |
| Learnability | How easy was the method to learn? (learnability) | [1 very hard – 5 very easy] |
| Structure my thinking | The method framed my thinking by providing me with a record of my previous design decisions | [1 absolutely disagree – 5 absolutely agree] |
| Technical /human aspects | The method helped me to address both the technical and the human factors part of sociotechnical systems | [1 absolutely disagree – 5 absolutely agree] |
| TSR useful | Task Support Requirements are useful for identifying human factors issues during sociotechnical systems design | [1 absolutely disagree – 5 absolutely agree] |
| Functional Allocation useful | Functional allocation analysis helped me to identify the best level of automation for the new system based on selected system-qualities | [1 absolutely disagree – 5 absolutely agree] |
| Produce effective design | The method helped me to produce an effective system design that solves or contributes towards the solution of a specific aspect of the COVID19 problem | [1 absolutely disagree – 5 absolutely agree] |
| Efficient design process | The method helped me to produce a design of the system in an efficient manner (guided me towards a solution) | [1 absolutely disagree – 5 absolutely agree] |
| Drill down | The method enabled me to view the problem at high level and then drill down into specific functional requirements of a new system that will address the problem | [1 absolutely disagree – 5 absolutely agree] |
Appendix B. Design Exploration Phase of the Method in the Automotive Vehicles-Safety Domain
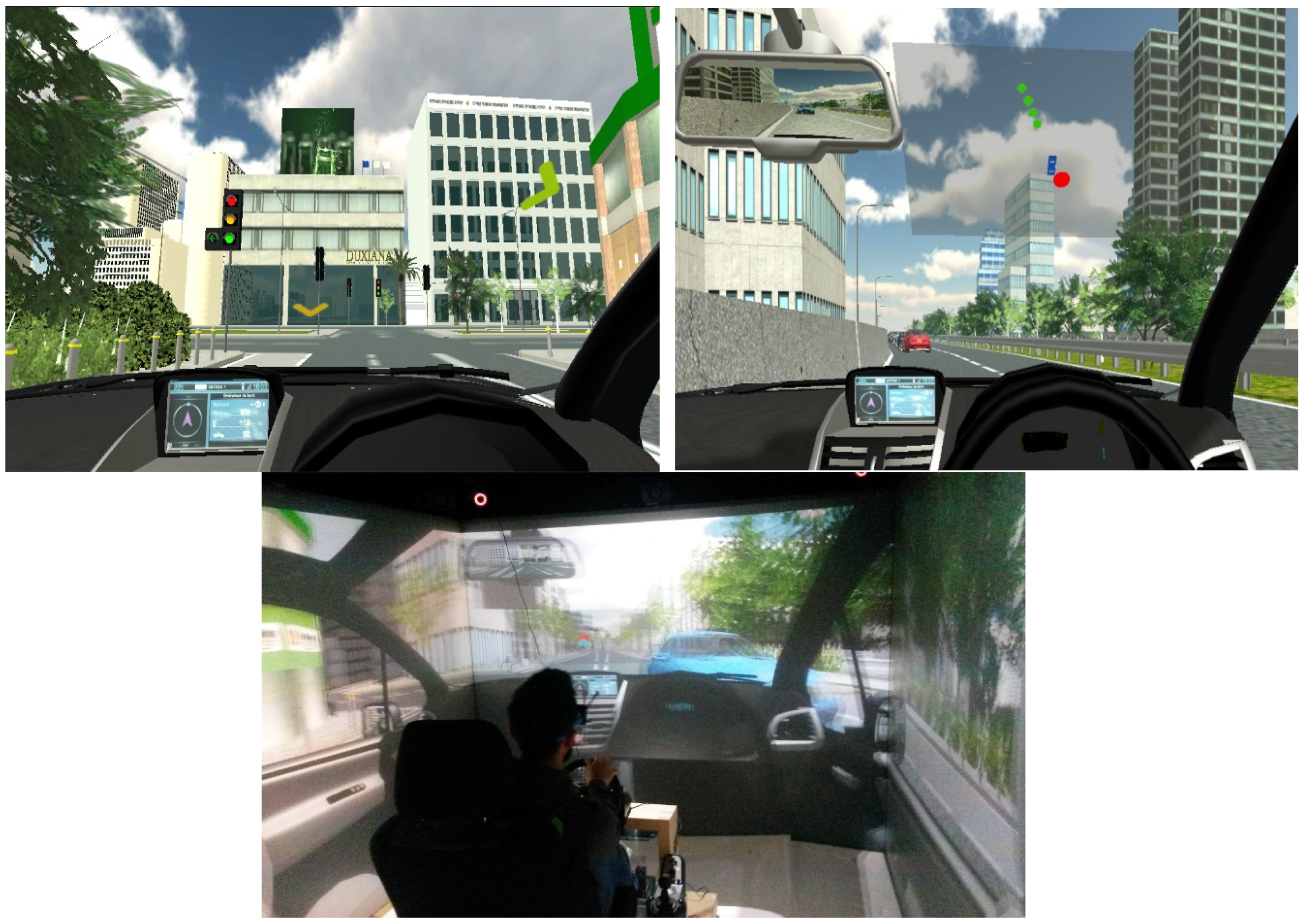
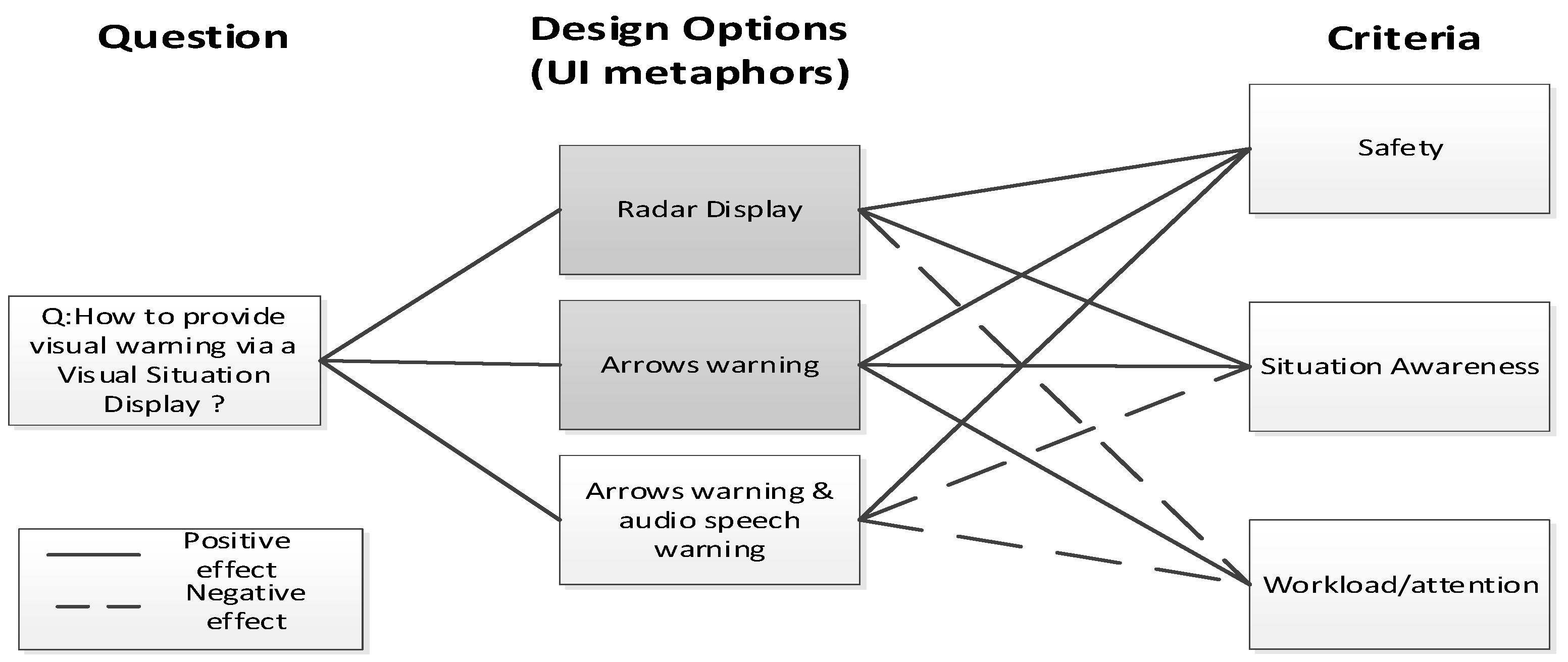

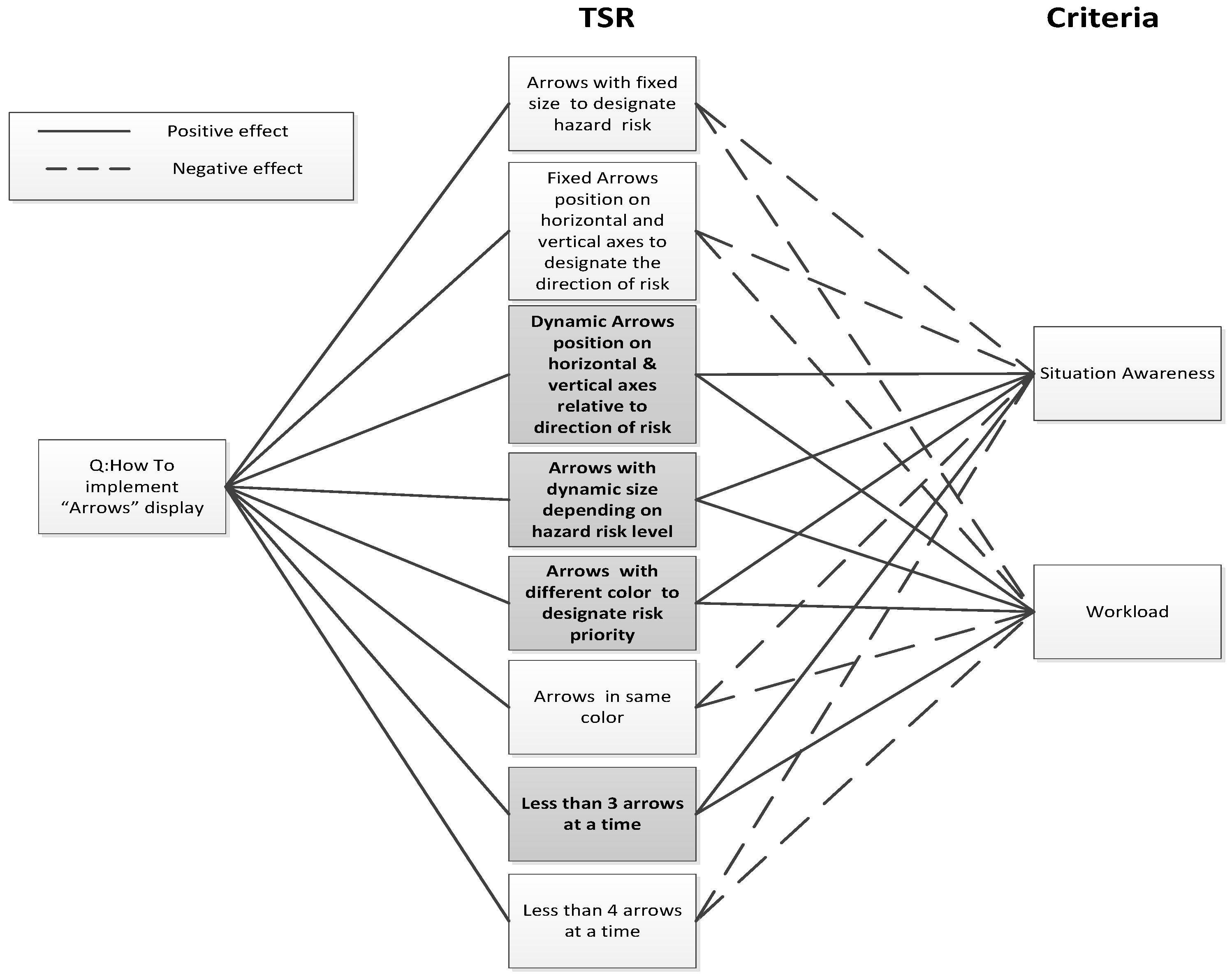
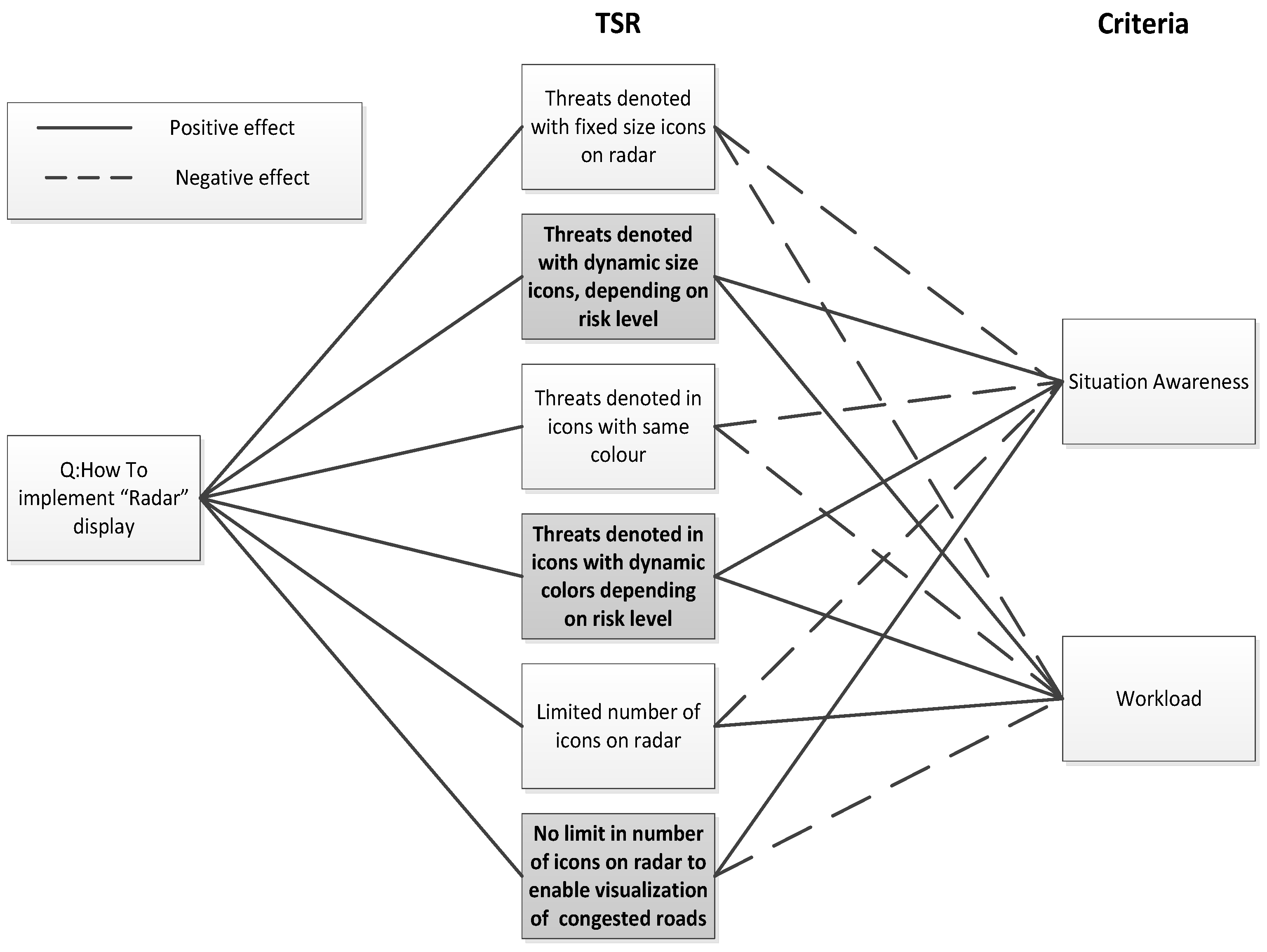
References
- E. L. Trist and K. W. Bamforth, “Some Social and Psychological Consequences of the Longwall Method of Coal-Getting: An Examination of the Psychological Situation and Defences of a Work Group in Relation to the Social Structure and Technological Content of the Work System,” Hum. Relations, vol. 4, no. 1, pp. 3–38, 1951.
