Submitted:
13 July 2024
Posted:
15 July 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Patient Demographics and Characteristics
2.2. Antibiotic Susceptibility Test Results
2.3. Phenotypic and Genotypic Identification of MRSA Isolates
2.4. Genomic Features
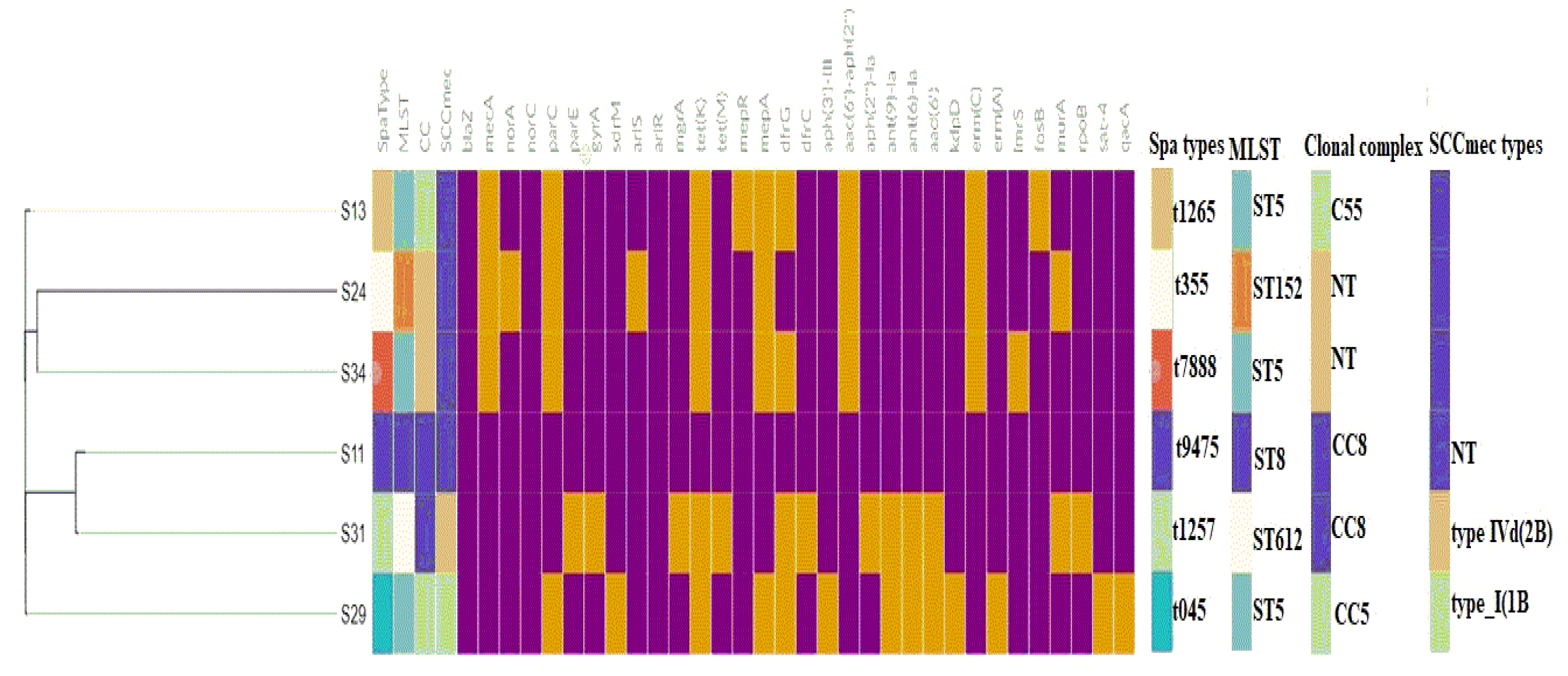
2.5.1. MLST, spa typing, and Clonal Complex
2.5.2. Mobilome (Plasmids, Insertion Sequences, Intact Prophages, and SCCmec Elements)
2.5.3. Virulome and Pathogenicity of S. aureus Strains
2.6. Genetic Environment of the ARGs and Virulence Genes
2.6.1. Regulatory Genes
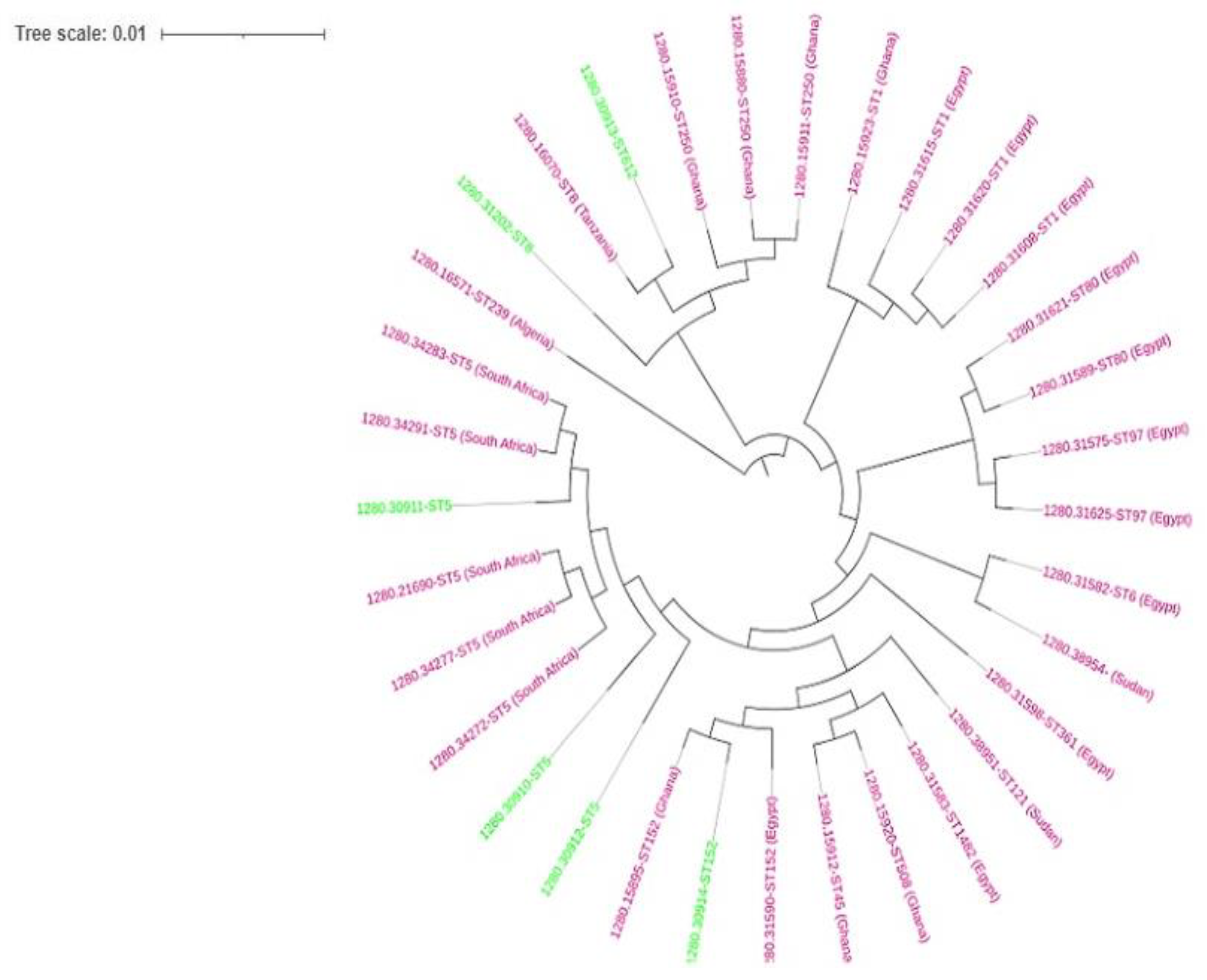
2.7. Phylogenomics
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethical Consideration
4.2. Sample Collection and Bacterial identification
4.3. Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing and MRSA detection
4.4. Whole-Genome Sequencing (WGS) and bioinformatic analysis
4.5. Genomic Analysis and Annotation
4.6. Single Nucleotide Polymorphism (SNP) Analysis in Antibiotic Resistance Strains
4.7. Phylogenomic Analysis
4.8. Nucleotide Sequence Accession Number
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Asadollahi, P.; Farahani, N.N.; Mirzaii, M.; Khoramrooz, S.S.; van Belkum, A.; Asadollahi, K.; Dadashi, M.; Darban-Sarokhalil, D. Distribution of the Most Prevalent Spa Types Among Clinical Isolates of Methicillin-Resistant and-Susceptible Staphylococcus Aureus Around the World: A Review. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Tu, C.; Tan, C.; El-Sayed Ahmed, M.A.E.G.; Dai, M.; Xia, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhong, L.L.; Shen, C.; Chen, G.; et al. Antimicrobial Resistance, Virulence Genes Profiling and Molecular Relatedness of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus Strains Isolated from Hospitalized Patients in Guangdong Province, China. Infect. Drug Resist. 2019, 12, 447–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, F.; He, W.; Xiao, S.; Wang, S.; Li, X.; Zeng, Q.; Ni, Y.; Han, L. Antimicrobial Resistance and Molecular Epidemiology of Staphylococcus Aureus Causing Bloodstream Infections at Ruijin Hospital in Shanghai from 2013 to 2018. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diekema, D.J.; Hsueh, P.R.; Mendes, R.E.; Pfaller, M.A.; Rolston, K. V.; Sader, H.S.; Jones, R.N. The Microbiology of Bloodstream Infection: 20-Year Trends from The SENTRY Antimicrobial Surveillance Program. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2019, 63, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, N.A.; Sharma-Kuinkel, B.K.; Maskarinec, S.A.; Eichenberger, E.M.; Shah, P.P.; Carugati, M.; Holland, T.L.; Fowler, V.G. Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus: An Overview of Basic and Clinical Research. