1. Introducción
El café es uno de los productos agrícolas más valiosos y comercializados mundialmente, siendo una fuente crucial de ingresos para numerosos países productores y millones de personas involucradas en su producción. Sin embargo, la falta de herramientas eficientes para evaluar el estado de maduración de los frutos antes de la cosecha presenta un desafío significativo. La toma de decisiones sobre el momento óptimo para la cosecha es fundamental para maximizar el rendimiento y la calidad del café, pero actualmente los productores carecen de métodos fiables para realizar esta evaluación de manera precisa y rápida [
1].
El propósito de este estudio es abordar esta problemática mediante la implementación de técnicas avanzadas de segmentación y aprendizaje profundo (Deep Learning) aplicadas a imágenes RGB de cultivos de cafetales. Estas técnicas prometen proporcionar un análisis más detallado y preciso de los parámetros clave, facilitando una estimación más exacta del rendimiento del cafeto. En un estudio realizado en Minas Gerais, Brasil, el uso de un UAV equipado con algoritmos de visión por computadora y una cámara RGB para recopilar datos de 144 arbustos de café durante un año demostró un error promedio porcentual absoluto (MAPE) del 31.75%, subrayando la potencial eficacia del aprendizaje automático y la tecnología UAV en la estimación del rendimiento del café [
2].
El campo de procesamiento de imágenes agrícolas enfrenta desafíos importantes, como lograr una segmentación precisa y clara de los frutos bajo diferentes condiciones de iluminación y entornos. Además, la complejidad de algunos métodos de segmentación puede limitar su efectividad en la clasificación automática de grandes conjuntos de datos agrícolas, lo que destaca la necesidad de mejorar estas técnicas para su óptima aplicación [
3]. Nuevos métodos de detección para estimar el rendimiento de frutos, junto con diversas arquitecturas de segmentación, representan un avance significativo en la industria cafetera [
4].
El desarrollo de un sistema inteligente de estimación del rendimiento de frutos presenta desafíos como la toma de muestras representativas de árboles y la captura eficiente de datos mediante arquitecturas de segmentación semántica basadas en Deep Learning. Este sistema podría escanear rápidamente áreas extensas de cafetales, analizando la cantidad de frutos, su madurez y otros factores relevantes, proporcionando información en tiempo real para la gestión de recursos y la planificación de la cosecha [
5]. En un contexto de crisis del café y dificultades socioeconómicas de los trabajadores, la adopción de tecnologías avanzadas se presenta como una esperanza para mejorar la sostenibilidad y rentabilidad de la industria cafetera [
6].
La predicción de la producción agrícola tradicionalmente se ha basado en métodos estadísticos, pero actualmente se explora el potencial del aprendizaje automático, especialmente las redes neuronales artificiales (RNA). La aplicación exitosa de estas técnicas puede reducir la incertidumbre en la producción agrícola y optimizar la cadena de suministro [
7]. Un ejemplo innovador es la estimación del potencial productivo de los cafetos mediante algoritmos de aprendizaje automático, integrando datos de sensores para proporcionar estimaciones precisas del rendimiento de los cultivos [
8].
Sin embargo, en la investigación agrícola existe una brecha significativa en la cuantificación precisa del fruto del café en la planta, lo que obstaculiza la toma de decisiones informadas sobre el manejo del cultivo y la estimación del rendimiento. Un enfoque innovador que combina el algoritmo YOLOv7 con técnicas semisupervisadas de anotación de imágenes ha mostrado una precisión promedio mínima del 3.78% en datos anteriores a la cosecha, destacando la capacidad de estos métodos para mejorar la exactitud de las estimaciones [
9]. La visión por computadora, al proporcionar una caracterización detallada de la uniformidad del color, contribuye significativamente a mejorar el rendimiento y la calidad en la producción agrícola [
10]. La estimación precisa de la calidad de los cultivos es crucial para los agricultores, ya que les ayuda a mejorar sus prácticas agrícolas, maximizando sus ganancias. Métodos tradicionales como el conteo manual de frutos son costosos, propensos a errores y consumen tiempo. El acceso a conjuntos de datos de alta calidad, disponibles en plataformas como Hugging Face en formato YOLO, es esencial para el desarrollo de soluciones automatizadas en la producción de café [
11].
Lograr una uniformidad en la maduración del fruto es un desafío significativo. La visión por computadora ha surgido como una técnica prometedora para una detección precisa de objetos y una caracterización detallada de la uniformidad del color, contribuyendo a mejorar el rendimiento y calidad en la producción agrícola [
12]. La agricultura inteligente fortalece la infraestructura tecnológica en la agroindustria del café, mejorando su competitividad. Sin embargo, los pequeños productores enfrentan desafíos significativos debido a su limitado acceso y baja adopción de tecnología avanzada, dificultando la implementación de prácticas agrícolas inteligentes [
13]. La implementación de nuevas tecnologías agrícolas plantea desafíos debido a la ineficiencia y costo de métodos tradicionales para estimar el rendimiento de los cultivos, subrayando la necesidad de desarrollar métodos automatizados precisos [
14].
La predicción oportuna y precisa del rendimiento del café es crucial para planificar las cosechas y aumentar la rentabilidad. Las estimaciones actuales, basadas en la cosecha de frutos de café en algunas plantas y extrapoladas al área total de producción, son laboriosas y subjetivas, destacando la necesidad de metodologías más rápidas y precisas [
15].
En este estudio, se plantea la hipótesis de que es posible estimar la producción de cafetales mediante el uso de técnicas de segmentación y deep learning aplicadas a imágenes RGB. El objetivo principal es desarrollar un método para estimar la producción de cultivos de cafetales utilizando estas técnicas avanzadas. Los resultados esperados de esta investigación podrían tener un impacto significativo en la gestión de cultivos y la planificación de la cosecha, proporcionando una herramienta valiosa para los productores de café.
2. Materiales y Métodos
En esta sección se detallan los materiales y métodos empleados para la estimación de la producción de cultivos de cafetales mediante técnicas de segmentación y deep learning. Este enfoque permite la identificación y el conteo preciso de los frutos de café en imágenes, optimizando la gestión agrícola y la planificación financiera [
16].
El estudio es de carácter cuantitativo y se basa en la aplicación de técnicas de segmentación y aprendizaje profundo para estimar la producción de un cafetal. Se ha diseñado una metodología específica de recolección de datos para abordar el objetivo general y validar la hipótesis planteada. El análisis cuantitativo de los resultados será fundamental para alcanzar las conclusiones de la investigación.
El diseño de la investigación es cuasi experimental, ya que implica la manipulación de variables asociadas con técnicas de segmentación y deep learning para evaluar su impacto en la estimación de la producción de café. Además, se adopta un enfoque transversal y prospectivo, recolectando datos en un momento específico y a medida que se desarrollan y aplican las técnicas. Este diseño es analítico, pues implica el análisis de dos variables.
