1. Introduction
The genus
Aquibium, derived from its isolation from aquatic environments, was first proposed by Kim
et al. and classified within the family Phyllobacteriaceae [
1]. At the time of writing, only three species within the genus
Aquibium have been validly published, according to the List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN,
http://lpsn.dsmz.de/search?word=Aquibium) [
2]. The type species is
Aquibium microcysteis, with the other two species,
Aquibium carbonis and
Aquibium oceanicum, having been reclassified from the genus
Mesorhizobium [
3]. While most species of
Mesorhizobium were isolated from the rhizosphere of leguminous plants,
Aquibium species originated from aquatic environments such as coal bed water [
4], deep-sea water [
5] and cultures of
Microcystis aeruginos [
1]. Genomic analysis suggested that
Aquibium species might be ancestral to those in
Mesorhizobium, with some
Mesorhizobium members acquiring nitrogen-fixing genes over the course of evolution [
6].
Species within
Aquibium consistently exhibit characteristics such as being Gram-straining-negative, aerobic, catalase- and oxidase-positive. The genomic DNA G+C content, predominant fatty acid and respiratory quinone for these species are 65.1-67.9 mol%, summed feature 8 (C
18:1ω7
c and/or C
18:1ω6
c) and ubiquinone-10 (Q-10), respectively [
1]. In this study, a novel strain, designated LZ166
T, was isolated from bathypelagic seawater in the western Pacific Ocean. A comprehensive investigation of morphology, physiology, chemotaxonomy and phylogeny was conducted to elucidate its taxonomy status and consequently denominate it as
Aquibium pacificus sp. nov.. Furthermore, genomic analyses were performed to delineate the mixotrophic lifestyle supported by flexible metabolic functions of carbon, nitrogen and sulfur in this novel strain.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Isolation and Culture
Strain LZ166T was isolated from the bathypelagic seawater of the western Pacific Ocean at station CTD-11 (1000 m depth, 16°13′12″ N, 130°22′12″ E) during the DY60 cruise in January 2021. Seawater samples were collected and filtered through a 0.2 μm polycarbonate (PC) membrane (Merck) on board. The membrane was then immediately transferred to Axygen screw cap tubes containing 30% (v/v) glycerol, and subsequently stored at -80 ℃ for preservation prior to laboratory analysis. Once in the laboratory, microbes attached to the membrane were washed off and serially diluted with sterile artificial seawater and spread onto Marine Agar (MA, BD Difco) plates. Individual colonies were isolated and transferred to fresh MA plates to obtain pure cultures. Strain LZ166T was successfully isolated and cultivated following these procedures. For long-term preservation, cultures were mixed with 30% glycerol and stored at -80 ℃.
Closely related type strains, including A. microcysteis NIBR3T and A. oceanicum B7T were purchased from the Korean Agricultural Culture Collection (KACC) and the Marine Culture Collection of China (MCCC), respectively. These type strains were used for comparison of phenotypic, physiological and chemotaxonomic characteristics with the isolated strain LZ166T in this study.
Additionally, strain LZ166T has been deposited in multiple culture collections, including the MCCC (accession number = MCCC M28807T), the KACC (accession number = KACC 23148T) and the Korean Culture Type Collection (KCTC, accession number = KCTC 82889T).
2.2. Morphology and Physiology
The cell size, morphology, and flagella pattern during the mid-exponential growth phase were examined using transmission electron microscope (model HT7800, Hitachi) after cells being negatively stained with uranyl acetate. Gram-straining experiment was carried out using a commercial Gram staining kit (Qingdao Hope Bio-Technology Co., Ltd), following the manufacturer’s protocol. The motility of strain LZ166
T was assessed both microscopically and by the semi-solid agar puncture method on MA medium containing 0.5% (w/v) agar. The growth of strain LZ166
T was examined on Marine Broth 2216 (MB, BD Difco) medium under a range of temperatures (4, 10, 15, 25, 28, 30, 34, 37, 41, 45, 55, 60 ℃), NaCl concentrations (0, 0.5, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 12, 15, 18, 20%, w/v) and pH conditions (3.0, 4.0, 5.0, 6.0, 7.0, 8.0, 9.0, 10.0, 11.0, 12.0), respectively. For NaCl concentrations, 0-2% and 3-20% medium were prepared based on 2216E and MB medium, respectively. The pH of MB medium was adjusted using various buffers to cover the desired pH range: 10 mM acetate/acetic acid buffer for pH 3.0-5.5, MES buffer for pH 5.0-6.5, PIPES buffer for pH 6.0-7.0, HEPES buffer for pH 7.0-8.0 and Tris and CAPSO buffer for pH values greater than 8.0 [
7]. The anaerobic growth was determined in an anaerobic chamber with pure N
2 using MB medium. Growth on nutrient agar (NA), R2A agar (BD Difco) and LB agar plates were also tested at 28 ℃.
Catalase activity was assessed by the formation of oxygen bubbles when the cells were exposed to a 3% (w/v) H
2O
2 solution [
1]. Oxidase activity was determined by the oxidation of 1% (w/v) N,N,N,N-tetramethyl-1,4-phenylenediamine (BioMérieux, France). The hydrolysis of skimmed milk, starch, cellulose and Tween 20, 40, 60, and 80 were examined on MA plates supplemented with the corresponding substrates. Additional biochemical properties were identified using API ZYM [
8] and 20NE strips (bioMérieux), following the manufacturer's protocol. Utilization of various carbon sources by strain LZ166
T were assessed with the Biolog GEN Ⅲ Microplates (Biolog), following the manufacturer’s instructions.
2.3. Chemotaxonomy
To analyze the cellular fatty acid and polar lipids, strain LZ166
T and closely related species were cultivated on MA medium at 28°C for 72 hours. Fatty acids were extracted, saponified, methylated and then determined using gas chromatography (Agilent Technologies 6850), as described by Li
et al [
7]. The composition of isoprenoid quinones from freeze-dried strains was extracted using chloroform/methanol (2:1, v:v), separated by thin layer chromatography (TLC) on silica gel GF254 plates (10 × 20 cm, Qingdao Haiyang Chemical Co., Ltd.), and redissolved in methanol. Redissolved isoprenoid quinones were then analyzed using high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC, Waters 2695) [
9]. Polar lipids were extracted and separated using two-dimensional TLC on silica gel 60 F254 plates (10 × 10 cm, Merck) with a first phase of chloroform/methanol/water (65:25:4, v:v:v) and a second phase of chloroform/acetic acid/methanol/water (80:15:12:5, v:v:v:v). The polar lipids were visualized using molybdatophosphoric acid, ninhydrin, molybdenum blue reagent and 1-naphthol-sulphuric acid, and identified based on their relative positions under different chromogenic agents [
9].