- C. W. Clegg, “Sociotechnical principles for system design,” Appl. Ergon., no. 31, pp. 463–477, 2000.
- A. Lee, “Editor’s comments: MIS quarterly’s editorial policies and practices,” MIS Q., 2001.
- H. P. N. Hughes, C. W. Clegg, L. E. Bolton, and L. C. Machon, “Systems scenarios: a tool for facilitating the socio-technical design of work systems,” Ergonomics, vol. 60, no. 10, pp. 1319–1335, 2017.
- S. Schneider, J. Wollersheim, H. Krcmar, and A. Sunyaev, “Erratum to: How do requirements evolve over time? A case study investigating the role of context and experiences in the evolution of enterprise software requirements,” J. Inf. Technol., vol. 33, no. 2, p. 171, Jun. 2018.
- H. N. N. Mohd and S. Shamsul, “Critical success factors for software projects: A comparative study,” Sci. Res. Essays, vol. 6, no. 10, pp. 2174–2186, May 2011.
- G. J. M. Read, P. M. Salmon, M. G. Lenné, and N. A. Stanton, “Designing sociotechnical systems with cognitive work analysis: putting theory back into practice,” Ergonomics, 2015.
- R. Challenger, C. W. Clegg, and C. Shepherd, “Function allocation in complex systems: reframing an old problem,” Ergonomics, vol. 56, no. 7, pp. 1051–1069, Jul. 2013.
- G. J. Hay, F. E. Klonek, and S. K. Parker, “Diagnosing rare diseases: A sociotechnical approach to the design of complex work systems,” Appl. Ergon., vol. 86, p. 103095, Jul. 2020.
- O. F. Hamim, M. Shamsul Hoque, R. C. McIlroy, K. L. Plant, and N. A. Stanton, “A sociotechnical approach to accident analysis in a low-income setting: Using Accimaps to guide road safety recommendations in Bangladesh,” Saf. Sci., vol. 124, p. 104589, Apr. 2020.
- L. de Vries and L.-O. Bligård, “Visualising safety: The potential for using sociotechnical systems models in prospective safety assessment and design,” Saf. Sci., vol. 111, pp. 80–93, Jan. 2019.
- D. P. Jenkins, N. A. Stanton, P. M. Salmon, G. H. Walker, and M. S. Young, “Using cognitive work analysis to explore activity allocation within military domains,” Ergonomics, vol. 51, no. 6, pp. 798–815, Jun. 2008.
- N. P. Patorniti, N. J. Stevens, and P. M. Salmon, “A systems approach to city design: Exploring the compatibility of sociotechnical systems,” Habitat Int., vol. 66, pp. 42–48, Aug. 2017.
- T. Carden, N. Goode, G. J. M. Read, and P. M. Salmon, “Sociotechnical systems as a framework for regulatory system design and evaluation: Using Work Domain Analysis to examine a new regulatory system,” Appl. Ergon., vol. 80, pp. 272–280, Oct. 2019.
- E. E. Makarius, D. Mukherjee, J. D. Fox, and A. K. Fox, “Rising with the machines: A sociotechnical framework for bringing artificial intelligence into the organization,” J. Bus. Res., vol. 120, pp. 262–273, Nov. 2020.
- D. A. Norman and P. J. Stappers, “DesignX: Complex Sociotechnical Systems,” She Ji, 2015.
- Ö. Kafali, N. Ajmeri, and M. P. Singh, “Normative requirements in sociotechnical systems,” in Proceedings - 2016 IEEE 24th International Requirements Engineering Conference Workshops, REW 2016, 2017.
- S. Dey and S. W. Lee, “REASSURE: Requirements elicitation for adaptive socio-technical systems using repertory grid,” Inf. Softw. Technol., 2017.
- E. Hollnagel, FRAM: The Functional Resonance Analysis Method. CRC Press, 2017.
- G. Baxter and I. Sommerville, “Interacting with Computers Socio-technical systems: From design methods to systems engineering,” Interact. Comput., vol. 23, no. 1, pp. 4–17, 2011.
- L. J. Hettinger, A. Kirlik, Y. M. Goh, and P. Buckle, “Modelling and simulation of complex sociotechnical systems: envisioning and analysing work environments,” Ergonomics, 2015.
- G. J. M. Read, P. M. Salmon, N. Goode, and M. G. Lenné, “A sociotechnical design toolkit for bridging the gap between systems-based analyses and system design,” Hum. Factors Ergon. Manuf., 2018.
- H. Wache and B. Dinter, “The Digital Twin – Birth of an Integrated System in the Digital Age,” in Proceedings of the 53rd Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, 2020.
- G. J. M. Read, P. M. Salmon, and M. G. Lenné, “When paradigms collide at the road rail interface: evaluation of a sociotechnical systems theory design toolkit for cognitive work analysis,” Ergonomics, vol. 59, no. 9, pp. 1135–1157, Sep. 2016.
- A. Sutcliffe, B. Gault, and N. Maiden, “ISRE: immersive scenario-based requirements engineering with virtual prototypes,” Requir. Eng., vol. 10, no. 2, pp. 95–111, May 2005.
- A. Gregoriades and A. Sutcliffe, “A socio-technical approach to business process simulation,” Decis. Support Syst., 2008.
- A. Gregoriades and A. Sutcliffe, “Scenario-based assessment of nonfunctional requirements,” IEEE Trans. Softw. Eng., 2005.
- A. Sutcliffe, W. C. Chang, and R. Neville, “Evolutionary requirements analysis,” in Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Requirements Engineering, 2003.
- J. Wolfartsberger, “Analyzing the potential of Virtual Reality for engineering design review,” Autom. Constr., vol. 104, pp. 27–37, Aug. 2019.
- R. K. Radha, “Flexible smart home design: Case study to design future smart home prototypes,” Ain Shams Eng. J., 2021.
- F. Dalpiaz, P. Giorgini, and J. Mylopoulos, “Adaptive socio-technical systems: a requirements-based approach,” Requir. Eng., vol. 18, no. 1, pp. 1–24, Mar. 2013.
- E. S. K. Yu and J. Mylopoulos, “From E-R To ‘a-R’ — Modelling Strategic Actor Relationships for Business Process Reengineering,” Int. J. Coop. Inf. Syst., vol. 04, no. 02n03, pp. 125–144, 1995.
- S. Liaskos, S. M. Khan, M. Soutchanski, and J. Mylopoulos, “Modeling and reasoning with decision-theoretic goals,” in Lecture Notes in Computer Science (including subseries Lecture Notes in Artificial Intelligence and Lecture Notes in Bioinformatics), 2013.
- E. Hollnagel and D. D. Woods, Joint Cognitive Systems: Foundations of Cognitive Systems Engineering. Taylor & Francis, 2005.
- D. Woods and E. Hollnagel, Joint cognitive systems: Patterns in cognitive systems engineering. CRC/Taylor & Francis, 2006.
- K. J. Vicente, Cognitive Work Analysis: Toward Safe, Productive, and Healthy Computer-Based Work. CRC Press, 1999.
- E. Mumford, Designing Human Systems for New Technology: The ETHICS Method. Manchester Business School, 1983.
- E. Mumford, “The story of socio-technical design: reflections on its successes, failures and potential,” Inf. Syst. J., vol. 16, no. 4, pp. 317–342, Oct. 2006.
- E. Mumford, S. Hickey, and H. Matthies, Designing Human Systems. LULU, 2006.
- E. Mumford, “The ETHICS Approach,” Commun. ACM, vol. 36, no. 4, pp. 82--83, Jun. 1993.
- D. Aveson and G. Fitzgerald, “Methodologies for Developing Information Systems: A Historical Perspective,” in The Past and Future of Information Systems: 1976--2006 and Beyond, 2006, pp. 27–38.
- P. Adman and L. Warren, “Participatory sociotechnical design of organizations and information systems – an adaptation of ETHICS methodology,” J. Inf. Technol., vol. 15, pp. 39–51, 2000.
- S. Hickey, H. Matthies, and E. Mumford, Designing human systems: An Agile Approach to ETHICS. 2006.
- P. Abrahamsson, O. Salo, J. Ronkainen, and J. Warsta, Agile software development methods: rewiew and analysis. Oulou, Finland: VTT Technical Reaserch Centre of Finland, 2002.