Las herramientas basadas en deep learning han sido desarrolladas para detectar, estimar y predecir la producción de manera eficaz [
17]. Se utilizarán varias herramientas para implementar las técnicas de segmentación y deep learning. Visual Studio Code es un IDE muy popular entre los desarrolladores de Python por sus numerosas características útiles y su gran flexibilidad [
18]. Jupyter es una plataforma interactiva de código abierto utilizada ampliamente en la investigación científica y ciencia de datos [
19]. Makesense AI es una aplicación en línea que permite etiquetar imágenes de manera eficiente, fundamental en aplicaciones de inteligencia artificial y deep learning [
20]. YOLO (You Only Look Once) es un algoritmo de visión por computadora utilizado para la detección de objetos en tiempo real, con varias versiones que incluyen mejoras significativas [
21]. Python, con su extensa biblioteca estándar y ecosistema de paquetes, es esencial para el procesamiento eficiente de datos en aplicaciones científicas, beneficiándose significativamente de su integración con NumPy [
22]. OpenCV es una biblioteca de visión por computadora utilizada para lograr una segmentación automatizada eficiente y precisa, mejorando algoritmos existentes mediante la identificación y clasificación de características específicas en imágenes [
23].
Los datos utilizados en esta investigación consistieron en fotografías de cafetos tomadas directamente en el campo en el distrito de Tabaconas, Provincia de San Ignacio, Departamento de Cajamarca, con las siguientes coordenadas geográficas: latitud -5.344413 y longitud -79.12255. La elevación media fue de 1161.03 metros con una precisión de 45.0 metros.
Se emplearon diversas técnicas para la estimación de la producción agrícola, asegurando la precisión y robustez del análisis. Se realizaron visitas de campo durante las épocas de cosecha para observar directamente los cafetales y capturar fotografías detalladas con cámaras de alta resolución (iPhone 7, 3024 × 4032 píxeles). Estas imágenes fueron clave para el análisis mediante técnicas de segmentación y Deep Learning. Se diseñó una ficha de observación digital para registrar sistemáticamente las condiciones y detalles relevantes durante la recolección y el entrenamiento de las imágenes. Se utilizaron herramientas especializadas como Makesense AI, YOLOv5 y OpenCV para el etiquetado, segmentación, y conteo de frutos en las imágenes recolectadas, facilitando un análisis detallado y preciso. Se realizaron pruebas específicas para evaluar el desempeño de los modelos de segmentación y Deep Learning en la estimación de la producción. Estas pruebas incluyeron la medición de métricas como precisión, exactitud, recall, F1-Score, y se generaron matrices de confusión para una evaluación detallada del rendimiento de los modelos. Durante las diferentes épocas de entrenamiento de las imágenes, se utilizó una ficha de observación digital para registrar minuciosamente los datos relevantes. Se capturaron un total de 201 imágenes con cámaras de alta resolución, de las cuales 160 fueron seleccionadas para el aumento de datos. Mediante un algoritmo de aumento de datos, estas 160 imágenes se incrementaron a un total de 1001 imágenes, mejorando la diversidad y representatividad del conjunto de datos.
Figure 1.
Ejemplo de repositorio de fotografías de arbusto de café. Fuente: Elaboración Propia.
Figure 1.
Ejemplo de repositorio de fotografías de arbusto de café. Fuente: Elaboración Propia.
Se realizó el proceso de segmentación de las fotografías de los arbustos de cafeto utilizando YOLOv5, una técnica de deep learning reconocida por su alta precisión y velocidad en la identificación y localización de objetos. Para este propósito, se utilizó una laptop Acer Aspire A315-57G, equipada con un procesador Intel Core i5 y 8 GB de memoria RAM. Para evaluar el rendimiento de los modelos, se empleó una matriz de confusión, una herramienta cuantitativa que ayudó a calcular métricas como precisión, exactitud, recall y F1-Score. Esta matriz proporcionó una visión detallada de la efectividad de cada método utilizado.
Consumo de CPU: Es la carga procesada por la unidad central de procesamiento durante la ejecución de las pruebas.
Table 1.
Descripción de las variables de la fórmula del Consumo del CPU.
Table 1.
Descripción de las variables de la fórmula del Consumo del CPU.
| Variable |
Descripción |
|
Cc
|
Consumo de CPU |
|
Ccj
|
Consumo de CPU en la prueba j
|
| n |
Total de pruebas |
Consumo de memoria: Indica la cantidad de memoria utilizada durante las pruebas.
Table 2.
Descripción de las variables de la fórmula del Consumo de la Memoria.
Table 2.
Descripción de las variables de la fórmula del Consumo de la Memoria.
| Variable |
Descripción |
|
Cm
|
Consumo de memoria. |
|
Cmj
|
Consumo de memoria en la prueba j. |
| n |
Total de pruebas. |
Fuente: Elaboración propia.
Tiempo de procesamiento: Representa el tiempo promedio de respuesta entre el inicio y el final de las pruebas.
Table 3.
Descripción de las variables de la fórmula del Tiempo de procesamiento.
Table 3.
Descripción de las variables de la fórmula del Tiempo de procesamiento.
| Variable |
Descripción |
|
Tr
|
Tiempo de respuesta. |
|
Tfj
|
Tiempo final de respuesta en la prueba j. |
|
Tfi
|
Tiempo inicial de respuesta en la prueba i |
| n |
Total de pruebas. |
Fuente: Elaboración propia.
Precisión: Proporción de verdaderos positivos con respecto al total de casos positivos reales.
Table 4.
Descripción de las variables de la fórmula de Precisión.
Table 4.
Descripción de las variables de la fórmula de Precisión.
| Variable |
Descripción |
| VP |
Verdaderos |
| FP |
Falsos positivos |
Fuente: Elaboración propia.
Exactitud: Representa la proporción de predicciones, tanto positivas como negativas, en relación con todas las predicciones realizadas.
Table 5.
Descripción de las variables de la fórmula de exactitud.
Table 5.
Descripción de las variables de la fórmula de exactitud.
| Variable |
Descripción |
| VN |
Verdaderos negativos |
| VP |
Verdaderos positivos. |
| FP |
Falsos positivos. |
| FN |
Falso Negativo |
Fuente: Elaboración propia.
Recall: Indica la proporción de casos positivos identificados correctamente entre todos los casos positivos reales, teniendo como fórmula.
Table 6.
Descripción de las variables de la fórmula de Recall.
Table 6.
Descripción de las variables de la fórmula de Recall.
| Variable |
Descripción |
| VP |
Verdaderos positivos. |
| FN |
Falsos negativos. |
Fuente: Elaboración propia.
F1-Sorce: Es una medida que combina precisión y recall en un solo valor. Se calcula utilizando la fórmula que toma en cuenta ambos valores.
Table 7.