2.4. 16S rRNA Gene Phylogeny
Genomic DNA of strain LZ166
T was extracted using a bacterial genomic DNA extraction kit (SBS Genetech Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The purified genomic DNA was quantified by NanoDrop 2000 spectrophotometer (Thermo Scientific). The complete 16S rRNA gene was amplified using universal primer 27F (5’-AGAGTTTGATCMTGGCTCAG-3’) and 1492R (5’-GGTTACCTTGTTACGACTT-3’). 16S rRNA genes were sequenced via the Sanger method (Applied BiosystemsTM 3730XL) by Sangon Biotech (Shanghai) Co., Ltd. The 16S rRNA gene sequence of LZ166
T was subjected to BLAST analysis on EzBioCloud platform (
https://www.ezbiocloud.net/identify) [
10]. Reference 16S rRNA genes sequences were download from the NCBI database. All 16S rRNA genes sequences were trimmed, aligned and then used to construct phylogenetic trees using MEGA software (v 7.0.21) [
11]. The trees were generated with 1000 bootstrap iterations and clustering using maximum likelihood (ML) [
12], neighbor joining (NJ) [
13] and minimum evolution (ME) [
14] methods. Evolutionary distances were calculated using Kimura 2-parameter model [
15]. The phylogenetic trees were visualized and decorated using ChiPlot (
https://www.chiplot.online/) [
16]. The complete 16S rRNA gene sequence was deposited in the GenBank database under accession number PP812687.
2.5. Genome Sequencing, Phylogenomic and Comparative Analysis
The genome DNA of strain LZ166
T was sequenced on the Illumina HiSeq X Ten sequencing platform by Shanghai Majorbio Bio-Pharm Technology Co., Ltd (China). The high-quality reads were assembled using SPAdes software (v 3.13.0) [
17]. Gene prediction was performed using Prokka (v 1.13) [
18]. In addition, rRNA and tRNA genes were identified using RNAmmer (v 1.2) [
19] and ARAGORN (v 1.2.41) [
20]. Genome sequences of reference species were obtained from NCBI. The G+C content of the chromosomal DNA was determined directly from the genome sequence. A phylogenetic tree based on genome sequences was constructed using PhyloPhlAn 3.0 (v 3.0.58) [
21]. Average nucleotide identity (ANI) and average amino identity (AAI) among strain LZ166
T and reference strains were calculated using PYANI (v 0.2.9) [
22] and CompareM (v 0.0.32,
https://github.com/donovan-h-parks/CompareM), respectively. Digital DNA-DNA hybridization (dDDH) estimated values were calculated using the GGDC 3.0 on TYGS (
https://ggdc.dsmz.de/ggdc.php) [
23]. The genomic overview was presented based on rapid annotation using the RAST server (
https://rast.nmpdr.org/rast.cgi) [
24]. The genome of strain LZ166
T was annotated against clusters of orthologous groups (COG) and carbohydrate-active enzymes (CAZy) databases using Eggnog-mapper (v 2.0) [
25]. The carbon, nitrogen and sulfur metabolic pathways were annotated using METABOLIC (v 4.0) [
26] and KofamKOALA [
27] against the KEGG database. The draft genomes sequence of strain LZ166
T was deposited in GenBank under accession number JBDPGJ000000000.
All strains were Gram-stain negative, aerobic, catalase- and oxidase-positive, able to grow on R2A and LB plates but unable to grow on NA plate or hydrolyze starch, cellulose, Tween 20, and 80. In API ZYM tests, all strains are positive for esterase (C4), esterase lipase (C8), leucine aminopeptidase and trypsin, weak positive for lipase (C14), valineamino peptidase cystine aminopeptidaseand, α-chymotryp, acid phosphatase, naphthol-AS-Bl-phosphoamidase, α-glucosidase, negative for α-galactosidase, β-galactosidase, β-glucuronidase, β-glucosidase, N-acetyl-β-glucosaminidase, α-mannosidase and α-fucosidase. In API 20E test, all strains were able to utilize urea, D-glucose and L-arabinose but hydrolyze aesculin weakly, unable to produce indole, ferment D-glucose, utilize arginine, gelatin, D-mannose, N-acetyl-glucosamine, D-maltose, capric acid, adipic acid, trisodium citrate, phnylacetic acid or reduce nitrate to nitrite and denitrification.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Morphology and Physiology
Strain LZ166
T is Gram-stain-negative, aerobic, catalase- and oxidase-positive. The cells are short rod-shaped (1.3-1.7 μm long, 1.0-1.1 μm wide), non-spore-forming, motile by a lateral flagella (
Figure S1). After incubation for 3 days on MA plate at 28 ºC, circular (1-2 mm, diameter), convex, smooth, creamy-white and non-transparent colonies were observed. Growth was observed at temperature ranging from 10-45 ℃ (optimum, 34-37 ℃), and in NaCl concentrations of 0-5% (w/v) (optimum, 1-3%), and at pH range of 5-10 (optimum, pH 6-8). Physiological and biochemical differences among strain LZ166
T,
A. microcysteis NIBR3
T and
A. oceanicum B7
T are detailed in
Table 1. The strain was positive for skimmed milk hydrolysis but negative for cellulose, starch, Tween 20, 40, 60 and 80 hydrolysis. Additionally, R2A and LB plates supported the heterotrophic growth of LZ166
T but NA plate not. Anaerobic growth was observed in MB medium. While most API ZYM results were consistent between LZ166
T and reference species, differences were noted in the activity of alkaline phosphatase and the utilization of D-mannitol, potassium gluconate and malic acid. Moreover, Biolog test suggested that LZ166
T was capable of utilizing a range of organic carbon sources, including dextrin, D-cellobiose, gentiobiose, D-turanose, α-D-glucose and D-fucose for heterotrophic growth (
Table S1).
3.2. Chemotaxonomy
The respiratory quinones of strain LZ166
T were determined as Q-10 (100%). The predominant respiratory quinones are consistent with the ubiquinone systems characteristic of the genus
Aquibium [
1]. The polar lipids of LZ166
T were composed of diphosphatidylglycerol (DPG), phosphatidylethanolamine (PE), glycolipid (GL) and phosphatidylglycerol (PG) (
Figure S2). DPG, PG and PE were also detected in the
A. microcysteis NIBR3
T,
A. carbonis B2.3
T and
A. oceanicum B7
T [
1], which supported the affiliation of strain LZ166
T to
Aquibium. However, the presence of GL can be used to differentiate the novel strain from the reference species, as it is unique to strain LZ166
T. The major cellular fatty acids (>5%) of strain LZ166
T are summed feature 8 (C
18:1ω7
c and/or C
18:1ω6
c, 39.3%), iso-C
17:0 (13.3%) 11-methyl C
18:1ω7
c (12.0%), C
19:0 cyclo
ω8
c (9.3%) and C
16:0 (5.5%) (
Table 2 and
Table S2). Although the fatty acid profiles of strain LZ166
T are similar to those of the reference strains in
Aquibium, their proportions differ from each other [
1].