- P. Checkland, Systems Thinking, Systems Practice. Chichester, UK: John Wiley and Sons, 1981.
- P. Checkland and J. Scholes, Soft Systems Methodology in Action. Wiley, 1991.
- J. Rasmussen, A. M. Pejtersen, and L. P. Goodstein, Cognitive Systems Engineering, 1st ed. New York, NY, USA: Wiley-Interscience, 1994.
- International Standard Organisation, “Ergonomics of Human-System Interaction - Part 210: Human-centered Design for Interective Systems,” Geneva, Switzerland, 2010.
- D. A. Norman, “Human-centered design considered harmful,” interactions, vol. 12, no. 4, p. 14, Jul. 2005.
- E. Hollnagel, Human reliability analysis: context and control. 1993.
- J. Reason, Human Error. Cambridge University Press, 1990.
- E. Hollnagel and A. Bye, “Principles for modelling function allocation,” Int. J. Hum. Comput. Stud., vol. 52, no. 2, pp. 253–265, 2000.
- J. Sharit, “Allocation of functions,” in Handbook of Human Factors and Ergonomics, G. Salvendy, Ed. New York: Wiley., 1998.
- P. M. Fitts, Human engineering for an effective air navigation and traffic control system. Washington, DC: National Research Council, 1951.
- C. Clegg, “Appropriate technology for humans and organizations,” J. Inf. Technol., vol. 3, no. 3, pp. 133–146, 1988.
- M. Vagia, A. A. Transeth, and S. A. Fjerdingen, “A literature review on the levels of automation during the years. What are the different taxonomies that have been proposed?,” Applied Ergonomics. 2016.
- J. D. Lee and B. D. Seppelt, “Human Factors and Ergonomics in Automation Design,” in Handbook of Human Factors and Ergonomics: Fourth Edition, 2012.
- J. C. F. de Winter and D. Dodou, “Why the Fitts list has persisted throughout the history of function allocation,” Cogn. Technol. Work, vol. 16, no. 1, pp. 1–11, Feb. 2014.
- A. Saeed, R. de Lemos, and T. Anderson, “On the safety analysis of requirements specifications for safety-critical software,” ISA Trans., vol. 34, no. 3, pp. 283–295, 1995.
- A. Simpson and J. Stoker, “Will it be Safe? --- An Approach to Engineering Safety Requirements,” in Components of System Safety, 2002, pp. 140–164.
- V. Ratan, K. Partridge, J. Reese, and N. Leveson, “Safety analysis tools for requirements specifications,” Proc. 11th Annu. Conf. Comput. Assur. COMPASS ’96, pp. 149–160, 1996.
- A. G. Sutcliffe and N. A. M. Maiden, “Bridging the requirements gap: policies, goals and domains,” in Proceedings of 1993 IEEE 7th International Workshop on Software Specification and Design, 1993, pp. 52–55.
- S. Lauesen and M. A. Kuhail, “Task descriptions versus use cases,” Requir. Eng., vol. 17, no. 1, pp. 3–18, 2012.
- S. Lauesen, “Task Descriptions as Functional Requirements,” IEEE Softw., vol. 20, no. 2, pp. 58–65, Mar. 2003.
- S. Lauesen, “Problem-Oriented Requirements in Practice -- A Case Study,” in Requirements Engineering: Foundation for Software Quality, 2018, pp. 3–19.
- K. Beckers, S. Faßbender, M. Heisel, and F. Paci, “Combining Goal-Oriented and Problem-Oriented Requirements Engineering Methods,” in Availability, Reliability, and Security in Information Systems and HCI, 2013, pp. 178–194.
- L. Chung, B. A. Nixon, E. Yu, and J. Mylopoulos, Non-Functional Requirements in Software Engineering. Boston, MA: Springer US, 2000.
- L. Chung, B. A. Nixon, E. Yu, and J. Mylopoulos, “Softgoal Interdependency Graphs,” in Non-Functional Requirements in Software Engineering, Boston, MA: Springer US, 2000, pp. 47–88.
- T. Marew, J.-S. Lee, and D.-H. Bae, “Tactics based approach for integrating non-functional requirements in object-oriented analysis and design,” J. Syst. Softw., vol. 82, no. 10, pp. 1642–1656, Oct. 2009.
- J. De Winter, P. Van Leeuwen, and R. Happee, “Advantages and disadvantages of driving simulators: a discussion,” in Measuring Behavior, 2012, pp. 47–50.
- R. Stone, “Virtual reality for interactive training: an industrial practitioner’s viewpoint,” Int. J. Hum. Comput. Stud., vol. 55, no. 4, pp. 699–711, 2001.
- F. Weidner, A. Hoesch, S. Poeschl, and W. Broll, “Comparing VR and non-VR driving simulations: An experimental user study,” Proc. - IEEE Virtual Real., pp. 281–282, 2017.
- S. W. A. Dekker, Ten questions about human error: a new view of human factors and system safety. Lawrence Erlbaum, 2005.
- A. Maclean, R. M. Young, V. M. E. Bellotti, and T. P. Moran, “Questions, Options and Criteria: Elements of Design Space Analysis,” Human-Computer Interact., vol. 6, no. 3/4, p. 208, 1991.
- A. Gregoriades and A. Sutcliffe, “Simulation-based evaluation of an in-vehicle smart situation awareness enhancement system,” Ergonomics, vol. 61, no. 7, pp. 947–965, 2018.
- R. Looije, M. A. Neerincx, and K. V. Hindriks, “Specifying and testing the design rationale of social robots for behavior change in children,” Cogn. Syst. Res., vol. 43, pp. 250–265, 2017.
- J. M. Bindewald, M. E. Miller, and G. L. Peterson, “A function-to-task process model for adaptive automation system,” J. Hum. Comput. Stud., vol. 72, no. 12, pp. 822–834, 2014.
- P. Milgram, A. Rastogi, and J. J. Grodski, “Telerobotic control using augmented reality,” in Proceedings 4th IEEE International Workshop on Robot and Human Communication, 1995, pp. 21–29.
- M.. Endsley and D.. Kaber, “Level of automation effects on performance, situation awareness and workload in a dynamic control task,” Ergonomics, vol. 42, no. 3, pp. 462–492, 1999.
- M. Endsley and E. O. Kiris, “The out-of-the-loop performance problem and level of control in automation,” Hum. Factors, vol. 37, no. 2, pp. 381–394, 1995.
- R. Parasuraman, T. B. Sheridan, and C. D. Wickens, “A model for types and levels of human interaction with automation,” IEEE Trans. Syst. Man, Cybern. Part ASystems Humans., vol. 30, no. 3, pp. 286–297, 2000.
- V. Riley, “A general model of mixed-initiative human-machine systems,” in 33rd Annual Human Factors Society Conference, 1989, pp. 124–128.
- Sheridan T.B., “Function allocation: algorithm, alchemy or apostasy?,” Int. J. Hum. Comput. Stud., vol. 52, pp. 203–216, 2000.
- B. H. Vrkljan and J. Miller-Polgar, “Advancements in vehicular technology: potential implications for the older driver,” Int. J. Veh. Inf. Commun. Syst., vol. 1, no. 1–2, 2005.
- I. J. Reagan, J. B. Cicchino, L. B. Kerfoot, and R. A. Weast, “Crash avoidance and driver assistance technologies – Are they used?,” Transp. Res. Part F Traffic Psychol. Behav., vol. 52, pp. 176–190, 2018.
- P. Green, “Driver Interface Safety and Usability Standards: An Overview,” in Driver Distraction: Theory, Effects, andMitigation, CRC Press, 2009.
- Mica, R. Endsley, “Situation Awareness,” in Handbook of Human Factors and Ergonomics: Fourth Edition, G. Salvendy, Ed. Hoboken, New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2012, pp. 553–568.
- J. A. Michon, “A critical review of driver models: What do we know, what should we do?,” in Human Behavior and Traffic Safety, 1985.
- M. L. Matthews, D. J. Bryant, R. D. G. Webb, and J. L. Harbluk, “Model for Situation Awareness and Driving: Application to Analysis and Research for Intelligent Transportation Systems,” Transp. Res. Rec. J. Transp. Res. Board, vol. 1779, no. 1, pp. 26–32, Jan. 2001.