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 203–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadyeh, E.; Azmi, K.; Seir, R.A.; Abdellatief, I.; Abdeen, Z. Molecular Characterization of Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus in West Bank-Palestine. Front. Public Heal. 2019, 7, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.; Zhou, W.; Zhan, Q.; Chen, Y.; Luo, Q.; Shen, P.; Xiao, Y. Genomic Epidemiology and Characterisation of Penicillin-Sensitive Staphylococcus Aureus Isolates from Invasive Bloodstream Infections in China: An Increasing Prevalence and Higher Diversity in Genetic Typing Be Revealed. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2022, 11, 326–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, W.; Liu, J.; Zhan, Y.; Wang, L.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, N.; Hou, N. Molecular Typing Revealed the Emergence of PVL-Positive Sequence Type 22 Methicillin-Susceptible Staphylococcus Aureus in Urumqi, North Western China. Infect. Drug Resist. 2019, 12, 1719–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, T.J. The MSCRAMM Family of Cell-Wall-Anchored Surface Proteins of Gram-Positive Cocci. Trends Microbiol. 2019, 27, 927–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, T.J.; Geoghegan, J.A.; Ganesh, V.K.; Hook, M. Adhesion, Invasion and Evasion: The Many Functions of the Surface Proteins of Staphylococcus Aureus. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2014, 12, 46–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warnes, S.L.; Highmore, C.J.; Keevil, C.W. Horizontal Transfer of Antibiotic Resistance Genes on Abiotic Touch Surfaces: Implications for Public Health. MBio 2012, 3, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K.H.; Greenwood-Quaintance, K.E.; Uhl, J.R.; Cunningham, S.A.; Chia, N.; Jeraldo, P.R.; Sampathkumar, P.; Nelson, H.; Patel, R. Molecular Epidemiology of Staphylococcus Aureus Bacteremia in a Single Large Minnesota Medical Center in 2015 As Assessed Using MLST, Core Genome MLST and Spa Typing. PLoS One 2017, 12, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perovic, O.; Iyaloo, S.; Kularatne, R.; Lowman, W.; Bosman, N.; Wadula, J.; Seetharam, S.; Duse, A.; Mbelle, N.; Bamford, C.; et al. Prevalence and Trends of Staphylococcus Aureus Bacteraemia in Hospitalized Patients in South Africa, 2010 to 2012: Laboratory-Based Surveillance Mapping of Antimicrobial Resistance and Molecular Epidemiology. PLoS One 2015, 10, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh-Moodley, A.; Lowe, M.; Mogokotleng, R.; Perovic, O. Diversity of SCCmec Elements and Spa Types in South African Staphylococcus Aureus MecA-Positive Blood Culture Isolates. BMC Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoako, D.G.; Somboro, A.M.; Abia, A.L.K.; Allam, M.; Ismail, A.; Bester, L.; Essack, S.Y. Genomic Analysis of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus Isolated from Poultry and Occupational Farm Workers in Umgungundlovu District, South Africa. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 670, 704–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.T.; Eckhardt, E.M.; Hansel, N.B.; Eliato, T.R.; Martin, I.W.; Andam, C.P. Genomic Epidemiology of Methicillin-Resistant and-Susceptible Staphylococcus Aureus from Bloodstream Infections. BMC Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaumburg, F.; Alabi, A.S.; Peters, G.; Becker, K. New Epidemiology of Staphylococcus Aureus Infection in Africa. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2014, 20, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strasheim, W.; Perovic, O.; Singh-Moodley, A.; Kwanda, S.; Ismail, A.; Lowe, M. Ward-Specific Clustering of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus Spa-Type T037 and T045 in Two Hospitals in South Africa: 2013 to 2017. PLoS One 2021, 16, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EUCAST European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, Breakpoint Tables for Interpretation of MICs and Zone Diameters. Version 8 2017. Accessed on November 2018. www.eucast.org/clinical_breakpoints/, 0–77.
- CLSI. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing; Twenty-Seventh Informational Supplement. CLSI Document M100-S27. 2017; ISBN 1562387855.
- Magiorakos, A.P.; Srinivasan, A.; Carey, R.B.; Carmeli, Y.; Falagas, M.E.; Giske, C.G.; Harbarth, S.; Hindler, J.F.; Kahlmeter, G.; Olsson-Liljequist, B.; et al. Multidrug-Resistant, Extensively Drug-Resistant and Pandrug-Resistant Bacteria: An International Expert Proposal for Interim Standard Definitions for Acquired Resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2012, 18, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francois, P.; Koessler, T.; Huyghe, A.; Harbarth, S.; Bento, M.; Lew, D.; Pittet, D.; Schrenzel, J. Rapid Staphylococcus Aureus Agr Type Determination by a Novel Multiplex Real-Time Quantitative PCR Assay. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2006, 44, 1892–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbanga, J.; Amoako, D.G.; Abia, A.L.K.; Allam, M.; Ismail, A.; Essack, S.Y. Genomic Insights of Multidrug-Resistant Escherichia Coli From Wastewater Sources and Their Association With Clinical Pathogens in South Africa. Front. Vet. Sci. 2021, 8, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, K.; Conly, J.; McClure, J.A.; Kurwa, H.A.; Zhang, K. Arginine Catabolic Mobile Element in Evolution and Pathogenicity of the Community-Associated Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus Strain USA300. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, T.J. Antibiotic Resistance in Staphylococcus Aureus. Current Status and Future Prospects. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2017, 41, 430–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, V.; Hermenegildo, S.; Ferreira, C.; Manaia, C.M.; Capita, R.; Alonso-Calleja, C.; Carvalho, I.; Pereira, J.E.; Maltez, L.; Capelo, J.L.; et al. Genetic Characterization of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus Isolates from Human Bloodstream Infections: Detection of MLSB Resistance. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asante, J.; Govinden, U.; Owusu-Ofori, A.; Bester, L.A.; Essack, S.Y. Molecular Characterization of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus Isolates from a Hospital in Ghana. African J. Clin. Exp. Microbiol. 2019, 20, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mkhize, S.; Amoako, D.G.; Shobo, C.O.; Zishiri, O.T.; Bester, L.A. Genotypic and Phenotypic Characterizations of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA) on Frequently Touched Sites from Public Hospitals in South Africa. Int. J. Microbiol. 2021; 6011045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, A.J.; Lindsay, J.A. The Distribution of Plasmids That Carry Virulence and Resistance Genes in Staphylococcus Aureus Is Lineage Associated. BMC Microbiol. 2012, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ocloo, R.; Newton-Foot, M.; Ziebuhr, W.; Whitelaw, A.C. Molecular Epidemiology and Antibiotic Resistance of Staphylococci Other than Staphylococcus Aureus in Children in Cape Town, South Africa. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pennone, V.; Prieto, M.; Avelino, Á.; Cobo-diaz, J.F. Antimicrobial Resistance Genes Analysis of Publicly Available Staphylococcus Aureus Genomes. 2022, 1–19.
- Shittu, A.O.; Adesoji, T.; Udo, E.E. DNA Microarray Analysis of Staphylococcus Aureus from Nigeria and South Africa. PLoS One 2021, 16, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, C.; Lee, S.; Kathariou, S. Dissemination and Conservation of Cadmium and Arsenic Resistance Determinants in Listeria and Other Gram-Positive Bacteria. Mol. Microbiol. 2020, 113, 560–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Trad, E.I.; Chew, C.H.; Che Hamzah, A.M.; Suhaili, Z.; Rahman, N.I.A.; Ismail, S.; Puah, S.M.; Chua, K.H.; Kwong, S.M.; Yeo, C.C. The Plasmidomic Landscape of Clinical Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus Isolates from Malaysia. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Q.; Cruz-Paredes, C.; Zhang, S.; Rousk, J. Can Heavy Metal Pollution Induce Bacterial Resistance to Heavy Metals and Antibiotics in Soils from An Ancient Land-Mine? J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 124962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleinert, F.; Kallies, R.; Hort, M.; Zweynert, A.; Szekat, C.; Nagel, M.; Bierbaum, G. Influence of IS256 on Genome Variability and Formation of Small-Colony Variants in Staphylococcus Aureus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, C.C.; Chen, C.C.; Lu, Y.C.; Chuang, Y.C.; Tang, H.J. The Clinical Significance of Silent Mutations with Respect to Ciprofloxacin Resistance in MRSA. Infect. Drug Resist. 2018, 11, 681–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mbelle, N.M.; Feldman, C.; Osei Sekyere, J.; Maningi, N.E.; Modipane, L.; Essack, S.Y. Publisher Correction: The Resistome, Mobilome, Virulome and Phylogenomics of Multidrug-Resistant Escherichia Coli Clinical Isolates from Pretoria, South Africa. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Baker, M.; Hu, Y.; Xu, J.; Yang, D.; Maciel-Guerra, A.; Xue, N.; Li, H.; Yan, S.; Li, M.; et al. Whole-Genome Sequencing and Machine Learning Analysis of Staphylococcus Aureus from Multiple Heterogeneous Sources in China Reveals Common Genetic Traits of Antimicrobial Resistance. mSystems 2021, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sands, K.; Carvalho, M.J.; Spiller, O.B.; Portal, E.A.R.; Thomson, K.; Watkins, W.J.; Mathias, J.; Dyer, C.; Akpulu, C.; Andrews, R.; et al. Characterisation of Staphylococci Species from Neonatal Blood Cultures in Low- and Middle-Income Countries. BMC Infect. Dis. 2022, 22, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawal, O.U.; Ayobami, O.; Abouelfetouh, A.; Mourabit, N.; Kaba, M.; Egyir, B.; Abdulgader, S.M.; Shittu, A.O. A 6-Year Update on the Diversity of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus Clones in Africa: A Systematic Review. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elshabrawy, W.; Elsayed Zaki, M.; Farag Kamel, M. Genetic and Phenotypic Study of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus Among Patients and Health Care Workers in Mansoura University Hospital, Egypt. Iran. J. Microbiol. 2017, 9, 82–88. [Google Scholar]
- Soliman, M.S.; Soliman, N.S.; El-Manakhly, A.R.; Elbanna, S.A.; Aziz, R.K.; El-Kholy, A.A. Genomic Characterization of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA) by High-Throughput Sequencing in A Tertiary Care Hospital. Genes (Basel). 2020, 11, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulgader, S.M.; van Rijswijk, A.; Whitelaw, A.; Newton-Foot, M. The Association Between Pathogen Factors and Clinical Outcomes in Patients With Staphylococcus Aureus Bacteraemia in a Tertiary Hospital, Cape Town. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 91, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Q.; Tang, X.; Dong, W.; Sun, N.; Yuan, W. A Review of Biofilm Formation of Staphylococcus Aureus and Its Regulation Mechanism. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasquez, M.T.; Lubkin, A.; Reyes-Robles, T.; Day, C.J.; Lacey, K.A.; Jennings, M.P.; Torres, V.J. Identification of a Domain Critical for Staphylococcus Aureus LuKED Receptor Targeting and Lysis of Erythrocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 17241–17250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, N.; Timofeyeva, Y.; Jamrozy, D.; Rojas, E.; Hao, L.; Silmon de Monerri, N.C.; Hawkins, J.; Singh, G.; Cai, B.; Liberator, P.; et al. Molecular Epidemiology and Expression of Capsular Polysaccharides in Staphylococcus Aureus Clinical Isolates in the United States. PLoS One 2019, 14, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S. , Singh, S. K., Chowdhury, I., & Singh, R. Understanding the Mechanism of Bacterial Biofilms Resistance to Antimicrobial Agents. Open Microbiol. J. 2017, 11, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popella, P.; Krauss, S.; Ebner, P.; Nega, M.; Deibert, J.; Götz, F. VraH Is the Third Component of the Staphylococcus Aureus VraDEH System Involved in Gallidermin and Daptomycin Resistance and Pathogenicity. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2016, 60, 2391–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bukowski, M.; Piwowarczyk, R.; Madry, A.; Zagorski-Przybylo, R.; Hydzik, M.; Wladyka, B. Prevalence of Antibiotic and Heavy Metal Resistance Determinants and Virulence-Related Genetic Elements in Plasmids of Staphylococcus Aureus. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulgader, S.M.; Shittu, A.O.; Nicol, M.P.; Kaba, M. Molecular Epidemiology of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus in Africa: A Systematic Review. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agabou, A.; Ouchenane, Z.; Essebe, C.N.; Khemissi, S.; Chehboub, M.T.E.; Chehboub, I.B.; Sotto, A.; Dunyach-Remy, C.; Lavigne, J.P. Emergence of Nasal Carriage of ST80 and ST152 PVL+ Staphylococcus Aureus Isolates from Livestock in Algeria. Toxins (Basel). 2017, 9, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ismail, H.; Govender, N.P.; Singh-Moodley, A.; Van Schalkwyk, E.; Shuping, L.; Moema, I.; Feller, G.; Mogokotleng, R.; Strasheim, W.; Lowe, M.; et al. An Outbreak of Cutaneous Abscesses Caused by Panton-Valentine Leukocidin-Producing Methicillin-Susceptible Staphylococcus Aureus Among Gold Mine Workers, South Africa, November 2017 to March 2018. BMC Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, H.; Wang, B.; Zhou, Y.; Xu, Y.; Rao, L.; Ai, W.; Guo, Y.; Wu, X.; Yu, J.; et al. Identification of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus ST8 Isolates in China with Potential High Virulence. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2022, 11, 507–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Isolate ID | Species | Sex | Ward | Age | Antibiotics | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PEN | AMP | FOX | CIP | MXF | LEV | GEN | AMK | ERY | CLI | TET | DOX | TGC | CHL | NIT | SXT | VAN | RIF | LZD | TEC | |||||