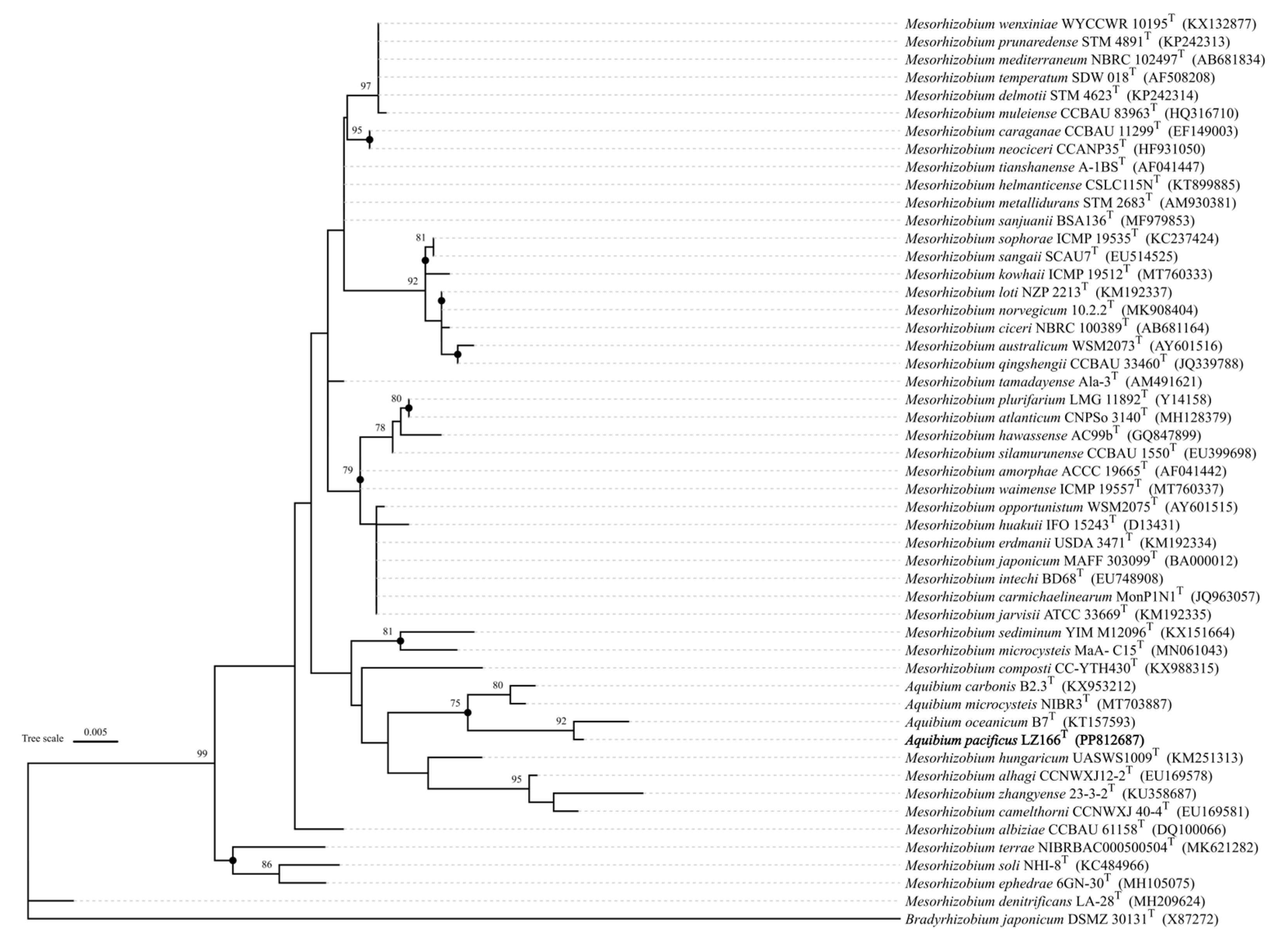
3.3. 16S rRNA Gene Phylogeny
16S rRNA gene sequence analysis indicated that LZ166
T exhibited the highest sequence similarity of 98.58% with
A. oceanicum B7
T, followed by
A. carbonis B2.7
T (97.94%) and
A. mycrocysteis NIBR3
T (96.71%), which were lower than the cut-off value of 98.65% [
28]. A ML tree based on 16S rRNA gene sequences was constructed and it clearly revealed that strain LZ166
T formed a separate lineage within the genus
Aquibium (
Figure 1). This topology was further confirmed by the ME (
Figure S3) and the NJ method (
Figure S4). The collective findings from the 16S rRNA gene phylogeny suggest that strain LZ166
T could represent a potential novel specie within
Aquibium.
3.4. Genomic Features
The genome size of strain LZ166
T is 6,119,659 bp with a chromosomal DNA G+C content of 64.7 mol%, which is similar to other species within the genus
Aquibium, which ranges from 65.1-67.9 mol% [
1]. 50 tRNA genes for 20 amino acids as well as one gene each for 5S rRNA, 16S rRNA and 23S rRNA were also identified in the genome of LZ166
T. A total of 5,513 protein-coding sequences (CDSs) were predicted, with the majority (5,220/5513, 94.7%) assigned to a putative function based on COG categories, while the rest were annotated as hypothetical proteins. Detailed information of genes classification according to RAST, COG and CAZy databases are given in
Figure S5.
The ANI and AAI values between LZ166
T and other closely related species in the genus
Aquibium are in the ranges of 76.79-90.73% and 79.03-88.50%, respectively (
Table S3). These values are below the 95-96% cut-off thresholds, previously proposed for species delineation [
29,
30,
31]. The dDDH estimated values between LZ166
T and other three species,
A. microcysteis NIBR3
T,
A. oceanicum B7
T and
A. carbonis B2.3
T were 22.8%, 36.1% and 22.2%, respectively (
Table S3), all of which are below the dDDH standard cut-off value of 70% [
31,
32]. Furthermore, a whole-genome phylogenetic tree (
Figure 2) was also constructed, which corroborated the phylogenetic relationships derived from the 16S rRNA genes phylogeny and genetic relatedness as depicted in
Figure 1. Altogether, these results suggest that strain LZ166
T represents a novel species within the genus
Aquibium.
According to the RAST annotation, 1398 genes were detected in the genome of strain LZ166
T and could be assigned to 279 subsystems belonging to 25 categories. Among 25 categories, amino acids and derivatives (241) was the most followed by carbohydrates (193), protein metabolism (172) and cofactors, vitamins, prosthetic groups, pigments (107). Most genes in amino acids and derivatives category connected to branched-chain amino acids. Most genes in carbohydrates category was relevant to TCA cycle belonging to central carbohydrate metabolism subcategory (
Figure S5A). COG analysis suggested that except those function unknown (S, 22.45%), amino acid transport and metabolism (E, 12.53%) was the most abundant category followed by carbohydrate transport and metabolism (G, 7.91%), transcription (K, 7.78%), energy production and conversion (C, 7.45%) and lipid transport and metabolism (I, 6.84%) (
Figure S5B). Additionally, a total of 71 genes in genome of strain LZ166
T matched CAZy families. Glycosyl transferases (GTs) was the largest CAZy family with 38 genes and followed by glycoside hydrolases (GHs, 29 genes), carbohydrate-binding modules (CBMs, 6 genes), carbohydrate esterases (CEs, 3 genes) and polysaccharide lyases (PLs, 1 gene). However, auxiliary activities (AAs) was detected (
Figure S5C).
3.5. Genomic Functional Analysis
3.5.1. Carbon Metabolism
The draft genome sequence of strain LZ166
T was utilized to infer its metabolic profiles, which was subsequently compared with those of three other
Aquibium species (
Figure 2). LZ166
T is capable of obtaining carbon from both inorganic and organic sources. A distinctive feature of LZ166
T genome is its potential for carbon dioxide fixation via the Calvin-Benson-Bassham (CBB) cycle. The genome contains a complete set of genes necessary for the CBB cycle, including those encoding key enzymes such as ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase (Rubisco) and phosphoribulokinase (PRK) [
33]. The Rubisco enzyme catalyzes the carboxylation of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate, resulting in the formation of 3-phosphoglycerate [
34]. To date, four forms of Rubisco have been identified, with form I being the most prevalent [
35]. The genome of LZ166
T encodes form I RubisCO (RcbL and RcbS), which shows the highest similarity (88.8% and 84.7%, respectively) to the enzymes from
Mesorhizobium mediterraneum. Although the
rcbL and
rcbS genes were predicted in the genome of LZ166
T, no complete carbon fixation pathways have been identified in the genomes of other
Aquibium species. This indicates that the
rcbL,
rcbS and
prk genes may serve as genetic markers to distinguish strain LZ166
T from other members of the genus. The presence of CBB pathway hints that LZ166
T may be capable of autotrophic metabolism. Additionally, the genome of strain LZ166
T also encodes genes involved in Embden-Meyerhof pathway (EMP), hexose monophosphate pathway (HMP), Entner-Doudoroff pathway (ED) and tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA), indicating a heterotrophic lifestyle that relies on organic matter for carbon and energy [
36]. Overall, the presence of both carbon fixation and organic matter breakdown genes in the genome of LZ166
T suggests a mixotrophic strategy, potentially allowing it to adapt to the dynamic and variable conditions of the marine environment [
37].