Descripción de las variables de la fórmula de F1-Sorce.
Table 7.
Descripción de las variables de la fórmula de F1-Sorce.
| Variable |
Descripción |
| precis |
Casos positivos realmente positivos. |
| recall |
Casos positivos identificados correctamente. |
Fuente: Elaboración propia.
3. Resultados
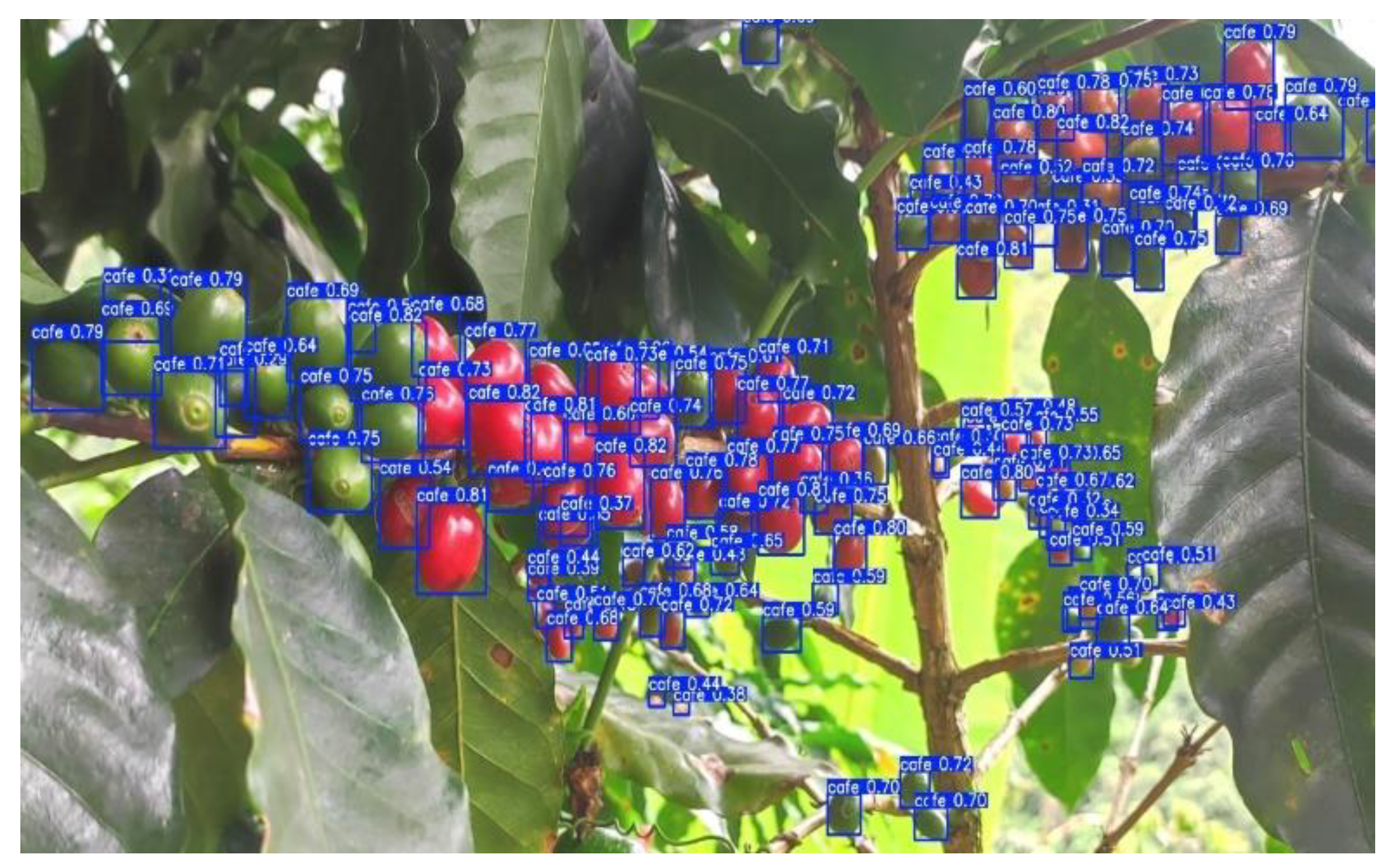
En esta sección, se presentan los resultados del modelo YOLOv5 aplicado a la detección de frutos de café. En la Figura 2 uestra cómo el modelo YOLOv5 ha identificado y delimitado los frutos de café presentes en la planta. Cada caja azul representa una detección del modelo, con una etiqueta que indica el objeto detectado (“café”) y un valor de confianza asociado a la detección. Este valor de confianza refleja la certeza del modelo respecto a la presencia de un fruto de café en la posición indicada
Figure 2.
Detección de frutos de café utilizando el modelo YOLOv5. Fuente: Elaboración propia.
Figure 2.
Detección de frutos de café utilizando el modelo YOLOv5. Fuente: Elaboración propia.
Las cajas delimitadoras azules encierran los frutos de café que el modelo ha identificado, y el valor de confianza, que varía entre 0.3 y 0.82, se muestra al lado de cada caja. Un valor de confianza más alto indica una mayor certeza del modelo en la precisión de la detección. Este resultado indica que el modelo puede identificar correctamente los frutos de café, mostrando una alta precisión y fiabilidad en la detección.
