Submitted:
13 July 2024
Posted:
16 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sequence Retrieval and Modeling HCV NS3/4A G3
2.2. 3D Structure Refinement and Validation
2.3. Ligand-Based Pharmacophore Modeling and Virtual Screening
2.4. Preparation of HCV NS3/4A and Covalent Docking Protocol
2.5. Molecular Dynamics Simulations
2.6. Binding Free Energy Calculations
3. Results and Discussion
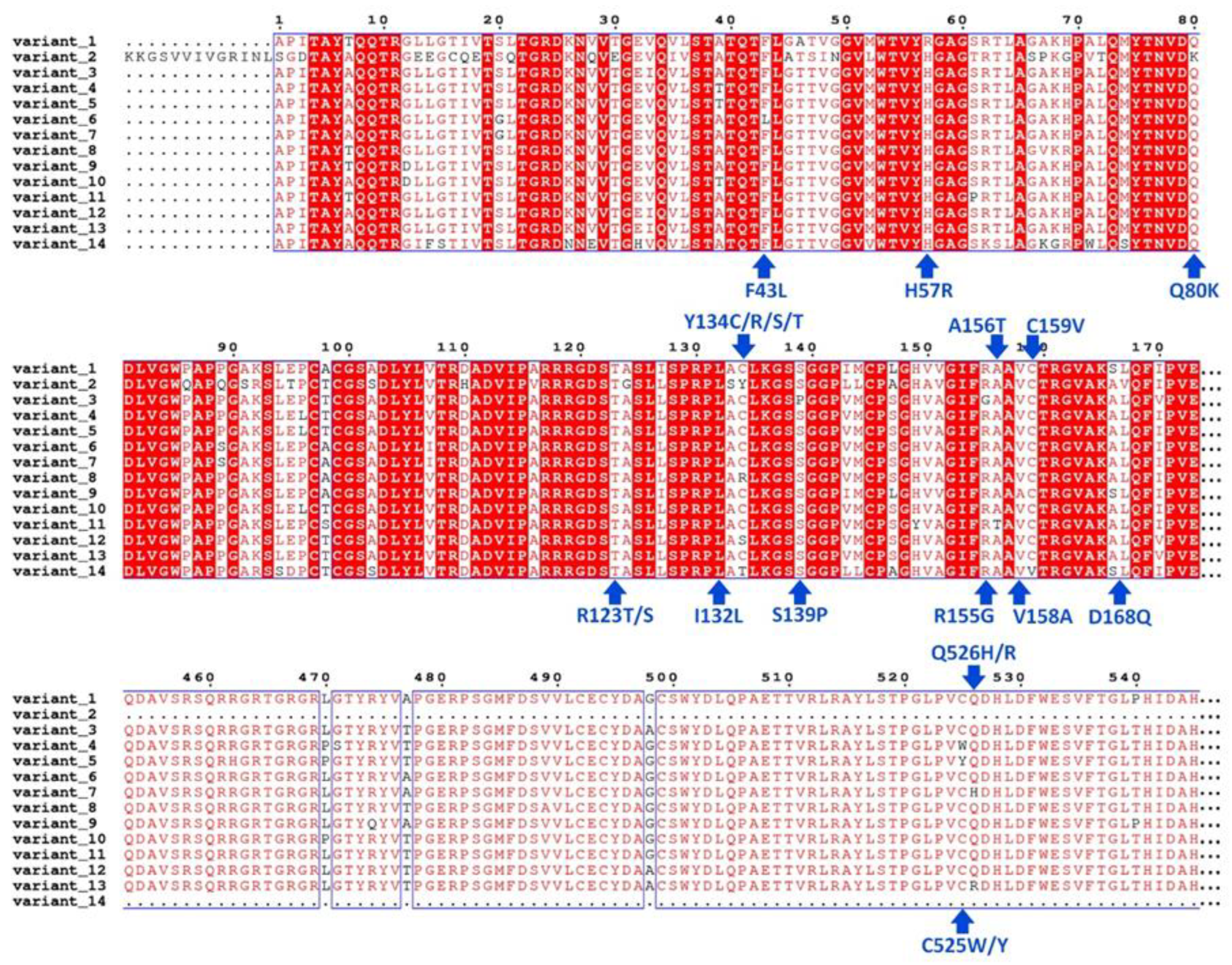
3.1. Analysis of Sequence Variation and Molecular Modeling
3.2. Ligand-Based Pharmacophore Search
3.3. Covalent Docking-Based Virtual Screening
3.4. Molecular Insights of Identified Potential Covalent Inhibitor (cpd-217)
3.5. The Stability and Flexibility of cpd-217 through MD Simulation
3.6. Binding Free Energy Calculated by MM/GBSA Method
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data and Software Availability
References
- Lindenbach, B.D.; Rice, C.M. Flaviviridae: the viruses and their replication, vol. 1; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Petruzziello, A.; Marigliano, S.; Loquercio, G.; Cozzolino, A.; Cacciapuoti, C. Global epidemiology of hepatitis C virus infection: An up-date of the distribution and circulation of hepatitis C virus genotypes. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 7824–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, A.A.; Martin, L.M.; Crone, C.; Ong, J.P.; Farmer, D.W.; Wise, T.; Robbins, S.C.; Younossi, Z.M. Depression, anemia and health-related quality of life in chronic hepatitis C. J. Hepatol. 2005, 44, 491–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoofnagle, J.H. Course and outcome of hepatitis C. Hepatology 2002, 36, S21–S29. [Google Scholar]
- Seeff, L.B. Natural history of chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology 2002, 36, s35–s46. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Simmonds, P. Genetic diversity and evolution of hepatitis C virus – 15 years on. J. Gen. Virol. 2004, 85, 3173–3188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.B.; Bukh, J.; Kuiken, C.; Muerhoff, A.S.; Rice, C.M.; Stapleton, J.T.; Simmonds, P. Expanded classification of hepatitis C virus into 7 genotypes and 67 subtypes: Updated criteria and genotype assignment web resource. Hepatology 2013, 59, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgia, S.M.; Hedskog, C.; Parhy, B.; Hyland, R.H.; Stamm, L.M.; Brainard, D.M.; Subramanian, M.G.; McHutchison, J.G.; Mo, H.; Svarovskaia, E.; et al. Identification of a Novel Hepatitis C Virus Genotype From Punjab, India: Expanding Classification of Hepatitis C Virus Into 8 Genotypes. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 218, 1722–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simmonds, P.; Bukh, J.; Combet, C.; Deléage, G.; Enomoto, N.; Feinstone, S.; Halfon, P.; Inchauspé, G.; Kuiken, C.; Maertens, G.; et al. Consensus proposals for a unified system of nomenclature of hepatitis C virus genotypes. Hepatology 2005, 42, 962–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organisation. Hepatitis C. 2019. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hepatitis-c (accessed on 1 May 2021).
- Messina, J.P.; Humphreys, I.; Flaxman, A.; Brown, A.; Cooke, G.S.; Pybus, O.G.; Barnes, E. Global distribution and prevalence of hepatitis C virus genotypes. Hepatology 2014, 61, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuypers, L.; Ceccherini-Silberstein, F.; Van Laethem, K.; Li, G.; Vandamme, A.; Rockstroh, J.K. Impact of HCV genotype on treatment regimens and drug resistance: a snapshot in time. Rev. Med Virol. 2016, 26, 408–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, D.G.; Sablon, E.; Chamberland, J.; Fournier, E.; Dandavino, R.; Tremblay, C.L. Hepatitis C Virus Genotype 7, a New Genotype Originating from Central Africa. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 967–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moradpour, D.; Penin, F.; Rice, C.M. Replication of hepatitis C virus. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2007, 5, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheel, T.K.H.; Rice, C.M. Understanding the hepatitis C virus life cycle paves the way for highly effective therapies. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 837–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benureau, Y.; Warter, L.; Malcolm, B.A.; Martin, A. A comparative analysis of the substrate permissiveness of HCV and GBV-B NS3/4A proteases reveals genetic evidence for an interaction with NS4B protein during genome replication. Virology 2010, 406, 228–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lackner, T.; Müller, A.; Pankraz, A.; Becher, P.; Thiel, H.-J.; Gorbalenya, A.E.; Tautz, N. Temporal Modulation of an Autoprotease Is Crucial for Replication and Pathogenicity of an RNA Virus. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 10765–10775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, C.T.; Murray, C.L.; Eastman, D.K.; Tassello, J.; Rice, C.M. Hepatitis C Virus p7 and NS2 Proteins Are Essential for Production of Infectious Virus. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 8374–8383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartenschlager, R.; Lohmann, V.; Penin, F. The molecular and structural basis of advanced antiviral therapy for hepatitis C virus infection. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 482–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raney, K.D.; Sharma, S.D.; Moustafa, I.M.; Cameron, C.E. Hepatitis C Virus Non-structural Protein 3 (HCV NS3): A Multifunctional Antiviral Target. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 22725–22731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezat, A.A.; El-Bialy, N.S.; Mostafa, H.I.A.; Ibrahim, M.A. Molecular Docking Investigation of the Binding Interactions of Macrocyclic Inhibitors with HCV NS3 Protease and its Mutants (R155K, D168A and A156V). Protein J. 2013, 33, 32–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, H.I.; El-Bialy, N.S.; Ezat, A.A.; Saleh, N.A.; Ibrahim, M.A. QSAR Analysis and Molecular Docking Simulation of Suggested Peptidomimetic NS3 Protease Inhibitors. Curr. Comput. Aided-Drug Des. 2014, 10, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Failla, C.; Tomei, L.; De Francesco, R. Both NS3 and NS4A are required for proteolytic processing of hepatitis C virus nonstructural proteins. J. Virol. 1994, 68, 3753–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCauley, J.A.; Rudd, M.T. Hepatitis C virus NS3/4a protease inhibitors. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2016, 30, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; De Clercq, E. Current therapy for chronic hepatitis C: The role of direct-acting antivirals. Antiviral Res. 2017, 142, 83–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Foy, E.; Ferreon, J.C.; Nakamura, M.; Ferreon, A.C.M.; Ikeda, M.; et al. Immune evasion by hepatitis C virus NS3/4A protease-mediated cleavage of the Toll-like receptor 3 adaptor protein TRIF. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2005, 102, 2992–2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foy, E.; Li, K.; Wang, C.; Sumpter, R.; Ikeda, M.; Lemon, S.M.; Gale, M. Regulation of Interferon Regulatory Factor-3 by the Hepatitis C Virus Serine Protease. Science 2003, 300, 1145–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawlotsky, J.; Chevaliez, S.; McHutchison, J.G. The Hepatitis C Virus Life Cycle as a Target for New Antiviral Therapies. Gastroenterology 2007, 132, 1979–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHutchison, J.G.; Patel, K. Future therapy of hepatitis C. Hepatology 2002, 36, S245–S252. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Malcolm, B.A.; Liu, R.; Lahser, F.; Agrawal, S.; Belanger, B.; Butkiewicz, N.; Chase, R.; Gheyas, F.; Hart, A.; Hesk, D.; et al. SCH 503034, a Mechanism-Based Inhibitor of Hepatitis C Virus NS3 Protease, Suppresses Polyprotein Maturation and Enhances the Antiviral Activity of Alpha Interferon in Replicon Cells. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 50, 1013–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwong, A.D.; Kauffman, R.S.; Hurter, P.; Mueller, P. Discovery and development of telaprevir: an NS3-4A protease inhibitor for treating genotype 1 chronic hepatitis C virus. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 993–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perni, R.B.; Almquist, S.J.; Byrn, R.A.; Chandorkar, G.; Chaturvedi, P.R.; Courtney, L.F.; Decker, C.J.; Dinehart, K.; Gates, C.A.; Harbeson, S.L.; et al. Preclinical Profile of VX-950, a Potent, Selective, and Orally Bioavailable Inhibitor of Hepatitis C Virus NS3-4A Serine Protease. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 50, 899–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arasappan, A.; Bennett, F.; Bogen, S.L.; Venkatraman, S.; Blackman, M.; Chen, K.X.; Hendrata, S.; Huang, Y.; Huelgas, R.M.; Nair, L.; et al. Discovery of Narlaprevir (SCH 900518): A Potent, Second Generation HCV NS3 Serine Protease Inhibitor. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 1, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashraf, M.U.; Iman, K.; Khalid, M.F.; Salman, H.M.; Shafi, T.; Rafi, M.; Javaid, N.; Hussain, R.; Ahmad, F.; Shahzad-Ul-Hussan, S.; et al. Evolution of efficacious pangenotypic hepatitis C virus therapies. Med. Res. Rev. 2018, 39, 1091–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heintges, T.; Encke, J.; zu Putlitz, J.; Wands, J.R. Inhibition of hepatitis C virus NS3 function by antisense oligodeoxynucleotides and protease inhibitor. J. Med Virol. 2001, 65, 671–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawlotsky, J.-M.; Negro, F.; Aghemo, A.; Berenguer, M.; Dalgard, O.; Dusheiko, G.; et al. EASL recommendations on treatment of hepatitis C 2018. J Hepatol. 2018, 69, 461–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumert, T.F.; Berg, T.; Lim, J.K.; Nelson, D.R. Status of Direct-Acting Antiviral Therapy for Hepatitis C Virus Infection and Remaining Challenges. Gastroenterology 2019, 156, 431–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falade-Nwulia, O.; Suarez-Cuervo, C.; Nelson, D.R.; Fried, M.W.; Segal, J.B.; Sulkowski, M.S. Oral direct-acting agent therapy for hepatitis C virus infection: a systematic review. Ann Intern Med. 2017, 166, 637–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- (AASLD) AA for the S of LD. HCV Guidance: Recommendations for Testing, Managing, and Treating Hepatitis C. Patients Who Develop Recurrent HCV Infection Post Liver Transplantation. Available online: https://www.hcvguidelines.org/unique-populations/post-liver-transplant (accessed on 1 May 2021).