The genome of strain LZ166
T, in common with those of other
Aquibium species, includes all the key genes that encode the aerobic carbon monoxide dehydrogenase (CoxSLM). While other
Aquibium species only contained the Form II
cox gene, LZ166
T distinctively harbors both Form I and Form II
cox genes (
Figure 2 and
Figure S6). Besides, at least three copies of
cox gene clusters could be found in the genome of LZ166
T. This dual presence of
cox genes indicates that LZ166
T might have the capacity to oxidize carbon monoxide (CO). The co-existence of the CBB pathway for carbon fixation and the CO oxidation pathway in the genome of LZ166
T suggests that this strain could utilize the energy derived from CO oxidation. This capability might, in turn, facilitate its autotrophic growth [
38]. It seems not surprising as some CO oxidizers have been confirmed to fix CO
2 through CBB cycle by using energy obtained from CO oxidation [
38].
3.5.2. Sulfur Metabolism
Sulfur metabolism is crucial for bacteria, providing not only the essential sulfur element but also a source of energy. The genome of strain LZ166
T encodes the complete set of genes for the SOX pathway (
soxABCDXYZ), which is responsible for oxidizing thiosulfate to sulfate [
39]. In addition to the SOX system, the LZ166
T genome also includes genes encoding flavocytochrome c-sulfide dehydrogenase (
fcc) and sulfide:quinone oxidoreductases (
sqr) genes, indicating that this strain potentially possesses the capacity to oxidize sulfide to elemental sulfur [
39]. The presence of the SOX system,
fcc and
sqr in other
Aquibium species suggests that sulfur oxidation is probably a common feature of this genus. However, an exception is
A. oceanicum B7
T, which lacks the
fcc gene despite its phylogenetic proximity to strain LZ166
T. Furthermore,
Aquibium species, including LZ166
T, encode the sulfite dehydrogenases (
soe) gene, which plays a role in sulfite oxidation [
39,
40]. Strain LZ166
T and other
Aquibium species possessed a complete assimilatory sulfate reduction pathway (
cysND,
cysC,
cysH,
cysJI), indicating that they can reduce sulfate into sulfide, even to L-cysteine (
cysK) [
41]. The presence of multiple sulfur oxidation pathways in the genome of LZ166
T underscores its capacity to oxidize sulfide, sulfite or thiosulfate, thereby conserving energy and potentially supporting chemoautotrophic growth.
3.5.3. Nitrogen Metabolism
The analysis of nitrogen metabolism using KEGG annotation revealed the absence of nitrogenase (
nifH) genes in strain LZ166
T as well as in other
Aquibium species, a distinguishing feature between the genus
Aquibium and
Mesorhizobium [
1]. Strain LZ166
T was found to harbor an incomplete denitrification pathway, characterized by the presence of key genes of
nirK and
nosZ, which encode nitrite reductase [
42] and nitrous oxide reductase [
43], respectively. This genetic profile implies the potential for LZ166
T to utilize nitrite or nitrous oxide as electron acceptors. However, neither nitric oxide reductase genes (
norB) [
44] nor dissimilatory nitrate reductase genes (
napA,
narG) [
42] and nitrite reductase genes (
nrfAH and
nirBD) [
45] could be identified in the genome. Additionally, assimilatory nitrate reduction pathway was annotated in the genome of LZ166
T, which contained the
nasDE genes, responsible for the conversion of nitrite to ammonia [
46]. However, assimilatory nitrate reductase gene
nasA [
47] is absent in LZ166
T genome. The genome of strain LZ166
T encodes glutamine synthase (
glnA) and glutamate synthase (
gltB) genes, enabling the assimilation of ammonium [
47]. Furthermore, the presence of urease (
ure) and glutamate dehydrogenase (
gdh) genes provided genomic evidence for strain LZ166
T to transform nitrogen from organic to inorganic forms [
42,
47].
A comprehensive overview of the metabolic pathways involved in the carbon, nitrogen and sulfur cycles for strain LZ166
T (
Figure 3) and the reference strains of the genus
Aquibium is presented in
Figure 2. Consequently, the genomic functional analysis underscores the metabolic versatility of strain LZ166
T.
3.6. Description of Aquibium pacificus sp. nov.
Aquibium pacifica (pa.ci’ fi.cus. L. gen. adj. Pacificus, pacific, pertaining to the Pacific ocean)
Cells are short rod-shaped (1.3-1.7 μm long, 1.0-1.1 μm wide) with a lateral flagella, aerobic, motile, gram-negative. Colonies are 1-2 mm in diameter, convex, smooth, creamy-white and non-transparent after incubation on MA plate for 3 days. Strains can grow on R2A, and LB medium but not on NA medium. Growth can be observed at 10-45 ℃ (optimum, 34-37 ℃), 0-5% (w/v) NaCl (optimum, 1-3%), and pH 5-10 (optimum, pH 6-8). Catalase, oxidase, esterase (C4), esterase lipase (C8), leucine aminopeptidase, trypsin, α-glucosidase are positive. Alkaline phosphatase, lipase (C14), valine aminopeptidase, cystine aminopeptidase, α-chymotryp, acid phosphatase, naphtol-AS-B1-phosphoamidase, are weakly positive. α-galactosidase, β-galactosidase, α-glucosidase, β-glucosidase, N-acetyl-β-glucosaminidase, α-mannosidase and α-fucosidase are negative. The strain is able to hydrolyze or assimilate urea, D-glucose, L-arabinose and D-mannitol, and shows weakly positive for aesculin hydrolysis. It is unable to reduce nitrate to nitrite, produce indole, ferment D-glucose, hydrolyze arginine or gelatin, or assimilate D-mannose, D-maltose, potassium gluconate, capric acid, adipic acid, malic acid, trisodium citrate or phenylacetic acid. Skimmed milk utilization is observed. The major fatty acid (>5%) are summed feature 8 (C18:1ω7c and/or C18:1ω6c), iso-C17:0 and 11-methyl C18:1ω7c, C19:0 cyclo ω8c and C16:0. DPG, PE, GL and PG are the major polar lipids. The predominant respiratory quinone is Q-10.
The type strain designated as LZ166T (= MCCC M28807T = KACC 23148T = KCTC 82889T) was isolated from deep seawater in the western Pacific Ocean. Genome size is 6,154,543 bp with 64.7% G+C content. The GenBank accession number of the 16S rRNA gene sequence and genome sequence of strain LZ166T are PP812687 and JBDPGJ000000000, respectively.