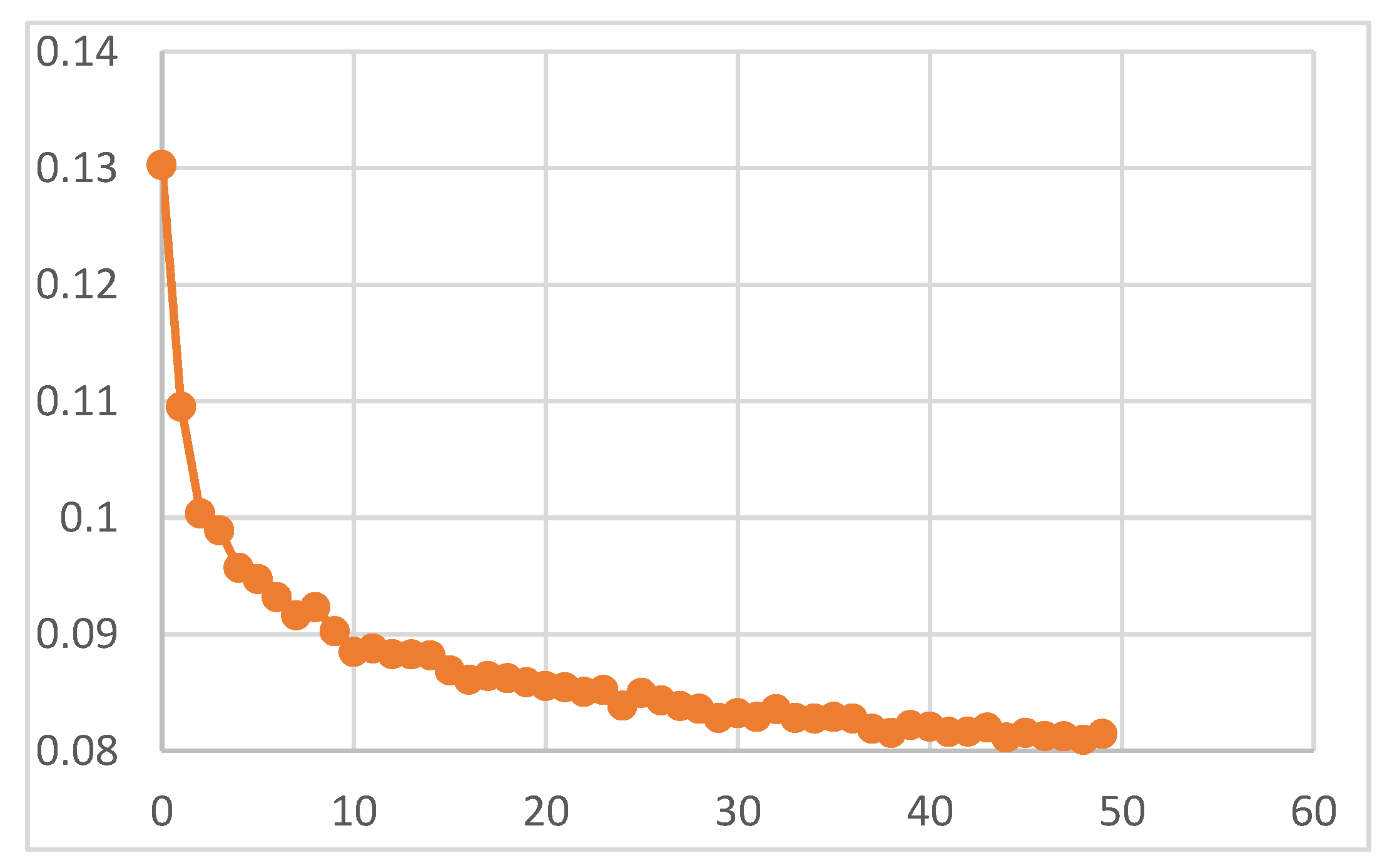
La Figura 3 muestra la evolución de la pérdida de la caja delimitadora a lo largo de las 50 épocas de entrenamiento del modelo YOLOv5. Al inicio, la pérdida es alta (alrededor de 0.13) y disminuye rápidamente durante las primeras 10 épocas, lo que indica un aprendizaje eficaz. Hacia la época 20, la pérdida se estabiliza en torno a 0.08, mostrando que el modelo ha alcanzado una precisión óptima en la detección de objetos.
Figure 3.
Evolución de la pérdida de la caja delimitadora durante las épocas de entrenamiento. Fuente: Elaboración Propia.
Figure 3.
Evolución de la pérdida de la caja delimitadora durante las épocas de entrenamiento. Fuente: Elaboración Propia.
La matriz de confusión fue utilizada para evaluar el modelo YOLOv5, utilizando verdaderos positivos, verdaderos negativos, falsos positivos y falsos negativos. Esta herramienta permite medir el rendimiento del modelo en términos de precisión, exactitud, recall y F1-Score, proporcionando una visión detallada de su efectividad en la detección y conteo de frutos de café.
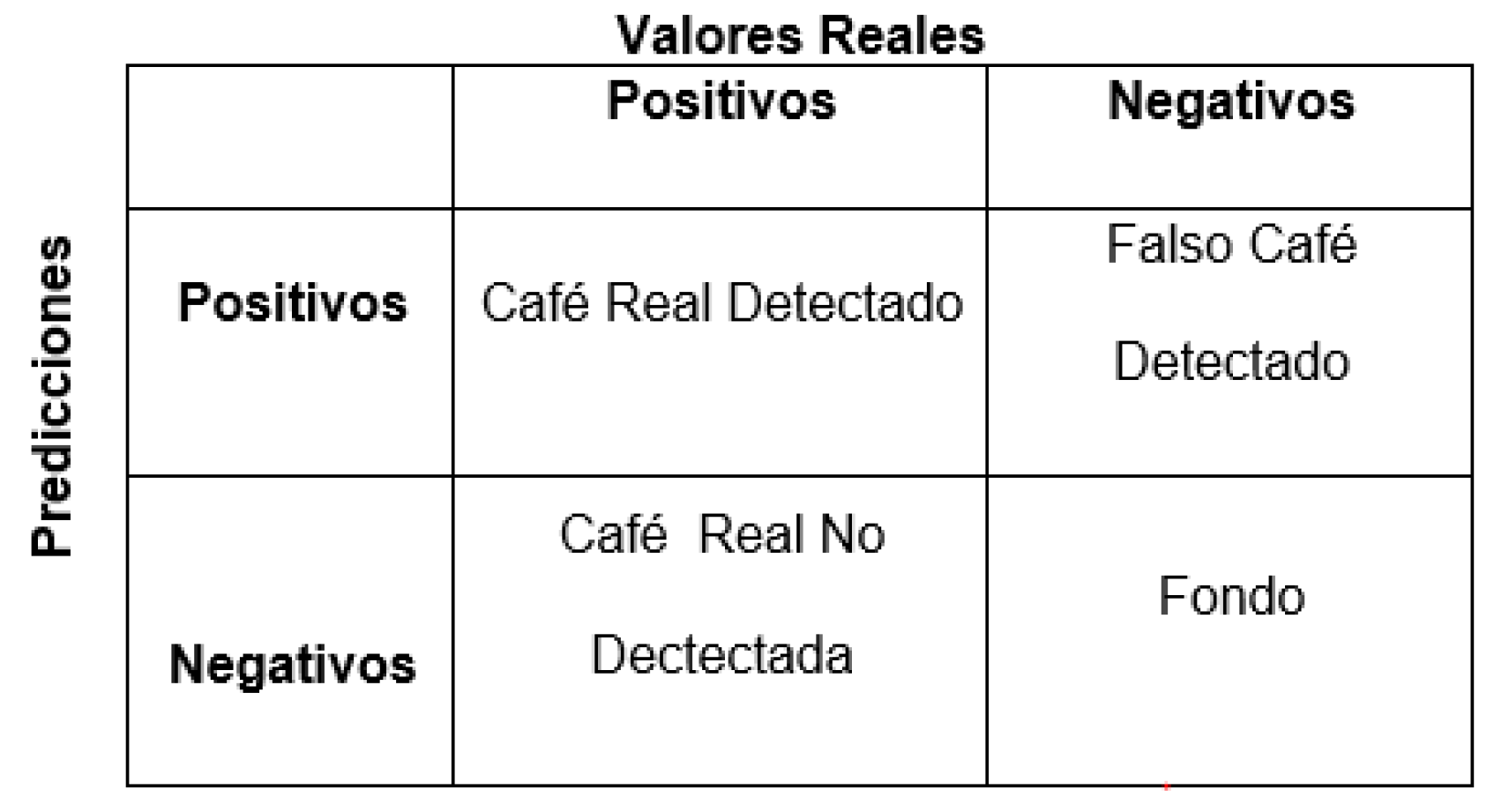
Métricas de evaluación: En la Figura 4 se presenta la matriz de confusión, que incluye las definiciones de Verdadero (V) y Falso (F) junto con Positivo (P) y Negativo (N) para este proyecto de investigación.