- N. J. Ward, “Automation of task processes: An example of intelligent transportation systems,” Hum. Factors Ergon. Manuf., vol. 10, no. 4, pp. 395–408, 2000.
- S. T. Iqbal and E. Horvitz, “Notifications and awareness,” in ACM conference on Computer supported cooperative work - CSCW ’10, 2010, no. May 2014, p. 27.
- S. J. J. Gould, D. P. Brumby, A. L. Cox, V. M. González, D. D. Salvucci, and N. A. Taatgen, “Multitasking and interruptions: a SIG on bridging the gap between research on the micro and macro worlds,” Chi 2012, 2012.
- B. Sheehan, F. Murphy, M. Mullins, and C. Ryan, “Connected and autonomous vehicles: A cyber-risk classification framework,” Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract., vol. 124, pp. 523–536, Jun. 2019.
- A. Papadoulis, M. Quddus, and M. Imprialou, “Evaluating the safety impact of connected and autonomous vehicles on motorways,” Accid. Anal. Prev., vol. 124, pp. 12–22, 2019.
- H. Xing, H. Qin, and J. W. Niu, “Driver’s Information Needs in Automated Driving,” in International Conference on Cross-Cultural Design, 2017.
- J. G. Miller, “Living systems: Basic concepts,” Behav. Sci., vol. 10, no. 3, pp. 193–237, 1965.
- C. Owsley, K. Ball, M. E. Sloane, D. L. Roenker, and J. R. Bruni, “Visual/cognitive correlates of vehicle accidents in older drivers.,” Psychol. Aging, vol. 6, no. 3, pp. 403–415, 1991.
- F. Schwarz and W. Fastenmeier, “Augmented reality warnings in vehicles: Effects of modality and specificity on effectiveness,” Accid. Anal. Prev., vol. 101, pp. 55–66, 2017.
- G. A. Alvarez and P. Cavanagh, “The Capacity of Visual Short-Term Memory Is Set Both by Visual Information Load and by Number of Objects,” Psychol. Sci., vol. 15, no. 2, pp. 106–111, 2004.
- K. Pammer, A. Raineri, V. Beanland, J. Bell, and M. Borzycki, “Expert drivers are better than non-expert drivers at rejecting unimportant information in static driving scenes,” Transp. Res. Part F Traffic Psychol. Behav., vol. 59, pp. 389–400, Nov. 2018.
- J. Gebauer, M. Shaw, and M. Gribbins, “Task-technology fit for mobile information systems,” JIT, vol. 25, no. 3, pp. 259–272, 2010.
- S. W. A. Dekker and E. Hollnagel, “Human factors and folk models,” Cogn. Technol. Work, vol. 6, pp. 79–86, 2004.
- S. W. A. Dekker and D. D. Woods, “MABA-MABA or Abracadabra? Progress on Human-Automation Co-ordination,” Cogn. Technol. Work, vol. 4, no. 4, pp. 240–244, 2002.
- D. A. Leonard and J. F. Rayport, “Managing Knowledge Assets, Creativity and Innovation,” Harv. Bus. Rev., vol. 75, no. 6, pp. 102–113, 1997.
- H. Beyer and K. Holtzblatt, “Contextual Design,” Interactions, vol. 6, no. 1, pp. 32–42, 1999.
- S. Bodker and C. N. Klokmose, “The human-artifact model: An activity theoretical approach to artifact ecologies,” Human-Computer Interact., vol. 26, no. 4, pp. 315–371, 2011.
- N. Naikar, R. Hopcroft, and A. Moylan, “Work domain analysis: Theoretical concepts and methodology,” Victoria, Australia, 2005.
- G. Praetorius, E. Hollnagel, and J. Dahlman, “Modelling Vessel Traffic Service to understand resilience in everyday operations,” Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf., vol. 141, pp. 10–21, Sep. 2015.
- T. A. Saurin and N. J. B. Werle, “A framework for the analysis of slack in socio-technical systems,” Reliab. Eng. Syst. Saf., vol. 167, pp. 439–451, 2017.
- O. Bertelsen and S. Bødker, “Activity Theory,” in HCI models, theories, and frameworks: Toward a multidisciplinary science, MK, 2003, pp. 291–324.
- Erik Hollnagel, Cognitive Reliability and Error Analysis Method (CREAM). Elsevier, 1998.
- R. Bailey, Human Performance Engineering: Designing High Quality Professional User Interfaces for Computer Products, Applications and Systems, 3rd ed. Prentice Hall, 1996.
- S. Robertson and J. Robertson, “Mastering the Requirements Process Getting Requirements Right,” Work, 2013.
- E. S. K. Yu, “Modeling organizations for information systems requirements engineering,” in [1993] Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Requirements Engineering, 1993, pp. 34–41.
- A. G. Sutcliffe and A. Gregoriades, “Automating Scenario Analysis of Human and System Reliability,” IEEE Trans. Syst. Man, Cybern. - Part A Syst. Humans, vol. 37, no. 2, pp. 249–261, Mar. 2007.
- Z. Guo, D. Zhou, J. Chen, J. Geng, C. Lv, and S. Zeng, “Using virtual reality to support the product’s maintainability design: Immersive maintainability verification and evaluation system,” Comput. Ind., vol. 101, pp. 41–50, Oct. 2018.
- B. Aykent, Z. Yang, F. Merienne, and A. Kemeny, “Simulation sickness comparison between a limited field of view virtual reality head mounted display (Oculus) and a medium range field of view static ecological driving simulator (Eco2),” in Driving Simulation Conference Europe, 2014.
- C. D. Wickens, “Multiple resources and performance prediction,” Theor. Issues Ergon. Sci., vol. 3, no. 2, pp. 159–177, 2002.
- S. Kim and A. K. Dey, “Simulated augmented reality windshield display as a cognitive mapping aid for elder driver navigation,” in 27th international conference on Human factors in computing systems - CHI 09, 2009, pp. 133–142.
- G. Jakus, C. Dicke, and J. Sodnik, “A user study of auditory, head-up and multi-modal displays in vehicles,” Appl. Ergon., vol. 46, no. Part A, pp. 184–192, 2015.
- S. Fadden, P. M. Ververs, and C. D. Wickens, “Costs and Benefits of Head-Up Display Use: A Meta-Analytic Approach,” Proc. Hum. Factors Ergon. Soc. Annu. Meet., vol. 42, no. 1, pp. 16–20, 1998.
- L. C. Thomas and C. D. Wickens, “Eye-tracking and Individual Differences in off-Normal Event Detection when Flying with a Synthetic Vision System Display,” Proc. Hum. Factors Ergon. Soc. Annu. Meet., vol. 48, no. 1, pp. 223–227, 2004.
- L. Prinzel and M. Risser, “Head-Up Displays and Attention Capture,” 2004.
- C. D. Wickens and A. L. Alexander, “Attentional Tunneling and Task Management in Synthetic Vision Displays,” Int. J. Aviat. Psychol., vol. 19, no. 2, pp. 182–199, Mar. 2009.
- P. M. Ververs and C. D. Wickens, “Head-up displays: effects of clutter, display intensity, and display location on pilot performance.,” Int J Aviat Psychol, vol. 8, no. 4, pp. 377–403, 1998.
- W. J Horrey, A. Alexander, and C. Wickens, “The Effects of Head-Up Display Clutter and In-Vehicle Display Separation on Concurrent Driving Performance,” in Human Factors and Ergonomics Society 47th Annual Meeting, 2003, pp. 1880–1884.
- E. Crundall, D. R. Large, and G. Burnett, “A driving simulator study to explore the effects of text size on the visual demand of in-vehicle displays,” Displays, vol. 43, pp. 23–29, 2016.
- M. Yeh, J. L. Merlo, C. D. Wickens, and D. L. Brandenburg, “Head Up versus Head Down: The Costs of Imprecision, Unreliability, and Visual Clutter on Cue Effectiveness for Display Signaling,” Hum. Factors, vol. 45, no. 3, pp. 390–407, 2003.
- J. Fagerlönn, “Urgent alarms in trucks: effects on annoyance and subsequent driving performance,” IET Intell. Transp. Syst., vol. 5, no. 4, pp. 252–258, Dec. 2011.