| S11 | MRSA | F | Surgical ward | 17 years | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | I | S | R | S | R | R | R |
| S29 | MRSA | M | Paediatric ward | <1 year | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | I | R | R | R | S | I | S | R | S | I | R | R |
| S31 | MRSA | F | Surgical ward | 3 years | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | R | S | R | S | R | S | R | R | R |
| S24 | MSSA | M | ICU | 33 years | R | S | S | R | R | R | S | S | R | R | R | I | S | I | R | R | S | R | I | I |
| S13 | MSSA | M | ICU | <1 year | R | S | S | R | R | R | I | R | I | R | I | R | S | S | S | I | S | S | I | R |
| S34 | MSSA | M | NICU | <1 year | R | S | S | R | R | R | I | R | I | R | R | R | S | I | S | S | S | I | S | S |
| Isolate ID | MRSA/MSSA | MLST | spa Type | Resistome | Plasmid replicon type | Insertion sequences | Confirmed CRISPRs (CAS) | Clonal complex | *SCCmec type | agr type b | ACME type | Pathogenicity score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S11 | MRSA | ST8 | t9475 | blaZ, mecA, aac(6’)-aph(2’‘), parC, dfrG, erm(C), grlA, tetK, mepR, mepA, norA, norC, fosB, arlR, arlS, mgrA, sdrM, kdpD | rep10, rep7a, rep7c | - | 6 (0) | CC8 | - | Type I | Type II | 0.982 (882) |
| S29 | MRSA | ST5 | t045 | blaZ, mecA, aph(3’)-III, aac(6’)-aph(2’‘), ant(6)-Ia, ant(9)-Ia, aad(6’), erm(C), erm(A), qacA, mepR, fosB, arlR, arlS, norA, norC, mgrA, sat-4 | rep10, rep21 | IS6, IS256 | 12 (0) | CC5 | SCCmec type I(1B) | Type II | - | 0.98 (914) |
| S31 | MRSA | ST612 | t1257 | blaZ, mecA, aac(6’)-aph(2’‘), aph(2’‘)-Ia, aad(6’), ant(6)-Ia, ant(9)-Ia , tet(M), mepR, mepA, dfrC, parC, erm(C), parE, gyrA, rpoB, fosB, arlR, arlS, norA, norC, murA, sdrM, kdpD | rep7c, rep20 | IS256, IS6 | 7 (0) | CC8 | SCCmec type IVd(2B) | Type I | - | 0.976 (978) |
| S24 | MSSA | ST152 | t355 | blaZ, dfrG, mepR, mgrA, arlR, kdpD, norC, sdrM, murA | rep16, rep5a | - | 8 (0) | - | - | Type IV | - | 0.975(225) |
| S13 | MSSA | ST5 | t1265 | blaZ, norA, norC, arlR, arlS, sdrM, mgrA, fosB, kdpD | rep20 | - | 9 (0) | CC5 | - | Type II | - | 0.985 (844) |
| S34 | MSSA | ST5 | t7888 | blaZ, norA, norC, sdrM, mepR, arlS, alrR, kdpD, mgrA, fosB, lmrS | rep19, rep16, rep20, rep5a | 1S6 | 7 (0) | - | Type II | - | 0.983 (871) |
| Strain (MLST) | Strain | Contig | Synteny of virulence genes and MGEs | Plasmid/chromosomal sequence with closest nucleotide homology (accession number) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S11 (ST8) | MRSA | 4 | pmtC:pmtB:pmtA:eap::scn::sak:::sph::lukG::lukH::intergrase:::agrB | S. aureus strain Laus385 chromosome (CP071350.1) |