4. Conclusions
The study presents the detailed characterization and taxonomic classification of Aquibium pacificus sp. nov., a newly identified mixotrophic bacterium isolated from the western Pacific Ocean's bathypelagic seawater. The 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis and genomic features, including ANI, AAI, and dDDH values, distinctly place LZ166T within the Aquibium genus, yet as a separate lineage. The physiological and biochemical characteristics of LZ166T were also found to be distinct from other species within the genus, highlighting its novelty. It hints a versatile metabolic profile, capable of both autotrophic and heterotrophic growth, with a genome that supports carbon fixation via the CBB cycle and inorganic sulfur oxidation. Notably, LZ166T lacks nitrogenase genes, indicating a divergence from nitrogen-fixing capabilities observed in other closely related genera. Its metabolic versatility, as evidenced by the presence of genes for carbon fixation and organic matter breakdown, positions it as a mixotrophic organism. The findings of this study extend the knowledge of Aquibium species and their ecological roles in the marine environment, emphasizing the adaptability of LZ166T to the dynamic deep-sea ecosystem.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org.
Author Contributions
J.F.: validation, formal analysis, investigation, data curation, writing—original draft preparation, and visualization. H.X.: validation and investigation. L.D.: formal analysis. Z.X.: investigation and data curation. H.J.: investigation and data curation. L.Q.: resources. W.J.: investigation. W.L.: conceptualization, resources, writing—review and editing, supervision, project administration and funding acquisition. S.Z.: conceptualization, resources, writing—review and editing, supervision, project administration and funding acquisition. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 42030412); the Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province (No. 2023J011379); Deep Sea Habitats Discovery Project (DY-XZ-04), and the COMRA Program (No. DY135-B2-01).
Data Availability Statement
The 16S rRNA gene sequence and genome sequence of strain LZ166T are available on GenBank under accession number PP812687 and JBDPGJ000000000, respectively.
Acknowledgments
We thank all participants of the Marine Culture Collection of China for kind help during experiment.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Kim, M.; Kim, W.; Park, W. Aquibium microcysteis gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from a Microcystis aeruginosa culture and reclassification of Mesorhizobium carbonis as Aquibium carbonis comb. nov. and Mesorhizobium oceanicum as Aquibium oceanicum comb. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2022, 72, 005230.
- Parte, A.C. LPSN—list of prokaryotic names with standing in nomenclature. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D613–D616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oren, A.; Garrity, G.M. Notification that new names of prokaryotes, new combinations, and new taxonomic opinions have appeared in volume 72, part 1 of the IJSEM. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2022, 72. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Xin, W.; Xu, Z.; Xiang, F.; Zhang, J.; Xi, L.; Qu, J.; Liu, J. Mesorhizobium carbonis sp. nov., isolated from coal bed water. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 2019, 112, 1221-1229.
- Fu, G.; Yu, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, Z.; Wu, D.; Su, Y.; Wang, R.; Han, S.; Wu, M.; Sun, C. Mesorhizobium oceanicum sp. nov., isolated from deep seawater. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2019; 112, 1221-1229. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, M.; Kim, W.; Park, Y.; Jung, J.; Park, W. Lineage-specific evolution of Aquibium, a close relative of Mesorhizobium, during habitat adaptation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2024, 90, e02091–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Ji, B.; Yuan, Q.; Wei, S.; Lai, Q.; Wu, K.; Jiang, L.; Shao, Z. Sulfurovum mangrovi sp. nov., an obligately chemolithoautotrophic, hydrogen-oxidizing bacterium isolated from coastal marine sediments. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2023, 73. [Google Scholar]
- Humble, M.W.; King, A.; Phillips, I. API ZYM: a simple rapid system for the detection of bacterial enzymes. J. Clin. Pathol. 1977, 30, 275–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minnikin, D.E.; O'Donnell, A.G.; Goodfellow, M.; Alderson, G.; Athalye, M.; Schaal, A.; Parlett, J.H. An integrated procedure for the extraction of bacterial isoprenoid quinones and polar lipids. J. Microbiol. Methods 1984, 2, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.; Ha, S.; Kwon, S.; Lim, J.; Kim, Y.; Seo, H.; Chun, J. Introducing EzBioCloud: a taxonomically united database of 16S rRNA gene sequences and whole-genome assemblies. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2017, 67, 1613–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felsenstein, J. Evolutionary trees from DNA sequences: a maximum likelihood approach. J. Mol. Evol. 1981, 17, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saitou, N.; Nei, M. The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1987, 4, 406–425. [Google Scholar]
- Rzhetsky, A.; Nei, M. A simple method for estimating and testing minimum-evolution trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1992, 9, 945–967. [Google Scholar]
- Kimura, M. A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J. Mol. Evol. 1980, 16, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.; Chen, Y.; Cai, G.; Cai, R.; Hu, Z.; Wang, H. Tree Visualization By One Table (tvBOT): a web application for visualizing, modifying and annotating phylogenetic trees. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, W587–W592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prjibelski, A.; Antipov, D.; Meleshko, D.; Lapidus, A.; Korobeynikov, A. Using SPAdes de novo assembler. Curr. Protoc. Bioinformatics 2020, 70, e102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seemann, T. Prokka: rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2068–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagesen, K.; Hallin, P.; Rødland, E.A.; Stærfeldt, H.-H.; Rognes, T.; Ussery, D.W. RNAmmer: consistent and rapid annotation of ribosomal RNA genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 3100–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laslett, D.; Canback, B. ARAGORN, a program to detect tRNA genes and tmRNA genes in nucleotide sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asnicar, F.; Thomas, A.M.; Beghini, F.; Mengoni, C.; Manara, S.; Manghi, P.; Zhu, Q.; Bolzan, M.; Cumbo, F.; May, U.; Sanders, J.G.; Zolfo, M.; Kopylova, E.; Pasolli, E.; Knight, R.; Mirarab, S.; Huttenhower, C.; Segata, N. Precise phylogenetic analysis of microbial isolates and genomes from metagenomes using PhyloPhlAn 3.0. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pritchard, L.; Glover, R.H.; Humphris, S.; Elphinstone, J.G.; Toth, I.K. Genomics and taxonomy in diagnostics for food security: soft-rotting enterobacterial plant pathogens. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 12–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier-Kolthoff, J.P.; Carbasse, J.S.; Peinado-Olarte, R.L.; Göker, M. TYGS and LPSN: a database tandem for fast and reliable genome-based classification and nomenclature of prokaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D801–D807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brettin, T.; Davis, J.J.; Disz, T.; Edwards, R.A.; Gerdes, S.; Olsen, G.J.; Olson, R.; Overbeek, R.; Parrello, B.; Pusch, G.D.; Shukla, M.; Thomason, J.A.; Stevens, R.; Vonstein, V.; Wattam, A.R.; Xia, F. RASTtk: a modular and extensible implementation of the RAST algorithm for building custom annotation pipelines and annotating batches of genomes. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantalapiedra, C.P.; Hernández-Plaza, A.; Letunic, I.; Bork, P.; Huerta-Cepas, J.; Tamura, K. eggNOG-mapper v2: functional annotation, orthology assignments, and domain prediction at the metagenomic scale. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 5825–5829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Tran, P.Q.; Breister, A.M.; Liu, Y.; Kieft, K.; Cowley, E.S.; Karaoz, U.; Anantharaman, K. METABOLIC: high-throughput profiling of microbial genomes for functional traits, metabolism, biogeochemistry, and community-scale functional networks. Microbiome 2022, 10, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aramaki, T.; Blanc-Mathieu, R.; Endo, H.; Ohkubo, K.; Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S.; Ogata, H. KofamKOALA: KEGG ortholog assignment based on profile HMM and adaptive score threshold. Bioinformatics 2019, 36, 2251–2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.; Oh, H.; Park, S.; Chun, J. Towards a taxonomic coherence between average nucleotide identity and 16S rRNA gene sequence similarity for species demarcation of prokaryotes. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2014, 64, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruchter, M.; Rosselló-Móra, R. Shifting the genomic gold standard for the prokaryotic species definition. PNAS 2009, 106, 19126–19131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konstantinidis, K.T.; Tiedje, J.M. Towards a genome-based taxonomy for prokaryotes. J. Bacteriol. 2005, 187, 6258–6264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, C.C.; Chimetto, L.; Edwards, R.A.; Swings, J.; Stackebrandt, E.; Thompson, F. Microbial genomic taxonomy. BMC Genomics 2013, 14, 913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auch, A.F.; von Jan, M.; Klenk, H.-P.; Göker, M. Digital DNA-DNA hybridization for microbial species delineation by means of genome-to-genome sequence comparison. Stand. Genomic Sci. 2010, 2, 117–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asplund-Samuelsson, J.; Hudson, E.P. Wide range of metabolic adaptations to the acquisition of the Calvin cycle revealed by comparison of microbial genomes. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2021, 17, e1008742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hügler, M.; Sievert, S.M. Beyond the Calvin cycle: autotrophic carbon fixation in the ocean. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2011, 3, 261–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabita, F.R.; Hanson, T.E.; Li, H.; Satagopan, S.; Singh, J.; Chan, S. Function, structure, and evolution of the RubisCO-like proteins and their RubisCO homologs. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2007, 71, 576–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patwardhan, S.; Phan, J.; Smedile, F.; Vetriani, C. The genome of Varunaivibrio sulfuroxidans strain TC8T, a metabolically versatile alphaproteobacterium from the Tor Caldara gas vents in the Tyrrhenian sea. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moran, M.A. The global ocean microbiome. Science 2015, 350, aac8455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, G.M.; Weber, C.F. Distribution, diversity and ecology of aerobic CO-oxidizing bacteria. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 5, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.; Liu, F.; Fang, W.; Yang, T.; Chen, G.-H.; He, Z.; Wang, S. Microbial sulfur metabolism and environmental implications. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 778, 146085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boughanemi, S.; Infossi, P.; Giudici-Orticoni, M.-T.; Schoepp-Cothenet, B.; Guiral, M. Sulfite oxidation by the quinone-reducing molybdenum sulfite dehydrogenase SoeABC from the bacterium Aquifex aeolicus. BBA-Bioenergetics 2020, 1861, 148279.
- Zhou, L.; Ou, P.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, W.; Yu, K.; Xie, K.; Zhuang, W.-Q. Assimilatory and dissimilatory sulfate reduction in the bacterial diversity of biofoulant from a full-scale biofilm-membrane bioreactor for textile wastewater treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 772, 145464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuypers, M.M.M.; Marchant, H.K.; Kartal, B. The microbial nitrogen-cycling network. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 263–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.D.; Han, H.; Yun, T.; Song, M.J.; Terada, A.; Laureni, M.; Yoon, S. Identification of nosZ-expressing microorganisms consuming trace N2O in microaerobic chemostat consortia dominated by an uncultured Burkholderiales. ISME J. 2022, 16, 2087–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braker, G.; Tiedje, J.M. Nitric oxide reductase (norB) genes from pure cultures and environmental samples. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 3476–3483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; He, T.; Zhang, M.; Zheng, C.; Yang, L.; Yang, L. Review of the mechanisms involved in dissimilatory nitrate reduction to ammonium and the efficacies of these mechanisms in the environment. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Lu, W.; Liu, Q.; Zhi, Y.; Zhou, P. The identification of the nitrate assimilation related genes in the novel Bacillus megaterium NCT-2 accounts for its ability to use nitrate as its only source of nitrogen. Funct. Integr. Genomics 2013, 14, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pajares, S.; Ramos, R. Processes and microorganisms involved in the marine nitrogen cycle: knowledge and gaps. Front. Mar. Sci. 2019, 6, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
Maximum likelihood phylogenetic tree based on 16S rRNA gene sequences showing the position between strain LZ166T and other closely related phylogenetic neighbours. Bootstrap numbers (>70%) were shown with 1000 calculations. Solid circle represented that branches were also recovered in the minimum evolution and neighbor joining trees. Bradyrhizobium japonicum DSMZ_30131T (X87272) was used as the out group. Bar, 0.005 substitutions per nucleotide position.
Figure 1.
Maximum likelihood phylogenetic tree based on 16S rRNA gene sequences showing the position between strain LZ166T and other closely related phylogenetic neighbours. Bootstrap numbers (>70%) were shown with 1000 calculations. Solid circle represented that branches were also recovered in the minimum evolution and neighbor joining trees. Bradyrhizobium japonicum DSMZ_30131T (X87272) was used as the out group. Bar, 0.005 substitutions per nucleotide position.
Figure 2.
Phylogenomic tree of LZ166T and its functional genes involved in carbon, sulfur and nitrogen metabolism in comparison with closely related species. Bradyrhizobium japonicum USDA 6T (GFC_000284375.1) was used as the out group. Bar, 0.1 substitutions per nucleotide position. Dark blocks, presence of corresponding functional genes. Grey blocks, absence or partial presence of corresponding functional genes. rcbL, ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase gene large chain. prk, phosphoribulokinase gene. CA, carbonic anhydrase gene. coxMSL, carbon monoxide dehydrogenase (form Ⅰ) gene. coxSLM, carbon monoxide dehydrogenase (form Ⅱ) gene. sox, thiosulfate oxidation genes cluster (soxABCDXYZ). fcc, flavocytochrome c-sulfide dehydrogenase gene. sqr, sulfide:quinone oxidoreductases gene. soe, sulfite dehydrogenase (quinone) gene. cys, assimilatory sulfate reduction genes cluster (cysNDCHJIK). sat, sulfate adenylyltransferase gene. aprAB, adenylylsulfate reductase gene. dsr, dissimilatory sulfite reductase gene. nifH, nitrogenase gene. nirK, copper-containing nitrite reductase (denitrification) gene. nosZ, nitrous oxide reductase gene. norB nitric oxide reductase gene. napA, periplasmic dissimilatory nitrate reductase gene. narG, membrane-bound dissimilatory nitrate reductase gene. nirBD, dissimilatory nitrite reductase (NADH) gene. nrfAH, dissimilatory nitrite reductase (cytochrome c-552). nasD, assimilatory nitrite reductase gene. nasA, assimilatory nitrate reductase. glnA, glutamine synthase gene. gltB, glutamate synthase gene. ure, urease gene. gdh, glutamate dehydrogenase gene.
Figure 2.