- Y. Zhang, X. Yan, and Z. Yang, “Discrimination of Effects between Directional and Nondirectional Information of Auditory Warning on Driving Behavior,” Discret. Dyn. Nat. Soc., vol. 2015, pp. 1–8, 2015.
- L. M. Stanley, “Haptic and Auditory Interfaces as a Collision Avoidance Technique during Roadway Departures and Driver Perception of These Modalities,” 2006.
- NHTSA, “Analysis of Lane Change Crashes,” 2003.
- S. G. Klauer, T. a. Dingus, V. Neale, J. D. Sudweeks, and D. J. Ramsey, “The Impact of Driver Inattention On Near Crash/Crash Risk: An Analysis Using the 100-Car Naturalistic Driving Study Data,” 2006.
- C. Ware, Information Visualization: Perception for Design. Elsevier Science, 2013.
- M. Beggiato, M. Pereira, T. Petzoldt, and J. Krems, “Learning and development of trust, acceptance and the mental model of ACC. A longitudinal on-road study,” Transp. Res. Part F Psychol. Behav., vol. 35, pp. 75–84, 2015.
- A. J. May, T. Ross, and S. H. Bayer, “Driver’s information requirements when navigating in an urban environment,” J. Navig., vol. 56, no. 1, pp. 89–100, 2003.
- M. R. Endsley and D. G. Jones, Designing for situation awareness: an approach to human-centered design, Second. CRC Press, 2012.
- DENSO, “Technology to Keep People Safe Wherever They Drive,” 2016.
- F. Biocca, C. Owen, A. Tang, and C. Bohil, “Attention Issues in Spatial Information Systems: Directing Mobile Users’ Visual Attention Using Augmented Reality,” J. Manag. Inf. Syst., vol. 23, no. 4, pp. 163–184, May 2007.
- Mercedes-Benz, “Active Blind Spot Assist,” 2016.
- D. R. Large, E. Crundall, G. Burnett, C. Harvey, and P. Konstantopoulos, “Driving without wings: The effect of different digital mirror locations on the visual behaviour, performance and opinions of drivers,” Appl. Ergon., vol. 55, pp. 138–148, 2016.
- H. Cheng, Z. Liu, N. Zheng, and J. Yang, “Enhancing a Driver’s Situation Awareness using a Global View Map,” in Multimedia and Expo, 2007 IEEE International Conference on, 2007.
- H. J. Oh, S. M. Ko, and Y. G. Ji, “Effects of Superimposition of a Head-Up Display on Driving Performance and Glance Behavior in the Elderly,” Int. J. Hum. Comput. Interact., vol. 32, no. 2, pp. 143–154, Feb. 2016.