| 6 | icaR::icaD:icaB:icaC:vraD:vraE:vraH::IS30:vraH::recombinase:IS6 | S. aureus strain TF3198 chromosome, complete genome (CP023561.1) | ||
| 10 | lukE:lukD::splA::epiE::splA:splB:splC:splD:splE:splF::pepA1:transposase | S. aureus strain 82 chromosome, complete genome (CP031661.1) | ||
| S29 (ST5) | MRSA | 53 | type I toxin-antitoxin system:IS6:cadD | S. aureus strain MIN-175 chromosome (CP086121.1) |
| 40 | clfA:vwb:emp | S. aureus strain ER02693.3 chromosome, complete genome (CP030605.1) | ||
| S31(ST612) | MRSA | 11 | pmtD:pmtC:pmtB:pmtA::eap:scn::sak | S. aureus strain 2395 USA500, complete genome (CP007499.1) |
| 15 | lukE:lukD::::splA:splB:splC:splF::type I restriction-modification system | S. aureus strain NRL 02/947 chromosome, complete genome (CP103850.1) | ||
| 19 | lukG:lukH:pathogenicity island:intergrase::phenol-soluble modulin:agrB | S. aureus strain 2395 USA500, complete genome (CP007499.1) | ||
| 22 | seq:sek:integrase::::emp:clfA | S. aureus strain 2395 USA500, complete genome (CP007499.1) | ||
| 33 | recombinase::universal stress protein:::cadD::seq:sek:integrase:::emp:clfA | S. aureus plasmid SAP017A, complete sequence (GQ900382.1) | ||
| 64 | sea:putative holin-like toxin | S. aureus strain R50 chromosome, complete genome (CP039167.1) | ||
| S13 (ST5) | MSSA | 4 | sbi:hlgA:hlgC:hlgB | S. aureus strain AR462 chromosome, complete genome (CP029086.1) |
| 5 | scpA:::eap::scn:sak::::::intergrase:sph:lukH:sbi:hlgA:hlgC:hlgB | S. aureus strain pt239 chromosome, complete genome (CP049467.1) | ||
| 15 | IS6::cadD:::sed:sej:ser::recombinases:cpA::eap::scn:sak::integrase:sph:lukH | S. aureus strain ER10678.3 plasmid pER10678.3A.1 (CP051928.1) | ||
| S24 ST152) | MSSA | 8 | arsB::crcB::scn:sak:::recombinase::type II toxin-antitoxin system toxin:intergrase | S. aureus strain UMCG579 chromosome, complete genome (CP091066.1) |
| 21 | cadD:type toxin-antitoxin::integrase | S. aureus strain GHA13 chromosome (CP043911.1) | ||
| 11 | BrxA/BrxB:::msrA:msrB:::norD::cspA:cvfB | S. aureus strain NGA84b chromosome, complete genome (CP051165.2) | ||
| S34 (ST5) | MSSA | 7 | eap/map::scn:sak::::sea:::type II toxin-antitoxin:integrase:sph:lukG:lukH | S. aureus strain HPV107 chromosome, complete genome (CP026074.1) |
| 8 | clfA:vwb:emp::thermonuclease protein:::sek:seq::pathogenicity island | S. aureus strain B4-59C chromosome, complete genome (CP042153.1) | ||
| 12 | sem:sei:seu:sen:seg:::lukE:lukD::splA:splB:splC:splD:splF | S. aureus strain ER03588.3 chromosome, complete genome (CP030595.1) | ||
| 14 | isdB:isdA:isdC:isdD:isdE:isdF::isdG::ecb::efb:scb | S. aureus strain B3-17D chromosome, complete genome (CP042157.1) | ||
| 20 | SSL13:SSL12:hyl | S. aureus strain NAS_AN_239 chromosome, complete genome (CP062409.1) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