Phylogenomic tree of LZ166T and its functional genes involved in carbon, sulfur and nitrogen metabolism in comparison with closely related species. Bradyrhizobium japonicum USDA 6T (GFC_000284375.1) was used as the out group. Bar, 0.1 substitutions per nucleotide position. Dark blocks, presence of corresponding functional genes. Grey blocks, absence or partial presence of corresponding functional genes. rcbL, ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase gene large chain. prk, phosphoribulokinase gene. CA, carbonic anhydrase gene. coxMSL, carbon monoxide dehydrogenase (form Ⅰ) gene. coxSLM, carbon monoxide dehydrogenase (form Ⅱ) gene. sox, thiosulfate oxidation genes cluster (soxABCDXYZ). fcc, flavocytochrome c-sulfide dehydrogenase gene. sqr, sulfide:quinone oxidoreductases gene. soe, sulfite dehydrogenase (quinone) gene. cys, assimilatory sulfate reduction genes cluster (cysNDCHJIK). sat, sulfate adenylyltransferase gene. aprAB, adenylylsulfate reductase gene. dsr, dissimilatory sulfite reductase gene. nifH, nitrogenase gene. nirK, copper-containing nitrite reductase (denitrification) gene. nosZ, nitrous oxide reductase gene. norB nitric oxide reductase gene. napA, periplasmic dissimilatory nitrate reductase gene. narG, membrane-bound dissimilatory nitrate reductase gene. nirBD, dissimilatory nitrite reductase (NADH) gene. nrfAH, dissimilatory nitrite reductase (cytochrome c-552). nasD, assimilatory nitrite reductase gene. nasA, assimilatory nitrate reductase. glnA, glutamine synthase gene. gltB, glutamate synthase gene. ure, urease gene. gdh, glutamate dehydrogenase gene.
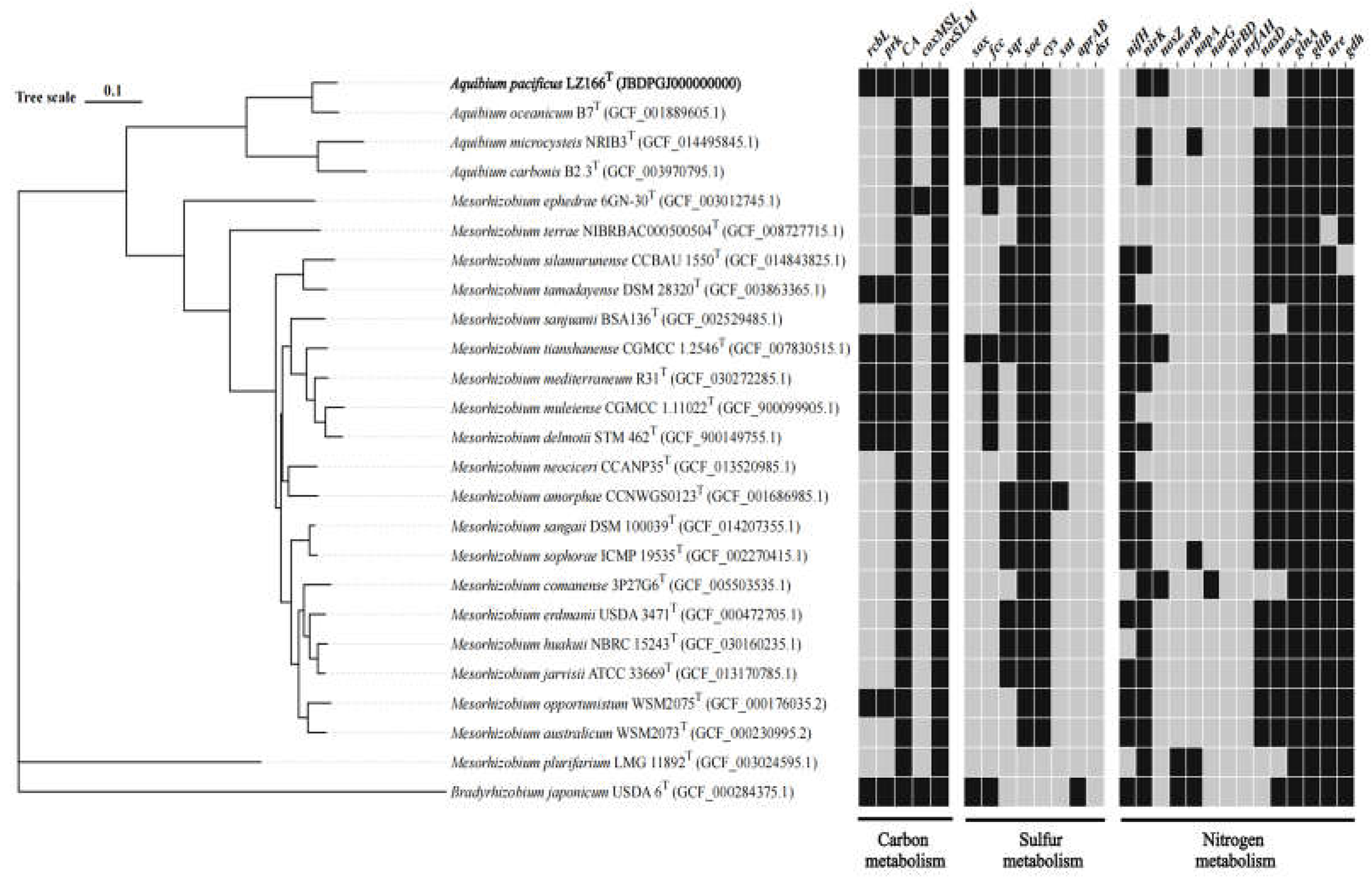
Figure 3.
Reconstructed carbon (pink), sulfur (green) and nitrogen (yellow) metabolism of strain LZ166T based on functional genes (corresponding enzymes are in red). ED, Entner-Doudoroff pathway. EMP, Embden-Meyerhof-Parnas pathway. HMP, hexose monophosphate pathway. CBB, Calvin -Benson-Bassham cycle. TCA, tricarboxylic acid cycle. GAP, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate. RU-5-P, ribulose-5-phosphate. PRK, phosphoribulokinase. RUBP, ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate. RuBisCO, ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase. 3-PGA, 3-phosphoglycerate. 1, 3-PGA, 1, 3-diphosphoglycerate. PAPS, phosphoadenosine phosphosulfate. APS, adenosine 5'-phosphosulfate. CA, carbonic anhydrase. Cox, carbon monoxide dehydrogenase. NirK, copper-containing nitrite reductase. NosZ, nitrous oxide reductase. NasD, assimilatory nitrite reductase. GlnA, glutamine synthase. GltB, glutamate synthase. Gdh, glutamate dehydrogenase. Ure, urease. CysK, cysteine synthase. CysI, sulfite reductase (NADPH) hemoprotein beta-component. CysJ, sulfite reductase (NADPH) flavoprotein alpha-component. CysH, PAPS reductase. CysC, adenylylsulfate kinase. CysN, sulfate adenylyltransferase subunit 1. CysD, sulfate adenylyltransferase subunit 2. SOX, thiosulfate oxidation enzymes. Soe sulfite dehydrogenase. Sqr, sulfide:quinone oxidoreductases. Fcc, flavocytochrome c-sulfide dehydrogenase.
Figure 3.