- Organization, WH. Guidelines for the care and treatment of persons diagnosed with chronic hepatitis C virus infection. 2018.
- Lin, K.; Perni, R.B.; Kwong, A.D.; Lin, C. VX-950, a Novel Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) NS3-4A Protease Inhibitor, Exhibits Potent Antiviral Activities in HCV Replicon Cells. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2006, 50, 1813–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, W.; Hu, Z.; Jiang, X.; Decicco, C.P. Alpha-ketoamides, alpha-ketoesters and alpha-diketones as HCV NS3 protease inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2000, 10, 711–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yip, Y.; Victor, F.; Lamar, J.; Johnson, R.; Wang, Q.M.; Glass, J.I.; Yumibe, N.; Wakulchik, M.; Munroe, J.; Chen, S.-H. P4 and P1′ optimization of bicycloproline P2 bearing tetrapeptidyl α-ketoamides as HCV protease inhibitors. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2004, 14, 5007–5011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telaprevir (Incivek) and boceprevir (Victrelis) for chronic hepatitis C. Med Lett Drugs Ther. 2011, 53, 57–59.
- da Costa Leite, L.F.C. , Mourão, R.H.V., de Lima, M.D.C.A., Galdino, S.L., Hernandes, M.Z., Neves, F.D.A.R., Vidal, S., Barbe, J. and da Rocha Pitta, I.; et al. Synthesis, biological evaluation and molecular modeling studies of arylidene-thiazolidinediones with potential hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic activities. Eur J Med Chem. 2007, 42, 1263–1271. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Isakov, V.; Koloda, D.; Tikhonova, N.; Kikalishvili, T.; Krasavina, E.; Lekishvili, K.; Malaya, I.; Ryska, M.; Samsonov, M.; Tolkacheva, V. Pharmacokinetics of the New Hepatitis C Virus NS3 Protease Inhibitor Narlaprevir following Single-Dose Use with or without Ritonavir in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 7098–7104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayevskaya, M.V.; Ivashkin, V.T.; Znoyko, O.O.; Klimova, E.A.; Abdurakhmanov, D.T.; Bakulin, I.G.; Bogomolov, P.O.; Burnevich, E.Z.; Galushko, M.Y.; Geyvandova, N.I.; Zhdanov, K.V. Klimova2 DTA. Efficacy and safety of the Russian protease inhibitor narlaprevir at treatment-naive and earlier treated noncirrhotic patients with the 1st genotype chronic hepatitis C (PIONEER study). Russ J Gastroenterol Hepatol Coloproctology 2017, 27, 41–51. [Google Scholar]
- Gane, E.J.; Stedman, C.A.; Ding, X.; Svarovskaia, E.; Symonds, W.T.; Hindes, R.G.; Berrey, M.M. Nucleotide Polymerase Inhibitor Sofosbuvir plus Ribavirin for Hepatitis C. New Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeuzem, S.; Ghalib, R.; Reddy, K.R.; Pockros, P.J.; Ben Ari, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Brown, D.D.; Wan, S.; DiNubile, M.J.; Nguyen, B.-Y.; et al. Grazoprevir–Elbasvir Combination Therapy for Treatment-Naive Cirrhotic and Noncirrhotic Patients With Chronic Hepatitis C Virus Genotype 1, 4, or 6 Infection. Ann. Intern. Med. 2015, 163, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rockstroh, J.K. Summary from AASLD 2015 for Hepatitis C Beyond 95% SVR cure rates: still room for improvement? 2015. Available online: https://www.natap.org/2015/AASLD/AASLD_165.htm (accessed on 1 May 2021).
- Bacon, B.R.; Gordon, S.C.; Lawitz, E.; Marcellin, P.; Vierling, J.M.; Zeuzem, S.; Poordad, F.; Goodman, Z.D.; Sings, H.L.; Boparai, N.; et al. Boceprevir for Previously Treated Chronic HCV Genotype 1 Infection. New Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 1207–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobson, I.M.; McHutchison, J.G.; Dusheiko, G.; Di Bisceglie, A.M.; Reddy, K.R.; Bzowej, N.H.; Marcellin, P.; Muir, A.J.; Ferenci, P.; Flisiak, R.; et al. Telaprevir for Previously Untreated Chronic Hepatitis C Virus Infection. New Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 2405–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, W.; Ban, Y.; Liu, H.; Yao, X. Computational study on the drug resistance mechanism against HCV NS3/4A protease inhibitors vaniprevir and MK-5172 by the combination use of molecular dynamics simulation, residue interaction network, and substrate envelope analysis. J Chem Inf Model. 2014, 54, 621–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, D.; Xue, W.; Zhang, W.; Liu, H.; Yao, X. Understanding the drug resistance mechanism of hepatitis C virus NS3/4A to ITMN-191 due to R155K, A156V, D168A/E mutations: a computational study. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA)-General Subj. 2012, 1820, 1526–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özen, A.; Sherman, W.; Schiffer, C.A. Improving the resistance profile of hepatitis C NS3/4A inhibitors: Dynamic substrate envelope guided design. J Chem Theory Comput. 2013, 9, 5693–5705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meeprasert, A.; Hannongbua, S.; Rungrotmongkol, T. Key binding and susceptibility of NS3/4A serine protease inhibitors against hepatitis C virus. J Chem Inf Model. 2014, 54, 1208–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Sun, H.; Li, Y.; Pan, P.; Li, D.; Hou, T. The competitive binding between inhibitors and substrates of HCV NS3/4A protease: a general mechanism of drug resistance. Antiviral Res. 2014, 103, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, W.; Pan, D.; Yang, Y.; Liu, H.; Yao, X. Molecular modeling study on the resistance mechanism of HCV NS3/4A serine protease mutants R155K, A156V and D168A to TMC435. Antiviral Res. 2012, 93, 126–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, M.I.; Rahman, M.; Hassan, M.U.; Iqbal, M. Prevalence of active hepatitis C virus infections among general public of Lahore, Pakistan. Virol. J. 2013, 10, 351–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goossens, N.; Negro, F. Is genotype 3 of the hepatitis C virus the new villain? Hepatology 2014, 59, 2403–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komatsu, T.E.; Boyd, S.; Sherwat, A.; Tracy, L.; Naeger, L.K.; O’rear, J.J.; Harrington, P.R. Regulatory Analysis of Effects of Hepatitis C Virus NS5A Polymorphisms on Efficacy of Elbasvir and Grazoprevir. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 586–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeuzem, S.; Mizokami, M.; Pianko, S.; Mangia, A.; Han, K.-H.; Martin, R.; Svarovskaia, E.; Dvory-Sobol, H.; Doehle, B.; Hedskog, C.; et al. NS5A resistance-associated substitutions in patients with genotype 1 hepatitis C virus: Prevalence and effect on treatment outcome. J. Hepatol. 2017, 66, 910–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrington, P.R.; Komatsu, T.E.; Deming, D.J.; Donaldson, E.F.; O'Rear, J.J.; Naeger, L.K. Impact of hepatitis C virus polymorphisms on direct-acting antiviral treatment efficacy: Regulatory analyses and perspectives. Hepatology 2017, 67, 2430–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanwal, F.; Kramer, J.R.; Ilyas, J.; Duan, Z.; El-Serag, H.B. HCV genotype 3 is associated with an increased risk of cirrhosis and hepatocellular cancer in a national sample of U.S. Veterans with HCV. Hepatology 2014, 60, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanwal, F.; Kramer, J.R.; Ilyas, J.; Duan, Z.; El-Serag, H.B. HCV genotype 3 is associated with an increased risk of cirrhosis and hepatocellular cancer in a national sample of U.S. Veterans with HCV. Hepatology 2014, 60, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorbo, M.C.; Cento, V.; Di Maio, V.C.; Howe, A.Y.; Garcia, F.; Perno, C.F.; Ceccherini-Silberstein, F. Hepatitis C virus drug resistance associated substitutions and their clinical relevance: Update 2018. Drug Resist. Updat. 2018, 37, 17–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soumana, D.I.; Yilmaz, N.K.; Ali, A.; Prachanronarong, K.L.; Schiffer, C.A. Molecular and Dynamic Mechanism Underlying Drug Resistance in Genotype 3 Hepatitis C NS3/4A Protease. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 11850–11859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, K.P.; Ali, A.; Aydin, C.; Soumana, D.; Özen, A.; Deveau, L.M.; Silver, C.; Cao, H.; Newton, A.; Petropoulos, C.J.; et al. The Molecular Basis of Drug Resistance against Hepatitis C Virus NS3/4A Protease Inhibitors. PLOS Pathog. 2012, 8, e1002832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlotsky, J.-M. Hepatitis C Virus Resistance to Direct-Acting Antiviral Drugs in Interferon-Free Regimens. Gastroenterology 2016, 151, 70–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarrazin, C. The importance of resistance to direct antiviral drugs in HCV infection in clinical practice. J. Hepatol. 2015, 64, 486–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, A.; Aydin, C.; Gildemeister, R.; Romano, K.P.; Cao, H.; Özen, A.; Soumana, D.; Newton, A.; Petropoulos, C.J.; Huang, W.; et al. Evaluating the Role of Macrocycles in the Susceptibility of Hepatitis C Virus NS3/4A Protease Inhibitors to Drug Resistance. ACS Chem. Biol. 2013, 8, 1469–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wyles, D.L.; Gutierrez, J.A. Importance of HCV genotype 1 subtypes for drug resistance and response to therapy. J. Viral Hepat. 