Figure 4.
Matriz de confusión para este proyecto de investigación. Fuente: Elaboración Propia.
Figure 4.
Matriz de confusión para este proyecto de investigación. Fuente: Elaboración Propia.
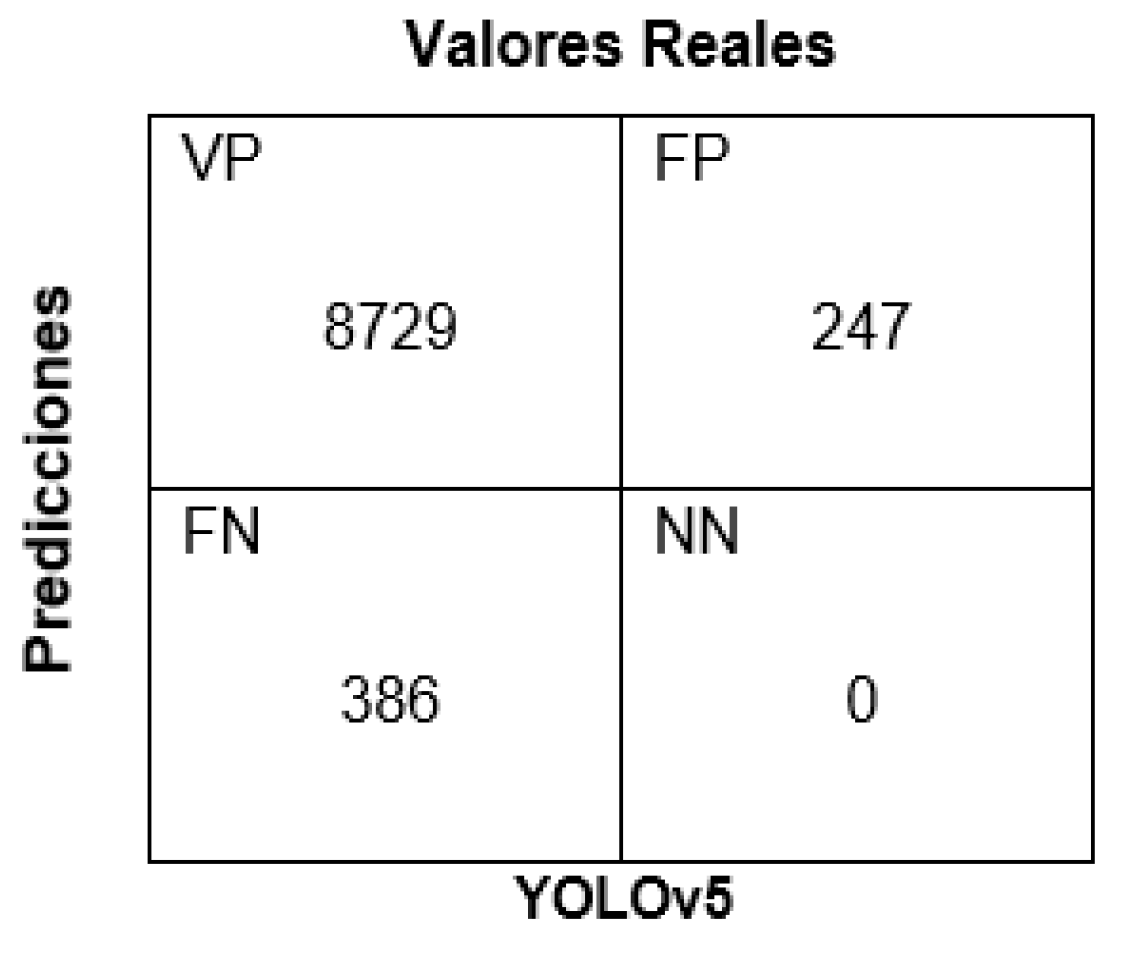
La Figura 5 muestra la matriz de confusión generada a partir de las imágenes reales y las predicciones realizadas por el modelo YOLOv5
Figure 5.
Matriz de confusión en YOLOv5.
Figure 5.
Matriz de confusión en YOLOv5.
Fuente: Elaboración Propia
Con los datos obtenidos, es posible calcular diversas métricas que permiten medir y evaluar el rendimiento del modelo de detección. Las métricas que se utilizarán para esta evaluación incluyen precisión, recall y F1 score. La precisión refleja la exactitud del modelo en términos de la cantidad de frutos de café detectados correctamente. Por otro lado, el recall indica la capacidad del modelo para identificar los frutos, es decir, el porcentaje de frutos de café correctamente identificados por el modelo.
En este estudio, se da prioridad a la métrica F1 score sobre las demás, ya que esta métrica integra tanto la precisión como el recall, otorgándoles igual importancia y proporcionando un único valor que permite comparar el rendimiento del modelo de manera integral. Además, considerando que el modelo se aplicará en condiciones de campo, es fundamental asegurar la detección precisa de los frutos de café, que pueden ser fácilmente confundidos con el entorno natural de las ramas y hojas del cafeto.
En la Tabla 8 se presentan los resultados obtenidos a partir de la matriz de confusión y las métricas calculadas.
Table 8.
Resultados del modelo Yolov5.
Table 8.