Reconstructed carbon (pink), sulfur (green) and nitrogen (yellow) metabolism of strain LZ166T based on functional genes (corresponding enzymes are in red). ED, Entner-Doudoroff pathway. EMP, Embden-Meyerhof-Parnas pathway. HMP, hexose monophosphate pathway. CBB, Calvin -Benson-Bassham cycle. TCA, tricarboxylic acid cycle. GAP, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate. RU-5-P, ribulose-5-phosphate. PRK, phosphoribulokinase. RUBP, ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate. RuBisCO, ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase. 3-PGA, 3-phosphoglycerate. 1, 3-PGA, 1, 3-diphosphoglycerate. PAPS, phosphoadenosine phosphosulfate. APS, adenosine 5'-phosphosulfate. CA, carbonic anhydrase. Cox, carbon monoxide dehydrogenase. NirK, copper-containing nitrite reductase. NosZ, nitrous oxide reductase. NasD, assimilatory nitrite reductase. GlnA, glutamine synthase. GltB, glutamate synthase. Gdh, glutamate dehydrogenase. Ure, urease. CysK, cysteine synthase. CysI, sulfite reductase (NADPH) hemoprotein beta-component. CysJ, sulfite reductase (NADPH) flavoprotein alpha-component. CysH, PAPS reductase. CysC, adenylylsulfate kinase. CysN, sulfate adenylyltransferase subunit 1. CysD, sulfate adenylyltransferase subunit 2. SOX, thiosulfate oxidation enzymes. Soe sulfite dehydrogenase. Sqr, sulfide:quinone oxidoreductases. Fcc, flavocytochrome c-sulfide dehydrogenase.
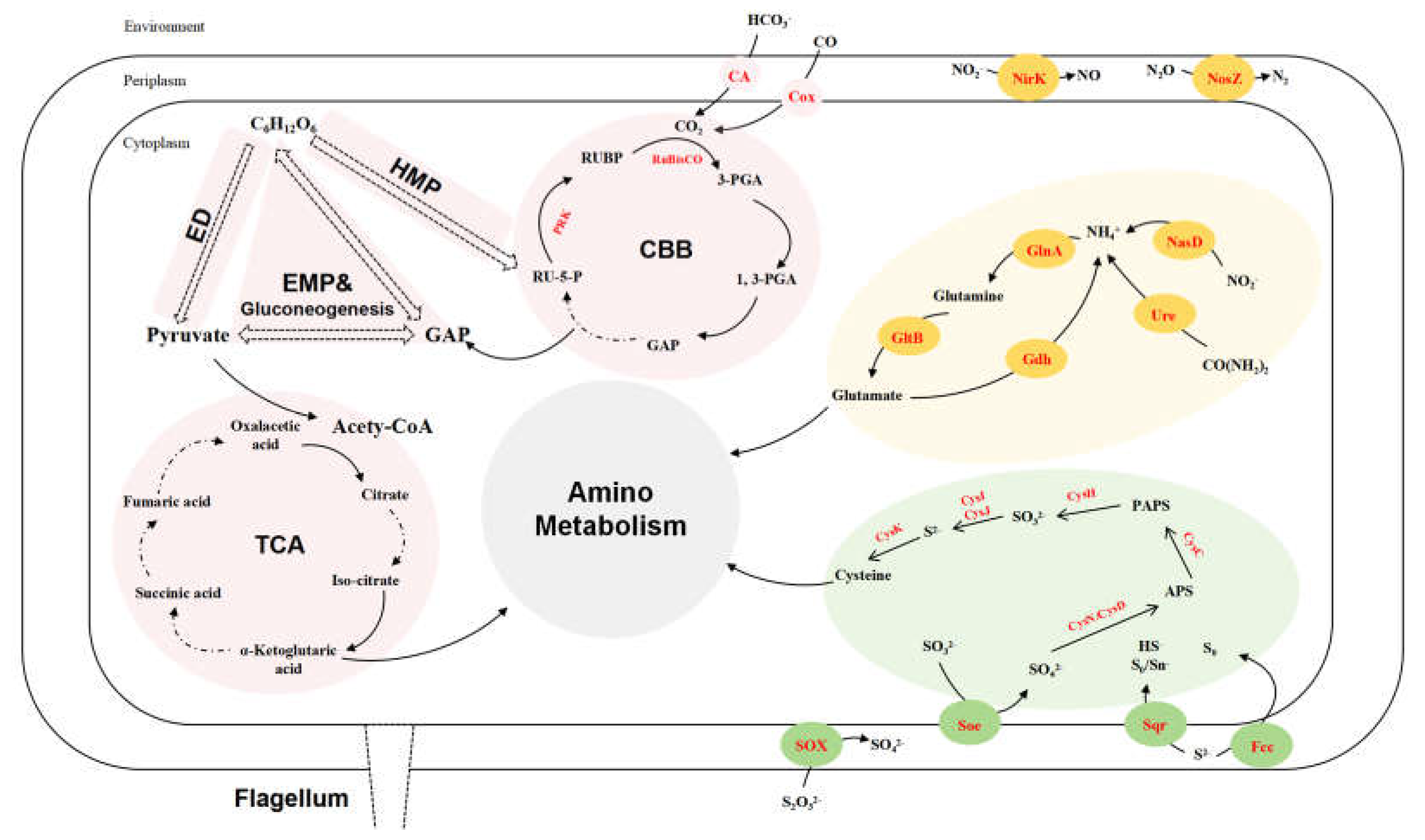
Table 1.
Comparison of the phenotypic characteristics of strain LZ166T with reference strains of the genus Aquibium.
Table 1.
Comparison of the phenotypic characteristics of strain LZ166T with reference strains of the genus Aquibium.
| Characteristic |
LZ166T
|
A. microcysteis
NIBR3T
|
A. oceanicum
B7T
|
| Cell size (μm) |
short rod-shaped
(1.3-1.7 × 1.0-1.1) |
rod-shaped
(1.2-2.5 × 0.4-0.6) a
|
oval-shaped
(1.2-2.5 × 0.4-0.6) b
|
| Flagella |
+ |
unknown |
- b
|
| Motility |
+ |
+ |
- b
|
Temperature range(optimum)
for growth (℃) |
10-45 (34-37) |
23-45 (33-37) a
|
25-40 (35) b
|
NaCl range (optimum)
for growth (w/v, %) |
0-5% (1-3%) |
0-4% (0%) a
|
0-8% (3%) b
|
pH range (optimum)
for growth |
5-10 (6-8) |
6-11 (8) a
|
5.5-9 (7) b
|
| Skimmed milk hydrolysis |
+ |
- |
- |
| Tween 40 hydrolysis |
- |
- |
+ |
| Tween 60 hydrolysis |
- |
- |
+ |
| Alkaline phosphatase |
w |
+ |
w |
| D-mannitol utilization |
+ |
- |
+ |
| Potassium gluconate utilization |
- |
- |
+ |
| Malic acid utilization |
- |
+ |
+ |
Table 2.
Comparison of major fatty acids (>5%) between strain LZ166T and closely related Aquibium species.
Table 2.
Comparison of major fatty acids (>5%) between strain LZ166T and closely related Aquibium species.
| Fatty acid (%) |
LZ166T
|
A. microcysteis
NIBR3T
|
A. oceanicum
B7T
|
| Saturated |
C16:0
|
5.5 |
3.6 |
5.3 |
| C18:0
|
4.1 |
5.8 |
6.9 |
| Branched |
iso-C17:0
|
13.3 |
4.3 |
5.5 |
| C19:0 cyclo ω8c
|
9.3 |
ND |
5.4 |
| Unsaturated |
11-methyl C18:1 ω7c
|
12.0 |
11.6 |
9.6 |
| Summed feature |
8* |
39.3 |
58.4 |
44.3 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).