- H. E. Petersen and D. J. Dugas, “The Relative Importance of Contrast and Motion in Visual Detection,” 1972.
- Rodovan Miucic, Connected Vehicles: Intelligent transportation systems. Springer, 2019.
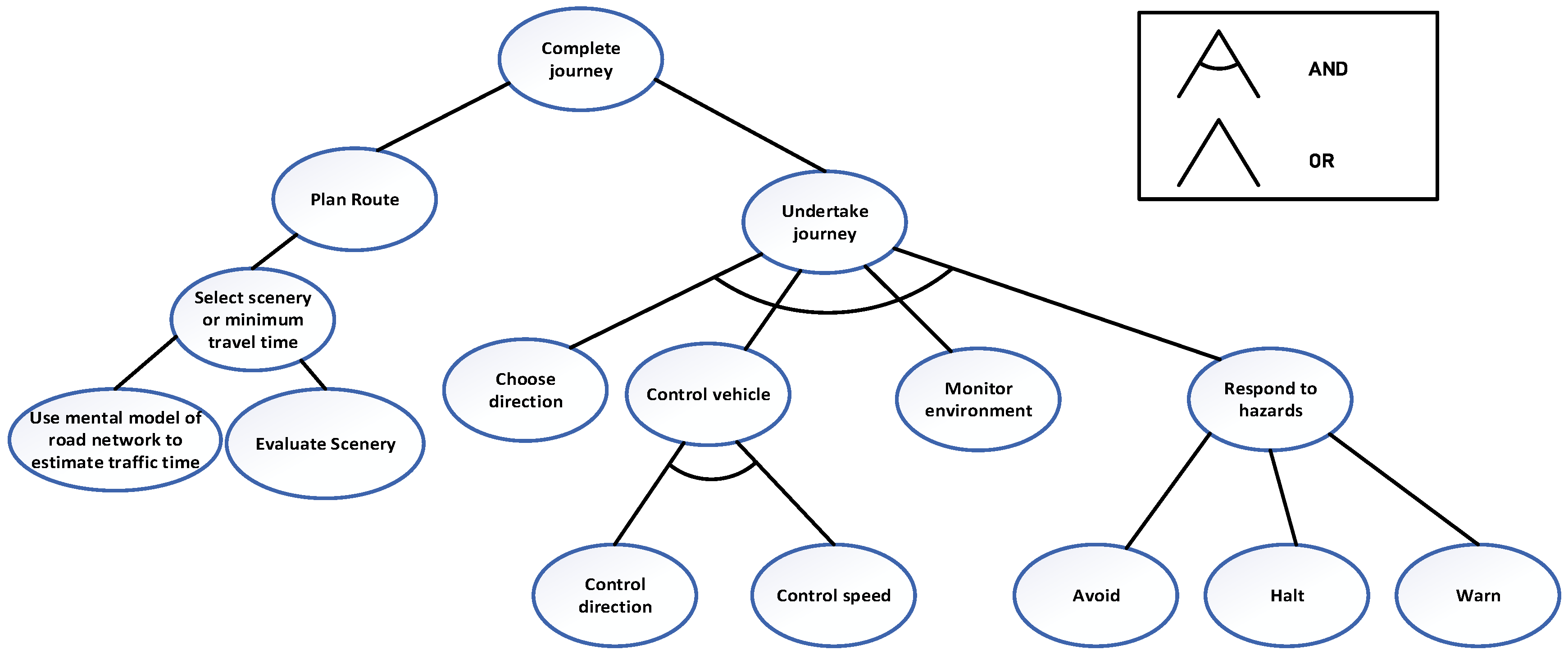
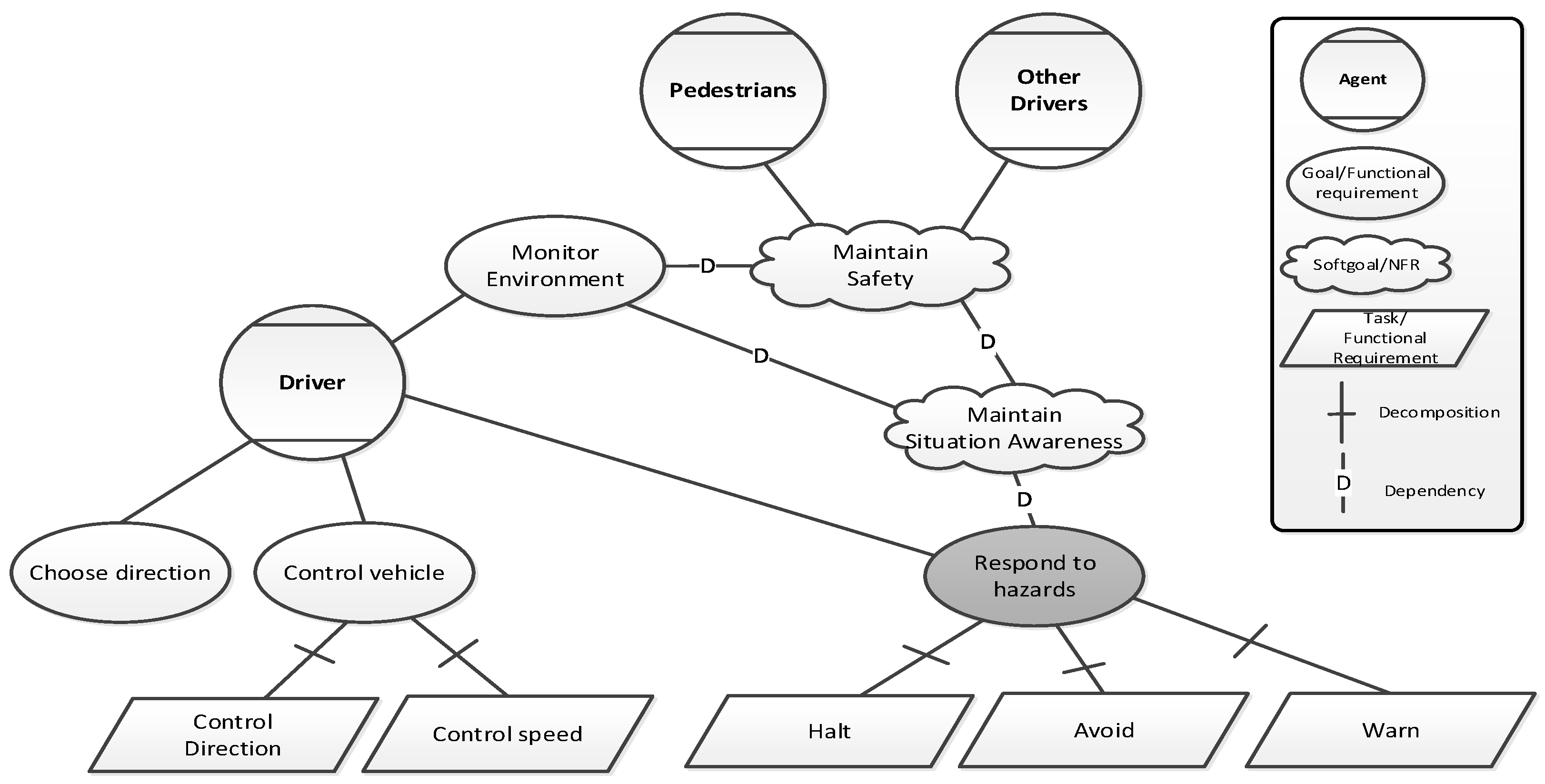
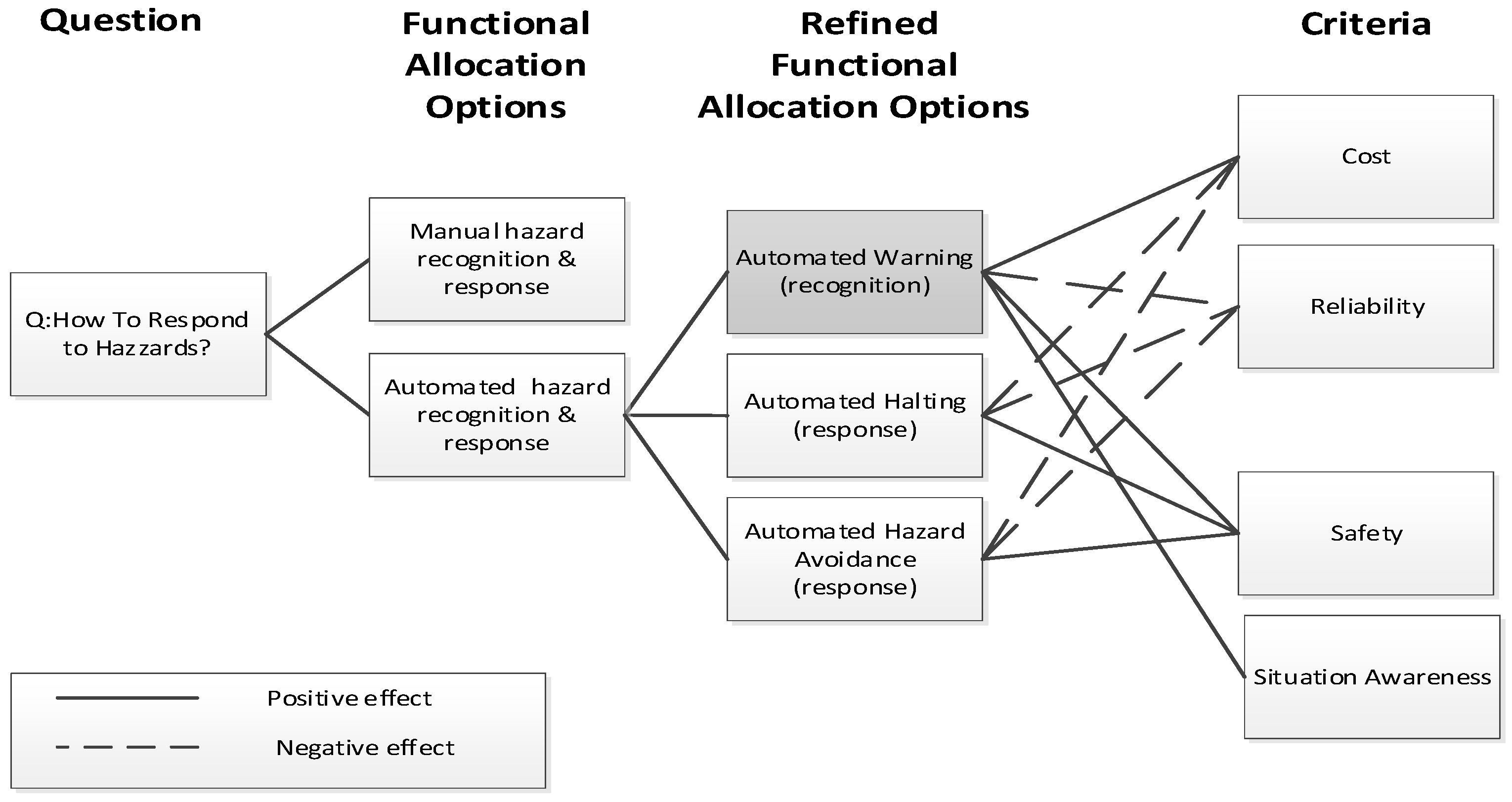
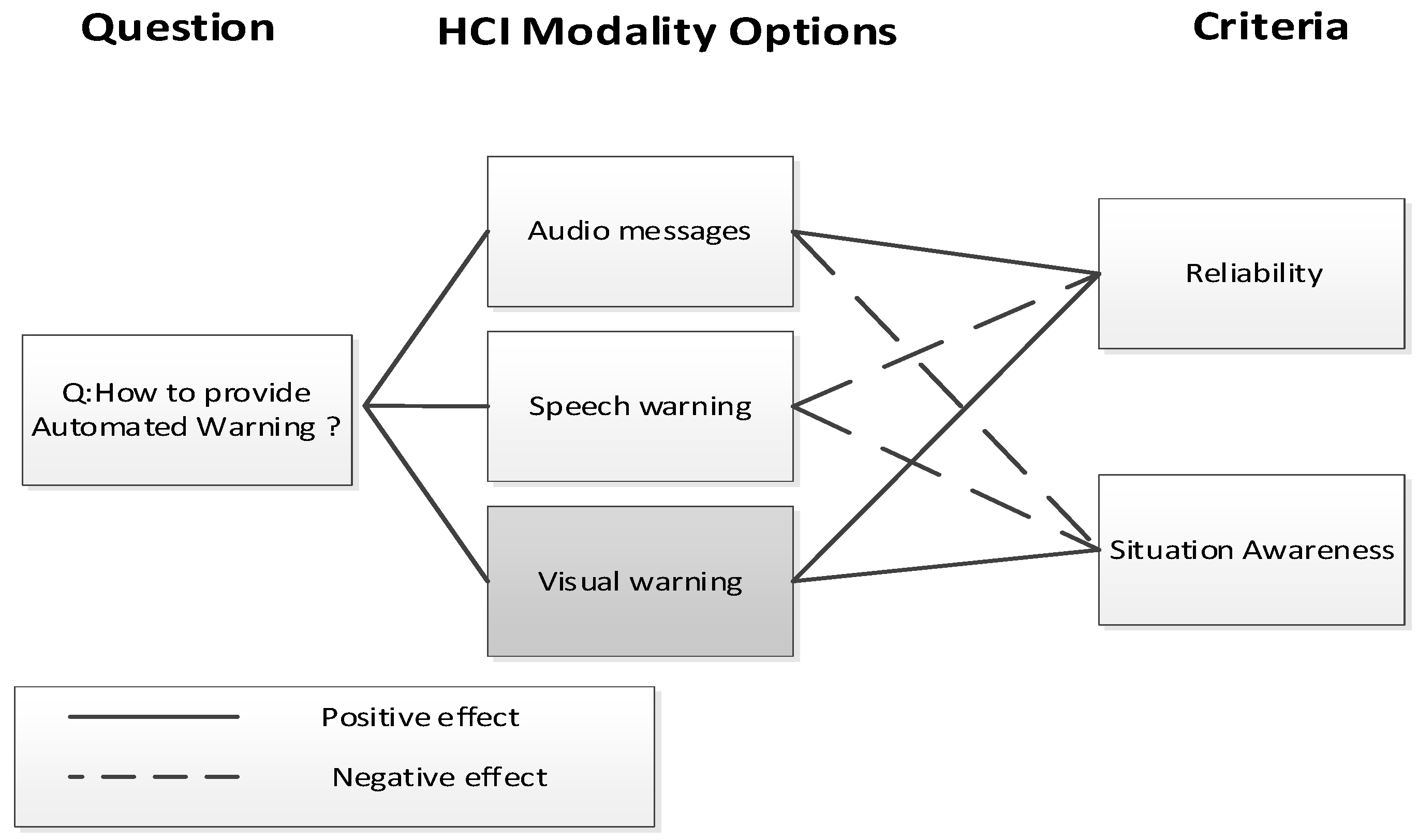
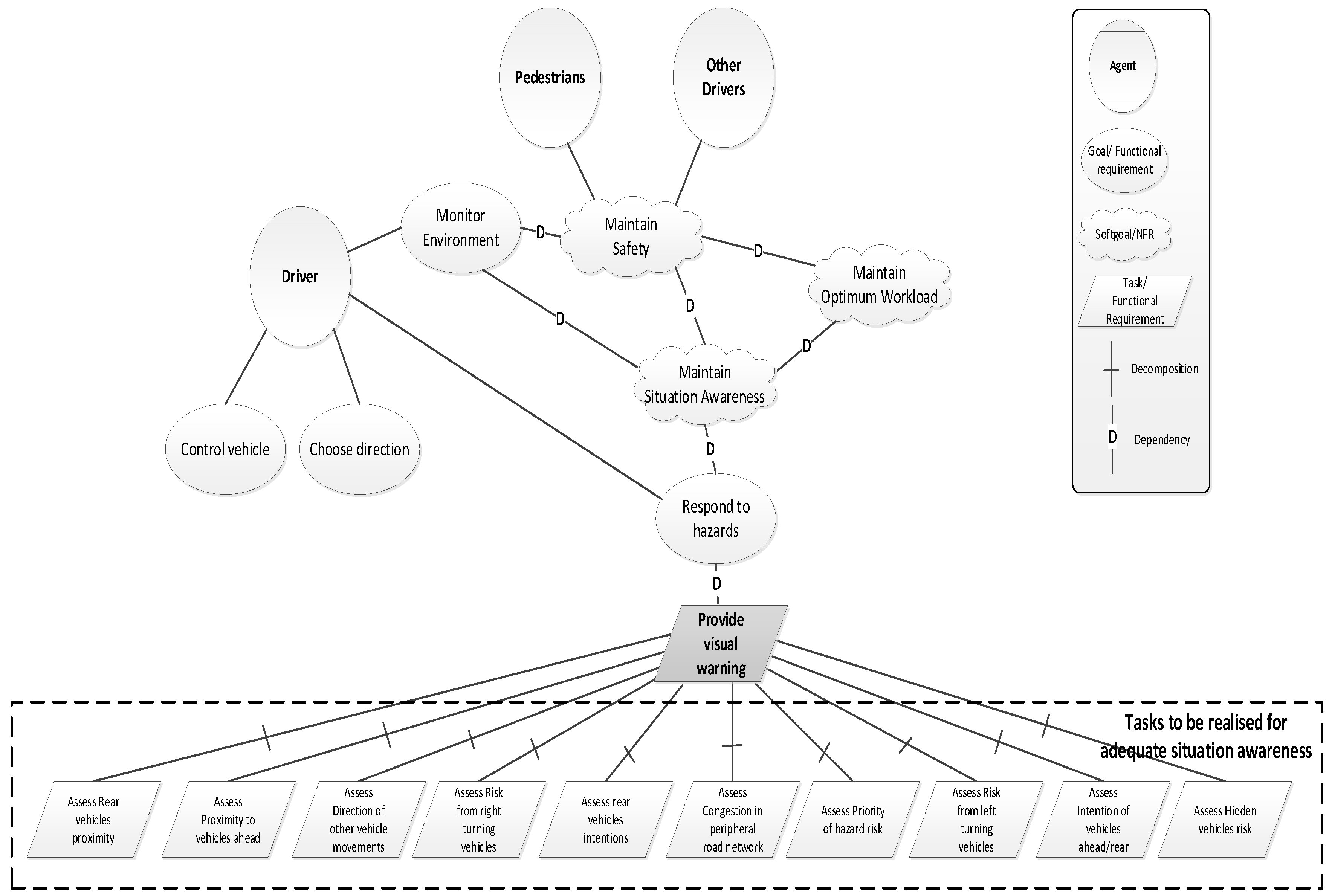
| Driver Tasks for adequate Situation Awareness | Capability of automation to implement requirement (H/M/L) | Reliability of automation in realising the requirement (H/M/L) | Functional Allocation (HUMAN/COMPUTER/HCI) |
TSRs: Information requirements specification for situation awareness support using automated warnings, (Visual situation display) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Assess proximity to vehicles ahead, in relation to host vehicle | H | H | HCI: visualise information for human to decide | Information on threat risks in different colours |
| Assess proximity to rear vehicles, in relation to host vehicle | H | H | HCI: visualise information for human to decide | Information on tailgating vehicle risk i |
| Assess direction of other vehicle movements | H | M | HCI: visualise information for human to decide | Information on risk-level of peripheral vehicles |
| Assess risks from right-turning vehicles at unsignalled intersections (right-hand rule) | M | L | HCI: visualise information for human to decide | Information on right-turning vehicles risk |
| Assess risks from left-turning vehicles at unsignalled intersections (left-hand rule) | M | L | HCI: visualise information for human to decide | Information on left-turning vehicles risk |
| Assess following vehicles risk (blind spot, tailgating) | H | H | HCI: visualise information for human to decide | Information on blind spot risk |
| Assess congestion information on peripheral roads | M | M | HCI: visualise information for human to decide | Information on peripheral road network traffic |