2014, 21, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahser, F.; Galloway, A.; Hwang, P.; Palcza, J.; Wahl, J.; Robertson, M.; et al. Interim analysis of a 3-year follow-up study of NS5A and NS3 resistance-associated variants (RAVs) after treatment with grazoprevir-containing regimens in patients with chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection. In Hepatology; WILEY-BLACKWELL: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Krishnan, P.; Tripathi, R.; Schnell, G.; Reisch, T.; Beyer, J.; Dekhtyar, T.; et al. O057: Long-term follow-up of treatment-emergent resistance-associated variants in NS3, NS5A and NS5B with paritaprevir/r-, ombitasvir-and dasabuvir-based regimens. J Hepatol. 2015, 62, S220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gane, E.J.; Svarovskaia, E.S.; Hyland, R.H.; Stamm, L.M.; Osinusi, A.; Brainard, D.M.; et al. resistance Analysis of Treatment-naïve and Daa-experienced Genotype 1 Patients with and without Cirrhosis Who Received Short-duration Treatment with Sofosbuvir/gs-5816+ Gs-9857: 713. Hepatology 2015, 62, 563A. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, M.; Mani, N.; Lin, C.; Ardzinski, A.; Nelson, M.; Reagan, D.; Bartels, D.; Zhou, Y.; Nicolas, O.; Rao, B.G.; et al. In Vitro Phenotypic Characterization of Hepatitis C Virus NS3 Protease Variants Observed in Clinical Studies of Telaprevir. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 6236–6245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatel-Chaix, L.; Baril, M.; Lamarre, D. Hepatitis C Virus NS3/4A Protease Inhibitors: A Light at the End of the Tunnel. Viruses 2010, 2, 1752–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poordad, F.; Pol, S.; Asatryan, A.; Buti, M.; Shaw, D.; Hézode, C.; Felizarta, F.; Reindollar, R.W.; Gordon, S.C.; Pianko, S.; et al. Glecaprevir/Pibrentasvir in patients with hepatitis C virus genotype 1 or 4 and past direct-acting antiviral treatment failure. Hepatology 2018, 67, 1253–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khattab, M.A.; Ferenci, P.; Hadziyannis, S.J.; Colombo, M.; Manns, M.P.; Almasio, P.L.; Esteban, R.; Abdo, A.A.; Harrison, S.A.; Ibrahim, N.; et al. Management of hepatitis C virus genotype 4: Recommendations of An International Expert Panel. J. Hepatol. 2010, 54, 1250–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.H.; Keeffe, E.B. Chronic hepatitis C: genotypes 4 to 9. Clin Liver Dis. 2005, 9, 411–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cento, V.; Mirabelli, C.; Salpini, R.; Dimonte, S.; Artese, A.; Costa, G.; Mercurio, F.; Svicher, V.; Parrotta, L.; Bertoli, A.; et al. HCV Genotypes Are Differently Prone to the Development of Resistance to Linear and Macrocyclic Protease Inhibitors. PLOS ONE 2012, 7, e39652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Courcambeck, J.; Bouzidi, M.; Perbost, R.; Jouirou, B.; Amrani, N.; Cacoub, P.; et al. Resistance of hepatitis C virus to NS3-4A protease inhibitors: mechanisms of drug resistance induced by R155Q, A156T, D168A and D168V mutations. Antivir Ther. 2006, 11, 847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batool, M.; Ahmad, B.; Choi, S. A Structure-Based Drug Discovery Paradigm. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slater, O.; Kontoyianni, M. The compromise of virtual screening and its impact on drug discovery. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2019, 14, 619–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirza, M.U.; Vanmeert, M.; Ali, A.; Iman, K.; Froeyen, M.; Idrees, M. Perspectives towards antiviral drug discovery against Ebola virus. J. Med Virol. 2018, 91, 2029–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Khaliq, M.; Suk, J.-E.; Patkar, C.; Li, L.; Kuhn, R.J.; Post, C.B. Antiviral Compounds Discovered by Virtual Screening of Small−Molecule Libraries against Dengue Virus E Protein. ACS Chem. Biol. 2008, 3, 765–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, F.R.S.; Nunes, D.A.F.; Lima, W.G.; Davyt, D.; Santos, L.L.; Taranto, A.G.; Ferreira, J.M.S. Identification of Zika Virus NS2B-NS3 Protease Inhibitors by Structure-Based Virtual Screening and Drug Repurposing Approaches. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2020, 60, 731–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, S.; Chan, J.F.-W.; Den-Haan, H.; Chik, K.K.-H.; Zhang, A.J.; Chan, C.C.-S.; Poon, V.K.-M.; Yip, C.C.-Y.; Mak, W.W.-N.; Zhu, Z.; et al. Structure-based discovery of clinically approved drugs as Zika virus NS2B-NS3 protease inhibitors that potently inhibit Zika virus infection in vitro and in vivo. Antivir. Res. 2017, 145, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, L.S.; Amaro, R.E.; Xu, D.; Li, W.W.; Arzberger, P.W.; McCammon, J.A. Ensemble-Based Virtual Screening Reveals Potential Novel Antiviral Compounds for Avian Influenza Neuraminidase. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 3878–3894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.T.H.; Ryu, H.-J.; Lee, S.-H.; Hwang, S.; Breton, V.; Rhee, J.H.; Kim, D. Virtual screening identification of novel severe acute respiratory syndrome 3C-like protease inhibitors and in vitro confirmation. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 21, 3088–3091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirza, M.U.; Froeyen, M. Structural elucidation of SARS-CoV-2 vital proteins: Computational methods reveal potential drug candidates against main protease, Nsp12 polymerase and Nsp13 helicase. J Pharm Anal. 2020, 10, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaikh, F.; Zhao, Y.; Alvarez, L.; Iliopoulou, M.; Lohans, C.T.; Schofield, C.J.; Padilla-Parra, S.; Siu, S.W.I.; Fry, E.E.; Ren, J.; et al. Structure-Based in Silico Screening Identifies a Potent Ebolavirus Inhibitor from a Traditional Chinese Medicine Library. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 2928–2937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousuf, Z.; Iman, K.; Iftikhar, N.; Mirza, M.U. Structure-based virtual screening and molecular docking for the identification of potential multi-targeted inhibitors against breast cancer. Breast Cancer: Targets Ther. 2017, 9, 447–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iman, K.; Mirza, M.U.; Mazhar, N.; Vanmeert, M.; Irshad, I.; Kamal, M.A.; Ikram, N.; Riaz, M. In silico Structure-based Identification of Novel Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors Against Alzheimer’s Disease. CNS Neurol. Disord. - Drug Targets 2018, 17, 54–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirza, M.U.; Saadabadi, A.; Vanmeert, M.; Salo-Ahen, O.M.; Abdullah, I.; Claes, S.; De Jonghe, S.; Schols, D.; Ahmad, S.; Froeyen, M. Discovery of HIV entry inhibitors via a hybrid CXCR4 and CCR5 receptor pharmacophore-based virtual screening approach. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 155, 105537–105537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearse, M.; Moir, R.; Wilson, A.; Stones-Havas, S.; Cheung, M.; Sturrock, S.; Buxton, S.; Cooper, A.; Markowitz, S.; Duran, C.; et al. Geneious Basic: An integrated and extendable desktop software platform for the organization and analysis of sequence data. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 1647–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, H.M.; Westbrook, J.; Feng, Z.; Gilliland, G.; Bhat, T.N.; Weissig, H.; Shindyalov, I.N.; Bourne, P.E. The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laskowski, R.A.; Swindells, M.B. LigPlot+: Multiple ligand–protein interaction diagrams for drug discovery. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2011, 51, 2778–2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maestro. Schrödinger Release 2021-3: Maestro; Schrödinger, LLC: New York, NY, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Sievers, F.; Higgins, D.G. Clustal Omega, accurate alignment of very large numbers of sequences. Methods Mol. Biol. 2014, 1079, 105–116. [Google Scholar]
- Robert, X.; Gouet, P. Deciphering key features in protein structures with the new ENDscript server. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, W320–W324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.; Zaretskaya, I.; Raytselis, Y.; Merezhuk, Y.; McGinnis, S.; Madden, T.L. NCBI BLAST: a better web interface. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, W5–W9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwede, T.; Kopp, J.; Guex, N.; Peitsch, M.C. SWISS-MODEL: an automated protein homology-modeling server. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 3381–3385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, L.; Park, H.; Seok, C. GalaxyRefine: protein structure refinement driven by side-chain repacking. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, W384–W388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Godzik, A. FATCAT: a web server for flexible structure comparison and structure similarity searching. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, W582–W585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawabata, T. MATRAS: a program for protein 3D structure comparison. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 3367–3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colovos, C.; Yeates, T.O. Verification of protein structures: Patterns of nonbonded atomic interactions. Protein Sci. 1993, 2, 1511–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiederstein, M.; Sippl, M.J. ProSA-web: interactive web service for the recognition of errors in three-dimensional structures of proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, W407–W410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SAVES Server. Available online: https://saves.mbi.ucla.edu/ (accessed on 1 May 2021).