Resultados del modelo Yolov5.
| |
Yolov5 |
| Precisión |
97.25% |
| Recall |
95.77% |
| F1- Score |
96.37% |
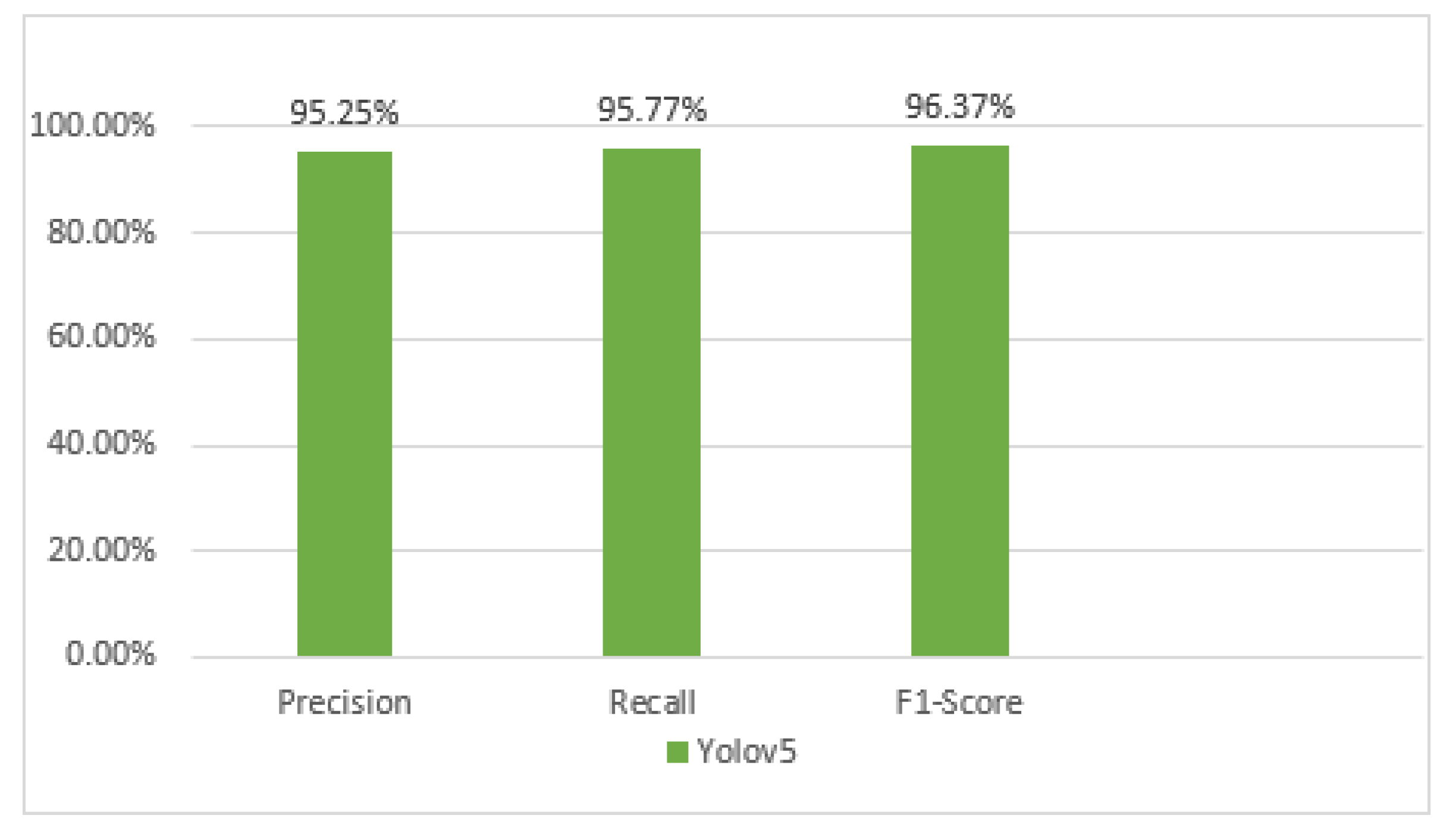
Figure 6.
Grafico de barra de las métricas calculadas de Yolov5.
Figure 6.
Grafico de barra de las métricas calculadas de Yolov5.
Fuente: Elaboración Propia.
La precisión del modelo se sitúa en 95.25%, lo que indica que la mayoría de las detecciones realizadas por el modelo son correctas. Esto refleja la alta capacidad del modelo para minimizar los falsos positivos, es decir, la detección errónea de objetos que no son frutos de café como si lo fueran.
Por otro lado, el recall del modelo es de 95.77%, lo que significa que el modelo detecta la mayoría de los frutos de café presentes en las imágenes. Esta métrica mide la capacidad del modelo para identificar todos los casos positivos, reduciendo al mínimo los falsos negativos, es decir, los frutos de café que no fueron detectados.
Además, el F1-Score del modelo es de 96.37%, una métrica que combina la precisión y el recall en un único valor equilibrado. Un F1-Score alto indica que el modelo tiene un rendimiento robusto en términos de precisión y recall, proporcionando un balance óptimo entre la detección correcta de frutos y la minimización de errores.
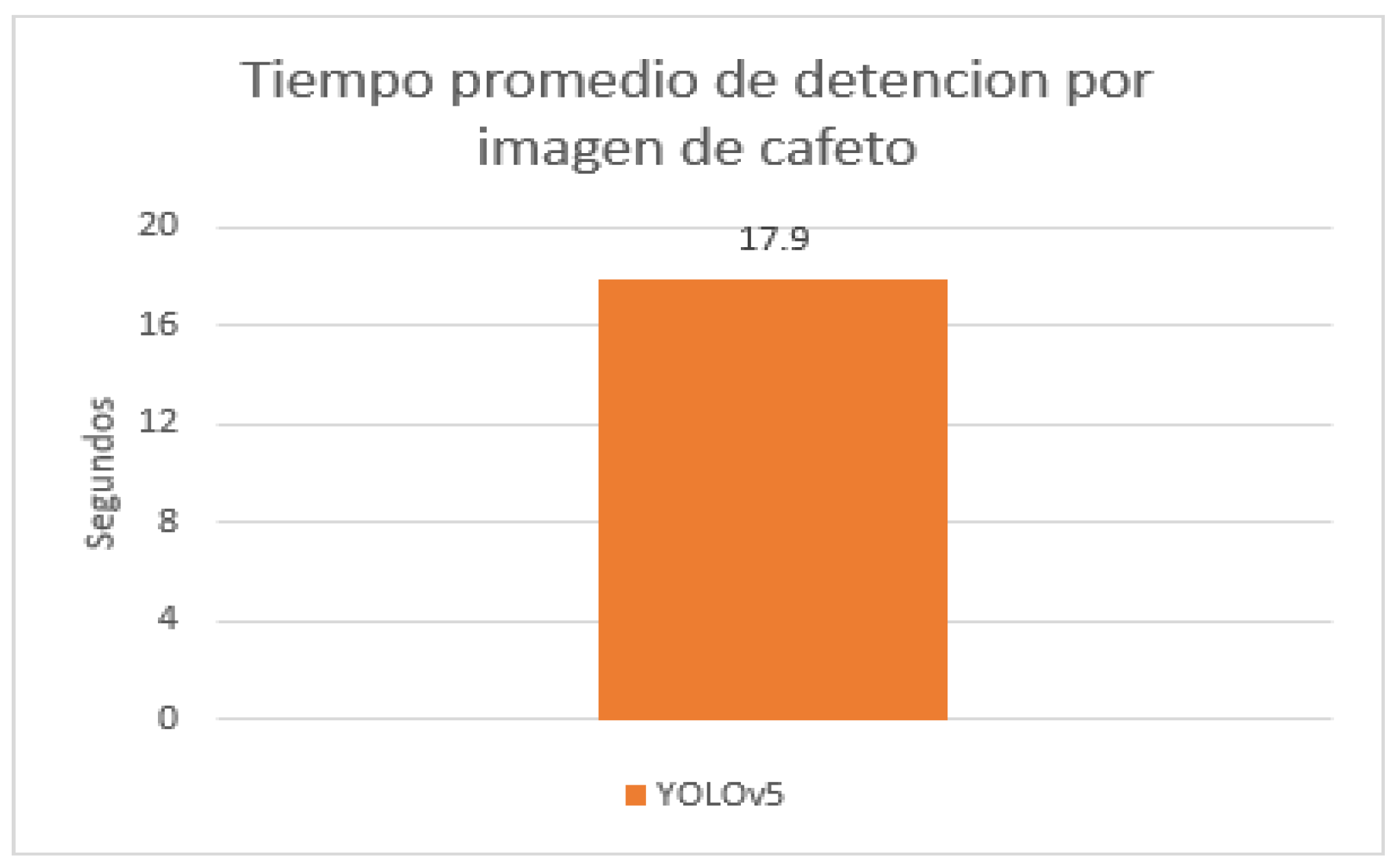
En la Figura 7 se observa que el tiempo promedio de detección por imagen de cafeto utilizando YOLOv5 es de 17.9 segundos. Este tiempo incluye todo el procesamiento necesario para identificar y etiquetar los frutos de café en cada imagen.