| Assess priority of hazards | M | M | HCI: visualise information for human to decide | Prioritise hazard risk information |
| Assess intention of other vehicles behind and ahead of host vehicle | L | L | Human task | None |
| Assess risks of hidden vehicles at intersections | H | M | HCI: visualise information for human to decide | Information on hidden vehicles risk information |
| Tasks performed by expert and novice participants during the practical part of the COVID19 case study | Percentage of Experts subjects that addressed the question correctly with score > 65/100 | Percentage of Novice subjects that addressed the question correctly with score > 65/100 |
|---|---|---|
| Write down the human task you focused on to address the problem (e.g., respond to hazards while driving a vehicle). Which Non-functional Requirement (human factors) is important to complete this task successfully? (e.g., maintain good driver situation awareness) | 77.7% (mean:66.11,SD:5.4) |
30% (mean:57.5,SD:15) |
| What is your recommended functional allocation for the above task and what were your selection criteria? (e.g., improve driver situation awareness through an in-vehicle warning system) | 77.7% (mean:77.5,SD:19.8) | 40% (mean:60,SD:20) |
| Specify the tasks required to be performed by a human or technology to realise the selected level of automation from previous step (e.g., monitor my vehicle’s blind spot while on motorway) | 77.7% (mean:68.6,SD:9.9) |
30% (mean:79.8,SD:20.12) |
| Specify the most appropriate functional allocation for each of the tasks you identified. What were the selection criteria you used? (e.g., automate the assessment of following vehicles’ proximity, let me decide what to do by consulting a user interface) | 88.8% (mean:74.6,SD:21.5) |
50% (mean:62.7,SD:26.12) |
| Write down the user interface’s functional requirements for each task from previous step. (e.g., present visual warnings on a head-up display depending on type and direction of blind spot risk) | 88.8% (mean:79.8,SD:20.12) |
30% (mean:60,SD:29.4) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