- Davis, I.W.; Leaver-Fay, A.; Chen, V.B.; Block, J.N.; Kapral, G.J.; Wang, X.; Murray, L.W.; Arendall, W.B.; Snoeyink, J.; Richardson, J.S.; et al. MolProbity: all-atom contacts and structure validation for proteins and nucleic acids. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, W375–W383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenberg D, Lüthy R, Bowie JU. [20] VERIFY3D: assessment of protein models with three-dimensional profiles. Methods in enzymology. Elsevier; 1997. pp. 396–404.
- Laskowski, R.A.; MacArthur, M.W.; Moss, D.S.; Thornton, J.M. PROCHECK: a program to check the stereochemical quality of protein structures. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1993, 26, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Couch, G.S.; Greenblatt, D.M.; Meng, E.C.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF Chimera?A visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, S.L.; Smondyrev, A.M.; Rao, S.N. PHASE: A Novel Approach to Pharmacophore Modeling and 3D Database Searching. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2006, 67, 370–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, S.L.; Smondyrev, A.M.; Knoll, E.H.; Rao, S.N.; Shaw, D.E.; Friesner, R.A. PHASE: a new engine for pharmacophore perception, 3D QSAR model development, and 3D database screening: 1. Methodology and preliminary results. J. Comput. Mol. Des. 2006, 20, 647–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irwin, J.J.; Shoichet, B.K. ZINC—A Free Database of Commercially Available Compounds for Virtual Screening. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2005, 45, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MolPort. MolPort Database. Available online: https://www.molport.com (accessed on 1 May 2021).
- Kim, S.; Chen, J.; Cheng, T.; Gindulyte, A.; He, J.; He, S.; Li, Q.; Shoemaker, B.A.; Thiessen, P.A.; Yu, B.; et al. PubChem in 2021: new data content and improved web interfaces. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D1388–D1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiss, R.; Sandor, M.; A Szalai, F. http://Mcule.com: a public web service for drug discovery. J. Chemin- 2012, 4, P17–P17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaulton, A.; Hersey, A.; Nowotka, M.; Bento, A.P.; Chambers, J.; Mendez, D.; Mutowo, P.; Atkinson, F.; Bellis, L.J.; Cibrián-Uhalte, E.; et al. The ChEMBL database in 2017. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunseri, J.; Koes, D.R. Pharmit: interactive exploration of chemical space. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, W442–W448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipinski, C.A.; Lombardo, F.; Dominy, B.W.; Feeney, P.J. Experimental and computational approaches to estimate solubility and permeability in drug discovery and development settings. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 1997, 23, 3–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-López, E.; Naveja, J.J.; Medina-Franco, J.L. DataWarrior: an evaluation of the open-source drug discovery tool. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2019, 14, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sastry, G.M.; Adzhigirey, M.; Day, T.; Annabhimoju, R.; Sherman, W. Protein and ligand preparation: Parameters, protocols, and influence on virtual screening enrichments. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2013, 27, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelley, J.C.; Cholleti, A.; Frye, L.L.; Greenwood, J.R.; Timlin, M.R.; Uchimaya, M. Epik: a software program for pK a prediction and protonation state generation for drug-like molecules. J. Comput. Mol. Des. 2007, 21, 681–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, M.H.M.; Søndergaard, C.R.; Rostkowski, M.; Jensen, J.H. PROPKA3: consistent treatment of internal and surface residues in empirical p K a predictions. J Chem Theory Comput. 2011, 7, 525–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LigPrep. Schrödinger Release 2021-3: LigPrep; Schrödinger, LLC: New York, NY, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, K.; Borrelli, K.W.; Greenwood, J.R.; Day, T.; Abel, R.; Farid, R.S.; Harder, E. Docking Covalent Inhibitors: A Parameter Free Approach To Pose Prediction and Scoring. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2014, 54, 1932–1940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LLC, S. Prime, Version 3.9; Schrödinger, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, K.; Shirts, M.R.; Friesner, R.A. Improved Methods for Side Chain and Loop Predictions via the Protein Local Optimization Program: Variable Dielectric Model for Implicitly Improving the Treatment of Polarization Effects. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2007, 3, 2108–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Abel, R.; Zhu, K.; Cao, Y.; Zhao, S.; Friesner, R.A. The VSGB 2.0 model: A next generation energy model for high resolution protein structure modeling. Proteins: Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2011, 79, 2794–2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roos, K.; Wu, C.; Damm, W.; Reboul, M.; Stevenson, J.M.; Lu, C.; Dahlgren, M.K.; Mondal, S.; Chen, W.; Wang, L.; et al. OPLS3e: Extending Force Field Coverage for Drug-Like Small Molecules. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2019, 15, 1863–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friesner, R.A.; Banks, J.L.; Murphy, R.B.; Halgren, T.A.; Klicic, J.J.; Mainz, D.T.; Repasky, M.P.; Knoll, E.H.; Shelley, M.; Perry, J.K.; et al. Glide: A New Approach for Rapid, Accurate Docking and Scoring. 1. Method and Assessment of Docking Accuracy. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 1739–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Case DA, Belfon K, Ben-Shalom I, Brozell SR, Cerutti D, Cheatham T, et al. Amber 2020. 2020.