Figure 7.
Gráfico de barra del tiempo promedio de detención por imagen de cafeto. Fuente: Elaboración Propia.
Figure 7.
Gráfico de barra del tiempo promedio de detención por imagen de cafeto. Fuente: Elaboración Propia.
4. Discusión
En esta investigacion realizada, la implementación del modelo YOLOv5 para la detección de frutos de café ha mostrado resultados prometedores. La alta precisión y fiabilidad del modelo en la identificación de los frutos, junto con las métricas de evaluación que incluyen precisión del 97.25%, recall del 95.77%, y un F1-Score del 96.37%, que destacan su capacidad para realizar detecciones precisas. Este enfoque no solo mejora la eficiencia en la detección de los frutos de café, sino que también establece una base sólida para su aplicación práctica en condiciones de campo, donde la precisión y la minimización de errores son críticas para la gestión agrícola efectiva.
Asimismo Joel Junior García Arteaga et al. [
24] implementaron cuatro modelos de aprendizaje automático utilizando Python y las librerías scikit-learn y Keras. Después del proceso de One Hot Encoding, el conjunto de datos aumentó de 13 a 44 variables, con un total de 83,247 registros, de los cuales el 70% (58,272) se usaron para entrenar los modelos y el 30% (24,975) para validar su rendimiento. La baja correlación entre las variables predictoras (sup_cosechada, producción) y las variables independientes, excepto entre sup_cosechada y sup_sembrada (95%), dificultó la generalización de la variable producción debido también a la distribución dispersa de la precipitación.
A igual que en la investigación de Wu, L. et al. [
23] se utilizó visión por computadora para lograr una segmentación automatizada eficiente y precisa. Los autores emplearon redes neuronales convolucionales (CNN), alcanzando una precisión del 95% en la segmentación automatizada, superando el 85% de los métodos tradicionales. En la segmentación de imágenes médicas, lograron una mejora del 10% en la precisión al identificar y clasificar tumores, alcanzando una precisión del 90%. En conclusión, el uso de CNN en visión por computadora mejora significativamente la precisión y eficiencia de la segmentación automatizada, siendo crucial para aplicaciones críticas.
En conclusión, aunque se han utilizado diversas aproximaciones y algoritmos para la segmentación y detección en imágenes con diferentes grados de éxito, el modelo YOLOv5 muestra un rendimiento competitivo en la detección de frutos de café, ofreciendo una alternativa precisa y eficiente para su aplicación en la agricultura. Estos avances no solo mejoran la gestión agrícola, sino que también sientan las bases para futuras aplicaciones en otros campos críticos, como la medicina y el procesamiento de imágenes
5. Conclusiones
El presente estudio ha logrado responder eficazmente a la interrogante sobre la estimación del rendimiento de cultivos de cafetales utilizando técnicas de segmentación en imágenes RGB y deep learning. A lo largo del proceso de investigación, se cumplieron los objetivos propuestos, demostrando la capacidad del modelo YOLOv5, complementado con algoritmos de conteo desarrollados con OpenCV, para identificar y contar frutos de café con alta precisión.
Durante el entrenamiento del modelo, se utilizaron fotografías capturadas en campo que incluían frutos en diversas posiciones, desde vistas cercanas hasta frutos parcialmente ocultos, permitiendo una generalización robusta del modelo. La técnica de etiquetado manual, llevada a cabo con la herramienta MakeSense, optimizó el proceso de creación del dataset y redujo considerablemente el tiempo necesario para el etiquetado.
El modelo YOLOv5 mostró ser eficiente en términos de tiempo de ejecución y manejo de falsos positivos, reflejando un buen desempeño general. Además, la integración de OpenCV para el conteo de frutos complementó eficazmente la segmentación y detección realizada por YOLOv5.
En síntesis, las técnicas de segmentación y deep learning, junto con los algoritmos de conteo desarrollados con OpenCV, han demostrado ser metodologías efectivas para la estimación de la producción de café. Los resultados obtenidos proporcionan una herramienta valiosa para los agricultores y productores, facilitando la toma de decisiones y mejorando la gestión de los cultivos. Esta investigación no sólo valida el enfoque propuesto, sino que también establece una base sólida para futuras mejoras y aplicaciones en la agricultura de precisión.
En el estudio de R. Rodríguez Morales et al. [
25], se desarrollaron y evaluaron algoritmos para la segmentación precisa de imágenes. Utilizando técnicas avanzadas, lograron aislar detalles con un 95% de éxito, reduciendo el ruido sin perder información importante, sus algoritmos mejoraron la claridad de las imágenes en un 20%. Además, demostraron un 80% de eficiencia en la aplicación a bases de datos extensas con mínimos ajustes de parámetros, destacándose por su eficiencia y versatilidad en el procesamiento de imagen.
Contribuciones de los autores
Conceptualización, H.G. (Huaman Gerrero), metodología, M.R. (Montalvan Ramos), software, M.R. (Montalvan Ramos), recursos, H.G. (Huaman Gerrero), investigación, M.R., H.G., redacción—preparación del borrador original, H.G. Todos los autores han leído y aprobado la versión publicada del manuscrito.
Financiamiento
Esta investigación no recibió financiamiento externo.
Agradecimientos
Agradezco sinceramente a los propietarios de las parcelas de café por su invaluable colaboración y agradezco a nuestro asesor, Dr. Forero Vargas Manuel Guillermo, por su experta guía y continuo apoyo. También a la Universidad Señor de Sipán, por proporcionar los recursos necesarios para llevar a cabo este estudio.
References
- H. C. Bazame, J. P. Molin, D. Althoff, y M. Martello, «Detection of coffee fruits on tree branches using computer vision», Sci. Agric., vol. 80, 2022. [CrossRef]
- B. D. S. Barbosa, G. A. E. S. Ferraz, L. Costa, Y. Ampatzidis, V. Vijayakumar, y L. M. dos Santos, «UAV-based coffee yield prediction utilizing feature selection and deep learning», Smart Agric. Technol., vol. 1, 2021. [CrossRef]
- J. Aldana-Aguilar y Y. Rodriguez-Gallo, «Estimation of Shade Levels in Coffee Cultivation Using Segmentation Methods and Deep Learning», presentado en Proceeding of the 2023 IEEE 41st Central America and Panama Convention, CONCAPAN XLI 2023, 2023. [CrossRef]
- H. C. Bazame, J. P. Molin, D. Althoff, M. Martello, y L. D. P. Corrêdo, «Mapping coffee yield with computer vision», Precis. Agric., vol. 23, n.o 6, pp. 2372-2387, 2022. [CrossRef]
- P. Maheswari, P. Raja, O. E. Apolo-Apolo, y M. Pérez-Ruiz, «Intelligent Fruit Yield Estimation for Orchards Using Deep Learning Based Semantic Segmentation Techniques—A Review», Front. Plant Sci., vol. 12, 2021. [CrossRef]
- M. C. Espindula et al., «Yield of robusta coffee in different spatial arrangements», Pesqui. Agropecu. Bras., vol. 56, 2021. [CrossRef]
- C. Ordóñez, C. Cobos, y J. Muñoz-Ordóñez, «Predicción del rendimiento de cultivos de café: un mapeo sistemático (Forecast yield prediction of coffee crops: a systematic mapping)», Ing. Compet., vol. 25, pp. 1-25, oct. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Y. Kittichotsatsawat, N. Tippayawong, y K. Y. Tippayawong, «Prediction of arabica coffee production using artificial neural network and multiple linear regression techniques», Sci. Rep., vol. 12, n.o 1, 2022. [CrossRef]
- J. P. Rodríguez, D. C. Corrales, D. Griol, Z. Callejas, y J. C. Corrales, «A non-destructive time series model for the estimation of cherry coffee production», Comput. Mater. Contin., vol. 70, n.o 3, pp. 4725-4743, 2022. [CrossRef]
- F. Eron, M. Noman, R. R. de Oliveira, y A. Chalfun-Junior, «Computer Vision-Aided Intelligent Monitoring of Coffee: Towards Sustainable Coffee Production», Sci. Hortic., vol. 327, 2024. [CrossRef]
- R. Sanya, A. L. Nabiryo, J. F. Tusubira, S. Murindanyi, A. Katumba, y J. Nakatumba-Nabende, «Coffee and cashew nut dataset: A dataset for detection, classification, and yield estimation for machine learning applications», Data Brief, vol. 52, p. 109952, feb. 2024. [CrossRef]
- H. C. Bazame, J. P. Molin, D. Althoff, y M. Martello, «Detection, classification, and mapping of coffee fruits during harvest with computer vision», Comput. Electron. Agric., vol. 183, p. 106066, abr. 2021. [CrossRef]
- S. Wulandari y Y. Ferry, «Strategies on technology management for coffee smallholder to promote the smart farming implementation», IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci., vol. 759, p. 012057, may 2021. [CrossRef]
- E. Silamat, H. Siregar, R. Pambudy, y H. Harianto, «Impact of grafting on local coffee production based on People’s plantations in Bengkulu Province of Indonesia», Nativa, vol. 12, n.o 1. pp. 90-96, 2024. [CrossRef]
- M. A. Zanella, R. Nogueira Martins, F. Moreira da Silva, L. C. C. Carvalho, M. de Carvalho Alves, y J. T. Fim Rosas, «Coffee yield prediction using high-resolution satellite imagery and crop nutritional status in Southeast Brazil», Remote Sensing Applications: Society and Environment, vol. 33. 2024. [CrossRef]
- K.-C. Chang y Y.-L. Lin, «Design of Coffee Yield Estimation System Using Computer Vision by Crowd Counting Model», presentado en 2023 International Conference on Consumer Electronics - Taiwan, ICCE-Taiwan 2023 - Proceedings, 2023, pp. 569-570. [CrossRef]
- M. Fu et al., «AIBugHunter: A Practical tool for predicting, classifying and repairing software vulnerabilities», Empir. Softw. Eng., vol. 29, n.o 1, 2024. [CrossRef]
- Mustelier HechavarrÃ\-a, F. E. Castro Dieguez, A. Verdecia Cabrera, A. A. Aliaga Benavides, y J. HechavarrÃ\-a Figueredo, «SIPEA: Web Application for Celia SÃ!`nchez Manduley Hospital in Manzanillo», Rev. Cuba. InformÃtica MÃcopyrightdica, vol. 14, dic. 2022, [En línea]. Disponible en: http://scielo.sld.cu/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1684-18592022000200005&nrm=iso.
- T. Weber, J. Ehe, y S. Mayer, «Extending Jupyter with Multi-Paradigm Editors», Proc. ACM Hum.-Comput. Interact., vol. 8, n.o EICS, 2024. [CrossRef]
- N. Naik, M. Ramanathan, y P. Ponnusamy, «Refined single-stage object detection deep-learning technique for chilli leaf disease detection», J. Electron. Imaging, vol. 32, n.o 3, 2023. [CrossRef]
- L. Zhang et al., «Marine zoobenthos recognition algorithm based on improved lightweight YOLOv5», Ecol. Inform., vol. 80, 2024. [CrossRef]
- P. Bridge et al., «Highdicom: a Python Library for Standardized Encoding of Image Annotations and Machine Learning Model Outputs in Pathology and Radiology», J. Digit. Imaging, vol. 35, n.o 6, pp. 1719-1737, 2022. [CrossRef]
- H. Wu, L. Xu, y N. Xiao, «Efficient and accurate segmentation of adhesive lamellae in tri-modal microstructure of titanium alloy based on OpenCV», Mater. Charact., vol. 208, 2024. [CrossRef]
- J. J. García Arteaga, J. J. Zambrano Zambrano, R. Alcivar Cevallos, y W. D. Zambrano Romero, «Predicción del rendimiento de cultivos agrícolas usando aprendizaje automático», Rev. Arbitr. Interdiscip. Koinonía, vol. 5, n.o Extra 2, pp. 144-160, 2020.
- R. R. Morales, Y. G. Suárez, E. T. García, y J. H. S. Azuela, «Autochthonous algorithms for digital image segmentation», An. Acad. Cienc. Cuba, vol. 13, n.o 1, 2023.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).