- Mirza, M.U.; Rafique, S.; Ali, A.; Munir, M.; Ikram, N.; Manan, A.; Salo-Ahen, O.M.H.; Idrees, M. Towards peptide vaccines against Zika virus: Immunoinformatics combined with molecular dynamics simulations to predict antigenic epitopes of Zika viral proteins. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbar, B.; Rafique, S.; Salo-Ahen, O.M.H.; Ali, A.; Munir, M.; Idrees, M.; Mirza, M.U.; Vanmeert, M.; Shah, S.Z.; Jabbar, I.; et al. Antigenic Peptide Prediction From E6 and E7 Oncoproteins of HPV Types 16 and 18 for Therapeutic Vaccine Design Using Immunoinformatics and MD Simulation Analysis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 3000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikram, N.; Mirza, M.U.; Vanmeert, M.; Froeyen, M.; Salo-Ahen, O.M.H.; Tahir, M.; Qazi, A.; Ahmad, S. Inhibition of Oncogenic Kinases: An In Vitro Validated Computational Approach Identified Potential Multi-Target Anticancer Compounds. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wolf, R.M.; Caldwell, J.W.; Kollman, P.A.; Case, D.A. Development and testing of a general amber force field. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1157–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgensen, W.L.; Chandrasekhar, J.; Madura, J.D.; Impey, R.W.; Klein, M.L. Comparison of simple potential functions for simulating liquid water. J. Chem. Phys. 1983, 79, 926–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryckaert, J.-P.; Ciccotti, G.; Berendsen, H.J.C. Numerical integration of the cartesian equations of motion of a system with constraints: Molecular dynamics of n-alkanes. J. Comput. Phys. 1977, 23, 327–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roe, D.R.; Cheatham, T.E., III. PTRAJ and CPPTRAJ: software for processing and analysis of molecular dynamics trajectory data. J Chem Theory Comput. 2013, 9, 3084–3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genheden, S.; Ryde, U.; Söderhjelm, P. Binding affinities by alchemical perturbation using QM/MM with a large QM system and polarizable MM model. J. Comput. Chem. 2015, 36, 2114–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.I.; Khan, Z.A.; Baig, M.H.; Ahmad, I.; Farouk, A.-E.; Song, Y.G.; et al. Comparative genome analysis of novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) from different geographical locations and the effect of mutations on major target proteins: An in silico insight. PLoS One 2020, 15, e0238344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, I.M.; Dore, G.J.; Foster, G.R.; Fried, M.W.; Radu, M.; Rafalsky, V.V.; Moroz, L.; Craxi, A.; Peeters, M.; Lenz, O.; et al. Simeprevir with pegylated interferon alfa 2a plus ribavirin in treatment-naive patients with chronic hepatitis C virus genotype 1 infection (QUEST-1): a phase 3, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2014, 384, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawitz, E.; Matusow, G.; DeJesus, E.; Yoshida, E.M.; Felizarta, F.; Ghalib, R.; Godofsky, E.; Herring, R.W.; Poleynard, G.; Sheikh, A.; et al. Simeprevir plus sofosbuvir in patients with chronic hepatitis C virus genotype 1 infection and cirrhosis: A phase 3 study (OPTIMIST-2). Hepatology 2016, 64, 360–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forns, X.; Lawitz, E.; Zeuzem, S.; Gane, E.; Bronowicki, J.P.; Andreone, P.; Horban, A.; Brown, A.; Peeters, M.; Lenz, O.; et al. Simeprevir With Peginterferon and Ribavirin Leads to High Rates of SVR in Patients With HCV Genotype 1 Who Relapsed After Previous Therapy: A Phase 3 Trial. Gastroenterology 2014, 146, 1669–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summa, V.; Ludmerer, S.W.; McCauley, J.A.; Fandozzi, C.; Burlein, C.; Claudio, G.; et al. MK-5172, a selective inhibitor of hepatitis C virus NS3/4a protease with broad activity across genotypes and resistant variants. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 4161–4167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawitz, E.; Yang, J.C.; Stamm, L.M.; Taylor, J.G.; Cheng, G.; Brainard, D.M.; Miller, M.D.; Mo, H.; Dvory-Sobol, H. Characterization of HCV Resistance from a 3-Day Monotherapy Study of Voxilaprevir, a Novel Pangenotypic NS3/4A Protease Inhibitor. Antivir. Ther. 2017, 23, 325–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forestier, N.; Susser, S.; Welker, M.W.; Weegink, C.J.; Reesink, H.W.; Zeuzem, S.; et al. Telaprevir resistance mutations in patients with hepatitis C who relapsed after sequential therapy with telaprevir, peg-interferon alfa 2a and ribavirin. In Hepatology; JOHN WILEY & SONS INC: HOBOKEN, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Susser, S.; Welsch, C.; Wang, Y.; Zettler, M.; Domingues, F.S.; Karey, U.; Hughes, E.; Ralston, R.; Tong, X.; Herrmann, E.; et al. Characterization of resistance to the protease inhibitor boceprevir in hepatitis C virus-infected patients. Hepatology 2009, 50, 1709–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McPhee, F.; Friborg, J.; Levine, S.; Chen, C.; Falk, P.; Yu, F.; Hernandez, D.; Lee, M.S.; Chaniewski, S.; Sheaffer, A.K.; et al. Resistance Analysis of the Hepatitis C Virus NS3 Protease Inhibitor Asunaprevir. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 3670–3681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenz, O.; Verbinnen, T.; Lin, T.-I.; Vijgen, L.; Cummings, M.D.; Lindberg, J.; et al. In vitro resistance profile of the hepatitis C virus NS3/4A protease inhibitor TMC435. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2010, 54, 1878–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triballeau, N.; Acher, F.; Brabet, I.; Pin, J.-P.; Bertrand, H.-O. Virtual screening workflow development guided by the “receiver operating characteristic” curve approach. Application to high-throughput docking on metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype 4. J Med Chem. 2005, 48, 2534–2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Xie, H.-Z.; Yang, S.-Y.; Chen, J.-J.; Ren, J.-X.; Wei, Y.-Q. Towards more accurate pharmacophore modeling: Multicomplex-based comprehensive pharmacophore map and most-frequent-feature pharmacophore model of CDK2. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2008, 27, 430–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venkatraman, S.; Bogen, S.L.; Arasappan, A.; Bennett, F.; Chen, K.; Jao, E.; Liu, Y.-T.; Lovey, R.; Hendrata, S.; Huang, Y.; et al. Discovery of (1R,5S)-N-[3-Amino-1-(cyclobutylmethyl)-2,3-dioxopropyl]- 3-[2(S)-[[[(1,1-dimethylethyl)amino]carbonyl]amino]-3,3-dimethyl-1-oxobutyl]- 6,6-dimethyl-3-azabicyclo[3.1.0]hexan-2(S)-carboxamide (SCH 503034), a Selective, Potent, Orally Bioavailable Hepatitis C Virus NS3 Protease Inhibitor: A Potential Therapeutic Agent for the Treatment of Hepatitis C Infection. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 6074–6086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.; Kwong, A.D.; Perni, R.B. Discovery and development of VX-950, a novel, covalent, and reversible inhibitor of hepatitis C virus NS3. 4A serine protease. Infect Disord Targets (Formerly Curr Drug Targets-Infectious Disord. 2006, 6, 3–16. [Google Scholar]
- Pillaiyar, T.; Meenakshisundaram, S.; Manickam, M. Recent discovery and development of inhibitors targeting coronaviruses. Drug Discov. Today 2020, 25, 668–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, B.; He, F.; Liu, D.; Fang, M.; Wu, Z.; Xu, D. AI-aided design of novel targeted covalent inhibitors against SARS-CoV-2. BioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howe, A.Y.M.; Venkatraman, S. The discovery and development of boceprevir: A novel, first-generation inhibitor of the hepatitis C virus NS3/4A serine protease. J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2013, 1, 22. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Romano, K.P.; Ali, A.; Royer, W.E.; Schiffer, C.A. Drug resistance against HCV NS3/4A inhibitors is defined by the balance of substrate recognition versus inhibitor binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2010, 107, 20986–20991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarrazin, C.; Kieffer, T.L.; Bartels, D.; Hanzelka, B.; Müh, U.; Welker, M.; Wincheringer, D.; Zhou, Y.; Chu, H.; Lin, C.; et al. Dynamic Hepatitis C Virus Genotypic and Phenotypic Changes in Patients Treated With the Protease Inhibitor Telaprevir. Gastroenterology 2007, 132, 1767–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Muöh, U.; Hanzelka, B.L.; Bartels, D.J.; Wei, Y.; Rao, B.G.; et al. Phenotypic and structural analyses of hepatitis C virus NS3 protease Arg155 variants: sensitivity to telaprevir (VX-950) and interferon α. J Biol Chem. 2007, 282, 22619–22628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durrant, J.D.; McCammon, J.A. Molecular dynamics simulations and drug discovery. BMC Biol. 2011, 9, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Kokubo, H. Exploring the Stability of Ligand Binding Modes to Proteins by Molecular Dynamics Simulations: A Cross-docking Study. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2017, 57, 2514–2522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, B.; Ashfaq, U.A.; Mirza, M.U. Medicinal plant phytochemicals and their inhibitory activities against pancreatic lipase: molecular docking combined with molecular dynamics simulation approach. Nat. Prod. Res. 2017, 32, 1123–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durdagi, S.; Qamar, M.T.U.; Salmas, R.E.; Tariq, Q.; Anwar, F.; Ashfaq, U.A. Investigating the molecular mechanism of staphylococcal DNA gyrase inhibitors: A combined ligand-based and structure-based resources pipeline. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2018, 85, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muneer, I.; Tusleem, K.; Abdul Rauf, S.; Hussain, H.M.J.; Siddiqi, A.R. Discovery of selective inhibitors for cyclic AMP response element-binding protein: a combined ligand and structure-based resources pipeline. Anticancer Drugs 2019, 30, 363–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Sun, H.; Pan, P.; Li, Y.; Li, D.; Hou, T. Exploring resistance mechanisms of HCV NS3/4A protease mutations to MK5172: insight from molecular dynamics simulations and free energy calculations. Mol Biosyst. 2015, 11, 2568–2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Geng, L.; Chen, B.-Z.; Ji, M. Computational study on the molecular mechanisms of drug resistance of Narlaprevir due to V36M, R155K, V36M+R155K, T54A, and A156T mutations of HCV NS3/4A protease. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2014, 92, 357–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, R.; Tripathi, T. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Protein and Protein–Ligand Complexes. In Computer-Aided Drug Design; Springer, 2020; pp. 133–161. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, E.; Sun, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Liu, H.; Zhang, J.Z.H.; Hou, T. End-Point Binding Free Energy Calculation with MM/PBSA and MM/GBSA: Strategies and Applications in Drug Design. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 9478–9508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guterres, H.; Im, W. Improving Protein-Ligand Docking Results with High-Throughput Molecular Dynamics Simulations. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2020, 60, 2189–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pikkemaat, M.G.; Linssen, A.B.; Berendsen, H.J.; Janssen, D.B. Molecular dynamics simulations as a tool for improving protein stability. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 2002, 15, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Hou, T.; Wang, W.; Liu, J.S. Detecting and understanding combinatorial mutation patterns responsible for HIV drug resistance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2010, 107, 1321–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, T.; McLaughlin, W.A.; Wang, W. Evaluating the potency of HIV-1 protease drugs to combat resistance. Proteins: Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2007, 71, 1163–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, T.; Yu, R. Molecular Dynamics and Free Energy Studies on the Wild-type and Double Mutant HIV-1 Protease Complexed with Amprenavir and Two Amprenavir-Related Inhibitors: Mechanism for Binding and Drug Resistance. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 1177–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Li, Y.; Tian, S.; Wang, J.; Hou, T. P-loop Conformation Governed Crizotinib Resistance in G2032R-Mutated ROS1 Tyrosine Kinase: Clues from Free Energy Landscape. PLOS Comput. Biol. 2014, 10, e1003729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Li, Y.; Shen, M.; Li, D.; Kang, Y.; Hou, T. Characterizing Drug–Target Residence Time with Metadynamics: How To Achieve Dissociation Rate Efficiently without Losing Accuracy against Time-Consuming Approaches. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2017, 57, 1895–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, T.; Zhang, W.; Wang, J.; Wang, W. Predicting drug resistance of the HIV-1 protease using molecular interaction energy components. Proteins: Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2008, 74, 837–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Yao, X.; Wang, C.; Han, J. In Silico Identification of the Potential Drug Resistance Sites over 2009 Influenza A (H1N1) Virus Neuraminidase. Mol. Pharm. 2010, 7, 894–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salo-Ahen, O.M.H.; Alanko, I.; Bhadane, R.; Bonvin, A.M.J.J.; Honorato, R.V.; Hossain, S.; Juffer, A.H.; Kabedev, A.; Lahtela-Kakkonen, M.; Larsen, A.S.; et al. Molecular Dynamics Simulations in Drug Discovery and Pharmaceutical Development. Processes 2020, 9, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Kollman, P.A. Computational study of protein specificity: The molecular basis of HIV-1 protease drug resistance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2001, 98, 14937–14942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Ainsworth, R.I.; Ding, B.; Hou, T.; Wang, W. Using Hierarchical Virtual Screening To Combat Drug Resistance of the HIV-1 Protease. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2015, 55, 1400–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.X.; Zheng, J.J. Computational studies of H5N1 influenza virus resistance to oseltamivir. Protein Sci. 2009, 18, 707–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Li, W.; Zheng, Q.; Zhang, H. A molecular dynamics investigation into the mechanisms of alectinib resistance of three ALK mutants. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 119, 5332–5342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Zheng, Q. Multiple Molecular Dynamics Simulations of the Inhibitor GRL-02031 Complex with Wild Type and Mutant HIV-1 Protease Reveal the Binding and Drug-Resistance Mechanism. Langmuir 2020, 36, 13817–13832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soumana, D.I.; Ali, A.; Schiffer, C.A. Structural analysis of asunaprevir resistance in HCV NS3/4A protease. ACS Chem Biol. 2014, 9, 2485–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagpal, N.; Goyal, S.; Wahi, D.; Jain, R.; Jamal, S.; Singh, A.; et al. Molecular principles behind Boceprevir resistance due to mutations in hepatitis C NS3/4A protease. Gene 2015, 570, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.; Wei, J. Molecular dynamics study on drug resistance mechanism of HCV NS3/4A protease inhibitor: BI201335. Mol Simul. 2015, 41, 674–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacArthur, M.W.; Thornton, J.M. Influence of proline residues on protein conformation. J. Mol. Biol. 1991, 218, 397–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prongay, A.J.; Guo, Z.; Yao, N.; Pichardo, J.; Fischmann, T.; Strickland, C.; et al. Discovery of the HCV NS3/4A protease inhibitor (1 R, 5 S)-N-[3-amino-1-(cyclobutylmethyl)-2, 3-dioxopropyl]-3-[2 (S)-[[[(1, 1-dimethylethyl) amino] carbonyl] amino]-3, 3-dimethyl-1-oxobutyl]-6, 6-dimethyl-3-azabicyclo [3.1. 0] hexan-2 (S)-carboxamide (Sch 503034) II. Key steps in structure-based optimization. Journal of medicinal chemistry 2007, 50, 2310–2318. [Google Scholar]

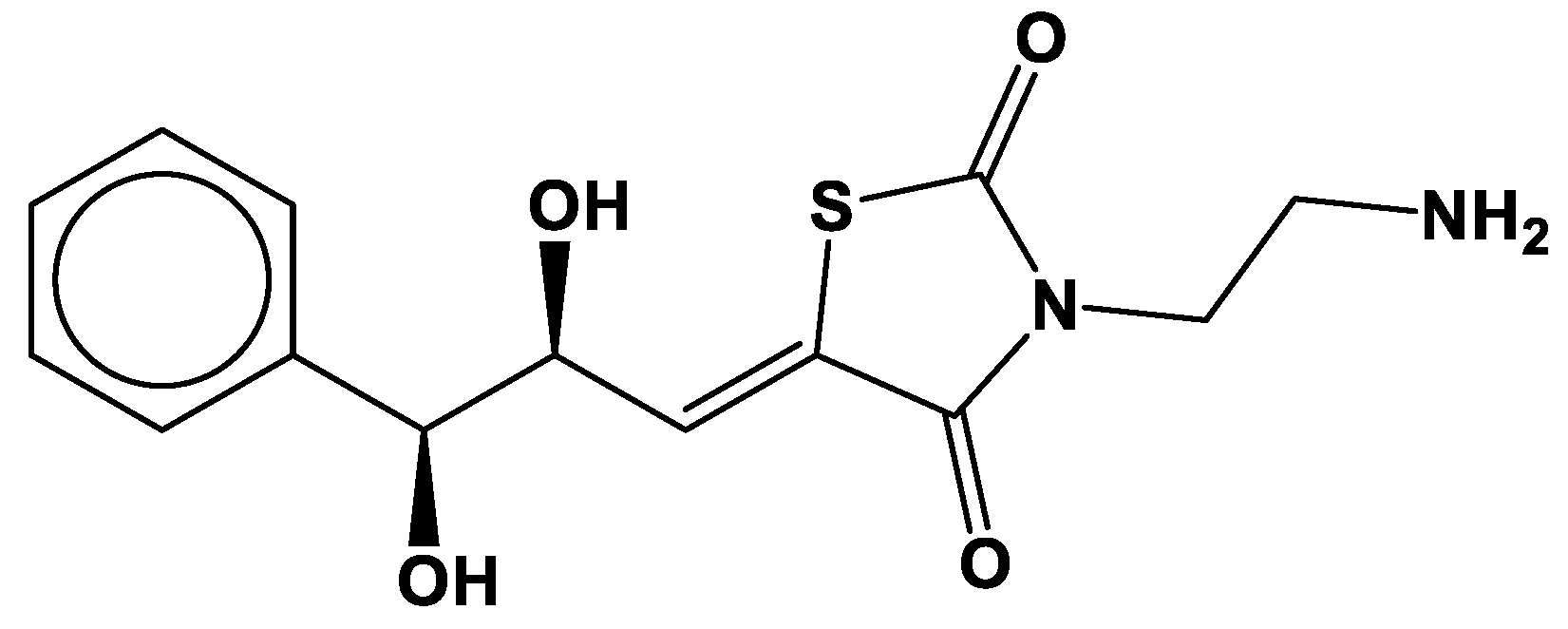
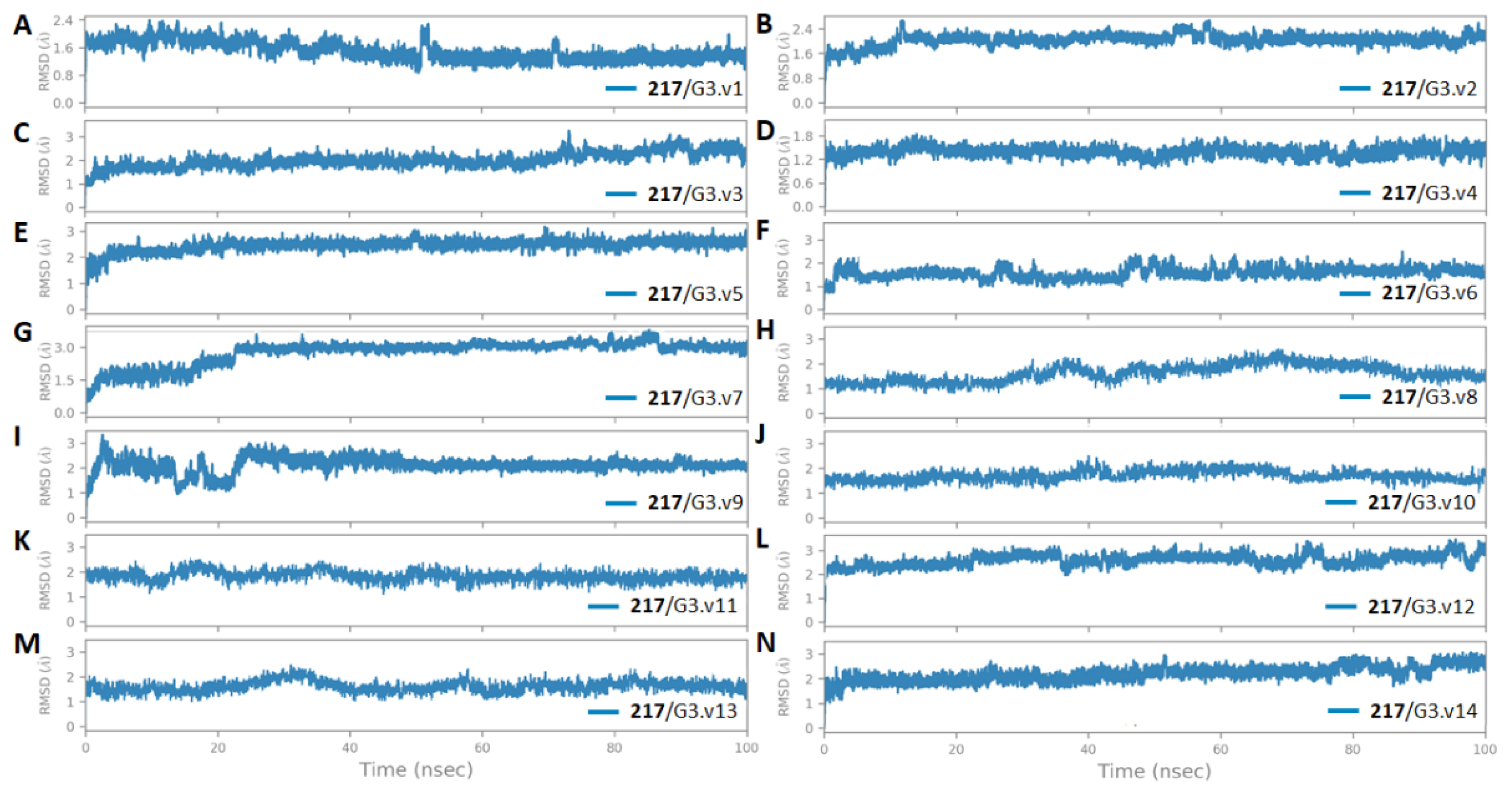
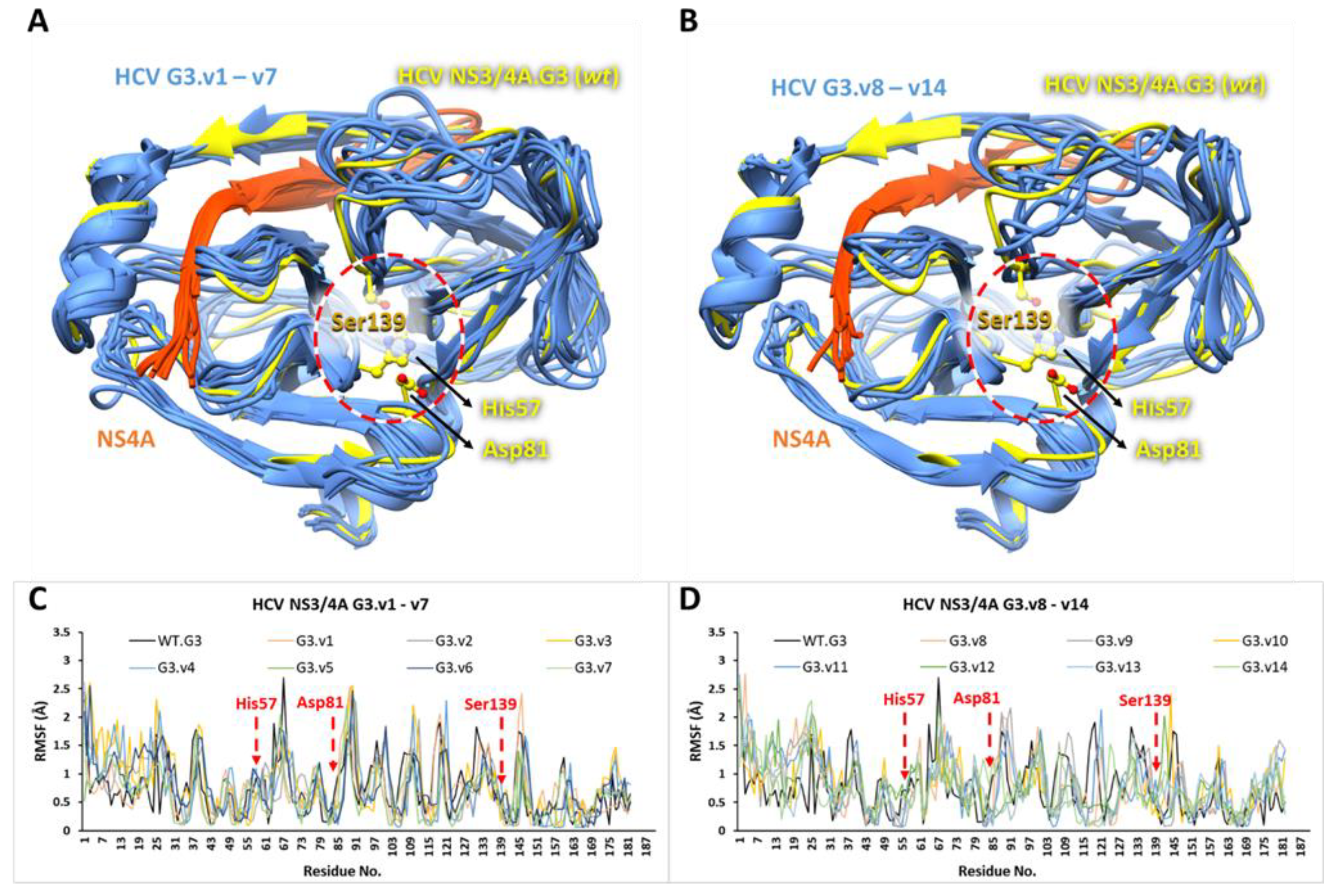
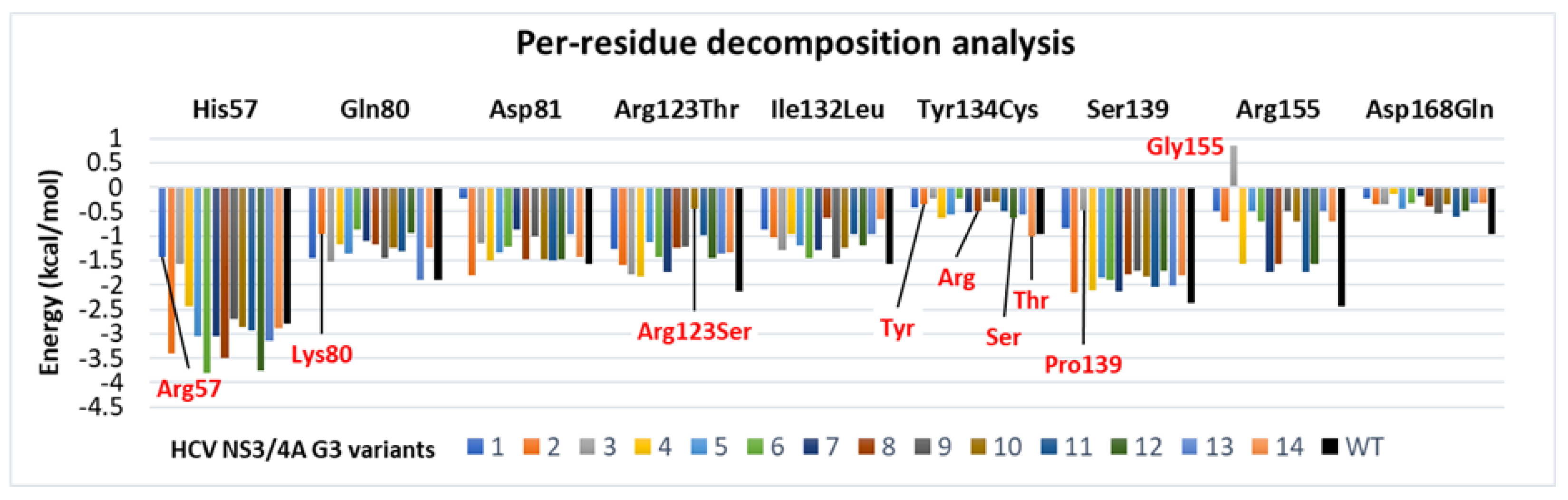
| Molecule Name | RMSD | Druglikeness | Mutagenic | Tumorigenic | cLogP | cLogS | Polar Surface Area | Reproductive Effective | Irritant |
| cpd-217 | 0.121 | -0.402 | none | none | -0.488 | -1.886 | 129.16 | none | none |
| Docking Score and Binding Interactions of cpd-217 | |||||||||
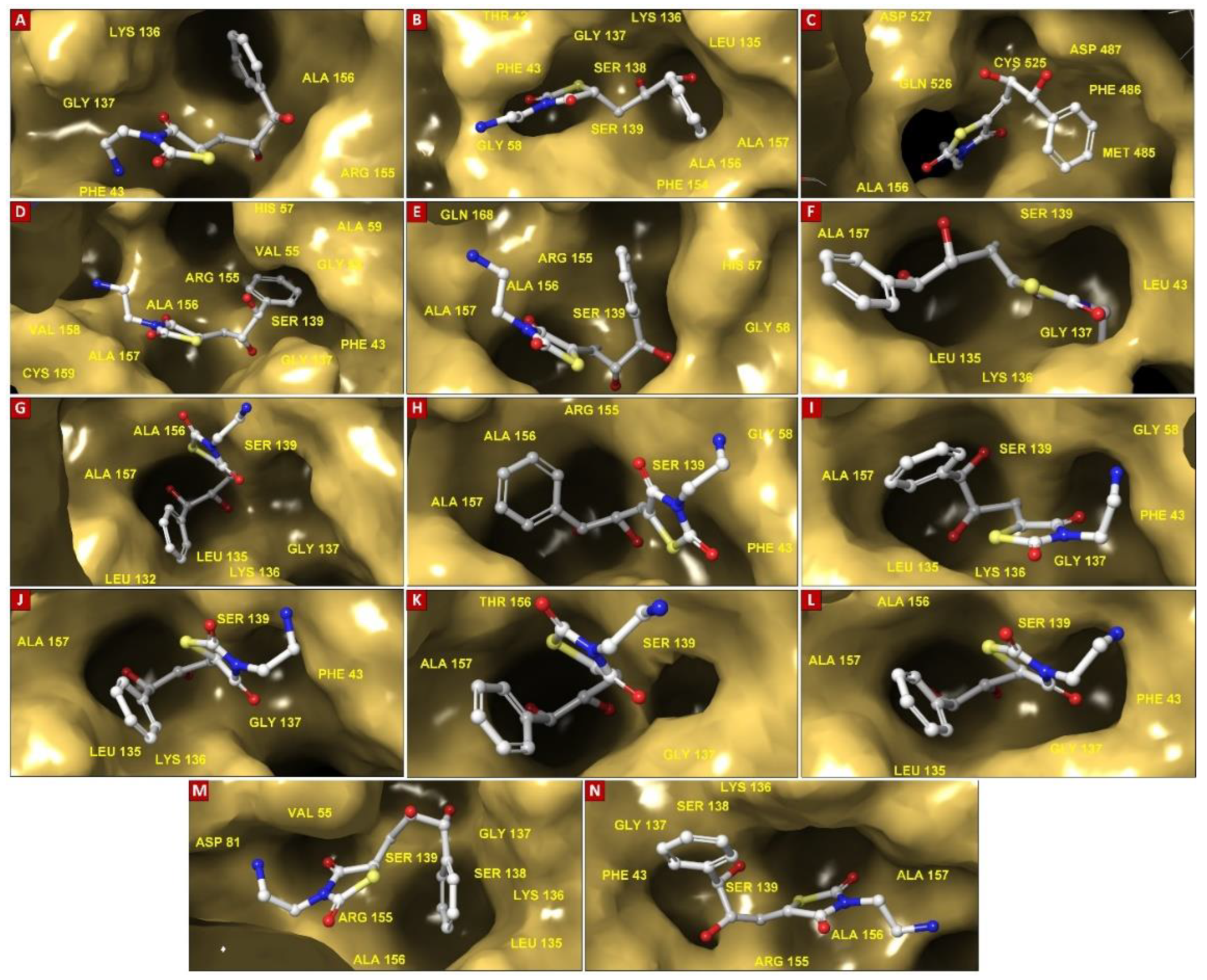
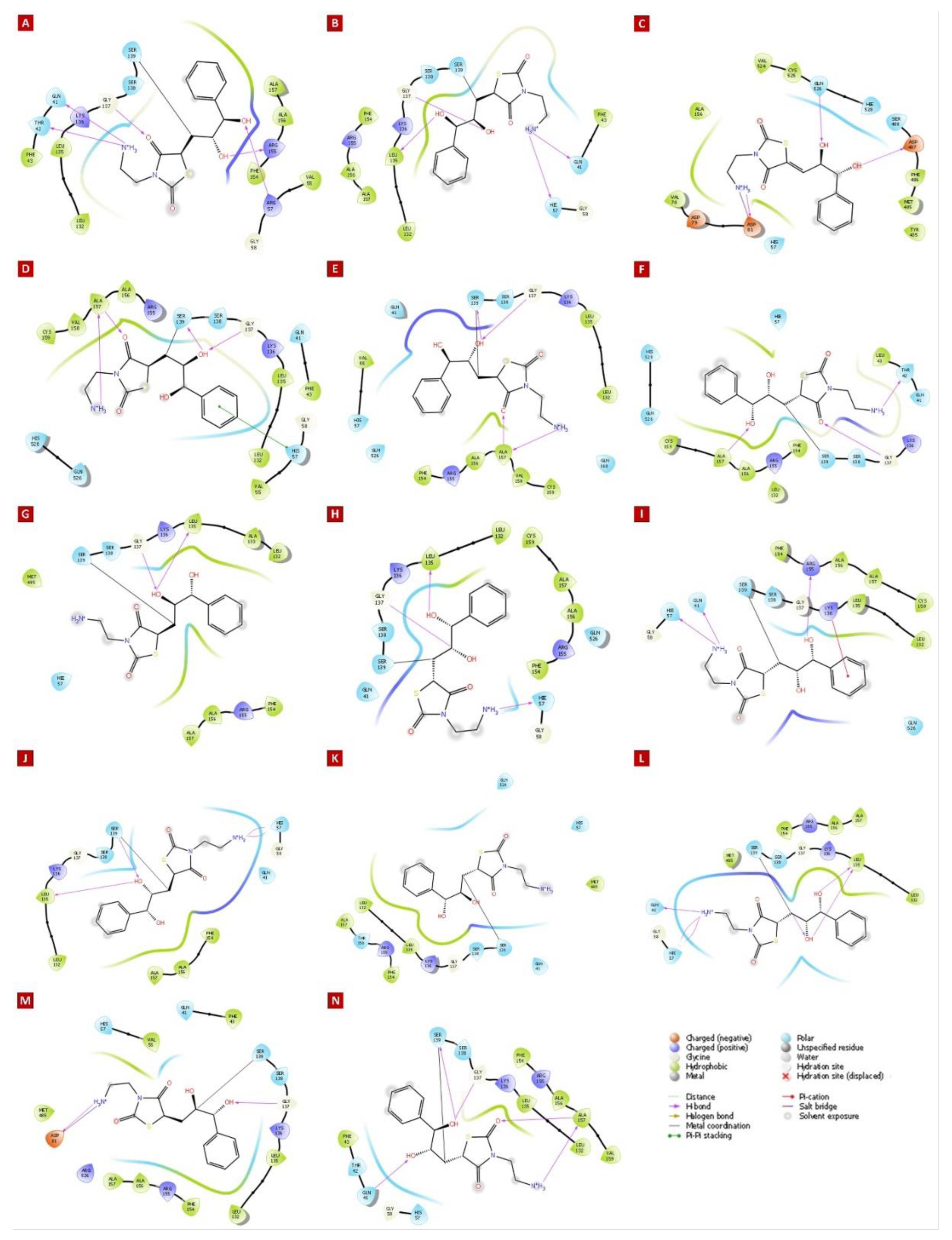
| HCV NS3/4A G3 Variant No. | Docking Score (kcal/mol) | Mutations within NS3/4A G3 sequences | Ligand-binding Residues | Covalent Bond with Ser139 | No. of H-bonds | H-Bond (residues involved) | salt bridge (residues involved) | Pi-cation interaction (residues involved) | Pi-Pi interaction (residues involved) |
| 1 | -6.588 | His57Arg, Arg123Thr, Ile132Leu, Tyr134Cys, Asp168Gln | Gln41, Thr42, Phe43, Val55, Arg57, Gly58, Leu132, Leu135, Lys136, Ser138, Ser139, Phe154, Arg155, Ala156, Ala157 | Yes | 5 | Gln41, Thr42, Arg57, Leu135, Arg155 | - | - | - |
| 2 | -5.308 | Gln80Lys, Arg123Thr, Ile132Leu, Asp168Gln | Gln41, Phe43, His57, Gly58, Leu132, Leu135, Lys136, Ser138, Ser139, Phe154, Arg155, Ala156, Ala157 | Yes | 4 | Gln41, His57, Leu135, Gly137 | - | - | - |
| 3 | -5.447 | Arg123Thr, Ile132Leu, Tyr134Cys, Ser139Pro, Arg155Gly, Asp168Gln | His57, Val78, Asp79, Asp81, Ala156, Met485, Phe486, Asp487, Ser488, Val524, Cys525, Gln526, His528 | No (S139P) | 3 | Asp81, Asp487, Gln526 | Asp81 | - | - |
| 4 | -6.397 | Arg123Thr, Ile132Leu, Tyr134Cys, Asp168Gln, Cys525Trp | Gln41, Phe43, Val55, His57, Gly58, Leu132, Leu135, Lys136, Gly137, Ser138, Ser139, Arg155, Ala156, Ala157, Val158, Cys159, Gln526, His528 | Yes | 4 | Gly137, Ser139, Ala157 | - | - | His57 |
| 5 | -5.986 | Arg123Thr, Ile132Leu, Try134Cys, Asp168Gln, Cys525Tyr | Gln41, Val55, His57, Leu132, Leu135, Lys136, Gly137, Ser138, Ser139, Phe154, Arg155, Ala156, Ala157, Val158, Cys159, Gln168 | Yes | 4 | Gly137, Ser139, Ala157 | - | - | - |
| 6 | -5.101 | Phe43Leu, Arg123Thr, Ile132Leu, Tyr134Cys, Asp168Gln | Gln41, Thr42, Leu43, His57, Gly58, Leu132, Lys136, Gly137, Ser138, Ser139, Phe154, Arg155, Ala156, Ala157, Cys159, Gln526, His528 | Yes | 3 | Thr42, Gly137, Ala157 | - | - | - |
| 7 | -5.395 | Arg123Thr, Ile132Leu, Tyr134Cys, Asp168Gln, Gln526His | His57, Leu132, Ala133, Leu135, Lys136, Gly137, Ser138, Ser139, Phe154, Arg155, Ala156, Ala157, Met485 | Yes | 2 | Leu135, Gly137 | - | - | - |
| 8 | -5.630 | Arg123Thr, Ile132Leu, Tyr134Arg, Asp168Gln | Gln41, His57, Gly58, Leu132, Leu135, Lys136, Gly137, Ser138, Ser139, Phe154, Arg155, Ala156, Ala157, Cys159, Gln526 | Yes | 3 | His57, Leu135, Gly137 | - | - | - |
| 9 | -5.184 | Arg123Thr, Ile132Leu, Tyr134Cys, Val158Ala, Asp168Gln | Gln41, His57, Gly58, Leu132, Leu135, Lys136, Gly137, Ser138, Ser139, Phe154, Arg155, Ala156, Ala157, Cys159, Gln526 | Yes | 3 | Gln41, His57, Arg155 | - | Lys136 | - |
| 10 | -4.722 | Arg123Ser, Ile132Leu, Tyr134Cys, Asp168Gln | Gln41, His57, Gly58, Leu132, Leu135, Lys136, Gly137, Ser138, Ser139, Phe154, Ala156, Ala157 | Yes | 4 | His57, Leu135, Ser139 | - | - | - |
| 11 | -4.169 | Arg123Thr, Ile132Leu, Tyr134Cys, Ala156Thr, Asp168Gln | Gln41, His57, Leu132, Leu135, Lys136, Gly137, Ser138, Ser139, Phe154, Arg155, Thr156, Ala157, Met485, Gln526 | Yes | 0 | - | - | - | - |
| 12 | -5.288 | Arg123Thr, Ile132Leu, Tyr134Ser, Asp168Gln | Gln41, His57, Gly58, Leu132, Leu135, Lys136, Gly137, Ser138, Ser139, Phe154, Arg155, Ala156, Ala157, Met485 | Yes | 6 | Gln41, His57, Leu135, Ser139 | - | - | - |
| 13 | -5.392 | Arg123Thr, Ile132Leu, Tyr134Cys, Asp168Gln, Gln526Arg | Gln41, Phe43, Val55, His57, Asp81, Leu132, Leu135, Lys136, Gly137, Ser138, Ser139, Phe154, Arg155, Ala156, Ala157, Met485, Arg526 | Yes | 2 | Asp81, Gly137 | Asp81 | - | - |
| 14 | -6.153 | Arg123Thr, Ile132Leu, Tyr134Thr, Cys159Val, Asp168Gln | Gln41, Thr42, Phe43, His57, Gly58, Leu132, Leu135, Lys136, Gly137, Ser138, Ser139, Phe154, Arg155, Ala156, Ala157, Val159 | Yes | 5 | Gln41, Gly137, Ser139, Ala157 | - | - | - |
| HCV | MMGBSA energy components (kcal/mol) |
Energy Shift ΔΔGshifta |
Variation (ΔAS)b | ||||||||
| Before MD | After MD (Last 50 ns) | ||||||||||
| ΔGtol | ΔEele | ΔEvdw | ΔEMM | ΔGsol | -TΔS | ΔGbind | |||||
| G3.v1 | -5.7 | -32.5 | -44.2 | -76.7 | 39.1 | 25.9 | -11.6 | -5.9 | 2.8 | ||
| G3.v2 | -6.9 | -29.1 | -43.2 | -72.3 | 36.4 | 20.3 | -15.6 | -8.7 | -1.2 | ||
| G3.v3 | -4.0 | -27.3 | -37.1 | -64.4 | 35.4 | 22.7 | -6.3 | -2.3 | 8.1 | ||
| G3.v4 | -4.4 | -32.4 | -38.1 | -70.5 | 38.2 | 22.4 | -9.9 | -5.5 | 4.5 | ||
| G3.v5 | -3.8 | -31.1 | -42.3 | -73.4 | 39.5 | 24.7 | -9.2 | -5.5 | 5.1 | ||
| G3.v6 | -4.1 | -29.1 | -40.2 | -69.3 | 37.2 | 23.0 | -9.1 | -5.0 | 5.3 | ||
| G3.v7 | -3.8 | -26.4 | -36.6 | -63.0 | 38.2 | 15.2 | -9.6 | -5.8 | 4.8 | ||
| G3.v8 | -3.8 | -31.0 | -36.4 | -67.4 | 37.2 | 19.0 | -11.2 | -7.4 | 3.2 | ||
| G3.v9 | -3.1 | -27.4 | -33.5 | -60.9 | 36.4 | 15.3 | -9.2 | -6.2 | 5.2 | ||
| G3.v10 | -3.0 | -28.1 | -37.1 | -65.2 | 36.1 | 20.0 | -9.1 | -6.1 | 5.3 | ||
| G3.v11 | -4.7 | -30.5 | -35.5 | -66.0 | 38.2 | 18.0 | -9.8 | -5.1 | 4.6 | ||
| G3.v12 | -4.4 | -31.4 | -40.1 | -71.5 | 39.1 | 21.0 | -11.4 | -7.0 | 3.0 | ||
| G3.v13 | -5.0 | -27.4 | -39.2 | -66.6 | 37.6 | 18.5 | -10.5 | -5.5 | 3.9 | ||
| G3.v14 | -5.2 | -32.1 | -43.3 | -75.4 | 38.2 | 22.1 | -15.1 | -9.9 | -0.7 | ||
| WT | -5.7 | -32.8 | -41.7 | -74.5 | 36.4 | 23.7 | -14.4 | -8.6 | 0.0 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





